
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Environ. Sci. , 24 January 2023
Sec. Conservation and Restoration Ecology
Volume 10 - 2022 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2022.1056751
This article is part of the Research Topic Women in Conservation and Restoration Ecology 2022 View all 12 articles
 Robyn James1,2*
Robyn James1,2* Jonathan R. B. Fisher3
Jonathan R. B. Fisher3 Chelsea Carlos-Grotjahn1
Chelsea Carlos-Grotjahn1 Marissa S. Boylan4
Marissa S. Boylan4 Baigalmaa Dembereldash5
Baigalmaa Dembereldash5 Meaza Z. Demissie6
Meaza Z. Demissie6 Crystal Diaz De Villegas7
Crystal Diaz De Villegas7 Bridget Gibbs1
Bridget Gibbs1 Ruth Konia8
Ruth Konia8 Kristen Lyons2
Kristen Lyons2 Hugh Possingham9
Hugh Possingham9 Cathy J. Robinson10
Cathy J. Robinson10 Tiantian Tang11
Tiantian Tang11 Nathalie Butt12
Nathalie Butt12The planet is facing climate and biodiversity loss crises that impact all of humanity and yet globally, women remain underrepresented in leading solutions to these urgent conservation challenges. As one of the world’s largest conservation non-profit organizations, The Nature Conservancy (TNC) provided a large case-study for understanding inequity for women in the conservation sector. In 2018, all 1,789 conservation and science staff at TNC were surveyed to understand how they are able to develop their careers and contribute to conservation research and decision making. Of the 904 responses (490 men and 414 women), results show that men influence conservation and science decisions more than women; women face multiple barriers across their conservation careers due to gender bias; women experience sexual harassment and discrimination, as well as fear retaliation more than men; and men reported the sector as a more equitable and favorable place for women than women themselves experienced. Our data demonstrates that gender equality (equal representation of men and women) does not automatically mean that women no longer face systemic inequity and that intersectional issues such as race, location and caring responsibilities can all make it even more difficult for women to excel. Respondents drew from experiences across their conservation careers, to suggest how the conservation sector could address these issues. Based on our findings, we recommend practical ways the conservation sector can improve gender equity, including via workplace and cultural change measures, as well as changes to recruitment, pay transparency, and career development policies.
Despite global emphasis on the benefits of, and need to, achieve gender equity across the sciences, progress remains slow. At current rates it will take generations, if ever, to fully address gender equity for women (Holman et al., 2018; Kuschel et al., 2020). Women are consistently paid less, promoted less often, cited less, as well as less likely to be invited to join editorial boards, research panels, and grant proposals (Ross et al., 2022). Demonstrating this inequality, less than 27% of authors nominated for the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Special Report on 1.5°C were women (IPCC, 2018). Meanwhile globally, women remain poorly represented, and in some cases completely absent, from climate negotiations (Gonda, 2019). Women have identified multiple intersecting and systemic barriers limiting their participation in the sciences. These include disproportionate family and caring responsibilities and active discrimination against them based on gender, race, and/or nationality (Gay-Antaki and Liverman, 2018).
There are limited published data outlining how conservation organizations consider gender within their own institutions (Jones and Solomon, 2019), and a tendency across the conservation sector to view gender inequity as an issue only for locally based community conservation, primarily in low-income and emerging economies, rather than an issue conservation organizations themselves need to address (Westberg and Powell, 2015; James et al., 2021). Despite this, evidence shows women are under-represented and/or excluded from decision making within organizations focused on conservation, climate, and natural resource management, as well as in research and policy-setting contexts (Jones and Solomon, 2019).
Studies across sectors show that women and men perceive the degree to which their organization addresses gender equity differently. Despite evidence of gender gaps, men (and many women) consistently perceive gender inequity is less than women actually experience, and there is often a reluctance by men to acknowledge or reflect on gender bias in their workplaces (Handley et al., 2015; García-González et al., 2019). Without both men and women sharing awareness of the problem of gender bias, making improvements remains difficult (Handley et al., 2015).
This discrepancy between the perceptions of women and men is heightened by intersectional identities. For example, a 2022 study of over 25,000 professionals working in science, technology, engineering, or math (STEM), revealed that white able-bodied heterosexual men (WAHM) experienced better treatment and rewards in STEM when compared with members of all other intersectional categories relating to gender, race, sexual identity, and disability status (Cech, 2022). The study revealed that, as a group, WAHM were more likely to benefit from workplace inclusion, respect, and rewards. Furthermore, this privilege could not be attributed to any other reasons, such as greater work commitment or training (Cech, 2022).
There is evidence that in some STEM fields—such as conservation archaeology in the U.S.—men earn up to 30% more than women; a higher gender pay gap than the U.S. national average (Davis, 2019). Gender salary discrepancies are highest in settings conducive to individual negotiating (Finley et al., 2021), and women are particularly disadvantaged in terms of pay negotiations when there is limited transparency around pay (Bennedsen, 2019). Women also experience a wage penalty for motherhood, circumstances that continue throughout their careers (Gangl and Ziefle, 2009; Gough and Noonan, 2013). In contrast, men earn a wage premium for fatherhood, especially high-earning men (Glauber, 2018).
Studies in the conservation sector have shown that long hours and travel are often expected (especially if people wish to have influence and advance their career), and this is harder for women given their traditionally greater share of caring responsibilities (Campos-Arceiz et al., 2013; Jones et al., 2020). Other research also demonstrates that traditional gender roles are commonly reflected within conservation organizations (Mahour, 2016). For example, women often occupy administrative roles (with a focus on so-called “soft skills”), while men are over-represented in positions of leadership, risk-taking, or those that involve travel and fieldwork (Westberg and Powell, 2015; Jones and Solomon, 2019). This often leaves women with lower status, lower paid roles, and leads to them being sidelined as scientific experts and/or decision-makers (CohenMiller et al., 2020; Westberg and Powell, 2015).
Across all scientific disciplines and career stages, women are less likely to be recognized for their scientific publications. Their work is often not appreciated, not known, as well as being often ignored (Ross et al., 2022). Such structural disadvantage is evident across science and conservation institutions, including The Nature Conservancy (TNC)—the focus of this paper. An analysis of rates of scientific publishing at TNC found that only 30% of authors were women (James et al., 2022).
This paper builds upon existing literature about gender inequity in the conservation sector by examining perspectives from over 900 conservation professionals at The Nature Conservancy. The Nature Conservancy is one of the largest conservation non-government organizations (NGO) in the world, with an annual revenue of over $USD 1.2BN and approximately 4,000 staff (The Nature Conservancy, 2021a). We drew from this large pool of conservation employees to undertake a large-scale study into how women and men experience working in the conservation sector (see Box 1). Respondents drew from their experiences across their conservation careers, often referring to experiences in different organizations, locations, roles, and career stages. By identifying how women and men participate in decision-making and build their careers, we were able to identify significant areas that limit women across the conservation sector. Our recommendations are informed by these rich quantitative and qualitative data and are designed to support conservation and climate organizations to acknowledge the problem and take steps to address gender inequity (e.g., James et al., 2022).
