- 1State Key Laboratory of New Targets Discovery and Drug Development for Major Diseases, Gannan Innovation and Translational Medicine Research Institute, Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou, China
- 2State Key Laboratory of New Targets Discovery and Drug Development for Major Diseases, Gannan Innovation and Translational Medicine Research Institute, Ganzhou, China
- 3Department of Cardiology, Renmin Hospital, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
- 4Medical Science Research Center, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
- 5State Key Laboratory of New Targets Discovery and Drug Development for Major Diseases, Gannan Innovation and Translational Medicine Research Institute, Key Laboratory of Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Diseases, Ministry of Education, Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou, China
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a multisystem metabolic disorder, marked by abnormal lipid accumulation and intricate inter-organ interactions, which contribute to systemic metabolic imbalances. NAFLD may progress through several stages, including simple steatosis (NAFL), non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), cirrhosis, and potentially liver cancer. This disease is closely associated with metabolic disorders driven by overnutrition, with key pathological processes including lipid dysregulation, impaired lipid autophagy, mitochondrial dysfunction, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, and local inflammation. While hepatic lipid metabolism in NAFLD is well-documented, further research into inter-organ communication mechanisms is crucial for a deeper understanding of NAFLD progression. This review delves into intrahepatic networks and tissue-specific signaling mediators involved in NAFLD pathogenesis, emphasizing their impact on distal organs.
1 Introduction
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a metabolic disorder characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the liver in the absence of alcohol or other known liver toxins. The disease progresses through various stages: from simple hepatic steatosis (NAFL) to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), then to liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and potentially hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (1). Current definitions of NAFLD emphasize the exclusion of other causes of liver disease and the presence of specific liver histopathological changes. Growing understanding of NAFLD pathophysiology highlights its strong link to metabolic dysregulation, with obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and hyperlipidemia as key risk factors. Recognizing these metabolic underpinnings, a 2022 consensus favored the term “metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease” (MAFLD) (2)to more comprehensively reflect the disease’s etiology. However, due to varying study aims and scope, the literature continues to utilize both NAFLD and MAFLD designations (3). This review, therefore, does not prioritize a specific terminological definition but rather examines the broader range of evidence related to NAFLD/MAFLD.
The increasing prevalence of NAFLD is linked to lifestyle factors, including physical inactivity and high caloric intake. As treatments for hepatitis C improve and cases of hepatitis B decrease, NAFLD is anticipated to become a leading cause of liver-related health issues and mortality, with predictions indicating it may surpass other conditions as the primary reason for liver transplantation by 2030 (4). Currently, therapeutic options are limited to dietary changes and exercise, with preclinical pharmacological interventions showing only modest efficacy or notable side effects. Although the FDA approved Resmetirom for NAFLD treatment in late 2023, its Phase III clinical data demonstrated only up to 30% effectiveness (5, 6). Therefore, there is an immediate necessity to broaden and thoroughly comprehend the mechanisms underlying NAFLD, as well as to identify practical therapeutic targets or interventions for its treatment.
The primary driver of fat accumulation in NAFLD is excessive dietary intake of sugars and fats. This abnormal fat buildup impairs lipid metabolism and transport, leading to the production of lipotoxic substances that trigger stress responses in hepatocyte organelles. These metabolic disturbances also affect other organs, altering their metabolism and prompting them to release signaling factors that influence NAFLD progression. NAFLD is recognized as a multisystem metabolic disorder (7), associated with various comorbidities including obesity, T2DM, hypertension, dyslipidemia, atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), and chronic kidney disease (CKD) (8–11).
This review delves into the intrahepatic network mechanisms underlying NAFLD pathogenesis and examines the roles of tissue-specific signaling mediators, emphasizing their impact on distant organs throughout NAFLD development and its complications. The discussion will begin with adipose tissue, closely linked to NAFLD pathophysiology, and extend to other critical tissues such as the intestine, skeletal muscle, and endocrine pancreas.
2 Methods
The purpose of this literature review was to identify comprehensive evidence that elucidates a network of inter-organ metabolic interactions in NAFLD, with a particular emphasis on the most recent data published within the last 3 years. To achieve this, we conducted a search on PubMed on September 1, 2024, utilizing the following filters:
Key Words: (NAFLD or MAFLD) AND (Adipose); (NAFLD) AND (Brain); (NAFLD) AND (Gastrointestinal tract); (NAFLD) AND (Pancreas); (NAFLD) AND (Bone); (NAFLD) AND (Skeletal muscle); (NAFLD) AND (Exercise).
Article type: Clinical Trial, Meta-Analysis, Randomized Controlled Trial, Review, Systematic Review.
Species: human, animals.
Age: child, adult male, adult female, elderly.
Publication date: within 3 years; Accepted PubMed articles outside of 3 years if they demonstrated strong relevance to the review’s objectives.
Inclusion criteria: Disease burden and epidemiology of NAFLD, Intrahepatic network mechanisms associated with the development of NAFLD, Association of NAFLD with other metabolic disorders and factors influencing its progression, Impact of NAFLD development on extrahepatic organs, Role of novel biomarkers indicating crosstalk between extrahepatic organs in NAFLD, Interventions targeting systemic metabolic dysfunction related to NAFLD.
Quality and limitations of cited studies.
Quality: Rigorous selection criteria were employed to ensure the inclusion of high-quality studies; Attention was paid to the most recent research data from the last 3 years, capturing the latest advancements in the field; The wide range of studies covered, including clinical trials, meta-analyses, and systematic reviews, provided a wealth of information for a comprehensive understanding of the relationships between organs in metabolic diseases associated with NAFLD.
Limitations: Many studies relied on preclinical models (e.g., mouse and rat models) to explore the correlation between NAFLD and metabolic factors, and the results of these models may not be fully applicable to humans, with certain limitations; due to the diverse types of included studies, there may be heterogeneity in study design, sample size, and research methodology, which may result in controversial findings; The inclusion of articles published only in English may have excluded high-quality studies in other languages, which may lead to a certain impact on the comprehensiveness of the findings; although only the latest research progress in the past 3 years has been included, due to the large number of NAFLD-related studies and the limited space, the authors may not be able to be as in-depth and detailed in discussing the individual studies, which may lead to certain important points or findings not being fully elaborated or verified.
2.1 Intrahepatic network and metabolic signaling in NAFLD
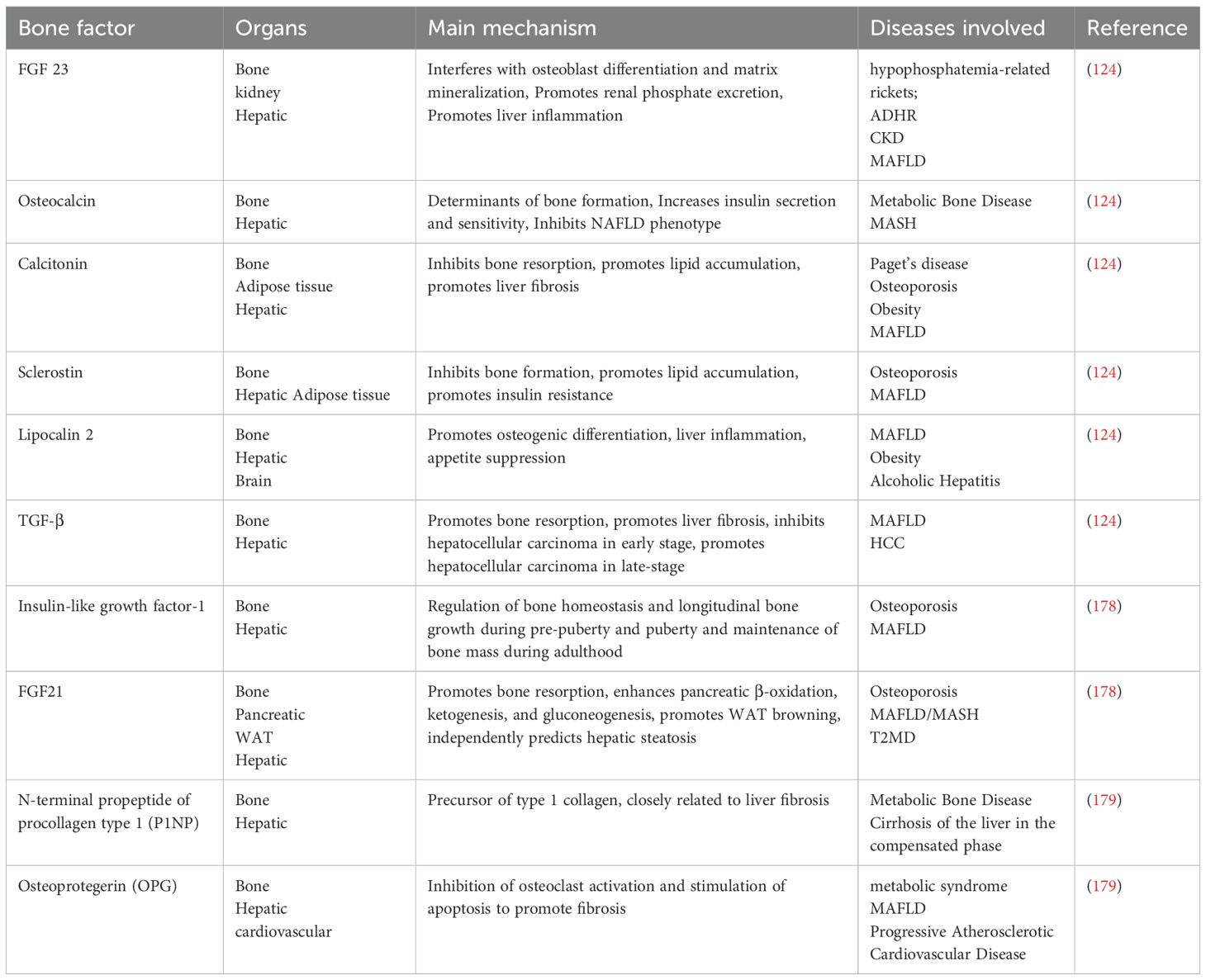
The excessive accumulation of lipids in the liver is a primary driver of NAFLD. Lipids, which act as pivotal signaling molecules across various pathways, are implicated in this process. Aberrant fat deposition in the liver not only contributes to hepatic inflammation and fibrosis but also disrupts the function of intrahepatic organelles and has detrimental effects on extrahepatic organs (12). Therefore, a thorough understanding of the origins and ultimate destinations of fatty acids within the liver is essential (Figure 1).
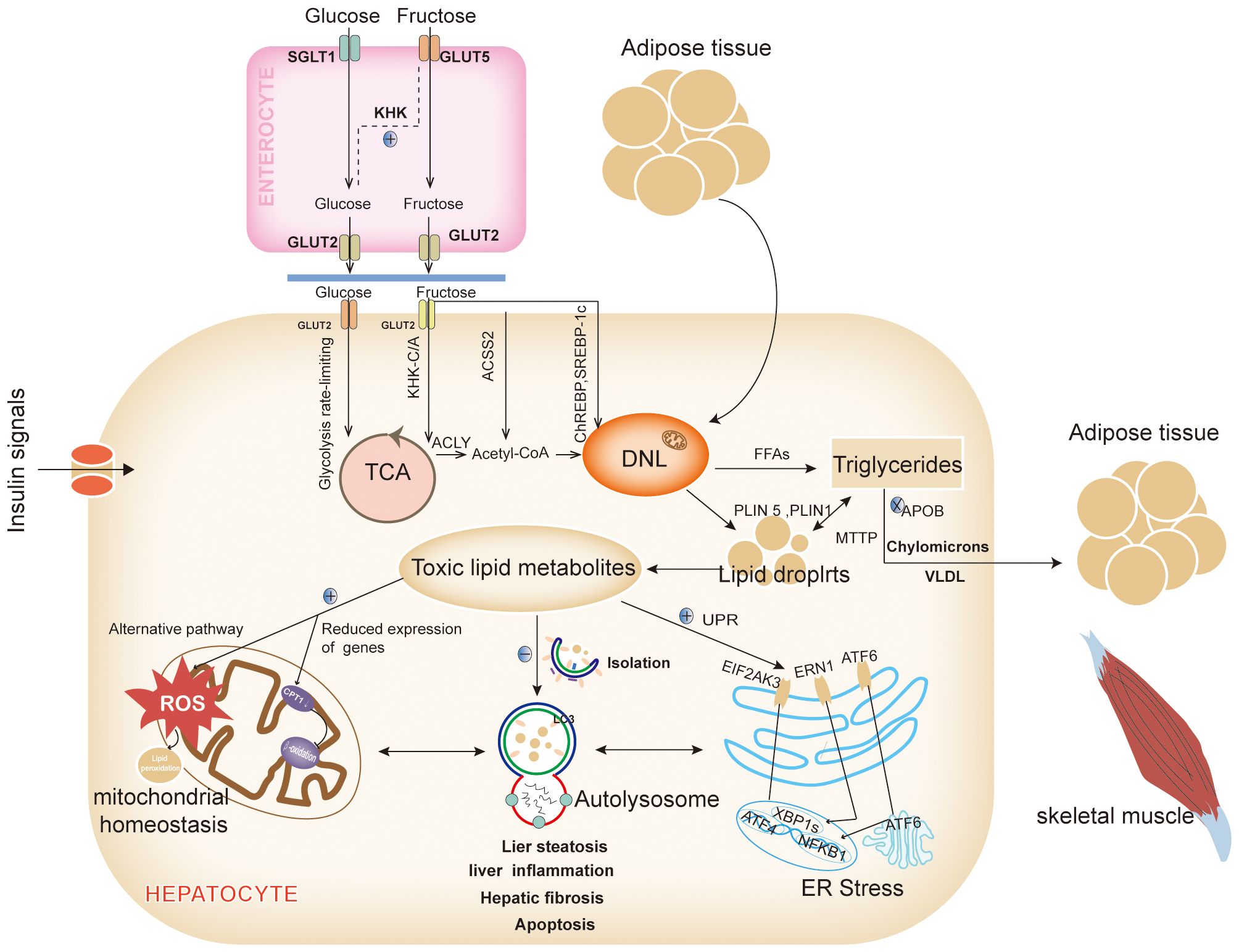
Figure 1. Intrahepatic network and metabolic signaling in NAFLD. The most important reason for the alteration of the metabolic signaling network in the liver is the abnormalities in the hepatic lipid synthesis pathway and/or lipid metabolism pathway, which leads to the abnormal accumulation of intrahepatic lipids, the generation of large amounts of lipotoxic substances in the liver, affects multiple metabolic pathways, disrupts the mitochondrial homeostasis, inhibits the clearance of lipid autophagy, and promotes the ER stress. DNL, Lipid de novo synthesis; GLUT 2, Glucose transporter 2; TCA, The tricarboxylic acid; KHK-C/A, Ketohexose kinase - C/A; ACLY, ATP citrate lyase; Acetyl-CoA, Acetyl-coenzyme a; CPT1α, Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1a; ACSS2, Acetyl-CoA synthetase 2; ChREBP, Carbohydrate-responsive element-binding proteins; LDs, lipid droplets; VLDLs, Very low-density lipoproteins; MTTP, Microsomal TAG transport protein; APOB, Apolipoprotein B; FFAs, Free fatty acids; PLIN, Perilipin; LC3, Light chain 3; UPR, Unfolded protein response; EIF2AK3(PERK), Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 alpha kinase 3; ATF 6, Activated transcription factor 6; ERN1(IRE1), ER to nucleus signaling 1; NFKB, Nuclear factor kappa B; XBP1s, X-box binding proteins 1; ROS, Reactive oxygen species (Drawing by Adobe Illustrator 2020).
2.1.1 Fatty acid synthesis
Under normal dietary and metabolic conditions, intrahepatic fatty acids primarily originate from dietary lipids and the mobilization of adipose tissue. However, in states of overnutrition or metabolic imbalance, dietary carbohydrates significantly contribute to the development of NAFLD. Although free saturated fatty acids (SFAs) more markedly increase intrahepatic triglyceride content compared to free sugars at equivalent intake levels (13), SFAs exert their effects mainly through adipose tissue lipids. In contrast, free sugars enhance hepatic lipid de novo synthesis (DNL). High-SFA foods are often perceived as greasy, making it challenging to consume them in quantities higher than free sugars (13).
