- Department of Environmental Science (ACES), Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden
Hazard assessment of microplastic is challenging because standard toxicity testing is targeting soluble (at least partially) chemicals. Adverse effects can occur when test organisms are exposed to turbid environments in the presence of various particulate matter (PM), both natural, such as clay and cellulose, and anthropogenic, such as microplastic. It is, therefore, relevant to compare responses to PM exposure between the microplastic and other suspended solids present at ecologically relevant concentrations. This comparison is possible when reference materials are included in the testing of microplastic hazard potential. Here, we evaluated growth inhibition in unicellular alga Raphidocelis subcapitata exposed to different PM (microplastic, kaolin, and cellulose; 10, 100, and 1,000 mg/L); algae without added solids were used as a control. Also, aggregate formation in the exposure systems was analyzed using particle size distribution (PSD) data. At 10–100 mg/L, no adverse growth effects were observed in any treatments; moreover, algal growth was significantly stimulated in kaolin and cellulose treatments compared to the control. However, at 1,000 mg/L, all tested materials exerted growth inhibition, with no significant differences among the materials. Comparing PSD s across the treatments showed that both PM concentration and size of the particle aggregates were significant growth predictors for all materials tested. Therefore, at high concentrations, both natural and anthropogenic materials have a similar capacity to cause growth inhibition. Linking effects in unicellular organisms to microplastic fragments remains a challenge since plastics incorporate chemicals that may leach and elicit specific effects relative to the particulates. The use of reference materials in hazard assessment of plastic litter is needed to delineate these effects.
Introduction
Plastics have become a global concern as a suite of emerging pollutants, and potential environmental impacts have been highlighted (Andrady and Neal, 2009; Rochman et al., 2019). However, plastic litter, including microplastic, is a new field in environmental pollution research with much-unsettled methodology, and standard methods for hazard assessment are not yet available (Adam et al., 2019). Current test methods in ecotoxicology are intended for soluble (at least partially) chemicals, whereas testing particle suspensions, such as microplastic, requires different approaches (Paul-Pont et al., 2018; Gerdes et al., 2019). Moreover, plastics are diverse: they represent different polymers and materials that include a broad array of chemical additives and come in many sizes, colors, and shapes (Rochman et al., 2019), which complicates comparisons between the effect studies (Reichelt and Gorokhova, 2020). It is also essential to keep in mind that plastic is only a kind of persistent solid waste pollution, and common approaches for the risk assessment are needed (Coe et al., 2019). Therefore, the development of adequate microplastic hazard assessment methods under reproducible settings is the key challenge for the plastic litter toxicology and the toxicology of anthropogenic solids at large.
Despite environmental health concerns, only a few studies have shown consistent adverse effects of microplastics (Foley et al., 2018; Reichelt and Gorokhova, 2020), usually observed at very high microplastic concentrations. As a rule, these concentrations exceed levels that are recognized as environmentally relevant (Lenz et al., 2016; Phuong et al., 2016). For such studies, a valid critique is a high probability that these effects are not necessarily specific to the microplastic but arise from the exposure to any suspended solids that have no nutrition value for animals and—in the case of photosynthetic microorganisms—a capacity to cause shading effects and sorb nutrients and microelements, thus decreasing their availability for the test algae (Ogonowski et al., 2018b). Hence, the existing protocols for hazard assessment do not explicitly address the effects of microplastic but those of particulate matter (PM) that change light and nutrient availability for the test organisms, such as algae and periphyton, during the exposure, with possible downstream effects on nutrient acquisition pathways, photosynthesis efficiency, and, ultimately, growth (Reichelt and Gorokhova, 2020).
So far, most efforts have focused on animal responses to microplastic exposure (Foley et al., 2018; Ogonowski et al., 2018b), whereas far less research has addressed possible effects of microplastic on primary producers (Yokota et al., 2017). The reported consequences of the interactions between primary producers and particles of fossil-based polymers in nano- and microparticle size range include alterations in algal photosynthesis (Bhattacharya et al., 2010), growth (Sjollema et al., 2016; Bergami et al., 2017), and colony morphology (Yokota et al., 2017). These changes can propagate in the food web, affecting consumers and, ultimately, system productivity. However, the reported effects are not consistent across the studies, and no-effect reports are also published (Prata et al., 2019). As shown in the recent meta-analysis of the growth inhibition effects in algae exposed to nano-and microplastic, the lack of proper controls and methodological variability between the studies make it difficult to understand the driving forces, such as particle size, concentration, polymer type, behind the observed effects (Reichelt and Gorokhova, 2020). What is also essential is that similar effects on the same endpoints can be induced by natural suspended solids, such as clay and sand (Bilotta and Brazier, 2008; Chapman et al., 2017). These solids are ubiquitous in natural waters, commonly reaching gram per liter concentrations (Cahoon et al., 1999; Bilotta and Brazier, 2008), i.e., levels far exceeding those of microplastic. The adverse effects of fine sediments on algae are well-known from ecological studies (Cahoon et al., 1999; Ogonowski et al., 2018b), and it is, therefore, relevant to compare the algal responses to particle exposure between the microplastic and other suspended solids present in the fresh- and marine surface waters at ecologically relevant concentrations (mg L–1 to g L–1).
Microalgae have a long history of use as test organisms in ecological and ecotoxicological assessments because of their high sensitivity toward various stressors, including environmental pollutants. In ecotoxicology, the standard algal growth inhibition test (Oecd., 2006) validated for several freshwater and marine species is widely used for hazard evaluation. When conducting this test with various effluents, it is recommended to measure total suspended solids and total settled solids because removing these fractions could influence the growth and, thus, toxicity estimates. The mechanisms of the growth inhibition in the presence of suspended solids, including microplastic, may vary, including shading effects and trapping of microalgae in the aggregates and subsequent inhibition of photosynthesis (He et al., 2017; Mao et al., 2018). Recently, such effects have been suggested to occur in the algae exposed to microplastic; moreover, increased production of organic carbon and its aggregation into gel particulates have been demonstrated in mesocosms amended with polystyrene microbeads (Galgani et al., 2019). Therefore, it is crucial to understand whether algae-microplastic aggregates have a higher capacity to inhibit growth compared to the aggregates with natural solids.
As a consequence of degradation processes, the plastic particles in the environment undergo weathering that changes their physicochemical properties, aggregation properties, and, possibly, hazard potential. Various forces, such as physical stress, UV-radiation, shifting temperatures, salinity, and oxidation, contribute to weathering resulting in changes in the surface properties and morphology (Jahnke et al., 2017). Moreover, microbial biofilms also contribute to these physicochemical alterations, affecting aggregation capacity (McGivney et al., 2020; Rogers et al., 2020). Considering the abundance of various non-plastic particulates in the pelagia, the occurrence of non-aggregated sphaerical particles in the water column is highly unlikely. Moreover, given that microbeads are a minor contributor to microplastic contamination globally, it is questionable whether the broad use of uniform spherical MP in experiments, including algal growth inhibition tests (Reichelt and Gorokhova, 2020), is justifiable from ecological and ecotoxicological viewpoints. Hence, using aged polymer fragments to mimic the environmentally realistic exposure scenario has been advocated (Ogonowski et al., 2018b). However, only a very few studies have evaluated the weathering effect in MP toxicity tests (Bråte et al., 2018; Fu et al., 2019), and found that aging of MP (e.g., PVC) would pose more substantial inhibitory effects on microalgae (Fu et al., 2019). The exact mechanisms of the elevated adverse effects remain, however, unclear.
The objectives of this study were to (1) compare effects of a fossil-based polymer and natural (kaolin and cellulose) particles on the growth performance in the standard algal growth inhibition test (Oecd., 2006); (2) compare algal growth response to weathered and virgin microplastic; and (3) evaluate relationships between particle aggregation in the experimental system and algal growth. The present study does not aim to generate a robust test design for suspended solids in general or microplastic specifically but rather is intended to create debate on the methodology of microplastic hazard assessment and possibly influence further research efforts toward this goal.
Materials and Methods
Test Organism
The freshwater unicellular green alga Raphidocelis subcapitata (Korshikov) Nygaard, Komárek, J. Kristiansen and O. M. Skulberg, 1987, formerly Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata and Selenastrum capricornutum, is a standard test organism in ecotoxicology (Oecd., 2006). It is a fast-growing species, sensitive to light and nutrients, and thus particularly well suited to evaluate stress effects on algal growth and production (Gonçalves et al., 2016). Raphidocelis subcapitata is one of the most commonly used algal species for testing microplastic effects (Reichelt and Gorokhova, 2020), and has also been used to evaluate plastic leachate toxicity (Capolupo et al., 2020). The algal culture for inoculation was grown for 1 week in Z8 media, at room temperature, with shaking (100–125 rpm) and the illumination of ∼40 μ E⋅m–2⋅s–1. Algal concentrations were determined by in vivo fluorescence using a 10 AUTM Field Fluorometer (Turner Designs, Sunnyvale, California, and United States).
Chemicals, Reference, and Test Materials
Kaolin (Sigma-Aldrich, K7375) and native fibrous cellulose (Macherey-Nagel, MN 301) were used as the reference materials. Kaolin contains mainly the clay mineral kaolinite, a hydrous aluminosilicate, whereas cellulose is the primary substance in plant cell walls. Both materials occur globally in suspended particulates and have been used as reference material when assessing microplastic effects (Gerdes et al., 2019) and as a test material when assessing the effects of exposure to total suspended solids (Robinson et al., 2009; Ogonowski et al., 2018a,b).