BOX 1 The case of The Nature Conservancy
The Nature Conservancy (TNC) was founded in the United States of America (U.S.) in 1951. It began as a land trust, originally with the intent of setting aside land for long-term protection and research (Adams, 2006). Its inception is interconnected with the broader U.S. conservation movement in the 1900s, which was led primarily by white men with a focus on buying and protecting land for biodiversity conservation and nature-based activities, including birdwatching, hiking, hunting, and fishing (Taylor, 2016). The conservation movement overall, is associated with processes of dispossession and social exclusion of both women and First Nations people across the U.S. (Zurba et al., 2019). Although still headquartered in the U.S., and with operations in all 50 states, TNC has extended its reach globally, to Latin America and the Caribbean in the 1980s, the Asia Pacific region in the 1990s, the African continent in 2007, and by 2014, the organization had also established in Europe. TNC now also focuses on global conservation issues across more than 70 countries, including climate change and biodiversity loss, with an increasing focus on people and social inclusion (The Nature Conservancy, 2021b). Despite the apparent globalization of the organization, conservation and science research and publications continue to be predominantly authored by men located in the U.S. (James et al., 2022). In 2019, an internal investigation revealed that women employees believed the organization’s male-dominated culture made it difficult for women to thrive (Coleman, 2019). Over time, and with changing leadership, including appointment of TNC’s first woman CEO in 2019, TNC has increasingly underscored the importance of gender equity both in the workplace and the conservation work (The Nature Conservancy, 2021b).
Using our experience across conservation, as well as the social and behavioral sciences, we developed an online survey to collect perspectives on each respondent’s involvement in science and conservation decision making, as well as their career satisfaction and opportunities and barriers to career development. Research complied with TNC’s Standard Operating Procedures for Research involving Human Subjects and was approved by the University of Queensland Institutional Human Research and Ethics Committee (Approval number: 2018001799).
The survey was designed to understand how respondents felt their gender influenced both their career and their influence in conservation. We focused only on staff working in conservation and/or science positions (excluding staff in other functions such as human resources, marketing, and information technology) as part of specifically understanding trends across the conservation sector. A total of 33 questions were asked to elicit personal reflections and experiences using a five-point Likert scale (refer to Table 1 for the questions). In addition, open-ended questions asked respondents to provide context about their experiences. While the survey was only sent out in English, before being circulated, the survey was tested three times with respondents from different locations, genders, and primary languages, and was revised where any confusion around the meaning of the questions was encountered (see also Letherby, 2011; Patton, 2015).
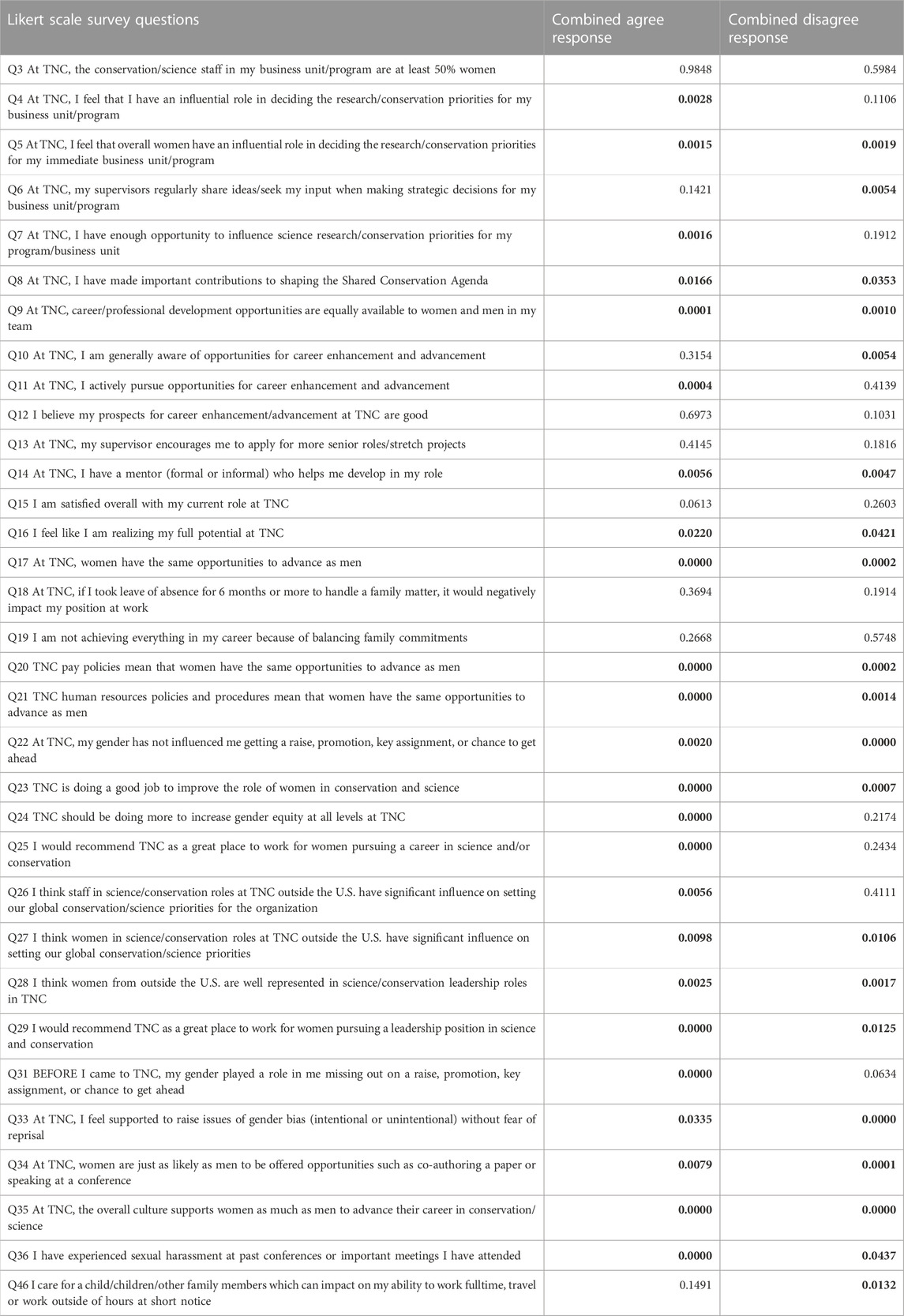
TABLE 1. Multinomial logistic regression analysis p-values indicating significant differences (p < 0.05; in bold) for the Likert question responses between women and men. “Agree” and “Strongly agree,” and “Disagree” and “Strongly disagree,” were aggregated to give “combined agree” and “combined disagree.” Of the 32 Likert scale survey questions the difference in responses was significant for combined agree and/or combined disagree for 27 of the 33 questions.
TNC Human Resources team generated an email list of all 1,789 staff within TNC who held conservation and/or science positions. All staff on the list self-identified as either male or female as listed in TNC’s human resources data (there were no other options available at that time). Although this study lacked available data to shift beyond a binary definition of gender or sex (woman/man, male/female), we acknowledge this does not reflect the lived experience of all staff at The Nature Conservancy, or in conservation more broadly and sexuality or gender identity can greatly impact people’s experiences within the workplace (Cech, 2022). Further, we use the term “gender” (grounded in identity) rather than “sex” (grounded in biology) since staff self-report their gender to human resources upon hiring; however, we recognize that only providing two options makes it likely that staff likely reported biological sex even if their gender identity was different.
