- 1Advanced Technology Development Centre, Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur, Kharagpur, India
- 2Department of Chemistry, Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur, Kharagpur, India
- 3Department of Chemistry, Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, Mumbai, India
The scientific community is engrossed in the thought of a probable solution to the future energy crisis keeping in mind a better environment-friendly alternative. Although there are many such alternatives, the green hydrogen energy has occupied most of the brilliant minds due to its abundance and numerous production resources. For the advancement of hydrogen economy, Government agencies are funding pertinent research projects. There is an avalanche of molecular systems which are studied by several chemists for storing atomic and molecular hydrogens. The present review on molecular hydrogen storage focuses on all-metal and nonmetal aromatic clusters. In addition to the effect of aromaticity on hydrogen trapping potential of different molecular moieties, the importance of using the conceptual density functional theory based reactivity descriptors is also highlighted. Investigations from our group have been revealing the fact that several aromatic metal clusters, metal doped nonmetal clusters as well as pure nonmetal clusters can serve as potential molecular hydrogen trapping agents. Reported systems include N4Li2, N6Ca2 clusters, Mgn, and Can (n = 8–10) cage-like moieties, B12N12 clathrate, transition metal doped ethylene complexes, M3+ (M = Li, Na) ions, E3-M2 (E = Be, Mg, Al; M = Li, Na, K) clusters, Li3Al4− ions, Li decorated star-like molecules, BxLiy (x = 3–6; y = 1, 2), Li-doped annular forms, Li-doped borazine derivatives, C12N12 clusters (N4C3H)6Li6 and associated 3-D functional material, cucurbiturils, lithium–phosphorus double-helices. Ni bound C12N12 moieties are also reported recently.
1 Introduction
With the ever-increasing utilization of energy, whose primary source has been fossil fuels for so long, the rate of carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere is increasing at an alarming rate. With this level of energy demand, fossil fuels will soon be exhausted unless more and more clean fuels are adopted. As of 2019, the International Energy Agency (IEA, 2019) reports the world total energy consumption, of which oil source constitutes 40.4%, followed by 19.7% consumption of electricity, 16.4, 10.4, and 9.5% of natural gas, biofuels, and coal, respectively, and 3.6% constitute other sources of energy. Although 2020 has witnessed a significant reduction in global CO2 emissions (by 2.4 gigatons) and a decline in the usage of electricity owing to the industrial sector shutdown as a part of COVID-19 restrictions, we are far from reaching the goal of saving the world from collapsing due to over usage of non-renewable energy resources. On the bright side, more and more countries are announcing pledges towards attaining net-zero emissions by the year 2050. To achieve such goals, more and more research projects are being undertaken to search for alternative reliable clean energy sources like hydrogen, nuclear, and efficiently harness the natural resources that we already have in the form of solar, hydro, and wind.
Hydrogen, as a fuel source, is ideal since we have an abundance of it, it causes no emission of harmful gases, and it has a much greater energy content per unit than fossil fuels (World Nuclear Association Website, 2016). The challenges that arise include the conversion of hydrogen from various sources like water and hydrocarbons to its free state, followed by its storage and transportation. The first challenge can be overcome by processes like electrolysis of water and steam reformation of small hydrocarbons, both of which have disadvantages of their own. While the former requires electricity, the latter produces CO2 as a by-product. Between the two, the electrolysis process seems more preferable since it can be made eco-friendly by using solar, wind, and hydro electricity. Again, there is a downside of higher cost. After the production of free molecular hydrogen, it needs to be stored in an environment with high pressure and very low temperatures. A better way is to adsorb or entrap H2 in molecular clusters and cages such that the desorption process would also be feasible. Such materials must follow certain standard requirements set by the United States Department of Energy (DOE) (U.S. Department of Energy, USCAR, 2017) to be considered as efficient storage material. In order for a compound to practically act as an effective hydrogen storage material, it must be highly stable, easily available, light weight, inexpensive, showing fast adsorption-desorption kinetics at ambient conditions, can achieve high gravimetric and volumetric hydrogen storage density, and favourable thermodynamic parameters. The appropriate binding energy range depends on the type of hydrogen adsorption on the storage material. For physisorption, it is very small (in the mili-eV range), for chemisorption the value ranges within 2–4 eV, and for the type between physisorption and chemisorption, the binding energy ranges from 0.1 to 0.8 eV. Interaction energy that lies in between that of physisorption and chemisorption is ideal for a better reversible hydrogen storage material.
Hydrogen adsorption can occur via physisorption, chemisorption, and by virtue of Kubas interaction (Kubas, 2001) in the case of transition metals (TM) which is essentially the sequential electron donation from σH to vacant dTM orbital, and a back donation from filled dTM to σ*H. The H2 storage capacity of a diverse range of molecular systems are explored like, nanomaterials based on carbon (Dresselhaus et al., 1999; Froudakis, 2002; Ding et al., 2001; Lochan and Head-Gordon, 2006; Ströbel et al., 2006; Xu et al., 2007), and aluminium nitride (Wang et al., 2009), Li-bound neutral and cationic Bn complexes (Bandaru et al., 2012), alkali-metal doped benzenoid systems (Srinivasu et al., 2009), polylithiated B N doped graphyne (Jana et al., 2018), clathrate-hydrate molecules (Chattaraj et al., 2011a), Boron–Li clusters (Wu et al., 2008; Yildirim and Güvenç, 2009), transition-metal doped BN systems (Shevlina and Guo, 2006), fullerene clusters (Peng et al., 2009), magnesium clusters (Wagemans et al., 2005), transition-metal coated boron buckyballs, B80 (Wu et al., 2009), and metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) (Rosi et al., 2003; Dinca et al., 2006), trigonal, aromatic all-metal Li3+ and Na3+ systems as well as alkaline-earth metal (Mn: M = Mg, Ca; n = 8–10) cages (Giri et al., 2011a), transition-metal–ethylene complexes (Chakraborty et al., 2011) and cage-like B12N12 clusters (Giri et al., 2011b).
The aromatic stability of a compound can influence the hydrogen adsorbing power of the molecular motif as described on alkali metal doped hydrocarbons by Srinivasu et al. (2009) Others are discussed in this review. The concept of aromaticity is not yet completely unfolded. It started with being able to explain the reason behind the extra stability in some cyclic hydrocarbons following certain rules prescribed by Hückel, 1931a, Hükel, 1931b, Hückel, 1932. Thorn and Hoffman (1979) then contributed to explaining those of metallabenzene compounds. The accurate measurement of this behaviour is somewhat challenging in the sense that there is no “one-size-fits-all” concept here. Numerous descriptors can measure aromaticity using various techniques but they are highly system-dependent. In this report, we have described the influence of aromatic behaviour on the H2 trapping potential of various all-metal and nonmetal systems where it is measured in terms of nucleus independent chemical shift (NICS) (Schleyer et al., 1996; Chen et al., 2005) values.
2 Computational Details
Computational chemistry packages, Gaussian 03 (Frisch et al., 2003) and Gaussian 09 (Frisch et al., 2009), are utilized to model the systems, followed by geometry optimization and frequency calculation. The levels of theory used in this study are MP2, MPW1K, M05–2X, M06, B3LYP, B3LYP-D3, ωB97X-D, and PBE0, with basis sets like 6-31G, 6–31+G(d), 6–311+G(d), 6–311+G (d,p), cc-pVDZ, and Def2-TZVP. The aromaticity is evaluated in terms of NICS values (Chen et al., 2005) at various distances from the molecular plane. Global and local reactivity descriptors like electronegativity (χ) (Parr et al., 1978), chemical hardness (η) (Parr and Pearson, 1983; Pearson, 1997) and electrophilicity index (ω) (Parr et al., 1999; Chattaraj and Roy, 2007; Chattaraj et al., 2011b) Fukui functions (f±k) (Parr and Yang, 1984), atomic charges (qk), and philicity (ω±k) (Chattaraj et al., 2003) derived from the Conceptual density functional theory (CDFT) help describe the molecular stability and reactivity. Following equations are followed for the calculation of the aforementioned descriptors:
where E stands for total energy and N for a total number of electrons in the system, εHOMO, εLUMO, IP, and EA refer to highest occupied and lowest unoccupied molecular orbital energies, ionization potential, and electron affinity, respectively. µ denotes chemical potential (Parr and Yang, 1989), ρ(r) denotes electron density, pk stands for the electron population at the kth atomic site, and α can be 0, +, or −, for radical, nucleophilic, and electrophilic attacks, respectively.
