
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ERRATUM article
Front. Ecol. Evol. , 28 March 2023
Sec. Conservation and Restoration Ecology
Volume 11 - 2023 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fevo.2023.1168225
This article is part of the Research Topic Origin, Conservation, and Restoration of the Threatened European Grassland Ecosystem in the Anthropocene View all 16 articles
This article is an erratum on:
Structurally rich dry grasslands – Potential stepping stones for bats in open farmland
An Erratum on
Structurally rich dry grasslands – Potential stepping stones for bats in open farmland
by Ewert, S. P., Knörnschild, M., Jung, K., and Frommolt, K.-H. (2023). Front. Ecol. Evol. 11:995133. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2023.995133
Due to a production error, there was a mistake in Table 1 as published. There were several formatting issues. The corrected Table 1 appears below.
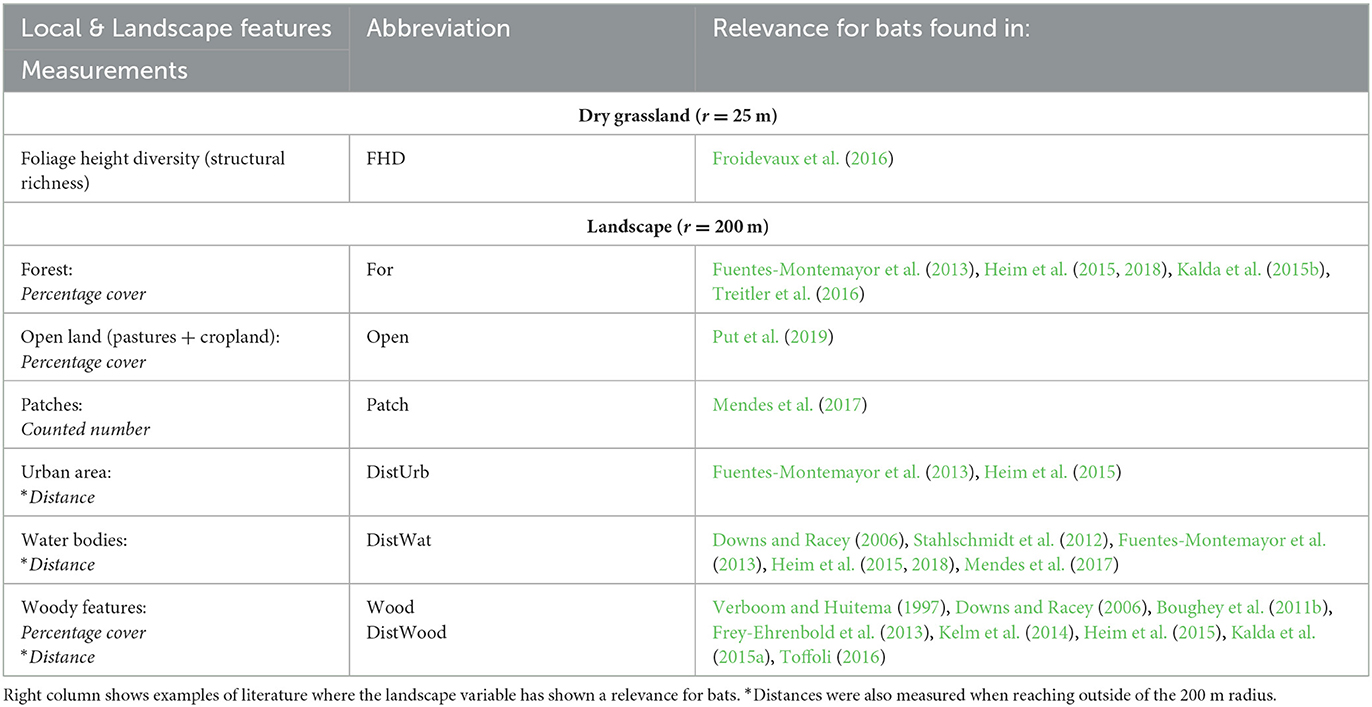
Table 1. Final choice of local and landscape features and their abbreviations used for further analysis.
The publisher apologizes for this mistake. The original article has been updated.
