- College of Statistics, Jiangxi University of Finance and Economics, Nanchang, China
Most cities in the Yellow River Basin are located in the central and western regions of China. Restricted by historical evolution, natural environment, resource endowments and other conditions, the economic and social development model of the Yellow River Basin region is outdated, and the level of economic and social development is relatively lagging, which hinders its coordinated development of ecology and economy. This paper uses the coupling coordination degree model, GIS spatial analysis method, NAR neural network model, spatial autoregression, and geographically weighted regression model to investigate the coupling coordination level, spatial differentiation characteristics, future development trend, and coupling driving factors of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin. The results show that From 2003 to 2018, the level of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in most areas of the Yellow River Basin gradually improved, presenting a spatial imbalance characteristic of “high in the east and low in the west. The coupling coordination degree of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in various regions of the Yellow River Basin increased year by year during the survey period. In 2018, most cities had been transformed into intermediate coordinated development areas, and most cities in Inner Mongolia and the middle and lower reaches south of the Yellow River have been upgraded to a well-coordinated development stage. The coupled and coordinated development relationship between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin has significant spatial agglomeration characteristics, and the local spatial positive correlation gradually increases. From 2019 to 2023, the average level of coupling coordination between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin during the forecast period is 0.802, 0.807, 0.809, 0.813, and 0.816, respectively, all of which have entered a stage of well-coordinated development. The coupled driving factors of ecological protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin are ranked from strong to weak: energy utilization, urbanization, water resources development, and industrialization. Among them, the degree of energy utilization is the root of the differentiation of coupling coordination between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in 74 regions of the Yellow River Basin. This study puts forward two strategic suggestions based on the optimal utilization strategy of energy and water resources and the coordinated promotion strategy of industrialization and urbanization, which has great practical and scientific significance for promoting the coordinated development of ecological environment protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin.
1 Introduction
The party and the government have highly valued the ecological protection and economic development of the Yellow River Basin. The establishment and implementation of the significant national strategy of ecological protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin have effectively promoted the region’s sustainable development. Research issues related to eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin have also become a hot topic and focus of academic attention. The ecological environment problem of the Yellow River Basin is a problem left over from history, and it is also one of the critical factors that affect the economic development of the Yellow River Basin (Chen J. D. et al., 2020). The ecological and environmental pollution problem caused by economic development is an objective existence. High-intensity industrial development has prompted rapid economic and social progress. The development achievements obtained are undeniable, but at the same time, it has also caused permanent damage to the ecological environment. Exploring the coordination of ecological and economic development in the Yellow River Basin is significant for improving its ecological environment and high-quality development.
The Yellow River Basin plays a pivotal role in China’s economic and social development and ecological security and is an important ecological barrier and economic zone in China. The eco-environmental protection issues in the Yellow River Basin have been closely concerned by the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China. The Yellow River Basin has many problems, such as soil erosion, severe land desertification, frequent surface mining collapse accidents, water shortages, and precipitation in the lower reaches of the Yellow River. Ecological and water resource problems have always been a significant concern in China. At the same time, the overall economic development of the basin is lagging, and there are many economic and social development problems, such as significant regional differences, low-end industrial structure, low level of scientific and technological innovation, sluggish development of high-tech industries, and extensive, large and deep poverty areas (Liu et al., 2020; Li et al., 2021). The ecological environment and economic development situation in the Yellow River Basin is grim. The existing research shows that the ecological security problems of the Yellow River Basin are prominently manifested in industrial structural risks, cross-regional pattern risks, and system imbalance risks (Deng, 2020). With the increasingly prominent contradiction between ecology and social and economic development, the government and enterprises should pay more attention to improving the ecological environment quality of the Yellow River Basin while avoiding these risks, which are directly related to the evolution trend of the country’s medium and long-term ecological security and environmental quality (Wang C. Y., 2020). In the final analysis, the essence of the ecological environment problem in the Yellow River Basin is the problem of economic development and social management, and its fundamental solution still needs to be traced back to the transformation of economic and social development (Guo, 2020). In order to thoroughly study the relationship between the ecological environment and economic development, scholars have conducted extensive discussions. Wang pointed out that eco-environmental protection and economic development can achieve a win-win situation. The critical point is to balance eco-environmental protection and economic development to enhance eco-environmental protection while promoting high-quality economic development (Wang, 2019). Pure scholars generally believe that adhering to the principle of ecological priority, strengthening regional division of labor, strengthening regional connections, and promoting industrial upgrading can realize the synergy of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin (Chen and Jin, 2019; An and Li, 2020; Wang W., 2020). Through empirical research, some scholars show that rational allocation of water resources, coordinated industrial development, and rationalization of mineral resources exploitation can provide a practical path for the coordinated development of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin (Jin et al., 2020; Ma et al., 2020; Xing et al., 2020). In addition, other scholars respectively studied the coupling and coordination relationship between ecological environment and economic development in China’s Silk Road Economic Belt, China’s tropical and subtropical regions, and Northeast China and provided effective development paths for different regional characteristics (Yang and Hu, 2019; Gao, 2020; Shi et al., 2020).
By sorting out the literature on the ecological environment and high-quality development of the Yellow River Basin at home and abroad, the author believes that there is still room for further improvement in the existing research. First, in the process of measuring the ecological environment protection and high-quality development level of the Yellow River Basin, most studies use a single weighting method such as the subjective weighting method or the objective weighting method, and the measurement method needs to be further improved. Second, most of the related studies on the coupling coordination between the ecological environment and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin directly measure the coupling coordination degree between the ecological environment protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin, but do not deeply explore the coupling mechanism between the two. In addition, most of the studies selected provinces and regions as the research objects, and a few studies selected a small number of prefecture-level cities as the research objects, with a small amount of data and lack of representativeness. Third, when analyzing the temporal and spatial differentiation characteristics of the coupling and coordination relationship between ecological environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin, most studies only use GIS spatial analysis methods to describe the temporal and spatial evolution characteristics of the coupling and coordination between ecological environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin (Zhao et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2022; Zhang and Shi, 2022). However, it did not further analyze its global and local spatial laws and further study the future development trend of the coupling and coordination relationship between ecological environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin. Fourth, the research on the driving factors of the coupling and coordination of ecological environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin is currently less involved and needs further in-depth research.
In view of this, this paper makes related improvements in these four aspects. First, this paper combines subjective and objective weight methods organically. It uses the combined weight method to measure the level of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin to get closer to the real level to get a more accurate coupling coordination degree. Secondly, 74 prefecture-level cities in the Yellow River Basin were selected as the research objects to explore the coupling mechanism between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin and then evaluate the coupling coordination, which not only expands the data sample size but also deepens the theoretical research in this field. The research results have more practical implications. Thirdly, the exploratory spatial data analysis method explores the global and local spatial rules of the coupling coordination between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin. The future development trend is explored by using NAR neural network model. Fourth, the study of the Yellow River basin eco-environmental protection and high-quality development mechanism of the effects of coupling, using the spatial autoregressive model and geographically weighted regression model analysis of the Yellow River basin eco-environmental protection and development of high-quality coupling driving force of the global and local laws, and further determine its global influence factors and local factors, in order to make up the blank in the research of this field.