In October 2018, the online survey was sent through Survey Monkey to the staff email list. To maximize the response rate, it was sent out by the TNC Chief Scientist (the most senior science position within the organization) who encouraged all conservation and science staff to complete it. Gender was not specifically mentioned in the cover letter to minimize the risk of respondents interpreting the survey as “for women” or “for women only,” given the common (and often incorrect) assumptions that “gender” is synonymous with “women” (Lau, 2020).
Once survey responses were received, they were sent to a representative in the Chief Diversity Officer’s office of TNC who combined them with extra demographic data, including location and gender. All data were kept confidential, and responses were anonymized to prevent anyone being identified.
Data analysis began with descriptive quantitative analysis of the online survey responses, including summaries of the sample and the measures, along with basic graphic analysis.
To identify significant differences between women’s and men’s answers to the Likert scale questions (Qs 3–29, 31–36, and 46), we aggregated “strongly (dis)agree” and “(dis)agree” into combined “agree” and “disagree” responses, respectively. We then ran multinomial logistic regressions with agree/disagree as the response variable, and gender as predictor for each question (Venables and Ripley, 2002). All analyses were run using R (R Core Team, 2021). Significance was given by p-values.
Respondents were invited to provide open-ended free text responses to questions relating to the following: “Please share any personal reflections about how you have been treated in relation to your gender” and “Do you have any recommendations to ensure women are included in science and conservation strategy and practice at TNC?” Answers from these open-ended questions were also analyzed to provide context to the quantitative data. The lead author read each response to gain an overall familiarization and understanding of the data. Each response was then assigned a broad theme and crosschecked by two other authors.
In 2018, there were 1,789 total Conservation and Science staff: 44% (781) women and 56% (1,008) men. We received a total of 904 responses to the survey: 414 (46%) women and 490 (54%) men), meaning a response rate of 53% for women and 49% for men. Respondents were also categorized by the region where they were physically located. Most respondents, 741 (82%), were in North America with the remainder 163 (18%) in Asia Pacific, Africa, Caribbean, Latin America, and Europe. In addition, a total of 402 respondents [225 (54%) of the women and 177 (36%) of the men] provided written responses to open-ended questions relating to their personal experiences of gender inequity throughout their conservation careers, and 485 respondents [252 (61%) of the women and 233 (48%) of the men] made suggestions for improving gender equity at TNC.
We have highlighted the following four themes that emerged from the data, each of which we discuss in sections below:
1) Men influence conservation and science outcomes more than women.
2) Women face multiple barriers across their conservation careers due to gender bias.
3) Women experience sexual harassment and discrimination, as well as fear retaliation, more than men.
4) Men overestimate gender equity for women in conservation.
The results to all quantitative questions, including level of significance based on the binomial logistic regression output p-values, are provided in Table 1. In most cases, differences between women’s and men’s responses were significant or highly significant (Table 1; Supplementary Material S1). Representative quotes associated with the four themes that emerged from our qualitative data analysis are provided in Table 2. Throughout this paper we also include example quotes in italics (including their anonymized ID and gender) to provide further context for each theme.
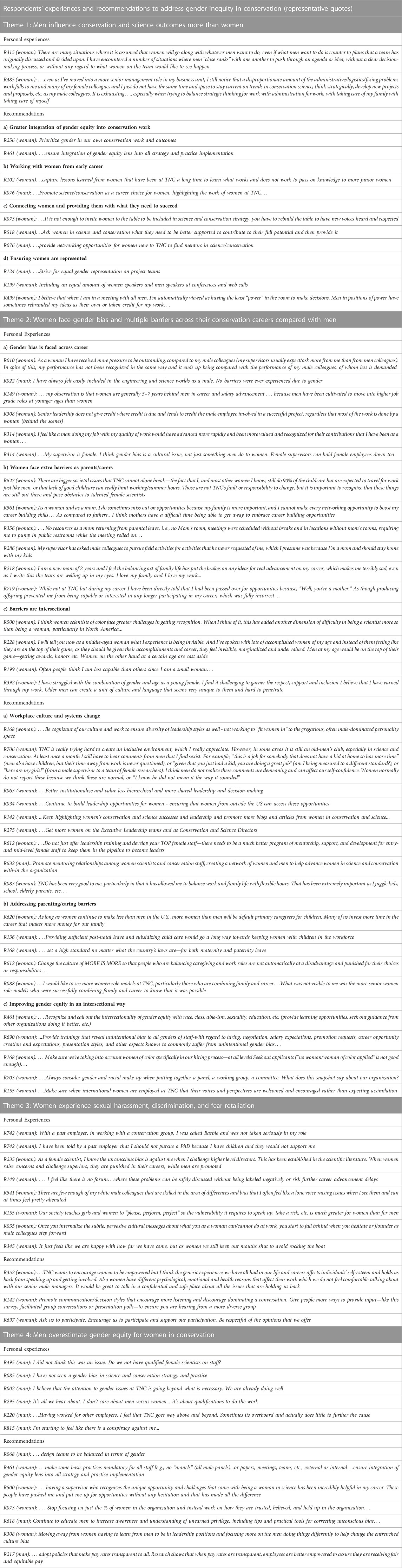
TABLE 2. Representative quotes associated with the four themes that emerged from our analysis. Quotes were drawn from two open-ended survey questions: Q40 Please share any personal reflections about how you have been treated in relation to your gender [N = 402: 225 (54%) women and 233 (36%) men] and Q37 Please list the top three issues/ideas your organization could address to ensure women are included in science and conservation strategy and practice at TNC [N = 485: 252 (61%) women and 233 (48%) men].
Overall, women felt less able to contribute to conservation and science than men. This ranged from large goal setting decisions for their organization to more specific conservation decisions for their management unit and immediate team. For example, only 49% of women compared with 65% of men agreed that they had enough influence in determining research and conservation priorities for their program (Q7; Table 1; Figure 1). These data were matched by written responses from women, who frequently described being sidelined, or overlooked, in relation to conservation science work (examples in Table 2).
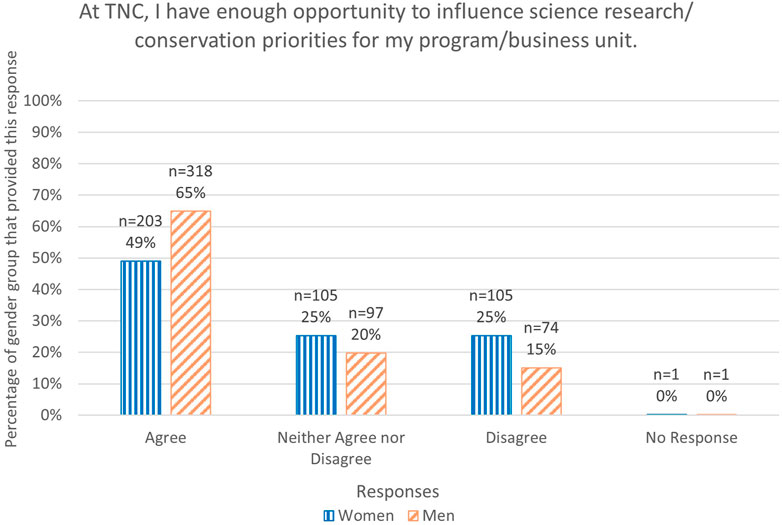
FIGURE 1. Graph of responses to Q7. At TNC I have enough opportunity to influence conservation and science priorities for my program as a percentage of the total number of respondents for each gender.
