
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Genet. , 26 February 2020
Sec. Evolutionary and Genomic Microbiology
Volume 11 - 2020 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2020.00007
Sepsis is a major threat with high mortality rate for critically ill patients. Response to pathogen infection by the host immune system is a key biological process involved in the onset and development of sepsis. Heterogeneous host genome variation, especially single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), has long been suggested to contribute to differences in disease progression. However, the function of SNPs located in non-coding regions remains to be elucidated. Recently, m6A mRNA modification levels were revealed to differ at SNPs. As m6A is a crucial regulator of gene expression, these SNPs might control genes by changing the m6A level on mRNA. To investigate the potential role of m6A SNPs in sepsis, we integrated m6A-SNP and expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs) data. Analysis revealed 15,720 m6A-cis-eQTLs and 381 m6A-trans-eQTLs associated with sepsis. We identified 1321 genes as locations of m6A-cis-eQTLs. These were enriched in platelet degranulation and Staphylococcus aureus infection pathways, which are vital for the pathophysiological process of sepsis. We conclude that m6A modification of mRNA plays a very important role in sepsis, with m6A-cis-eQTLs potentially having the most effect on individual variation in sepsis progression.
Sepsis is a serious systemic inflammatory response caused by bacterial, viral and fungal infection, and is one of the major causes of death in critical care patients (Rello et al., 2017). Data from developed countries estimate more than 30 million cases of sepsis and about 20 million cases of severe sepsis globally every year, which may result in more than 5 million deaths. Sepsis detection mainly depends on clinical diagnosis, but early clinical characteristics are not specific, and the lack of timely and reliable early warning diagnosis indicators is an important reason behind the high mortality among sepsis patients (Napolitano, 2018).
During the pathophysiological process of sepsis, pathogens and their toxins invade the vascular circulation, activate the host’s cellular immune system, generate cytokines and cause systemic inflammatory response syndrome (Rubio et al., 2019). Sepsis can affect various organs and systems of the body, causing necrosis and dysfunction of tissues and cells, and even multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (Ismail Hassan et al., 2020). Vascular endothelial cell damage, platelet function and immune dysfunction are key factors affecting disease progression (Khakpour et al., 2015; Guo and Rondina, 2019). Thus, resolving knowledge of pathogen invasion in sepsis will benefit diagnosis and treatment to reduce mortality of patients.
Treatment of sepsis is mostly aimed at pathogen control, including the early use of broad-spectrum antibiotics (Zhou et al., 2019). Removing the pathogen toxin is also very important. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (Gram-negative bacteria), lipoteichoic acid (LTA) (Gram-positive bacteria) and mannan (PLM) (fungi) all bind to toll-like receptors (TLRs) of innate immune cells (Yang et al., 2018). The lipid part of LPS can bind to TLR4 on many cells, LTA can bind to TLR2 and TLR6, and PLM can bind to TLR2, TLR4 and TLR6, activating the nuclear transcription factor-B (NF-B) signal pathway and the subsequent pro-inflammatory/anti-inflammatory cytokine response (Salomao et al., 2008). Blocking the pathogen toxin is therefore a critical step for preventing disease progression in sepsis patients.
Conversely, studies have shown that the susceptibility and prognosis of sepsis are genetically related to the host (Chapman and Hill, 2012; Rautanen et al., 2015). Heterogeneous host genome variation plays an important role in sepsis patients, suggesting another critical factor for diagnosis and treatment of sepsis. Genomic variation can produce gene expression differences among individuals. The location of expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs) has been analyzed to resolve the relationship between sepsis and the host immune response and various signaling pathways (Davenport et al., 2016). However, most reported single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are in non-coding regions and have no obvious biological significance. The development of genetics and epigenetics research has revealed that some SNPs can influence RNA modification to control RNA secondary structure or regulate RNA protein interaction, modifying the function of enhancers, silencers and exon splicing (Ramaswami et al., 2015; Mao et al., 2016; Wu and Hurst, 2016). These studies show that some SNPs as well as eQTLs affect the stability and function of RNA, which is the basic mechanism of host genome variation associated with the disease.
Methylation of the sixth N atom on the adenine base is part of an important regulatory mechanism affecting RNA stability and functionality (Yue et al., 2015). In eukaryotes, m6A is the most common post-transcriptional modification of RNA; it can affect the specific recognition of a protein complex and RNA and thus affect the intracellular transport, shear processing, degradation and translation of mRNA, finally regulating gene expression (Dominissini et al., 2012; Alarcon et al., 2015). Key regulatory factors of m6A RNA modification, such as METTL3, METTL 14 and FTO, can control the occurrence and development of many diseases by regulating the level of m6A RNA modification (Li et al., 2017; Lang et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2019; Yue et al., 2019).
m6A-SNPs can be considered an important functional genetic variation, providing new clues for understanding the molecular mechanism of genetic variation. A large number of m6A-SNPs related to bone mineral density, periodontitis, rheumatoid arthritis and coronary heart disease have been identified through integration analysis of the m6A-SNP list (Mo et al., 2018a; Mo et al., 2018b; Mo et al., 2018c; Lin et al., 2020). They integrated GWAS data and m6A methylation to scope its role in disease. However, there is no report on the role of m6A modification in the development of sepsis. Identification of m6A-eQTLs associated with sepsis will extend our knowledge of the genetic mechanism of m6A modification in sepsis. We therefore used the open eQTLs data set to explore the potential role of m6A-eQTLs in the pathogenesis of sepsis.