The remainder of this paper is coordinated as follows. Section 2 analyzes the coupling mechanism of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development and the influence mechanism of coupling driving factors, Section 3 briefly describes the research area, constructs the index system of ecological environmental protection, high-quality development, and their coupling driving factors, explains the data sources and processing methods, and shows the methodology models and algorithms, Section 4 introduces the current coupling and coordination relationship between ecological environment protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin, predicts its future development trend, and probes into the coupling driving force of ecological environment protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin from both global and local aspects. Section 5 sums up the conclusions and policy advocacy.
2 Theoretical analysis
2.1 Study on coupling mechanism of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development
2.1.1 The role of eco-environmental protection in high-quality development
High-quality environmental protection is a prerequisite for high-quality development (Shi, 2020). In essence, eco-environmental protection and high-quality development go hand in hand. To protect the ecological environment is to promote high-quality development. The role of eco-environmental protection in high-quality development can be understood from both sides of supply and demand. Level from the supply side, an excellent ecological environment is an important capital of regional economic development. An excellent eco-environmental protection advantage can be converted into various ecological and economic advantages, such as ecological agriculture, ecological industry, and ecological tourism (Zhang et al., 2019; Elahi et al., 2021a; Elahi et al., 2022). These advantages can improve the regional ecological product value, speed up the regional industrial transformation and product structure upgrade, and enhance the region’s level of green economy development. At the same time, it can attract many enterprises and investors to invest and even cooperate with foreign businessmen so as to improve the opening level of the region and promote the high-quality development of the region (Yong, 2016; Ren and Wen, 2018). From the demand side, a high-quality ecological environment is the essential condition of human survival and the foundation of human development (Ren and Zhang, 2019). Production noise pollution, radiofrequency electromagnetic radiation, excessive discharge of radioactive wastes and wastewater, waste gas, and waste residue containing various organic chemicals in human production activities will enter the human body through a variety of ways and means, causing harm to human health. In the high-quality stage of development, local governments not only focus on the level of economic growth but pay more attention to the balance of the whole social welfare distribution level, with a particular focus on the difference between urban and rural income and consumption levels. Local governments not only pay attention to the level of economic growth but also pay more attention to the balanced level of social welfare distribution, especially the income and consumption gap between urban and rural areas. They want to improve the income and welfare level of urban and rural low-income groups and narrow the gap between urban and rural rich and poor. When the income and welfare level of the vast majority of people are significantly improved, it not only increases people’s demand for goods and services, but also greatly enhances the demand for ecological environment.
2.1.2 The role of high-quality development in eco-environmental protection
At the same time, the impact of high-quality development on eco-environmental protection has both positive and negative aspects. On the one hand, high-quality development can promote eco-environmental protection. In the high-quality development stage, to improve the ecological environment for the survival of humans, countries, and regions will further increase investment in eco-environmental protection, promote a series of pollution control and resource conservation, ecological restoration for the construction of major projects. This can not only improve the quality of the ecological environment on the whole but also react to economic development, drive economic growth, and bring significant economic and social benefits and health benefits. On the other hand, high-quality development has a restrictive effect on eco-environmental protection. In the process of pursuing economic development, it is inevitable to consume a certain amount of natural resources and discharge a large amount of waste gas, wastewater, and waste residue, which greatly reduces the coverage of land and vegetation, causes damage to the ecological environment and greatly restricts the development process of eco-environmental protection. Therefore, eco-environmental protection and high-quality development are mutually reinforcing. High-level quality eco-environmental protection is the essential prerequisite for high-quality development, and high-quality development is the fundamental guarantee for eco-environmental protection and restoration. High-quality development promotes the construction of the ecological environment while restricting the development process of eco-environmental protection. There is an apparent interaction and coupling relationship between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development.
2.2 Study on the influencing mechanism of coupling driving factors between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development
In 2018, energy consumption per unit of industrial added value and per capita in the Yellow River Basin was about 1.38 times and 1.55 times China’s overall energy consumption. In the past, China blindly pursued the economic growth mode relying on high energy consumption, which led to the continuous deterioration of the ecological environment and other problems. Overall, the excessive use of energy consumption from fossil fuels caused several problem climate changes (Elahi et al., 2021b). If China continues to rely on this manner of economic growth and continues to develop over-used energy, land, water resources, etc., it will not only cause environmental pollution and ecological damage but also lead to a continuous increase in China’s demand for imported energy and excessive dependence on imported energy, which will make China’s economic development unsustainable. In 2018, the utilization rate of water resources in the Yellow River basin reached 75 percent, far exceeding the internationally recognized warning line of 40 percent (Wang, 2014). Human activities and climate change in the Yellow River basin water resources continue to reduce (Xu et al., 2020), coupled with the extensive economic growth mode caused by the unreasonable demand, causing problems such as water resources allocation is not reasonable if it continues to maintain a high water resources exploitation and utilization, over-exploitation of groundwater, can lead to ground subsidence threat to society and people’s safety. This will not only aggravate the pollution of the ecological environment but also affect the high-quality development level of the Yellow River basin.
Industrialization is still a vital driving force for economic growth in the Yellow River basin, especially in the central and western regions (Yang and Hu, 2019). Under the vision of development in the new era, we are pursuing a new type of high-quality industrialization that is green, low-carbon, intensive, efficient, and innovation-driven. It has become an irresistible trend to accelerate the transformation of industrialization and stimulate the innovation driving force of enterprises. At the same time, the higher level of industrialization will bring more serious industrial pollution, and eco-environmental protection measures are not in place in time, which will lead to serious damage to the ecological environment. On the one hand, the high level of industrialization can improve the high-quality development level of the Yellow River Basin. On the other hand, it will bring severe eco-environmental pollution, resulting in the risk of imbalance between the eco-environmental protection and high-quality development of the Yellow River Basin. In 2018, the urbanization rate of permanent residents in the Yellow River Basin was 56.82%. In the future, urbanization in the Yellow River Basin still has perfect space for development, and the realization of high-quality development will inevitably put forward higher requirements for urbanization. The promotion of new-type urbanization will also lead to the pollution and waste of land and water resources, the increase of urban environmental load, the reduction of biodiversity, and other ecological and environmental problems, which will have a negative impact on the coupling and coordination relationship between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development.
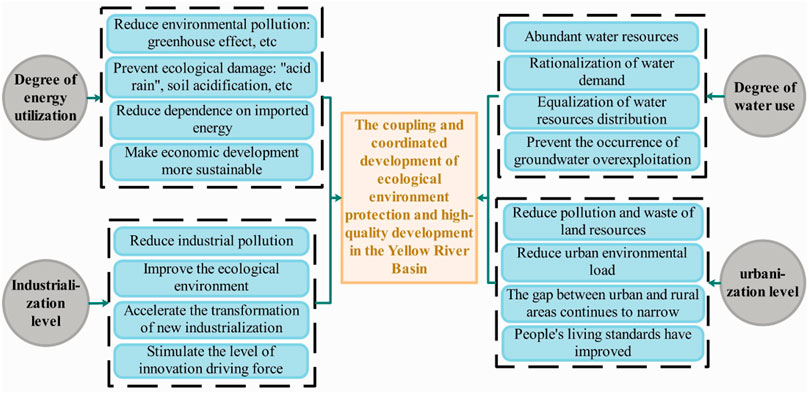
Based on this, this paper further draws the influencing mechanism diagram of the driving factors for the coupling and coordinated development of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin, as shown in Figure 1.
