- 1Department of Functional and Evolutionary Ecology, Faculty of Life Sciences, University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
- 2Department for Application Architecture and Development, Zentralanstalt für Meteorologie und Geodynamik (ZAMG), Vienna, Austria
- 3Systema GmbH, Vienna, Austria
- 4Research and Innovation Centre, Fondazione Edmund Mach, S. Michele all’Adige, Italy
- 5Department of Limnology and Bio-Oceanography, Faculty of Life Sciences, University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
- 6Department of Water, Atmosphere and Environment, Institute of Hydrobiology and Aquatic Ecosystem Management, University of Natural Resources and Life Sciences, Vienna, Austria
- 7Research Department for Limnology, University of Innsbruck, Mondsee, Austria
Macrophytes play an important role in shallow lakes if large standing crop can be achieved. Here we stress the role of submerged macrophytes for benthic-pelagic coupling in the shallow oxbow lake Alte Donau (Austria) during restoration triggered by sufficient light availability (12% surface ambient light, photic>12% depth,
Introduction
Benthic-pelagic coupling addresses any form of exchange between these two spatially different habitats (Vadeboncoeur et al., 2002; Gyllström and Hansson, 2004; Søndergaard et al., 2005; Ferreira et al., 2018; Urrutia-Cordero et al., 2020; Mei et al., 2021). Even if studies about benthic-pelagic coupling go back to early work in aquatic sciences (e.g., Johnson and Wiederholm, 1992; Gyllström and Hansson, 2004), a broader emphasis is put today on this issue in view of anthropogenic pressure and climate change (Griffiths et al., 2017; Ferreira et al., 2018; Urrutia-Cordero et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2021). In the present study, we stress the role of submerged macrophytes for benthic-pelagic coupling in a shallow oxbow lake triggered by sufficient light availability.
According to Puche et al. (2021), the connectivity of “macrophyte-meadows” is mediated by primary producers and herbivores to both, the benthic and the pelagic habitat. This implies that “underwater meadows,” which are often categorized as being part of the benthic habitat (“benthic macrophytes”), should not be strictly assigned to either one of the two habitats. Macrophytes play a crucial role in particular in shallow lakes, however, their settlement on lake bottom depends on water transparency (Istvánovics et al., 2008; Jůza et el., 2019; Chorus et al., 2020; Dubey et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2022). Therefore, macrophyte meadows are not obligate habitats such as the benthic and the pelagic zone in shallow lakes. They are more specific to lake ecology and thus less often studied than benthic or pelagic issues. Unlike small benthic organisms or flat mats of algal filaments, which live in the close vicinity of the lake bottom, underwater meadows, such as in Alte Donau, build a thick layer of 0.5–1.20 m height (Löffler, 1988). Mature macrophyte meadows of dense stands of charophytes or vascular plants build their own unique habitat architecture (Hacker and Steneck, 1990), often characterized by an underwater canopy including (1) a large interstitial water volume between thallus or plant shoots and (2) an immensely large bio-surface formed by charophyte thalli or vascular plant shoots. In case of macrozoobenthos studies, this specific habitat is commonly named “phytal” (Hacker and Steneck, 1990; Eidinger, 2018; Janecek et al., 2018).
In Alte Donau, the shallow oxbow lake of the presented study, high macrophyte yields have been recorded twice: firstly, in the mesotrophic reference year 1987, when dense charophyte meadowscovered almost the whole lake bottom and were dominated by Nitellopsis obtusa. Secondly, in the period from 2004 to 2019 after the re-settlement of macrophytes due to lake restoration, when a high macrophyte yield could be accomplished again. With the re-establishment of macrophytes, the vascular plant Myriophyllum spicatum had become the dominant species, while charophytes were relatively sparse (Pall, 2018; Teubner et al., 2020). Although various vascular plant species and charophytes were planted during lake restoration, M. spicatum grew fastest and its canopy formation did not allow any other macrophytes to spread out spatially in Alte Donau (Pall, 2018). This macrophyte species often succeeds after being planted by macrophyte management (Yu et al., 2016; Gao et al., 2020). M. spicatum can also be the most abundant vascular submerged aquatic plant in natural habitats, i.e., in large lakes, along whole rivers and across biogeographical regions (Lake Võrtsjärv: Feldmann and Nõges, 2007; Danube River: Janauer et al., 2021; from temperate to tropical freshwater ecoregions due to broad thermal tolerance: Lind et al., 2022).
The macrophyte development is mainly controlled by underwater light climate (Istvánovics et al., 2008; Jůza et al., 2019; Baart et al., 2010; Dubey et al., 2021; Zhu et al., 2021). Therefore, in the present study about the emergence of macrophytes and benthic-pelagic coupling, we focus on light availability along the benthic and pelagic habitat. We analyse the progression of the size of the photic benthic and pelagic habitat, respectively, and how their extensions are spatially linked to each other.
In a previous study about the long-term restoration development of Alte Donau, we underscored water transparency as a socio-ecological indicator for urban waters. Water clarity can be also used as key parameter for bridging the criteria of ecosystem service supply and sustainable ecosystem health (Teubner et al., 2020; Teubner et al., 2021), which is most applicable for assessing the ecosystem services of waters in urban areas (e.g., Kumar and Shekhar, 2021; Cui et al., 2022). In the present 28-year study, we re-assess the underwater light climate for macrophyte growth by retrieving underwater light attenuation from Secchi depth (
Methods
Site description and sampling sites
The oxbow lake Alte Donau (Figures 1A–D), part of the capital city Vienna, comprises two main impoundments, the north basin (sampling site AD1, AD2) and south basin (sampling sites AD3, AD4), and a small appendix, Kaiserwasser (AD5, Figure 1A). Although the reed vegetation along lake shores have also been restored (Figure 1E), the focus in the present study about benthic-pelagic coupling is on submerged vegetation (Figure 1D). Regular sampling for water chemistry (total phosphorus, TP; chlorophyll-a, Chl-a; dissolved organic carbon, DOC), water temperature (surface water temperature, SWT; depth integrated water temperature, WT) and Secchi depth (
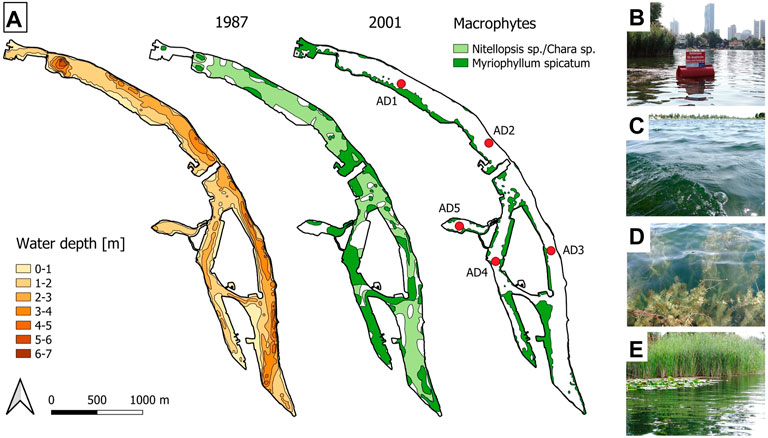
FIGURE 1. Alte Donau oxbow lake maps (A): bathymetric chart (left) and lake area covered by underwater vegetation during macrophyte dominated reference year 1987 (middle) and early phase of re-establishment of macrophytes in 2001 including locations of sampling sites AD1-AD5 (right). Photos (B–E) relate to sampling sites with reed belt between AD2 and AD3 (B), deep lake site at AD3 (C), dense macrophyte stands of Myriophyllum spicatum at AD4 (D) and experimental lake area “Kaiserwasser” at AD5 (E). (B–C) taken in 2015, from www.lakeriver.at. Lake maps in A (left and middle) are redrawn from Löffler (1988), and (right) modified from Pall (2018).
Mesotrophic reference condition, eutrophication and restoration schedule over 27 years
The mesotrophic cyprinid-state of Alte Donau in 1987, characterized by dense meadows of underwater vegetation mainly of harophytes (biomass contribution: 74% of tons dry weight (DW) and 77% of tons fresh weight (FW), respectively), is described by a multidisciplinary author consortium in Löffler (1988). Even though first signs of increasing nutrients, a slight macrophyte decline, and other aspects of habitat deterioration related to recreational use were critically documented at that time, recent studies (e.g., Dokulil et al., 2018a; Teubner et al., 2020, 2021), as well as the present study claim that the year of 1987 describes reference conditions. An intensive multidisciplinary study started again with nutrient enrichment from 1993 onwards (Dokulil et al., 2018a). The hypertrophic situation with algal turbidity (cyanobacterial blooms, e.g., of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii) (stage 1) is documented for 1993 and 1994. In-lake restoration treatment started with chemical RIPLOX-precipitation (phosphate precipitation with iron chloride and sediment oxidation with nitrate; Ripl, 1978) in 1995 and 1996, and resulted in a prompt drop of summer phytoplankton (1995–2000, stage 2). Years 2001–2006 were dedicated to the re-establishment of macrophytes (stage 3) followed by the stage of “sustained restoration development” (2007–2019, stage 4). Further details about the long-term restoration measures in the years 1993–2014 most relevant for the present study are available for water chemistry in Donabaum and Riedler, (2018), for phyto- and zooplankton in Teubner et al. (2018a, b), for macrozoobenthos in Janecek et al. (2018), and macrophytes and helophytes in Pall (2018) and in Pall and Goldschmid (2018). Time series data plotted in this study do not only present a more recent development in Alte Donau until 2019 but also go far beyond aspects shown in Dokulil et al. (2018a, longest time series ends there in 2014).
Lake morphometry and photic hypsographic curve in view of underwater light availability
The depth contour lines of lake morphometry refer to https://data.wien.gv.at. The mean depth of Alte Donau (
Concentration of TP, the response to this total pool of phosphorus by algal development (algal biomass estimated by Chl-a concentration), and followed up alterations of water turbidity (estimated by
Water transparency expressed by
The seasonally different background of light attenuation refers to the seasonal time-lag between concentration development of Chl-a and DOC in Alte Donau. A seasonal loop pattern is thus found when plotting
Winter
Spring
Summer
Autumn
Teubner et al. (2020) used underwater light attenuation to identify three depth layers of specific ambient light requirements for photosynthetic domains of phytoplankton and submerged macrophytes: (1)
The depth of 12% of surface ambient light,
The percentage of surface ambient light at Secchi depth
In analogy, the percentage of surface ambient light at mean lake depth (
Macrophyte biomass yield and phosphorus nutrient-pool
Lake macrophyte biomass was estimated by echo-sounding of the whole lake (Löffler, 1988; Jäger et al., 2004; Pall, 2018) each year, the identification of species and collection of plant material for lab analysis by scuba-diving. In more recent years, the yield by underwater mowing was used to verify biomass estimates from echo-sounding. Macrophyte surveys relate to the aboveground biomass during peak growing seasons (summer surveys) and were considered as proxy for annual yield of the whole water basin throughout this study. In the reference year of mesotrophic state in 1987, charophytes were dominant and contributed to about three quarters of the total macrophyte DW biomass, while M. spicatum (and further spermatophytes of less importance) to the remaining one quarter (Löffler, 1988). In 1993, when macrophyte biomass was very low under hypertrophic conditions, the portion of charophytes was still high (90% N. obtusa) (Pall, 2018). In years of significant re-establishment of macrophytes, however, M. spicatum became the most dominant species from 2005 onwards, e.g., contributing about 90% to total biomass in 2014 (further details see Pall, 2018). These changing proportions between charophytes and Myriophyllum were taken into account for converting DW to FW of macrophyte biomass and vice versa (Figure 2A, left panels) and for calculating the nutrient content of macrophyte tissues (Figure 2B) according to Löffler (1988) (phosphorus content for M. spicatum: mean 1.54 mg g−1(DW), median 1.21 mg g−1(DW) and for charophytes: mean 1.51 mg g−1(DW), median 1.11 mg g−1(DW)), plant cover height and bio-surface of macrophyte plants. Fresh weight and nutrient content of macrophyte tissues were analysed from mono species plant samples which were prewashed with water (Löffler, 1988).
