
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Endocrinol. , 16 August 2024
Sec. Reproduction
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2024.1411000
This article is part of the Research Topic Roles of the First and Second Messengers in Reproduction View all 5 articles
 Chen Chen1
Chen Chen1 Zefan Huang1
Zefan Huang1 Shijue Dong1
Shijue Dong1 Mengqian Ding1
Mengqian Ding1 Jinran Li2
Jinran Li2 Miaomiao Wang1
Miaomiao Wang1 Xuhui Zeng1*
Xuhui Zeng1* Xiaoning Zhang1*
Xiaoning Zhang1* Xiaoli Sun2*
Xiaoli Sun2*Calcium (Ca2+) is a second messenger for many signal pathways, and changes in intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) are an important signaling mechanism in the oocyte maturation, activation, fertilization, function regulation of granulosa and cumulus cells and offspring development. Ca2+ oscillations occur during oocyte maturation and fertilization, which are maintained by Ca2+ stores and extracellular Ca2+ ([Ca2+]e). Abnormalities in Ca2+ signaling can affect the release of the first polar body, the first meiotic division, and chromosome and spindle morphology. Well-studied aspects of Ca2+ signaling in the oocyte are oocyte activation and fertilization. Oocyte activation, driven by sperm-specific phospholipase PLCζ, is initiated by concerted intracellular patterns of Ca2+ release, termed Ca2+ oscillations. Ca2+ oscillations persist for a long time during fertilization and are coordinately engaged by a variety of Ca2+ channels, pumps, regulatory proteins and their partners. Calcium signaling also regulates granulosa and cumulus cells’ function, which further affects oocyte maturation and fertilization outcome. Clinically, there are several physical and chemical options for treating fertilization failure through oocyte activation. Additionally, various exogenous compounds or drugs can cause ovarian dysfunction and female infertility by inducing abnormal Ca2+ signaling or Ca2+ dyshomeostasis in oocytes and granulosa cells. Therefore, the reproductive health risks caused by adverse stresses should arouse our attention. This review will systematically summarize the latest research progress on the aforementioned aspects and propose further research directions on calcium signaling in female reproduction.
As one of the most important second messengers vital for cellular signaling and homeostasis in cells (1), Ca2+ is involved in regulating almost all biological functions of the body, such as fertilization, proliferation, development, learning and memory, contraction and secretion (2). To perform these functions, free Ca2+ is present in different concentrations in the organelle, cytoplasm, nucleus and extracellular microenvironment. In most cell types, the concentrations of Ca2+ are about 100 nM in the resting state, while the extracellular concentrations of Ca2+ are typically 1-2 mM (1) and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) concentrations of Ca2+ are approximately 0.5-1 mM (3). Unlike other second messengers, Ca2+ cannot be metabolized and is essential for life, so cells precisely regulate [Ca2+]i through calcium ion channels, abundant calcium buffering proteins and specialized calcium extrusion proteins such as calcium pumps (1).
Ca2+ signaling is fundamental to oocyte maturation and activation (4). In all studied animals, oocytes are arrested in the meiotic prophase I while they undergo growth and differentiation. In this stage, the oocyte nucleus is large and is termed the germinal vesicle (GV), hence, oocytes at this stage are also called GV oocytes. The GV oocytes remodel the Ca2+ signaling machinery (5) and store macromolecular components required for fertilization of oocytes and early embryonic development (6). Following hormonal stimulation, the oocyte emerges from this prolonged meiotic arrest and undergoes a complex differentiation pathway involving both meiosis and extensive cytoplasmic rearrangement. This prepares the oocyte for its transition from egg to embryo after fertilization (7). Ca2+ signaling initiating development has been extensively studied in many mammalian and non-mammalian eggs (8–10). Ca2+ channels or Ca2+ transporters in the cell membrane regulate multiple aspects of meiotic maturation and fertilization of mammalian oocytes by controlling the spatiotemporal distribution of Ca2+, such as the resumption of meiotic maturation, polymerization, and depolymerization of microtubules, assembly and disassembly of spindle bodies, and withdrawal of meiosis after fertilization. The role of Ca2+ in egg maturation, fertilization and the application of Ca2+ signaling in assisted reproduction have been well described in several reviews (4, 11–13) over the past few years. Therefore, the aforementioned three sections have been succinctly summarized and updated in our paper. The following three parts will be discussed in detail, focusing on calcium homeostasis in granulosa cells (GC) and cumulus cells (CC), partners and pathways in oocyte Ca2+ signaling and adverse stress-induced calcium signaling related ovarian dysfunction.
