
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
GENERAL COMMENTARY article
Front. Genet. , 19 September 2014
Sec. Computational Genomics
Volume 5 - 2014 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2014.00320
This article is part of the Research Topic Computational epigenomics: challenges and opportunities View all 12 articles
This article is a commentary on:
Comparative evaluation of DNase-seq footprint identification strategies
A commentary on
Comparative evaluation of DNase-seq footprint identification strategies
by Barozzi, I., Bora, P., and Morelli, M. J. (2014). Front. Genet. 5:278. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00278
Figure 1 of the article Comparative evaluation of DNase-seq footprint identification strategies, by Barozzi et al. (2014) contained a minor mistake, which we correct here. In panel E, the y axis ranges from 0.5 to 1 and not from 0 to 1 as indicated in the original figure. We resubmit a corrected version of Figure 1.
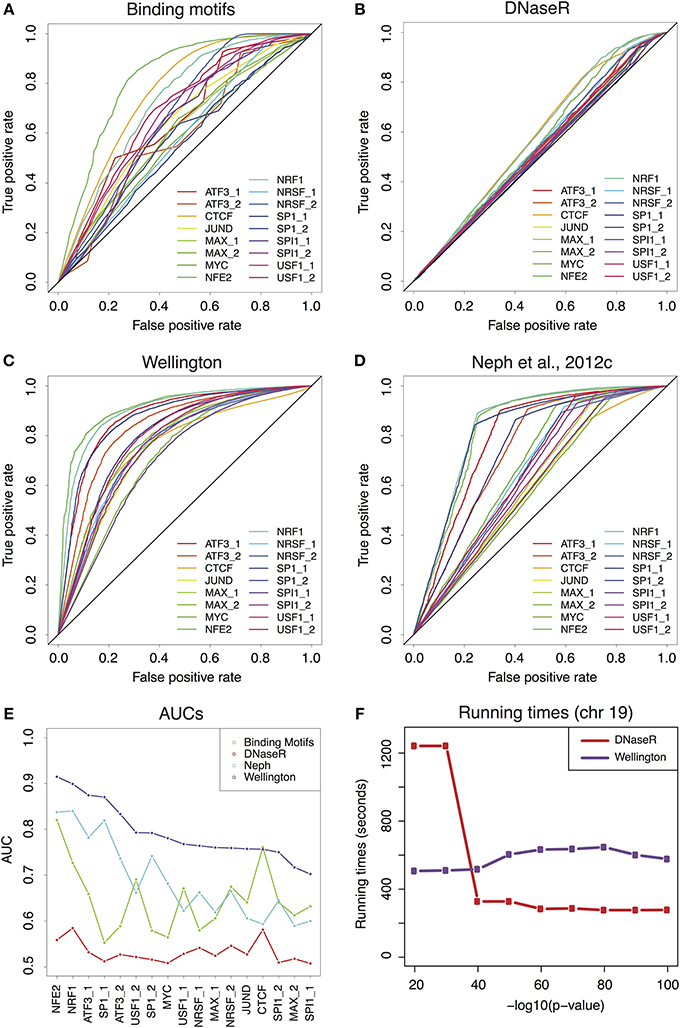
Figure 1. (A) Receiver-Operator Characteristic (ROC) curves for the predictions provided by the binding motifs alone. (B–D) ROCs for the sets of footprints obtained by DNaseR, Wellington and for the set used in Neph et al.(2012c). (E) Area Under the Curve (AUC) corresponding to the ROCs of (A–D) Wellington scores consistently better than all theother methods. (F) Running times for DNaseR and Wellington on chromosome19, for different significance thresholds.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Keywords: DNase-seq, footprinting, gene regulatory networks, bioinformatics tools and databases, comparison of methods
Citation: Barozzi I, Bora P and Morelli MJ (2014) Corrigendum: Comparative evaluation of DNase-seq footprint identification strategies. Front. Genet. 5:320. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00320
Received: 26 August 2014; Accepted: 26 August 2014;
Published online: 19 September 2014.
Edited and reviewed by: Mark D. Robinson, University of Zurich, Switzerland
Copyright © 2014 Barozzi, Bora and Morelli. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence:bWFyY28ubW9yZWxsaUBpaXQuaXQ=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.