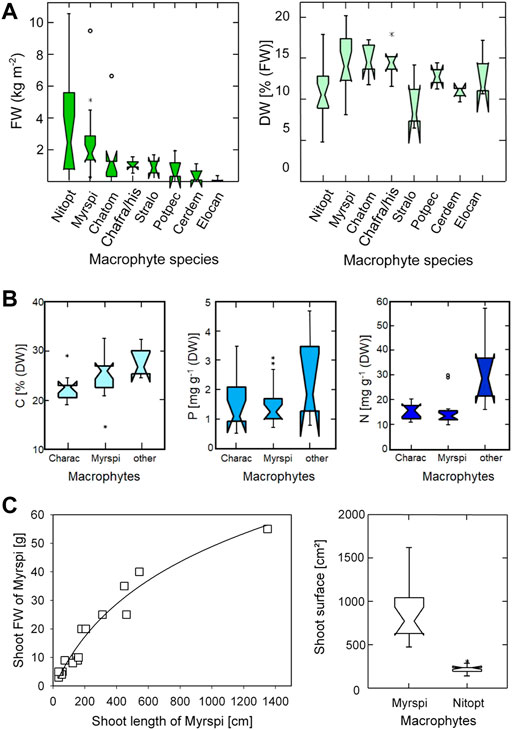
FIGURE 2. Background measurements for quantifying the impact of aquatic vegetation on the lake ecosystem. (A): Macrophyte fresh weight (FW in kg per m2, n = 61, left panel) and dry weight (DW, right panel) as % of fresh weight (n = 61); (B) Macrophyte tissue nutrient concentration as % of DW for carbon (C, n = 35). Phosphorus (P, n = 35) and nitrogen (N, n = 35) as mg per g DW. (C) Morphometry of macrophytes. Left panel: shoot fresh weight as a function of shoot length for Myrspi (n = 18, logarithmic regression line with R2 = 0.94); right panel: shoot surfaces of individual plants of the two most dominant species, Myrspi (n = 16) and Nitopt (n = 13). Data for all notched boxplots (A–C) are retrieved from Löffler (1988). Notched boxplots of A to C refer to sampling in June and July 1987, Line plot of C covers sampling in August 2017. Abbreviation of water plants: Cerdem, Ceratophyllum demersum L.; Charac, Characeae; Chafra/his, Chara fragilis Desv./hispida L; Chatom, Chara tomentosa L.; Elocan, Elodea canadensis Michaux; Myrspi, Myriophyllum spicatum L.; Nitopt, Nitellopsis obtusa (Desv.) J Groves; Potpec, Potamogeton pectinatus L.; Stralo, Stratiotes aloides L.
Stimulation of vernal macrophyte development by short-term water-level draw-down in spring was first tested in 2002 and then introduced on a regular basis from 2003 onwards as a macrophyte management measure in Alte Donau. Concurrently, mowing in summer 2003 started removing macrophyte biomass during the growing season to some extent. The mowing program has been intensified since 2018, after 3 years of particularly high macrophyte biomass (2015–2017).
Data about the phosphorus concentration in sediment cores and the phosphorus release from sediment during hypertrophic state (1994) are provided in Supplementary Material S3.
Macrophyte bio-surface
Determining the macrophyte bio-surface for the whole lake aimed at estimating (1) the potential for nutrient uptake via the thalli or shoots in addition to the rhizoids or roots, and (2) the macrophyte capacity of providing phytal habitat for invertebrates. The bio-surface was calculated from the total biomass of the macrophytes, their growth height and their surface per growth height. According to Löffler (1988), the mean plant shoot length in summer for M. spicatum is 192 cm (median: 172 cm, n = 16), and thalli length for charophytes 97 cm (median: 77 cm, n = 12; N. obtusa, Chara tomentosa). The bio-surface for Myriophyllum (4.5 cm2 per cm shoot length) is higher than for charophytes (3.6 cm2 per cm thalli length, Löffler, 1988). Accordingly, stands covered with M. spicatum provide a much higher surface area per m2 sediment area, than charophytes, as shown for individual plants (Figure 2C, right panel). The shoot fresh weight as function of shoot length for M. spicatum is shown in Figure 2C (left panel, mean: 0.085 g cm−1, median: 0.078 g cm−1, n = 18). The length of shoots is measured with a ruler. The shoot fresh weight is captured as macrophyte displacement volume (e.g., Christie et al., 2009; Nagengast and Kuczyńska-Kippen, 2015), i.e., by measuring the difference of water volume with and without plant shoot in a graduated measuring cylinder (conversion: 1 ml macrophyte shoot displacement volume = 1 g fresh weight of macrophyte shoot). Estimating the displacement volume is a standard method for estimating phytoplankton biovolume or biomass from microscopical counting (using cell dimensions for calculating the cell-biovolume, e.g., Rott, 1981; Rott et al., 2007) using the same conversion (1 cm³ phytoplankton biovolume = 1 g phytoplankton biomass).
Statistical treatment of time series data
Although there was a regular biweekly sampling scheme for pelagic observations, sampling was not always carried out in exactly 2-week intervals over the 28-year study period. Therefore, available data of all parameters over the whole study period were linearly interpolated at daily resolution (Livingstone, 2003; Sapna et al., 2015) and were averaged afterwards over a 2-week period. These biweekly interpolated data are used throughout this study with the only exception of retrieving
Results
Alte Donau oxbow lake map and macrophyte cover
The elongated shape of lake morphometry of the former main stretch of the Danube River, the oxbow lake Alte Donau, is shown in Figures 1A–C. Year 1987, the reference year (Figure 1A, middle panel), gives evidence that the shallowness of the water body suits well for building up dense meadows of underwater vegetation. Recovering from the hypertrophic state, macrophyte resettlement started at shallow littoral shore sites as depicted for 2001 in Figure 1A (right panel).
Basic pelagic-benthic parameters of trophic situation and underwater light
Time series data, which start with the mesotrophic reference year 1987, progress until to the 2 years of hypertrophic state in 1993 and 1994 and further subsequent lake treatment years up to 2019, are displayed for the pelagic trophic state and macrophyte development together with various facets of water transparency in Figure 3. The long-term development of concentrations of Chl-a and TP are associated to each other (Figures 3A,B). Annual maxima in summer, which are most clearly seen for Chl-a for the period 1993–2003 and for TP for the whole observation period, coincide with the summer maxima of SWT shown in Figure 3C. After chemical phosphate precipitation and successive macrophyte re-settlement (stage 2 and 3 of lake restoration treatment), the concentrations of both TP and Chl-a fell to low levels in 2004, with a simultaneous increase in
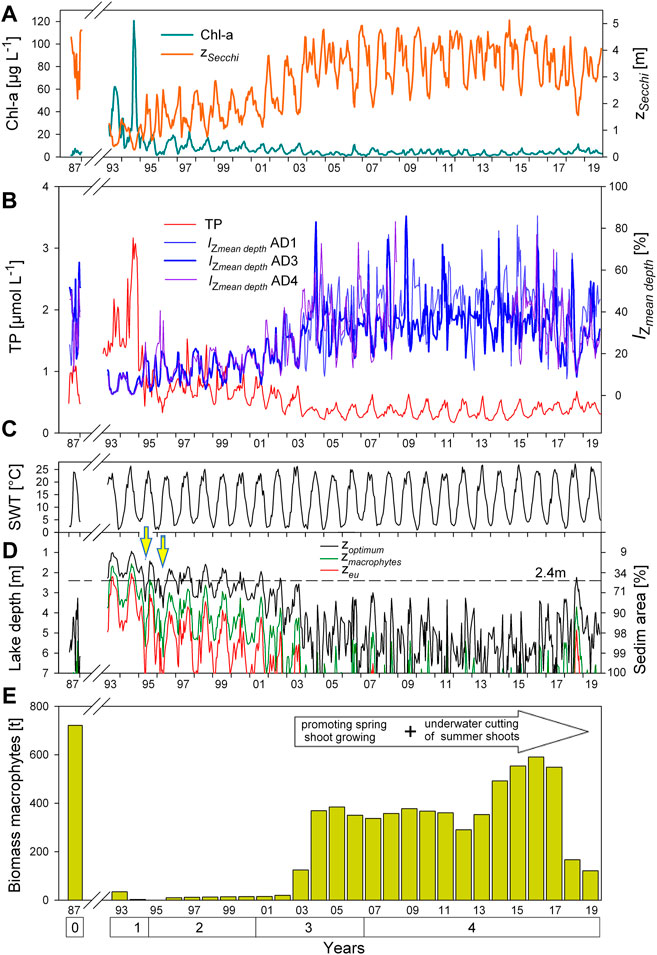
FIGURE 3. Time series of pelagic-benthic settings characterizing the macrophyte dominated, mesotrophic reference conditions in 1987 (stage 0), the hypertrophic algal turbidity (stage 1), the restoration with chemical phosphate precipitation treatment (stage 2), the re-settlement of macrophytes (stage 3) and the sustained recovery (stage 4). /(A–B) Seasonal development of drivers of pelagic turbidity, i.e., planktonic algae (indicated by Chl-a concentration per L) and total phosphorus (TP concentration per L) compared with the seasonality of water transparency measured by
A different picture comes up when assessing the exposure depth to 12% surface ambient light,
Optimum light exposure on the pelagic and benthic habitat
Empirical time series data over 28 years thus show that year-to-year progression of macrophyte yield is linked to an achievement of optimum light requirements,
Figure 4 shows the change over time for the % photic>12% pelagic habitat and % photic>12% benthic habitat (lake bottom) during the 28-year study. In the reference year 1987, almost 100% of both, water volume and sediment surface area, were exposed to 12% surface ambient light. Highest algal turbidity in 1993/1994 stands for far less than half of the lake water volume (<< 50%) and far less than a quarter of the lake sediment surface area (<< 25%) that is being exposed to optimal light availability during summer. With the beginning of the lake restoration, i.e., during the first year of phosphate precipitation in 1995, already more than half of the water volume in summer was exposed to at least 12% surface ambient light. In summer of 2003, i.e., with a delay of 8 years, the same light exposure exceeded half of the sediment surface area (see white arrows in Figure 4, see above description for Figure 3 with regard to 2003 being a transition year). In summer 2004, at least three quarters (>75%) of both the lake volume and the sediment surface area were exposed to 12% surface ambient light (green arrows in Figure 4). After 13 years of stable light availability during summertime with almost 100% for both the pelagic and the benthic habitat (2005–2017), light availability shortly decreased again in midsummer 2018 (see seasonality patterns based on WT). Already less than half of the sediment surface area but still slightly more than three quarters of the water body were exposed to optimum light intensity during this year.