3 Case Studies
3.1 ALL-METAL Clusters
3.1.1 Mg/Can and Li/Na3+ Clusters
The hydrogen storage potential of magnesium and calcium cages (Mgn and Can; n = 8–10) along with that of trigonal alkali-metal cationic clusters (Li3+ and Na3+) were explored by Giri et al. (2011a) with a CDFT approach. The stability of 1H2-trapped Mgn and Can complexes increases with increase in n. It is, however, interesting to discover that these bare cages could not be stabilized i.e., before trapping the H2 molecule within them. Again, in the cases of H2-bound Li3+ and Na3+ systems, the stability is found to increase with the increase in the number of bound H2 molecules. Upon binding with the clusters, most of the H2 retains their molecular identity, except in a few of the nH2Li3+ systems where one of the H2 molecules dissociates and binds itself in the atomic form. This behaviour is also observed in the case of H2-trapped Ca10 cage (Figure 1). The planarity of the Li3+ and Na3+ clusters remained intact in the H2-bound complexes. Further analysis of the changes in the CDFT based reactivity indices, viz., electronegativity (χ) hardness (η) and electrophilicity (ω), revealed a gradual decrease in the ω values with an increase in the number of H2 molecules.
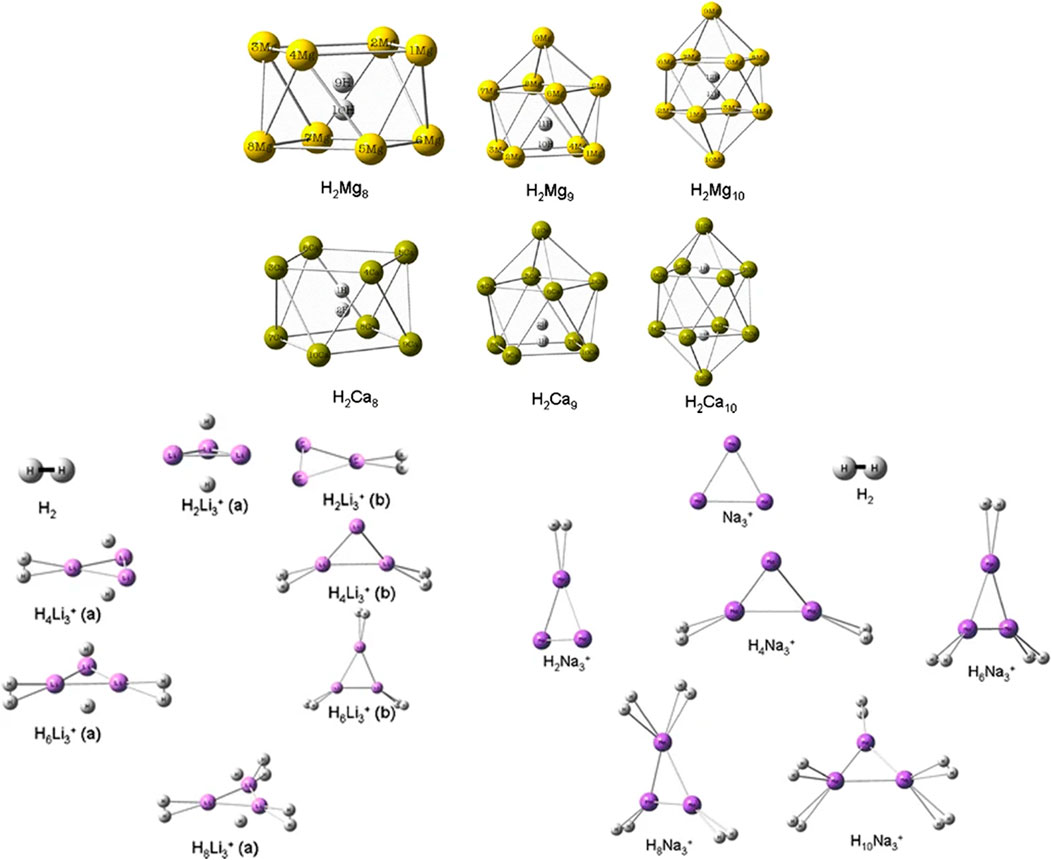
FIGURE 1. Optimized geometries of H2Mn (M = Mg, Ca; n = 8–10), xH2-trapped Li3+, and yH2-trapped Na3+ clusters at B3LYP/6–311 + G(d) level of theory (Reproduced with permission from Springer Nature Customer Service Centre GmbH: Journal of Molecular Modeling (Giri et al., 2011a), Copyright © 2010, Springer-Verlag).
The NICS (0, 1) values calculated for the top and bottom M4 rings (M = Mg, Ca) of the H2-encapsulated Mgn and Can cages are found to be negative, indicating the existence of diatropic ring current at the said positions. Similarly, negative NICSzz (0) values for the poly-hydrogenated trigonal clusters also established the aromatic stability with gradual H2 uptake. Further, from a thermodynamic point of view, the negative values of the reaction energy (∆Eb, kcal/mol) for the sequential H2 binding on the Li3+ and Na3+ systems provide some theoretical justification towards their possible usage as hydrogen storage materials (Table 1).

TABLE 1. Reaction energy in kcal/mol for the gradual hydrogen loading on Li3+ and Na3+ clusters (Adapted with permission from Springer Nature Customer Service Centre GmbH: Journal of Molecular Modeling (Giri et al., 2011a), Copyright © 2010, Springer-Verlag).
3.1.2 Be3M2, Mg3M2, and Al4M2 (M = Li, Na, K) Clusters
The aromaticity of all-metal Al42− system was previously reported (both theoretically and experimentally) (Li et al., 2001), followed by that of Be32− and Mg32− systems (Kuznetsov and Boldyrev, 2004; Roy and Chattaraj, 2008; Giri et al., 2010). All these systems owe their aromatic behaviour to the presence of delocalized π-electrons. The motivation for using these systems with the alkali metal counterion M+ (M = Li, Na, and K) (Srinivasu et al., 2012) is backed by the logic that due to high polarization, the M centers will be highly electropositive and hence can serve as a suitable site for hydrogen adsorption. The optimized geometries of the systems under study are provided in Figure 2, and their hydrogen adsorbed structures are depicted in Figure 3. The positive charges carried by the M centers were found to be proportional to the difference in electronegativity values between the two types of metal species in the complex. This difference is lower in Mg3M2 as compared to that in Be3M2 and Al4M2, which causes a lower charge transfer from M to the Mg3 ring compared to the others. This, in turn, results in poor H2 adsorption in the Mg3M2 complexes (interaction energy of −0.5 kcal/mol per H2, compared to the same ranging between −1.8 to −3.1 and −2.7 to −3.2 kcal/mol per H2 for Be3M2 and Al4M2, respectively). Now, from the perspective of the alkali metals, a high ionic radius and low charge density (i.e., low ionic potential) on the potassium atom results in a very weak interaction with the K atom containing systems (as low as −0.6 kcal/mol per H2). Both Be3Li2 and Be3Na2 are found to adsorb six hydrogen molecules each (three per alkali metal atom), whereas Al4Li2 and Al4Na2 are capable of binding eight molecules each (four H2 per alkali metal atom). The gravimetric weight percentage of hydrogen adsorption for the former two are 22.64 and 14.12, those for Al4Li2 and Al4Na2 are 11.59 and 9.4, respectively. Evidently, Be3Li2 is preferred to Al4Li2 in terms of the gravimetric density, whereas with respect to the binding energy per H2 molecule, Al4Li2 is preferred as a better hydrogen storage material.
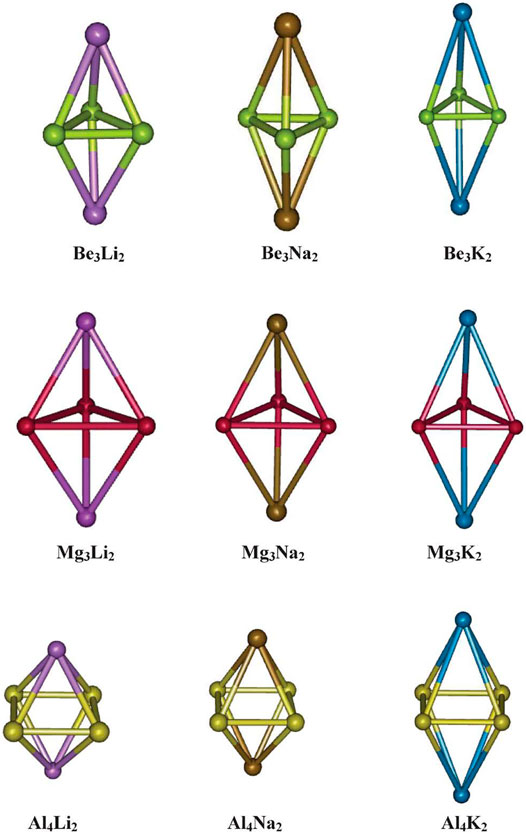
FIGURE 2. Optimized geometries of Be3M2, Mg3M2, and Al4M2 (M = Li, Na, and K) (Reproduced from Srinivasu et al., 2012 with permission from the Royal Society of Chemistry).