A list of m6A-SNPs was obtained from the m6Avar database (http://m6avar.renlab.org), with high (13,703 SNPs), medium (54,222) and low (245,076) confidence levels (Zheng et al., 2018). SNPs were obtained from dbSNP and TCGA. Other molecular interaction databases including starBase2 and CLIPdb were used during construction of this database.
eQTL data were obtained through published articles (Davenport et al., 2016). In this study, 265 peripheral blood leukocyte samples from patients with sepsis were collected and their transcriptional profiles were detected. Genomic SNPs determining gene expression differences between cases were mapped as eQTLs, divided into cis- and trans-eQTLs. cis-eQTLs were restricted to 1 Mb regions between the SNP and associated probe. There were 644,390 SNPs associated with 17,347 mapping probes in sepsis patients.
m6A-SNPs obtained from the m6avar database were compared with previously described cis-eQTLs and trans-eQTLs to obtain m6A-cis-eQTLs and m6A-trans-eQTLs. A manffoman map was constructed according to p-values from statistical analysis of the original eQTLs. Since there were far fewer m6A-trans-eQTLs, corresponding genes were only analyzed for m6A-cis-eQTL locations. The number of m6A-cis-eQTLs possessed by these genes was determined. GO enrichment analysis was performed using the DAVID TOOL (https://david.ncifcrf.gov/summary.jsp) with the whole human genome as background. The GAD-DISEASE CLASS, GO biological process, GO molecular function, GO cellular component and KEGG pathways were used to classify these genes according their functional annotation.
The database defined an SNP as one in which the typical sequence motif for m6A modification, such as DRACH, was changed (Zheng et al., 2018). High-confidence m6A-SNPs were identified from seven miCLIP and two PA-m6A-seq experiments, suggesting SNPs located close to the m6A site that may destroy the DRACH motif, such as D(A/G/U) to C, R(G/A) to C/T, A to C/G/U, C to G/A/U and H(A/C/U) to G. Medium-confidence m6A-SNPs were selected from 244 MeRIP-Seq experiments, which identify the intersection between SNP and m6A sites. Whether or not a SNP changes the DRACH motif or other characteristic sequences modified by m6A methylation was predicted by the random forest model. Low-confidence m6A-SNPs were predicted from the genome by random forest algorithms. We found 15,720 m6A-cis-eQTLs and 381 m6A-trans-eQTLs by integrated analysis of eQTLs associated with sepsis and more than 300,000 SNPs in the m6Avar database (Figures 1A, B, Table S1). According to the original sepsis eQTL study, a threshold of 1.00E-04 was used to test the association between m6A-eQTLs and gene expression in sepsis. As shown in Figure 1A, the p-values of m6A-cis-eQTLs ranged from 2.00E-04 to 5.19E-065, whereas p-values of m6A-trans-eQTLs ranged from 2.00E-09 to 5.93E-058. The m6A-cis-eQTLs were distributed on each chromosome with a similar pattern, displaying a gap close to the centromere. Among all m6A-cis-eQTLs, rs10239340 on chromosome 7 had the highest significance at p = 5.19E-065, followed by rs9849087 on chromosome 3 (p = 6.86E-062) (Table 1). Among the m6A-trans-eQTLs, rs10876864 on chromosome 12 had the highest significance at p = 5.93E-058, followed by rs11171739 on chromosome 12 (p = 1.56E-041) (Table 2).
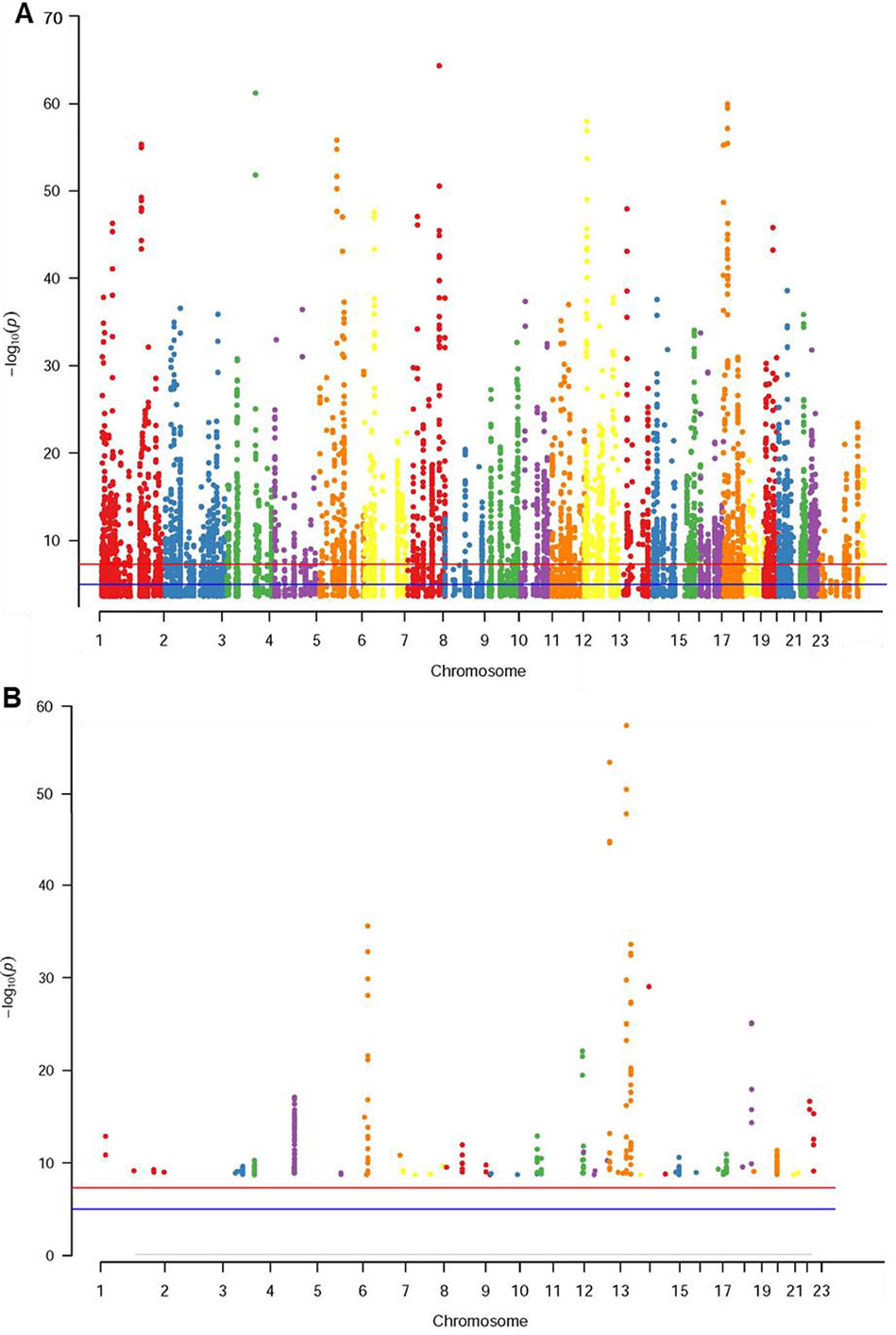
Figure 1 Manhattan plot of genome‐wide identified m6A-eQTLs in sepsis patients. The Manhattan plot displayed −log10 (p values) for each of m6A-eQTLs associated with sepsis. (A) m6A-cis-eQTLs (B) m6A-trans-eQTLs.