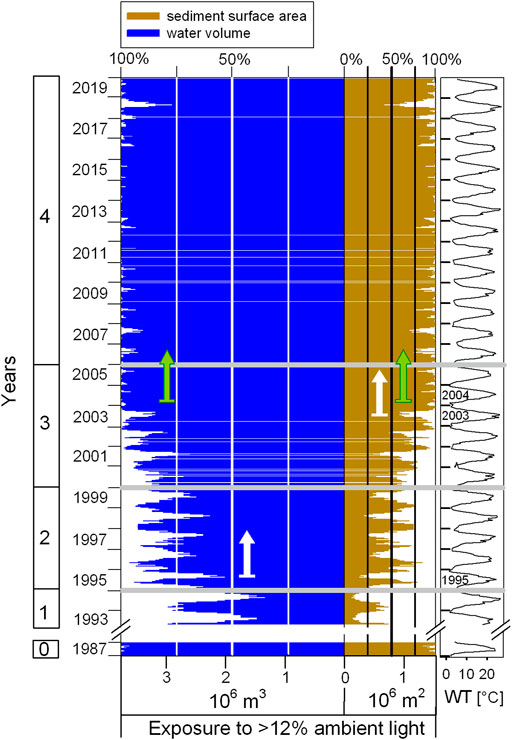
FIGURE 4. Time series of exposure to optimum light on the pelagic (water volume, % photic pelagic>12% habitat size) and benthic habitat (sediment surface area, % photic benthic>12% habitat size) during lake restoration. White arrows indicate the first year since the beginning of lake restoration measures when at least 50% of total water volume (1995) and of total sediment area (2003), respectively, were exposed to at least 12% surface ambient light during growing season. Green arrows mark optimum light conditions throughout the whole water body (almost 100% lake volume) and the whole lake bottom (almost 100% lake sediment area), reached in 2004. WT graphically illustrates the seasonal progression during 28 years of measurement, thick grey lines the stages of lake restoration measures as in Figure 3. All time series data are averages over the three main sampling sites, shown in biweekly intervals. See also Figure 5 for further details.
Photic hypsographic curve
Over the years of lake restoration, the time shift between lake water (photic>12% pelagic habitat) and lake bottom surface light exposure (photic>12% benthic habitat) is due to the characteristic of lake morphometry of this shallow oxbow lake, as illustrated by the photic hypsographic curve (Figure 5). The cumulative lake water volume above a given lake depth is a convex curve, while those for the cumulative lake sediment surface area is a slightly concave curve. Following the direction of incident sun light, lake volume and lake underwater sediment area are cumulated from the top of the lake to the lake bottom in this photic hypsographic curve. With the spatial coincidence of
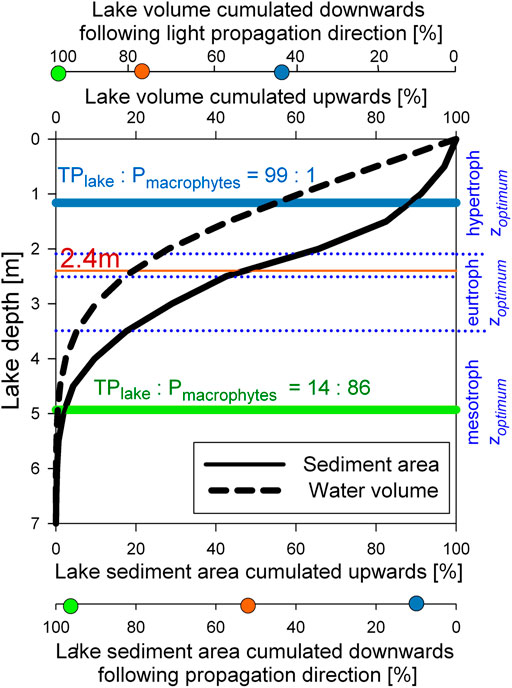
FIGURE 5. Photic hypsographic curves comparing the photic pelagic (refers to lake volume) and photic benthic (refers to lake sediment area) habitat size at a given lake depth or at certain value of
Phosphorus storage pool built up by submerged macrophytes
The time series for TPlake (annual peak concentration per lake volume) and Pmacrophytes (P bound by macrophytes calculated from annual biomass yield, see also methods) is shown in Figure 6. During the algal turbid hypertrophic state in 1993/1994, elevated TPlake values correspond to low or zero Pmacrophytes. After the chemical phosphate precipitation treatment in 1995/1996, values of TPlake slight recovery afterwards before further steadily decreasing until 2002. Pmacrophytes, however, remained stable at a low level over these 6 years. In 2003, identified as transition year by macrophyte yield (see results for Figure 3), Pmacrophytes significantly increased for the first time during the whole restoration period and was about twice as high as TPlake. In the following year, 2004, Pmacrophytes increased at the expense of TPlake as the pelagic summer peak became particular low. The role of macrophytes as a phosphorus storage pool became quantitatively relevant for the ecosystem in 2004, as Pmacrophytes values were exceeding TPlake by about one order of magnitude (2004: Pmacrophytes is 9.2 times higher than TPlake). This storage capacity was maintained the following years until 2017. The highest storage capacity by Pmacrophytes relative to TPlake was outlined during in the period 2015–2017, when Pmacrophytes was higher than TPlake by a factor between 10.8 and 12.3. The last 2 years of investigation, characterized by a decline of macrophyte yield (see methods), referred to a situation like in 2004 when Pmacrophytes was about twice as large as TPlake alone.
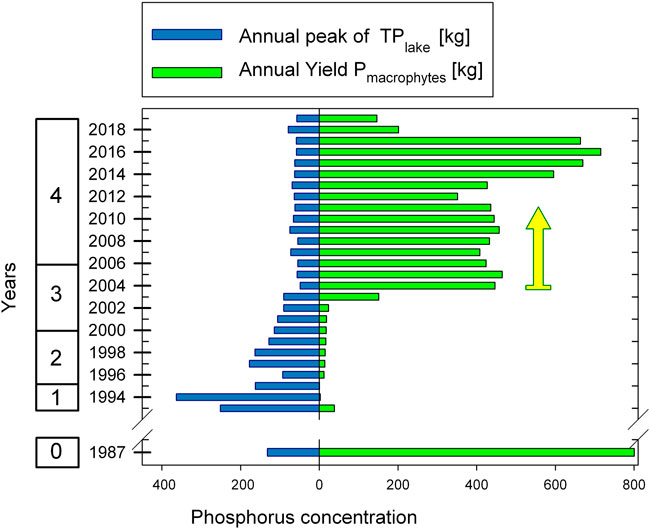
FIGURE 6. Time-series of the phosphorus storage pool built up by submerged macrophytes. Annual yield of P bounded in macrophytes (Pmacrophytes) compared with annual peak of lake TP (TPlake). The arrow points to the year 2004, when Pmacrophytes concentrations exceeded the annual peak concentration of TPlake by one order of magnitude during the re-settlement of macrophytes.
Lake macrophyte bio-surface in comparison with lake sediment surface area
Beside the role of macrophytes as P-storage pool, macrophytes are provisioning an additional habitat through their bio-surface. Figure 7 A shows the annual bio-surface of macrophytes in comparison with the size of the total sediment surface area. The highest bio-surface is estimated for the reference-year 1987, during which the underwater meadow was mainly comprised of charophytes. With eutrophication and beginning of restoration, until 2002, macrophyte formation and, accordingly, the macrophyte bio-surface was less than the surface area provided by the sediment of the whole lake bottom. In year 2003, for the first time since the beginning of the restoration, the bio-surface exceeded the surface area of the sediment by a factor of 3.6. In 2004 and following years until 2013 the excess reached one order of magnitude. In the following 4-year period (2014–2017), highest bio-surface of macrophyte assemblage dominated by M. spicatum exceeded the sediment surface area of the whole lake bottom by a factor of 16.8, which was in the same range as the bio-surface during mesotrophic conditions, when macrophyte meadows were mainly build up by charophytes.
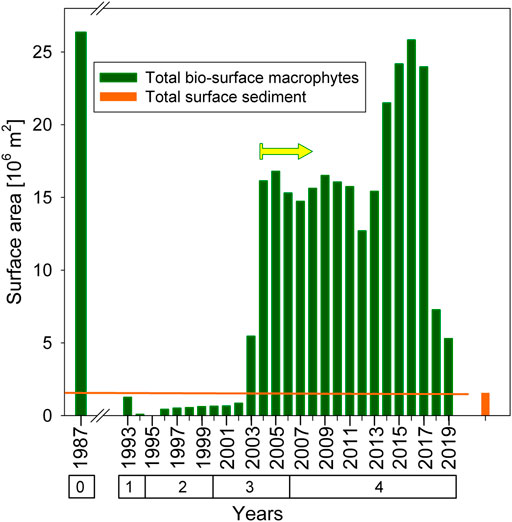
FIGURE 7. Time-series of total macrophyte bio-surface in comparison with total sediment surface area, both estimated for the whole lake Alte Donau. The arrow indicates the year 2004, when the total bio-surface of macrophytes exceeded the total sediment surface by one order of magnitude during re-settlement of macrophytes.
Discussion
At a first glance, macrophytes do not seem to be in a top position when referring to the superiority between the two main light utilizing domains, as the planktonic algae near the lake surface are spatially much closer to the source of incident light than bottom dwelling macrophytes. However, this changes when macrophytes can grow successfully (Jeppesen et al., 2012). In fact, macrophytes play an important role for a shallow lake ecosystem if large standing crop can be achieved.
Many publications estimate macrophyte yield by biomass (Berghahn et al., 2007; Exler and Janauer, 2012; Pall, 2018) or macrophyte coverage (Ibelings et al., 2007; Cheruvelil and Soranno, 2008; Dembowska et al., 2018; Ferreira et al., 2018), but the magnitude beyond the stated yield is often not shown. Addressing the phosphorus storage capacity by macrophyte tissue underpins the ecological-biochemistry role of macrophyte yield, which is most relevant for lake restoration to sustain TP at a low concentration level in the lake (Granéli and Solander, 1988; Clarke, 2002; Kufel and Kufel, 2002; Søndergaard et al., 2002; Hupfer and Dollan, 2003; Honti et al., 2020). Capturing the role of bio-surface for provisioning an additional habitat structure would refer to the spatial context of macrophyte yield. The latter contributes to the debate whether recourses or habitats are primarily controlling an ecosystem (Craig et al., 2015). Mature macrophyte stands are thus of great importance for providing ecosystem services in many ways (e.g., Nõges et al., 2010; Jeppesen et al., 2012; Thomaz, 2021).