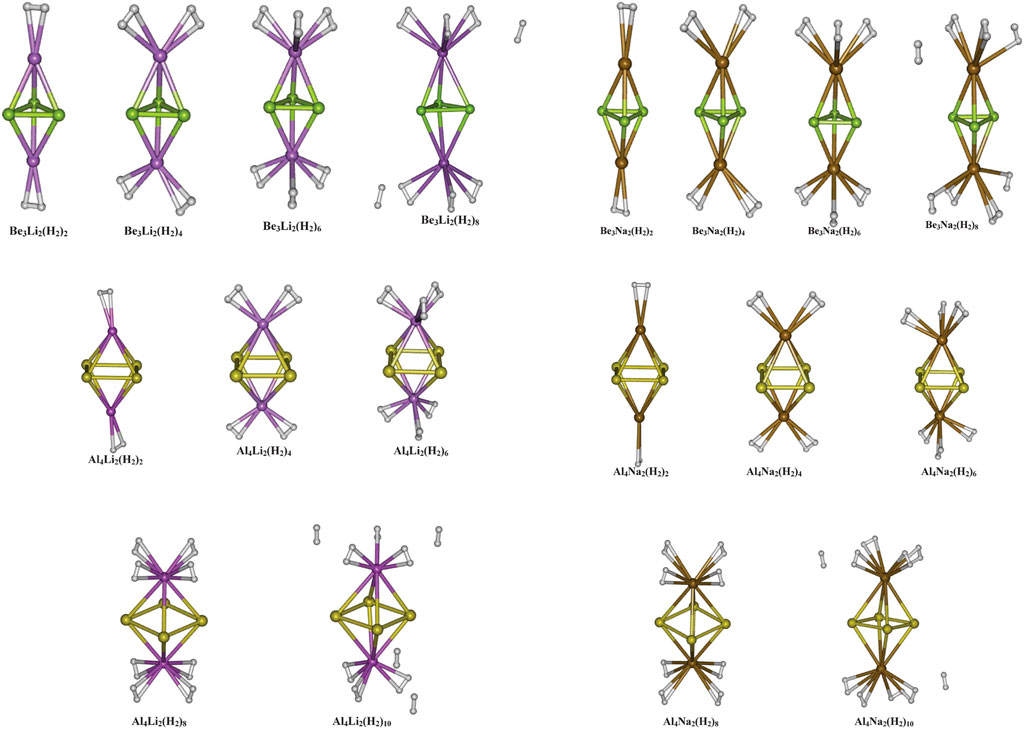
FIGURE 3. Optimized geometries of the hydrogen loaded Be3M2, and Al4M2 (M = Li, and Na) systems (Reproduced from Srinivasu et al., 2012 with permission from the Royal Society of Chemistry).
The stability of these hydrogenated systems is established in terms of higher energy gaps (5.17–6.40 eV) between their respective HOMO and LUMO. The variation in total energy (E), χ, η, and ω also serve as good descriptors for judging the reactivity and stability of the molecular species. A uniform decrease in E, and decrease in ω values with increasing H2 adsorption describes the stabilization of the metal clusters upon hydrogenation. η also shows a gradual increase in most of the cases. The aromaticity of Be3M2 and its hydrogenated species calculated in terms of NICS values at 0, 0.5, and 1 are highly negative and show very low variation with the number of H2 molecules loaded. For the Al4M2 cluster, however, most of the NICS values are found to be positive, even though it is an established fact that the Al42− species has aromatic stability. The variation of aromaticity with the number of adsorbed H2 molecule is also found to be quite random and significantly high. Clearly, NICS is not a good indicator for the Al4M2 clusters.
3.2 NON-METALLIC Aromatic Clusters
3.2.1 Planar Molecular Stars
Several non-metallic aromatic/anti-aromatic clusters are also explored to understand the influence of aromaticity on their hydrogen adsorbing or trapping potential. Replacing the H atoms from planar hydrocarbon rings like C4H4, C5H5−, and C6H6 with Li atoms results in the formation of star-shaped molecular clusters since the Li atoms prefer to bind two adjacent C atoms via a bridging bond (Figure 4) (Giri et al., 2011c). The partial positive charges on the Li centers enable them to readily adsorb H2 molecules. Each Li atom in C5Li5− can efficiently bind with only one H2 (binding energy of −2.1 kcal/mol per H2), whereas those in the neutral clusters (i.e., in C4Li4 and C6Li6) can bind up to two H2 molecules with binding energies ranging within −2.5 to −3.3 kcal/mol per H2. A thorough analysis of the NICS-scan (0–5 Å) plots (Figure 5) for each of the studied species provides useful information regarding the variation in the degree of aromaticity/anti-aromaticity with gradual hydrogen loading. The antiaromatic nature of C4H4 is found to be enhanced in its lithium analogue. It further increases in the 4H2@C4Li4 system, followed by a decrease in 8H2@C4Li4 where the NICS (0) value falls below those of the parent moieties (Figure 5A). Since the C4Li4 species is more likely to exist in the 8H2-bound form, it can be arguably stated that hydrogen adsorption on C4Li4 reduces its antiaromatic nature, which is favourable in terms of explaining the stability of these clusters. In the case of the aromatic C5H5− ring, lithiation increases its aromatic nature as evident from Figure 5B. The 5H2-bound C5Li5− complex follows the same trend as the parent moieties while moving from NICS (4) to NICS (1), i.e., they gradually decrease with decreasing distance from the ring center. However, unlike the parent moieties, 5H2@C5Li5− shows an unexpected rise in NICS (0) value rendering it anti-aromatic. Again, unlike in C5-species, the aromaticity reduces in the lithium analogue of C6H6 complex. Although all the species maintain their aromatic behaviour, the degree of aromaticity initially decreases with hydrogen loading (i.e., in 6H2@C6H6) with a final increase in the 12H2@C6H6 species (Figure 5C). These plots provide ample evidence regarding the dominant π-ring current in the C6 species compared to that in the C5 complexes, which results in an enhanced H2-trapping ability in the former.
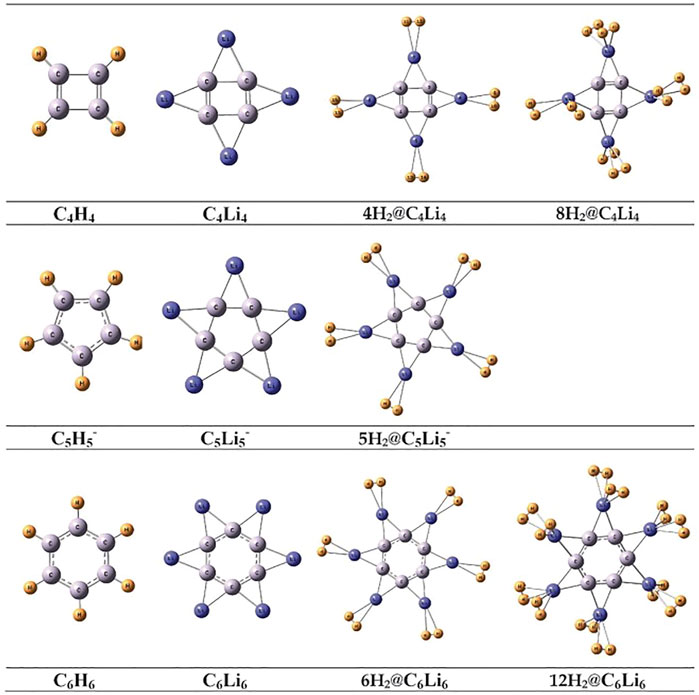
FIGURE 4. Optimized geometries of CnHn (n = 4–6), their Li analogues, and H2 trapped CnLin (n = 4–6) systems at B3LYP/6–311+G (d,p) level of theory (Reproduced from Giri et al., 2011c with permission from the PCCP Owner Societies).