We then surveyed the relationship between eQTLs associated with sepsis and controllers of m6A modification such as writers, erasers and readers (METTL3, METTL14, WTAP, FTO, ALKBH5, YTHDC1, YTHDC2, YTHDF1, YTHDF2, YTHDF3) (Table S2). There was one eQTL in YTHDF3 (rs7464, p = 2.42E-04), and 20 eQTLs in YTHDC2 (p-values ranging from 2.64E-07 to 2.15E-04). Other m6A controllers were not associated with any sepsis-related eQTLs. However, none of the m6A controllers was identified as a significant gene for m6A-eQTLs.
To investigate the biological function of m6A associated with sepsis, we analyzed genes corresponding to m6A-cis-eQTLs. There were 1321 genes with an average of 11.8 m6A-cis-eQTLs, ranging from 1 to 195 (Table S3). There were 1038 genes with more than one m6A-cis-eQTL, and 52 genes had more than 50 m6A-cis-eQTLs. In particular, 10 genes had more than 100 m6A-cis-eQTLs: RAD51C, LOC100129, LY6G5C, TRIM27, LOC642073, RFP, ABCC5, CLEC12A, WDR6 and CAT (Table 3). The most significant p-values for each m6A-cis-eQTL associated with sepsis ranged from 2.91E-012 to 1.14E-058. CLEC12A had 121 m6A-cis-eQTLs with highly significant p-values.
To further survey the biological function of genes linked to m6A-cis-eQTLs associated with sepsis, we performed GO enrichment analysis in a whole-genome background (Figure 2, Table S3). Among biological processes, genes containing m6A-cis-eQTLs were enriched in diverse pathways such as phagocytosis, negative regulation of gene expression, and platelet degranulation. Among cellular components, genes corresponding to m6A-cis-eQTLs were enriched in different compartments such as cytosol, membrane, lysosome and platelet alpha granule lumen.
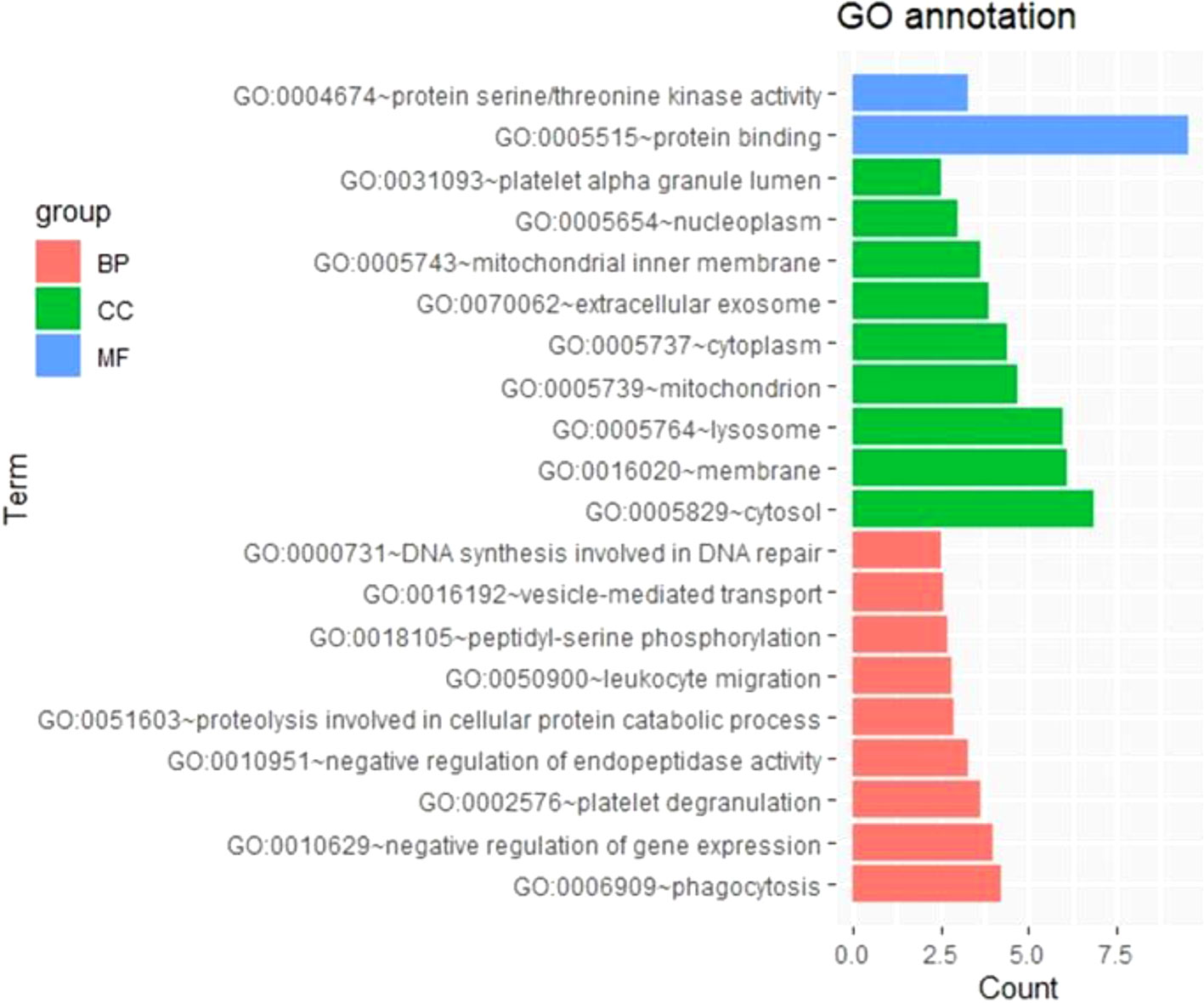
Figure 2 GO enrichment analysis displayed genes respond to m6A-cis-eQTLs are enriched in various biological processes (BP), molecular function (MF) and cellular component (CC). Note that platelet degranulation (BP) and platelet alpha granule lumen (CC) are significant pathway.