3 Study area and materials
3.1 Study area
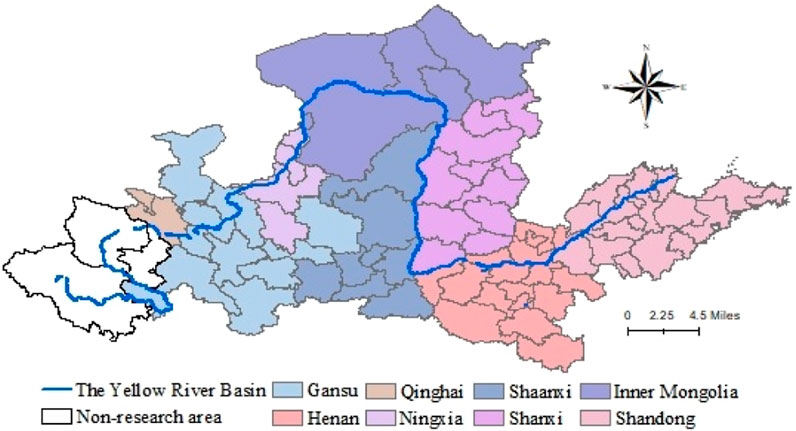
Seventy-seven prefecture-level cities (prefectures and leagues) in eight provinces and autonomous regions, including Shanxi, Shandong, Henan, Shaanxi, Gansu, Qinghai, Inner Mongolia, and Ningxia, are taken as the research scope of the Yellow River Basin region (Figure 2). Since it is difficult to obtain relevant index data for Hainan Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, Huangnan Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, and Guoluo Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture in Qinghai Province, these three autonomous prefectures are excluded from the research area of this paper, namely 74 prefecture-level cities. By 2017, the Yellow River basin had 95 sections of grade III and below water quality, accounting for 69.34 percent of the total. The total water consumption for eco-environmental protection was 36.11 billion cubic meters, accounting for 97.44 percent of the total water intake. The Yellow River Basin has severe water pollution, poor water pollution control ability, insufficient eco-environmental protection, a low recycling utilization rate of water resources, and a problem with water resources guarantee. It not only faces the threat of water resources shortage but also has the dangerous situation of an “overhanging river” (Teng et al., 2021), which also blocks the high-quality economic development of the Yellow River Basin. Therefore, it is crucial to explore the coupling and coordination relationship between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin and its driving factors for determining the future development direction of the Yellow River Basin and formulating relevant development strategies.
3.2 The construction of index system
3.2.1 Construction of eco-environmental protection index system
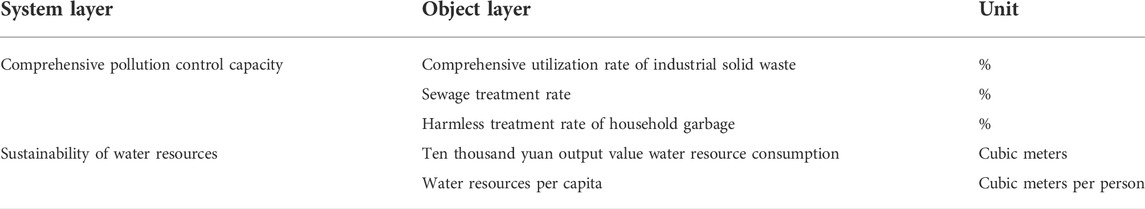
The ecological environment pollution and water resource shortage in the Yellow River Basin are the most crucial work of eco-environmental protection. Based on this, this paper constructed an eco-environmental protection evaluation index system consisting of comprehensive pollution control ability and water resource sustainability ability, as shown in Table 1.
3.2.2 Construction of high-quality development index system
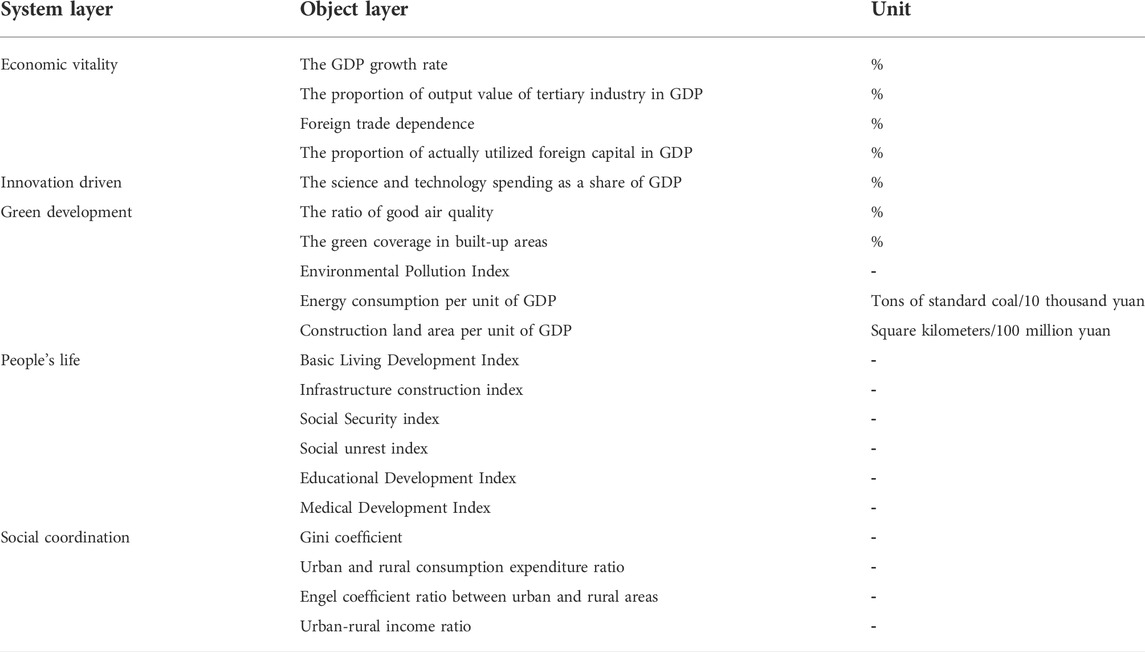
Given the problems faced by high-quality economic development in the Yellow River Basin, such as slowing economic growth rate, uneven internal development, outdated industrial structure, insufficient innovation momentum, serious ecological damage, and the apparent gap between urban and rural areas, as well as the phenomenon of people’s hope for a better life, this paper refers to the classification standard of high-quality development by Li et al. (2019). From the economic vitality, innovation drive, green development, people’s life, and social coordination, five big ideas considering the index system, economic growth, industrial structure, opening to the outside world, investment in science and technology, environmental pollution, resource utilization, the social harmony and fundamental public service level and so on to establish evaluation index system of high-quality development, as shown in Table 2.