Among free sugars, fructose, and glucose are the primary source materials for DNL. Glucose enters the bloodstream via the intestinal sodium-dependent glucose cotransporter protein 1 (14) and is subsequently transported to hepatocytes by the insulin-independent glucose transporter-2 (GLUT -2), where it is either stored as glycogen or metabolized for energy (14). Fructose, on the other hand, is particularly harmful. While glucose is regulated and undergoes a rate-limiting glycolytic process in hepatocytes (14), fructose can bypass these regulatory mechanisms (14). Low doses of fructose are metabolized to glucose in the intestines via GLUT-5 and then enter the liver as glucose (13). However, high doses of fructose exceed intestinal clearance capacity and are absorbed as fructose through the fructose-specific GLUT2. Inside the liver, fructose is phosphorylated by ketohexose kinase-C/A (KHK-C/A), leading to citric acid production through adenosine triphosphate (ATP) citrate lyase, which provides cytoplasmic acetyl-CoA for DNL (15, 16). Additionally, KHK-C upregulates acetylation of global proteins, including carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1α (CPT1α), thereby promoting lipogenesis and inhibiting lipolysis (17). High fructose intake also accelerates the provision of cytoplasmic acetyl-CoA for DNL via acetyl-CoA synthetase 2 (ACSS2) (16). Moreover, excess fructose metabolism depletes ATP, activates the adenosine monophosphate (AMP) deaminase pathway, and leads to overproduction of uric acid, which reduces fatty acid β-oxidation and further promotes DNL (18). Excess fructose activates various signaling pathways, such as carbohydrate-responsive element-binding protein (ChREBP), which in turn upregulates the expression of acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), fatty acid synthase (FAS), and other enzymes involved in DNL (19).
Fructose also affects NAFLD development through extrahepatic organs. It increases intestinal epithelial permeability, allowing toxic microbial metabolites to enter the liver and activate inflammatory signals in hepatocytes and immune cells. Prolonged fructose intake exacerbates intestinal dysbiosis, which further amplifies inflammatory responses. Additionally, fructose affects the central nervous system, influencing neuronal and hormonal signals related to appetite and promoting increased food intake.
2.1.2 Fatty acid metabolism
Fatty acids enter the liver through two primary pathways: 1) regulated by metabolic signals and oxidative processes, and 2) stored as lipid droplets (LDs). A small proportion of fatty acids entering the liver is utilized for energy through β-oxidation. However, the majority of these fatty acids respond to metabolic signals and are exported from the liver as triglycerides (TAGs) via celiac microparticles and very low-density lipoproteins (VLDLs). These lipoproteins facilitate the delivery of energy to peripheral tissues, including adipose tissue, skeletal muscle, and the heart. An abnormal accumulation of free fatty acids (FFAs) within the liver occurs when metabolic signals, such as those from insulin, glucagon, and thyroid hormones, are disrupted. Additionally, genetic defects, such as mutations in the microsomal triglyceride transport protein and apolipoprotein B, can inhibit the loading of TAGs into VLDLs, thereby impeding their export from the liver through apolipoproteins (20).
Excess fatty acids that are not oxidized for energy are stored in the liver as LDs after packaging by the ER. The liver’s capacity to store LDs is limited, and excessive accumulation leads to LDs lipolysis, which releases FFAs and results in inflammatory damage and hepatocyte death. Alterations in the structure and function of LDs are crucial in the development of NAFLD (21). For instance, overexpression of Perilipin (PLIN) 5, a Perilipin family protein associated with LD development, has been linked to increased fibrosis and apoptosis (22), while PLIN1 shifted-code variants have been associated with hepatic vascularization (23). Conversely, the function of LDs is closely related to mitochondria and autophagy, which are essential for maintaining lipid metabolism homeostasis (24).
2.1.3 Lipid autophagy
Excess lipids are eliminated from the liver through the process of lipid autophagy, which prevents the abnormal accumulation of lipids. In response to in vivo signaling, LDs recruit light chain 3 (LC3), initiating the formation of restriction membranes via autophagy-related protein 7 (ATG7)-dependent mechanisms. These restriction membranes, known as autophagosomes, encapsulate the LDs and transport them to lysosomes for degradation (25). However, a high-fat diet (HFD) induces LC3 positivity in hepatic LDs, leading to a reduction in autophagic isolation (25). Chronic overnutrition diminishes hepatic ATG7 levels, thereby impairing autophagic activity (26). This impairment is evident in ATG7 knockout mice, which exhibit reduced lipolysis, up-regulated expression of thermogenic genes, and restored adipose tissue development in brown and inguinal adipose tissue (27). Autophagy in adipose tissue is critical for recruiting various cell types involved in fat storage, including neurons in the hypothalamus, foam cells derived from macrophages, lymphocytes, adipocytes, and gastrointestinal epithelial cells (24). Disruption of hepatic autophagy contributes to insulin resistance (IR) and exacerbates ER stress (26).
2.1.4 ER stress
The ER is particularly susceptible to lipotoxicity, which can disrupt the regulation of the unfolded protein response (UPR). The UPR is orchestrated by three key transmembrane proteins located in the ER: eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 alpha kinase 3 (EIF2AK3, also known as PERK), activating transcription factor (ATF) 6, and ER to nucleus signaling 1 (ERN1, also known as IRE1). These proteins collectively modulate cellular inflammation and apoptosis (28). EIF2AK3 facilitates the nuclear translocation of ATF4, thereby promoting autophagy. Concurrently, EIF2AK3 activates the phosphatidylinositide-3-kinase(PI3K) -AKT serine/threonine kinase 1 (AKT1) signaling cascade and cooperates with the ERN1-triggered 5’ AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway to drive autophagy and inhibit apoptosis (29). ERN1 further mediates the translocation of mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 (MAPK8, also known as JNK1) and nuclear factor kappa B (NFKB), enhancing the expression of genes associated with apoptosis and inflammation. Additionally, ERN1 activates X-box binding protein 1, which triggers the c-Jun N-terminal kinase(JNK) and NFKB kinase subunit β (IKBKB)- NFKB1 signaling pathways, influencing inflammatory processes and reactive oxygen species production (29). ATF6, upon translocating to the Golgi, undergoes cleavage and subsequently translocates to the nucleus, where it upregulates genes involved in apoptosis, autophagy, and inflammation (28). Furthermore, ER stress induces angiopoietin-like protein 8, inhibiting lipoprotein lipase activity and promoting autophagy (30).
2.1.5 Mitochondrial homeostasis
Mitochondria are the principal sites for fatty acid β-oxidation, with FFAs entering the mitochondria for oxidative catabolism via the CPT1 protein located in the outer mitochondrial membrane. Inhibition of CPT1 impairs fatty acid β-oxidation, leading to reduced degradation of FFAs. In the hypothalamus, AMPK phosphorylates ACC and lowers malonyl-CoA levels to regulate CPT1 activity. This regulatory axis has been explored as a target for therapeutic interventions in NASH (31). When FFAs overload occurs in the liver, the mitochondrial respiratory chain activity is upregulated, enhancing various specific fatty acid oxidation processes including propionic acid oxidation, unsaturated fatty acid oxidation, alpha-oxidation, and omega-oxidation. This upregulation leads to an overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) beyond the capacity of normal antioxidant defenses, resulting in oxidative stress and progression towards NASH. Concurrently, the surplus ROS triggers lipid peroxidation, producing harmful byproducts such as 4-Hydroxynonenal and malondialdehyde, these compounds exacerbate mitochondrial dysfunction and damage plasma and intracellular membranes, contributing to cell necrosis (32). Researches have shown reduced expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ)- coactivator 1α(PGC-1α), nuclear respiratory factor 1, and mitochondrial transcription factor A in the livers of individuals with NAFLD, indicating that mitochondrial number and function are crucial in NAFLD pathogenesis (33). Additionally, lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3 (LPCAT3) is significantly inhibited in human NASH livers. LPCAT3 deficiency increases the saturation of phospholipids in the mitochondrial inner membrane and heightens stress-induced mitochondrial autophagy, leading to decreased mitochondrial content, increased fragmentation, and subsequent inflammatory and fibrotic consequences associated with NASH (34).
2.2 Extrahepatic organ-specific network
2.2.1 Adipose tissue
Changes in adipose tissue biology are pivotal in the onset of NAFLD, affecting both energy balance and immune modulation. Adipose tissue, as a key organ in inter-organ communication, releases a variety of signaling molecules that relay energy-related information to other tissues (35).
Leptin: Leptin, encoded by the Lepob gene and secreted by subcutaneous adipose tissue, regulates numerous aspects of energy metabolism. Elevated leptin levels are inversely related to NAFLD development (36). Leptin modulates NAFLD through several mechanisms: 1) It inhibits hypothalamic orexigenic neurons (Neuropeptide Y/Agouti-related protein, NPY/AgRP) and activates opioid Pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC)-expressing neurons, reducing appetite and energy intake (37). 2) It stimulates sympathetic signaling in white adipose tissue (WAT) and brown adipose tissue (BAT), enhancing thermogenesis and energy expenditure. Leptin also influences subcutaneous WAT lipolysis via the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis (38). 3) Leptin promotes glucose uptake in extrahepatic tissue (BAT, brain, heart, etc.) and reduces intrahepatic gluconeogenesis. A 2022 study demonstrated that leptin stimulates the export of hepatic VLDL-loaded triacylglycerols to adipose tissue via brain-vagus nerve-hepatic communication (39). 4) It regulates energy metabolism by binding to the leptin receptor, activating various signaling pathways including Janus Kinase 2 (JAK2)-Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3(STAT3), PI3K-AKT, and extracellular protein kinases pathways, with JAK2/STAT3 being particularly significant (40). Targeted deletion of JAK2 in liver cells prevents steatosis and glucose intolerance induced by HFD (41), while the absence of STAT3 results in increased feeding behavior and obesity (42). Elevated leptin levels are often associated with obesity, a known risk factor for NAFLD (43).
Adiponectin: This adipokine, secreted as lipocalin, has been shown to enhance insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation, and in some cases, promote weight loss (44). Lipocalin signals primarily through lipocalin receptors 1 and 2 (AdipoR1 and AdipoR2). AdipoR1, predominantly expressed in skeletal muscle, interacts closely with the AMPK pathway. Its functional mechanisms include: 1) Activation of insulin receptor substrate 1/2, thereby engaging the PI3K/AKT pathway to enhance insulin sensitivity (44). 2) Activation of the p38 MAPK pathway, leading to GLUT-4 translocation in muscle cells and affecting muscle glucose utilization. 3) Hydrolysis of ceramide to sphingosine via the liver kinase B1 -AMPK pathway, which increases Sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) levels, restores impaired insulin signaling, and boosts lipid metabolism (45). 4) Reduction of oxidative stress and JNK signaling pathways via the AMPK-forkhead box protein O (FoxO) signaling axis, thereby counteracting hepatic steatosis (46). 5) Promotion of nitric oxide production via AMPK-activated endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), which induces vasorelaxation, and inhibition of IkappaB kinase/NFKB/Phosphatase and tensin homolog-induced apoptosis via AMPK activation (47). AdipoR2, mainly located in the liver, is associated with the PPARα pathway, enhancing fatty acid oxidation and energy expenditure through increased expression of acetyl coenzyme A oxidase and uncoupling proteins (48). Additionally, AdipoR2, like AdipoR1, exhibits ceramidase activity, facilitating ceramides hydrolysis. S1P, generated by sphingosine kinases 1 and 2, is activated through S1P receptor 3-sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1(SREBP1) and PPARγ pathways, upregulating stearoyl coenzyme A desaturase (SCD) and enhancing lipid metabolism (49). Unlike leptin, adiponectin levels rise with moderate weight gain but decrease with excessive obesity (50).
Resistin: Resistin, produced by WAT in mice and also observed in human preadipocytes and mature adipose tissues (51), is associated with IR and contributes to NAFLD, atherosclerosis, CVD, and CKD, as supported by an expanding array of research (52). Elevated resistin levels in NASH patients correlate with liver inflammation and fibrosis (53), likely due to its pro-inflammatory properties mediated through NFκB and MAPK pathways. Resistin activates the PI3K-AKT-NFKB cascade or directly stimulates NFKB, leading to the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-12 (54). Additionally, stimulation of p38 MAPK and JNK enhances pro-inflammatory cytokines production, with p38 MAPK activation reducing eNOS levels and obstructing vasodilation (55). Recent findings indicate that variations in the resistin gene may influence the risk of developing NAFLD (56).
Other adipokines: Adipsin (complement factor D) is a serine protease that catalyzes C3-converting enzyme production. Its levels are significantly reduced in obese and diabetic mouse models. Adipsin enhances glucose-stimulated insulin secretion via the C3a pathway, its knockout in HFD-induced mice results in impaired glucose tolerance (57). FABP4 is associated with metabolism-related CVD mortality and promotes hepatic glucose production (58). Endothelin (endotrophin), secreted by adipose tissue, stimulates fibrosis production and exacerbates HFD-induced local inflammation; its effects are mitigated by endothelin inhibition (59).
2.2.2 Brain
Neural nuclei and networks within the brain orchestrate the integration of key metabolic hormones and neuropeptides from the periphery sources, thereby facilitating adaptive adjustments in food intake and energy expenditure. Central to these processes are the hypothalamic nuclei, which play a pivotal role in energy metabolism. For instance, the arcuate nucleus (ARC) for the hypothalamus, containing both projection and neuroendocrine neurons, releases peptides related to ingestion such as NPY, AgRP, POMC, and dopamine, as well as metabolism-related hormones like growth hormone (60). The regulation of metabolic activities pertinent to NAFLD is primarily mediated through two major pathways: energy intake and energy expenditure.
Food intake pathways: Feeding regulation is managed by the hypothalamus through the opposing actions of AgPR and α-melanocyte stimulating hormone (α-MSH). AgRp, released by NPY/AgRP neurons, counteracts α-MSH, produced by POMC neurons (61). α-MSH binds to melanocortin-3 and -4 receptors (MC3R and MC4R), suppressing appetite and promoting catabolic processes. Conversely, in starvation or insufficient energy supply, AgPR inhibits α-MSH, stimulating appetite and increasing food intake (61). In diet-induced obese mice, the absence of G-protein-signaling modulator 1 in POMC neurons leads to improved glucose regulation, enhanced insulin sensitivity, and reduced hepatic steatosis. This is due to increased autophagy and heightened leptin sensitivity via the PI3K/AKT/mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathways, which, in turn, boost POMC expression and α-MSH production (62).
Key receptors for the interaction between NPY/AgRP and α-MSH, MC3R, and MC4R are also strongly associated with NAFLD. MC4R deficiency in mice leads to binge eating and obesity (63), and mutation in the MC4R gene in humans is linked to severe early-onset obesity (64). Notably, MC4R-knockout mice fed HFD develop clinical and pathological features resembling human NASH (65). Moreover, hypothalamic MC4R dysfunction has been implicated in IR, dyslipidemia, liver failure, and HCC development. Forcibly shortening MC4R-carrying cilia in hypothalamic neurons impairs neuronal sensitivity to melanocortin, resulting in obesity and leptin resistance (66).
In addition to the ARC, other hypothalamic nuclei contribute to feeding regulation. Damage to the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus (PVN) in rats leads to overeating and obesity consequences (67). The PVN synthesizes catabolic neuropeptides that promote fatty acid oxidation and lipolysis. Recent studies have shown that forebrain-hypothalamic ER stress-driven circuits mediate hepatic steatosis during obesity, and selective inhibition of PVN ER stress reduces hepatic steatosis in obese individuals (68). Disruption of the ventral medial hypothalamus (VMH) results in binge eating, obesity, and hyperglycemia (69). Neurons in the VMH detect glucose and leptin levels, releasing anorexic neuropeptides such as brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). BDNF is associated with improved cognitive function and reduced depressive symptoms; reduced levels of BDNF can contribute to binge eating and subsequent obesity (70).