To elucidate the molecular pathways involving genes corresponding to m6A-cis-eQTLs, we carried out KEGG pathway enrichment analysis (Figure 3, Table S3). Results revealed that these genes were enriched in multiple pathways such as Lysosome, Staphylococcus aureus infection, Tuberculosis, and Platelet activation. Among these, Lysosome was the most significant with p-value = 1.05E-05, followed by S. aureus infection with p-value = 6.44E-04.
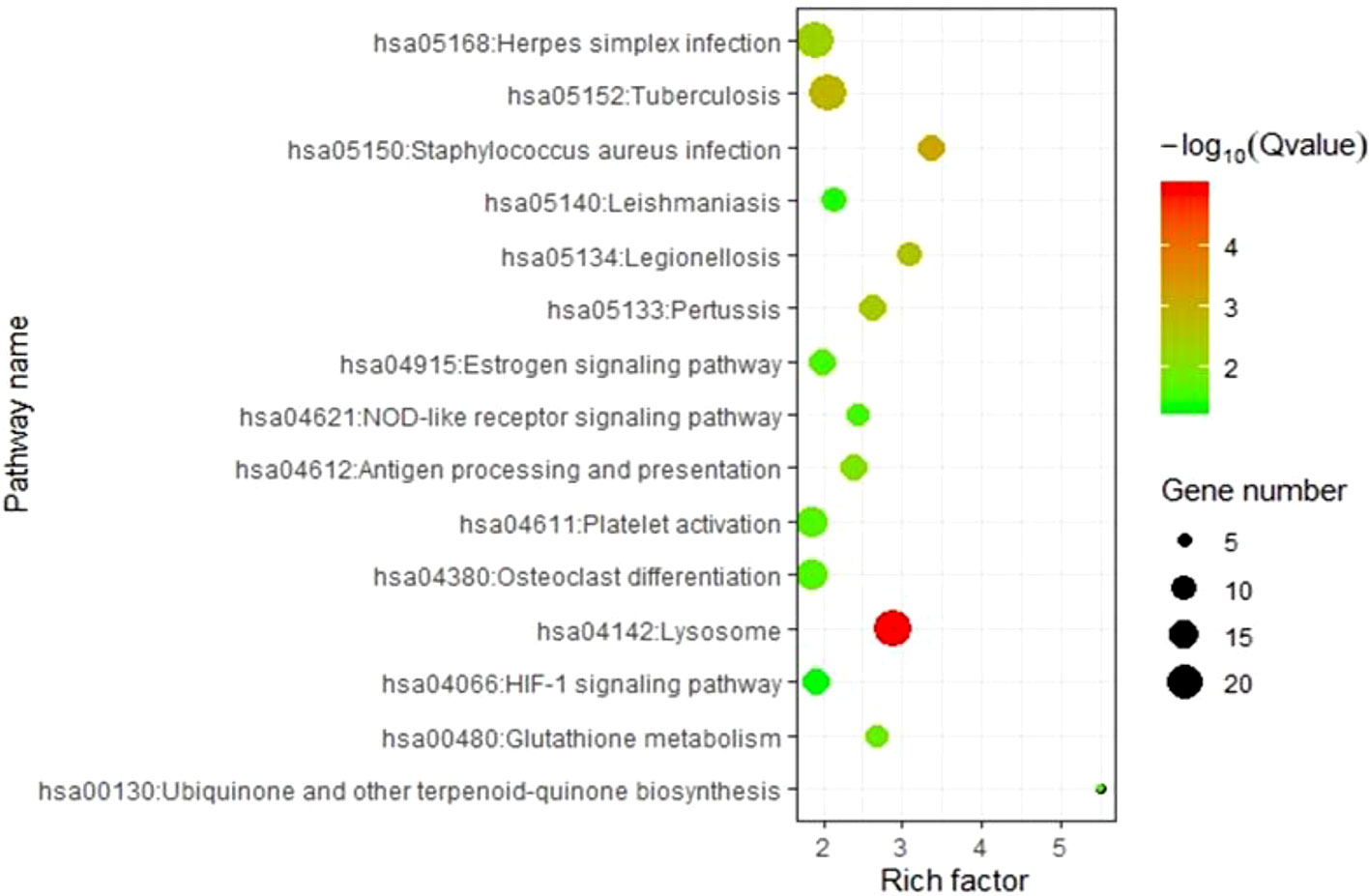
Figure 3 KEGG analysis revealed genes respond to m6A-cis-eQTLs are enriched diverse pathways. Note that Staphylococcus aureus infection pathway is with high significance.