Retrieving underwater light availability from
The perspective of
The relevance of lake morphometry for the size of photic>12% pelagic and photic>12% benthic habitat
With an increase of the water transparency as the major target of lake restoration (Chorus et al., 2020; Teubner et al., 2020), light availability increases not only in the pelagic habitat but also in the benthic habitat, where it initializes macrophyte growth on sediment surface (Istvánovics et al., 2008; Pall, 2018; Dubey et al., 2021). The emergence of macrophytes raises the question to what extent in time and space an improvement of water transparency is reflected by an increase of photic>12% pelagic habitat size (% of total water volume) on the one side and by an increase of photic>12% benthic habitat size (% of total sediment surface area) on the other. Most studies, however, focus just on one of the two habitats. Concerning the photic control of either the pelagic or the benthic habitat often takes advantage of
While in this study we primarily looked on how restoration effort by increasing water transparency succeeded, we now discuss how vulnerable the ecosystem can be in view of deterioration associated with ongoing lowering of water clarity. As exemplified for Alte Donau, during the last 3 years of decreased macrophyte yield (see intense mowing in the methods), the size of the photic>12% benthic habitat became markedly smaller but was not responded by a remarkable concentration increase of TPlake. According to the finding by the photic hypsographic curve for Alte Donau, the slower a restoration progresses to overcome the delay of an enlargement photic>12% benthic habitat, the faster the turn back might be, as the photic>12% benthic habitat is primarily affected by this. Such an accelerated deterioration of a shallow lake might indeed succeed if submerged vegetation is only sparely developed. A sudden turn back to an algal turbid lake, however, is not observed in case of well-established underwater vegetation meadows. Such a situation is described for 1987 in Alte Donau, by an already present process of slow macrophyte loss during late mesotrophic state (see method). The advance of the photic>12% pelagic at the expense of photic>12% benthic habitat with ongoing deterioration of water quality and, i.e., an increase of pelagic algal turbidity, might thus largely depend on the extent of the standing crop of macrophytes. In case macrophyte stands are already established in such a situation, tall growing species including phytal photosynthetic microbiota might still have access to sufficient incident light. For both, macrophyte meadows and phytoplankton, photosynthetic organisms are known to have a high capacity for succeeding well under different light conditions. Greisberger and Teubner (2007) have exemplified the wide range of pigment adjustment of phytoplankton to ambient light conditions changing over seasons. Macrophytes such as charophytes, for example, are also known to adjust to a large range of light conditions within a certain range. Some are even known for their dim-light requirement most relevant to survive at deeper water layers (Schagerl and Pichler, 2000; Zhang et al., 2018). As submerged macrophytes built up their own thalli or shoot architecture, they thus do not necessarily suffer from light limitation in deep bottom layers, but take advantage of having grown towards the lake surface as survival strategy which would delay the death of aquatic vascular plants or charophytes and thus also buffer short-term deterioration in water quality. This is in agreement with the finding that established macrophyte stands contribute to stabilize a lake system (Scheffer et al., 1993; Jeppesen et al., 2012). A further decrease of water transparency due to an ongoing eutrophication scenario, however, would finally favour again an accelerated overshooting growth of light harvesting pelagic organisms at the expense of macrophytes determined by photic hypsographic conditions mentioned before. The remaining photic>12% benthic habitat would then become dramatically smaller in size over time and
Underwater light climate: The achievement of optimum rather than minimum light requirement plays a role
In general, plants respond not only to quality and quantity of light by an adjustment of their pigment composition to accomplish growth and thus biomass yield. Light is also ecologically important at the level of light signal perception (Smith, 2000). The water level draw-down of about 25 cm for only few days in spring (see method), might be percepted as light signal triggering vernal development by seed germination, leaf expansion and shoot development of submerged macrophytes even in slightly deeper layers of the littoral zone (Dokulil M. T. et al., 2018; Pall, 2018; Pall and Goldschmid, 2018; Teubner et al., 2020). According to Pall (2018), it is seen as an important restoration measure for the successful re-establishment of macrophytes as short-term vernal water level draw-down from 2002 onwards was concomitant with an increase in macrophyte yield in Alte Donau. With the present study, we still see the importance of vernal water draw-down. Nevertheless, to accomplish large macrophyte yields, the availability of sufficient light during the main growing season might be of particular importance. In this point we go further than in the previous study (Teubner et al., 2020), where an emphasis was put on
The importance of macrophyte habitat structure beyond the biomass yield
With the significant increase of macrophyte yield due to lake restoration, about 50%–80% of the macrophyte biomass of the reference year was recovered. This macrophyte yield stands for a huge phosphorus storage pool, as Pmacrophyte exceeded TPlake by about one order of magnitude. Furthermore, these macrophyte stands provisioned with their bio-surface an additional habitat which extended the size of the benthic habitat at lake bottom by even more than one order of magnitude.
Both the phosphorus content and the nutrient elemental stoichiometry of the aquatic plants vary among plant species or locations (e.g., Lukatelich et al., 1987; Mazej and Germ, 2008; Wang et al., 2018). Despite this rather narrow range of variation for phosphorus acquisition among plant species, the essential role of macrophytes for lake ecosystems lies in their phosphorus storage capacity, which means retaining this nutrient element and thus making a large amount of phosphorus not bio-available for the development of photosynthetic plankton micro-organisms during the growing season of a current year. In view of an overwhelming phosphorus pool retained in macrophyte stands under sustained low TP concentration (Lukatelich et al., 1987), we primarily see macrophytes as a significant sink for phosphorus in Alte Donau. This interpretation is in agreement with other studies claiming that macrophyte stands can be considered as permanent or at least temporary phosphorus sink and hamper a fast phosphorus turnover in the lake (Granéli and Solander, 1988; Donk et al., 1993; Clarke, 2002; Kufel and Kufel, 2002; Søndergaard et al., 2002; Hupfer and Dollan, 2003; Honti et al., 2020). An overwintering of macrophytes in Alte Donau in recent mild winters (K. Pall, personal communication) extends their storage capacity even beyond the growing season (other lakes: e.g., Jeppesen et al., 2020; Brzozowski and Pełechaty, 2022). The plankton community is in principle also known to act as a sink for phosphorus if grown under phosphorus deficiency, i.e., after phosphate precipitation treatment in Alte Donau (Teubner et al., 2003); but when compared with the huge storage pool of mature macrophyte stands it appears less relevant in terms of its quantity.
Macrophyte and phytoplankton phosphorus acquisition
Discussing the ecological role of macrophytes and phytoplankton as a phosphorus storage pool raises the question about the physiological background of phosphorus acquisition for both photosynthetic domains. Phosphorus is known to be the most limiting nutrient element in freshwaters (Vollenweider, 1968; Schindler, 1977; Moss et al., 2013). An acquisition by luxury phosphate consumption building up huge cell-internal phosphate storage pools (polyphosphates) on the one hand, and a bio-active uptake system which allows to utilize ephemeral nano-scale phosphate patches efficiently (e.g., Falkner et al., 1989) on the other hand, roughly describe the wide scenarios of sophisticated phosphate incorporation by photosynthetic organisms. Phosphorus uptake often relies on a cascade of high and low affinity uptake systems (Epstein, 1972) depending on the supply and degree of starvation of organisms. Many phytoplankton species can thus cope well with an environment of either low or high phosphate supply (e.g., Istvánovics, 2008), which is also the case for many vascular plants (Raghothama, 1999). The growth inhibition of charophytes by “toxic” maximum phosphorus concentrations (Forsberg, 1964), might be again not out of the rule among primary producers since phytoplankton taxa in laboratory cultures also cannot survive after excessive phosphorus uptake (for cyanobacteria: K. Teubner, personal communication; green algae: Li et al., 2018).
The utmost phosphorus acquisition for seasonal development of underwater vegetation coincides with that of the phytoplankton, in particular if the vegetative parts of macrophytes grow periodically in the water (Reitsema et al., 2021). The demand of phosphorus for macrophyte growth is highest in spring (Vymazal, 2007). This agrees with Alte Donau (Pall, 2018), where the net change rate of macrophyte biomass increase was highest during the beginning of the growing season (04.05.-26.05.2000), coincident with the vernal phytoplankton increase with peaking net change rate in the second half of May 2000 (calculated from Teubner et al., 2018a). Also, global warming, which has been shown to have an impact on Alte Donau (Teubner et al., 2018b; Teubner et al., 2020), might affect the phenology of both plankton and macrophytes through time-shifts of vernal leaf-out and overwintering or relative growth rate, as also reported from other lakes (e.g., Zhang et al., 2015; Jeppesen et al., 2020; Brzozowski and Pełechaty, 2022). This all together might provide arguments that in principle both, macrophytes and phytoplankton, are closely related concerning the general rules and time pattern of phosphorus acquisition.
Concerning the benthic-pelagic coupling, we need to understand how lake phosphorus pools are utilized differently by macrophytes than by phytoplankton. Charophyte growth experiments of laboratory cultures (Zhang et al., 2018) and field bioassays (e.g., Forsberg, 1964; Siong and Asaeda, 2006) did not answer the ecologically relevant question to what extent these algae by cells or by full habitus are incorporating bioavailable phosphorus sources from the pelagic habitat, while pelagic phosphorus is known to be important for growth of vascular submerged plants (Bristow and Whitcombe, 1971; Pelton et al., 1998) and planktonic algae (Dyhrman 2016). A large amount of pelagic phosphorus, however, is known to be bound by encrustation on macrophyte bio-surface (photosynthetically mediated calcite-phosphorus precipitation) mainly attributed to the charophytes (Kufel et al., 2013; Herbst et al., 2018; Sand-Jensen et al., 2018) in addition to some vascular macrophytes (e.g., Ostrofsky and Miller, 2017; for roots see Hupfer and Dollan, 2003). Despite a few exceptions (e.g., Schlegel et al., 2000), such bio-active encrustation is quantitatively rather negligible for algal plankton. In this view, the large bio-surface of healthy macrophyte stands in Alte Donau might be of advantage for bio-surface bounding or for cellular incorporation of pelagic phosphorus sources for building up dense underwater vegetation meadows as long as sufficient ambient underwater light is available and no other conditions occur that inhibit growth (e.g., by allelopathic effects, Gross, 2003). Box (1986) and Wüstenberg et al. (2011) furthermore verified that charophyte species in principle are able to utilize phosphorus efficiently by their rhizoids and thus can mobilize a certain amount of bio-available phosphorus from benthic habitat, as the vascular macrophytes commonly also do by their rhizomes (Bristow and Whitcombe, 1971; Melzer, 1999; Kleeberg, 2013; Zhang et al., 2019), but not phytoplankton organisms if strictly living in the pelagic zone. These studies thus argue that macrophyte-meadows, in particular if build up by charophytes, stabilize well low phosphate concentrations in lakes. It underpins the ecological importance of phosphorus allocation into the submerged macrophyte domain as most relevant for sustained lake restoration (Hilt et al., 2006; Kufel et al., 2013). The latter aspect indeed might have played an important role also in Alte Donau, as phosphorus binding capacity of the sediment was relatively high. The strongly calcareous sediment prevented P-release from sediment even under anoxic conditions (Ripl and Wolter, 1995; sediment characteristics in Supplementary Material S3).