Energy expenditure pathway: Energy expenditure is regulated by the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system (SNS/PSNS). When the hypothalamic thermoregulatory center senses temperatures below a critical threshold, excitatory neurons in the ventral medial nucleus of the hypothalamus and sympathetic nerves stimulate brown adipose tissue thermogenesis and skeletal muscle activity through norepinephrine and β-adrenergic receptor interactions. The hypothalamic glucose-regulatory center senses low blood glucose levels, subsequently inhibiting insulin secretion and increasing blood glucose via the SNS. Abnormal signals can mislead the hypothalamus into inappropriate energy metabolism adjustments. For instance, co-injected leptin and insulin into the lateral ventricle induces WAT browning and promotes energy expenditure (71). Although the precise role of the PSNS in NAFLD development remains largely undefined, PSNS activation has been shown to significantly reduce hepatic fat accumulation and inflammation in mice subjected to streptozotocin and HFD (72).
The brainstem also plays a critical role in regulating energy homeostasis by receiving local signals from the liver and intestines via extensive vagal innervation. The nucleus of the solitary tract integrates signals from visceral organs and transmits them to higher brain regions (73). In HFD-fed mice and obese individuals, reduced neuronal excitability and disruption of vagal transmission pathways result in impaired hormone activation, such as Cholecystokinin, peptide tyrosine, and glucagon-like peptide-1(GLP-1)) leading to decreased receptor sensitivity (74). This requires stronger stimuli, such as gastric expansion or hormone release, to initiate vagal transmission. Dysbiosis of gut microbiota and resultant endotoxemia are associated with dysfunction in the gut-brain vagal pathway, contributing to obesity and NAFLD.
Circadian Rhythm Persistence and Periodicity: Circadian rhythm persistence and periodicity are crucial for maintaining normal blood glucose and lipids levels. The suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) is the primary region responsible for generating and regulating circadian rhythm in mammals (75). The SCN controls sugar utilization and protein synthesis through the release of melatonin and glucocorticoids from the central nervous system (76). It generates rhythmic signals that stimulate organs such as the liver to express genes encoding enzymes and transport proteins involved in lipogenesis and lipolysis (77). Disruption in the regular pattern and timing of these circadian rhythms can lead to hyperglycemia and dyslipidemia (78). Furthermore, disruption of the brain and muscle aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like 1 (BMAL1), a key regulator of biological clocks, has been shown to prevent obesity and metabolic complications associated with HFD. The absence of BMAL1 also inhibits hepatic steatosis and suppresses the expression of differentiation clusters such as CD36 and PPARγ (79).
2.2.3 Gastrointestinal tract
In recent years, the “liver-gut axis”, and “liver-gut microbial axis” have emerged as prominent areas of research in the quest for therapeutic approaches to NAFLD. The gastrointestinal tract, being the principal site for the metabolism and transport of major nutrients, not only provides the precursors necessary for the development of NAFLD but also secretes various signaling molecules that influence intra- and extra-hepatic organ interactions critical to the progression of this disease.
Growth hormone-releasing peptide (Ghrelin): Ghrelin, a peptide synthesized in the stomach, exists in two isoforms: acylated ghrelin (AG) and deacylated ghrelin (DAG). In patients with obesity and NAFLD, there is an elevated AG/DAG ratio alongside decreased levels of DAG (80). Increased AG levels are linked to hepatic steatosis in NAFLD patients (81). AG promotes abnormal intrahepatic lipid storage in NAFLD through several mechanisms: it stimulates appetite via the growth hormone secretagogue receptor and activates hypothalamic centers involved in feeding, which boosts caloric intake and induces adipogenesis while decreasing β-oxidation in WAT (82). Additionally, AG through AMPK signaling, encourages TAG storage in the liver, leading to lipid oxidation and mitochondrial dysfunction (83), and modulates interaction between mTOR and PPARγ to further promote adipogenesis (80). Ghrelin also directly facilitates adipogenesis and inhibits lipolysis (83).
Ghrelin may exacerbate NAFLD by advancing the disease to a more severe stage. However, it also acts as an antifibrotic agent by inhibiting hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) activation triggered by fibrotic cytokines such as Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1 and liver-expressed-antimicrobial peptide 2. Ghrelin’s role in hepatic fibrosis in individuals with obesity and NAFLD is complex, potentially involving a compensatory response to counteract TNF-α induced apoptosis and autophagy (80, 84). Furthermore, Ghrelin has been shown to alleviate TNF-α-induced apoptosis and autophagy in human hepatocytes through AMPK/mTOR pathways (80). Thus, maintaining Ghrelin levels within physiological ranges is crucial, as elevated Ghrelin can impair pancreatic β-cell function and decrease insulin sensitivity (85).
GLP-1 and glucagon-releasing peptide (GIP): GLP-1, secreted by intestinal L-cells, enhances insulin release in response to increased glucose levels post-ingestion (86). Besides its role in glycemic control, GLP-1 significantly reduces liver fat accumulation caused by excess lipids and FFAs, thereby hindering NAFLD progression (87). GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) have been shown to decrease glucose levels, IR, and hepatic lipid content in models of fatty liver. These agents down SREBP-1c and SCD-1 expression in hepatocytes while upregulating PPARα expression, leading to reduced adipogenesis and enhanced free fatty acid β-oxidation (88). Clinical trials have consistently demonstrated that GLP-1RAs effectively reduce hepatic steatosis and improve glycemic control in NAFLD patients. Similarly, GIP produced by proximal small intestinal K cells has been shown to mitigate hepatic steatosis, reduce hepatic inflammation, inhibit hepatic injury, and improve NASH when used in combination with GLP-1RAs (89, 90), though its specific effects on adipose tissue and metabolism remain less clear.
The efficacy of GLP-1 RAs in NAFLD is heterogeneous. While generally improving liver histology and reducing transaminase levels with a favorable safety profile, their effects vary according to specific drug type (91). Liraglutide demonstrates efficacy in reducing hepatic steatosis and hepatocellular ballooning, and may lower gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) levels; however, its association with ALT and AST changes is less clear, and its utility in advanced fibrosis remains uncertain, with potential for even promoting fibrosis progression in some cases (91). Conversely, exenatide shows benefit in improving NASH-related fibrosis, correlating with reductions in GGT, ALT, and AST; however, optimal efficacy often requires combination with lifestyle interventions or insulin to address hepatic steatosis (91). Intriguingly, population-based studies comparing GLP-1 RAs with other antihyperglycemic agents reveal a significant association with reduced liver-related mortality but not with NAFLD morbidity, cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, composite hepatic events, or other hepatic outcomes (92).Further research clarifying the optimal therapeutic range for various GLP-1 RAs subtypes would contribute significantly to optimizing NAFLD management and reducing the associated medication burden.
Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) 19: FGF19, predominantly expressed in the ileum, regulates systemic lipid and glucose metabolism through endocrine mechanisms (93). By phosphorylating STAT3 and downregulating PPARγ-coactivator 1β expression, FGF19 inhibits lipogenic enzyme expression. It also influences NAFLD development through the bile acid (BA)-farnesoid X receptor (FXR) axis (94).
Intestinal microbiota: The human gut harbors the largest and most complex microbial community, playing a pivotal role in inter-organ communication. Research indicates that the composition and density of gut microbiota differ significantly between NAFLD patients and healthy individuals, with a notable correlation between intestinal permeability, bacterial proliferation, and the severity of hepatic steatosis (95).
The gut microbiota’s primary mechanism of inter-organ interaction involves the fermentation of undigested dietary components, leading to the production of metabolites such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). SCFAs are particularly influential in the progression of NAFLD, with elevated levels of total SCFAs commonly observed in NAFLD patients (96). SCFAs affect NAFLD development through multiple pathways: 1) They are absorbed through the intestinal tract, enter the liver via the bloodstream, and contribute to fat synthesis (97). 2) SCFAs stimulate gastrointestinal hormone secretion and, upon binding to G protein-coupled receptors 41 and 43 on intestinal endothelial cells, influence hormone release into the systemic circulation (97); They also bind to free fatty acid receptors 2 and 3, inhibiting Ghrelin activity and enhancing GLP-1 expression (96). By modulating gastrointestinal hormones, SCFAs affect the hypothalamic centers regulating appetite (96). 4) SCFAs promote leptin secretion from adipose tissue, mitigating excessive obesity (97). 5) They inhibit insulin-mediated fat accumulation in the gut, skeletal muscle, adipose tissue, and liver via GPCRs.
Additionally, gut microbes influence NAFLD through BA metabolism regulation. BAs are crucial for cholesterol (CHOL) and lipid breakdown and are involved in metabolic disorders such as obesity, IR, and NAFLD (98). The gut microbiota contributes to BA production and their conversion to various metabolites (99). Modified BAs, particularly hyodeoxycholic acid (HDCA) varieties, negatively correlate with NAFLD presence and severity (100). HDCA enhances probiotic growth and lipolysis through hepatic PPARα signaling, which increases hepatic FXR expression (100). Activated FXR promotes CHOL conversion to BAs, reducing fat accumulation and inflammation, thus alleviating NAFLD (101). HDCA also upregulates hepatic Oxysterol 7-α Hydroxylase (CYP7B1) and inhibits intestinal FXR (100), a unique mechanism that could be pivotal in NAFLD treatment, as CYP7B1 is downregulated in NAFLD, NASH without fibrosis, and T2DM (102).
Recent studies show that CHOL-lowering probiotics improve NAFLD in FXR knockout mice (103) and BA transporter inhibitors (SC-435) increase FGF15 levels, alter BA and microbiota profiles, and improve steatohepatitis in animal models (103). Gut symbionts mitigate metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) through secondary BA biosynthesis (104). These findings underscore the potential of the gut microbiota-liver axis in advancing NAFLD treatment strategies.
The gut microbiota plays a critical role in modulating the innate immune response through its interaction with Toll-like receptors (TLRs). Alterations in gut microbial composition (dysbiosis) and increased intestinal permeability lead to increased translocation of bacterial products, such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS), which act as pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs). These PAMPs, along with damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) released from injured hepatocytes, engage TLRs, initiating inflammatory signaling cascades. TLRs, pattern recognition receptors, are thus central to the interplay between the gut microbiome and the liver. Specifically, Hepatocyte injury triggers immune cell activation via DAMP-TLR9 signaling (105), while invading pathogens activate TLR pathways through PAMPs (106). Importantly, gut dysbiosis and increased intestinal permeability significantly increase PAMP presentation; conversely, the preservation of the intestinal epithelial barrier by probiotics negatively regulates TLR activation, suppressing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-8 and IL-1β and consequently attenuating NAFLD development (107). This underscores the therapeutic potential of manipulating the gut microbiota to modulate TLR signaling and improve NAFLD.
TLR4 and TLR2 are key receptors mediating interactions with the gut microbiota: TLR2 recognizes Gram-positive bacterial components, while TLR4 recognizes Gram-negative components, such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (106). The LPS/TLR4 pathway is a central driver of MAFLD pathogenesis (106). TLR4 activation is not only induced by portal vein LPS accumulation due to gut dysbiosis, but also by hepatic fetuin-A and the obesity-associated adipokine lipocalin-2, further contributing to IR in MAFLD (108, 109). Interestingly, long-chain SFAs, despite lacking direct TLR4 ligand activity, can activate TLR4 signaling and promote inflammation (110). Downstream TLR4 signaling pathways implicated in NAFLD include TLR4/TGF-β1-mediated autophagy (111), LPS/TLR4/FoxO3 signaling in NAFL/NASH (112), and hepatic TLR4-triggered intercellular Jagged1/Notch signaling in NASH-associated fibrosis (113). Antibiotic-mediated reduction of microbial load, or direct TLR4 signaling blockade, can attenuate hepatitis and liver fibrosis (113, 114). Therefore, targeting the LPS/TLR4 pathway presents a promising therapeutic strategy for NAFLD-associated inflammation and fibrosis. Beyond TLR4 and TLR2, other TLRs (TLR3, TLR5, TLR7, TLR8, TLR9), recognizing diverse microbial components (viruses, bacterial proteins, CpG motifs, single-stranded RNAs), may also contribute to NAFLD pathogenesis and inflammatory responses via distinct signaling cascades (106).
2.2.4 Pancreas
The pancreas comprises four primary endocrine cell types (α, β, D, and PP cells) that respond to circulating blood glucose levels and secrete various hormones and peptides influencing NAFLD progression intra- and extra-hepatically. Particularly interesting are the roles of pancreatic β-cells and α-cells in this context.
Pancreatic β-cells: Pancreatic β-cells are responsible for insulin secretion, the principal hormone for glucose regulation. IR is a well-established risk factor for NAFLD; however, insulin sensitizers alone are insufficient for NAFLD management (115). Evidence suggests that this inadequacy may stem from impaired β-cell function (116) and a correlation between β-cell dysfunction or compensatory β-cell insufficiency and NAFLD (117, 118). Moreover, β-cells may secrete peptides that modulate NAFLD progression. For instance, islet amyloid from β-cells has been shown to influence glucagon secretion and central satiety signaling and affect blood glucose levels by delaying postprandial gastric emptying (119). Additionally, pancreatic-derived factor secreted from β-cell granules functions as a signaling peptide with a role in glucose and lipid metabolism (120). Thus, β-cell function could serve as a novel diagnostic predictor for NAFLD (118).
Pancreatic α-cells: Pancreatic α-cells secrete glucagon, a key regulator of NAFLD development. The “liver-alpha cell axis (LACA)” concept describes how circulating amino acids stimulate α-cells to produce glucagon, which subsequently enhances amino acid metabolism and urea production in the liver (121). Disruption of the hepatic-α-cell axis has been linked to hepatic steatosis and IR (122), and common metabolic disorders such as NAFLD, T2DM, and obesity are known to impair LACA (121). Thus, preserving the hepatic-α cell axis and preventing its disruption by steatosis may offer a novel therapeutic approach for NAFLD (123).
2.2.5 Bone
Beyond its structural and supportive functions, the skeleton acts as an endocrine organ, with osteoblast-derived osteokines significantly influencing MAFLD progression via modulation of hepatic glycolipid metabolism through the bone-liver axis (124). Bone metabolism, critically dependent on the balance between bone resorption and formation, is implicated in MAFLD pathogenesis. This review examines the roles of key bone factors involved in these processes.
Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs): BMPs regulating various key cytokine signaling pathways (e.g., Wnt, Notch, and FGF) through the TGF-β/BMP signaling cascade, are central to bone and cartilage development and repair (125). Different BMP isoforms exert diverse effects in MAFLD, largely through adipose tissue-liver crosstalk. BMP4, highly expressed in human liver and adipose tissue, correlates with adipocyte size and insulin sensitivity. Conversely, BMP6, upregulated specifically in NAFLD, inhibits HSC activation in murine NASH models, correlating with hepatic steatosis but not inflammation or hepatocyte injury (126, 127). BMP8B deficiency attenuates HSC activation, reduces inflammation, and modifies wound healing, thereby limiting NASH progression; conversely, BMP8B supplementation induces a NASH phenotypes (128). Finally, BMP9, reduced in metabolic syndrome, decreases white adipocyte size and promotes brown adipogenesis, potentially alleviating NAFLD by improving lipid and glucose metabolism via PPARα signaling (129). These findings suggest that BMPs may represent promising therapeutic targets for metabolic syndrome prevention and treatment.
Osteopontin (OPN): OPN implicated in biomineralization, bone remodeling, and wound healing, exhibits elevated serum and hepatic levels in NAFLD. In non-obese individuals, elevated serum OPN disrupts hepatic phosphatidylcholine and cholesterol metabolism, contributing to NAFLD progression (130). OPN’s role in NAFLD appears modulated by obesity status, NASH progression, and patient age; OPN upregulation signifies liver injury and fibrosis in NASH, while OPN deficiency mitigates systemic inflammation, inhibits the progression of HCC to less differentiated tumors, and improves overall survival (131). These findings position OPN as a potential therapeutic target in advanced chronic liver disease. Furthermore, OPN acts as an inflammatory cytokine, activating hepatic signaling and promoting M1 macrophage polarization (132). In HFD mice, elevated plasma OPN promotes inflammation and macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue; OPN knockdown reduces adipose tissue inflammation and IR (133), suggesting OPN targeting as a preventative strategy for obesity-associated metabolic diseases like NAFLD and type 2 diabetes (132).