Women were also less involved in conservation implementation and described the disproportionate administrative responsibilities they were expected to carry out related to project and staff management. For example, 54% of women, compared with just 38% of men, were responsible for providing support to other conservation and research staff (Q1; Figure 2). Such activities significantly restrict time available for conservation and science related work. For example: …even as I’ve moved into a more senior management role in my business unit, I still notice that a disproportionate amount of the administrative/logistics/fixing problems work falls to me and many of my female colleagues and I just don’t have the same time and space to stay current on trends in conservation science, think strategically, develop new projects and proposals, etc. as my male colleagues. It is exhausting…, especially when trying to balance strategic thinking for work with administration for work, with taking care of my family with taking care of myself [R485 (woman)] (Table 2).
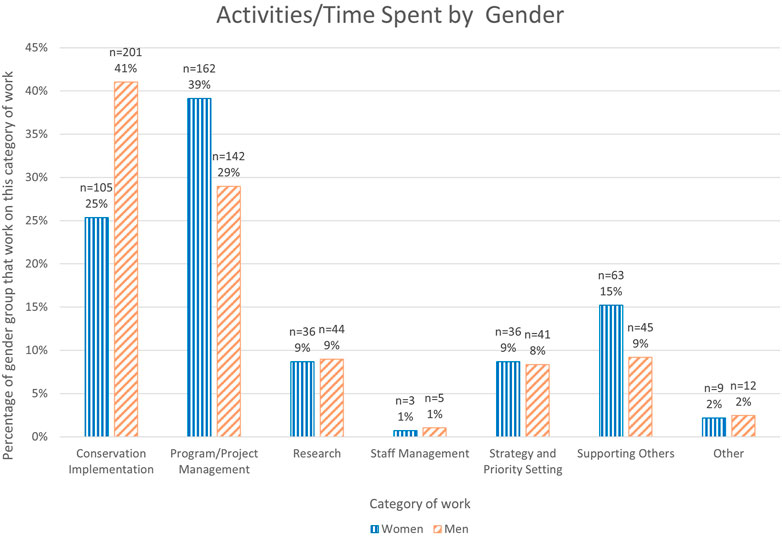
FIGURE 2. Graph of responses to Q1. Is your role predominantly? (Chosen from a drop down list). As a percentage of the total number of respondents for each gender.
Women reported that their gender had played a key role in restricting their careers in conservation and science. For example, 29% of women reported that before they came to TNC their gender had played a role in them missing out on a raise, promotion, key assignment, or chance to get ahead whereas only 4% of men reported this (Q31; Table 1; Figure 3). This was backed by findings from qualitative data, where women gave examples of the long-term career and salary outcomes of this trend. I feel like a man doing my job with my quality of work would have advanced more rapidly and been more valued and recognized for their contributions than I have been as a woman…[R314 (woman)] (Table 2).
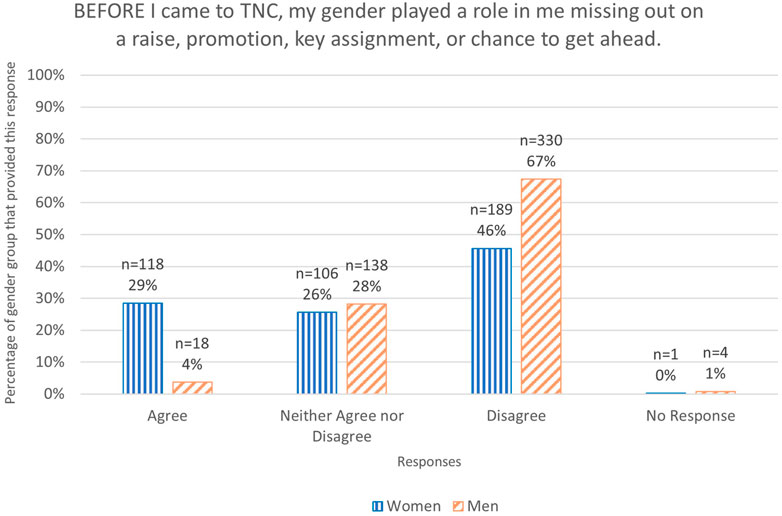
FIGURE 3. Graph of responses to Q31. BEFORE I came to TNC, my gender played a role in me missing out on a raise, promotion, key assignment, or chance to get ahead. As a percentage of the total number of respondents for each gender.
Women also reported that they did not have the same opportunities in their careers as men (Figure 4) and that the expectations placed upon them were higher compared to their men counterparts. Various barriers were cited at all career stages from early career to senior leadership (representative quotes in Table 2). In stark contrast to the experiences of inequity cited by women, nearly all men commented that gender had not held them back or ever been an issue for them. I have always felt easily included in the engineering and science worlds as a male. No barriers were ever experienced due to gender [R022 (man)] (Table 2).
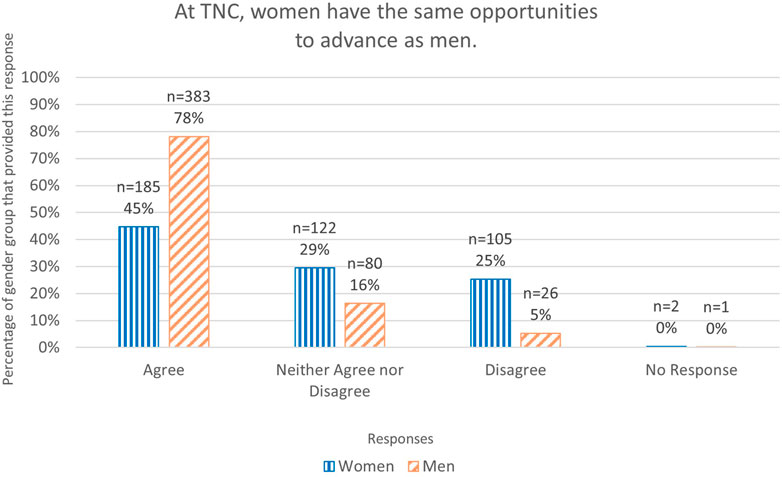
FIGURE 4. Graph of responses to Q17. At TNC, women have the same opportunities to advance as men. As a percentage of the total number of respondents for each gender.
This disadvantage was not associated with a lack of effort by women in pursuing career advancement and leadership opportunities. For example, 65% of women noted they actively pursued opportunities for career enhancement and advancement, compared with 52% of men (Q11; Table 1). Despite this, women described career pathways and models of leadership as being largely defined by men and subject to entrenched gender bias. Respondents highlighted that cultural change was needed in conservation, including support for a diversity of leadership styles, as well as mentoring, sponsoring, and championing women across their careers. Be cognizant of our culture and work to ensure diversity of leadership styles as well—not working to “fit women in” to the gregarious, often male-dominated personality space [R168 (woman)] (Table 2).