To characterize the relationship between sepsis and genes corresponding to m6A-cis-eQTLs, we performed enrichment analysis using the disease database. Results showed that TNF, HSPA1A, HSPA1B, TREM1, SOD2 and MIF genes related to sepsis correspond to m6A-cis-eQTLs.
We identified 17 genes related to platelet degranulation, SERPING1, CD63, CTSW, TIMP1, CD9, VWF, ORM1, LAMP2, APP, CLEC3B, ITIH4, ABCC4, SERPINA1, CFD, QSOX1, ORM2 and SRGN, corresponding to m6A-cis-eQTLs associated with sepsis (Table S3).
We identified 12 genes related to S. aureus infection, C3AR1, FCGR2B, FCAR, C5, ITGB2, FPR2, C2, HLA-DPB1, CFD, HLA-DOB, ITGAM and PTAFR, corresponding to m6A-cis-eQTLs associated with sepsis (Table S3).
Disease-related genes show genetic variation in the population, which can affect the occurrence and development of the disease including cancer, sepsis and infectious. For a long time, research on the functional mechanism of these genetic variations has focused on changes in biological functional activity of the encoded proteins. However, a large number of SNPs found in genome-wide association analysis do not correspond to functional regions of proteins. Similarly, eQTLs are not located in promoter regions regulating gene expression. In recent years, a large number of m6A methylation modifications have been identified on mRNA of eukaryotes (Yue et al., 2015). These regulate a series of biological processes by affecting the splicing, translocation, degradation and translation of mRNA involved in the occurrence and development of many diseases. Some SNPs that do not change the coded amino acid can regulate mRNA function by affecting the level of m6A modification, thus changing protein abundance. m6A-SNPs can change m6A modification levels to affect mRNA degradation rate; for example, change in mRNA secondary structure caused by altered m6A modification can affect mRNA binding with translation machinery. Similarly, m6A-SNPs can also affect mRNA transport from nucleus to cytoplasm. When m6A-SNPs are located at splicing sites, they can affect production of mature mRNA with correct biological function. Thus, m6A-SNPs can cumulatively regulate the function of key regulatory genes in the process of disease occurrence and development through multiple effects.
The role of m6A modification on mRNA in the pathogenesis of sepsis has not previously been reported. Therefore, study of m6A-eQTLs might aid in resolving the underlying mechanism of the pathogenesis of sepsis. By analyzing results of published research on eQTLs associated with sepsis and comparing them with overlapping m6A-SNPs in the m6AVAR database, we identified a large number of m6A-eQTLs related to sepsis, including 15,720 cis-eQTLs and 381 trans-eQTLs. As we expected, these m6A-eQTLs were distributed across all chromosomes, suggesting that m6A methylation of mRNA plays an important role in sepsis as in other diseases.
Among genes corresponding to m6A-eQTLs, we found some suggested as key players in the pathogenesis of sepsis. HSPA1B, with 61 m6A-cis-eQTLs, also named HSP70, is involved in the inflammatory response, which is an important biological step in the development of sepsis (Table S2). Research on different phases of sepsis found that HSPA1B can be considered a serum marker for the acute proinflammatory phase (Gasparotto et al., 2018). Study on Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome in sepsis found that increased HSPA1B has an anti-inflammatory effect (Wang et al., 2016). In rats, raloxifene prevents severe sepsis through induction of HSPA1B with an anti-inflammatory effect (Shen et al., 2017). Hesperidin can protect against lung injury induced by sepsis, also through induction of HSPA1B. Another protein, KNK43, also takes part in the HSPA1B pathway to coordinate the inflammatory response (Yuan et al., 2019). There is evidence that heat stress induces HSPA1B to prevent lethal sepsis (Matsathit et al., 2016). These results indicate that m6A-eQTLs exist in the key regulatory genes of sepsis and m6A methylation is closely involved in the process of sepsis, while genetic variation may cause a large number of individual differences through the mechanism of m6A methylation of mRNA.
We used GO enrichment analysis to characterize critical biological processes associated with an abundance of sepsis m6A-eQTLs. The platelet degranulation process was associated with 17 genes identified in this study. It is well accepted that platelet degranulation is a typical biomarker of sepsis. In the development of sepsis, platelet dysfunction plays a critical role in tissue injury (Assinger et al., 2019). Early onset neonatal sepsis can be predicted by platelet/lymphocyte ratio (Arcagok and Karabulut, 2019). A high level of platelet-derived growth factor B (PDGFB) is found in survivors of sepsis (Dou et al., 2019), and PDGFB can reduce the mortality of sepsis by blocking inflammatory responses (Dou et al., 2019). In sepsis-associated liver injury, AST/platelet ratio might be an early onset predictor (Dou et al., 2019). The underlying mechanism of platelet dysfunction in sepsis remains to be elucidated. Here, we revealed that genes corresponding to m6A-eQTLs are enriched in the platelet degranulation process, suggesting that m6A methylation is closely involved in the pathologies of sepsis. Published literature supports the relationship between the 17 platelet degranulation related genes corresponding to m6A-eQTLs and sepsis. ORM2 interacts with TLR2 signaling involved in the pathobiology of sepsis (Sumanth et al., 2019). CFD and VWF are important biomarkers of acute mortality for severe sepsis (Avriel et al., 2014; Gragnano et al., 2017). TIMP1 could be used as prognostic marker for the onset of sepsis (Nino et al., 2017). Sepsis is attenuated by inhibition of ABCC4 in rats (Xia et al., 2019). Reduction of CD63 increases the mortality rate of sepsis in mice through its function in the immune response (Yang et al., 2016; Alvarez-Estrada et al., 2019). The above evidence strongly supports our view that m6A methylation plays an extremely important role in the pathological basis of sepsis. We suggest that m6A-eQTLs may be a potential predictor of different clinical characteristics of the sepsis disease caused by genetic variation in individuals.