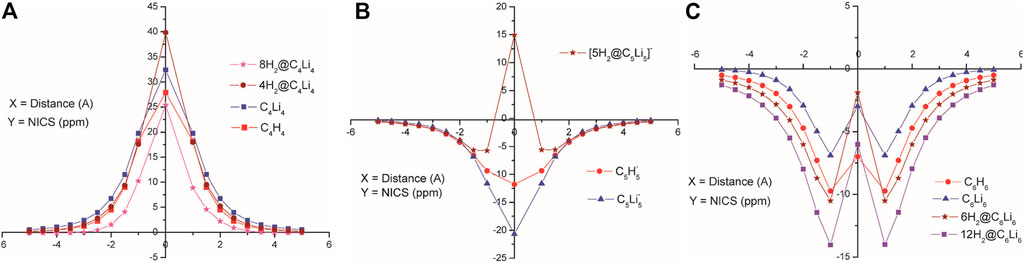
FIGURE 5. NICS-scan plots for the parent moieties, their Li analogues, and hydrogen loaded systems of (A) C4Li4, (B) C5H5−, and (C) C6H6 species (Reproduced from Giri et al., 2011c with permission from the PCCP Owner Societies).
3.2.2 Li-Doped Annular Systems and 3D Molecular Stars
The H2 binding ability of a series of lithium ion complexed hydrocarbons (Li+ above and below the planar ring), viz., C6H6, C10H8, and C14H10 are explored in the same study (Giri et al., 2011c), along with that of an F− ion stabilized tropylium complex. Each Li atom in these systems can store up to four H2 molecules (Figure 6A). The same is true for the C7H7F system, even though, unlike the Li+-complexed hydrocarbons, C7H7+ loses its planarity and hence aromaticity on complexation with F−. Other 3D molecular star-like systems like C5Li7+ (π-aromatic and σ-nonaromatic) and its Si analogue (σ- and π-aromatic) can bind up to a maximum of 21 H2 molecules (three per Li center) with a gravimetric wt% of 28.0 and 18.3, respectively (Pan et al., 2012; Perez-peralta et al., 2011; Tiznado et al.,2009) (Figure 6B). The Ge analogue has a maximum capacity of 19 H2 molecules with 9.3 wt% of H2 (Contreras et al., 2013). It is a well-known fact that temperature and pressure can act as tuning parameters in various adsorption/desorption processes. An interesting study performed on a series of Li clusters (BLi6+, O2Li5+, N2Li7+, B2Li11+, OLi3+, C2Li9+, F2Li3+, and FLi2+) was reported by Pan et al. (2012) where they have achieved enhanced interaction between Li and H2 by applying an external electric field. By gradually varying the field in the range 0.001–0.005 au, the negative ∆E value increases indicating improved interaction.
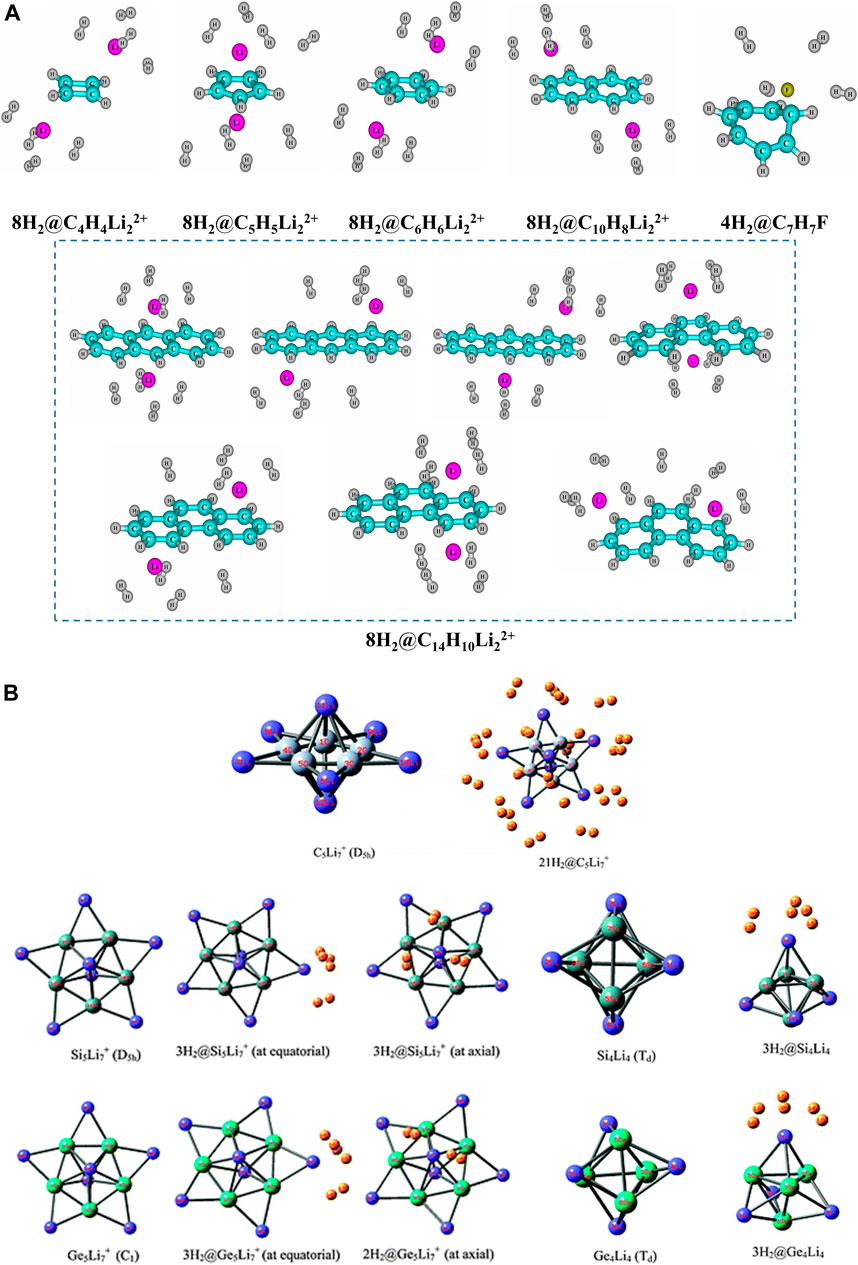
FIGURE 6. Optimized geometries of (A) maximum H2-loaded Li+/F−-doped annular systems, (B) 3D molecular star-like systems, C5Li7+ and its Si and Ge analogues (Reproduced from (A) Giri et al., 2011c, and (B) Pan et al., 2012 with permission from the PCCP Owner Societies).
3.2.3 Lithium Doped Boron Hydrides
A discussion on hydrogen storage warrants the inclusion of boron hydrides. Metal borohydrides like LiBH4 and NaBH4 are reported to be good hydrogen storage materials (Kojima et al., 2002; Züttel et al., 2003; Liang et al., 2010). The effect of aromaticity on the structural preference of both neutral and ionic boron hydrides with the general formula B3Hn (n = 3–9) was reported by Korkin et al. (1995). A similar study (Bandaru et al., 2012) was performed on several boron-lithium complexes with the general formula BxLiy (x = 2–6; y = 1, 2) where the cationic species show a higher H2 binding capacity than their neutral counterparts owing to the greater net positive charge on the Li centers in the former. Among various boron hydrides, B3H32− can be considered as the iso-electronic boron-analogue of the aromatic cyclopropenium ion (Garratt, 1986; Minkin et al., 1994). A theoretical study on B3H32− and its various Li doped species performed by Pan et al. (2011) investigates the H2 storage process via an interaction that lies somewhere between physisorption and chemisorption. The aromaticity of these systems is evident from the negative values of NICS (0) (ranging within −3.32–−29.38) and NICS (1) (varies from −7.48 to −17.91). The parent moiety itself is capable of adsorbing a maximum of 11 H2 molecules. Here, the importance of the dispersion interaction is clearly reflected from the interaction energy values obtained before and after including the dispersion corrected terms in the theoretical calculations. For example, the interaction energy per H2 molecule in the maximum H2-loaded systems ranges within −1.2–−1.9 kcal/mol, which changes to a range of −2.6–−5.6 kcal/mol after dispersion correction. Although judging by parameters like the H2 binding capacity, and gravimetric wt% of H2, the B3H32- system seems to be a preferable choice, it is yet to be experimentally realized. In that regard, B3 (μ-Li)3H3+ species is a better alternative with high aromatic stability. The H2 molecules are mostly bound by weak interaction and most of the adsorption process shown here is energonic in nature. Thus an optimal condition for these processes to be feasible would be that of high pressure (P) and low temperature (T). A T-P phase diagram (Figure 7) for the adsorption of 6 H2 molecules on B3 (μ-Li)3H3+ depicts the variation of free energy change with the change in T and P, where black markers indicate regions of favourable adsorption and red markers indicate that of favourable desorption.