Vitamin D (VD): VD plays a multifaceted role in MAFLD, although its precise effects remain debated. While serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] negatively correlates with ghrelin in NAFLD and modulates fatty acid metabolism via the PPARα pathway, ameliorating hepatic steatosis and protecting against advanced fibrosis (134), the active form, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D [1,25(OH)2D], inhibits MAFLD progression by reducing TAGs, lipid peroxidation, and cellular damage through the SIRT1/AMPK pathway (135). Furthermore, VD3 reduces hepatic oxidative stress and inflammation via the SREBP-1c/PPARα-NFκB/IRS2 signaling pathway (136). However, conflicting evidence exists, with some studies showing VD3 exacerbation of hepatic steatosis while its analog, calcipotriol, reduces inflammation (137). These discrepancies may stem from variations in VD levels, forms, and selective VDR activation, along with the restoration of mitochondrial contact sites (137, 138). Despite this complexity, randomized controlled trials demonstrate the beneficial effects of high-dose cholecalciferol on serum ALT, hsCRP, and lipid profiles in NAFLD patients (139, 140), highlighting the need for further investigation into the diverse regulatory mechanisms of different VD forms and levels in MAFLD pathogenesis.
Other bone factors: summarizing the relevant hepatic bone crosstalk and NAFLD related reviews in the past two years, and summarizing the bone factors in them (Table 1).
Osteoporosis (OP): The co-occurrence of OP and NAFLD is well-established, yet the precise nature and mechanisms underlying their interaction remain unclear. While recent studies (within the past two years) suggest a causal link between NAFLD and OP (141, 142), the reverse causality remains less defined.
The observed correlation between NAFLD and OP is likely influenced by several factors, including age, sex, ethnicity, bone site-specific bone mineral density (BMD), and the severity and co-morbidities associated with NAFLD (143). Cross-sectional studies reveal a complex picture: BMD in younger patients appears unaffected by steatosis or non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) (144), while in children, reduced BMD correlates with the histological severity of NAFLD, particularly NASH (144). In contrast, adult studies reveal a negative correlation between BMD and advanced hepatic fibrosis in diabetic men aged ≥50 years with MAFLD, with increased spinal fracture risk associated with advanced fibrosis in men ≥40 years (145, 146);. Furthermore, in women, menopausal age significantly influences OP risk in the context of NAFLD, demonstrating a negative correlation between BMD and advanced hepatic fibrosis in postmenopausal diabetic women with MAFLD (145, 147). These findings highlight the need for further investigation to elucidate the complex interplay between NAFLD and OP across different demographic groups and disease stages.
The relationship between MAFLD-associated hepatic fibrosis and the risk of reduced BMD and osteoporosis in T2DM patients may be significantly influenced by obesity. Studies suggest that the observed correlation disappears when analyzed independently of obesity, potentially due to the strong association between NAFLD-related hepatic fibrosis, lower BMD, and impaired bone microarchitecture in obese individuals (148, 149). Furthermore, ethnic disparities exist, with differences in BMD and osteoporotic fracture risk observed between Asian and non-Asian populations, possibly reflecting underlying skeletal differences (150). Epidemiological data, such as the 2017-2018 US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) analysis, show a negative correlation between NAFLD and lumbar spine BMD (151), while other contemporary analyses have demonstrated a causal link between NAFLD and forearm BMD (152). Despite the ongoing debate regarding the precise nature of the NAFLD-OP association, the available evidence underscores the need for individualized preventative and therapeutic strategies tailored to specific patient populations presenting with co-morbid NAFLD and OP.
2.2.6 Skeletal muscle
Skeletal muscle, a crucial organ for energy expenditure and thermogenesis, is intricately linked to metabolic diseases. Petermann-Rocha et al. found in a cross-sectional study that reduced muscle mass and strength exacerbate NAFLD over time (153). Similarly, Iwaki et al. demonstrated that sarcopenia not only increases the risk of NAFLD but also accelerates its progression (154). This phenomenon is further elucidated by studies indicating that elevated levels of muscle growth inhibitory hormones—myokines responsible for muscle atrophy—are associated with poorer survival rates in cirrhotic patients (155). Consequently, considerable research has focused on identifying specific myokines and their signaling pathways as potential therapeutic targets for NAFLD.
Exercise and dietary modifications are established strategies for preventing and delaying NAFLD. Given its unique role in locomotion, skeletal muscle has garnered significant attention. During physical activity, skeletal muscle secretes various myokines and generates numerous metabolites, though only a subset of these have been implicated in inter-organ communication relevant to NAFLD (156).
Exercise-induced activation of PGC-1α prompts skeletal muscle to release irisin. Irisin not only induces the browning of WAT and enhances energy metabolism (157), but also interacts with Myeloid differentiation factor 2 (MD2), thereby blocking the MD2-TLR4 interaction (158). This action inhibits downstream MAPK and NF-κB pathways, preventing the release of pro-inflammatory factors. Furthermore, exercise-induced PGC-1α regulates the release of muscle-derived amino acid metabolites such as β-aminoisobutyric acid (159) and 3-hydroxybutyric acid, which influence NAFLD by modulating lipid synthesis and fatty acid oxidation processes (160). Additionally, FGF21 produced in response to exercise promotes lipolysis of LDs, mitigates LD accumulation, and attenuates NAFLD while slowing hepatic senescence through the AMPK/UNC-51-like kinase 1 (ULK1) pathway (161). FGF21 also enhances glucose utilization in skeletal muscle, contributing to increased energy expenditure (162).
Exercise-induced metabolites impact NAFLD through their effects on both skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. For example, IL-15 fosters muscle hypertrophy, while leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) supports muscle regeneration and influences NAFLD development through muscle remodeling (163). Similarly, cysteine-rich acid secretory protein inhibits adipogenesis, IL-6 promotes lipolysis, and BDNF activates the AMPK pathway in adipose tissue, thus controlling lipid oxidation and reducing NAFLD (163).
The role of skeletal muscle in NAFLD progression underscores the potential of targeting skeletal muscle-derived myokines to influence disease outcomes. For instance, skeletal muscle-specific IRF4 knockout mice fed a NASH diet showed improvements in hepatic steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis, despite no change in body weight. This effect is mediated by IRF4’s regulation of the myokine follicle-stimulating hormone-like protein 1 (164).
Despite the promise of myokines as therapeutic agents for NAFLD, challenges remain. Many myokines share similarities with adipose-derived factors, raising the risk of misclassification when determining their functions (165). Moreover, the variation in myokine levels in human myofibroblasts or NAFLD populations is minimal, complicating efforts to directly demonstrate their effects on NAFLD.
While the application of exercise interventions in NAFLD management presents challenges, various exercise modalities offer distinct therapeutic benefits. Aerobic training (AT) effectively reduces hepatic steatosis and systemic inflammation, potentially improving histological markers in MAFLD (166, 167). Resistance training (RT) enhances insulin sensitivity and promotes muscle hypertrophy, leading to improvements in cardiac and hepatic function (168, 169). High-intensity interval training (HIIT) offers unique metabolic advantages, including enhanced mitochondrial function, improved whole-body lipid metabolism, increased exercise capacity, and enhanced peripheral insulin sensitivity, demonstrating safety and efficacy in NASH (170, 171). A comparative analysis of these modalities is crucial for optimizing NAFLD treatment strategies.
Comparative analyses reveal modality-specific benefits. AT demonstrates superior efficacy in lowering ALT and AST levels, making it particularly suitable for overweight individuals, older adults, pregnant women, and those with arthritis due to its low-impact nature and enhancement of cardiorespiratory fitness (172). RT provides a viable alternative for individuals unable to tolerate AT, effectively improving AST levels and promoting muscle strength. HIIT, while also effective in reducing ALT and AST, appeals to younger, healthier individuals, athletes, and some patients with chronic conditions owing to its efficiency and flexibility (173). While HIIT improves cardiorespiratory fitness and metabolism, integrated programs combining AT and RT show superior efficacy in improving lipid profiles, specifically lowering TC and TG, while raising HDL-C and lowering LDL-C (174). This integrated approach may represent the optimal strategy for maximizing physical conditioning, improving cardiovascular health, and reducing hepatic fat accumulation in NAFLD patients (174). Ultimately, a personalized approach to exercise prescription, tailored to individual needs and capabilities, is essential for optimizing both health outcomes and quality of life.
3 Conclusion and future directions
Undoubtedly, NAFLD (or MAFLD) has a complicated etiology that includes coordinated regulation of several organs. These organs exert direct influences (e.g., leptin inhibiting hepatic fat storage), indirect effects (e.g., leptin influencing appetite and reducing food intake), and the activation of the same molecules across different signaling pathways, collectively forming intricate organ networks (Figure 2). These insights provide additional targets for understanding and treating NAFLD.
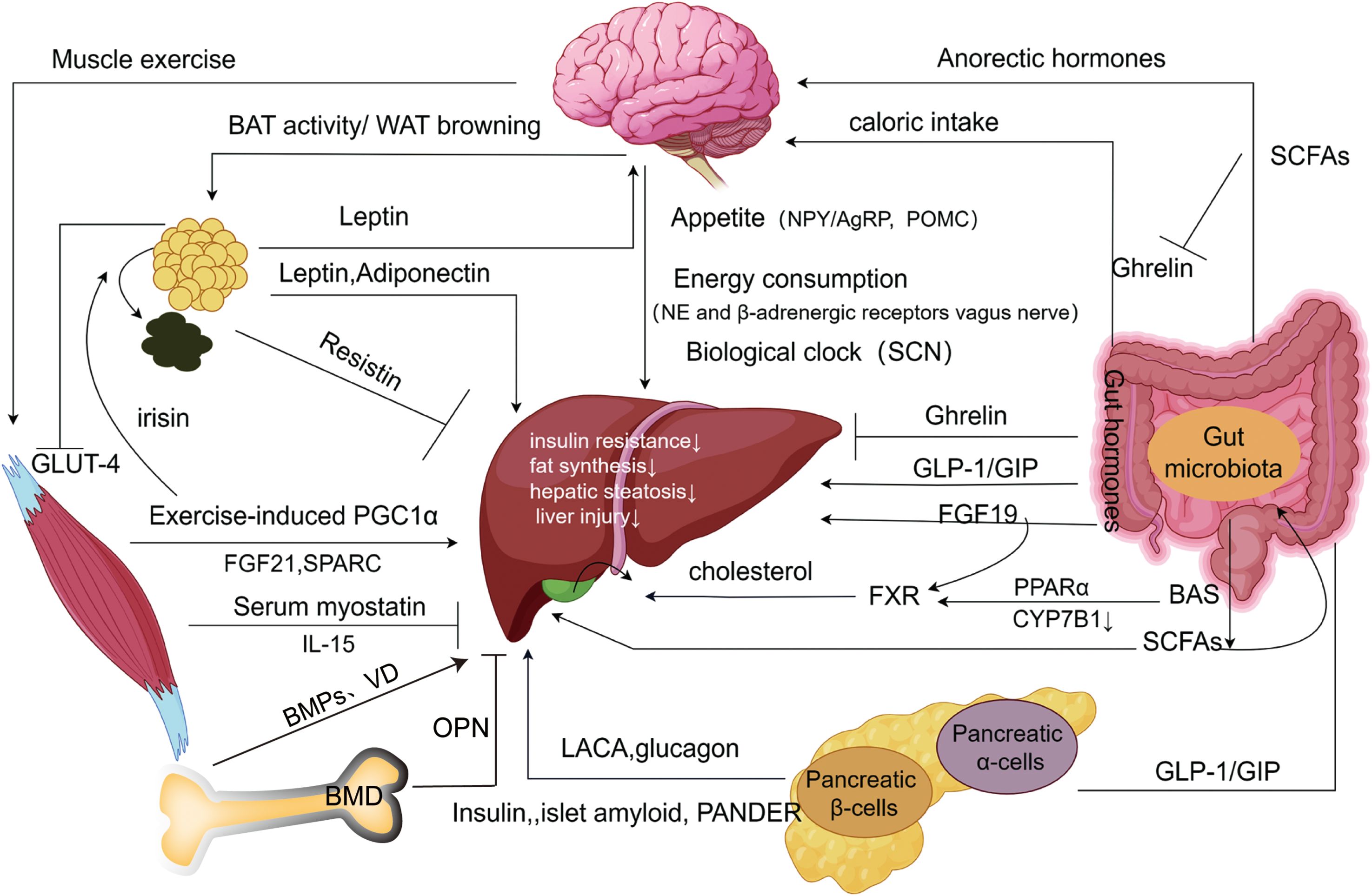
Figure 2. Extrahepatic organ-specific networks associated with NAFLD. Adipose tissue produces adipokines that inhibit hepatic steatosis, inhibit hepatic inflammatory injury, and increase insulin sensitivity through “the hepatic-fatty axis”, “hepatic-fatty-cerebral axis”, and “hepatic-fatty-skeletal muscle axis”, which may be a form of feedback regulation. The brain receives metabolism-related signals from external organs (adipose tissue, gastrointestinal tract, etc.), to improve impaired NAFLD via food intake, energy expenditure, and biological clock pathways. The gastrointestinal tract influences extrahepatic organs such as the brain and pancreas to inhibit the development of NAFLD by releasing intestinal hormones with associated peptide metabolism, while gut microbes have a similar effect by altering short-chain fatty acids and bile acids. The endocrine pancreas improves insulin resistance and inhibits steatosis through the “hepatic-alpha-cell axis”, and “hepatic-β-cells axis”. Exercise-induced skeletal muscle production of myokines and metabolites promotes white fat burning in extrahepatic adipose tissue and inhibits intrahepatic lipogenesis, inhibiting the progression of NAFLD. Bone metabolism produces bone factors that affect hepatic steatosis, hepatitis, and liver fibrosis through the “liver-bone axis”, and with the change in bone density, the development of NAFLD will also be affected. SCN, Suprachiasmatic nucleus; NPY/AgRP, Neuropeptide Y/Agouti-related protein; PPARα, Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α; GLP-1, Glucagon-like peptide-1; GIP, Glucagon-releasing peptide; SCFAs, Short-chain fatty acids; CYP7B1, Hepatic Oxysterol 7-α Hydroxylase; LACA, Liver-alpha cell axis; WAT, White adipose tissue; BAT, Brown adipose tissue; SPARC, Cysteine-rich acid secretory protein. BMPs, Bone morphogenetic proteins; OPN, Osteobridging proteins; VD, Vitamin D; BMD, Bone mineral density (Drawing by Figdraw 2.0).