KEGG pathway enrichment analysis in this study revealed 12 genes corresponding to m6A-eQTLs associated with sepsis enriched in the S. aureus infection pathway. S. aureus is one of the major pathogenic bacteria in sepsis (Machado et al., 2019). Among the 12 genes corresponding to sepsis m6A-eQTLs in this pathway, platelet activating factor receptor (PTAFR) is induced in sepsis patients infected with Gram-negative bacteria (Dhainaut et al., 1994). Inhibition of PTAFR can block severe sepsis (Moreno et al., 2006). FPR2 is also induced in the early phase of sepsis and functions in cerebral inflammation (Gavins et al., 2012; Sordi et al., 2013). ITGB2 has been identified as an important factor in the inflammatory response to sepsis (Kragstrup et al., 2017). FCAR, a typical innate receptor for bacteria, is suggested to be an important protector against sepsis through mediation of bacterial phagocytosis (Chiamolera et al., 2001; de Tymowski et al., 2019). Such a high proportion of m6A-eQTLs related to S. aureus response genes indicates that m6A methylation plays an extremely important role in the occurrence and development of sepsis. The m6A-eQTLs we identified will be of value in the prognosis and diagnosis of sepsis.
In conclusion, we identified a large number of m6A-eQTLs potentially having critical functions in the pathogenesis and development of sepsis. These SNPs may contribute to the effect of genetic variation on the different outcomes of the disease. By mining the published literature, we found that these m6A-eQTLs are enriched in the platelet degranulation process and S. aureus infection pathway. Both are critical biological processes controlling the pathogenesis and development of sepsis, suggesting that mRNA m6A methylation plays a crucial role in sepsis.
All datasets generated for this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material.
XS and NL designed the project and wrote the manuscript. XS performed bioinformatics analysis. YD, GT and YL helped analysis of data and revised the manuscript.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
This work was supported by Fujian provincial Health and Family Planning Young and Middle Aged Talents Training Project (2018-ZQN-56);Quanzhou Science and Technology Plan Project (2018N025S).
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fgene.2020.00007/full#supplementary-material
Alarcon, C. R., Lee, H., Goodarzi, H., Halberg, N., Tavazoie, S. F. (2015). N6-methyladenosine marks primary microRNAs for processing. Nature 519 (7544), 482–485. doi: 10.1038/nature14281
Alvarez-Estrada, A., Rodriguez-Ferri, E. F., Martinez-Martinez, S., Alvarez, B., Fernandez-Caballero, T., Dominguez, J., et al. (2019). TLR2, Siglec-3 and CD163 expressions on porcine peripheral blood monocytes are increased during sepsis caused by Haemophilus parasuis. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 64, 31–39. doi: 10.1016/j.cimid.2019.02.001
Arcagok, B. C., Karabulut, B. (2019). Platelet to lymphocyte ratio in neonates: a predictor of early onset neonatal sepsis. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 11 (1), e2019055. doi: 10.4084/mjhid.2019.055
Assinger, A., Schrottmaier, W. C., Salzmann, M., Rayes, J. (2019). Platelets in sepsis: an update on experimental models and clinical data. Front. Immunol. 10, 1687. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01687
Avriel, A., Paryente Wiessman, M., Almog, Y., Perl, Y., Novack, V., Galante, O., et al. (2014). Admission cell free DNA levels predict 28-day mortality in patients with severe sepsis in intensive care. PloS One 9 (6), e100514. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100514
Chapman, S. J., Hill, A. V. (2012). Human genetic susceptibility to infectious disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 13 (3), 175–188. doi: 10.1038/nrg3114
Chiamolera, M., Launay, P., Montenegro, V., Rivero, M. C., Velasco, I. T., Monteiro, R. C. (2001). Enhanced expression of Fc alpha receptor I on blood phagocytes of patients with gram-negative bacteremia is associated with tyrosine phosphorylation of the FcR-gamma subunit. Shock 16 (5), 344–348. doi: 10.1097/00024382-200116050-00004
Davenport, E. E., Burnham, K. L., Radhakrishnan, J., Humburg, P., Hutton, P., Mills, T. C., et al. (2016). Genomic landscape of the individual host response and outcomes in sepsis: a prospective cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 4 (4), 259–271. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(16)00046-1
de Tymowski, C., Heming, N., Correia, M. D. T., Abbad, L., Chavarot, N., Le Stang, M. B., et al. (2019). CD89 Is a Potent Innate Receptor for Bacteria and Mediates Host Protection from Sepsis. Cell Rep. 27 (3), 762–775 e5. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.03.062
Dhainaut, J. F., Tenaillon, A., Le Tulzo, Y., Schlemmer, B., Solet, J. P., Wolff, M., et al. (1994). Platelet-activating factor receptor antagonist BN 52021 in the treatment of severe sepsis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter clinical trial. BN 52021 sepsis study group. Crit. Care Med. 22 (11), 1720–1728. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199422110-00005
Dominissini, D., Moshitch-Moshkovitz, S., Schwartz, S., Salmon-Divon, M., Ungar, L., Osenberg, S., et al. (2012). Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature 485 (7397), 201–206. doi: 10.1038/nature11112