3.2.3 Construction of coupled driving factor index system
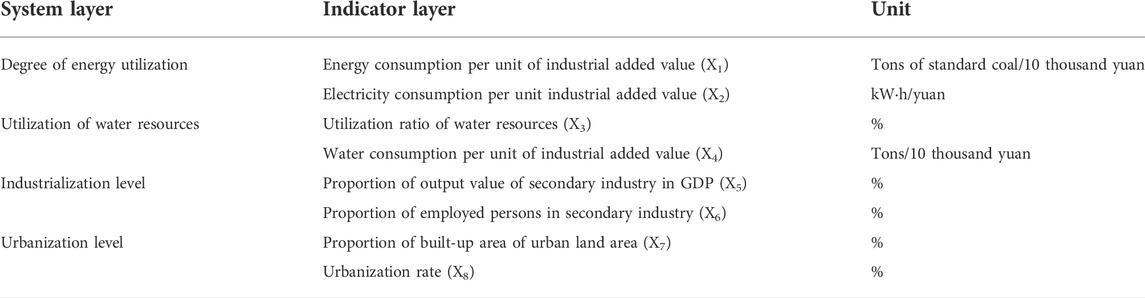
According to the theoretical analysis, the degree of energy utilization, water resources development, industrialization, and urbanization are the critical factors affecting the coupling and coordinated development of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin. Based on this, this paper established the driving factor index system of the coupling and coordinated development of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin, as shown in Table 3.
3.3 Data sources and processing
The study period was from 2003 to 2018. The statistical data in this study were obtained from China statistical yearbook, China city statistical yearbook, China’s urban construction, China’s regional economic statistical yearbook, China statistical yearbook, China’s water resources yearbook, China city life and price yearbook database, China’s urban and rural construction, EPS database, statistical yearbook, the provincial people’s government of provinces and cities, the bureau of statistics, the ecological environment agency’s website. This paper uses the linear fitting method to estimate the missing data and uses the extreme value method to standardize the data. At the same time, this paper further adopts the efficacy coefficient method to modify it to ensure that each data value is not zero.
3.4 Research methods
3.4.1 Coupling coordination evaluation model
Referring to the concept of “capacity coupling” in physics (Chen et al., 2020; Dong et al., 2021), this paper measures the interactive coupling strength between eco-environmental protection (A1) and high-quality development (A2) in the coupling coordinated evaluation index system of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin. For a binary system A1, A2, the deviation coefficient of the two can be expressed as (Lu et al., 2016):
Where,
Where,
Coupling degree C can only describe the influence intensity of coordinated development between eco-environmental protection systems and high-quality development systems but cannot accurately reflect the comprehensive, coordinated development level between the systems. Therefore, this paper further introduces the development degree T of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development, comprehensively evaluating the level of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in this region. The coupling coordination degree D of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development is constructed by the geometric average of development degree T and coupling degree C. The coupling coordination degree D can truly reflect the coupled and coordinated relationship between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in a specific region.
Where, T is the development degree of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development, α and β are the weights of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development, respectively, and their specific values can be determined according to the relative importance of the two systems. The author holds that eco-environmental protection and high-quality development are equally important, that is, α = β = 1, D is the coupling coordination degree of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development, A1 and A2 are the comprehensive evaluation value of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin respectively.
Refer to the classification standards of other scholars (Chen Y et al. 2020). This paper divides the coupling coordination degree D between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development into ten types, and the corresponding grade types are shown in Table 4.
3.4.2 Nonlinear autoregressive neural network model
The nonlinear autoregressive (NAR) neural network model is suitable for solving nonlinear fitting problems and is widely used in hydrological, biological information, and ecological security (Cheng et al., 2019). In this study, we applied NAR neural network model to predict the coupling coordination degree between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in each region of the Yellow River Basin in the next five years and explored the future development trend of the coupling coordination relationship.
3.4.3 Spatial regression model
The spatial regression model mainly solves the problems related to spatial dependence in linear regression analysis (Xiao, 2008). This study applies a spatial regression model to describe and visualize the global law of the coupling driving force between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin.
3.4.4 Geographically weighted regression model
The geographically weighted regression model is used to reflect the influence of observation points at different locations on the regression parameters by embedding the spatial location of the data into the regression parameters (Kan et al., 2019). This study applies a geographically weighted regression model to describe and visualize the local laws of the coupling driving force of ecological protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin.
4 Empirical analysis
4.1 Analysis on the coupling coordination relationship between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development
4.1.1 The coupling and coordination relationship between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development
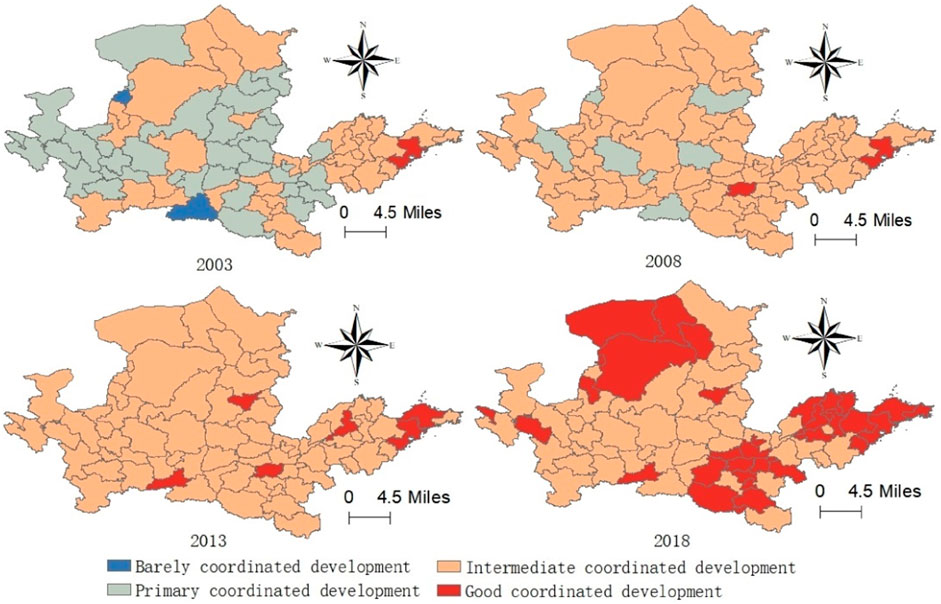
The coupling coordination evaluation model was used to calculate the coupling coordination degree of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin from 2003 to 2018, and the spatial evolution map was drawn by selecting the coupling coordination degree of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in 74 regions of the Yellow River Basin in 2003, 2008, 2013, and 2018, as shown in Figure 3.
From 2003 to 2018, the coupling coordination degree of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in all regions of the Yellow River Basin increased year by year. The coupling coordination degree of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Lower Reaches of the Yellow River Basin was always higher than that in the upper and middle reaches of the Yellow River Basin. In 2018, the coupling coordination degree of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the lower reaches of the Yellow River Basin was upgraded to a well-coordinated development level. In 2003, the distribution of the coupling and coordinated development between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin was loose, and there were four levels of coupling and coordinated development, which were barely coordinated development level, primary coordinated development level, intermediate coordinated development level, and well-coordinated development level. Among them, there are many areas in the primary coordinated development level of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development, and the areas in the well-coordinated development stage are mainly concentrated in the Shandong Peninsula in the lower reaches of the Yellow River Basin. Regions with an intermediate level of coordinated development are primarily concentrated in Inner Mongolia, Shandong, Ningxia, Henan, and Shaanxi. Shizuishan and Shangluo are only in barely coordinated development. Compared with 2003, the coupling coordination degree of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin region in 2008 improved significantly, from the primary coordinated development level to the intermediate coordinated development level of the large area. Shizuishan and Shangluo areas with the lowest coupling coordination degree also improved to the primary coordinated development level, and Zhengzhou also from the intermediate level of coordinated development to a good level of coordinated development. In 2013, the Yellow River basin area of the eco-environmental protection and development of high-quality coupling coordination development level up to intermediate coordinated development level comprehensively, coupling coordination level in the well-coordinated development phase of the area is still mainly concentrated in the lower reaches of the Yellow River in Shandong district, as well as the capital city of Shanxi, Shaanxi, Henan, Taiyuan, Zhengzhou and Xi’an. In 2018, have produced a batch of the Yellow River basin area of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development of coupling coordination degree in well-coordinated development level area, mainly with Henan region of Inner Mongolia, at this point, the eco-environmental protection and development of high-quality coupling coordination level in well-coordinated development level of the region are mainly concentrated in the Yellow River upstream and downstream of the Yellow River basin, region, in the middle reaches of the Yellow River basin, the level of coupling and coordinated development between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development is weak.