As a test microplastic, we used polyethylene terephthalate (PET, Goodfellow GmbH, product number ES306312) mixed with Milli-Q water passed through a 40-μm sieve to produce a size fraction similar to that of kaolin and cellulose. According to the manufacturer, the material contains 1 ppm acetaldehyde, translating to a maximum of 0.001 mg/L in the test system. This concentration is about three orders of magnitude lower than EC50 for growth inhibition in green algae (Tsai and Chen, 2007). To investigate whether microplastic aging affects particle aggregation and algal response, we used both virgin and weathered PET particles, denoted as PET and PETw, respectively. The stock of PETw was prepared by UV exposure of the milled PET for 28 days (Oelschlägel et al., 2018) and size-fractionated in the same way as PET (Supplementary Text S1 and Supplementary Material). Stocks of both reference and test materials contained 0.01% v/v of a non-ionic surfactant (Tween-80, Sigma-Aldrich), which was also added to the control media at the final concentration of 0.0001%. In the experimental treatments, the concentration of Tween-80 never exceeded 0.0001%, which is well below the levels regarded as non-toxic for green algae (Ma et al., 2004). In the stock suspensions, both PET materials (median size ∼11 and 12 μm for virgin and weathered PET, respectively) and kaolin (∼9 μm) showed unimodal size distributions, whereas cellulose (∼16 μm) had polymodal distribution and broader size range. See Supplementary Text S1, Supplementary Table S1, and Supplementary Figure S1 for the description of the particle preparation and size distributions of the stock suspensions used to prepared exposure media at different nominal concentrations of suspended solids.
Standard growth media (Z8) contained all nutrients at surplus for the entire growth period of the algae in the incubation system: NaNO3 (6 mM), CaCl2⋅2H2O (73 mg L–1), MgSO3⋅7H2O (25 mg L–1), K2HPO4 (31 mg L–1), Na2CO3 (21 mg L–1), FeCl3⋅6H2O (28 mg/L) 0.001 M HCl, ZnSO4⋅7H2O (5 μ g/L), MnCl2⋅4H2O (10 μ g/L), H3BO3 (5 μg L–1), CuSO4⋅5H2O (0.5 μg L–1), CoCl2⋅6H2O (2 μg L–1), NaMoO4⋅2H2O (1.5 μg L–1), VOSO4⋅2H2O (0.5 μg L–1), Na2SeO4⋅10H2O (0.5 μg L–1), pH adjusted to 6.6–7.0. The chemicals were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Germany).
Experimental Setup
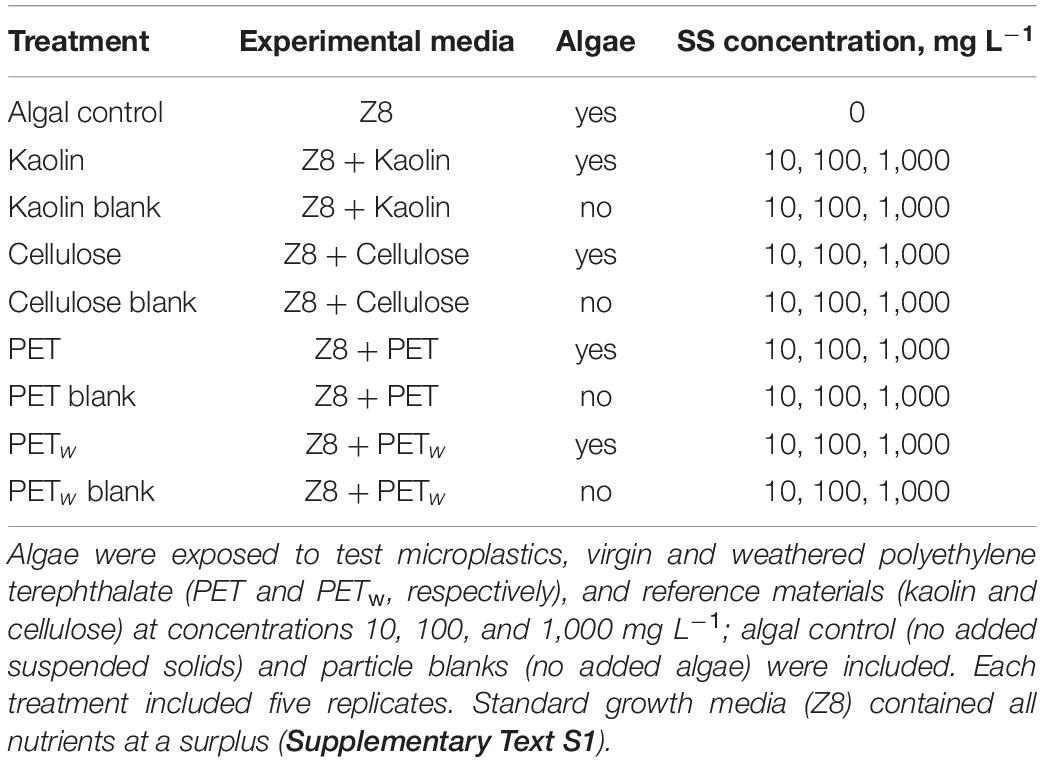
Five experimental media with different suspended solids were prepared by mixing stock suspensions of the test material and used as treatments with nominal concentrations of suspended solids (SS) 10, 100, and 1,000 mg L–1 (Table 1). The particle number concentrations for the lowest concentration treatment were 1.14, 0.93, and 0.94 particles × 107 L–1 for kaolin (specific gravity 2.36), cellulose (0.50), and PET materials (1.34), respectively. This design resulted in 12 different combinations of material × concentration factors for algal exposure and a single control with no added solids; five replicates were used for each of these incubations. Also, particle blanks were used for each material × concentration combination (Table 1) to control for contamination with microorganisms (algae and bacteria) and any background fluorescence induced by the test and reference materials under experimental conditions. When measuring fluorescence in the treatment tubes, the mean value of the particle blanks was subtracted from each replicate for the respective material × concentration combination.
A standard growth inhibition assay with R. subcapitata was conducted (Oecd., 2006) with some modifications. The assay is based on in vivo chlorophyll a (Chl a) measurement that exhibits endogenous red fluorescence (autofluorescence). The quantification of Chl a is useful for monitoring photosynthetic capacity and detection of stimulating or inhibiting effects. The algae were harvested from the culture and diluted with Z8 media to 105 cell mL–1 and then mixed with the experimental media (Table 1) to the final cell density of 5 × 103 cells mL–1. These suspensions were transferred to 10 mL glass tubes filled to the top and sealed to avoid air bubbles. All tubes were mounted on a plankton wheel rotating at 0.5 rpm and incubated at room temperature and fluorescent light at 140 ± 10 μ E⋅m–2 s–1. Light intensity was measured in the exposure area using photosynthetically active radiation sensor Quantum (Skye, United Kingdom). The algae were allowed to grow throughout the lag phase and exponential growth for 72 h, and fluorescence was measured at time points 0, 24, 48, and 72 h. Over the range of cell densities used in this experiment, the fluorescence was linearly related to the cell number as established by comparing the fluorescence measurements and cell counts with a hemocytometer. Upon the experiment termination, samples of the suspended matter were collected from each replicate and used for particle size distribution (PSD) analysis to establish relationships between the growth parameters and particle aggregation.
Growth Analysis
The algal growth response was inferred from the change in the Chl a fluorescence. Growth kinetics of the algae was examined using time-specific measurements fitted to an exponential growth curve with lag phase (Baranyi and Roberts, 1994); see Supplementary Text S2 for the calculation details and explanations for algal growth kinetics. With DMFit software1, the growth curves were constructed to estimate lag phase duration (λ, h) and maximal growth during the exponential phase (μ, d–1). The lag phase duration reveals how fast test organisms acclimate to experimental conditions, while the growth rate in the exponential phase indicates proliferation in the adapted population. Model fit was evaluated by the coefficient of determination (R2) and performance by the root mean square error (RMSE). An additional parameter, the change in fluorescence intensity between the observation points, was used to calculate the area under the curve (AUC), representing algal production during the observation period. This endpoint is commonly used in algal growth inhibition assay as it integrates the change in photosynthetically active biomass during both the lag and growth phases being an approximation of cumulative biomass at each time point (Vaas et al., 2012).
Particle Distribution Analysis
The particle size distribution (PSD) was measured with a Spectrex laser particle counter (Spectrex, model PC-2000, Redwood City, United States). The size spectra were determined for 1—100 μm range (Supplementary Text S1), and processed with GRADISTAT program, version 8.0 (Blott and Pye, 2001) according to the method by Folk and Ward (Folk and Ward, 1957) to obtain mean particle size, sample sorting (variance), skewness, kurtosis, median particle size (D50), and two points which describe the coarsest and the finest parts of the distribution (D90 and D10, respectively), and D90—D10 range. These parameters are commonly used in concert for characterization of PSD in powders and heterogeneous granular materials, such as soil and sediment (Blott and Pye, 2001).