Dou, J., Zhou, Y., Cui, Y., Chen, M., Wang, C., Zhang, Y. (2019). AST-to-platelet ratio index as potential early-warning biomarker for sepsis-associated liver injury in children: a database study. Front. Pediatr. 7, 331. doi: 10.3389/fped.2019.00331
Gasparotto, J., Girardi, C. S., Somensi, N., Ribeiro, C. T., Moreira, J. C. F., Michels, M., et al. (2018). Receptor for advanced glycation end products mediates sepsis-triggered amyloid-beta accumulation, Tau phosphorylation, and cognitive impairment. J. Biol. Chem. 293 (1), 226–244. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.786756
Gavins, F. N., Hughes, E. L., Buss, N. A., Holloway, P. M., Getting, S. J., Buckingham, J. C. (2012). Leukocyte recruitment in the brain in sepsis: involvement of the annexin 1-FPR2/ALX anti-inflammatory system. FASEB J. 26 (12), 4977–4989. doi: 10.1096/fj.12-205971
Gragnano, F., Sperlongano, S., Golia, E., Natale, F., Bianchi, R., Crisci, M., et al. (2017). The role of von Willebrand Factor in vascular inflammation: from pathogenesis to targeted therapy. Mediators Inflammation 2017, 5620314. doi: 10.1155/2017/5620314
Guo, L., Rondina, M. T. (2019). The era of thromboinflammation: platelets are dynamic sensors and effector cells during infectious diseases. Front. Immunol. 10, 2204. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02204
Ismail Hassan, F., Didari, T., Khan, F., Niaz, K., Mojtahedzadeh, M., Abdollahi, M. (2020). A review on the protective effects of metformin in sepsis-induced organ failure. Cell J. 21 (4), 363–370. doi: 10.22074/cellj.2020.6286
Khakpour, S., Wilhelmsen, K., Hellman, J. (2015). Vascular endothelial cell Toll-like receptor pathways in sepsis. Innate. Immun. 21 (8), 827–846. doi: 10.1177/1753425915606525
Kragstrup, T. W., Juul-Madsen, K., Christiansen, S. H., Zhang, X., Krog, J., Vorup-Jensen, T., et al. (2017). Altered levels of soluble CD18 may associate immune mechanisms with outcome in sepsis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 190 (2), 258–267. doi: 10.1111/cei.13016
Lang, F., Singh, R. K., Pei, Y., Zhang, S., Sun, K., Robertson, E. S. (2019). EBV epitranscriptome reprogramming by METTL14 is critical for viral-associated tumorigenesis. PloS Pathog. 15 (6), e1007796. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007796
Li, Z., Weng, H., Su, R., Weng, X., Zuo, Z., Li, C., et al. (2017). FTO Plays an Oncogenic Role in Acute Myeloid Leukemia as a N(6)-Methyladenosine RNA Demethylase. Cancer Cell 31 (1), 127–141. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.11.017
Lin, W., Xu, H., Wu, Y., Wang, J., Yuan, Q. (2020). In silico genome-wide identification of m6A-associated SNPs as potential functional variants for periodontitis. J. Cell Physiol. 235 (2), 900–908. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29005
Machado, H., Weng, L. L., Dillon, N., Seif, Y., Holland, M., Pekar, J. E., et al. (2019). Strain-specific metabolic requirements revealed by a defined minimal medium for systems analyses of Staphylococcus aureus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 85 (21), e01773–19. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01773-19
Mao, F., Xiao, L., Li, X., Liang, J., Teng, H., Cai, W., et al. (2016). RBP-Var: a database of functional variants involved in regulation mediated by RNA-binding proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 44 (D1), D154–D163. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1308
Matsathit, U., Mekseepralard, C., Wongsawatkul, O., Ratanachamnong, P., Upapan, P., Phivthong-Ngam, L. (2016). Thermal Steam Aerosolization Protects Against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Sepsis in Rats. J. Med. Assoc. Thai. 99 Suppl 8, S206–S215.
Mo, X. B., Zhang, Y. H., Lei, S. F. (2018a). Genome-wide identification of m(6)A-associated SNPs as potential functional variants for bone mineral density. Osteoporos. Int. 29 (9), 2029–2039. doi: 10.1007/s00198-018-4573-y
Mo, X. B., Zhang, Y. H., Lei, S. F. (2018b). Genome-Wide Identification of N(6)-Methyladenosine (m(6)A) SNPs Associated With Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Genet. 9, 299. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00299
Mo, X. B., Lei, S. F., Zhang, Y. H., Zhang, H. (2018c). Detection of m(6)A-associated SNPs as potential functional variants for coronary artery disease. Epigenomics 10 (10), 1279–1287. doi: 10.2217/epi-2018-0007
Moreno, S. E., Alves-Filho, J. C., Rios-Santos, F., Silva, J. S., Ferreira, S. H., Cunha, F. Q., et al. (2006). Signaling via platelet-activating factor receptors accounts for the impairment of neutrophil migration in polymicrobial sepsis. J. Immunol. 177 (2), 1264–1271. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.2.1264
Napolitano, L. M. (2018). Sepsis 2018: definitions and guideline changes. Surg. Infect. (Larchmt) 19 (2), 117–125. doi: 10.1089/sur.2017.278
Nino, M. E., Serrano, S. E., Nino, D. C., McCosham, D. M., Cardenas, M. E., Villareal, V. P., et al. (2017). TIMP1 and MMP9 are predictors of mortality in septic patients in the emergency department and intensive care unit unlike MMP9/TIMP1 ratio: multivariate model. PloS One 12 (2), e0171191. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171191
Ramaswami, G., Deng, P., Zhang, R., Anna Carbone, M., Mackay, T. F. C., Billy Li, J. (2015). Genetic mapping uncovers cis-regulatory landscape of RNA editing. Nat. Commun. 6, 8194. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9194