Our data revealed that both men and women believed that family and care commitments could negatively impact their careers. Both genders (30% of women and 28% of men), for example, felt that they were not achieving everything in their career because of seeking to balance family commitments (Q19; Table 1). And 42% of men and 48% of women felt that if they took a leave of absence for 6 months or more to handle a family matter, it would negatively impact their position at work (Q18; Table 1). Furthermore, similar percentages (42% of women and 46% of men) agreed that care for a child/children, or other family members would impact their ability to work fulltime, travel, or work outside business hours at short notice (Q46; Table 1).
So, although both men and women felt that care commitments could impact their career, qualitative data highlighted some of the specific ways in which gender-defined roles including caring and parenting impact women disproportionately. These included, lack of financial support (parental leave), or a lack of structural support such as breastfeeding areas for women returning to work. Assumptions that women returning to work would not be capable or interested in traveling, attending meetings and workshops, or undertaking field work was cited as another challenge (Table 2). The weight of such inequalities bears down on women, with several women describing the stress of balancing the needs of a family with a strong desire to advance their careers. In responding to these challenges, respondents made suggestions that included setting high standards on caring leave policies across countries, making equitable pay for women a reality, tailoring specific support for mothers, flexible working hours, and the recognition that societal norms mean women have disproportionate caring responsibilities.
Respondents also noted that women experience barriers in their conservation careers due to multiple intersecting factors, including race, ethnicity, age, physical abilities, and geographic location. For example, only 8% of women and 14% of men felt women from outside the U.S. were well represented in science/conservation leadership roles in TNC (Q28). Women with intersectional identities described various experiences of unconscious bias and discrimination during their conservation careers. Respondents offered rich suggestions on how to improve gender equity in an intersectional way. These related to training for leaders in bias and privilege, recruitment programs and quotas, mentoring, and sponsorship.…Always consider gender and racial make-up when putting together a panel, a working group, a committee. What does this snapshot say about our organization? [R703 (woman)] (Table 2).
Women also reported higher rates of sexual harassment and discrimination across their careers in conservation, with 15% of women compared to just 2% of men, reporting that they had experienced sexual harassment at conservation related conferences or important meetings (Q36; Table 1).
There also continue to be barriers for women in speaking out about diverse forms of gender-based discrimination and harassment, with 18% of women compared to 6% of men, describing not feeling supported to raise issues of gender bias (intentional or unintentional) without fear of reprisal (Q33; Table 1). Women commented that they often felt that there was no safe mechanism to raise issues and that they did not feel supported to do so without fear of retaliation. They also felt that often managers were not skilled in understanding or addressing issues of discrimination. Some women reported workplace cultures that actively silenced such problems. Women also expressed that gender norms are pervasive across society, leading women to internalize and/or privatize these structural barriers as personal problems best managed individually (Table 2).
By far the most significant differences between men and women across the survey related to how well respondents thought gender and inequity was being addressed in conservation, and how supportive they thought their workplace was for women. Across all issues, from women’s influence and leadership in conservation to work culture, career advancement and pay, men perceived the conservation sector as significantly more equitable than how women actually experienced it. For example, only 48% of women compared with 74% of men, indicated that human resources policies and procedures supported equal opportunities for women (Q21; Table 1; Figure 5). When asked if they thought policies and procedures supported equitable pay, 63% of men compared with just 32% of women thought there was equity (Q20; Table 1). Furthermore, 79% of men and only 58% of women, felt that the overall culture of their organization supports women as much as men to advance their career in conservation/science (Q35; Table 1). Overall, 78% of men compared with just 44% of women, felt that women have the same opportunities to advance as men (Q17; Table 1; Figure 5). In addition, 82% of men compared with only 64% women, believed that women had an influential role in deciding the research/conservation priorities for their programs (Q5; Table 1) with one man stating: I did not think this was an issue. Do we not have qualified female scientists on staff? [R495 (man)] (Table 2). The trend continued, only 56% of women compared with 78% of men felt that their organization was doing a good job to improve the role of women in conservation and science (Q23; Table 1). This is reflected in the divergent experiences described by women and men. For example, some men felt that the focus on gender within their organization had gone too far, with adverse outcomes for the organization and themselves: …Having worked for other employers, I feel that TNC goes way above and beyond. Sometimes it is overboard and actually does little to further the cause [R220 (man)] (Table 2).
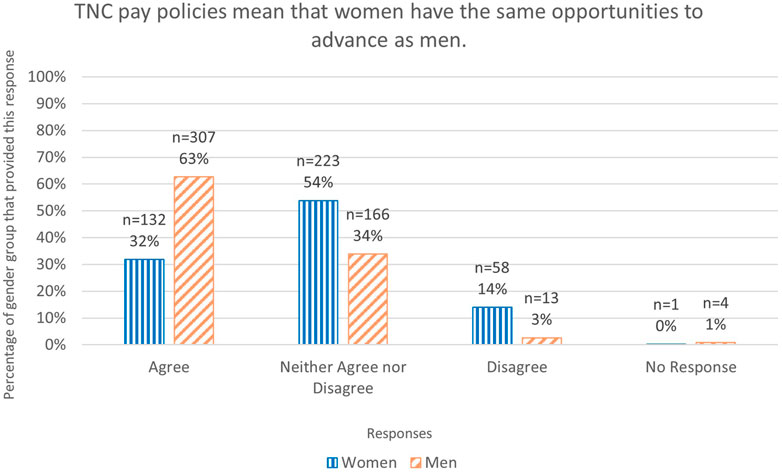
FIGURE 5. Graph of responses to Q20. TNC pay policies mean that women have the same opportunities to advance as men. As a percentage of the total number of respondents for each gender.
Regardless of these findings, most respondents, although still significantly more men than women (91% of men and 78% of women), would recommend their organization as a great place to work for women pursuing a career in science and/or conservation (Q25; Table 1). This figure dropped to 63% of women and 85% of men for a leadership position (Q29; Table 1). These findings were backed by other questions, with 73% of women compared with 50% of men, reporting that their organization should be doing more to increase gender equity at all levels (Q24; Table 1).
Several women respondents highlighted that society/sector wide inequity was pervasive and appreciated the efforts of their organization in addressing gender bias and inequity. Suggestions from respondents to further address gender bias included balancing gender on teams/panels/workgroups, trainings on gender bias (including unconscious bias), going beyond gender diversity to true gender inclusion, provision of support for early career women scientists, as well as the promotion of diverse leadership styles (so women do not have to fit into “male culture” to succeed) (Table 2).
The conservation sector has passionate, ambitious, and committed individuals who want to make meaningful contributions (Pienkowski et al., 2022). But many people seem unaware of how gender inequity impacts both science and conservation efforts as well as individual’s career progression. The fact that only 44% of women, but 78% of men think that women and men have the same opportunity to advance in their conservation careers, reveals a significant problem. Men’s lack of awareness may be compounded by the reluctance of women to discuss discrimination they experience. Significantly, 18% of women reported fearing reprisal if they raised concerns about discrimination or harassment; other sectors have shown this fear is justified. There is evidence that situations often get worse for women when they speak out in the workplace (Rudman et al., 2012; Gianakos et al., 2022).