Boughey, K. L., Lake, I. R., Haysom, K. A., and Dolman, P. M. (2011b). Improving the biodiversity benefits of hedgerows: how physical characteristics and the proximity of foraging habitat affect the use of linear features by bats. Biol. Conserv. 144, 1790–1798. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2011.02.017
Downs, N. C., and Racey, P. A. (2006). The use by bats of habitat features in mixed farmland in Scotland. Acta Chiropterologica 8, 169–185. doi: 10.3161/150811006777070893
Frey-Ehrenbold, A., Bontadina, F., Arlettaz, R., and Obrist, M. K. (2013). Landscape connectivity, habitat structure and activity of bat guilds in farmland-dominated matrices. J. Appl. Ecol. 50, 252–261. doi: 10.1111/1365-2664.12034
Froidevaux, J. S. P., Zellweger, F., Bollmann, K., Jones, G., and Obrist, M. K. (2016). From field surveys to LiDAR: shining a light on how bats respond to forest structure. Remote Sens. Environ. 175, 242–250. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2015.12.038
Fuentes-Montemayor, E., Goulson, D., Cavin, L., Wallace, J. M., and Park, K. J. (2013). Fragmented woodlands in agricultural landscapes: the influence of woodland character and landscape context on bats and their insect prey. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 172, 6–15. doi: 10.1016/j.agee.2013.03.019
Heim, O., Lenski, J., Schulze, J., Jung, K., Kramer-Schadt, S., Eccard, J. A., et al. (2018). The relevance of vegetation structures and small water bodies for bats foraging above farmland. Basic Appl. Ecol. 27, 9–19. doi: 10.1016/j.baae.2017.12.001
Heim, O., Treitler, J. T., Tschapka, M., Knornschild, M., and Jung, K. (2015). The importance of landscape elements for bat activity and species richness in agricultural areas. PLoS One 10:e0134443. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134443
Kalda, O., Kalda, R., and Liira, P. (2015a). Multi-scale ecology of insectivorous bats in agricultural landscapes. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 199, 105–113. doi: 10.1016/j.agee.2014.08.028
Kalda, R., Kalda, O., Lõhmus, K., and Liira, J. (2015b). Multi-scale ecology of woodland bat the role of species pool, landscape complexity and stand structure. Biodivers. Conserv. 24, 337–353. doi: 10.1007/s10531-014-0811-6
Kelm, D. H., Lenski, J., Kelm, V., Toelch, U., and Dziock, F. (2014). Seasonal bat activity in relation to distance to hedgerows in an agricultural landscape in Central Europe and implications for wind energy development. Acta Chiropterologica 16, 65–73. doi: 10.3161/150811014x683273
Mendes, E. S., Fonseca, C., Marques, S. F., Maia, D., and Pereira, M. J. R. (2017). Bat richness and activity in heterogeneous landscapes: guild-specific and scale-dependent? Landsc. Ecol. 32, 295–311. doi: 10.1007/s10980-016-0444-0
Put, J. E., Fahrig, L., and Mitchell, G. W. (2019). Bats respond negatively to increases in the amount and homogenization of agricultural land cover. Landsc. Ecol. 34, 1889–1903. doi: 10.1007/s10980-019-00855-2
Stahlschmidt, P., Pätzold, A., Ressl, L., Schulz, R., and Brühl, C. A. (2012). Constructed wetlands support bats in agricultural landscapes. Basic Appl. Ecol. 13, 196–203. doi: 10.1016/j.baae.2012.02.001
Toffoli, R. (2016). The importance of linear landscape elements for bats in a farmland area: the influence of height on activity. J. Landsc. Ecol. 9, 49–62. doi: 10.1515/jlecol-2016-0004
Treitler, J. T., Heim, O., Tschapka, M., and Jung, K. (2016). The effect of local land use and loss of forests on bats and nocturnal insects. Ecol. Evol. 6, 4289–4297. doi: 10.1002/ece3.2160
Keywords: dry grasslands, bats (Chiroptera), agricultural intensification, landscape, structural richness, acoustic monitoring, habitat fragments
Citation: Frontiers Production Office (2023) Erratum: Structurally rich dry grasslands – Potential stepping stones for bats in open farmland. Front. Ecol. Evol. 11:1168225. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2023.1168225
Received: 17 February 2023; Accepted: 17 February 2023;
Published: 28 March 2023.
Approved by:
Frontiers Editorial Office, Frontiers Media SA, SwitzerlandCopyright © 2023 Frontiers Production Office. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Frontiers Production Office, cHJvZHVjdGlvbi5vZmZpY2VAZnJvbnRpZXJzaW4ub3Jn
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.