Macrophytes providing additional habitat structure
Building up an additional habitat structure in a lake can be considered of utmost importance for the ecosystem rather than just providing biomass resources (Kuczyńska-Kippen and Nagengast, 2003; Craig et al., 2015). The spatial importance of the emergence of macrophytes is seen in the immensely large bio-surface area providing further living space for phytal organisms which goes beyond the size of the lake bottom area in Alte Donau. The significance of the phytal habitat could be verified by a 28 times higher abundance of individuals for Chironomidae, followed by other MZB species, when compared with those in the lake sediment in Alte Donau (see Supplementary Material S4). This one order of magnitude higher phytal abundance underscores the vitality of such a habitat architecture of submerged macrophytes and agrees with other studies where submerged macrophytes allocated higher yields of MZB than compared with non-living substate or littoral submerged shoots of Phragmites australis (e.g., Feldmann and Nõges, 2007; Yofukuji et al., 2021). Nevertheless, densities of phytal MZB organisms can largely vary as micro-conditions of these specific environments are highly variable in space and time (Cremona et al., 2008), are superimposed by eutrophication (e.g., Kahlert and Pettersson, 2002), exposed to bio-chemical (allelopathic substances; Gross, 2003) or physical stress (flow-velocity in flood-plain systems; Funk et al., 2013) which finally may hamper development of attached living biota on aquatic submerged plants. Thinking about the suitability of macrophytes as microhabitat, might extend to the question of how attached organisms live. They aggregate in biofilms (Battin et al., 2016), and benefit from various photosynthetic nutrient sources delivered by the macrophyte host (Ali et al., 2019; Wolters et al., 2019) or by attached living phytal algae and other microorganisms (Dodds, 1991; Wagner et al., 2017; Rojo et al., 2020). Han et al. (2018) describe in detail the ecologically most relevant benefit by such a specific “submerged macrophyte-biofilm system”. It underpins that the macrophytes might be seen as an ecological habitat entity for building up their own network for connecting food and energy exchange (see also Zhang et al., 2016; Wolters et al., 2019).
Another important role of macrophyte habitat architecture for aquatic ecosystems is seen in the provisioning of food and shelter for spawning and nursery of vertebrates as discussed for fish in different studies (Petr, 2000; Meulenbroek et al., 2018; Figueiredo et al., 2013; Yofukuji et al., 2021; macrophytes themself can be a significant food source for fish: Yu et al., 2016; Löffler, 1988; Zhen et al., 2018). Also for Alte Donau, Waidbacher and Drexler (2018) verified macrophytes and phytal biota as important food sources and macrophyte stands as valued niches for young fish. They claim that underwater macrophyte cutting for enhancing the recreational use of Alte Donau, can cause a dramatic damage to young fish (loss of one young fish per 2–2.5 kg of harvested FW macrophytes in 2005, 2006). The denser the macrophyte stands are, the more fish are expected to be harboured. The fish harboured from sparse to dense macrophyte stands increased on average from 2 to 30 individuals per “air-lift” catch (frame size = 2 × 2m) in Alte Donau (Waidbacher and Drexler, 2018). This increase of fish abundance by a factor of 15 underpins the ecological value in particular for a mature macrophyte habitat architecture and agrees with later fish surveys. According to Gassner et al. (2014), the abundance of fish in shallow zones of Alte Donau in 2013 was twice as high as in other Austrian lakes with fish assemblages dominated by bleak (Alburnus alburnus) and confirms that fish take advantage from macrophytes in lakes (e.g., Yu et al., 2016). As long as water transparency suits well for cyprinid fish when searching for prey (Wanzenböck and Schiemer, 1989; Figueiredo et al., 2013), the potential of food source provided by additional macrophyte habitat structure is undoubtfully important.
These few aspects about MZB and fish in Alte Donau verify again the ecological importance of macrophytes for building up a unique habitat architecture as a third main component in the network between the benthic (lake bottom) and pelagic (lake open water) living space.
Conclusion
In terms of implications for lake management derived from our study, we can state that focusing on optimum light conditions (12% surface ambient light,
According to our study, a delay in the light exposure of the lake bottom area compared to the lake water volume is implicitly related to lake basin morphometry (identified by photic hypsographic curve) and might thus differ among lakes. Only the time span (number of years) that is required to overcome this delay depends on the efficiency of restoration measures and thus relates to a sustained lake treatment in the long-term.
On the one side, mature macrophyte stands have a huge storage capacity of phosphorus (macrophyte tissue) being one order of magnitude higher than peak concentrations of TP of the whole lake water body. On the other side, mature macrophyte stands provide a huge structural bio-surface that is one order of magnitude larger in size than the whole lake sediment area, and thus can harbour an enhanced number of further freshwater biota. Hence, according to our study, massive stands of macrophytes can be seen as a significant sink for phosphorus in the ecological-biochemical context and can also be understood to provision an immensely large bio-surface of additional living space in the spatial context. Our results therefore support the finding that a mature vital macrophyte habitat architecture can indeed serve as an important structural element linked to the benthic and pelagic habitat in a lake. We thus conclude, that the emergence of massive vital architecture built by submerged macrophytes, which is most important for the sustainability of water quality and for providing ecosystem services, goes far beyond being understood as being part of the benthic habitat. According to our main findings, submerged macrophytes might be rather seen as a third important unique habitat in addition to the benthic and pelagic habitat in shallow lakes.
Data availability statement
The datasets generated for this study are available on request to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
KT mainly conceived the manuscript idea, data analysis, preparation of graphs and text. IT conducted advanced data processing concerning underwater light attenuation and photic habitat sizes, writing and critical reading at all stages of ms preparation. MT contributed to the main idea and writing about ecological perspective, in particular of underwater light. KP contributed by providing raw data for the hypsographic curve and strong expertise in macrophyte biology and management, co-preparation of graphs, critical review of the ms. WK re-assessed measurements of underwater light. S-SD and HW contributed to fish relevant results, graphic preparation and writing of ms. MD contributed to methods of optical properties, sediment measures and restoration perspective Alte Donau, critical contribution at all stages of manuscript preparation and writing. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
This study was funded and promoted in many ways by the City of Vienna, Municipal Department 45 (Water Management). The authors acknowledge the University of Vienna for financial support through its Open Access Publishing Fund.
Acknowledgments
We thank Karl Donabaum and the Municipal Department—45 (Water Management - Vienna) for supporting the study and providing long-term data of Alte Donau for the period 1993–2019. We also thank Klaus-Dieter Wolter (Systeminstitut Aqua Terra) for valuable comments issued on sediment characteristics in Alte Donau (see Supplementary Material S3), Lothar Täuscher on benthos communities and three reviewers for their valuable comments.
Conflict of interest
KP is CEO of the Systema GmbH.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fenvs.2022.901924/full#supplementary-material
References
Ali, F., Jilani, G., Fahim, R., Bai, L., Wang, C., Tian, L., et al. (2019). Functional and structural roles of wiry and sturdy rooted emerged macrophytes root functional traits in the abatement of nutrients and metals. J. Environ. Manag. 249, 109330. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109330
Baart, I., Gschöpf, C., Blaschke, A. P., Preiner, S., and Hein, T. (2010). Prediction of potential macrophyte development in response to restoration measures in an urban riverine wetland. Aquat. Bot. 93 (3), 153–162. doi:10.1016/j.aquabot.2010.06.002
Battin, T. J., Besemer, K., Bengtsson, M. M., Romani, A. M., and Packmann, A. I. (2016). The ecology and biogeochemistry of stream biofilms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 14 (4), 251–263. doi:10.1038/nrmicro.2016.15
Berghahn, R., Mohr, S., Feibicke, M., Meinecke, S., and Sperfeld, E. (2007). Endpoint ‘floating leaves’ of Potamogeton natans: A new method to evaluate the development of macrophytes in pond mesocosms. Env. Sci. Poll. Res. Int. 14 (3), 190–193. doi:10.1065/espr2006.07.324
Bjørrisen, P. K. (1988). Phytoplankton exudation of organic matter: Why do healthy cells do it? 1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 33 (1), 151–154. doi:10.4319/lo.1988.33.1.0151
Box, R. J. (1986). Quantitative short-term uptake of inorganic phosphate by the Chara hispida rhizoid. Plant Cell Environ. 9 (6), 501–506. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.1986.tb01767.x
Bragg, O. M., Duck, R. W., Rowan, J. S., and Black, A. R. (2003). “Review of methods for assessing the hydromorphology of lakes,” in Final report project WFD06 (Edinburgh: Scotland and Northern Ireland Forum for Environmental Research), 138.
Bristow, J. M., and Whitcombe, M. (1971). The role of roots in the nutrition of aquatic vascular plants. Am. J. Bot. 58 (1), 8–13. doi:10.1002/j.1537-2197.1971.tb09939.x
Brzozowski, M., and Pełechaty, M. (2022). Overwintering of an endangered charophyte during milder winters in Central Europe enhances lake water quality. Limnologica 92, 125944. doi:10.1016/j.limno.2021.125944
Chang, N., Luo, L., Wang, X. C., Song, J., Han, J., and Ao, D. (2020). A novel index for assessing the water quality of urban landscape lakes based on water transparency. Sci. Total Environ. 735, 139351. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139351
Chen, Y., Qin, B., Teubner, K., and Dokulil, M. T. (2003). Long-term dynamics of phytoplankton assemblages: Microcystis-domination in Lake Taihu, a large shallow lake in China. J. Plankton Res. 25 (4), 445–453. doi:10.1093/plankt/25.4.445
Cheruvelil, K. S., and Soranno, P. A. (2008). Relationships between lake macrophyte cover and lake and landscape features. Aquat. Bot. 88 (3), 219–227. doi:10.1016/j.aquabot.2007.10.005
Chorus, I., Köhler, A., Beulker, C., Fastner, J., van de Weyer, K., Hegewald, T., et al. (2020). Decades needed for ecosystem components to respond to a sharp and drastic phosphorus load reduction. Hydrobiologia 847 (21), 4621–4651. doi:10.1007/s10750-020-04450-4
Christie, H., Norderhaug, K. M., and Fredriksen, S. (2009). Macrophytes as habitat for fauna. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 396, 221–233. doi:10.3354/meps08351
Clarke, S. J. (2002). Vegetation growth in rivers: Influences upon sediment and nutrient dynamics. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 26 (2), 159–172. doi:10.1191/0309133302pp324ra
Craig, N., Jones, S. E., Weidel, B. C., and Solomon, C. T. (2015). Habitat, not resource availability, limits consumer production in lake ecosystems. Limnol. Oceanogr. 60 (6), 2079–2089. doi:10.1002/lno.10153
Cremona, F., Planas, D., and Lucotte, M. (2008). Biomass and composition of macroinvertebrate communities associated with different types of macrophyte architectures and habitats in a large fluvial lake. Fundam. Appl. Limnol. 171 (2), 119–130. doi:10.1127/1863-9135/2008/0171-0119
Cui, Y., Yan, Z., Wang, J., Hao, S., and Liu, Y. (2022). Deep learning–based remote sensing estimation of water transparency in shallow lakes by combining Landsat 8 and Sentinel 2 images. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 29 (3), 4401–4413. doi:10.1007/s11356-021-16004-9
Dembowska, E. A., Mieszczankin, T., and Napiórkowski, P. (2018). Changes of the phytoplankton community as symptoms of deterioration of water quality in a shallow lake. Environ. Monit. Assess. 190 (2), 95–11. doi:10.1007/s10661-018-6465-1
Dodds, W. K. (1991). Community interactions between the filamentous alga Cladophora glomerata (L.) Kuetzing, its epiphytes, and epiphyte grazers. Oecologia 85 (4), 572–580. doi:10.1007/bf00323770
Dokulil M. T., Donabaum K., and Teubner K. (Editors) (2018a). The Alte Donau: Successful restoration and sustainable management - an ecosystem case study of a shallow urban lake (aquatic ecology series 10) (Cham: Springer). doi:10.1007/978-3-319-93270-5
Dokulil, M. T., Donabaum, K., and Teubner, K. (Editors) (2018a). “Eutrophication, management and sustainable development of urban lakes: General considerations and specific solutions for Alte Donau - a synthesis,” in The Alte Donau: Successful restoration and sustainable management - an ecosystem case study of a shallow urban lake (aquatic ecology series 10). Editors M. T. Dokulil, K. Donabaum, and K. Teubner (Cham: Springer), 149–163. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-93270-5_20
Donabaum, K., and Riedler, P. (2018). “Long-term changes of the physico-chemical conditions in Alte Donau,” in The Alte Donau: Successful restoration and sustainable management - an ecosystem case study of a shallow urban lake (aquatic ecology series 10). Editors M. T. Dokulil, K. Donabaum, and K. Teubner (Cham: Springer), 55–69. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-93270-5_6
Donk, E. V., Gulati, R. D., Iedema, A., and Meulemans, J. T. (1993). “Macrophyte-related shifts in the nitrogen and phosphorus contents of the different trophic levels in a biomanipulated shallow lake,” in Nutrient dynamics and retention in land/water ecotones of lowland, temperate lakes and rivers (Dordrecht: Springer), 19–26. doi:10.1007/978-94-011-1602-2_3
Doyle, B. C., de Eyto, E., Dillane, M., Poole, R., McCarthy, V., Ryder, E., et al. (2019). Synchrony in catchment stream colour levels is driven by both local and regional climate. Biogeosciences 16 (5), 1053–1071. doi:10.5194/bg-16-1053-2019
Dubey, D., Kumar, S., and Dutta, V. (2021). Impact of nutrient enrichment on habitat heterogeneity and species richness of aquatic macrophytes: Evidence from freshwater tropical lakes of central ganga plain, India. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. (Tehran). 19, 5529–5546. doi:10.1007/s13762-021-03438-4
Dyhrman, S. T. (2016). “Nutrients and their acquisition: Phosphorus physiology in microalgae,” in The physiology of microalgae (Springer), 155–183. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-24945-2_8
Eidinger, S. (2018). Macrophytes as habitat for aquatic invertebrates in the Lower Lobau floodplains. Vienna: Institute of Hydrobiology, University Boku. PhD Thesis.