Our survey revealed that women felt less able to access and perform in leadership positions. Several women commented that they felt pressure to fit into culture that did not value a more collaborative style of leadership. Preventing women from progressing into leadership and then leading authentically is not only detrimental for individual women but can also hurt the organization. For example, the largest global study of women in the workplace, conducted across over 400 organizations collectively employing more than 12 million people, demonstrated that women are (a) more likely to be strong leaders that support staff and teams, (b) are more likely to advance diversity, equity, and inclusion efforts, and (c) do the work to speak out against discrimination in the workplace and mentor others (McKinsey, 2019).
Evidence across sectors shows that all people, regardless of their gender, consistently overestimate women’s representation, and therefore, general progress towards gender equity. Focusing too much on how gender equity is good or has improved can, perhaps counter-intuitively, stall further progress (Ryan, 2022). In addition, men and women who overestimate progress towards gender equity in their workplaces are more likely to show gender bias in performance reviews: candidates randomly assigned a female name were more likely to be evaluated poorly, recommended to be paid less, and discouraged from seeking promotion (Begeny et al., 2020). Furthermore, studies of traditionally male dominated science fields (i.e., conservation) that have moved towards greatly increasing numbers of women represented, demonstrated that those who thought bias was no longer a problem were most likely to perpetuate gender bias (Begeny et al., 2020).
This is concerning when again, our results revealed that men consistently overestimated gender equity across questions relating to conservation decision making and leadership, and workplace culture and policies. Given that 78% of men thought there was already equal opportunity between the genders, it is likely to be challenging to work on improving it (only half of men thought their organization should do more to improve gender equity, whereas three quarters of women did). Accordingly, we see that raising awareness about existing inequities across conservation is crucial for everyone (not just women).
One way to both highlight inequities and address them is greater transparency for pay, benefits, and career advancement. Only 32% of women compared with around 63% of men felt that pay policies are equitable. There is clear evidence that disclosing salary range on recruitment and publishing pay data closes the gender pay gap. For example, in Denmark, a study of the gender pay gap before and after legislation mandating pay transparency noted that the pay gap closed by 13% (Bennedsen, 2019).
Interestingly, our results show no significant difference between men and women on how family and caring commitments impacted their careers. Given that evidence across sectors shows that women have far greater caring responsibilities both inside and outside the workplace, this may indicate that their organization’s approach to flexible work is helpful. However, evidence from our qualitative data and from other sectors shows that women do still typically shoulder most of these caring responsibilities (Knudsen and Wærness, 2008). For example, women, and especially working mothers, do significantly more housework and childcare than working fathers; worldwide women spend 300% more time on unpaid care work than men (OECD Development Centre, 2015; McKinsey, 2019).
Intersectionality recognizes that people are subject to multiple layers of social division and power, including race, gender, age, class, and wealth, which all interact with each other to determine how people can benefit or be disadvantaged in the world (Hill-Collins and Bilge, 2016). This includes recognizing that gender diverse people (including non-binary, trans, and others) experience unique and compounding challenges, some (but not all) of which may align with those experienced by cisgender women, especially when they are perceived by others as women (regardless of their biological sex and gender identity) (Davis and Yeung, 2022). The qualitative answers from our respondents highlighted intersecting issues including race, nationality, location, age, and caring roles that intersected to further impact each woman’s ability to influence conservation and build their careers.
For example, across international organizations, inequity can also show up as a lack of representation in leadership and decision making for women outside where the organization is headquartered, such as Europe and the U.S. There was recognition that a dedicated and sustained effort is needed for international organizations to fully include women located outside of the headquartered location. This could include diversity quotas for conservation leadership positions and career development opportunities. Support needs to be deliberate and include dedicated resources such as language translation and travel funds to ensure women can fully participate. These opportunities need to be designed so women are welcomed virtually where travel is unachievable. For example, this study would have been improved if resources had been available to translate our survey instrument into the primary language of all survey recipients. It is also important to note that conservation and science organizations work within countries that have different legal frameworks and minimum requirements for benefits such as paid parental leave. There is opportunity for international organizations to design policies that enable all women, regardless of which nationality they are or country they are located in, to benefit from equitable workplace standards, salary and benefit packages.
Many respondents identified the need for more training; some responses focused on women (leadership skills and mentoring, for example), and some responses focused on men or all staff (training about gender bias, diversity, equity, and inclusion). It is important to note that, focusing on training individual women (or men) rather than addressing inequitable systems and workplace cultures is helpful but insufficient when used as the primary approach to address gender equity issues in the workplace. It is much easier for an organization to focus on offering women extra coaching to take career risks, negotiate, overcome imposter syndrome, and boost leadership skills, rather than addressing the workplace systems and cultures that reward men for risk taking and limited care of their teams, whilst punishing women for the same behavior (McKinsey, 2021). Research suggests that women do not begin their careers with lower ambition or confidence, but that these are eroded by workplace cultures (Ryan, 2022). Therefore, any training to build skills for women must be accompanied by educating men on inequity and how to be better colleagues, as well as having women serve as mentors to men, and making changes to organizational policy and culture which go beyond individuals. The role of training should be to help women thrive within equitable organizations, not to ask them to make further changes and accommodations to survive within inequitable ones.
Based on the extensive literature on women and equity in the workplace, the quantitative survey, and over 1,800 suggestions in the open-ended section of the results, we propose a series of recommendations that individuals and organizations can apply to improve gender equity in conservation. These involve continual reviewing and adjusting policies, systems, and norms to create a culture that fully leverages the benefits of diversity, one in which women and all employees feel comfortable and able to reach their potential:
Ensure that diversity, equity, and inclusion are publicly stated and lived values of the organization and that they are actively resourced and demonstrated by leadership.
a. Conservation organizations and their leadership publicly pledge and then ensure intersectional gender diversity on panels, boards, and executive leadership teams.
b. Senior leaders fully and publicly support efforts to create more equitable workplaces—and are accountable for progress on ambitious diversity goals and metrics.
c. Actively recruit and value leaders with diverse and collaborative styles and approaches.
d. Build capacity and resource specialist leaders and teams to address gender inequity in conservation and the workplace.
e. Partner with organizations that specialize in addressing gender inequity and workplace culture across an organization rather than focusing on individual change. Fully resource best practice recommendations.
Women do better where organizations are transparent, consistent, and accountable in their actions. Women also need to know that they are being promoted and paid equitably. Overall, women fall behind men when pay and progression is not transparent and relies on individual negotiation.
a. Set clear goals to improve intersectional gender representation in departments, roles, and especially in conservation leadership positions.
b. Track diversity metrics by gender, race/ethnicity, and the intersection of the two.
c. Collect and publish data on progress towards these goals.
d. Publish pay equity analyses and corrections, and internally share data on pay, promotions, and other rewards to ensure career development and progression is equitable. This needs to be disaggregated by gender and other variables including race and location.
e. Publish salaries for advertised positions.
Women face challenges in science and conservation at all career stages.
a. Continue to reduce bias in hiring through bias awareness training for recruitment teams, diverse interview panels, and removing gendered language from job descriptions.
b. Track hiring and promotions to determine whether women, and especially women of color, and women in low to middle income countries, are being hired and promoted at similar rates to other employees. If there are gaps at certain levels or functions, adjust, including doubling down on best practices in those areas.
c. Provide dedicated sponsorship programs —that is, people who can provide new opportunities and connections—for women and especially women of color and women outside where international organizations are headquartered, especially the Global South.
d. Undertake anti-bias training for managers responsible for performance reviews and promotions. Monitor and adapt training programs.