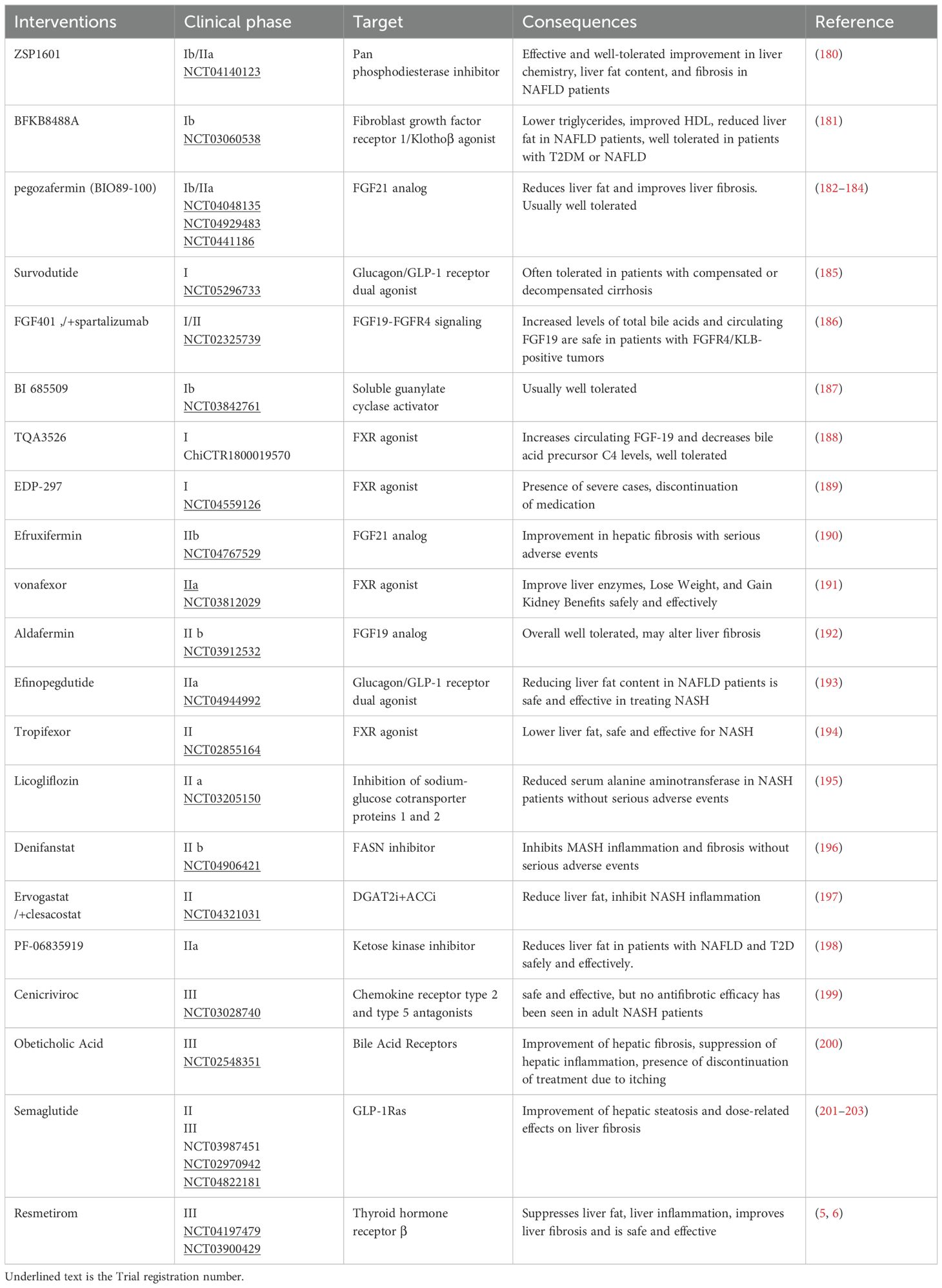
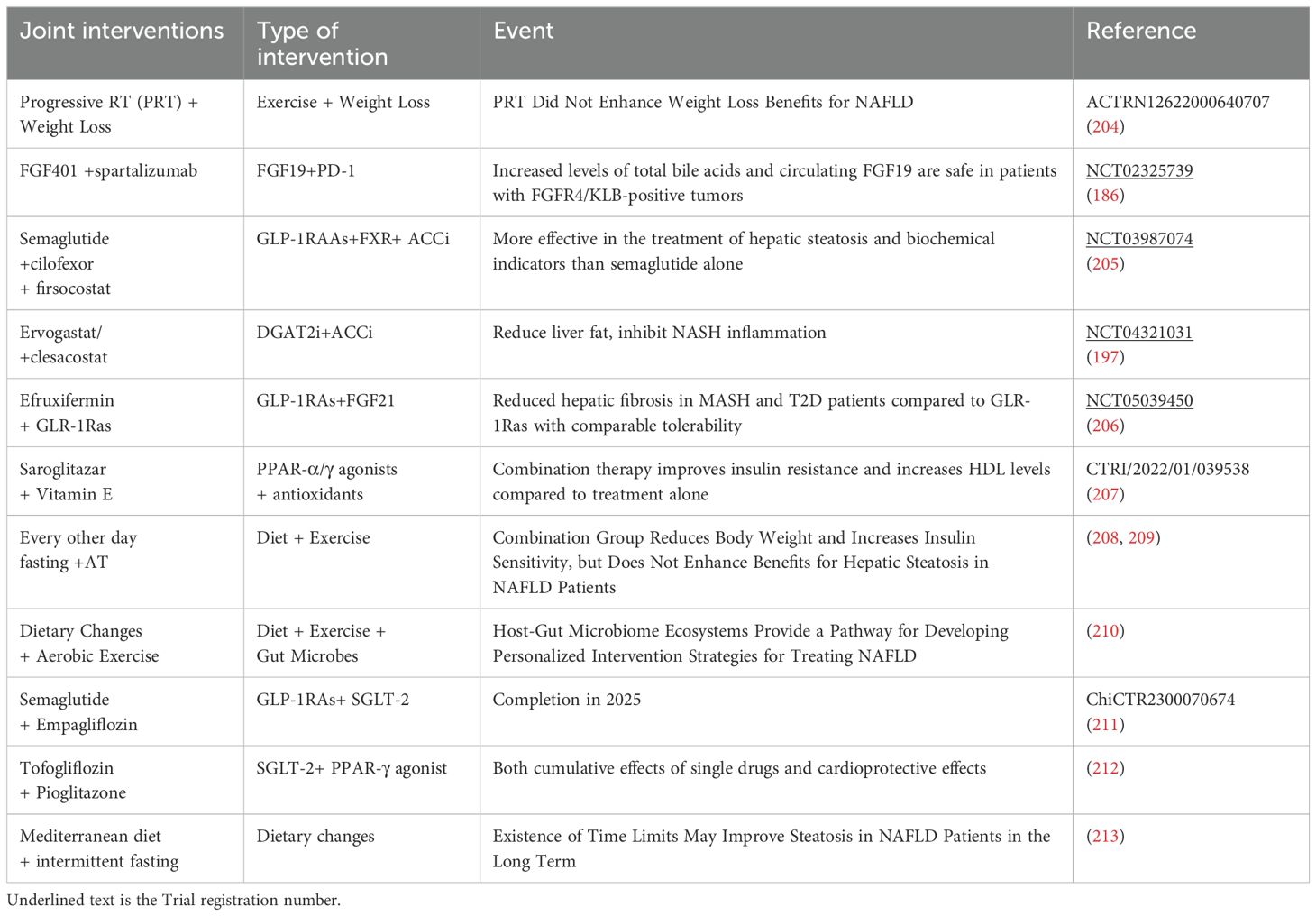
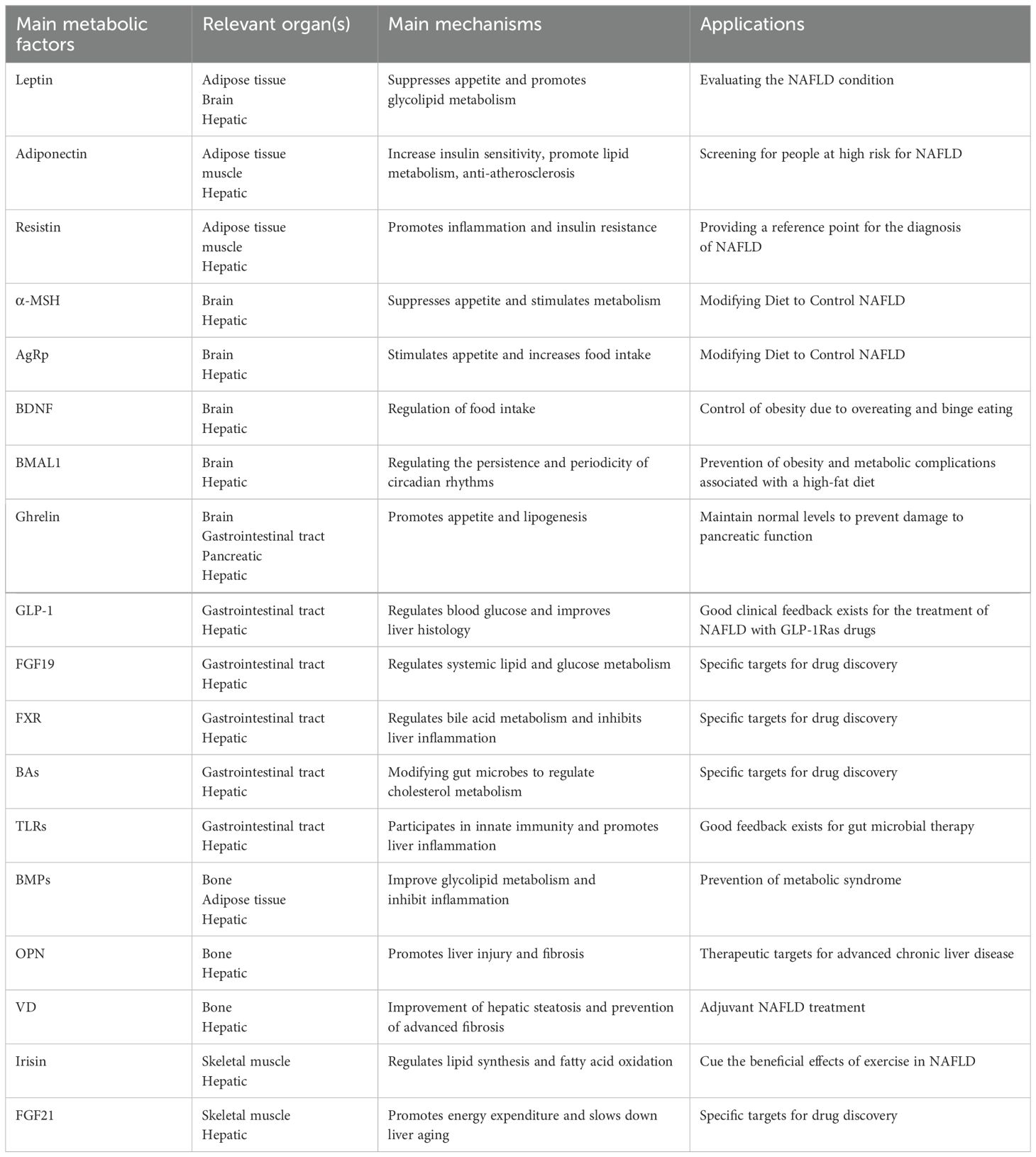
This review analyzed clinical trials (Phase I-III) related to NAFLD (Table 2), revealing a predominant focus on intrahepatic signaling pathways and the hepato-intestinal axis in current drug development efforts. While diet and exercise remain cornerstones of NAFLD management, the efficacy of combined interventions, particularly GLP-1 RAs in conjunction with other therapies, has shown promise (Table 3). Future research should prioritize combination therapies targeting both the liver-gut axis and the emerging liver-gut-bone/skeletal muscle axis, while continuing to explore novel therapeutic targets. However, the potential therapeutic value of other extrahepatic metabolic factors warrants further investigation (Table 4).
Furthermore, new research shows that over 55% of people with T2DM also have NAFLD (175), which is a definitive pathogenic factor for CKD, significantly increasing CKD risk among MAFLD patients (176). NAFLD patients face elevated risks of cardiovascular events, with ASCVD being a primary cause of mortality (177). Exploring mechanisms of inter-organ crosstalk not only offers new perspectives for developing NAFLD therapies but also identifies novel targets for intervening in other metabolic-related extra-liver diseases.
Author contributions
Y-HF: Writing – original draft. SZ: Writing – review & editing. YW: Writing – review & editing. HW: Writing – review & editing. HL: Writing – review & editing. LB: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The National Science Foundation of China (82270615, LB), the Jiangxi Province Thousand Talents Project (jxsq2023101065, LB), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province of China for Distinguished Young Scholars (20232ACB216001, LB).
Acknowledgments
Figure 1 was drawn in Adobe Illustrator 2020, and Figure 2 was produced in Figdraw 2.0. Thanks to them for the technical support.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Friedman SL, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Rinella M, Sanyal AJ. Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies. Nat Med. (2018) 24:908–22. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0104-9
2. Eslam M, Newsome PN, Sarin SK, Anstee QM, Targher G, Romero-Gomez M, et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J Hepatol. (2020) 73:202–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.03.039
3. Gofton C, Upendran Y, Zheng MH, George J. MAFLD: How is it different from NAFLD? Clin Mol Hepatol. (2023) 29:S17–s31. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2022.0367
4. Terrault NA, Francoz C, Berenguer M, Charlton M, Heimbach J. Liver transplantation 2023: status report, current and future challenges. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2023) 21:2150–66. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.04.005
5. Harrison SA, Taub R, Neff GW, Lucas KJ, Labriola D, Moussa SE, et al. Resmetirom for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Nat Med. (2023) 29:2919–28. doi: 10.1038/s41591-023-02603-1
6. Harrison SA, Bedossa P, Guy CD, Schattenberg JM, Loomba R, Taub R, et al. A phase 3, randomized, controlled trial of resmetirom in NASH with liver fibrosis. New Engl J Med. (2024) 390:497–509. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2309000
7. Byrne CD, Targher G. NAFLD: a multisystem disease. J Hepatol. (2015) 62:S47–64. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.12.012
8. Chan KE, Koh TJL, Tang ASP, Quek J, Yong JN, Tay P, et al. Global prevalence and clinical characteristics of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis and systematic review of 10 739 607 individuals. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2022) 107:2691–700. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgac321
9. Jung CY, Koh HB, Park KH, Joo YS, Kim HW, Ahn SH, et al. Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and risk of incident chronic kidney disease: A nationwide cohort study. Diabetes Metab. (2022) 48:101344. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2022.101344
10. Liu Z, Suo C, Shi O, Lin C, Zhao R, Yuan H, et al. The health impact of MAFLD, a novel disease cluster of NAFLD, is amplified by the integrated effect of fatty liver disease-related genetic variants. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2022) 20:e855–75. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.12.033
11. Seo JY, Cho EJ, Kim MJ, Kwak MS, Yang JI, Chung SJ, et al. The relationship between metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and low muscle mass in an asymptomatic Korean population. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2022) 13:2953–60. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13099
12. Anwar SD, Foster C, Ashraf A. Lipid disorders and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease. Endocrinol Metab Clinics North Am. (2023) 52:445–57. doi: 10.1016/j.ecl.2023.01.003
13. Yki-Järvinen H, Luukkonen PK, Hodson L, Moore JB. Dietary carbohydrates and fats in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2021) 18:770–86. doi: 10.1038/s41575-021-00472-y
14. Jung S, Bae H, Song WS, Jang C. Dietary fructose and fructose-induced pathologies. Annu Rev Nutr. (2022) 42:45–66. doi: 10.1146/annurev-nutr-062220-025831
15. Herman MA, Birnbaum MJ. Molecular aspects of fructose metabolism and metabolic disease. Cell Metab. (2021) 33:2329–54. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2021.09.010
16. Jang C, Hui S, Lu W, Cowan AJ, Morscher RJ, Lee G, et al. The small intestine converts dietary fructose into glucose and organic acids. Cell Metab. (2018) 27:351–61. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.12.016
17. Helsley RN, Park SH, Vekaria HJ, Sullivan PG, Conroy LR, Sun RC, et al. Ketohexokinase-C regulates global protein acetylation to decrease carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1a-mediated fatty acid oxidation. J Hepatol. (2023) 79:25–42. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.02.010
18. Johnson RJ, Lanaspa MA, Sanchez-Lozada LG, Tolan D, Nakagawa T, Ishimoto T, et al. The fructose survival hypothesis for obesity. Philos Trans R Soc London Ser B Biol Sci. (2023) 378:20220230. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2022.0230
19. Kim MS, Krawczyk SA, Doridot L, Fowler AJ, Wang JX, Trauger SA, et al. ChREBP regulates fructose-induced glucose production independently of insulin signaling. J Clin Invest. (2016) 126:4372–86. doi: 10.1172/jci81993
20. Di Filippo M, Moulin P, Roy P, Samson-Bouma ME, Collardeau-Frachon S, Chebel-Dumont S, et al. Homozygous MTTP and APOB mutations may lead to hepatic steatosis and fibrosis despite metabolic differences in congenital hypocholesterolemia. J Hepatol. (2014) 61:891–902. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.05.023
21. Scorletti E, Carr RM. A new perspective on NAFLD: Focusing on lipid droplets. J Hepatol. (2022) 76:934–45. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.11.009
22. Yin X, Dong L, Wang X, Qin Z, Ma Y, Ke X, et al. Perilipin 5 regulates hepatic stellate cell activation and high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Anim Models Exp Med. (2024) 7:166–78. doi: 10.1002/ame2.12327
23. Afonso MB, Islam T, Magusto J, Amorim R, Lenoir V, Simões RF, et al. RIPK3 dampens mitochondrial bioenergetics and lipid droplet dynamics in metabolic liver disease. Hepatol (Baltimore Md). (2023) 77:1319–34. doi: 10.1002/hep.32756
24. Martinez-Lopez N, Singh R. Autophagy and lipid droplets in the liver. Annu Rev Nutr. (2015) 35:215–37. doi: 10.1146/annurev-nutr-071813-105336
25. Singh R, Kaushik S, Wang Y, Xiang Y, Novak I, Komatsu M, et al. Autophagy regulates lipid metabolism. Nature. (2009) 458:1131–5. doi: 10.1038/nature07976
26. Yang L, Li P, Fu S, Calay ES, Hotamisligil GS. Defective hepatic autophagy in obesity promotes ER stress and causes insulin resistance. Cell Metab. (2010) 11:467–78. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2010.04.005
27. Zhang X, Wu D, Wang C, Luo Y, Ding X, Yang X, et al. Sustained activation of autophagy suppresses adipocyte maturation via a lipolysis-dependent mechanism. Autophagy. (2020) 16:1668–82. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1703355
28. Ajoolabady A, Liu S, Klionsky DJ, Lip GYH, Tuomilehto J, Kavalakatt S, et al. ER stress in obesity pathogenesis and management. Trends Pharmacol Sci. (2022) 43:97–109. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2021.11.011
29. Hotamisligil GS. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the inflammatory basis of metabolic disease. Cell. (2010) 140:900–17. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.02.034
30. Zhang R. The ANGPTL3-4-8 model, a molecular mechanism for triglyceride trafficking. Open Biol. (2016) 6:150272. doi: 10.1098/rsob.150272
31. Yang H, Deng Q, Ni T, Liu Y, Lu L, Dai H, et al. Targeted Inhibition of LPL/FABP4/CPT1 fatty acid metabolic axis can effectively prevent the progression of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis to liver cancer. Int J Biol Sci. (2021) 17:4207–22. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.64714
32. Long EK, Olson DM, Bernlohr DA. High-fat diet induces changes in adipose tissue trans-4-oxo-2-nonenal and trans-4-hydroxy-2-nonenal levels in a depot-specific manner. Free Radic Biol Med. (2013) 63:390–8. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.05.030
33. Aharoni-Simon M, Hann-Obercyger M, Pen S, Madar Z, Tirosh O. Fatty liver is associated with impaired activity of PPARγ-coactivator 1α (PGC1α) and mitochondrial biogenesis in mice. Lab Investig J Tech Methods Pathol. (2011) 91:1018–28. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2011.55
34. Tian Y, Jellinek MJ, Mehta K, Seok SM, Kuo SH, Lu W, et al. Membrane phospholipid remodeling modulates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis progression by regulating mitochondrial homeostasis. Hepatol (Baltimore Md). (2024) 79:882–97. doi: 10.1097/hep.0000000000000375
35. Ghesmati Z, Rashid M, Fayezi S, Gieseler F, Alizadeh E, Darabi M. An update on the secretory functions of brown, white, and beige adipose tissue: Towards therapeutic applications. Rev Endocrine Metab Disord. (2024) 25:279–308. doi: 10.1007/s11154-023-09850-0
36. Guo Z, Du H, Guo Y, Jin Q, Liu R, Yun Z, et al. Association between leptin and NAFLD: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Eur J Med Res. (2023) 28:215. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01147-x
37. Kalra SP, Dube MG, Pu S, Xu B, Horvath TL, Kalra PS. Interacting appetite-regulating pathways in the hypothalamic regulation of body weight. Endocrine Rev. (1999) 20:68–100. doi: 10.1210/edrv.20.1.0357
38. Perry RJ, Shulman GI. The role of leptin in maintaining plasma glucose during starvation. Postdoc J. (2018) 6:3–19. doi: 10.14304/surya.jpr.v6n3.2
39. Metz M, Beghini M, Wolf P, Pfleger L, Hackl M, Bastian M, et al. Leptin increases hepatic triglyceride export via a vagal mechanism in humans. Cell Metab. (2022) 34:1719–1731.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2022.09.020
40. Casado ME, Collado-Pérez R, Frago LM, Barrios V. Recent advances in the knowledge of the mechanisms of leptin physiology and actions in neurological and metabolic pathologies. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24(2):1422. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021422
41. Shi SY, Martin RG, Duncan RE, Choi D, Lu SY, Schroer SA, et al. Hepatocyte-specific deletion of Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) protects against diet-induced steatohepatitis and glucose intolerance. J Biol Chem. (2012) 287:10277–88. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.317453
42. Wauman J, Zabeau L, Tavernier J. The leptin receptor complex: heavier than expected? Front Endocrinol. (2017) 8:30. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2017.00030
43. Fernandois D, Vázquez MJ, Barroso A, Paredes AH, Tena-Sempere M, Cruz G. Multi-organ increase in norepinephrine levels after central leptin administration and diet-induced obesity. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24(23):16909. doi: 10.3390/ijms242316909
44. Achari AE, Jain SK. Adiponectin, a therapeutic target for obesity, diabetes, and endothelial dysfunction. Int J Mol Sci. (2017) 18(6):1321. doi: 10.3390/ijms18061321
45. Awazawa M, Ueki K, Inabe K, Yamauchi T, Kaneko K, Okazaki Y, et al. Adiponectin suppresses hepatic SREBP1c expression in an AdipoR1/LKB1/AMPK dependent pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2009) 382:51–6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.02.131
46. Kim SM, Grenert JP, Patterson C, Correia MA. CHIP(-/-)-mouse liver: adiponectin-AMPK-FOXO-activation overrides CYP2E1-elicited JNK1-activation, delaying onset of NASH: therapeutic implications. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:29423. doi: 10.1038/srep29423
47. Fang X, Palanivel R, Cresser J, Schram K, Ganguly R, Thong FS, et al. An APPL1-AMPK signaling axis mediates beneficial metabolic effects of adiponectin in the heart. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. (2010) 299:E721–9. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00086.2010
48. Yamauchi T, Nio Y, Maki T, Kobayashi M, Takazawa T, Iwabu M, et al. Targeted disruption of AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 causes abrogation of adiponectin binding and metabolic actions. Nat Med. (2007) 13:332–9. doi: 10.1038/nm1557
49. Ruiz M, Devkota R, Panagaki D, Bergh PO, Kaper D, Henricsson M, et al. Sphingosine 1-phosphate mediates adiponectin receptor signaling essential for lipid homeostasis and embryogenesis. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:7162. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34931-0
50. Singh P, Sharma P, Sahakyan KR, Davison DE, Sert-Kuniyoshi FH, Romero-Corral A, et al. Differential effects of leptin on adiponectin expression with weight gain versus obesity. Int J Obes. (2005) 40(2):266–74. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2015.181
51. Degawa-Yamauchi M, Bovenkerk JE, Juliar BE, Watson W, Kerr K, Jones R, et al. Serum resistin (FIZZ3) protein is increased in obese humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2003) 88:5452–5. doi: 10.1210/jc.2002-021808
52. Filková M, Haluzík M, Gay S, Senolt L. The role of resistin as a regulator of inflammation: Implications for various human pathologies. Clin Immunol (Orlando Fla). (2009) 133:157–70. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2009.07.013
53. Shen C, Zhao CY, Wang W, Wang YD, Sun H, Cao W, et al. The relationship between hepatic resistin overexpression and inflammation in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. BMC Gastroenterol. (2014) 14:39. doi: 10.1186/1471-230x-14-39