Exler, N., and Janauer, G. (2012). “A novel hydro-acoustic approach on assessing aquatic macrophyte biomass data,” in 39th IAD conference (Hungary: Szentendre), 117–121.
Falkner, G., Falkner, R., and Schwab, A. J. (1989). Bioenergetic characterization of transient state phosphate uptake by the cyanobacterium Anacystis nidulans. Arch. Microbiol. 152 (4), 353–361. doi:10.1007/BF00425173
Feldmann, T., and Nõges, P. (2007). Factors controlling macrophyte distribution in large shallow Lake Võrtsjärv. Aquat. Bot. 87 (1), 15–21. doi:10.1016/j.aquabot.2007.01.004
Ferreira, T. F., Crossetti, L. O., Marques, D. M. M., Cardoso, L., Fragoso, C. R., and van Nes, E. H. (2018). The structuring role of submerged macrophytes in a large subtropical shallow lake: Clear effects on water chemistry and phytoplankton structure community along a vegetated-pelagic gradient. Limnologica 69, 142–154. doi:10.1016/j.limno.2017.12.003
Figueiredo, B. R. S., Mormul, R. P., and Benedito, E. (2013). Non-additive effects of macrophyte cover and turbidity on predator–prey interactions involving an invertivorous fish and different prey types. Hydrobiologia 716 (1), 21–28. doi:10.1007/s10750-013-1540-7
Finstad, A. G., Helland, I. P., Ugedal, O., Hesthagen, T., and Hessen, D. O. (2014). Unimodal response of fish yield to dissolved organic carbon. Ecol. Lett. 17 (1), 36–43. doi:10.1111/ele.12201
Forsberg, C. (1964). Phosphorus, a maximum factor in the growth of Characeae. Nature 201 (4918), 517–518. doi:10.1038/201517a0
Funk, A., Gschöpf, C., Blaschke, A. P., Weigelhofer, G., and Reckendorfer, W. (2013). Ecological niche models for the evaluation of management options in an urban floodplain—Conservation vs. restoration purposes. Environ. Sci. Policy 34, 79–91. doi:10.1016/j.envsci.2012.08.011
Gao, Y., Yin, C., Zhao, Y., Liu, Z., Liu, P., Zhen, W., et al. (2020). Effects of diversity, coverage and biomass of submerged macrophytes on nutrient concentrations, water clarity and phytoplankton biomass in two restored shallow lakes. Water 12 (5), 1425. doi:10.3390/w12051425
Gassner, H., Luger, M., Achleitner, D., and Pamminger-Lahnsteiner, B. (2014). Alte Donau (2013) - standardisierte Fischbestandserhebung und Bewertung des fischökologischen Zustandes gemäß EU-WRRL. Bericht, 34 Seiten. Mondsee: Bundesamt für Wasserwirtschaft, Institut für Gewässerökologie, Fischereibiologie und Seenkunde, Scharfling, 5310.
Granéli, W., and Solander, D. (1988). Influence of aquatic macrophytes on phosphorus cycling in lakes. Hydrobiologia 170 (1), 245–266. doi:10.1007/BF00024908
Greisberger, S., and Teubner, K. (2007). Does pigment composition reflect phytoplankton community structure in differing temperature and light conditions in a deep alpine lake? An approach using HPLC and delayed fluorescence techniques 1. J. Phycol. 43, 1108–1119. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8817.2007.00404.x
Griffiths, J. R., Kadin, M., Nascimento, F. J., Tamelander, T., Törnroos, A., Bonaglia, S., et al. (2017). The importance of benthic–pelagic coupling for marine ecosystem functioning in a changing world. Glob. Chang. Biol. 23 (6), 2179–2196. doi:10.1111/gcb.13642
Gross, E. M. (2003). Allelopathy of aquatic autotrophs. Crit. Rev. plant Sci. 22 (3-4), 313–339. doi:10.1080/713610859
Gyllström, M., and Hansson, L. A. (2004). Dormancy in freshwater zooplankton: Induction, termination and the importance of benthic-pelagic coupling. Aquat. Sci. 66 (3), 274–295. doi:10.1007/s00027-004-0712-y
Hacker, S. D., and Steneck, R. S. (1990). Habitat architecture and the abundance and body-size-dependent habitat selection of a phytal amphipod. Ecology 71 (6), 2269–2285. doi:10.2307/1938638
Håkanson, L. (1977). On lake form, lake volume and lake hypsographic survey. Geogr. Ann. Ser. A, Phys. Geogr. 59 (1-2), 1–29. doi:10.1080/04353676.1977.11879944
Han, B., Zhang, S., Wang, P., and Wang, C. (2018). Effects of water flow on submerged macrophyte-biofilm systems in constructed wetlands. Sci. Rep. 8, 2650. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-21080-y
Herbst, A., von Tümpling, W., and Schubert, H. (2018). The seasonal effects on the encrustation of charophytes in two hard-water lakes. J. Phycol. 54 (5), 630–637. doi:10.1111/jpy.12772
Hickley, P., Boar, R. R., and Mavuti, K. M. (2003). Bathymetry of lake bogoria, Kenya. J. East Afr. Nat. Hist. 92 (1), 107–117. doi:10.2982/0012-8317(2003)92[107:BOLBK]2.0.CO;2
Hilt, S., Gross, E. M., Hupfer, M., Morscheid, H., Mählmann, J., Melzer, A., et al. (2006). Restoration of submerged vegetation in shallow eutrophic lakes – A guideline and state of the art in Germany. Limnologica 36, 155–171. doi:10.1016/j.limno.2006.06.001
Honti, M., Gao, C., Istvánovics, V., and Clement, A. (2020). Lessons learnt from the long-term management of a large (re) constructed wetland, the Kis-Balaton protection system (Hungary). Water 12 (3), 659. doi:10.3390/w12030659
Hupfer, M., and Dollan, A. (2003). Immobilisation of phosphorus by iron-coated roots of submerged macrophytes. Hydrobiologia 506 (1), 635–640. doi:10.1023/B:HYDR.0000008605.09957.07
Ibelings, B. W., Portielje, R., Lammens, E. H., Noordhuis, R., van den Berg, M. S., Joosse, W., et al. (2007). Resilience of alternative stable states during the recovery of shallow lakes from eutrophication: Lake Veluwe as a case study. Ecosystems 10 (1), 4–16. doi:10.1007/s10021-006-9009-4
Istvánovics, V., Honti, M., Kovács, Á., and Osztoics, A. (2008). Distribution of submerged macrophytes along environmental gradients in large, shallow Lake Balaton (Hungary). Aquat. Bot. 88 (4), 317–330. doi:10.1016/j.aquabot.2007.12.008
Istvánovics, V. (2008). The role of biota in shaping the phosphorus cycle in lakes. Freshw. Rev. 1 (2), 143–174. doi:10.1608/FRJ-1.2.2
Jäger, P., Pall, K., and Dumfarth, E. (2004). A method of mapping macrophytes in large lakes with regard to the requirements of the Water Framework Directive. Limnologica 34 (1-2), 140–146. doi:10.1016/S0075-9511(04)80033-1
Janauer, G. A., Exler, N., Anačkov, G., Barta, V., Berczik, Á., Boža, P., et al. (2021). Distribution of the macrophyte communities in the Danube reflects river serial discontinuity. Water 13 (7), 918. doi:10.3390/w13070918
Janecek, B., Leitner, P., Moog, O., and Teubner, K. (2018). “Effect of restoration measures on the benthic invertebrates of a Danube backwater (Alte Donau),” in The Alte Donau: Successful restoration and sustainable management – an ecosystem case study of a shallow urban lake (aquatic ecology series 10). Editors M. T. Dokulil, K. Donabaum, and K. Teubner (Cham: Springer), 243–274. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-93270-5_14
Jeppesen, E., Canfield, D. E., Bachmann, R. W., Søndergaard, M., Havens, K. E., Johansson, L. S., et al. (2020). Toward predicting climate change effects on lakes: A comparison of 1656 shallow lakes from Florida and Denmark reveals substantial differences in nutrient dynamics, metabolism, trophic structure, and top-down control. Inland Waters 10 (2), 197–211. doi:10.1080/20442041.2020.1711681
Jeppesen, E., Søndergaard, M., Søndergaard, M., and Christoffersen, K. (Editors) (2012). The structuring role of submerged macrophytes in lakes (Vol. 131) (Springer).