4.1.2 Prediction of coupling coordination between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development
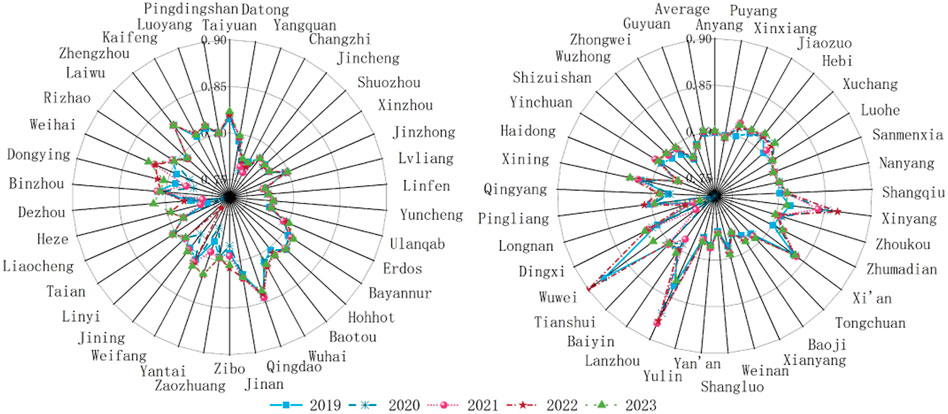
In order to further understand the changing trend of the coupling coordination degree between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin in the future, NAR neural network model was further used to predict the coupling coordination degree between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin in the next five years, as shown in Figure 4.
The results show that the average level of coupling coordination between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin will gradually increase in the next five years, and realize the transition from an intermediate coordinated development stage to a well-coordinated development stage, but there is still a significant gap from high-quality, coordinated development level. From 2019 to 2023, the coupling coordination degree of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in most Yellow River Basin areas shows a wave change trend. Compared with 2018, the coupling coordination degree of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in most areas of the Yellow River Basin shows an increasing trend in 2023. The overall coordinated development of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin is optimistic, but the severe challenges we face cannot be ignored. Qingdao, Wuhai, and Zhengzhou, which have a high degree of coupling coordination between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development, have a slow growth rate of 0.032, 0.058, and 0.177%, respectively, due to their lack of growth momentum, which makes it difficult to improve to the level of high-quality coordinating development. The coupling coordination degree between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in Dezhou, Yantai, Weihai, and Xuchang fluctuated greatly, and the change law was not apparent. As a result, the coupling coordination degree between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development predicted by Dezhou, Yantai, Weihai, and Xuchang fluctuated wildly, but the overall trend also increased. From 2019 to 2023, Jining, Pingdingshan, Anyang, Xinyang, Baiyin, Tianshui, Wuwei, Dingxi, and Shizuishan changed from intermediate coordinated development levels to well-coordinated development levels.
4.2 Coupling driving force analysis of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development
4.2.1 Global law analysis of coupling driving force between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development
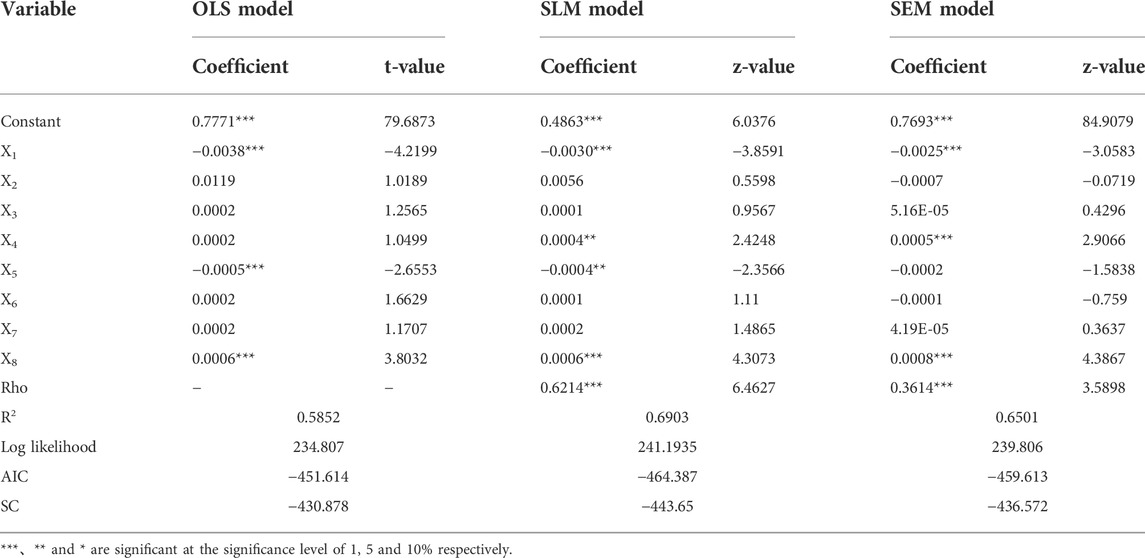
This paper selects indicators with correlation coefficients more significant than 80% from the principal components with cumulative contribution rates of more than 85%. Finally, eight indicators, including energy consumption per unit of industrial added value, electricity consumption per unit of industrial added value, and the utilization ratio of water resources, are determined as independent variables of the regression model through multicollinearity diagnosis. This paper further studied the coupling driving factors of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin in 2018 and constructed the OLS model, SLM model, and SEM model. The estimation results showed that the SLM model had the best fitting effect than the OLS and SEM models (Table 5).