Data Analysis and Statistics
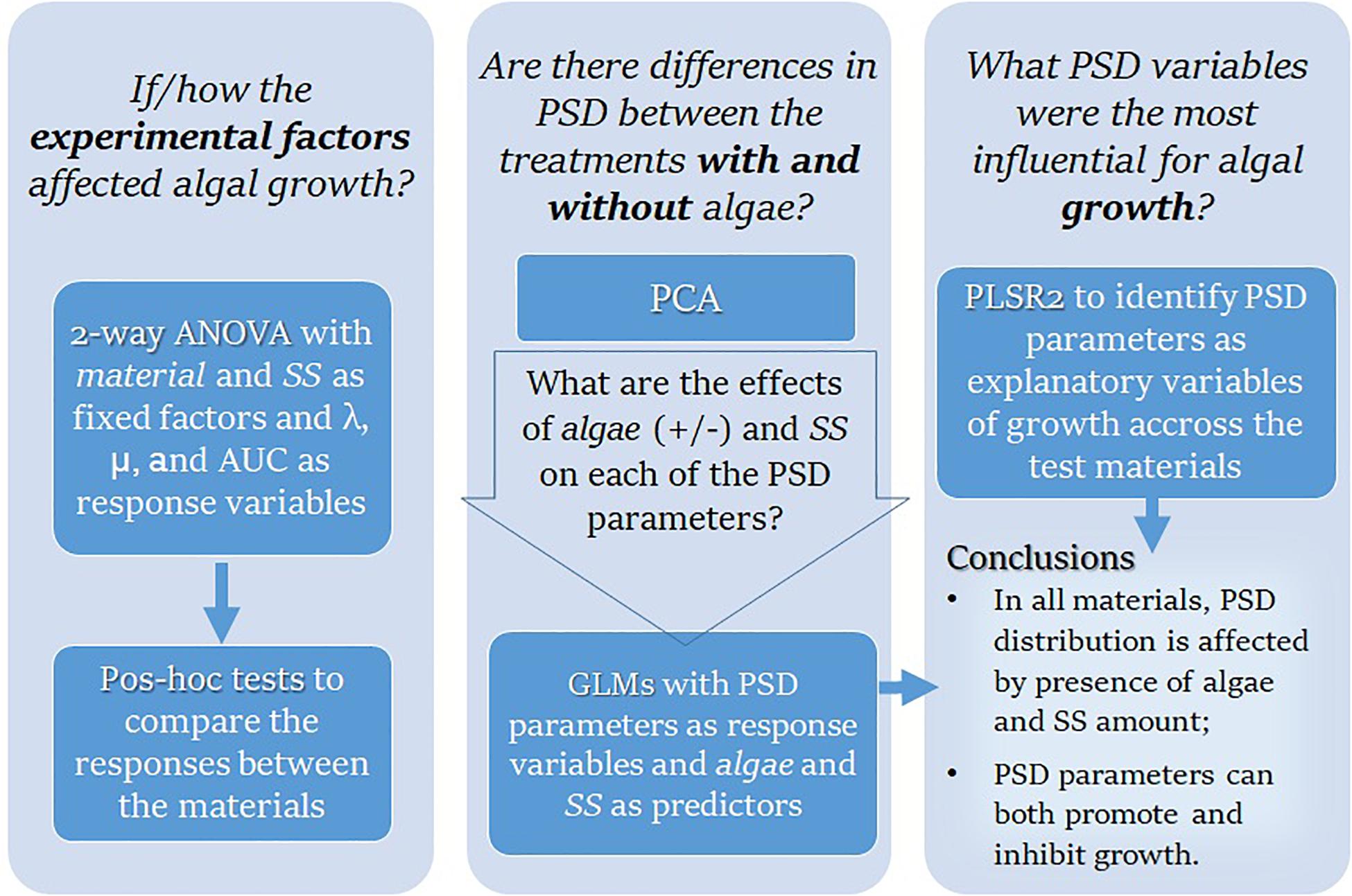
If not stated otherwise, the results are expressed as mean value ± standard deviation (SD), the alpha level was set to 5%, and the data analysis was conducted with JMP,® Version 14.0 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, 1989–2019). The outline of the research questions addressed in the data analysis and the methods used is shown in Figure 1.
First, we used two-way ANOVA to evaluate the effects of suspended solids concentration (SS, mg/L) and test material on the algal growth parameters (λ, μ, and AUC) in different treatments. When the material × concentration interaction was significant, the main effects were not interpreted. In the follow-up analysis, the effect of material was evaluated for each concentration level using a two-stage Benjamini, Krieger, and Yekutieli (Benjamini et al., 2006) procedure for controlling the false discovery rate (FDR) in the multiple comparisons. The data were not transformed as the model residuals were normally distributed. Within-treatment variability was accessed using the coefficient of variation (CV%).
The PSD parameters estimated by GRADISTAT for all treatments were first examined by Principal Components Analysis (PCA) using PAST software, version 3.22 (Hammer et al., 2001), to explore the overall differences between the treatments with and without algae and examine the relationships between the PSD characteristics. Then, for each material, we used Generalized Linear Model (GLM, log-link, normal error structure) analysis to test the effects of algae in the system (present/absent) and SS concentration (10–1,000 mg L–1) as predictors of the PSD characteristics (mean particle size, variance, skewness, kurtosis, D50, D90, D10, and D10—D90); the interaction term algae × SS was included in each model. The data used in GLMs were Box-Cox transformed and centered. The model residuals were examined using QQ plots.
Finally, Partial Least Square Regression (PLSR) was used to study the relationships between the exposure variables (PSD metrics and SS concentration; X variables) and the growth parameters (λ, μ, and AUC; Y variables); see Supplementary Text S3 for the details on PLSR design. The analysis was carried out for each material as well as for the pooled data set using the non-linear iterative partial least squares (NIPALS) algorithm; the data were centered and scaled. For cross-validation and determination of the optimal number of latent variables, we applied the leave-one-out method and predicted residual error sum of squares (PRESS) statistic as implemented in the PLS platform of the software to separate terms that do not make an important contribution to the dimensionality reduction involved in PLSR (Variable Importance in Projection; VIP < 0.8) and those that might (VIP ≥ 0.8). For each X variable, VIP value was used to assess its importance in determining the PLSR projection model (Wold et al., 2001).
Results
Growth Response to Suspended Solids
Positive growth and growth models with high R2-values (>0.97 in all cases) were observed in all treatments during the exposure, albeit with different growth trajectories (Figure 2). There were significant effects of exposure on all growth parameters (λ, μ, and AUC; Table 2); however, the significant interaction effects for μ and AUC indicated that the differences between the test materials as well as between the exposed and non-exposed algae, were concentration-specific. In the follow-up pairwise comparisons, both positive and negative effects of material were observed compared to the particle-free control (Supplementary Table S2); moreover, these effects occurred in both microplastic and reference material treatments (Figure 2).
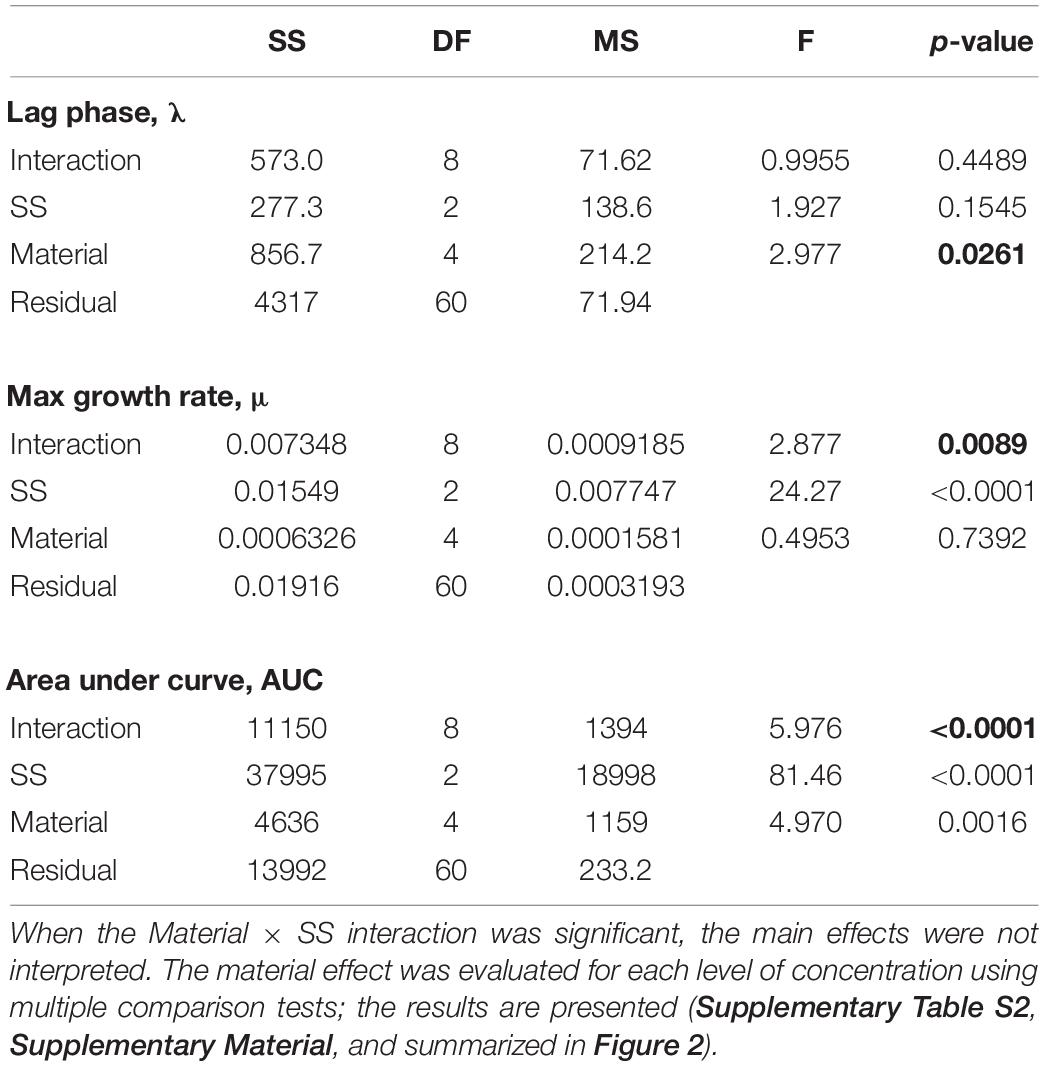
Table 2. | Two-way ANOVA models testing effects of suspended solids concentration (SS, mg/L) and test material (Control, Kaolin, Cellulose, PET, and PETw) on the algal growth parameters (λ, μ, and AUC). Significant effects are in bold face.