Johnson, R. K., and Wiederholm, T. (1992). Pelagic-benthic coupling—The importance of diatom interannual variability for population oscillations of monoporeiaaffinis. Limnol. Oceanogr. 37, 1596–1607. doi:10.4319/lo.1992.37.8.1596
Jůza, T., Duras, J., Blabolil, P., Sajdlová, Z., Hess, J., Chocholoušková, Z., et al. (2019). Recovery of the Velky Bolevecky pond (Plzen, Czech Republic) via biomanipulation–key study for management. Ecol. Eng. 136, 167–176. doi:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2019.06.025
Kahlert, M., and Pettersson, K. (2002). The impact of substrate and lake trophy on the biomass and nutrient status of benthic algae. Hydrobiologia 489 (1), 161–169. doi:10.1023/A:1023280720576
Kleeberg, A. (2013). Impact of aquatic macrophyte decomposition on sedimentary nutrient and metal mobilization in the initial stages of ecosystem development. Aquat. Bot. 105, 41–49. doi:10.1016/j.aquabot.2012.12.003
Kuczyńska-Kippen, N., and Nagengast, B. (2003). The impact of the spatial structure of hydromacrophytes on the similarity of rotifera communities (Budzyńskie Lake, Poland). Hydrobiologia 506 (1), 333–338. doi:10.1023/B:HYDR.0000008542.76373.44
Kufel, L., Biardzka, E., and Strzałek, M. (2013). Calcium carbonate incrustation and phosphorus fractions in five charophyte species. Aquat. Bot. 109, 54–57. doi:10.1016/j.aquabot.2013.04.002
Kufel, L., and Kufel, I. (2002). Chara beds acting as nutrient sinks in shallow lakes—A review. Aquat. Bot. 72 (3-4), 249–260. doi:10.1016/S0304-3770(01)00204-2
Larsson, U., and Hagström, A. (1979). Phytoplankton exudate release as an energy source for the growth of pelagic bacteria. Mar. Biol. 52 (3), 199–206. doi:10.1007/BF00398133
Li, Q., Fu, L., Wang, Y., Zhou, D., and Rittmann, B. E. (2018). Excessive phosphorus caused inhibition and cell damage during heterotrophic growth of Chlorella regularis. Bioresour. Technol. 268, 266–270. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2018.07.148
Lind, L., Eckstein, R. L., and Relyea, R. A. (2022). Direct and indirect effects of climate change on distribution and community composition of macrophytes in lentic systems. Biol. Rev. 97, 1677–1690. doi:10.1111/brv.12858
Livingstone, D. M. (2003). Impact of secular climate change on the thermal structure of a large temperate central European lake. Clim. Change 57 (1–2), 205–225. doi:10.1023/a:1022119503144
Löffler, H. (1988). Alte Donau. Limnologische projektstudie – ökosystem Alte Donau. Wien: Endbericht, 272.
Lukatelich, R. J., Schofield, N. J., and McComb, A. J. (1987). Nutrient loading and macrophyte growth in Wilson Inlet, a bar-built southwestern Australian estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 24 (2), 141–165. doi:10.1016/0272-7714(87)90062-X
Mazej, Z., and Germ, M. (2008). Seasonal changes in the contents of nutrients in five macrophyte species from the lake Velenjsko jezero (Slovenia). Acta Biol. Slov. 51, 3–11.
Mei, X., Razlutskij, V., Rudstam, L. G., Jeppesen, E., Liu, Z., Tang, Y., et al. (2021). Effects of omnivorous fish on benthic-pelagic habitats coupling in shallow aquatic ecosystems: A minireview. Hupo Kexue 33 (3), 667–674. doi:10.18307/2021.0304
Melzer, A. (1999). “Aquatic macrophytes as tools for lake management,” in The ecological bases for lake and reservoir management (Dordrecht: Springer), 181–190.
Meulenbroek, P., Drexler, S., Huemer, D., Gruber, S., Krumböck, S., Rauch, P., et al. (2018). Species-specific fish larvae drift in anthropogenically constructed riparian zones on the Vienna impoundment of the River Danube, Austria: Species occurrence, frequencies, and seasonal patterns based on DNA barcoding. River Res. Appl. 34 (7), 854–862. doi:10.1002/rra.3303
Moss, B., Jeppesen, E., Søndergaard, M., Lauridsen, T. L., and Liu, Z. (2013). Nitrogen, macrophytes, shallow lakes and nutrient limitation: Resolution of a current controversy? Hydrobiologia 710 (1), 3–21. doi:10.1007/s10750-012-1033-0
Nagengast, B., and Kuczyńska-Kippen, N. (2015). Macrophyte biometric features as an indicator of the trophic status of small water bodies. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 44 (1), 38–50. doi:10.1515/ohs-2015-0005
Nõges, T., Luup, H., and Feldmann, T. (2010). Primary production of aquatic macrophytes and their epiphytes in two shallow lakes (Peipsi and Võrtsjärv) in Estonia. Aquat. Ecol. 44 (1), 83–92. doi:10.1007/s10452-009-9249-4
ÖNORM M6231 (2001). Richtlinie für die Ökologische Untersuchung und Bewertung von Stehenden Gewässern. Wien: Österreichisches Normungsinstitut, 58.
Ostrofsky, M. L., and Miller, C. (2017). Photosynthetically-mediated calcite and phosphorus precipitation by submersed aquatic vascular plants in Lake Pleasant, Pennsylvania. Aquat. Bot. 143, 36–40. doi:10.1016/j.aquabot.2017.09.002
Padisák, J., Crossetti, L. O., and Naselli-Flores, L. (2009). Use and misuse in the application of the phytoplankton functional classification: A critical review with updates. Hydrobiologia 621 (1), 1–19. doi:10.1007/s10750-008-9645-0
Pall, K., and Goldschmid, U. (2018). “Restoration of the littoral zone,” in The Alte Donau: Successful restoration and sustainable management - an ecosystem case study of a shallow urban lake (aquatic ecology series 10). Editors M. T. Dokulil, K. Donabaum, and K. Teubner (Cham: Springer), 337–354. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-93270-5_18
Pall, K. (2018). “Wax and wane of macrophytes,” in The Alte Donau: Successful restoration and sustainable management - an ecosystem case study of a shallow urban lake, (aquatic ecology series 10). Editors M. T. Dokulil, K. Donabaum, and K. Teubner (Cham: Springer), 89–107. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-93270-5_8
Paul, L. (1989). Interrelationships between optical parameters. Acta Hydrophys. Berl. 33 (1), 41–63.
Pelton, D. K., Levine, S. N., and Braner, M. (1998). Measurements of phosphorus uptake by macrophytes and epiphytes from the LaPlatte River (VT) using 32P in stream microcosms. Freshw. Biol. 39 (2), 285–299. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2427.1998.00281.x
Petr, T. (2000). “Interactions between fish and aquatic macrophytes in inland waters: A review,” in FAO fisheries technical paper, No. 396 (Rome, Italy: FAO), 185.
Puche, E., Rodrigo, M. A., Segura, M., and Rojo, C. (2021). Habitat coupling mediated by the multi-interaction network linked to macrophyte meadows: Ponds versus lakes. Aquat. Sci. 83 (3), 55–18. doi:10.1007/s00027-021-00809-4
Raghothama, K. G. (1999). Phosphate acquisition. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 50, 665–693. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.50.1.665
Reitsema, R. E., Meire, P., and Schoelynck, J. (2018). The future of freshwater macrophytes in a changing world: Dissolved organic carbon quantity and quality and its interactions with macrophytes. Front. Plant Sci. 9, 629. doi:10.3389/fpls.2018.00629
Reitsema, R. E., Preiner, S., Meire, P., Hein, T., Dai, Y., and Schoelynck, J. (2021). Environmental control of macrophyte traits and interactions with metabolism and hydromorphology in a groundwater-fed river. River Res. Appl. 37 (2), 294–306. doi:10.1002/rra.3708
Ripl, W. (1978). Oxidation of lake sediments with nitrate - a restoration method for former recipients. Lund, Sweden: Institute of Limnology, University of Lund. CODEN LUNBDS/(NBLI-1001)/1-151, ISSN 0348-0798.
Ripl, W., and Wolter, K. D. (1995). “Sanierung Alte Donau,” in Begleituntersuchung zur kombinierten Eisen- und Nitratbehandlung (Wien: Zwischenbericht im Auftrag der Stadt Wien, MA 45 Wasserbau), 77.
Rojo, C., Sanchez-Carrillo, S., Rodrigo, M. A., Puche, E., Cirujano, S., and Alvarez-Cobelas, M. (2020). Charophyte stoichiometry in temperate waters. Aquat. Bot. 161, 103182. doi:10.1016/j.aquabot.2019.103182
Rott, E., Salmaso, N., and Hoehn, E. (2007). Quality control of utermöhl-based phytoplankton counting and biovolume estimates—An easy task or a gordian knot? Hydrobiologia 578 (1), 141–146. doi:10.1007/s10750-006-0440-5
Rott, E. (1981). Some results from phytoplankton counting intercalibrations. Schweiz. z. Hydrol. 43 (1), 34–62. doi:10.1007/BF02502471
Sand-Jensen, K., Jensen, R. S., Gomes, M., Kristensen, E., Martinsen, K. T., Kragh, T., et al. (2018). Photosynthesis and calcification of charophytes. Aquat. Bot. 149, 46–51. doi:10.1016/j.aquabot.2018.05.005
Sapna, S., Gray, D. K., Read, J. S., O’Reilly, C. M., Schneider, P., Qudrat, A., et al. (2015). A global database of lake surface temperatures collected by in situ and satellite methods from 1985–2009. Sci. Data 2, 150008. doi:10.1038/sdata.2015.8
Schagerl, M., and Pichler, C. (2000). Pigment composition of freshwater charophyceae. Aquat. Bot. 67 (2), 117–129. doi:10.1016/S0304-3770(99)00095-9
Scheffer, M., Hosper, S. H., Meijer, M. L., Moss, B., and Jeppesen, E. (1993). Alternative equilibria in shallow lakes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 8 (8), 275–279. doi:10.1016/0169-5347(93)90254-M
Schindler, D. W. (1977). Evolution of phosphorus limitation in lakes: Natural mechanisms compensate for deficiencies of nitrogen and carbon in eutrophied lakes. Science 195 (4275), 260–262. doi:10.1126/science.195.4275.260
Schlegel, I., Krienitz, L., and Hepperle, D. (2000). Variability of calcification of Phacotus lenticularis (Chlorophyta, Chlamydomonadales) in nature and culture. Phycologia 39 (4), 318–322. doi:10.2216/i0031-8884-39-4-318.1
Siong, K., and Asaeda, T. (2006). Does calcite encrustation in Chara provide a phosphorus nutrient sink? J. Environ. Qual. 35 (2), 490–494. doi:10.2134/jeq2005.0276
Smith, H. (2000). Phytochromes and light signal perception by plants—An emerging synthesis. Nature 407 (6804), 585–591. doi:10.1038/35036500
Solheim, A. L., Rekolainen, S., Moe, S. J., Carvalho, L., Phillips, G., Ptacnik, R., et al. (2008). Ecological threshold responses in European lakes and their applicability for the water framework directive (WFD) implementation: Synthesis of lakes results from the REBECCA project. Aquat. Ecol. 42 (2), 317–334. doi:10.1007/s10452-008-9188-5
Somogyi, B., Boros, E., Szabó-Tugyi, N., Kovács, A. W., and Vörös, L. (2022). Dense macrophyte cover has significant structural and functional influence on planktonic microbial communities leading to bacterial success. Sci. Tot. Environ. 829, 154576. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154576
Søndergaard, M., Jensen, J. P., Jeppesen, E., and Møller, P. H. (2002). Seasonal dynamics in the concentrations and retention of phosphorus in shallow Danish lakes after reduced loading. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 5 (1), 19–29. doi:10.1080/14634980260199936
Søndergaard, M., Jensen, J. P., and Jeppesen, E. (2005). Seasonal response of nutrients to reduced phosphorus loading in 12 Danish lakes. Freshw. Biol. 50 (10), 1605–1615. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2427.2005.01412.x
Søndergaard, M., Phillips, G., Hellsten, S., Kolada, A., Ecke, F., Mäemets, H., et al. (2013). Maximum growing depth of submerged macrophytes in European lakes. Hydrobiologia 704 (1), 165–177. doi:10.1007/s10750-012-1389-1
Kumar, D., and Shekhar, S. (2021). Developing an approach for assessing urban blue-green spaces towards sustainable urban growth through retrospective cyber metrics analysis of operational estimations approaches. J. Landsc. Ecol. 14 (3), 12–51. doi:10.2478/jlecol-2021-0016
Teubner, K., Crosbie, N., Donabaum, K., Kabas, W., Kirschner, A., Pfister, G., et al. (2003). Enhanced phosphorus accumulation efficiency by the pelagic community at reduced phosphorus supply: a lake experiment from bacteria to metazoan zooplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 48 (3), 1141–1149. doi:10.4319/lo.2003.48.3.1141
Teubner, K., Großschartner, M., and Teubner, I. E. (2018b). “Response of zooplankton to restoration and climate warming in Alte Donau,” in The Alte Donau: Successful restoration and sustainable management - an ecosystem case study of a shallow urban lake (aquatic ecology series 10). Editors M. T. Dokulil, K. Donabaum, and K. Teubner (Cham: Springer), 163–212. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-93270-5_11
Teubner, K., Kabas, W., and Teubner, I. E. (2018a). “Phytoplankton in Alte Donau: Response to trophic change from hypertrophic to mesotrophic over 22 years,” in The Alte Donau: Successful restoration and sustainable management – an ecosystem case study of a shallow urban lake (aquatic ecology series 10). Editors M. T. Dokulil, K. Donabaum, and K. Teubner (Cham: Springer), 107–147. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-93270-5_09
Teubner, K., Morscheid, H., Tolotti, M., Greisberger, S., Morscheid, H., and Kucklentz, V. (2004). Bedingungen für Auftreten Toxinbildender Blaualgen (Cyanobakterien) in bayerischen Seen und anderen stehenden Gewässern. München: Bayerisches Landesamt für Wasserwirtschaft, 1–105.