SLM model estimation results show that spatial disturbance correlation significantly impacts the coupling coordination degree of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin. Globally, energy consumption per unit of industrial added value, water consumption per unit of industrial added value, the proportion of output value of the secondary industry in GDP, and urbanization rate are significant indicators of the coupling coordination degree between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin, which are all significant at the level of 1%. The degree of energy utilization, water resources development, industrialization, and urbanization are the main driving factors of the coupling coordination degree of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin. Energy consumption per unit of industrial added value and the proportion of output value of the secondary industry in GDP have a significant negative impact on the coupling coordination degree between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin. Low energy use efficiency is one of the critical factors leading to the coupling imbalance between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin. Since the city has not successfully transformed into new industrialization, the high industrialization level will lead to substantial industrial pollution. Today’s eco-environmental protection facilities and measures cannot solve the problem of such severe ecological pollution, causing severe eco-environmental pollution, thus affecting the coupling coordination level of the Yellow River basin eco-environmental protection and high-quality development. The water consumption per unit of industrial added value and urbanization rate significantly impact the coupling coordination degree of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin. While reducing the water consumption per unit of industrial added value, industrial enterprises increase the content of cadmium, nickel, mercury, and other heavy metals in the unit of industrial production, which aggravates the eco-environmental pollution and reduces the level of eco-environmental protection, thus weakening the coupling coordination between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin. The urbanization rate is an important index to measure the urbanization level of a country or region. Obviously, the high level of urbanization positively influences the coupling coordination degree of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin. The Yellow River Basin should focus on promoting the construction of basic projects such as water resource pollution prevention and water conservation, promoting the construction of new urbanization, stimulating the innovation-driven consciousness of enterprises, establishing and improving the incentive mechanism of enterprise water pollution assessment, further improving the urbanization level of the Yellow River Basin, and improving the efficiency of energy and water resources utilization. Through a series of measures to enhance the level of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development of the Yellow River Basin, promote the coordinated development of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development of the Yellow River Basin.
4.2.2 Local law analysis of coupling driving force between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development
This paper uses the geographically weighted regression model to analyze the coupling coordination degree between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development and the spatial stability of each influencing factor in the Yellow River Basin in 2018.
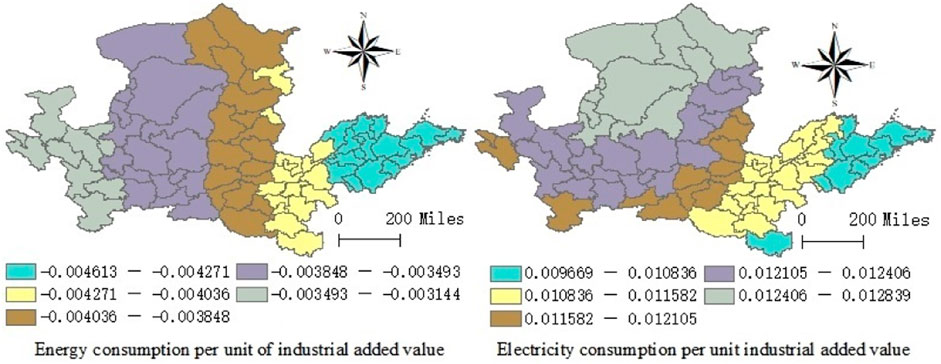
The regression results of the GWR model indicate that energy consumption per unit of industrial added value and electricity consumption per unit of industrial added value has strong spatial heterogeneity. The regression coefficient values show that energy consumption per unit of industrial added value and electricity consumption per unit of industrial added value have significant negative and positive impacts on the coupling coordination degree of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in 74 regions of the Yellow River Basin, respectively. Meanwhile, the effect of electricity consumption per unit of industrial added value on the coupling coordination degree of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in 74 regions of the Yellow River Basin is much greater than that of energy consumption per unit of industrial added value. Therefore, the degree of energy utilization is the main factor that leads to the change in the coupling coordination between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in 74 regions of the Yellow River Basin. The increase in electricity consumption has increased the use of advanced energy, significantly reduced the burning of wood, straw, straw, coal, and other low-level energy significantly improved the level of urban ecological environment, improved the living environment of urban residents, and realized the coordinated development of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development. The effect of electricity consumption per unit of industrial added value on the coupling coordination between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development is positively correlated. The spatial distribution of the estimated coefficient shows that the impact of energy consumption per unit of industrial added value on the coupling coordination degree of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in 74 regions of the Yellow River Basin gradually weakens from east to west. The influence of electricity consumption per unit of industrial added value on the coupling coordination degree of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in 74 regions of the Yellow River Basin gradually increases from southeast to northwest (Figure 5).
Six indicators, such as water resource utilization rate, water consumption per unit industrial added value, and the proportion of output value of the secondary industry in GDP, have different impacts on the coupling coordination degree of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in 74 regions of the Yellow River Basin (Figure 6). The spatial distribution diagram of the GWR model estimated coefficients shows that the spatial distribution of the impacts of water resources exploitation and utilization ratio and the proportion of output value of the secondary industry in GDP on the coupling coordination degree of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in 74 regions of the Yellow River Basin is similar to the energy consumption per unit industrial added value, which is gradually decreasing from east to west. The spatial distribution of the impacts of water consumption per unit of industrial added value, the built-up area in urban land area, and urbanization rate on the coupling coordination degree of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in 74 regions of the Yellow River Basin are, on the contrary, showing that it gradually weakens from west to east. The spatial distribution of the influence of the proportion of employed persons in the secondary industry on the coupling coordination degree is also contrary to the power consumption per unit of industrial added value, which shows that the proportion of employed persons in the secondary industry gradually increases from the northwest to the southeast. The 74 regions in the Yellow River Basin should cooperate by region and take effective measures to ensure the coordinated development of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the light of their own regional development characteristics, aiming at the shortcomings of energy, water resources, industry, and urban development, to promote the coordinated development of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin.
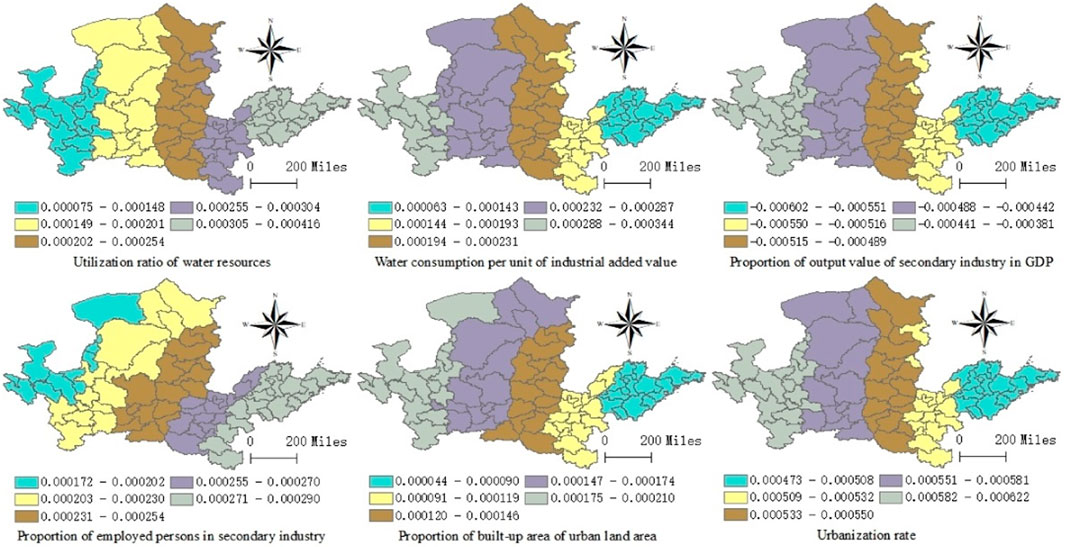
FIGURE 6. Spatial distribution of estimated coefficients of water resources utilization, industrialization and urbanization.