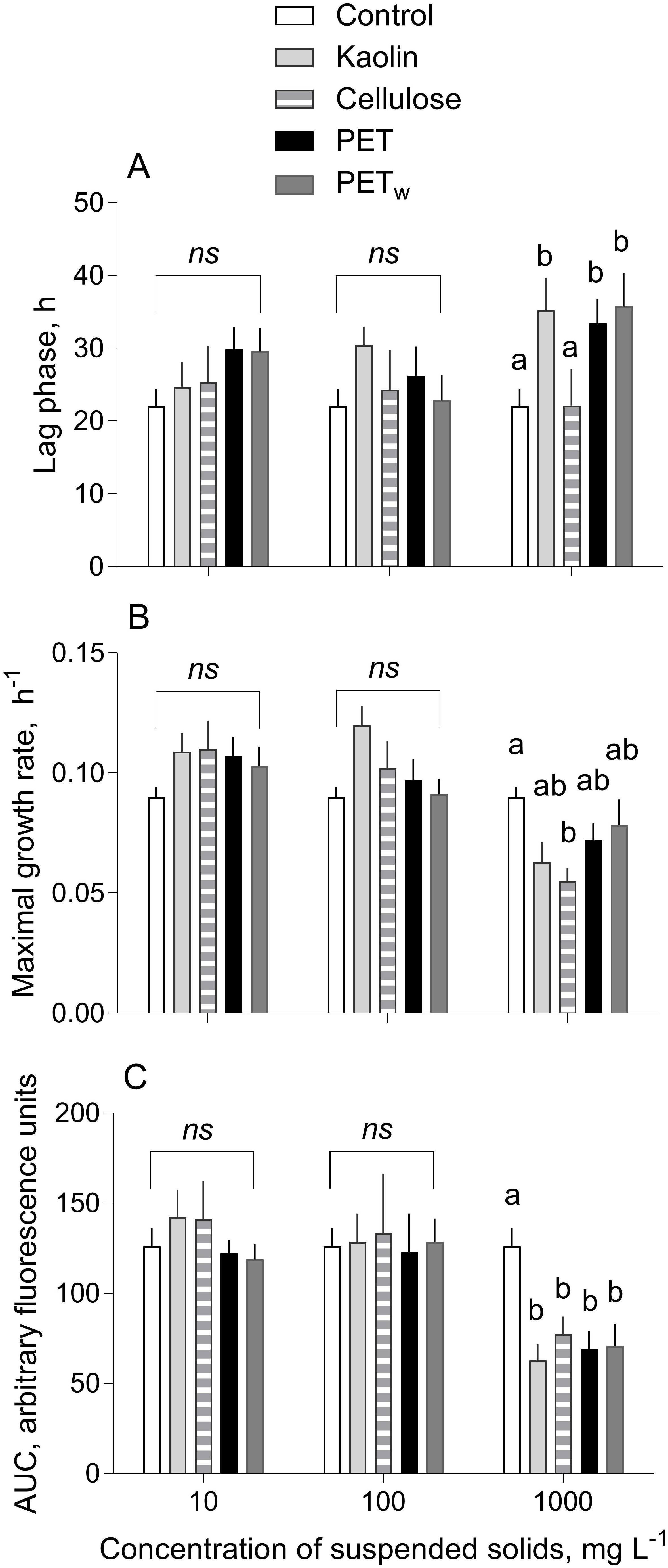
Figure 2. | Kinetic parameters (mean and SD; n = 5) of growth responses in R. subcapitata exposed to microplastics and reference materials (A) Lag phase (λ, h) preceding the active growth, (B) maximal growth rate (μ, d– 1) estimated for the exponential period, and (C) area under the curve (AUC) representing algal production during the observation period. Non-matching letters indicate a significant treatment difference evaluated by the multiple comparisons test with FDR correction; ns denotes a lack of significant differences between the materials within the test concentration of suspended solids; see Supplementary Table S2 for the pairwise comparisons.
Both λ and μ values varied among the treatments, with significant deviations observed only at the highest concentration (1,000 mg L–1; Figures 2A,B). The lag phase was significantly longer in the algae exposed to 1,000 mg L–1 for all materials tested, except cellulose, compared to that in control (Figure 2A and Supplementary Table S2A). The major deviations from the control were observed for the maximal growth rate in the algae exposed to cellulose, with a significant decrease at 1,000 mg L–1, whereas there were no significant effects for the other materials (Figure 2B and Supplementary Table S2B). Similarly, the most pronounced changes were found for the AUC values indicating a significant decrease in all tested materials at 1,000 mg L–1 (Figure 2C and Supplementary Table S2C). Notably, the within-treatment variability for AUC decreased significantly with time and increased with concentration (Figure 3).
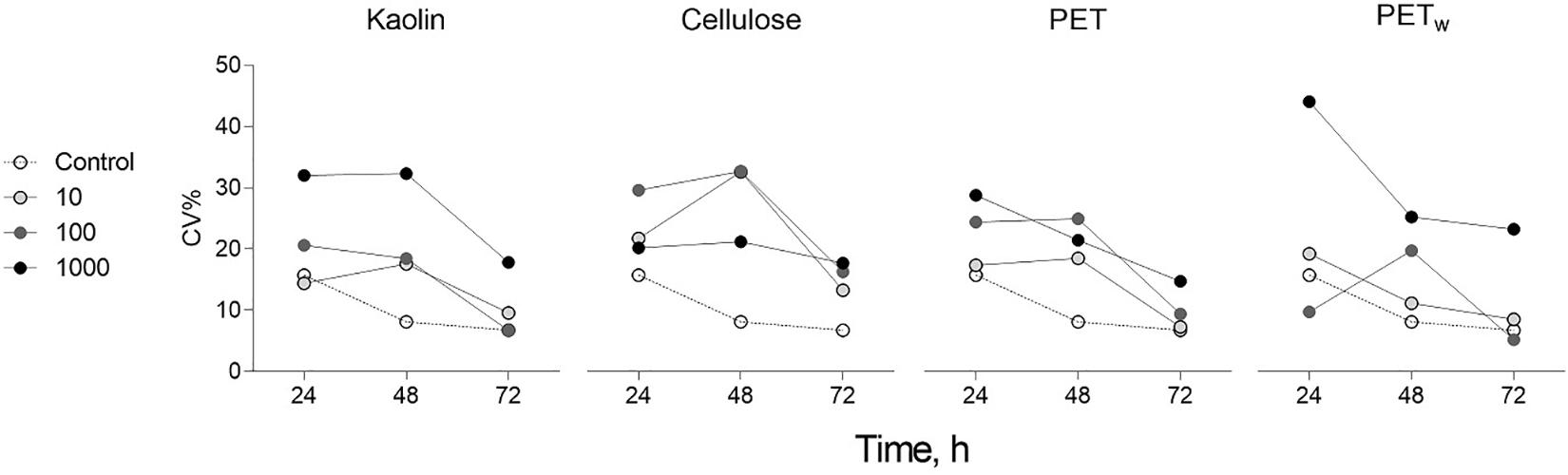
Figure 3. | Change in the coefficient of variation (CV%) of AUC values for growth curves of R. subcapitata exposed to microplastics and reference materials over the course of the experiment (72 h). The AUC values were grouped by test material (kaolin, cellulose, PET, and PETw) and test concentration (10, 100, and 1,000 mg L– 1; n = 5); control values are shown on each plot for comparison.
There was an overall positive relationship between the maximal growth rate and lag phase duration across the treatments at concentrations of 10 and 100 mg L–1 (Figure 4). However, the algae exposed to 1,000 mg L–1 were deviating significantly from this relationship because of the lower μ values in the algae exposed to all test materials at this concentration (Figure 2B).
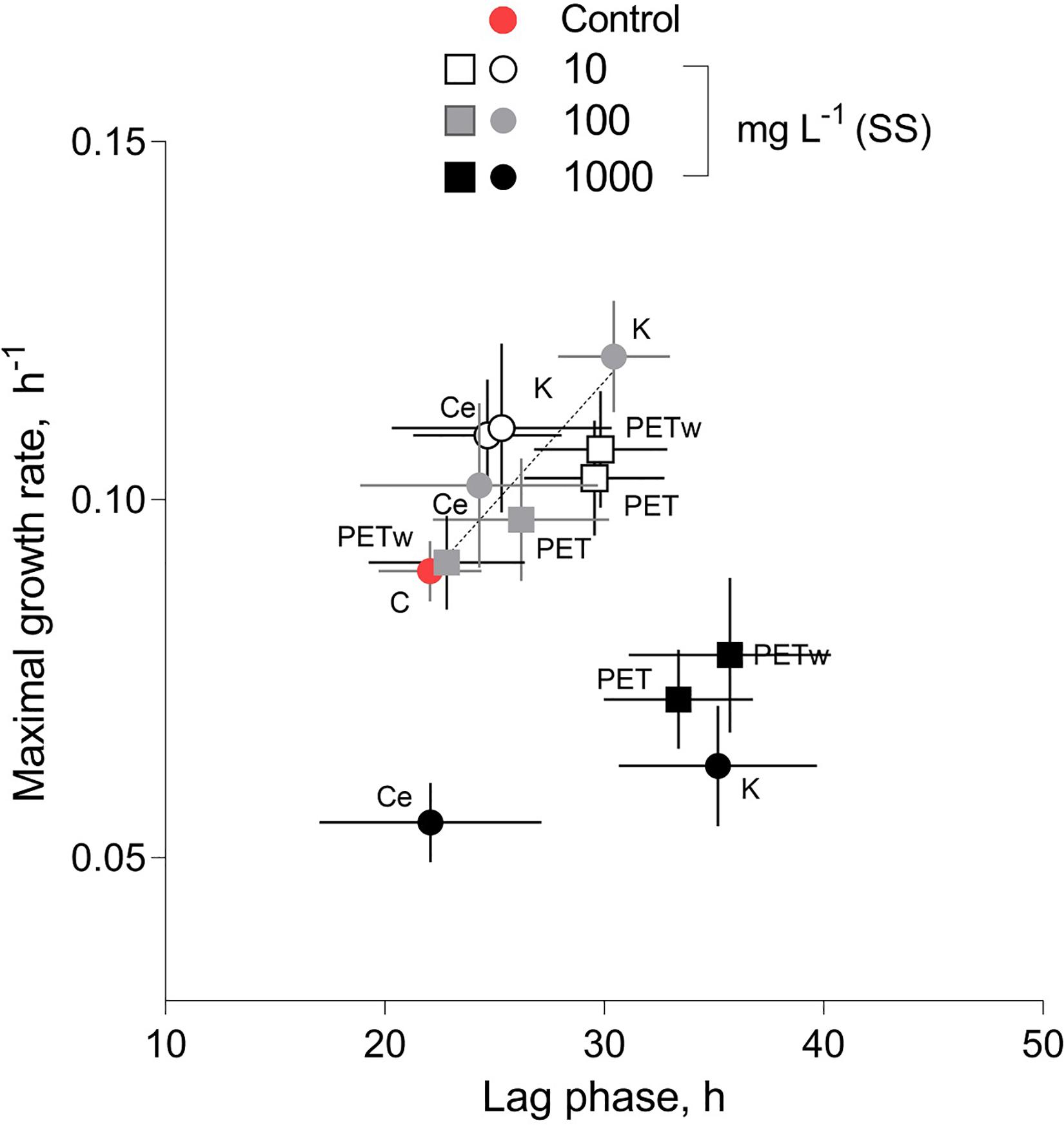
Figure 4. | Relationship between the maximal growth rate (μ, d− 1) and duration of the lag phase (λ, h) in R. subcapitata exposed to microplastic (virgin and weathered PET) and reference materials (kaolin, K, and cellulose, Ce) at concentrations of suspended solids (SS) 10, 100, and 1,000 mg L− 1. No suspended matter was added to the medium in control. Data are shown as means and SD (n = 5).