Teubner, K. (2000). Synchronised changes of planktonic cyanobacterial and diatom assemblages in North German waters reduce seasonality to two principal periods. Arch. Hydrobiol. Spec. Iss Adv. Limnol. 55, 564–580.
Teubner, K., Teubner, I. E., Pall, K., Kabas, W., Tolotti, M., Ofenböck, T., et al. (2021). “New emphasis on water clarity as socio-ecological indicator for urban water - a short illustration,” in Rivers and floodplains in the anthropocene - upcoming challenges in the Danube River basin, extended abstracts 43rdIAD-conference (Germany: Eichstadt-Ingolstadt University Library), 70–78. doi:10.17904/ku.edoc.28094
Teubner, K., Teubner, I., Pall, K., Kabas, W., Tolotti, M., Ofenböck, T., et al. (2020). New emphasis on water transparency as socio-ecological indicator for urban water: Bridging ecosystem service supply and sustainable ecosystem health. Front. Environ. Sci. 8, 573724. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2020.573724
Thomaz, S. M. (2021). Ecosystem services provided by freshwater macrophytes. Hydrobiologia, 1–21. doi:10.1007/s10750-021-04739-y
Tolotti, M., and Thies, H. (2002). Phytoplankton community and limnochemistry of Piburger See (Tyrol, Austria) 28 years after lake restoration. J. Limnol. 61 (1), 77–88. doi:10.4081/jlimnol.2002.77
Urrutia-Cordero, P., Zhang, H., Chaguaceda, F., Geng, H., and Hansson, L. A. (2020). Climate warming and heat waves alter harmful cyanobacterial blooms along the benthic–pelagic interface. Ecology 101 (7), e03025. doi:10.1002/ecy.3025
Vadeboncoeur, Y., Vander Zanden, M. J., and Lodge, D. M. (2002). Putting the lake back together: Reintegrating benthic pathways into lake food web models. Bioscience 52 (1), 44–54. doi:10.1641/0006-3568(2002)052[0044:PTLBTR]2.0.CO;2
Vollenweider, R. A. (1968). Die wissenschaftlichen Grundlagen der Seen und Fließgewässereutrophierung unter besonderer Berücksichtigung des Phosphors und des Stickstoffs als Eutrophierungsfaktoren. Paris: OECD, DAS/CSI/68.27.
Vuorio, K., Järvinen, M., and Kotamäki, N. (2020). Phosphorus thresholds for bloom-forming cyanobacterial taxa in boreal lakes. Hydrobiologia 847 (21), 4389–4400. doi:10.1007/s10750-019-04161-5
Vymazal, J. (2007). Removal of nutrients in various types of constructed wetlands. Sci. total Environ. 380 (1-3), 48–65. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.09.014
Wagner, K., Bengtsson, M. M., Findlay, R. H., Battin, T. J., and Ulseth, A. J. (2017). High light intensity mediates a shift from allochthonous to autochthonous carbon use in phototrophic stream biofilms. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 122 (7), 1806–1820. doi:10.1002/2016JG003727
Waidbacher, H., and Drexler, S.-S. (2018). “Fish assemblages of the ‘Alte Donau’ system: Communities under various pressures,” in The Alte Donau: Successful restoration and sustainable management - an ecosystem case study of a shallow urban lake (aquatic ecology series 10). Editors M. T. Dokulil, K. Donabaum, and K. Teubner (Cham: Springer), 275–313. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-93270-5_15
Wang, Z., Wu, Z., Wang, Y., and Yu, D. (2018). Variations in species-level N: P stoichiometry of charophytes and aquatic angiosperms on the Tibetan plateau. Front. Plant Sci. 9, 870. doi:10.3389/fpls.2018.00870
Wanzenböck, J., and Schiemer, F. (1989). Prey detection in cyprinids during early development. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 46 (6), 995–1001. doi:10.1139/f89-129
Wolters, J. W., Reitsema, R. E., Verdonschot, R. C., Schoelynck, J., Verdonschot, P. F., and Meire, P. (2019). Macrophyte-specific effects on epiphyton quality and quantity and resulting effects on grazing macroinvertebrates. Freshw. Biol. 64 (6), 1131–1142. doi:10.1111/fwb.13290
Wüstenberg, A., Pörs, Y., and Ehwald, R. (2011). Culturing of stoneworts and submersed angiosperms with phosphate uptake exclusively from an artificial sediment. Freshw. Biol. 56 (8), 1531–1539. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2427.2011.02591.x
Yofukuji, K. Y., Cardozo, A. L. P., Quirino, B. A., Aleixo, M. H. F., and Fugi, R. (2021). Macrophyte diversity alters invertebrate community and fish diet. Hydrobiologia 848 (4), 913–927. doi:10.1007/s10750-020-04501-w
Yu, J., Zhen, W., Guan, B., Zhong, P., Jeppesen, E., and Liu, Z. (2016). Dominance of Myriophyllum spicatum in submerged macrophyte communities associated with grass carp. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 417, 24. doi:10.1051/kmae/2016011
Zhang, H., Zhang, P., Wang, H., García Molinos, J., Hansson, L. A., He, L., et al. (2021). Synergistic effects of warming and eutrophication alert zooplankton predator–prey interactions along the benthic–pelagic interface. Glob. Chang. Biol. 27 (22), 5907–5919. doi:10.1111/gcb.15838
Zhang, Q., Dong, X., Yang, X., Liu, E., Lin, Q., Cheng, L., et al. (2022). Aquatic macrophyte fluctuations since the 1900s in the third largest Chinese freshwater lake (Lake Taihu): Evidences, drivers and management implications. CATENA 213, 106153. doi:10.1016/j.catena.2022.106153
Zhang, Q., Liu, Y. P., Luo, F. L., Dong, B. C., and Yu, F. H. (2019). Does species richness affect the growth and water quality of submerged macrophyte assemblages? Aquat. Bot. 153, 51–57. doi:10.1016/j.aquabot.2018.11.006
Zhang, S., Libbenga, M., Vennik, M., and van Duijn, B. (2018). “The culture of Chara sp. for research: Does and don’ts. Chapter 2,” in The Chara plasma membrane system: An ancestral model for plasma membrane transport in plant cells (Leiden, The Netherlands: Universiteit Leiden), 27–45.
Zhang, S., Pang, S., Wang, P., Wang, C., Guo, C., Addo, F. G., et al. (2016). Responses of bacterial community structure and denitrifying bacteria in biofilm to submerged macrophytes and nitrate. Sci. Rep. 6 (1), 36178. doi:10.1038/srep36178
Zhang, X., Odgaard, R., Olesen, B., Lauridsen, L. T., Liboriussen, L., Søndergaard, M., et al. (2015). Warming shows differential effects on late-season growth and competitive capacity of Elodea canadensis and Potamogeton crispus in shallow lakes. Inland Waters 5 (4), 421–432. doi:10.5268/IW-5.4.830
Zhen, W., Zhang, X., Guan, B., Yin, C., Yu, J., Jeppesen, E., et al. (2018). Stocking of herbivorous fish in eutrophic shallow clear-water lakes to reduce standing height of submerged macrophytes while maintaining their biomass. Ecol. Eng. 113, 61–64. doi:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2017.10.011
Zhu, Y., Zhang, Q., Liu, J., Zhang, C., Wu, C., Song, Q., et al. (2021). Effects of riparian land use on underwater light intensity of submerged macrophytes colonization in middle-small rivers. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae J. Environ. Sci. 41 (6), 2414–2420.
Keywords: lake restoration and management, eutrophicaion, aquatic vegetation, water transparency, Secchi depth, underwater light climate, photic hypsographic curve
Citation: Teubner K, Teubner IE, Pall K, Tolotti M, Kabas W, Drexler S-S, Waidbacher H and Dokulil MT (2022) Macrophyte habitat architecture and benthic-pelagic coupling: Photic habitat demand to build up large P storage capacity and bio-surface by underwater vegetation. Front. Environ. Sci. 10:901924. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2022.901924
Received: 22 March 2022; Accepted: 12 August 2022;
Published: 23 September 2022.
Edited by:
Xiufeng Zhang, Jinan University, ChinaReviewed by:
Yali Tang, Jinan University, ChinaMarcus W. Beck, Tampa Bay Estuary Program, United States
Copyright © 2022 Teubner, Teubner, Pall, Tolotti, Kabas, Drexler, Waidbacher and Dokulil. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Katrin Teubner, S2F0cmluLlRldWJuZXJAdW5pdmllLmFjLmF0
 Katrin Teubner
Katrin Teubner Irene E. Teubner
Irene E. Teubner Karin Pall
Karin Pall Monica Tolotti
Monica Tolotti Willi Kabas5
Willi Kabas5