54. Jamaluddin MS, Weakley SM, Yao Q, Chen C. Resistin: functional roles and therapeutic considerations for cardiovascular disease. Br J Pharmacol. (2012) 165:622–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01369.x
55. Chen C, Jiang J, Lü JM, Chai H, Wang X, Lin PH, et al. Resistin decreases expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase through oxidative stress in human coronary artery endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circulatory Physiol. (2010) 299:H193–201. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00431.2009
56. Nouri S, Navari M, Shafiee R, Mahmoudi T, Rezamand G, Asadi A, et al. The rs1862513 promoter variant of resistin gene influences susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Rev da Associacao Med Bras (1992). (2024) 70:e20231537. doi: 10.1590/1806-9282.20231537
57. Flier JS, Cook KS, Usher P, Spiegelman BM. Severely impaired adipsin expression in genetic and acquired obesity. Sci (New York NY). (1987) 237:405–8. doi: 10.1126/science.3299706
58. Gilani A, Stoll L, Homan EA, Lo JC. Adipose signals regulating distal organ health and disease. Diabetes. (2024) 73:169–77. doi: 10.2337/dbi23-0005
59. Sun K, Park J, Gupta OT, Holland WL, Auerbach P, Zhang N, et al. Endotrophin triggers adipose tissue fibrosis and metabolic dysfunction. Nat Commun. (2014) 5:3485. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4485
60. Roh E, Song DK, Kim MS. Emerging role of the brain in the homeostatic regulation of energy and glucose metabolism. Exp Mol Med. (2016) 48:e216. doi: 10.1038/emm.2016.4
61. Ollmann MM, Wilson BD, Yang YK, Kerns JA, Chen Y, Gantz I, et al. Antagonism of central melanocortin receptors in vitro and in vivo by agouti-related protein. Science. (1997) 278:135–8. doi: 10.1126/science.278.5335.135
62. Tang M, Zhang Y, Zhang R, Zhang Y, Zheng J, Wang D, et al. GPSM1 in POMC neurons impairs brown adipose tissue thermogenesis and provokes diet-induced obesity. Mol Metab. (2024) 79:101839. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2023.101839
63. Zhang Y, Kilroy GE, Henagan TM, Prpic-Uhing V, Richards WG, Bannon AW, et al. Targeted deletion of melanocortin receptor subtypes 3 and 4, but not CART, alters nutrient partitioning and compromises behavioral and metabolic responses to leptin. FASEB J. (2005) 19:1482–91. doi: 10.1096/fj.05-3851com
64. Tao YX. Molecular mechanisms of the neural melanocortin receptor dysfunction in severe early onset obesity. Mol Cell Endocrinol. (2005) 239:1–14. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2005.04.012
65. Trevaskis JL, Gawronska-Kozak B, Sutton GM, McNeil M, Stephens JM, Smith SR, et al. Role of adiponectin and inflammation in insulin resistance of Mc3r and Mc4r knockout mice. Obes (Silver Spring). (2007) 15:2664–72. doi: 10.1038/oby.2007.318
66. Oya M, Miyasaka Y, Nakamura Y, Tanaka M, Suganami T, Mashimo T, et al. Age-related ciliopathy: Obesogenic shortening of melanocortin-4 receptor-bearing neuronal primary cilia. Cell Metab. (2024) 36:1044–1058.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2024.02.010
67. Foster MT, Song CK, Bartness TJ. Hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus lesion involvement in the sympathetic control of lipid mobilization. Obes (Silver Spring). (2010) 18:682–9. doi: 10.1038/oby.2009.345
68. Blackmore K, Houchen CJ, Simonyan H, Arestakesyan H, Stark AK, Dow SA, et al. A forebrain-hypothalamic ER stress driven circuit mediates hepatic steatosis during obesity. Mol Metab. (2024) 79:101858. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2023.101858
69. Ameroso D, Meng A, Chen S, Felsted J, Dulla CG, Rios M. Astrocytic BDNF signaling within the ventromedial hypothalamus regulates energy homeostasis. Nat Metab. (2022) 4:627–43. doi: 10.1038/s42255-022-00566-0
70. Ichimura-Shimizu M, Kojima M, Suzuki S, Miyata M, Osaki Y, Matsui K, et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor knock-out mice develop non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J Pathol. (2023) 261:465–76. doi: 10.1002/path.6204
71. Morrison SF, Madden CJ, Tupone D. Central neural regulation of brown adipose tissue thermogenesis and energy expenditure. Cell Metab. (2014) 19:741–56. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2014.02.007
72. Hur MH, Song W, Cheon DH, Chang Y, Cho YY, Lee YB, et al. Chemogenetic stimulation of the parasympathetic nervous system lowers hepatic lipid accumulation and inflammation in a nonalcoholic steatohepatitis mouse model. Life Sci. (2023) 321:121533. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.121533
73. López-Gambero AJ, Martínez F, Salazar K, Cifuentes M, Nualart F. Brain glucose-sensing mechanism and energy homeostasis. Mol Neurobiol. (2019) 56:769–96. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1099-4
74. Duca FA, Sakar Y, Covasa M. Combination of obesity and high-fat feeding diminishes sensitivity to GLP-1R agonist exendin-4. Diabetes. (2013) 62:2410–5. doi: 10.2337/db12-1204
75. Lebeaupin C, Vallée D, Hazari Y, Hetz C, Chevet E, Bailly-Maitre B. Endoplasmic reticulum stress signalling and the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. (2018) 69:927–47. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.06.008
76. Speksnijder EM, Bisschop PH, Siegelaar SE, Stenvers DJ, Kalsbeek A. Circadian desynchrony and glucose metabolism. J Pineal Res. (2024) 76:e12956. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12956
77. Pan X, Mota S, Zhang B. Circadian clock regulation on lipid metabolism and metabolic diseases. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2020) 1276:53–66. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-6082-8_5
78. Turek FW, Joshu C, Kohsaka A, Lin E, Ivanova G, McDearmon E, et al. Obesity and metabolic syndrome in circadian Clock mutant mice. Science. (2005) 308:1043–5. doi: 10.1126/science.1108750
79. Zhan C, Chen H, Zhang Z, Shao Y, Xu B, Hua R, et al. BMAL1 deletion protects against obesity and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease induced by a high-fat diet. Int J Obes. (2024) 48:469–76. doi: 10.1038/s41366-023-01435-w
80. Ezquerro S, Mocha F, Frühbeck G, Guzmán-Ruiz R, Valentí V, Mugueta C, et al. Ghrelin reduces TNF-α-induced human hepatocyte apoptosis, autophagy, and pyroptosis: role in obesity-associated NAFLD. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2019) 104:21–37. doi: 10.1210/jc.2018-01171
81. Estep M, Abawi M, Jarrar M, Wang L, Stepanova M, Elariny H, et al. Association of obestatin, ghrelin, and inflammatory cytokines in obese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Obes Surg. (2011) 21:1750–7. doi: 10.1007/s11695-011-0475-1
82. Poher AL, Tschöp MH, Müller TD. Ghrelin regulation of glucose metabolism. Peptides. (2018) 100:236–42. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2017.12.015
83. Tuero C, Becerril S, Ezquerro S, Neira G, Frühbeck G, Rodríguez A. Molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying the hepatoprotective role of ghrelin against NAFLD progression. J Physiol Biochem. (2023) 79:833–49. doi: 10.1007/s13105-022-00933-1
84. Ezquerro S, Tuero C, Becerril S, Valentí V, Moncada R, Landecho MF, et al. Antagonic effect of ghrelin and LEAP-2 on hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis in obesity-associated nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Eur J Endocrinol. (2023) 188:564–77. doi: 10.1093/ejendo/lvad071
85. Napolitano T, Silvano S, Vieira A, Balaji S, Garrido-Utrilla A, Friano ME, et al. Role of ghrelin in pancreatic development and function. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2018) 20 Suppl 2:3–10. doi: 10.1111/dom.13385
86. Guo H, Li H, Wang B, Ding W, Ling L, Yang M, et al. Protective effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 analog on renal tubular injury in mice on high-fat diet. Cell Physiol Biochem. (2017) 41:1113–24. doi: 10.1159/000464118
87. Zhou R, Lin C, Cheng Y, Zhuo X, Li Q, Xu W, et al. Liraglutide alleviates hepatic steatosis and liver injury in T2MD rats via a GLP-1R dependent AMPK pathway. Front Pharmacol. (2020) 11:600175. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.600175
88. Desjardins EM, Wu J, Lavoie DCT, Ahmadi E, Townsend LK, Morrow MR, et al. Combination of an ACLY inhibitor with a GLP-1R agonist exerts additive benefits on nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and hepatic fibrosis in mice. Cell Rep Med. (2023) 4:101193. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101193
89. Ying Z, van Eenige R, Ge X, van Marwijk C, Lambooij JM, Guigas B, et al. Combined GIP receptor and GLP1 receptor agonism attenuates NAFLD in male APOE∗3-Leiden.CETP mice. EBioMedicine. (2023) 93:104684. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2023.104684
90. Hartman ML, Sanyal AJ, Loomba R, Wilson JM, Nikooienejad A, Bray R, et al. Effects of novel dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide on biomarkers of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. (2020) 43:1352–5. doi: 10.2337/dc19-1892
91. Dong Y, Lv Q, Li S, Wu Y, Li L, Li J, et al. Efficacy and safety of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clinics Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. (2017) 41:284–95. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2016.11.009
92. Khanmohammadi S, Habibzadeh A, Kamrul-Hasan ABM, Schuermans A, Kuchay MS. Glucose-lowering drugs and liver-related outcomes among individuals with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review of longitudinal population-based studies. Diabetic Med: J Br Diabetic Assoc. (2024) 41:e15437. doi: 10.1111/dme.15437
93. Wu X, Ge H, Gupte J, Weiszmann J, Shimamoto G, Stevens J, et al. Co-receptor requirements for fibroblast growth factor-19 signaling. J Biol Chem. (2007) 282:29069–72. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C700130200
94. Miyata M, Sakaida Y, Matsuzawa H, Yoshinari K, Yamazoe Y. Fibroblast growth factor 19 treatment ameliorates disruption of hepatic lipid metabolism in farnesoid X receptor (Fxr)-null mice. Biol Pharm Bull. (2011) 34:1885–9. doi: 10.1248/bpb.34.1885
95. Miele L, Valenza V, La Torre G, Montalto M, Cammarota G, Ricci R, et al. Increased intestinal permeability and tight junction alterations in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatol (Baltimore Md). (2009) 49:1877–87. doi: 10.1002/hep.22848
96. Zhou M, Johnston LJ, Wu C, Ma X. Gut microbiota and its metabolites: Bridge of dietary nutrients and obesity-related diseases. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2023) 63:3236–53. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2021.1986466
97. Hu J, Lin S, Zheng B, Cheung PCK. Short-chain fatty acids in control of energy metabolism. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2018) 58:1243–9. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2016.1245650
98. Jia W, Wei M, Rajani C, Zheng X. Targeting the alternative bile acid synthetic pathway for metabolic diseases. Protein Cell. (2021) 12:411–25. doi: 10.1007/s13238-020-00804-9
99. Su X, Gao Y, Yang R. Gut microbiota derived bile acid metabolites maintain the homeostasis of gut and systemic immunity. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1127743. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1127743
100. Kuang J, Wang J, Li Y, Li M, Zhao M, Ge K, et al. Hyodeoxycholic acid alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease through modulating the gut-liver axis. Cell Metab. (2023) 35:1752–66. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2023.07.011
101. Ni Y, Lu M, Xu Y, Wang Q, Gu X, Li Y, et al. The role of gut microbiota-bile acids axis in the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Front Microbiol. (2022) 13:908011. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.908011
102. Lake AD, Novak P, Shipkova P, Aranibar N, Robertson D, Reily MD, et al. Decreased hepatotoxic bile acid composition and altered synthesis in progressive human nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. (2013) 268:132–40. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2013.01.022
103. Yang M, Wang H, Bukhari I, Zhao Y, Huang H, Yu Y, et al. Effects of cholesterol-lowering probiotics on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in FXR gene knockout mice. Front Nutr. (2023) 10:1121203. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1121203
104. Nie Q, Luo X, Wang K, Ding Y, Jia S, Zhao Q, et al. Gut symbionts alleviate MASH through a secondary bile acid biosynthetic pathway. Cell. (2024) 187:2717–2734.e33. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.03.034
105. Handa P, Vemulakonda A, Kowdley KV, Uribe M, Méndez-Sánchez N. Mitochondrial DNA from hepatocytes as a ligand for TLR9: Drivers of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis? World J Gastroenterol. (2016) 22:6965–71. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i31.6965
106. Khanmohammadi S, Kuchay MS. Toll-like receptors and metabolic (dysfunction)-associated fatty liver disease. Pharmacol Res. (2022) 185:106507. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106507
107. Nabavi-Rad A, Sadeghi A, Asadzadeh Aghdaei H, Yadegar A, Smith SM, Zali MR. The double-edged sword of probiotic supplementation on gut microbiota structure in Helicobacter pylori management. Gut Microbes. (2022) 14:2108655. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2022.2108655
108. Zhu X, Zeng C, Yu B. White adipose tissue in metabolic associated fatty liver disease. Clinics Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. (2024) 48:102336. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2024.102336
109. Miao X, Alidadipour A, Saed V, Sayyadi F, Jadidi Y, Davoudi M, et al. Hepatokines: unveiling the molecular and cellular mechanisms connecting hepatic tissue to insulin resistance and inflammation. Acta Diabetol. (2024) 61:1339–61. doi: 10.1007/s00592-024-02335-9
110. Lancaster GI, Langley KG, Berglund NA, Kammoun HL, Reibe S, Estevez E, et al. Evidence that TLR4 is not a receptor for saturated fatty acids but mediates lipid-induced inflammation by reprogramming macrophage metabolism. Cell Metab. (2018) 27:1096–1110.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.03.014
111. Tawfiq RA, Nassar NN, Hammam OA, Allam RM, Elmazar MM, Abdallah DM, et al. Obeticholic acid orchestrates the crosstalk between ileal autophagy and tight junctions in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Role of TLR4/TGF-β1 axis. Chemico-biol Interactions. (2022) 361:109953. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2022.109953