Particle Aggregation in the System
All test materials were found to aggregate during the exposure compared to their respective stocks (Supplementary Figure S3). Moreover, the aggregation was significantly more substantial in the treatments with algae than in the particle controls (Table 3 and Supplementary Figure S4). Principal component analysis (PCA) using the PSD characteristics determined for each material and treatment indicated that two principal components exceeded 5% of the total explained variance. Moreover, 83–94% and 6–15% of the accumulated dispersion were represented by PC1 and PC2, respectively, while only PC1 passed the broken-stick test (Supplementary Figure S5). The PCA biplot demonstrated separation between the treatments with and without algae for all four materials, with more apparent separation observed for cellulose and PETw, whereas some overlap was found in the biplots for kaolin and PET treatments (Figure 5). The loadings on PC1 indicate the importance of the particle size metrics (mean and median particle sizes, D10, D90, and D90–D10), whereas variance, skewness, and kurtosis were not influential for the discrimination between the treatments with and without algae (Supplementary Figure S6).
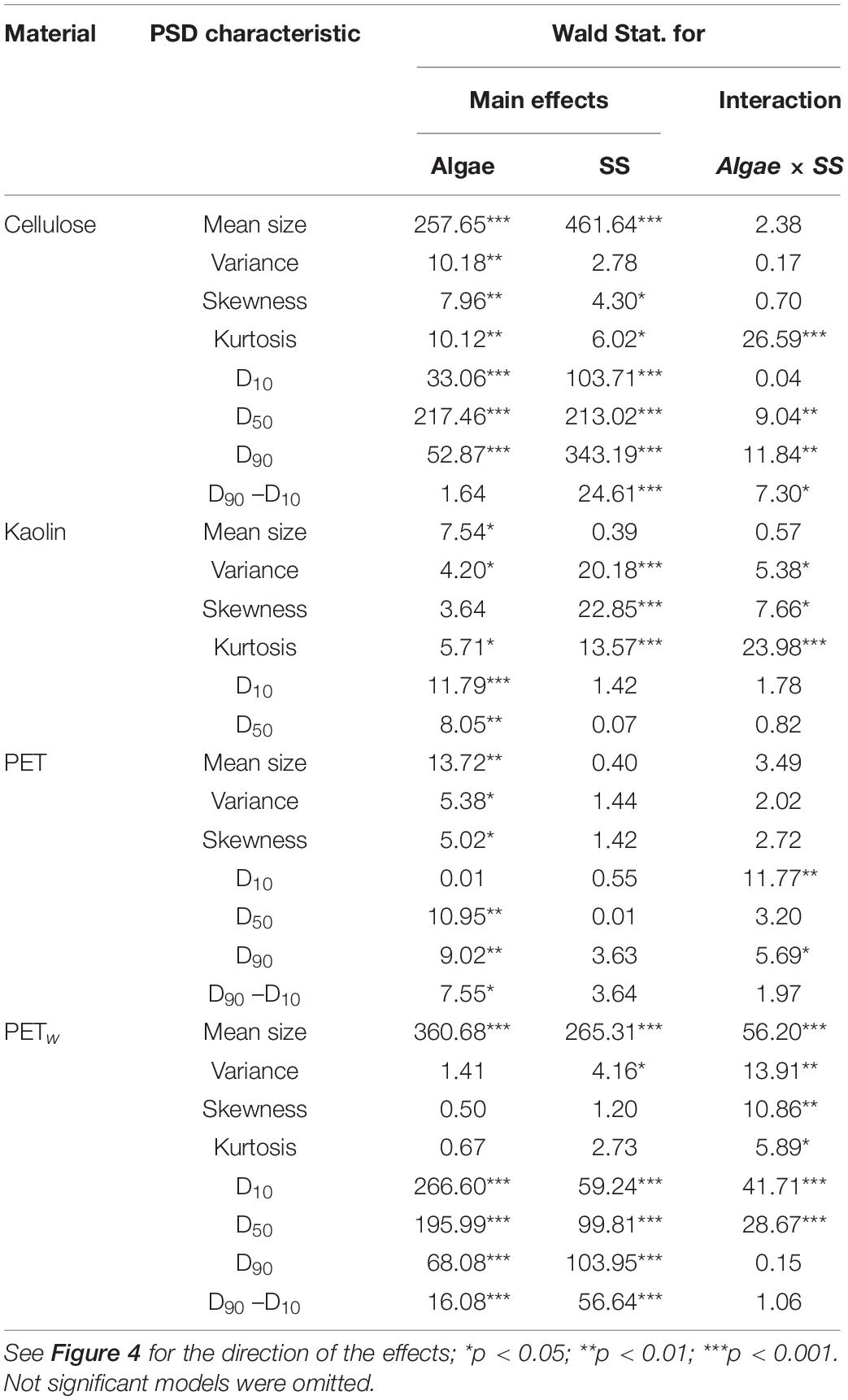
Table 3. | Outcome of Generalized Linear Models (GLMs) testing effects of the algae (Algae; present/absent) and suspended solids concentration (SS, mg L–1) on the PSD characteristics for each reference (kaolin and cellulose) and test (PET and PETw) material.
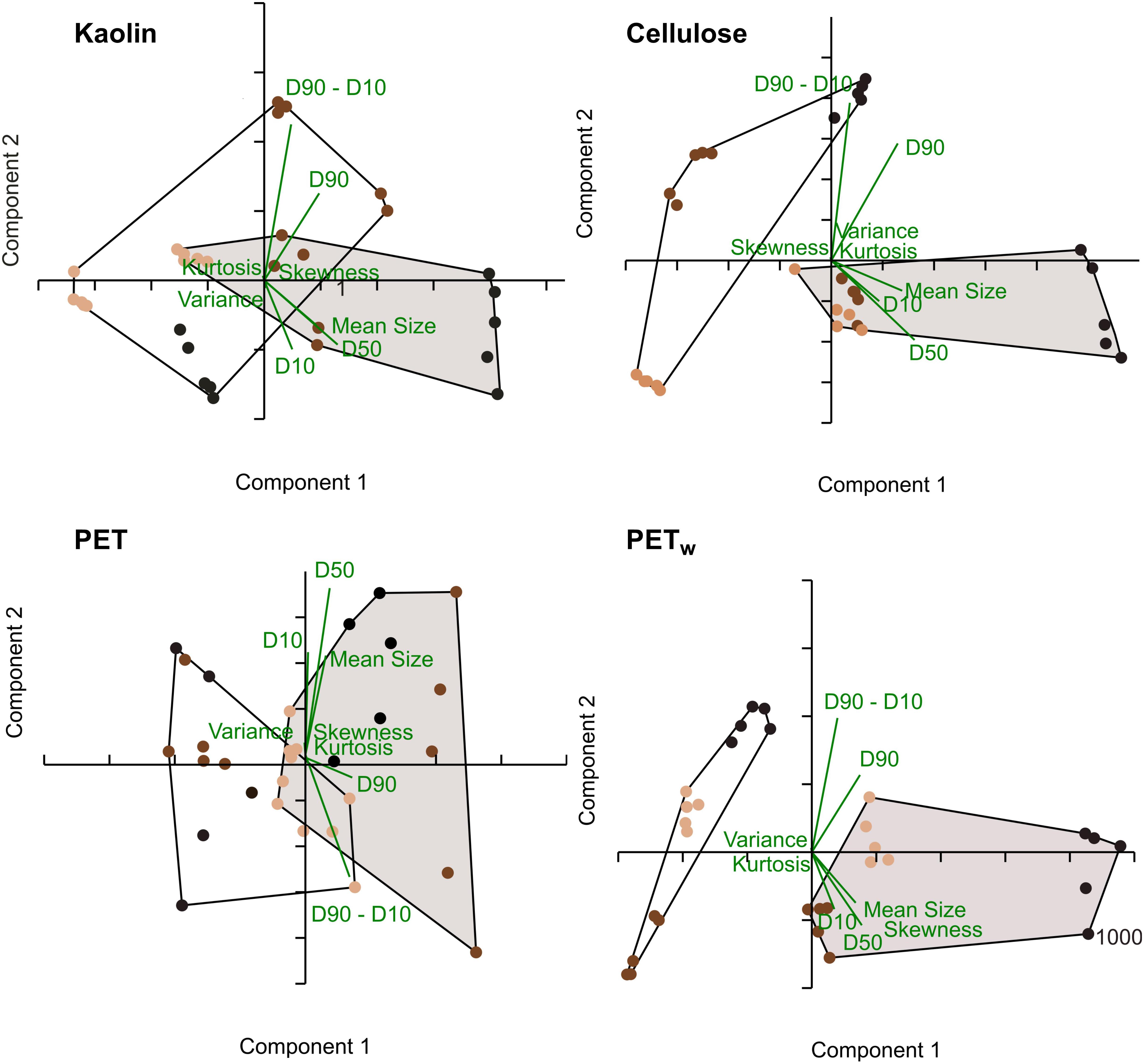
Figure 5. | PCA biplot for the PSD characteristics for the reference (kaolin and cellulose) and test (PET and PETw) materials in the treatments with algae (shaded convex hulls) and without algae (open convex hulls). The color code for the test concentrations: light brown: 10 mg L− 1, dark brown: 100 mg L− 1, and black: 1,000 mg L− 1; n = 5 in all cases. The PCA loadings are shown in green.