Women have suffered higher rates of burnout during the pandemic and shoulder most caring responsibilities in and outside the workplace. The workplace culture across conservation consistently expects and rewards people who work and travel excessively. Women also shoulder higher office and family caring responsibilities and face career limitations when they become parents.
a. Establish work norms that promote flexibility in hours and location of work while also setting clear and fair boundaries so that people are not expected to always be working.
b. Establish equitable parental leave policies across countries, subsidized childcare, and flexible schedules.
c. Encourage virtual meetings and follow up for those who cannot easily travel or attend after-hours events.
Training and mentoring is important for everyone to understand unconscious bias in individuals and systems and ways to address it. However, it cannot be the primary way to address gender bias, as advocacy and systems change is crucial. However, it is one important piece and can help move allies from awareness to action.
a. Provide quality and well-resourced training and awareness for all employees (not just women). This includes (but is not limited to) effective training in unconscious bias and effective hiring and retention strategies. Training and awareness must be ongoing and targeted at men as much as women. There must also be follow-up to understand how training was understood and applied.
a. Establish and resource employee resource groups and other official networks to allow women to discuss and address workplace issues that emerge.
b. Ask women across the organization what they need through anonymous surveys and through networks. Listen and be ready to respond and to resource their recommendations.
c. Establish programs for official mentoring, coaching, allyship, and sponsorship for early-mid career women to be connected to advocates across the organization.
d. Focus on intersectionality and allyship, which improves the work experience, particularly for women of color, parents, carers, and women from the Global South.
a. Create or revise reporting and support mechanisms to be current best practice and centered and informed by the rights and safety of the person raising an issue of sexual discrimination or harassment. Ensure there is access to dedicated professionals qualified in trauma informed responses and processes.
b. Regularly check workplace culture through anonymous surveys where gender disaggregated results are reported back to teams.
c. Continually reinforce workplace values which do not tolerate sexual discrimination and harassment.
a. Set goals and measures for representation that also explicitly cover intersectionality. Continual work is needed to understand how these recommendations address the challenges identified by women with various intersectional identities (e.g., race, disability, sexual orientation, country of origin, etc.).
b. It is also imperative that we move to considering gender in non-binary terms in conservation.
Comprehensive evidence shows that women do face bias across science, conservation, and research, from pay and benefits, promotions, publishing, funding, and hiring to decision making and setting strategic direction (Grogan 2019; Ross et al., 2022; Ryan, 2022). It is impossible and unrealistic for individuals to solve the problems they face, and it is also unacceptable to rely on individuals to forfeit their career goals and conservation influence because organizations are not designed for women to excel (Grogan, 2019).
Although most research papers conclude with suggestions for future research, we feel strongly that there is already sufficient robust evidence, some of it referenced in this paper, that supports action towards our recommendations. We strongly suggest that the next steps should be that conservation organizations commit to implementing actions towards gender equity and then report on their progress in a transparent and accessible way. Further research could then involve the success of various interventions, and the difference those interventions make for different women, and subsequently for the effectiveness of conservation and climate action. Conservation, and the climate and biodiversity crisis urgently need women to be fully involved.
The raw data supporting the conclusion of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by the University of Queensland Institutional Human Research and Ethics Committee. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
RJ developed the concept for the paper and designed the research with advice from JF, KL, and HP. RJ led the development and writing of the manuscript with guidance from JF, KL, and NB, and inputs from all co-authors. RJ with support from CC-G, BG, MB, and NB led data analysis. RJ and NB led the statistical analysis. All co-authors reviewed and approved the MS.
We thank Meghan Bresnahan, Kate Cranney, Sarah Gammage, Justine Hausheer, Philippa McKay, and the entire TNC Women in Nature Employee Resource Group Steering Committee for advice and support in developing this research. We are also indebted to Alienor Chauvenet for her statistics expertise. We are grateful to the many women who have mentored and inspired us as we journey on our conservation and science careers. The authors acknowledge the challenges, barriers, and systemic forces that can make it difficult for women to succeed in conservation, and we pledge to applying this research as part of our commitment to equitable conservation. We also extend our appreciation to The Nature Conservancy for such transparency in supporting us to develop and publish this research so that others, not only within our organization, but across the conservation sector, may also benefit from this research and recommendations.
Some authors are current or former employees of TNC, but all data was carefully anonymized before being analyzed. The results have been reported here without review or interference from the organization and under careful adherence of the Ethics Approval by the University of Queensland Institutional Human Research and Ethics Committee (Approval number: 2018001799) in which potential of conflict issues were comprehensively addressed.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fenvs.2022.1056751/full#supplementary-material
Adams, J. S. (2006). The future of the wild: Radical conservation for a crowded world. Massachusetts: Beacon Press.
Begeny, C. T., Ryan, M. K., Moss-Racusin, C. A., and Ravetz, G. (2020). In some professions, women have become well represented, yet gender bias persists: Perpetuated by those who think it is not happening. Sci. Adv. 6 (26), 7814. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aba7814
Bennedsen, M. (2019). Do firms respond to gender pay gap transparency. Massachusetts: National Bureau of Economic Research.
Campos-Arceiz, A., Koh, L. P., and Primack, R. B. (2013). Are conservation biologists working too hard? Biol. Conserv. 166, 186–190. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2013.06.029
Cech, E. A. (2022). The intersectional privilege of white able-bodied heterosexual men in STEM. Sci. Adv. 8(24), 1558. doi:10.1126/sciadv.abo1558
CohenMiller, A. S., Koo, S., Collins, N., and Lewis, J. L. (2020). Exposing gender in science: A visual analysis with lessons for gender awareness and science diplomacy. Gend. Technol. Dev. 24 (2), 215–235. doi:10.1080/09718524.2019.1695519
Coleman, Z. (2019). Two executives depart Nature Conservancy after harassment probe. Arlington County: Politico. https://www.politico.com/story/2019/05/29/the-nature-conservancy-harassment-probe-1488630.