5 Conclusion and implications
5.1 Conclusion
Starting from the current situation of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin, this paper constructs the coupling coordination index system of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin. This paper uses the coupling coordination evaluation model, GIS analysis method, and NAR neural network model to measure the coupling coordination relationship between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in 74 regions of the Yellow River Basin from 2003 to 2018, analyzing the Spatio-temporal differentiation and predict the future trend. Finally, the spatial autoregressive and geographically weighted regression models were used to explore the global and local laws of the coupling driving forces of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin. The main conclusions are as follows:
1) From the perspective of the coupling coordination degree between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin, the coupling coordination overall shows an upward trend, but the regional differences are apparent. The regions with well-coordinated development between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development are mainly concentrated in Henan, Inner Mongolia, and the Shandong Peninsula. In contrast, the regions with low-level coordinated development are Longnan in Gansu province, Luliang in Shanxi Province, and Yulin in Shaanxi Province. In terms of spatial distribution, the initial loose distribution has been transformed into the current tight distribution, and the spatial agglomeration characteristics have been significantly enhanced. According to this development trend, the coupling coordination between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin will gradually improve in the next five years. The overall transformation from an intermediate coordinated development stage to a well-coordinated development stage will be realized.
2) From the perspective of the future development trend of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin, the coupling coordination degree of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin will show wave changes in the future overall development will show an increasing trend. The average coupling coordination degree between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin will change from an intermediate coordinated development stage to a well-coordinated development stage. Although the overall coordinated development of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin is optimistic, the severe challenges cannot be ignored.
3) From the perspective of the coupling driving force of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin, the level of energy utilization, water resource utilization, industrialization level, and urbanization level are all critical driving factors for the coupling coordination of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin. The degree of power consumption, development and utilization of water resources, urban water use efficiency, employment structure, land use, and population structure have positive and significant effects on coupling coordination. In contrast, the degree of energy consumption and output value structure has adverse and significant effects. Locally, the degree of energy utilization is the root of the differentiation of the coupling coordination between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin. In space, the impact of energy consumption on the coupling coordination between eco-environmental protection and high-quality development is negative, gradually weakening from east to west. In contrast, the effect of electricity consumption is positive, increasing progressively from southeast to northwest.
5.2 Implications
Due to the interaction of resource endowment, historical conditions, spatial structure, social and economic development foundation, direction, and policy, the coupling coordination degree of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in different regions of the Yellow River Basin is quite different. The author believes that the policy recommendations for realizing the coupled and coordinated development of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin can include the following:
1) Based on the optimal utilization strategy of energy and water resources. Firstly, the government should first strengthen control over energy and resources, urge enterprises to use coal, oil, fossil fuels, and other non-renewable resources scientifically and rationally, and carry out in-depth work related to energy conservation and consumption reduction. Secondly, the government should strengthen energy recycling, reduce the total energy consumption from the source, and ensure sufficient energy resource reserves. Last but not least, the government should increase our capacity for independent innovation, actively seek new energy sources that can replace non-renewable energy sources, and adopt clean energy sources that can be recycled.
2) Based on the coordinated industrialization-urbanization strategy. First of all, local governments should make full use of the natural resource endowment of the region, strengthen the government’s macro-control, promote the optimal allocation of resources, optimize foreign trade structure, promote the optimization and upgrading of industrial structure, and improve the modern industrial system. Second, Each region should strengthen the work of collaboration between regions, strive to build several creative elements, fully equipped with system science industry cluster, coordinate labor elements and industry configuration, build a good employment environment, improve employment entrepreneurship support policies, adjust the structure of employment, strengthen the employment quality, create industry employment double drive mode. Finally, Each region also should optimize urban spatial layout, adjust urban and rural population structure, improve urban land planning policies, strengthen public infrastructure construction, improve relevant social welfare security policies, and promote new industrialization and new urbanization.
Constrained by the availability of data and the structure of space, this paper only selects the environmental pollution control ability and the water resources sustainability index with the characteristics of water resource scarcity in the Yellow River Basin for research in evaluating the level of eco-environmental protection. In future research, the level of eco-environmental protection can be extended to the ecological protection level, which includes the eco-environmental protection level and the ecological species protection level. Ecological species protection indexes include the genetic diversity index, species diversity index, and ecosystem diversity index. If the ecological species protection index can be obtained, the study on the coupling coordination between ecological protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin can be improved. Future research will focus on the ecological footprint of the Yellow River basin decoupling effect of the development of high-quality research, objective cognitive state of sustainable development of the ecosystem of the Yellow River basin area of land, further deepening the development of the Yellow River basin area a series of studies, such as economic and social development path, the industrial adjustment, ecological environment policy and industrial policy and decoupling effect, etc. In addition, future research will be devoted to making scientific planning and suggestions on the survival and social and economic development of people in the Yellow River Basin to expand to other regions as far as possible and benefit all humankind.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
Conceptualization, YX and XL; methodology, YX; formal analysis, YX; writing—original draft preparation, YX; writing—review and editing, YX and XL. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
An, S. W., and Li, R. P. (2020). The connotation and promotion strategy of high quality development in the Yellow River Basin. Reform (1), 76–86.
Chen., J. D., Li, Z. W., Dong, Y. Z., Song, M. L., Shahbaz, M., Xie, Q. J., et al. (2020). Coupling coordination between carbon emissions and the eco-environment in China. J. Clean. Prod. 276, 123848. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123848
Chen, X. D., and Jin, B. (2019). The focus of high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin. Reform 11, 25–32.