Effect of Aggregation on Algal Growth
Significant PLSR models for growth parameters (Y variables) on PSD and SS concentration in the exposure systems (X variables) were obtained for all materials tested (Table 4 and Supplementary Figure S7). The predictive capacity for all models was high, with Q2 varying from 74 to 96% (Table 4). In these models, 90–99% of the X-parameters variance explained 66–71% of the variance of the Y-variables (Table 4). Compared to the lag phase, the maximal growth rate and the AUC were better predicted by the X-variables, particularly in the algae exposed to kaolin and PET (Supplementary Figure S7). In all models, SS concentration, mean, and median particle sizes were identified as significant growth predictors (Table 4); other PSD characteristics in different combinations for different materials were also significant (Supplementary Figure S7).
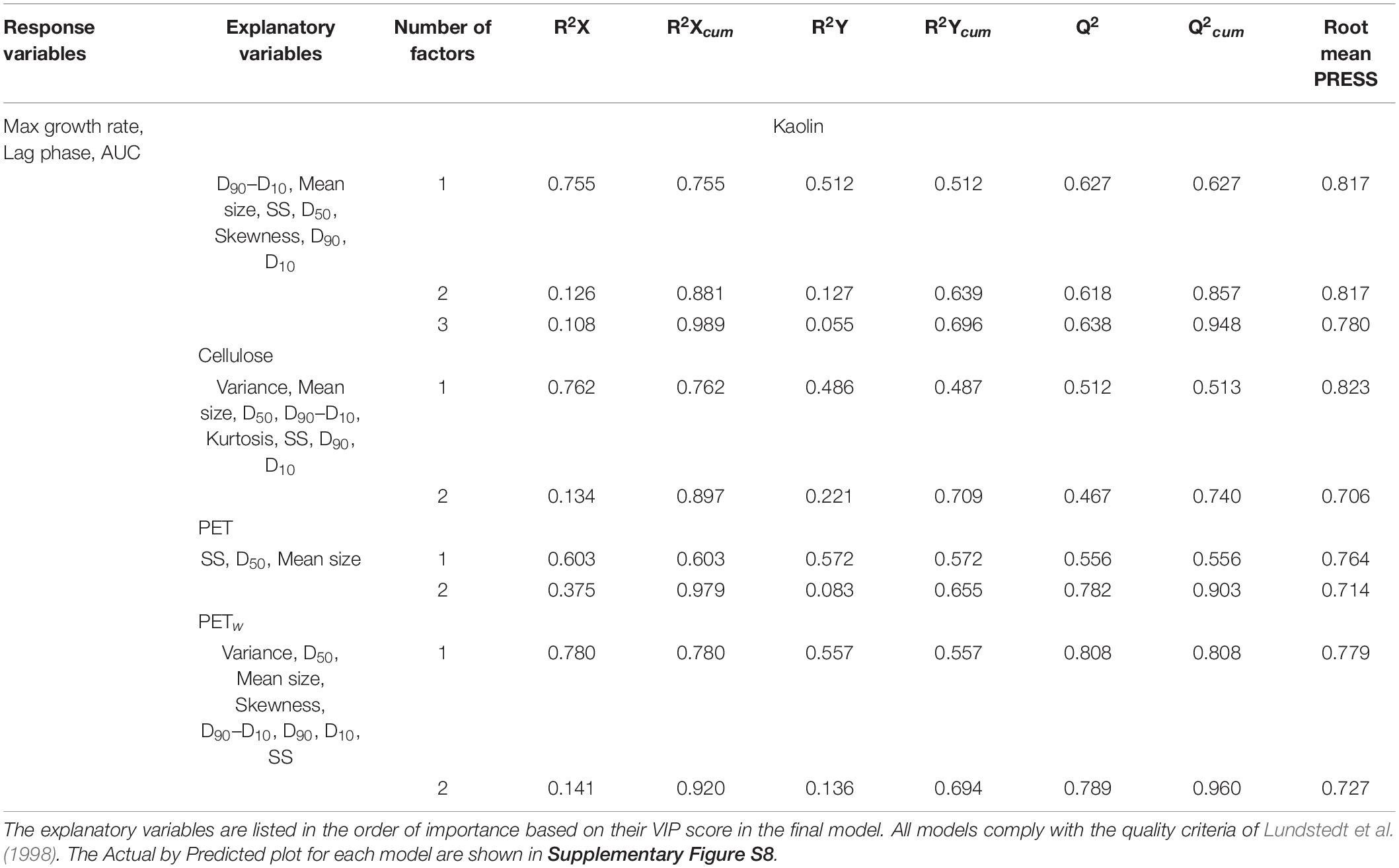
Table 4. | Significant PLSR models (p < 0.05) with growth parameters as dependent variables (all models) and PSD characteristics of the suspended solids and their concentration (SS) as explanatory variables for algae exposed to each reference and test material.
For all materials, the overall growth performance was negatively related to particle size (mean size and D50; Supplementary Figure S7). For kaolin, the SS concentration effects on the maximal growth and AUC values were weakly positive, whereas, for all other materials, it was negative, with the most substantial effects observed in the algae exposed to virgin PET. Other significant variables in the PLSR models were Variance and Skewness that were positive predictors in cellulose and PETw models, whereas the particle range interval D90–D10 was a significant negative predictor in kaolin and PETw models (Supplementary Figure S7).
Discussion
A step toward hazard assessment of plastic litter is to move it beyond its current exploratory state to experimental designs that provide delineation of microplastic effects from those of any suspended solids. Parallels can be drawn across particles and materials, regardless of whether they are natural solids, engineered nanomaterials, or plastics. On the other hand, it is essential to understand where the similarities end to avoid redundant testing and inappropriate methods and endpoints.
Using a combination of the standard growth inhibition test and PSD analysis, we found that both reference (kaolin and cellulose) and PET (virgin and weathered) materials with similar PSD s inhibited growth at the highest concentration (1,000 mg/L) but not at the lower concentrations. Similar results concerning the effect concentration were obtained for a green alga Scenedesmus obliquus exposed to polystyrene (PS; 0.07 μm particle size) by Besseling et al. (2014), who reported ∼3% inhibition rate at 1,000 mg/L and non-significant effects at lower concentrations. However, for another green alga Dunaliella tertiolecta, even lower concentrations of the same polymer (PS; particle size 0.05 μm, 250 mg/L) caused 57% growth inhibition (Sjollema et al., 2016). However, the effect mechanisms for nanoparticles are likely to be different from the micrometer-sized particles, as shown for nanoparticle-cell interactions that involve extracellular proteins in the algal cell membrane, with downstream effects on nutrient acquisition (Yue et al., 2017) or changes in colloidal stability affecting bio-physical interactions with cell walls (Gonzalo et al., 2014). In line with this, Nolte et al. (2017) using Raphidocelis subcapitata, i.e., the same green alga as in the present study, exposed to functionalized PS (0.11 μm) found 20–50% growth inhibition at concentrations 10–100 mg L–1. Therefore, it is most likely the particle size, physicochemical properties, and chemical additives that leach out during the exposure, and not the polymer itself, govern algal responses in growth inhibition assays.
The responses may also vary during the exposure and depending on the growth phases, thus setting test duration requirements. For instance, in a green alga Chlorella pyrenoidosa, a reduction in growth was observed during the lag phase, with some inhibition in the exponential phase, but during the stationary phase, this trend was reversed due to a compensatory growth that exceeded the values observed in control (Mao et al., 2018). Such biphasic responses indicate that even when growth inhibition occurs, the algal populations are able to adapt and sustain productivity. In line with this, we found that at 10–100 mg L–1, there was a significant positive correlation between the lag phase and the maximal growth rate during the exponential phase suggesting a compensatory growth due to adaptation during the exposure. A similar correlation between the growth parameters has been reported for algae exposed to other stressors (Andriukonis and Gorokhova, 2017). We also observed differential responses in the growth parameters, with the lag phase being the least affected by the test material (Figure 2A) and the total productivity represented by AUC values showing the most deviations from the controls (Figure 2C). Notably, while the lag phase in the lowest concentration was prolonged (albeit not significantly), the compensatory growth in 10–100 mg L–1 treatments was manifested as higher maximal growth during the exponential growth phase and the resulting total production that tended to be higher in the treatments with reference materials at 10 mg L–1 but not the polymers (Figure 2). At 100 mg L–1, although a compensatory growth (33% higher than in control) was observed in kaolin treatment (Figure 2B), it was neither significant when corrected for multiple comparisons (Supplementary Table S2) nor sufficient to support the same production as in control (Figure 1C). At 1,000 mg L–1, the significantly prolonged lag phase and lowered maximal growth rate resulted in significant production loss in all tested materials. Overall, the trends and the relationships between the growth parameters (Figure 4) were similar for all materials tested, suggesting the similarity of the adaptation mechanisms across all materials tested.
Low concentrations of suspended particles might also stimulate algal growth when the particles are both smaller (Zhao et al., 2019) and bigger (Chae et al., 2019) than the cell size. In line with that, some field studies suggested that, under certain conditions and at concentrations < 100 mg L–1, particulate matter may stimulate algal growth (Birkett et al., 2007). At 10–100 mg L–1, the growth tended to be promoted in kaolin and cellulose exposures but not in the microplastic exposures. Moreover, the observed differences in AUC between the reference materials and PETw were mainly due to this stimulatory effect in the kaolin and cellulose treatments. The growth stimulation decreased in the 100 mg L–1 treatments and became significantly inhibitory at 1,000 mg L–1 in all treatments. It is unlikely that kaolin and cellulose powder provided any additional nutrients to the algae; instead, the algal growth was most probably promoted by the topography of the heteroaggregates formed by algae and kaolin/cellulose at relatively low concentrations of suspended solids.