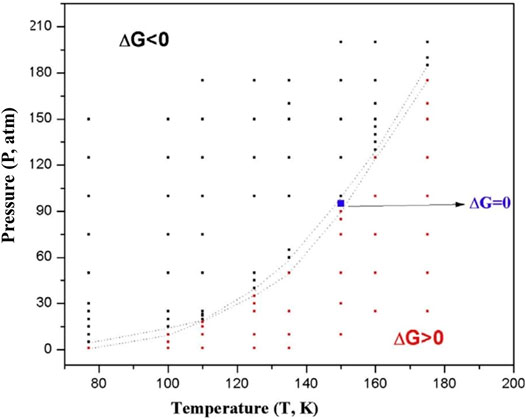
FIGURE 7. T-P phase diagram for the adsorption of six H2 molecules on B3 (μ-Li)3H3+. The black markers indicate regions of favourable adsorption and red markers indicate that of favourable desorption (Reproduced from Pan et al., 2011 with permission from John Wiley and Sons. Copyright © 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.).
3.2.4 Planar N42− and N64− Rings
A study (Duley et al., 2011) reported on the aromaticity and hydrogen storage in the inorganic analogues of cyclobutadiene and benzene rings, i.e., N42− and N64− reveals the anti-aromatic and aromatic natures, respectively. The NICS-scan plots of all four systems are provided in Figure 8 where it can be clearly seen that the NICS variation of N62− follows a similar trend as that of the benzene, whereas this is not the case for N42− and cyclobutadiene. The otherwise antiaromatic N42− ring shows aromaticity at a distance of 1 Å above the molecular plane, and gradually decreases away from the ring. Thus, a positive NICS (0) value and a negative NICS (1) value makes it σ-antiaromatic and π-aromatic. These anionic clusters are stabilized by complexation with lithium and calcium counterions to form N4Li2 and N6Ca2 (optimized structures provided in Figure 9). Each Li center is found to bind with up to four H2 (∆E = −1.2 kcal/mol) and each Ca center adsorbs up to six H2 molecules (∆E = −1.3 kcal/mol).
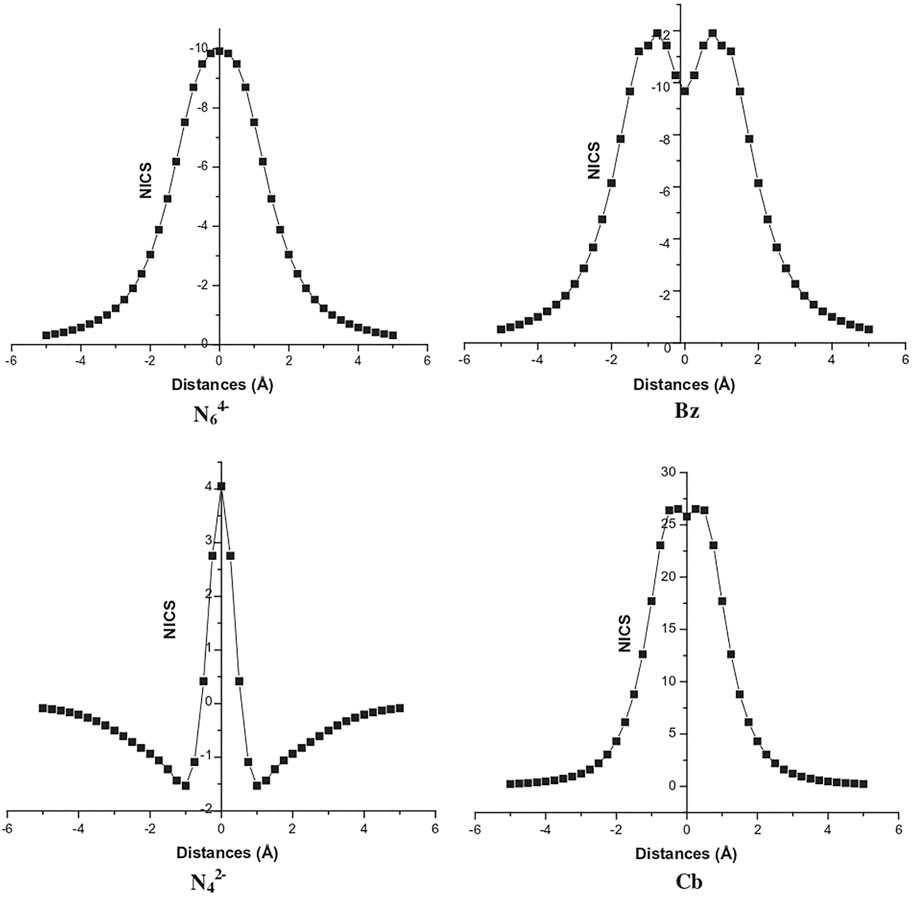
FIGURE 8. NICS-scan plots for N64−, benzene (Bz), N42−, and Cyclobutadiene (Cb) (Reprinted from Duley et al., 2011 with permission from Elsevier. Copyright© 2011 Elsevier B.V.).
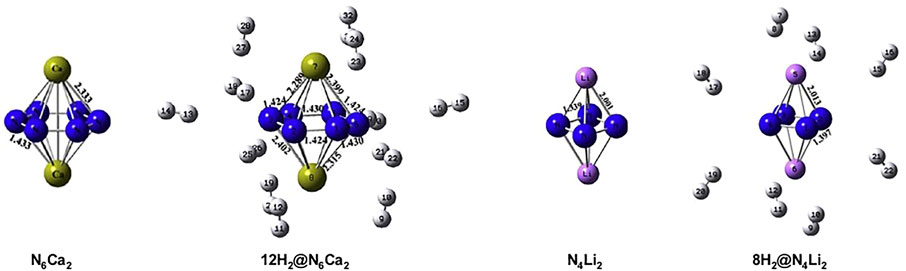
FIGURE 9. Optimized geometries of N6Ca2, N4Li2, and their respective maximum hydrogen loaded systems at B3LYP/6-31G(d) level of theory (Reproduced from Duley et al., 2011 with permission from Elsevier. Copyright© 2011 Elsevier B.V.).
3.2.5 C12N12, B12N12, and Ni-Decorated C12N12 Cages
C12N12 cage can have three possible isomers, viz., C12N12-A, C12N12-B, and C12N12-C with the optimized structures having D6d, C3, and C2 point group symmetries, respectively (Figure 10A) (Mondal et al., 2013). Unlike isomers A and B, C is an open cage structure and hence is the most stable of the lot. Although the NICS (0) for all the isomers are found to be negative, isomers A and B do not obey the Spherical Aromaticity rule [2(N+1)2 π-electrons], and isomer C does not follow the Open-Shell Spherical Aromaticity rule [(2N2 + 2N + 1) π-electrons]. Although, the hydrogen may be expected to bind at three possible sites: N, C, and bridging C and N, the minimum energy structures are obtained only for the N-site adsorption. All the isomers are capable to bind 12 H2 molecules providing a gravimetric wt% of 7.2 (Figure 10B). These clusters can have potential applications as high energy density materials (HEDMs) since they have high heat of formation values (∆H0f). These ∆H0f values (1747.759, 1758.442, and 1813.864 kcal/mol for isomers A, B, and C, respectively) are calculated using the following isodesmic reaction:
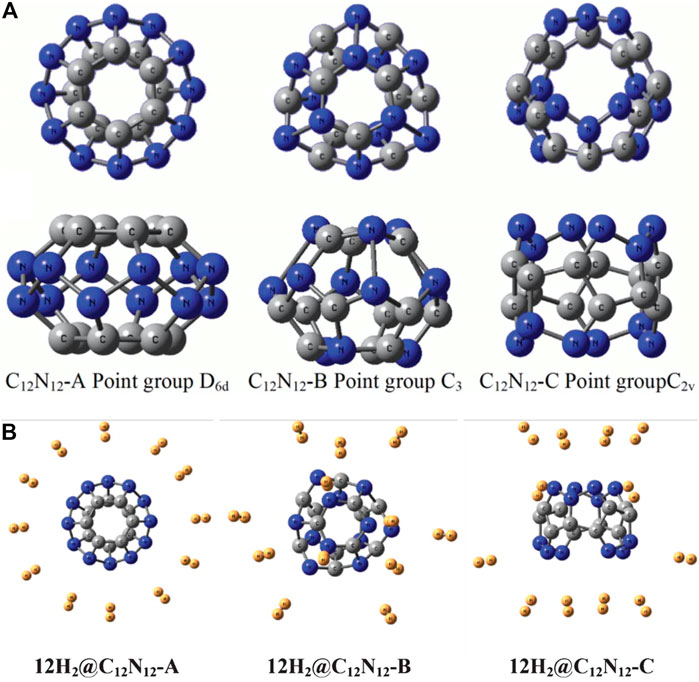
FIGURE 10. The optimized geometries of (A) the three isomers of C12N12 cage (top and side view), and (B) their respective 12 H2 loaded structures at B3LYP-D3/6-31G(d) level of theory (Reproduced from Mondal et al., 2013 with permission from the Royal Society of Chemistry).