Chen, Y., Zhang, K. Y., and Chen, X. D. (2020). Ecological protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River basin. Reg. Econ. Rev. (1), 8–22. doi:10.14017/j.cnki.2095-5766.2020.0003
Cheng, F. Z., Li, T., Wei, Y. M., and Fan, T. J. (2019). The VEC-NAR model for short-term forecasting of oil prices. Energy Econ. 78, 656–667. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2017.12.035
Deng, X. Y. (2020). Ecological and environmental risks in the Yellow River Basin from the perspective of holism and its countermeasures. Dongyue Trib. 41 (10), 150–155. doi:10.15981/j.cnki.dongyueluncong.2020.10.017
Dong, G. L., Ge, Y. B., Zhu, W. Y., Qu, Y. B., and Zhang, W. X. (2021). Coupling coordination and spatiotemporal dynamic evolution between green urbanization and green finance: A case study in China. Front. Environ. Sci. 8, 621846. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2020.621846
Elahi, E., Khalid, Z., Tauni, M. Z., Zhang, H. X., and Xing, L. R. (2021a). Extreme weather events risks to crop-production and the adaptation of innovative management strategies to mitigate the risk: A retrospective survey of rural Punjab. Technovation, 102255. Pakistan. doi:10.1016/j.technovation.2021.102255
Elahi, E., Khalid, Z., and Zhang, Z. X. (2021b). Understanding farmers’ intention and willingness to install renewable energy technology: A solution to reduce the environmental emissions of agriculture. Appl. Energy 309, 118459. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2021.118459
Elahi, E., Zhang, Z. X., Khalid, Z., and Xu, H. Y. (2022). Application of an artificial neural network to optimise energy inputs: An energy- and cost-saving strategy for commercial poultry farms. Energy 244, 123169. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2022.123169
Gao, L. A. (2020). Identification and optimization of coupling coordination between economic development and ecological environment: A case study of Northeast China. Statistics Inf. Forum 35 (1), 74–81. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1007-3116.2020.01.009
Guo, H. (2020). Sustainable development and eco-environmental protection in high quality Development of the Yellow River Basin. J. Humanit. (1), 17–21. doi:10.15895/j.cnki.rwzz.20191129.005
Jin, F. J., Ma, L., and Xu, D. (2020). Environmental stress and optimized path of industrial development in the Yellow River Basin. Resour. Sci. 42 (1), 127–136. 1. Key Laboratory of Regional Sustainable Development Modeling of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, CAS, Beijing 100101, China2. College of Resources and Environment, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China. doi:10.18402/resci.2020.01.13
Kan, B. Y., Pu, L. J., Xu, C. Y., Zhu, M., Huang, S. H., and Xie, Z. D. (2019). Driving factors of residential land price spatial heterogeneity in Nanjing urban area based on GWR model. Econ. Geogr. 39 (3), 100–107. doi:10.15957/j.cnki.jjdl.2019.03.012
Li, J. C., Shi, L. M., and Xu, A. T. (2019). Discussion on high quality development evaluation index system. Stat. Res. 36 (1), 4–14. doi:10.19343/j.cnki.11-1302/c.2019.01.001
Li, L. S., Zhao, H. B., Guo, F. Y., and Wang, Y. (2021). Spatial-temporal pattern evolution of high-quality industrial development in Urban agglomerations in the Yellow River Basin. Geogr. Sci. 41 (10), 1751–1762. doi:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.10.007
Liu, K., Qiao, Y. R., Shi, T., and Zhou, Q. (2020). Study on coupling coordination and spatiotemporal heterogeneity between economic development and ecological environment of cities along the Yellow River Basin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 20, 6898–6912. doi:10.1007/s11356-020-11051-0
Liu, Y. S., Xia, Jun., Wang, Y. S., Song, J. X., Zhao, X. Z., and Liu, X. Q. (2022). Coordination and high quality development of man-land system in the Yellow River Basin. J. Northwest Univ. Sci. Ed. 52 (3), 357–270. doi:10.16152/j.cnki.xdxbzr.2022-03-001
Lu, J., Chang, H., Zhao, S. P., and Xu, C. J. (2016). Evolution characteristics of coupling relationship among energy, economy and environment in Shandong Province. Econ. Geogr. 36 (9), 42–48. doi:10.15957/j.cnki.jjdl.2016.09.006
Ma, L., Tian, H. Z., and Kang, L. (2020). Eco-environmental impact and spatial control of mineral resources exploitation in the Yellow River Basin. Resour. Sci. 42 (1), 137–149. 1. Key Laboratory of Regional Sustainable Development Modeling, Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, CAS, Beijing 100101, China2. College of Resources and Environment, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China. doi:10.18402/resci.2020.01.14
Ren, B. P., and Wen, F. A. (2018). The criteria, determinants and approaches of High quality development in China in the new era. Reform (4), 5–16.
Ren, B. P., and Zhang, Q. (2019). Strategic design and Support system construction of high quality development in the Yellow River Basin. Reform (10), 26–34.
Shi, T. (2020). Coupling coordination degree and spatial network effect of ecological protection and high-quality economic development in the Yellow River Basin. Reg. Econ. Rev. (3), 25–34. doi:10.14017/j.cnki.2095-5766.2020.0048
Shi, T., Yang, S. Y., Zhang, W., and Zhou, Q. (2020). Coupling coordination degree measurement and spatiotemporal heterogeneity between economic development and ecological environment — empirical evidence from tropical and subtropical regions of China. J. Clean. Prod. 244, 118739. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118739
Teng, T. W., Shen, D. H., and Hu, S. L. (2021). Spatial pattern evolution and influencing factors of air pollution in the Yellow River Basin. Geogr. Sci. 41 (10), 1852–1861. doi:10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2021.10.017
Wang, B. S. (2019). Discuss the understanding of high level protection of ecological environment promoting high quality development of economy. Theor. Res. Urban Constr. Electron. version) (9), 160. doi:10.19569/j.cnki.cn119313/tu.201909142
Wang, B. (2014). Study on the dynamics of coordinated development of regional economy and ecological environment in China based on coupling model. Changsha: Hunan university.
Wang, C. Y. (2020). To promote ecological protection and high-quality development of the Yellow River basin under the guidance of xi jinping thought on ecological civilization. China Ecol. Civiliz. (1), 74–77.
Wang, W. (2020). Exploring the path of promoting high-quality development by eco-environmental protection. Resour. Econ. Environ. Prot. (8), 15. doi:10.16317/j.cnki.12-1377/x.2020.08.013
Xing, X., Xiu, C. B., and Liu, Y. C. (2020). Study on the coupling coordination between water resources utilization efficiency and economic development in the Yellow River Basin. Soft Sci. 34 (08), 44–50. doi:10.13956/j.ss.1001-8409.2020.08.08
Xu, W. J., Zhang, X. P., Xu, Q., Gong, H. L., Li, Q., Liu, B., et al. (2020). Study on the coupling coordination relationship between water-use efficiency and economic development. Sustainability 12 (3), 1246. doi:10.3390/su12031246
Yang, Y., and Hu, N. (2019). The spatial and temporal evolution of coordinated ecological and socioeconomic development in the provinces along the Silk Road Economic Belt in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 4, 101466. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2019.101466
Yong, Y. R. (2016). Promote supply-side management with big data of environmental protection. Chin. J. Environ. Manag. (3), 25–34. doi:10.16868/j.cnki.1674-6252.2016.04.109
Zhang, Y. L., Xiao, X., Zheng, C. H., Xue, L., Guo, Y. R., Wu, Q. T., et al. (2019). Is tourism participation in protected areas the best livelihood strategy from the perspective of community development and environmental protection? J. Sustain. Tour. 28 (4), 587–605. doi:10.1080/09669582.2019.1691566
Zhang, Y., and Shi, H. M. (2022). Evaluation of coupling coordination degree between high quality urbanization development and ecological environment in the Yellow River Basin. Statistics Decis. 38 (10), 71–75. doi:10.13546/j.cnki.tjyjc.2022.10.014
Zhao, J. J., Liu, Y., Zhu, Y. K., Qin, S. L., Wang, Y. H., and Miao, C. H. (2020). Spatiotemporal differentiation and influencing factors of the coupling and coordinated development of new urbanization and ecological environment in the Yellow River Basin. Resour. Sci. 42 (1), 159–171. doi:10.18402/resci.2020.01.16
Keywords: yellow river basin, eco-environmental protection, high-quality development, coupled and coordinated development, driving factors
Citation: Xin Y and Liu X (2022) Coupling driving factors of eco-environmental protection and high-quality development in the yellow river basin. Front. Environ. Sci. 10:951218. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2022.951218
Received: 23 May 2022; Accepted: 11 July 2022;
Published: 05 August 2022.
Edited by:
Qingsong He, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, ChinaReviewed by:
Luigi Aldieri, University of Salerno, ItalyEhsan Elahi, Shandong University of Technology, China
Muhammad Sohail Amjad Makhdum, Government College University, Pakistan
Copyright © 2022 Xin and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yun Xin, eHlqeHVmZUAxNjMuY29t
 Yun Xin
Yun Xin Xiaoyu Liu
Xiaoyu Liu