112. Samy AM, Kandeil MA, Sabry D, Abdel-Ghany AA, Mahmoud MO. Exosomal miR-122, miR-128, miR-200, miR-298, and miR-342 as novel diagnostic biomarkers in NAFL/NASH: Impact of LPS/TLR-4/FoxO3 pathway. Archiv Der Pharmazie. (2024) 357:e2300631. doi: 10.1002/ardp.202300631
113. Yu J, Zhu C, Wang X, Kim K, Bartolome A, Dongiovanni P, et al. Hepatocyte TLR4 triggers inter-hepatocyte Jagged1/Notch signaling to determine NASH-induced fibrosis. Sci Trans Med. (2021) 13(599):eabe1692. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abe1692
114. Xue J, Zhao M, Liu Y, Jia X, Zhang X, Gu Q, et al. Hydrogen inhalation ameliorates hepatic inflammation and modulates gut microbiota in rats with high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Eur J Pharmacol. (2023) 947:175698. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175698
115. Rakoski MO, Singal AG, Rogers MA, Conjeevaram H. Meta-analysis: insulin sensitizers for the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Alimentary Pharmacol Ther. (2010) 32:1211–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2010.04467.x
116. VanWagner LB, Ning H, Allen NB, Siddique J, Carson AP, Bancks MP, et al. Twenty-five-year trajectories of insulin resistance and pancreatic β-cell response and diabetes risk in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. (2018) 38:2069–81. doi: 10.1111/liv.13747
117. Pagano G, Pacini G, Musso G, Gambino R, Mecca F, Depetris N, et al. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome: further evidence for an etiologic association. Hepatol (Baltimore Md). (2002) 35:367–72. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2002.30690
118. Chen X, Xiao J, Pang J, Chen S, Wang Q, Ling W. Pancreatic β-cell dysfunction is associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nutrients. (2021) 13(9):3139. doi: 10.3390/nu13093139
119. Mathiesen DS, Lund A, Vilsbøll T, Knop FK, Bagger JI. Amylin and calcitonin: potential therapeutic strategies to reduce body weight and liver fat. Front Endocrinol. (2020) 11:617400. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.617400
120. López-Bermudo L, Luque-Sierra A, Maya-Miles D, Gallego-Durán R, Ampuero J, Romero-Gómez M, et al. Contribution of liver and pancreatic islet crosstalk to β-cell function/dysfunction in the presence of fatty liver. Front Endocrinol. (2022) 13:892672. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.892672
121. Pixner T, Stummer N, Schneider AM, Lukas A, Gramlinger K, Julian V, et al. The relationship between glucose and the liver-alpha cell axis - A systematic review. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2022) 13:1061682. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1061682
122. Gar C, Haschka SJ, Kern-Matschilles S, Rauch B, Sacco V, Prehn C, et al. The liver-alpha cell axis associates with liver fat and insulin resistance: a validation study in women with non-steatotic liver fat levels. Diabetologia. (2021) 64:512–20. doi: 10.1007/s00125-020-05334-x
123. Winther-Sørensen M, Galsgaard KD, Santos A, Trammell SAJ, Sulek K, Kuhre RE, et al. Glucagon acutely regulates hepatic amino acid catabolism and the effect may be disturbed by steatosis. Mol Metab. (2020) 42:101080. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2020.101080
124. Li Z, Wen X, Li N, Zhong C, Chen L, Zhang F, et al. The roles of hepatokine and osteokine in liver-bone crosstalk: Advance in basic and clinical aspects. Front Endocrinol. (2023) 14:1149233. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1149233
125. Wu M, Chen G, Li YP. TGF-β and BMP signaling in osteoblast, skeletal development, and bone formation, homeostasis and disease. Bone Res. (2016) 4:16009. doi: 10.1038/boneres.2016.9
126. Baboota RK, Rawshani A, Bonnet L, Li X, Yang H, Mardinoglu A, et al. BMP4 and Gremlin 1 regulate hepatic cell senescence during clinical progression of NAFLD/NASH. Nat Metab. (2022) 4:1007–21. doi: 10.1038/s42255-022-00620-x
127. Vachliotis ID, Anastasilakis AD, Rafailidis V, Polyzos SA. Osteokines in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Curr Obes Rep. (2024) 13:703–23. doi: 10.1007/s13679-024-00586-9
128. Vacca M, Leslie J, Virtue S, Lam BYH, Govaere O, Tiniakos D, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein 8B promotes the progression of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Nat Metab. (2020) 2:514–31. doi: 10.1038/s42255-020-0214-9
129. Sun QJ, Cai LY, Jian J, Cui YL, Huang CK, Liu SQ, et al. The role of bone morphogenetic protein 9 in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Front Pharmacol. (2020) 11:605967. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.605967
130. Nuñez-Garcia M, Gomez-Santos B, Buqué X, García-Rodriguez JL, Romero MR, Marin JJG, et al. Osteopontin regulates the cross-talk between phosphatidylcholine and cholesterol metabolism in mouse liver. J Lipid Res. (2017) 58:1903–15. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M078980
131. Wang S, Gao J, Yang M, Zhang G, Yin L, Tong X. OPN-mediated crosstalk between hepatocyte E4BP4 and hepatic stellate cells promotes MASH-associated liver fibrosis. Adv Sci (Weinheim Baden-Wurttemberg Germany). (2024) 29:e2405678. doi: 10.1002/advs.202405678
132. Han H, Ge X, Komakula SSB, Desert R, Das S, Song Z, et al. Macrophage-derived osteopontin (SPP1) protects from nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology. (2023) 165:201–17. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.03.228
133. Song Z, Chen W, Athavale D, Ge X, Desert R, Das S, et al. Osteopontin takes center stage in chronic liver disease. Hepatol (Baltimore Md). (2021) 73:1594–608. doi: 10.1002/hep.31582
134. Du T, Xiang L, Zhang J, Yang C, Zhao W, Li J, et al. Vitamin D improves hepatic steatosis in NAFLD via regulation of fatty acid uptake and β-oxidation. Front Endocrinol. (2023) 14:1138078. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1138078
135. Chang E. Vitamin D mitigates hepatic fat accumulation and inflammation and increases SIRT1/AMPK expression in AML-12 hepatocytes. Mol (Basel Switzerland). (2024) 29(6):1401. doi: 10.3390/molecules29061401
136. Reda D, Elshopakey GE, Albukhari TA, Almehmadi SJ, Refaat B, Risha EF, et al. Vitamin D3 alleviates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in rats by inhibiting hepatic oxidative stress and inflammation via the SREBP-1-c/PPARα-NF-κB/IR-S2 signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol. (2023) 14:1164512. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1164512
137. Yang A, Chen Y, Gao Y, Lv Q, Li Y, Li F, et al. Vitamin D(3) exacerbates steatosis while calcipotriol inhibits inflammation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Sod1 knockout mice: a comparative study of two forms of vitamin D. Food Funct. (2024) 15:4614–26. doi: 10.1039/d4fo00215f
138. Kim GH, Jeong HJ, Lee YJ, Park HY, Koo SK, Lim JH. Vitamin D ameliorates age-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by increasing the mitochondrial contact site and cristae organizing system (MICOS) 60 level. Exp Mol Med. (2024) 56:142–55. doi: 10.1038/s12276-023-01125-7
139. Mohamed AA, Halim AA, Mohamed S, Mahmoud SM, Bahgat Eldemiry EM, Mohamed RS, et al. The effect of high oral loading dose of cholecalciferol in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients. A randomized placebo controlled trial. Front Pharmacol. (2023) 14:1149967. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1149967
140. Alarfaj SJ, Bahaa MM, Yassin HA, El-Khateeb E, Kotkata FA, El-Gammal MA, et al. A randomized placebo-controlled, double-blind study to investigate the effect of a high oral loading dose of cholecalciferol in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients, new insights on serum STAT-3 and hepassocin. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2023) 27:7607–19. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202308_33413
141. Cui A, Xiao P, Fan Z, Lei J, Han S, Zhang D, et al. Causal association of NAFLD with osteoporosis, fracture and falling risk: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. Front Endocrinol. (2023) 14:1215790. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1215790
142. Pan B, Cai J, Zhao P, Liu J, Fu S, Jing G, et al. Relationship between prevalence and risk of osteoporosis or osteoporotic fracture with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoporosis Int. (2022) 33:2275–86. doi: 10.1007/s00198-022-06459-y
143. Hansen SG, Wernberg CW, Grønkjær LL, Jacobsen BG, Caterino TD, Krag A, et al. Are nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and bone mineral density associated? - A cross-sectional study using liver biopsy and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. JBMR Plus. (2023) 7:e10714. doi: 10.1002/jbm4.10714
144. Khan S, Kalkwarf HJ, Hornung L, Siegel R, Arce-Clachar AC, Sheridan R, et al. Histologic severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease associates with reduced bone mineral density in children. Digest Dis Sci. (2023) 68:644–55. doi: 10.1007/s10620-022-07563-z
145. Pan B, Zhao Y, Chen C, Cai J, Li K, Wang Y, et al. The relationship between advanced liver fibrosis and osteoporosis in type 2 diabetes patients with MAFLD. Endocrine. (2024) 85:206–21. doi: 10.1007/s12020-024-03724-4
146. Zhai T, Chen Q, Xu J, Jia X, Xia P. Prevalence and trends in low bone density, osteopenia and osteoporosis in U.S. Adults with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, 2005-2014. Front Endocrinol. (2021) 12:825448. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.825448
147. Dingpeng L, Bihui B, Ruixuan X, Fei Y, Xingwen X, Demin L. Distribution and diagnostic modeling of osteoporosis and comorbidities across demographic factors: A cross-sectional study of 2224 female patients. Exp Gerontol. (2024) 198:112638. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2024.112638
148. Barchetta I, Lubrano C, Cimini FA, Dule S, Passarella G, Dellanno A, et al. Liver fibrosis is associated with impaired bone mineralization and microstructure in obese individuals with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatol Int. (2023) 17:357–66. doi: 10.1007/s12072-022-10461-1
149. Zhang W, Li Y, Li S, Zhou J, Wang K, Li Z, et al. Associations of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and hepatic fibrosis with bone mineral density and risk of osteopenia/osteoporosis in T2DM patients. Front Endocrinol. (2023) 14:1278505. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1278505
150. Su YH, Chien KL, Yang SH, Chia WT, Chen JH, Chen YC. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with decreased bone mineral density in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Bone Mineral Res. (2023) 38:1092–103. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.4862
151. Xie R, Liu M. Relationship between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and degree of hepatic steatosis and bone mineral density. Front Endocrinol. (2022) 13:857110. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.857110
152. Liu Y, Yuan M, He J, Cai L, Leng A. The impact of non-alcohol fatty liver disease on bone mineral density is mediated by sclerostin by mendelian randomization study. Calcified Tissue Int. (2024) 114:502–12. doi: 10.1007/s00223-024-01204-5
153. Petermann-Rocha F, Gray SR, Forrest E, Welsh P, Sattar N, Celis-Morales C, et al. Associations of muscle mass and grip strength with severe NAFLD: A prospective study of 333,295 UK Biobank participants. J Hepatol. (2022) 76:1021–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.01.010
154. Iwaki M, Kobayashi T, Nogami A, Saito S, Nakajima A, Yoneda M. Impact of sarcopenia on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Nutrients. (2023) 15(4):891. doi: 10.3390/nu15040891
155. Nishikawa H, Enomoto H, Ishii A, Iwata Y, Miyamoto Y, Ishii N, et al. Elevated serum myostatin level is associated with worse survival in patients with liver cirrhosis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2017) 8:915–25. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12212
156. Polyzos SA, Vachliotis ID, Mantzoros CS. Sarcopenia, sarcopenic obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Metabolism. (2023) 147:155676. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2023.155676
157. Eckel J. Myokines in metabolic homeostasis and diabetes. Diabetologia. (2019) 62:1523–8. doi: 10.1007/s00125-019-4927-9
158. Zhu W, Sahar NE, Javaid HMA, Pak ES, Liang G, Wang Y, et al. Exercise-induced irisin decreases inflammation and improves NAFLD by competitive binding with MD2. Cells. (2021) 10(12):3306. doi: 10.3390/cells10123306
159. Roberts LD, Boström P, O’Sullivan JF, Schinzel RT, Lewis GD, Dejam A, et al. [amp]]beta;-Aminoisobutyric acid induces browning of white fat and hepatic β-oxidation and is inversely correlated with cardiometabolic risk factors. Cell Metab. (2014) 19:96–108. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2013.12.003
160. Barlow JP, Solomon TP. Do skeletal muscle-secreted factors influence the function of pancreatic β-cells? Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. (2018) 314:E297–e307. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00353.2017
161. Gao Y, Zhang W, Zeng LQ, Bai H, Li J, Zhou J, et al. Exercise and dietary intervention ameliorate high-fat diet-induced NAFLD and liver aging by inducing lipophagy. Redox Biol. (2020) 36:101635. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101635
162. Kharitonenkov A, Shiyanova TL, Koester A, Ford AM, Micanovic R, Galbreath EJ, et al. FGF-21 as a novel metabolic regulator. J Clin Invest. (2005) 115:1627–35. doi: 10.1172/jci23606
163. So B, Kim HJ, Kim J, Song W. Exercise-induced myokines in health and metabolic diseases. Integr Med Res. (2014) 3:172–9. doi: 10.1016/j.imr.2014.09.007
164. Guo S, Feng Y, Zhu X, Zhang X, Wang H, Wang R, et al. Metabolic crosstalk between skeletal muscle cells and liver through IRF4-FSTL1 in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:6047. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-41832-3
165. Duan Y, Li F, Wang W, Guo Q, Wen C, Li Y, et al. Interleukin-15 in obesity and metabolic dysfunction: current understanding and future perspectives. Obes Rev. (2017) 18:1147–58. doi: 10.1111/obr.12567
166. Wu B, Xu C, Tian Y, Zeng Y, Yan F, Chen A, et al. Aerobic exercise promotes the expression of ATGL and attenuates inflammation to improve hepatic steatosis via lncRNA SRA. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:5370. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-09174-0
167. O’Gorman P, Naimimohasses S, Monaghan A, Kennedy M, Melo AM, Fhloinn DN, et al. Improvement in histological endpoints of MAFLD following a 12-week aerobic exercise intervention. Alimentary Pharmacol Ther. (2020) 52:1387–98. doi: 10.1111/apt.15989