The Ni-decorated analogue (Jana et al., 2020) of the cage can have three possible binding modes: bridging between C and N (denoted as XCN isomer), between 2 C atoms (XCC isomer), or between 2 N atoms (XNN isomer) (Figure 11A). Higher numbers of Ni decoration (up to four) in the N-(μ-Ni)-N bridging mode reveals the variation in aromaticity and H2-binding potential with the number of Ni atoms (Figure 11B). The reason for selecting N-(μ-Ni)-N bridging mode for this purpose is the highest amount of positive charge on the Ni center of the XNN isomer. The isodesmic reactions used to determine the ∆H0f of Ni-C12N12 (4,239.470 kcal/mol) and 4Ni-C12N12 (4,520.528 kcal/mol) are as follows:
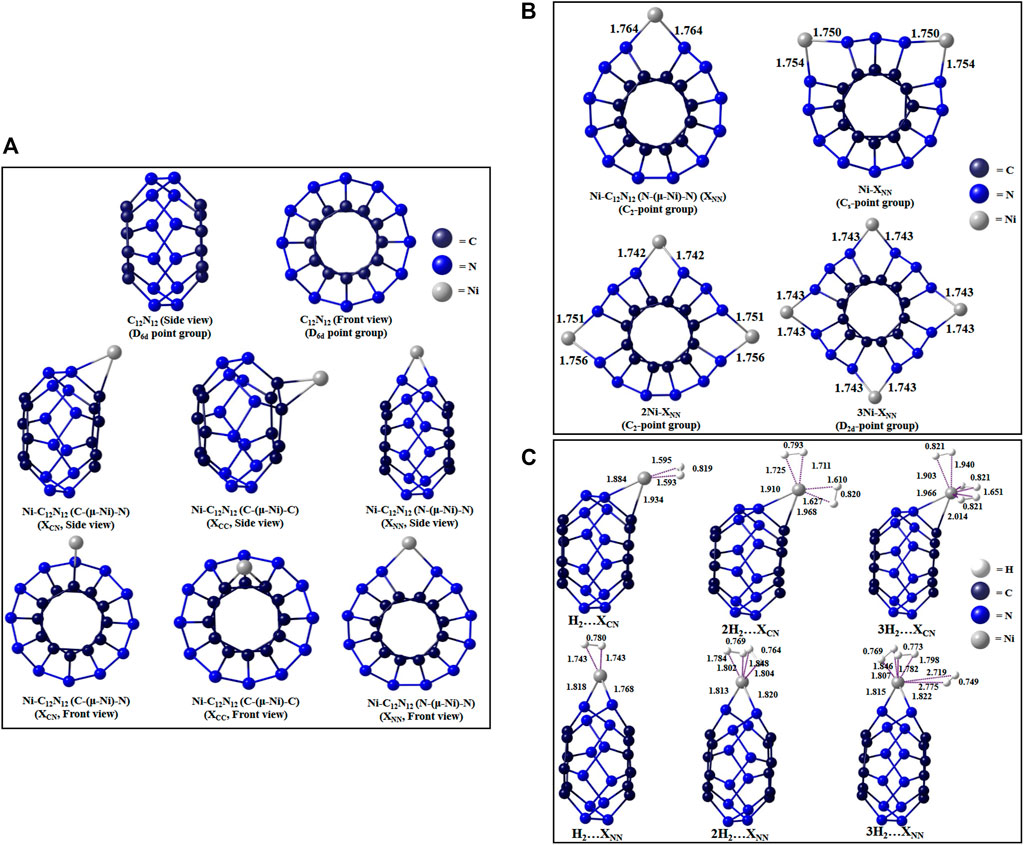
FIGURE 11. Optimized structures of (A) C12N12 and its three Ni-bound isomers, (B) nNi-decorated C12N12, (C) H2-trapped single Ni-bound C12N12 clusters at ωB97X-D/Def-TZVP level. (Reproduced from Jana et al., 2020 with permission from VBRI Press. Copyright ©2010–2021 VBRI Press)
Each Ni center on C12N12 is capable to adsorb up to three H2 molecules (Figure 11C). In the single Ni-doped clusters, the aromaticity increases in the order XCN < XCC < XNN, and in the case of multiple Ni-doping, the aromaticity increases uniformly with the number of Ni atoms.
The boron analogue of the C12N12 cage, i.e., B12N12 can trap hydrogen both endohedrally and exohedrally (Giri et al., 2011b). A total of 12 hydrogen molecules can be adsorbed in this cage system, the interaction energy per H2 molecule varies from −11.5 to −12 kcal/mol. The change in the reactivity descriptors with the gradual hydrogen uptake validates the CDFT based electronic structure principles. The aromaticity in terms of NICS (0) values of all the nH2@B12N12 (n = 0–12) species are plotted and presented in Figure 12. It is evident that among all the hydrogen-loaded species, the four, eight, and twelve numbers of H2 loaded clusters have high aromatic stability.
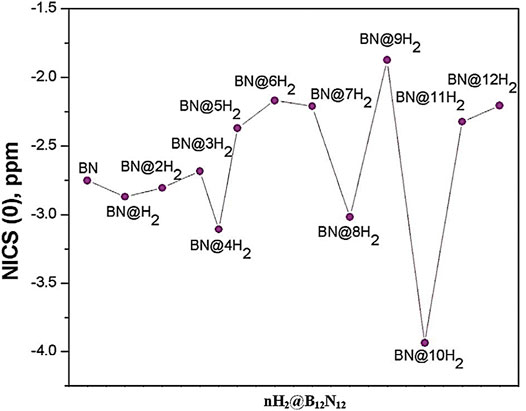
FIGURE 12. NICS (0) profile of all the hydrogen trapped B12N12 species. (Reproduced from Giri et al., 2011b with permission from Taylor & Francis. Copyright © 2011 Santanab Giri et al.)
In this report, we have described the influence of aromatic behaviour on the H2 trapping potential of various all-metal and nonmetal systems where it is measured in terms of nucleus independent chemical shift (NICS) values. The effect of aromaticity is not uniform throughout all systems. In some systems, the variation of aromaticity with the number of adsorbed H2 molecule is quite uniform and systemic, like in the cases of C4Li4, C5Li5−, and C6Li6 rings, N42− and N64− rings, the nNi-decorated C12N12 clusters. While for others, like that in the Al4M2 clusters, it is found to be quite random and significantly high. It deserves a careful scrutiny.
4 Conclusion
In this review, we have covered several case studies predicting all-metal and non-metal aromatic clusters with potential applications in hydrogen storage and highlighted the effect of aromaticity on the hydrogen uptake potential. The aromatic stabilization present in these clusters enables them to be applicable as promising building blocks for nanomaterials. The NICS-scan plots turn out to be very helpful in understanding the degree and trend in the variation of the aromatic/anti-aromatic nature. The presence of an electropositive center in the molecular clusters provides a suitable site for the H2 molecules to undergo a dipole–induced dipole interaction for adsorption. Temperature and pressure are good tuning parameters in controlling the adsorption/desorption process. In this context, a T-P phase diagram can provide proper guidance as to which temperature and pressure range could be ideal to undergo a favourable adsorption process. We have also highlighted the use of external electric field in tuning the H2 loading and release processes and hence overall improving the H2 trapping capacity of the cluster in question. For future research, the search for chemical frameworks with large surface area and high porosity can be made for better reversible hydrogen storage via physisorption having interaction energy closer to that of chemisorption, with a target of improving the gravimetric and volumetric storage capacity, favourable rates of adsorption and desorption, operating temperatures, and thermal conductivity. Molecular frameworks offering higher surface area to volume ratio can increase volumetric capacity. The binding energies can be increased by tuning the pore volume, and the thermal conductivity can be improved with the help of new and developed heat exchangers.