Rautanen, A., Mills, T. C., Gordon, A. C., Hutton, P., Steffens, M., Nuamah, R., et al. (2015). Genome-wide association study of survival from sepsis due to pneumonia: an observational cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 3 (1), 53–60. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(14)70290-5
Rello, J., Valenzuela-Sanchez, F., Ruiz-Rodriguez, M., Moyano, S. (2017). Sepsis: a review of advances in management. Adv. Ther. 34 (11), 2393–2411. doi: 10.1007/s12325-017-0622-8
Rubio, I., Osuchowski, M. F., Shankar-Hari, M., Skirecki, T., Winkler, M. S., Lachmann, G., et al. (2019). Current gaps in sepsis immunology: new opportunities for translational research. Lancet Infect. Dis. 19 (12), e422–e436 doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(19)30567-5
Salomao, R., Martins, P. S., Brunialti, M. K., Fernandes Mda, L., Martos, L. S., Mendes, M. E., et al (2008). TLR signaling pathway in patients with sepsis. Shock 30 Suppl 1, 73–77. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e318181af2a
Shen, H. H., Huang, S. Y., Cheng, P. Y., Chu, Y. J., Chen, S. Y., Lam, K. K., et al. (2017). Involvement of HSP70 and HO-1 in the protective effects of raloxifene on multiple organ dysfunction syndrome by endotoxemia in ovariectomized rats. Menopause 24 (8), 959–969. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000000864
Sordi, R., Menezes-de-Lima, O., Jr., Horewicz, V., Scheschowitsch, K., Santos, L. F., Assreuy, J. (2013). Dual role of lipoxin A4 in pneumosepsis pathogenesis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 17 (2), 283–292. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2013.06.010
Sumanth, M. S., Abhilasha, K. V., Jacob, S. P., Chaithra, V. H., Basrur, V., Willard, B., et al. (2019). Acute phase protein, alpha - 1- acid glycoprotein (AGP-1), has differential effects on TLR-2 and TLR-4 mediated responses. Immunobiology 224 (5), 672–680. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2019.06.003
Wang, Y. L., Shen, H. H., Cheng, P. Y., Chu, Y. J., Hwang, H. R., Lam, K. K., et al. (2016). 17-DMAG, an HSP90 Inhibitor, Ameliorates multiple organ dysfunction syndrome via Induction of HSP70 in Endotoxemic rats. PloS One 11 (5), e0155583. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155583
Wang, Q., Chen, C., Ding, Q., Zhao, Y., Wang, Z., Chen, J., et al. (2019). METTL3-mediated m(6)A modification of HDGF mRNA promotes gastric cancer progression and has prognostic significance. Gut. 10 (3), gutjnl-2019–319639 doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-319639
Wu, X., Hurst, L. D. (2016). Determinants of the Usage of Splice-Associated cis-Motifs Predict the Distribution of Human Pathogenic SNPs. Mol. Biol. Evol. 33 (2), 518–529. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msv251
Xia, W., Zhang, H., Pan, Z., Li, G., Zhou, Q., Hu, D., et al. (2019). Inhibition of MRP4 alleviates sepsis-induced acute lung injury in rats. Int. Immunopharmacol. 72, 211–217. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.04.009
Yang, H., Wang, H., Levine, Y. A., Gunasekaran, M. K., Wang, Y., Addorisio, M., et al. (2016). Identification of CD163 as an antiinflammatory receptor for HMGB1-haptoglobin complexes. JCI Insight 1 (7), 126617. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.85375
Yang, F. M., Zuo, Y., Zhou, W., Xia, C., Hahm, B., Sullivan, M., et al. (2018). sNASP inhibits TLR signaling to regulate immune response in sepsis. J. Clin. Invest. 128 (6), 2459–2472. doi: 10.1172/JCI95720
Yuan, X., Kang, Q., He, X., Guo, D. (2019). Protective effect of hesperidin against sepsis-induced lung injury by inducing the heat-stable protein 70 (Hsp70)/Toll-Like receptor 4 (TLR4)/Myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (MyD88) pathway. Med. Sci. Monit. 25, 107–114. doi: 10.12659/MSM.912490
Yue, Y., Liu, J., He, C. (2015). RNA N6-methyladenosine methylation in post-transcriptional gene expression regulation. Genes Dev. 29 (13), 1343–1355. doi: 10.1101/gad.262766.115
Yue, B., Song, C., Yang, L., Cui, R., Cheng, X., Zhang, Z., et al. (2019). METTL3-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification is critical for epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of gastric cancer. Mol. Cancer 18 (1), 142. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1065-4
Zheng, Y., Nie, P., Peng, D., He, Z., Liu, M., Xie, Y., et al. (2018). m6AVar: a database of functional variants involved in m6A modification. Nucleic Acids Res. 46 (D1), D139–D145. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx895
Keywords: M6A, methylation, eQTL, sepsis, Staphylococcus aureus
Citation: Sun X, Dai Y, Tan G, Liu Y and Li N (2020) Integration Analysis of m6A-SNPs and eQTLs Associated With Sepsis Reveals Platelet Degranulation and Staphylococcus aureus Infection are Mediated by m6A mRNA Methylation. Front. Genet. 11:7. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00007
Received: 01 November 2019; Accepted: 06 January 2020;
Published: 26 February 2020.
Edited by:
Baolei Jia, Chung-Ang University, South KoreaReviewed by:
Hui-Bin Huang, Tsinghua University, ChinaCopyright © 2020 Sun, Dai, Tan, Liu and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xuri Sun, c3VueHVyaTEyMzQ1QDE2My5jb20=; eHVyaV9zdW5AZmptdS5lZHUuY24=; Neng Li, bGluZW5nQGZqbXUuZWR1LmNu
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.