During the incubation, the aggregation occurred in both particle blanks (no algae) and all treatments with algae (Supplementary Figure S3). Moreover, the aggregation was significantly facilitated by the presence of algae compared to the blanks, indicating that heteroaggregates, i.e., aggregates formed by test particles and algal cells, had different PSD characteristics compared to homoaggregates, i.e., those formed by test particles only in the blank treatment for each material (Supplementary Figure S4). The production of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) by algae was a likely driver facilitating heteroaggregate formation (Costa et al., 2018) and morphology (Figure 5). It has been suggested that EPS production is enhanced in algal cells exposed to foreign matter, such as polymer particles, facilitating aggregation (Bergami et al., 2017). Similarly, Lagarde et al. (2016) explained the observed variability in heteroaggregate formation as a result of different composition of EPS produced by algae in response to polymer material. Moreover, certain algal species produce more hydrophobic EPS resulting in bigger aggregates (Chen et al., 2011; Long et al., 2015). In time series, dose-response aggregation kinetics has been reported with a positive relationship between the aggregate size and mass concentration of particulate matter (Chen et al., 2011). In situ, however, the interactions between microorganisms, natural particulates, and microplastics may change the pollutant characteristics over time and define how and why cells attach to plastic particles. The attachment patterns can also vary depending on the microbial communities present in the system as well as other particulates (Rogers et al., 2020), which can be addressed in the test designs by using treatments with ambient water with natural bacterioplankton in addition to the treatments with sterile exposure media. Thus, the aggregate formation is species-, media-, and polymer-material-dependent (Long et al., 2015), making it challenging to incorporate it in microplastic hazard assessment and evaluate the effects of exposure to mixed particulates (including microplastic) in bioassays. However, in the effect studies, these dependencies can be evaluated.
We used a plankton wheel to prevent sedimentation that kept the test particles and the algae in suspension during the exposure. Clearly, control of sedimentation and aggregation should be an essential methodological requirement in effect studies with particulate materials if we are to provide reliable data for the hazard assessment. During the toxicity testing, the aggregation can effectively remove particles from the system, thus decreasing particle number concentrations and adverse effects. For example, Fu et al. (2019) observed higher toxicity of PVC for algae at low levels (10 mg L–1) compared to higher concentrations (1,000 mg L–1). They explained this phenomenon as a result of particle aggregation and sedimentation in the experimental system (Fu et al., 2019), thus, efficiently decreasing the exposure. Moreover, homoaggregate formation implies a lower collision/encounter rate between the test particles and algal cells and thus a lower probability of direct interactions. Heteroaggregates, on the other hand, provide a different habitat for algae that are embedded in the aggregates, where the nutrient and light regimes may differ from that experienced by solitary cells, with concomitant effects on algal growth. Notably, these growth effects induced by aggregation with, for example, mineral particles, can be both positive and negative (Cuadros, 2017). We found that algal growth was affected primarily by the aggregate size and its variability, and to a lesser extent by the concentration of the suspended solids in the system (Table 4). In line with the nitrient/light limitation reasoning, smaller aggregates supported higher growth, whereas a higher concentration of the suspended solids had inhibitory effects in all but the kaolin treatments (Supplementary Figure S7).
No differences in any of the growth parameters were observed between the treatments with PET and PETw (Figure 2). However, there was a significantly higher within-treatment variability in the PETw treatment at the highest concentration (Figure 3). Moreover, there were significant differences in the PSD parameters between the weathered and virgin PET treatments following the exposure, with higher aggregation in the presence of algae for PETw compared to PET. Also, the PSD-predictors driving algal growth in PETw treatment were more diverse and included Variance and Skewness as positive drivers, suggesting that morphological variability of the aggregates (1) has increased following the weathering treatment, (2) facilitated cell-particles interactions, and (3) may become decisive in governing growth of algae and, perhaps, other microorganisms when present. Due to the changes in functional groups and an increase in the particle surface area, weathered PVC has been reported to induce more substantial growth inhibition in freshwater alga Chlorella vulgaris (Fu et al., 2019). This, however, can also be related to the increased leaching of chemicals associated with the weathered material. For our experiment, we selected PET as a test material having no measurable leachate toxicity on our test alga (Capolupo et al., 2020) in order to focus on the particle-alga interactions and the potential differences between the weathered and virgin particles of the same material as well as between the polymer and the reference materials. Our findings suggest that significant growth predictors in the PETw exposure were more similar to the cellulose treatment than to the PET treatment (Supplementary Figure S7). Thus, plastic-microorganism interactions change with the plastic aging, but these changes may lead to convergence of the physicochemical properties in different materials, and they do not necessarily lead to more severe impacts on biota.
In conclusion, we need to be able to generate high-quality data on the plastic litter effects in biota, which is particularly challenging for the smaller size fractions of the plastic litter because of the inavoidable interactions with other particulate materials present in the environment but also interactions with microorganisms resulting in aggregation and secondary effects. We found no indication that PET particles, regardless of the weathering status, induced higher growth inhibition in unicellular algae than the naturally occurring particles represented by kaolin and cellulose. The comparison among PSD s across the treatments showed that both particulate matter concentration and topography of the particle aggregates were significant growth predictors for algae exposed to any test material, which must be taken into account when developing protocols for hazard assessment of plastic litter and other solid waste.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found below: GitHub, https://github.com/elenagoro/MP_algae.
Author Contributions
EG and KE designed the experiment. KE performed the experiment and collected data. EG and SR wrote the manuscript and conducted statistical analysis. All authors contributed to the data interpretation and writing.
Funding
This research was supported by the Joint Programming Initiative Healthy and Productive Seas and Oceans (JPI Oceans, WEATHER-MIC project, grant no. 942-2015-1866 to EG); The Swedish Innovation Agency (VINNOVA) and the joint Baltic Sea research and development program (BONUS, Blue Baltic) for MICROPOLL project (grant No. 2017-00979 to EG); The Swedish Environmental Protection Agency (Naturvårdsverket) for MIxT project (grant No. 802-0160-18 to EG).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
Zandra Gerdes and Birgitta Liewenborg (ACES, Stockholm University) are thanked for suggestions on the experimental design and technical assistance.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fenvs.2020.551075/full#supplementary-material
Footnotes
References
Adam, V., Yang, T., and Nowack, B. (2019). Toward an ecotoxicological risk assessment of microplastics: Comparison of available hazard and exposure data in freshwaters: Environmental risk assessment of microplastics. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 38, 436–447. doi: 10.1002/etc.4323
Andrady, A. L., and Neal, M. A. (2009). Applications and societal benefits of plastics. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 364, 1977–1984. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2008.0304
Andriukonis, E., and Gorokhova, E. (2017). Kinetic 15N-isotope effects on algal growth. Sci. Rep. 7:44181. doi: 10.1038/srep44181
Baranyi, J., and Roberts, T. A. (1994). A dynamic approach to predicting bacterial growth in food. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 23, 277–294. doi: 10.1016/0168-1605(94)90157-90150
Benjamini, Y., Krieger, A. M., and Yekutieli, D. (2006). Adaptive linear step-up procedures that control the false discovery rate. Biometrika 93, 491–507. doi: 10.1093/biomet/93.3.491
Bergami, E., Pugnalini, S., Vannuccini, M. L., Manfra, L., Faleri, C., Savorelli, F., et al. (2017). Long-term toxicity of surface-charged polystyrene nanoplastics to marine planktonic species Dunaliella tertiolecta and Artemia franciscana. Aquat. Toxicol. 189, 159–169. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2017.06.008
Besseling, E., Wang, B., Lürling, M., and Koelmans, A. A. (2014). Nanoplastic Affects Growth of S. obliquus and Reproduction of D. magna. Environ. Sci. Technol. 48, 12336–12343. doi: 10.1021/es503001d
Bhattacharya, P., Lin, S., Turner, J. P., and Ke, P. C. (2010). Physical Adsorption of Charged Plastic Nanoparticles Affects Algal Photosynthesis. J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 16556–16561. doi: 10.1021/jp1054759
Bilotta, G. S., and Brazier, R. E. (2008). Understanding the influence of suspended solids on water quality and aquatic biota. Water Res. 42, 2849–2861. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2008.03.018
Birkett, C., Tollner, E. W., and Gattie, D. K. (2007). Total Suspended Solids and Flow Regime Effects on Periphyton Development in a Laboratory Channel. Trans. ASABE 50, 1095–1104. doi: 10.13031/2013.23118
Blott, S. J., and Pye, K. (2001). GRADISTAT: a grain size distribution and statistics package for the analysis of unconsolidated sediments. Earth Surf. Process. Landforms 26, 1237–1248. doi: 10.1002/esp.261
Bråte, I. L. N., Blázquez, M., Brooks, S. J., and Thomas, K. V. (2018). Weathering impacts the uptake of polyethylene microparticles from toothpaste in Mediterranean mussels (M. galloprovincialis). Sci. Total Environ. 626, 1310–1318. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.141
Cahoon, L. B., Nearhoof, J. E., and Tilton, C. L. (1999). Sediment Grain Size Effect on Benthic Microalgal Biomass in Shallow Aquatic Ecosystems. Estuaries 22, 735. doi: 10.2307/1353106
Capolupo, M., Sørensen, L., Jayasena, K. D. R., Booth, A. M., and Fabbri, E. (2020). Chemical composition and ecotoxicity of plastic and car tire rubber leachates to aquatic organisms. Water Res. 169:115270. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.115270
Chae, Y., Kim, D., and An, Y.-J. (2019). Effects of micro-sized polyethylene spheres on the marine microalga Dunaliella salina: focusing on the algal cell to plastic particle size ratio. Aquat. Toxicol. 216:105296. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2019.105296
Chapman, P. M., Hayward, A., and Faithful, J. (2017). Total Suspended Solids Effects on Freshwater Lake Biota Other than Fish. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 99, 423–427. doi: 10.1007/s00128-017-2154-y
Chen, C.-S., Anaya, J. M., Zhang, S., Spurgin, J., Chuang, C.-Y., Xu, C., et al. (2011). Effects of Engineered Nanoparticles on the Assembly of Exopolymeric Substances from Phytoplankton. PLoS One 6:21865. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021865
Coe, J. M., Bud Antonelis, G., and Moy, K. (2019). Taking control of persistent solid waste pollution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 139, 105–110. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.12.004
Costa, O. Y. A., Raaijmakers, J. M., and Kuramae, E. E. (2018). Microbial Extracellular Polymeric Substances: Ecological Function and Impact on Soil Aggregation. Front. Microbiol. 9:1636. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01636
Cuadros, J. (2017). Clay minerals interaction with microorganisms: a review. Clay Miner. 52, 235–261. doi: 10.1180/claymin.2017.052.2.05
Foley, C. J., Feiner, Z. S., Malinich, T. D., and Höök, T. O. (2018). A meta-analysis of the effects of exposure to microplastics on fish and aquatic invertebrates. Sci. Total Environ. 63, 550–559. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.046
Folk, R. L., and Ward, W. C. (1957). Brazos River Bar: A Study in the Significance of Grain Size Parameters. J. Sediment. Petrol. 27, 3–26. doi: 10.1306/74d70646-2b21-11d7-8648000102c1865d
Fu, D., Zhang, Q., Fan, Z., Qi, H., Wang, Z., and Peng, L. (2019). Aged microplastics polyvinyl chloride interact with copper and cause oxidative stress towards microalgae Chlorella vulgaris. Aquat. Toxicol. 216:105319. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2019.105319
Galgani, L., Tsapakis, M., Pitta, P., Tsiola, A., Tzempelikou, E., Kalantzi, I., et al. (2019). Microplastics increase the marine production of particulate forms of organic matter. Environ. Res. Lett. 14:124085. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/ab59ca
Gerdes, Z., Hermann, M., Ogonowski, M., and Gorokhova, E. (2019). A novel method for assessing microplastic effect in suspension through mixing test and reference materials. Sci. Rep. 9:10695. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-47160-47161
Gonçalves, A. L., Pires, J. C. M., and Simões, M. (2016). The effects of light and temperature on microalgal growth and nutrient removal: an experimental and mathematical approach. RSC Adv. 6, 22896–22907. doi: 10.1039/C5RA26117A
Gonzalo, S., Llaneza, V., Pulido-Reyes, G., Fernández-Piñas, F., Bonzongo, J. C., Leganes, F., et al. (2014). A Colloidal Singularity Reveals the Crucial Role of Colloidal Stability for Nanomaterials In-Vitro Toxicity Testing: nZVI-Microalgae Colloidal System as a Case Study. PLoS One 9:109645. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109645
Hammer, Ø, Harper, D. A. T., and Ryan, P. D. (2001). PAST: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol. Electronic. 4:9.