Author Contributions
PC came up with the concept and design of the review, wrote the abstract, reviewed the final manuscript. RP contributed towards the literature survey, writing the manuscript. All authors contributed to manuscript revision, read, and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Acknowledgments
PC would like to thank Dr. Weijie Yang for kindly inviting him to contribute an article to the research topic “Computational Design of Advanced Materials for Hydrogen Storage and Production” in the journal, Frontiers in Energy Research. He also thanks DST, New Delhi, for the J. C. Bose National Fellowship, grant number SR/S2/JCB-09/2009, and his students whose work is presented in this article. RP thanks CSIR for her fellowship.
References
Bandaru, S., Chakraborty, A., Giri, S., and Chattaraj, P. K. (2012). Toward Analyzing Some Neutral and Cationic Boron-Lithium Clusters (BxLiy x = 2–6; y = 1, 2) as Effective Hydrogen Storage Materials: A Conceptual Density Functional Study. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 112, 695–702. doi:10.1002/qua.23055
Chakraborty, A., Giri, S., and Chattaraj, P. K. (2011). Analyzing the Efficiency of M N -(C2H4) (M = Sc, Ti, Fe, Ni; N = 1, 2) Complexes as Effective Hydrogen Storage Materials. Struct. Chem. 22, 823–837. doi:10.1007/s11224-011-9754-7
Chattaraj, P. K., and Roy, D. R. (2007). Update 1 of: Electrophilicity index. Chem. Rev. 107, PR46–PR74. doi:10.1021/cr078014b
Chattaraj, P. K., Maiti, B., and Sarkar, U. (2003). Philicity: a Unified Treatment of Chemical Reactivity and Selectivity. J. Phys. Chem. A. 107, 4973–4975. doi:10.1021/jp034707u
Chattaraj, P. K., Bandaru, S., and Mondal, S. (2011a). Hydrogen Storage in Clathrate Hydrates. J. Phys. Chem. A. 115, 187–193. doi:10.1021/jp109515a
Chattaraj, P. K., Giri, S., and Duley, S. (2011b). Update 2 of: Electrophilicity index. Chem. Rev. 111, PR43–PR75. doi:10.1021/cr100149p
Chen, Z., Wannere, C. S., Corminboeuf, C., Puchta, R., and Schleyer, P. V. R. (2005). Nucleus-independent Chemical Shifts (NICS) as an Aromaticity Criterion. Chem. Rev. 105, 3842–3888. doi:10.1021/cr030088+
Contreras, M., Osorio, E., Ferraro, F., Puga, G., Donald, K. J., Harrison, J. G., et al. (2013). Isomerization Energy Decomposition Analysis for Highly Ionic Systems: Case Study of Starlike E5Li7+Clusters. Chem. Eur. J. 19, 2305–2310. doi:10.1002/chem.201203329
Dincǎ, M., Dailly, A., Liu, Y., Brown, C. M., Neumann, D. A., and Long, J. R. (2006). Hydrogen Storage in a Microporous Metal−Organic Framework with Exposed Mn2+ Coordination Sites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 16876–16883. doi:10.1021/ja0656853
Ding, R. G., Lu, G. Q., Yan, Z. F., and Wilson, M. A. (2001). Recent Advances in the Preparation and Utilization of Carbon Nanotubes for Hydrogen Storage. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol., 1, 7–29. doi:10.1166/jnn.2001.012
Dresselhaus, M. S., Williams, K. A., and Eklund, P. C. (1999). Hydrogen Adsorption in Carbon Materials. MRS Bull. 24, 45–50. doi:10.1557/S0883769400053458
Duley, S., Giri, S., Sathyamurthy, N., Islas, R., Merino, G., and Chattaraj, P. K. (2011). Aromaticity and Hydrogen Storage Capability of Planar and Rings. Chem. Phys. Lett. 506, 315–320. doi:10.1016/j.cplett.2011.03.037
Frisch, M. J., Trucks, G. W., Schlegel, H. B., Scuseria, G. E., Robb, M. A., Cheeseman, J. R., et al. (2003). Gaussian 03, Revision B. 03. Pittsburgh, PA: Gaussian, Inc.
Frisch, M. J., Trucks, G. W., Schlegel, H. B., Scuseria, G. E., Robb, M. A., Cheeseman, J. R., et al. (2009). Gaussian 09. Wallingford CT: Gaussian, Inc.
Froudakis, G. E. (2002). Hydrogen Interaction with Carbon Nanotubes: a Review of Ab Initio Studies. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 14, R453–R465. doi:10.1088/0953-8984/14/17/201
Giri, S., Roy, D. R., Duley, S., Chakraborty, A., Parthasarathi, R., Elango, M., et al. (2009). Bonding, Aromaticity, and Structure of Trigonal Dianion Metal Clusters. J. Comput. Chem. 31, 1815. doi:10.1002/jcc.21452
Giri, S., Chakraborty, A., and Chattaraj, P. K. (2011a). Potential Use of Some Metal Clusters as Hydrogen Storage Materials-A Conceptual DFT Approach. J. Mol. Model. 17, 777–784. doi:10.1007/s00894-010-0761-1
Giri, S., Chakraborty, A., and Chattaraj, P. (2011b). Stability and Aromaticity of nH2@B12N12(n=1-12) Clusters. Nano Rev. 2, 5767. doi:10.3402/nano.v2i0.5767
Giri, S., Bandaru, S., Chakraborty, A., and Chattaraj, P. K. (2011c). Role of Aromaticity and Charge of a System in its Hydrogen Trapping Potential and Vice Versa. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 13, 20602–20614. doi:10.1039/C1CP21752F
Hückel, E. (1931a). Quantentheoretische beitra¨ge zum benzolproblem I. Die elektronenkonfiguration des benzols und verwandter verbindungen. Z. Phys. Chem. 70, 204–286.
Hückel, E. (1931b). Quanstentheoretische beitra¨ge zum benzolproblem II. Quantentheorie der induzierten polarita¨ten. Z. Phys. Chem. 72, 310–337.
Hückel, E. (1932). Quantentheoretische beitra¨gezum problem der aromatischen und ungesa¨ttigten Verbindungen. III. Z. Phys. Chem. 76, 628–648.
IEA (2019). Share of World Total Final Consumption by Source. Paris: IEA. Available at: https://www.iea.org/data-and-statistics/charts/share-of-world-total-final-consumption-by-source-2019 (Accessed September 20, 2021).
Jana, G., Pal, R., and Chattaraj, P. K. (2018). Hydrogen Storage in Lithium Adsorbed and Polylithiated (OLi2) Heteroatom (B, N) Modified (2, 2) γ-graphyne Nanotube and its CO Sensing Potential: A Computational Study. J. Ind. Chem. Soc. 95, 1457–1464. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Ranita-Pal-2/publication/332497267_Hydrogen_storage_in_lithium_adsorbed_and_polylithiated_OLi_2_heteroatom_B_N_modified_22_-graphyne_nanotube_and_its_CO_sensing_potential_A_computational_study/links/60fe9f4a1e95fe241a8bdbde/Hydrogen-storage-in-lithium-adsorbed-and-polylithiated-OLi-2-heteroatom-B-N-modified-2-2-graphyne-nanotube-and-its-CO-sensing-potential-A-computational-study.pdf.
Jana, G., Pal, R., Mondal, S., and Chattaraj, P. K. (2020). Do The Ni Binding Modes on C12N12 Cluster Influence its H2 Trapping Capability? Adv. Mater. Lett. 11, 20041500. doi:10.5185/amlett.2020.041500
Kojima, Y., Suzuki, K.-i., Fukumoto, K., Sasaki, M., Yamamoto, T., Kawai, Y., et al. (2002). Hydrogen Generation Using Sodium Borohydride Solution and Metal Catalyst Coated on Metal Oxide. Int. J. Hydrogen Energ. 27, 1029–1034. doi:10.1016/S0360-3199(02)00014-9
Korkin, A. A., Schleyer, P. V. R., and McKee, M. L. (1995). Theoretical Ab Initio Study of Neutral and Charged B3Hn (N = 3-9) Species. Importance of Aromaticity in Determining the Structural Preferences. Inorg. Chem. 34, 961–977. doi:10.1021/ic00108a031
Kubas, G. J. (2001). Metal Dihydrogen and Bond Complexes-Structure, Theory and Reactivity. New York: Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishing.