Davis, N. B., and Yeung, S. T. (2022). Transgender equity in the workplace: A systematic review. SAGE open 12 (1), 215824402210828. doi:10.1177/21582440221082863
Davis, S. L. (2019). Understanding and improving gender equity in conservation. J. Am. Inst. Conservation 58 (4), 202–216. doi:10.1080/01971360.2019.1612723
Finley, A. R., Hall, C. M., and Marino, A. R. (2021). Negotiation and executive gender pay gaps in nonprofit organizations. Rev. Account. Stud. 27, 1357–1388. doi:10.1007/s11142-021-09628-2
Gangl, M., and Ziefle, A. (2009). Motherhood, labor force behavior, and women's careers: An empirical assessment of the wage penalty for motherhood in britain, Germany, and the United States. Demography 46 (2), 341–369. doi:10.1353/dem.0.0056
García-González, J., Forcén, P., and Jimenez-Sanchez, M. (2019). Men and women differ in their perception of gender bias in research institutions. PloS One 14 (12), e0225763. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0225763
Gay-Antaki, M., and Liverman, D. (2018). Climate for women in climate science: Women scientists and the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 115 (9), 2060–2065. doi:10.1073/pnas.1710271115
Gianakos, A. L., Freischlag, J. A., Mercurio, A. M., Haring, R. S., LaPorte, D. M., Mulcahey, M. K., et al. (2022). Bullying, discrimination, harassment, sexual harassment, and the fear of retaliation during surgical residency training: A systematic review. World J. Surg. 46, 1587–1599. doi:10.1007/s00268-021-06432-6
Glauber, R. (2018). Trends in the motherhood wage penalty and fatherhood wage premium for low, middle, and high earners. Demography 55 (5), 1663–1680. doi:10.1007/s13524-018-0712-5
Gonda, N. (2019). Re-politicizing the gender and climate change debate: The potential of feminist political ecology to engage with power in action in adaptation policies and projects in Nicaragua. Geoforum 106, 87–96. doi:10.1016/j.geoforum.2019.07.020
Gough, M., and Noonan, M. (2013). A review of the motherhood wage penalty in the United States. Sociol. Compass 7 (4), 328–342. doi:10.1111/soc4.12031
Grogan, K. E. (2019). How the entire scientific community can confront gender bias in the workplace. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 3 (1), 3–6. doi:10.1038/s41559-018-0747-4
Handley, I. M., Brown, E. R., Moss-Racusin, C. A., and Smith, J. L. (2015). Quality of evidence revealing subtle gender biases in science is in the eye of the beholder. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 112(43), 13201–13206. doi:10.1073/pnas.1510649112
Holman, L., Stuart-Fox, D., and Hauser, C. E. (2018). The gender gap in science: How long until women are equally represented? PLoS Biol. 16 (4), e2004956. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.2004956
IPCC (2018). Global Warming of 1.5°C. An IPCC Special Report on the impacts of global warming of 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels and related global greenhouse gas emission pathways, in the context of strengthening the global response to the threat of climate change, sustainable development, and efforts to eradicate poverty. Switzerland: IPCC.
James, R., Ariunbaatar, J., Bresnahan, M., Carlos-Grotjahn, C., Fisher, J. R. B., Gibbs, B., et al. (2022). Gender and conservation science: Men continue to out-publish women at the world's largest environmental conservation non-profit organization, Conservation Sci. Pract. 4, e12748. doi:10.1111/csp2.12748
James, R., Gibbs, B., Whitford, L., Leisher, C., Konia, R., and Butt, N. (2021). Conservation and natural resource management: Where are all the women? Oryx 55, 860–867. doi:10.1017/S0030605320001349
Jones, M. S., and Solomon, J. (2019). Challenges and supports for women conservation leaders. Conservation Sci. Pract. 1 (6), e36. doi:10.1111/csp2.36
Jones, M. S., Teel, T. L., Martinez, D. E., and Solomon, J. (2020). Conflict and adaptation at the intersection of motherhood and conservation leadership. Biol. Conserv. 243, 108487. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2020.108487
Knudsen, K., and Wærness, K. (2008). National context and spouses’ housework in 34 countries. Eur. Sociol. Rev. 24 (1), 97–113. doi:10.1093/esr/jcm037
Kuschel, K., Ettl, K., Díaz-García, C., and Alsos, G. A. (2020). Stemming the gender gap in STEM entrepreneurship – insights into women’s entrepreneurship in science, technology, engineering and mathematics. Int. Entrepreneursh. Manag. J. 16 (1), 1–15. doi:10.1007/s11365-020-00642-5
Lau, J. D. (2020). Three lessons for gender equity in biodiversity conservation. Conserv. Biol. 34 (6), 1589–1591. doi:10.1111/cobi.13487
Letherby, G. (2011). “Feminist methodology,” in The SAGE handbook of innovation in social research methods (California: SAGE Publications Ltd).
Mahour, K. (2016). Role of women in environment conservation. J. Adv. Laboratory Res. Biol. 7 (1), 17–26.
McKinsey (2019). Women in the workplace report. Available at: https://www.mckinsey.com/featured-insights/gender-equality/women-in-the-workplace-2019.
McKinsey (2021). Women in the workplace report. Available at: https://www.mckinsey.com/featured-insights/gender-equality/women-in-the-workplace-2021.
OECD Development Centre (2015). Social institutions & gender index synthesis report 2014. Available at: https://www.genderindex.org/wp-content/uploads/files/docs/BrochureSIGI2015.pdf.
Patton, M. (2015). Qualitative research & evaluation methods: Integrating theory and practice. Fourth edition. California: SAGE Publications, Inc.
Pienkowski, T., Keane, A., Castelló y Tickell, S., Hazenbosch, M., Arlidge, W. N. S., Baranyi, G., et al. (2022). Balancing making a difference with making a living in the conservation sector. Conserv. Biol. 36 (3), e1346. doi:10.1111/cobi.13846
R Core Team (2021). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing.
Ross, M. B., Glennon, B. M., Murciano-Goroff, R., Berkes, E. G., Weinberg, B. A., and Lane, J. I. (2022). Women are credited less in science than men. Nature 608, 135–145. doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04966-w
Rudman, L. A., Moss-Racusin, C. A., Phelan, J. E., and Nauts, S. (2012). Status incongruity and backlash effects: Defending the gender hierarchy motivates prejudice against female leaders. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 48 (1), 165–179. doi:10.1016/j.jesp.2011.10.008
Ryan, M. (2022). To advance equality for women, use the evidence. Nature 604 (7906), 403. doi:10.1038/d41586-022-01045-y
Taylor, D. (2016). The rise of the American conservation movement: Power, privilege, and environmental protection. North Carolina: Duke University Press.
The Nature Conservancy (2018). Annual report. Available at: https://www.nature.org/content/dam/tnc/nature/en/documents/2018_AR_Complete.pdf.
The Nature Conservancy (2021b). The nature conservancy annual report. Available at: https://www.nature.org/en-us/about-us/who-we-are/accountability/annual-report/2021-annual-report/.
The Nature Conservancy (2021a). The nature conservancy through the years. Available at: https://www.nature.org/en-us/about-us/who-we-are/our-history/.
Venables, W. N., and Ripley, B. D. (2002). in Modern applied statistics with S. Fourth Edition (New York: Springer).
Westberg, L., and Powell, S. (2015). Participate for women's sake?: A gender analysis of a Swedish collaborative environmental management project. Soc. Nat. Resour. (11) 28, 1233–1248. doi:10.1080/08941920.2015.1014594
Keywords: conservation, women, climate change, gender, leadership, science, bias, biodiversity loss
Citation: James R, Fisher JRB, Carlos-Grotjahn C, Boylan MS, Dembereldash B, Demissie MZ, Diaz De Villegas C, Gibbs B, Konia R, Lyons K, Possingham H, Robinson CJ, Tang T and Butt N (2023) Gender bias and inequity holds women back in their conservation careers. Front. Environ. Sci. 10:1056751. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2022.1056751
Received: 29 September 2022; Accepted: 15 December 2022;
Published: 24 January 2023.
Edited by:
Diana Hamilton, Mount Allison University, CanadaReviewed by:
Eugenia Zandonà, Rio de Janeiro State University, BrazilCopyright © 2023 James, Fisher, Carlos-Grotjahn, Boylan, Dembereldash, Demissie, Diaz De Villegas, Gibbs, Konia, Lyons, Possingham, Robinson, Tang and Butt. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Robyn James, cmphbWVzQHRuYy5vcmc=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.