He, Q., Qiu, Y., Liu, H., Sun, X., Kang, L., Cao, L., et al. (2017). New insights into the impacts of suspended particulate matter on phytoplankton density in a tributary of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sci. Rep. 7, 1–11. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-13235-13230
Jahnke, A., Arp, H. P. H., Escher, B. I., Gewert, B., Gorokhova, E., Kühnel, D., et al. (2017). Reducing Uncertainty and Confronting Ignorance about the Possible Impacts of Weathering Plastic in the Marine Environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 4, 85–90. doi: 10.1021/acs.estlett.7b00008
Lagarde, F., Olivier, O., Zanella, M., Daniel, P., Hiard, S., and Caruso, A. (2016). Microplastic interactions with freshwater microalgae: Hetero-aggregation and changes in plastic density appear strongly dependent on polymer type. Environ. Pollut. 215, 331–339. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.05.006
Lenz, R., Enders, K., and Nielsen, T. G. (2016). Microplastic exposure studies should be environmentally realistic. PNAS 113, E4121–E4122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1606615113
Long, M., Moriceau, B., Gallinari, M., Lambert, C., Huvet, A., Raffray, J., et al. (2015). Interactions between microplastics and phytoplankton aggregates?: Impact on their respective fates. Mar. Chem. 175, 39–46. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2015.04.003
Lundstedt, T., Seifert, E., Abramo, L., and Thelin, B. (1998). Experimental design and optimization. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 42, 3–40.
Ma, J., Lin, F., Zhang, R., Yu, W., and Lu, N. (2004). Differential sensitivity of two green algae. Scenedesmus quadricauda and Chlorella vulgaris, to 14 pesticide adjuvants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 58, 61–67. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2003.08.023
Mao, Y., Ai, H., Chen, Y., Zhang, Z., Zeng, P., Kang, L., et al. (2018). Phytoplankton response to polystyrene microplastics: Perspective from an entire growth period. Chemosphere 208, 59–68. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.05.170
McGivney, E., Cederholm, L., Barth, A., Hakkarainen, M., Hamacher-Barth, E., Ogonowski, M., et al. (2020). Rapid Physicochemical Changes in Microplastic Induced by Biofilm Formation. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 8:205. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00205
Nolte, T. M., Hartmann, N. B., Kleijn, J. M., Garnæs, J., van de Meent, D., Jan Hendriks, A., et al. (2017). The toxicity of plastic nanoparticles to green algae as influenced by surface modification, medium hardness and cellular adsorption. Aquat. Toxicol. 183, 11–20. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2016.12.005
Oecd. (2006). Test No. 201: Alga, Growth Inhibition Test, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2: Effects on Biotic Systems. Paris: OECD. Available online at: https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264069923-en (accessed February 2, 2020).
Oelschlägel, K., Pfeiffer, J., and Potthoff, A. (2018). “Imitating the Weathering of Microplastics in the Marine Environment,” in Proceedings of the International Conference on Microplastic Pollution in the Mediterranean Sea, eds M. Cocca, E. Di Pace, M. E. Errico, G. Gentile, A. Montarsolo, and R. Mossotti (New York, NY: Springer), 171–179. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-71279-6_23
Ogonowski, M., Edlund, U., Gorokhova, E., Linde, M., Ek, K., Liewenborg, B., et al. (2018a). Multi-level toxicity assessment of engineered cellulose nanofibrils in Daphnia magna. Nanotoxicology 12, 509–521. doi: 10.1080/17435390.2018.1464229
Ogonowski, M., Gerdes, Z., and Gorokhova, E. (2018b). What we know and what we think we know about microplastic effects – A critical perspective. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 1, 41–46. doi: 10.1016/j.coesh.2017.09.001
Paul-Pont, I., Tallec, K., Gonzalez-Fernandez, C., Lambert, C., Vincent, D., Mazurais, D., et al. (2018). Constraints and Priorities for Conducting Experimental Exposures of Marine Organisms to Microplastics. Front. Mar. Sci. 5:252. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2018.00252
Phuong, N. N., Zalouk-Vergnoux, A., Poirier, L., Kamari, A., Châtel, A., Mouneyrac, C., et al. (2016). Is there any consistency between the microplastics found in the field and those used in laboratory experiments? Environ. Pollut. 211, 111–123. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2015.12.035
Prata, J. C., da Costa, J. P., Lopes, I., Duarte, A. C., and Rocha-Santos, T. (2019). Effects of microplastics on microalgae populations: A critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 665, 400–405. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.132
Reichelt, S., and Gorokhova, E. (2020). Micro- and Nanoplastic Exposure Effects in Microalgae: A Meta-Analysis of Standard Growth Inhibition Tests. Front. Environ. Sci. 8:131. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2020.00131
Robinson, S. E., Capper, N. A., and Klaine, S. J. (2009). The effects of continuous and pulsed exposures of suspended clay on the survival, growth, and reproduction of Daphnia magna. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 29, 168–175. doi: 10.1002/etc.4
Rochman, C. M., Brookson, C., Bikker, J., Djuric, N., Earn, A., Bucci, K., et al. (2019). Rethinking microplastics as a diverse contaminant suite. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 38, 703–711. doi: 10.1002/etc.4371
Rogers, K. L., Carreres−Calabuig, J. A., Gorokhova, E., and Posth, N. R. (2020). Micro-by-micro interactions: How microorganisms influence the fate of marine microplastics. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 5, 18–36. doi: 10.1002/lol2.10136
Sjollema, S. B., Redondo-Hasselerharm, P., Leslie, H. A., Kraak, M. H. S., and Vethaak, A. D. (2016). Do plastic particles affect microalgal photosynthesis and growth? Aquatic Toxicol. 170, 259–261. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2015.12.002
Tsai, K.-P., and Chen, C.-Y. (2007). An algal toxicity database of organic toxicants derived by a closed-system technique. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 26:1931. doi: 10.1897/06-612R.1
Vaas, L. A. I., Sikorski, J., Michael, V., Göker, M., and Klenk, H.-P. (2012). Visualization and Curve-Parameter Estimation Strategies for Efficient Exploration of Phenotype Microarray Kinetics. PLoS One 7:e34846. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034846
Wold, S., Sjöström, M., and Eriksson, L. (2001). PLS-regression: a basic tool of chemometrics. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 58, 109–130. doi: 10.1016/S0169-7439(01)00155-151
Yokota, K., Waterfield, H., Hastings, C., Davidson, E., Kwietniewski, E., and Wells, B. (2017). Finding the missing piece of the aquatic plastic pollution puzzle: Interaction between primary producers and microplastics: Aquatic plastic pollution puzzle. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2, 91–104. doi: 10.1002/lol2.10040
Yue, Y., Li, X., Sigg, L., Suter, M. J.-F., Pillai, S., Behra, R., et al. (2017). Interaction of silver nanoparticles with algae and fish cells: a side by side comparison. J. Nanobiotechnol. 15:16. doi: 10.1186/s12951-017-0254-259
Keywords: algal growth inhibition test, plastic litter, suspended solids, particle size distribution, plastic weathering, aged plastic, hazard assessment, microplastic
Citation: Gorokhova E, Ek K and Reichelt S (2020) Algal Growth at Environmentally Relevant Concentrations of Suspended Solids: Implications for Microplastic Hazard Assessment. Front. Environ. Sci. 8:551075. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2020.551075
Received: 11 April 2020; Accepted: 20 October 2020;
Published: 19 November 2020.
Edited by:
Antonia Praetorius, University of Amsterdam, NetherlandsReviewed by:
Garth Aidan Covernton, University of Victoria, CanadaJesse Patrick Harrison, CSC-IT Center for Science, Finland
Copyright © 2020 Gorokhova, Ek and Reichelt. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Elena Gorokhova, ZWxlbmEuZ29yb2tob3ZhQGFjZXMuc3Uuc2U=
 Elena Gorokhova
Elena Gorokhova Karin Ek
Karin Ek Sophia Reichelt
Sophia Reichelt