Kuznetsov, A. E., and Boldyrev, A. I. (2004). A Single π-bond Captures 3, 4 and 5 Atoms. Chem. Phys. Lett. 388, 452–456. doi:10.1016/j.cplett.2004.02.083
Li, X., Kuznetsov, A. E., Zhang, H.-F., Boldyrev, A. I., and Wang, L.-S. (2001). Observation of All-Metal Aromatic Molecules. Science 291, 859–861. doi:10.1126/science.291.5505.859
Liang, Y., Dai, H.-B., Ma, L.-P., Wang, P., and Cheng, H.-M. (2010). Hydrogen Generation from Sodium Borohydride Solution Using a Ruthenium Supported on Graphite Catalyst. Int. J. Hydrogen Energ. 35, 3023–3028. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2009.07.008
Lochan, R. C., and Head-Gordon, M. (2006). Computational Studies of Molecular Hydrogen Binding Affinities: The Role of Dispersion Forces, Electrostatics, and Orbital Interactions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 8, 1357–1370. doi:10.1039/B515409J
Minkin, V., Glukhovtsev, M., and Simkin, E. (1994). Aromaticity and Antiaromaticity. Electronic and Structural Aspects. New York: Wiley-Interscience.
Mondal, S., Srinivasu, K., Ghosh, S. K., and Chattaraj, P. K. (2013). Isomers of C12N12 as Potential Hydrogen Storage Materials and the Effect of the Electric Field Therein. RSC Adv. 3, 6991–7000. doi:10.1039/C3RA00013C
Pan, S., Giri, S., and Chattaraj, P. K. (2011). A Computational Study on the Hydrogen Adsorption Capacity of Various Lithium-Doped boron Hydrides. J. Comput. Chem. 33, 425–434. doi:10.1002/jcc.21985
Pan, S., Merino, G., and Chattaraj, P. K. (2012). The Hydrogen Trapping Potential of Some Li-Doped star-like Clusters and Super-alkali Systems. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 14, 10345–10350. doi:10.1039/C2CP40794A
Parr, R. G., and Pearson, R. G. (1983). Absolute Hardness: Companion Parameter to Absolute Electronegativity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 105, 7512–7516. doi:10.1021/ja00364a005
Parr, R. G., and Yang, W. (1984). Density Functional Approach to the Frontier-Electron Theory of Chemical Reactivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 106, 4049–4050. doi:10.1021/ja00326a036
Parr, R. G., and Yang, W. (1989). Density Functional Theory of Atoms and Molecules. New York: Oxford University Press.
Parr, R. G., Donnelly, R. A., Levy, M., and Palke, W. E. (1978). Electronegativity: the Density Functional Viewpoint. J. Chem. Phys. 68, 3801–3807. doi:10.1063/1.436185
Parr, R. G., Szentpály, L. V., and Liu, S. (1999). Electrophilicity index. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 121, 1922–1924. doi:10.1021/ja983494x
Peng, Q., Chen, G., Mizuseki, H., and Kawazoe, Y. (2009). Hydrogen Storage Capacity of C60(OM)12 (M=Li and Na) Clusters. J. Chem. Phys. 131, 214505. doi:10.1063/1.3268919
Perez-Peralta, N., Contreras, M., Tiznado, W., Stewart, J., Donald, K. J., and Merino, G. (2011). Stabilizing Carbon-Lithium Stars. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 13, 12975–12980. doi:10.1039/C1CP21061K
Rosi, N. L., Eckert, J., Eddaoudi, M., Vodak, D. T., Kim, J., O'Keeffe, M., et al. (2003). Hydrogen Storage in Microporous Metal-Organic Frameworks. Science 300, 1127–1129. doi:10.1126/science.1083440
Roy, D. R., and Chattaraj, P. K. (2008). Reactivity, Selectivity, and Aromaticity of Be32- and its Complexes. J. Phys. Chem. A. 112, 1612–1621. doi:10.1021/jp710820c
Schleyer, P. V. R., Maerker, C., Dransfeld, A., Jiao, H., and van Eikema Hommes, N. J. R. (1996). Nucleus-independent Chemical Shifts: a Simple and Efficient Aromaticity Probe. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 118, 6317–6318. doi:10.1021/ja960582d
Shevlin, S. A., and Guo, Z. X. (2006). Transition-metal-doping-enhanced Hydrogen Storage in boron Nitride Systems. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 153104. doi:10.1063/1.2360232
Srinivasu, K., Chandrakumar, K. R. S., and Ghosh, S. K. (2009). Computational Investigation of Hydrogen Adsorption by Alkali-Metal-Doped Organic Molecules: Role of Aromaticity. ChemPhysChem 10, 427–435. doi:10.1002/cphc.200800520
Srinivasu, K., Ghosh, S. K., Das, R., Giri, S., and Chattaraj, P. K. (2012). Theoretical Investigation of Hydrogen Adsorption in All-Metal Aromatic Clusters. RSC Adv. 2, 2914–2922. doi:10.1039/C2RA00643J
Ströbel, R., Garche, J., Moseley, P. T., Jörissen, L., and Wolf, G. (2006). Hydrogen Storage by Carbon Materials. J. Power Sourc. 159, 781–801. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2006.03.047
Tiznado, W., Perez-Peralta, N., Islas, R., Toro-Labbe, A., Ugalde, J. M., and Merino, G. (2009). Designing 3-D Molecular Stars. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 9426–9431. doi:10.1021/ja903694d
U.S. Department of Energy, USCAR (2017). Target Explanation Document: Onboard Hydrogen Storage for Light-Duty Fuel Cell Vehicles. Available: https://www.energy.gov/sites/default/files/2017/05/f34/fcto_targets_onboard_hydro_storage_explanation.pdf (Accessed September 20, 2021).
Wagemans, R. W. P., van Lenthe, J. H., de Jongh, P. E., Van Dillen, A. J., and de Jong, K. P. (2005). Hydrogen Storage in Magnesium Clusters: Quantum Chemical Study. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 16675–16680. doi:10.1021/ja054569h
Wang, Q., Sun, Q., Jena, P., and Kawazoe, Y. (2009). Potential of AlN Nanostructures as Hydrogen Storage Materials. ACS Nano 3, 621–626. doi:10.1021/nn800815e
World Nuclear Association Website (2016). Heat Values of Various Fuels. Available at: https://www.world-nuclear.org/information-library/facts-and-figures/heat-values-of-various-fuels.aspx (Accessed September 20, 2021).
Wu, X., Gao, Y., and Zeng, X. C. (2008). Hydrogen Storage in Pillared Li-Dispersed boron Carbide Nanotubes. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 8458–8463. doi:10.1021/jp710022y
Wu, G., Wang, J., Zhang, X., and Zhu, L. (2009). Hydrogen Storage on Metal-Coated B80 Buckyballs with Density Functional Theory. J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 7052–7057. doi:10.1021/jp8113732
Xu, W., Takahashi, K., Matsuo, Y., Hattori, Y., Kumagai, M., Ishiyama, S., et al. (2007). Investigation of Hydrogen Storage Capacity of Various Carbon Materials. Int. J. Hydrogen Energ. 32, 2504–2512. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2006.11.012
Yildirim, E. K., and Güvenç, Z. B. (2009). A Density Functional Study of Small Li-B and Li-B-H Clusters. Int. J. Hydrogen Energ. 34, 4797–4816. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2009.03.051
Keywords: hydrogen storage, aromaticity, all-metal clusters, nonmetal clusters, conceptual density functional theory
Citation: Pal R and Chattaraj PK (2021) Aromatic Clusters as Potential Hydrogen Storage Materials. Front. Energy Res. 9:786967. doi: 10.3389/fenrg.2021.786967
Received: 30 September 2021; Accepted: 20 October 2021;
Published: 03 November 2021.
Edited by:
Weijie Yang, North China Electric Power University, ChinaReviewed by:
Xiaoshuo Liu, Southeast University, ChinaChongchong Wu, University of Calgary, Canada
Xun-Lei Ding, North China Electric Power University, China
Copyright © 2021 Pal and Chattaraj. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Pratim Kumar Chattaraj, cGtjQGNoZW0uaWl0a2dwLmFjLmluOw==, MDAwMC0wMDAyLTU2NTAtNzY2Ng==
 Ranita Pal
Ranita Pal Pratim Kumar Chattaraj
Pratim Kumar Chattaraj