168. Bronczek GA, Soares GM, Marmentini C, Boschero AC, Costa-Júnior JM. Resistance training improves beta cell glucose sensing and survival in diabetic models. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23(16):9427. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169427
169. Jafarikhah R, Damirchi A, Rahmani Nia F, Razavi-Toosi SMT, Shafaghi A, Asadian M. Effect of functional resistance training on the structure and function of the heart and liver in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:15475. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-42687-w
170. Wang Y, Guo Y, Xu Y, Wang W, Zhuang S, Wang R, et al. HIIT ameliorates inflammation and lipid metabolism by regulating macrophage polarization and mitochondrial dynamics in the liver of type 2 diabetes mellitus mice. Metabolites. (2022) 13(1):14. doi: 10.3390/metabo13010014
171. Keating SE, Croci I, Wallen MP, Cox ER, Thuzar M, Pham U, et al. High-intensity interval training is safe, feasible and efficacious in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A randomized controlled trial. Digest Dis Sci. (2023) 68:2123–39. doi: 10.1007/s10620-022-07779-z
172. Lee DC, Brellenthin AG, Lanningham-Foster LM, Kohut ML, Li Y. Aerobic, resistance, or combined exercise training and cardiovascular risk profile in overweight or obese adults: the CardioRACE trial. Eur Heart J. (2024) 45:1127–42. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehad827
173. Xing S, Xie Y, Zhang Y, Zhang R, Zeng D, Yue X. Effect of different training modalities on lipid metabolism in patients with type ii diabetes mellitus: a network meta-analysis. Ann Med. (2024) 56:2428432. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2428432
174. Xue Y, Peng Y, Zhang L, Ba Y, Jin G, Liu G. Effect of different exercise modalities on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:6212. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-51470-4
175. En Li Cho E, Ang CZ, Quek J, Fu CE, Lim LKE, Heng ZEQ, et al. Global prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut. (2023) 72:2138–48. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2023-330110
176. Wang TY, Wang RF, Bu ZY, Targher G, Byrne CD, Sun DQ, et al. Association of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease with kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2022) 18:259–68. doi: 10.1038/s41581-021-00519-y
177. Pan Z, Shiha G, Esmat G, Méndez-Sánchez N, Eslam M. MAFLD predicts cardiovascular disease risk better than MASLD. Liver Int. (2024) 44:1567–74. doi: 10.1111/liv.15931
178. Zhao J, Lei H, Wang T, Xiong X. Liver-bone crosstalk in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Clinical implications and underlying pathophysiology. Front Endocrinol. (2023) 14:1161402. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1161402
179. Drapkina OM, Elkina AY, Sheptulina AF, Kiselev AR. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and bone tissue metabolism: current findings and future perspectives. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24(9):8445. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098445
180. Hu Y, Li H, Zhang H, Chen X, Chen J, Xu Z, et al. ZSP1601, a novel pan-phosphodiesterase inhibitor for the treatment of NAFLD, A randomized, placebo-controlled phase Ib/IIa trial. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:6409. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42162-0
181. Wong C, Dash A, Fredrickson J, Lewin-Koh N, Chen S, Yoshida K, et al. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1/Klothoβ agonist BFKB8488A improves lipids and liver health markers in patients with diabetes or NAFLD: A phase 1b randomized trial. Hepatol (Baltimore Md). (2023) 78:847–62. doi: 10.1002/hep.32742
182. Loomba R, Lawitz EJ, Frias JP, Ortiz-Lasanta G, Johansson L, Franey BB, et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of pegozafermin in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1b/2a multiple-ascending-dose study. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2023) 8:120–32. doi: 10.1016/s2468-1253(22)00347-8
183. Loomba R, Sanyal AJ, Kowdley KV, Bhatt DL, Alkhouri N, Frias JP, et al. Randomized, controlled trial of the FGF21 analogue pegozafermin in NASH. New Engl J Med. (2023) 389:998–1008. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2304286
184. Bhatt DL, Bays HE, Miller M, Cain JE 3rd, Wasilewska K, Andrawis NS, et al. The FGF21 analog pegozafermin in severe hypertriglyceridemia: a randomized phase 2 trial. Nat Med. (2023) 29:1782–92. doi: 10.1038/s41591-023-02427-z
185. Lawitz EJ, Fraessdorf M, Neff GW, Schattenberg JM, Noureddin M, Alkhouri N, et al. Efficacy, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of survodutide, a glucagon/glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor dual agonist, in cirrhosis. J Hepatol. (2024) 81:837–46. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2024.06.003
186. Chan SL, Schuler M, Kang YK, Yen CJ, Edeline J, Choo SP, et al. A first-in-human phase 1/2 study of FGF401 and combination of FGF401 with spartalizumab in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma or biomarker-selected solid tumors. J Exp Clin Cancer Res: CR. (2022) 41:189. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02383-5
187. Lawitz EJ, Reiberger T, Schattenberg JM, Schoelch C, Coxson HO, Wong D, et al. Safety and pharmacokinetics of BI 685509, a soluble guanylyl cyclase activator, in patients with cirrhosis: A randomized Phase Ib study. Hepatol Commun. (2023) 7(11):e0276. doi: 10.1097/hc9.0000000000000276
188. Xu J, Zhang H, Chen H, Zhu X, Jia H, Xu Z, et al. Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of a novel farnesoid X receptor (FXR) agonist-TQA3526 in healthy Chinese volunteers: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, dose-escalation, food effect phase I study. Ann Med. (2023) 55:2264850. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2023.2264850
189. Marotta C, Ahmad A, Luo E, Oosterhaven J, van Marle S, Adda N. EDP-297: A novel, farnesoid X receptor agonist-Results of a phase I study in healthy subjects. Clin Trans Sci. (2023) 16:338–51. doi: 10.1111/cts.13453
190. Harrison SA, Frias JP, Neff G, Abrams GA, Lucas KJ, Sanchez W, et al. Safety and efficacy of once-weekly efruxifermin versus placebo in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (HARMONY): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2b trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2023) 8:1080–93. doi: 10.1016/s2468-1253(23)00272-8
191. Ratziu V, Harrison SA, Loustaud-Ratti V, Bureau C, Lawitz E, Abdelmalek M, et al. Hepatic and renal improvements with FXR agonist vonafexor in individuals with suspected fibrotic NASH. J Hepatol. (2023) 78:479–92. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.10.023
192. Harrison SA, Abdelmalek MF, Neff G, Gunn N, Guy CD, Alkhouri N, et al. Aldafermin in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (ALPINE 2/3): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2b trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2022) 7:603–16. doi: 10.1016/s2468-1253(22)00017-6
193. Romero-Gómez M, Lawitz E, Shankar RR, Chaudhri E, Liu J, Lam RLH, et al. A phase IIa active-comparator-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of efinopegdutide in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. (2023) 79:888–97. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.05.013
194. Sanyal AJ, Lopez P, Lawitz EJ, Lucas KJ, Loeffler J, Kim W, et al. Tropifexor for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: an adaptive, randomized, placebo-controlled phase 2a/b trial. Nat Med. (2023) 29:392–400. doi: 10.1038/s41591-022-02200-8
195. Harrison SA, Manghi FP, Smith WB, Alpenidze D, Aizenberg D, Klarenbeek N, et al. Licogliflozin for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2a study. Nat Med. (2022) 28:1432–8. doi: 10.1038/s41591-022-01861-9
196. Loomba R, Bedossa P, Grimmer K, Kemble G, Bruno Martins E, McCulloch W, et al. Denifanstat for the treatment of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis: a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2b trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2024) 9:1090–100. doi: 10.1016/s2468-1253(24)00246-2
197. Amin NB, Darekar A, Anstee QM, Wong VW, Tacke F, Vourvahis M, et al. Efficacy and safety of an orally administered DGAT2 inhibitor alone or coadministered with a liver-targeted ACC inhibitor in adults with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): rationale and design of the phase II, dose-ranging, dose-finding, randomised, placebo-controlled MIRNA (Metabolic Interventions to Resolve NASH with fibrosis) study. BMJ Open. (2022) 12:e056159. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-056159
198. Saxena AR, Lyle SA, Khavandi K, Qiu R, Whitlock M, Esler WP, et al. A phase 2a, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, three-arm, parallel-group study to assess the efficacy, safety, tolerability and pharmacodynamics of PF-06835919 in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2023) 25:992–1001. doi: 10.1111/dom.14946
199. Anstee QM, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Wai-Sun Wong V, Abdelmalek MF, Rodriguez-Araujo G, Landgren H, et al. Cenicriviroc lacked efficacy to treat liver fibrosis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: AURORA phase III randomized study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2024) 22:124–34. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.04.003
200. Younossi ZM, Stepanova M, Nader F, Loomba R, Anstee QM, Ratziu V, et al. Obeticholic acid impact on quality of life in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: REGENERATE 18-month interim analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2022) 20:2050–2058.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.07.020
201. Loomba R, Abdelmalek MF, Armstrong MJ, Jara M, Kjær MS, Krarup N, et al. Semaglutide 2·4 mg once weekly in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis-related cirrhosis: a randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2023) 8:511–22. doi: 10.1016/s2468-1253(23)00068-7
202. Ratziu V, Francque S, Behling CA, Cejvanovic V, Cortez-Pinto H, Iyer JS, et al. Artificial intelligence scoring of liver biopsies in a phase II trial of semaglutide in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatol (Baltimore Md). (2024) 80:173–85. doi: 10.1097/hep.0000000000000723
203. Newsome PN, Sanyal AJ, Engebretsen KA, Kliers I, Østergaard L, Vanni D, et al. Semaglutide 2.4 mg in participants with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis: baseline characteristics and design of the phase 3 ESSENCE trial. Alimentary Pharmacol Ther. (2024) 60:1525–33. doi: 10.1111/apt.18331
204. Freer CL, George ES, Tan SY, Abbott G, Dunstan DW, Daly RM. Effect of progressive resistance training with weight loss compared with weight loss alone on the fatty liver index in older adults with type 2 diabetes: secondary analysis of a 12-month randomized controlled trial. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. (2022) 10(5):e002950. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2022-002950
205. Alkhouri N, Herring R, Kabler H, Kayali Z, Hassanein T, Kohli A, et al. Safety and efficacy of combination therapy with semaglutide, cilofexor and firsocostat in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: A randomised, open-label phase II trial. J Hepatol. (2022) 77:607–18. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.04.003
206. Harrison SA, Frias JP, Lucas KJ, Reiss G, Neff G, Bollepalli S, et al. Safety and efficacy of efruxifermin in combination with a GLP-1 receptor agonist in patients with NASH/MASH and type 2 diabetes in a randomized phase 2 study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2024) 23(1):103–13. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2024.02.022
207. Mir BA, Sharma B, Sharma R, Bodh V, Chauhan A, Majeed T, et al. A prospective randomised comparative four-arm intervention study of efficacy and safety of saroglitazar and vitamin E in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)/non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)-SVIN TRIAL. J Clin Exp Hepatol. (2024) 14:101398. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2024.101398
208. Ezpeleta M, Gabel K, Cienfuegos S, Kalam F, Lin S, Pavlou V, et al. Effect of alternate day fasting combined with aerobic exercise on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized controlled trial. Cell Metab. (2023) 35:56–70. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2022.12.001
209. Ezpeleta M, Gabel K, Cienfuegos S, Kalam F, Lin S, Pavlou V, et al. Alternate-day fasting combined with exercise: effect on sleep in adults with obesity and NAFLD. Nutrients. (2023) 15(6):1398. doi: 10.3390/nu15061398
210. Cheng R, Wang L, Le S, Yang Y, Zhao C, Zhang X, et al. A randomized controlled trial for response of microbiome network to exercise and diet intervention in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:2555. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29968-0
211. Lin YH, Zhang ZJ, Zhong JQ, Wang ZY, Peng YT, Lin YM, et al. Semaglutide combined with empagliflozin vs. monotherapy for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetes: Study protocol for a randomized clinical trial. PloS One. (2024) 19:e0302155. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0302155
212. Yoneda M, Kobayashi T, Honda Y, Ogawa Y, Kessoku T, Imajo K, et al. Combination of tofogliflozin and pioglitazone for NAFLD: Extension to the ToPiND randomized controlled trial. Hepatol Commun. (2022) 6:2273–85. doi: 10.1002/hep4.1993
Keywords: non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, Inter-organ crosstalk, fatty acid synthesis, mitochondrial homeostasis, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress
Citation: Fan Y-H, Zhang S, Wang Y, Wang H, Li H and Bai L (2025) Inter-organ metabolic interaction networks in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Front. Endocrinol. 15:1494560. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1494560
Received: 11 September 2024; Accepted: 16 December 2024;
Published: 09 January 2025.
Edited by:
Gabriel Rufino Estrela, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIH), United StatesReviewed by:
Bing Bo, Henan University, ChinaShaghayegh Khanmohammadi, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Iran
Copyright © 2025 Fan, Zhang, Wang, Wang, Li and Bai. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hongliang Li, bGlobEB3aHUuZWR1LmNu; Lan Bai, YmFpbGFuQGdtdS5lZHUuY24=
 Yu-Hong Fan
Yu-Hong Fan Siyao Zhang
Siyao Zhang Ye Wang
Ye Wang Hongni Wang
Hongni Wang Hongliang Li
Hongliang Li Lan Bai
Lan Bai