In mice (14) and humans (15), most GV-intact oocytes exhibit persistent Ca2+ oscillations, which may be related to the cell cycle and germinal vesicle breakdown (GVBD). In addition, the [Ca2+]i increase caused by the surge of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) (16) and other factors may also be involved in GVBD, recovery of oocyte meiosis (17, 18), and ovulation. Since calcium signaling is essential for oocyte maturation, we will divide this content into two parts, including (1) the function of Ca2+ during oocyte maturation (GV-MII) and (2) the source and regulation of Ca2+ during oocyte maturation.
The development of oocytes from GV stage to metaphase I is closely related to increased [Ca2+]i. Previous studies have reported that follicle-stimulating hormone receptor (FSHR) may be present in oocytes (19). FSH binding to oocyte FSHRs was capable of mobilizing [Ca2+]i elevation that could be one of the initiators for the initiation of GVBD (16). In a recent study, it was reported that FSH could also induce an increase of [Ca2+]i in the GC (20). Similar to FSH, the Gonadotrophin-releasing hormone (GnRH) stimulated a transient increase in [Ca2+]i in rat GC (21). However, the significance of these increases in oocyte maturation requires further investigation. Different from FSH and GnRH, estrogen has adverse effects on spontaneous Ca2+ oscillations. It was reported that estrogen shortened the duration of spontaneous Ca2+ oscillations in a dose-dependent manner (1-1000 nM), and produced an irregular pattern of the oscillations (22). Whether spontaneous Ca2+ oscillations in the GV phase are necessary for oocytes to enter the GVBD phase remains controversial. Studies in mouse oocytes have shown that spontaneous Ca2+ oscillations in GV oocytes were absent when [Ca2+]i was chelated using 1,2-bis(o-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N’,N’-tetraacetic acid tetra(acetoxymethyl) ester (BAPTA)-AM, but this did not affect the occurrence of GVBD. This result implies that spontaneous Ca2+ oscillations in GV oocytes and GVBD occurrence do not seem to be causally related in mice (14, 23). In contrast, in pig oocytes (24, 25), BAPTA-AM treatment inhibited GVBD, suggesting that elevated [Ca2+]i is a prerequisite for GVBD and meiotic progression. Therefore, the role of spontaneous Ca2+ oscillations in GVBD, even if redundant, cannot be ruled out. These differences in response may be due to the large variation in spontaneous maturation rates between species (26).
The contribution of Ca2+ involvement in GVBD is still controversial (23–25), but there is a consensus on the important role of Ca2+ in oocyte meiosis. It has been shown that incubation of GV oocytes in a matrix lacking external Ca2+ (23) or blocking Ca2+ channels with verapamil can inhibit first polar body formation (24, 27–29). Although the first polar bodies did not form after incubating GV oocytes in the absence of external Ca2+, oocytes were not prevented from progressing through meiosis I (23, 30). When high concentrations of Ca2+ chelators were used to bind [Ca2+]i, mouse oocyte meiosis was completely inhibited. This suggests that elevated [Ca2+]i promotes the recovery of oocyte meiosis (23, 30). The proper [Ca2+]i is also necessary for oocyte maturation. When the bovine MII-stage cumulus-oocyte complexes (COCs) were treated with BAPTA-AM, the intracellular [Ca2+]i was significantly lower. The decrease in cytoplasmic Ca2+ halted the nuclear maturation of oocytes, impaired cytoplasmic maturation, and diminished the developmental potential of somatic cell nuclear transfer embryos. These results indicate that Ca2+ is an important factor affecting the maturation of bovine oocytes (31).
ER stores are one of the most important sources of Ca2+ during oocyte maturation. ER are divided into smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) and granular endoplasmic reticulum (GER). SER’s role in calcium storage and release and GER’s role in protein synthesis are critical during oocyte maturation. In ER stores, inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors (IP3Rs) are the primary Ca2+ release channels. Most GV-intact oocytes isolated from mice’s antral follicles exhibit persistent and regular [Ca2+]i oscillations (14), which may be related to the cell cycle and GVBD. To investigate the source of Ca2+ in spontaneous Ca2+ oscillations, the researchers continuously injected inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) into mouse oocytes that spontaneously stopped Ca2+ oscillations. As a result, the oocytes produced new Ca2+ oscillations that were similar in amplitude and frequency to spontaneous Ca2+ oscillations. Moreover, spontaneous Ca2+ oscillations can be blocked by the injection of heparin, an IP3 receptor antagonist (32). These results suggest that IP3-induced Ca2+ release is the primary mechanism responsible for spontaneous Ca2+ oscillations during oocyte maturation (32).
Investigations have shown that Ca2+ release from eggs significantly increased when IP3 was artificially injected compared to GV oocytes (9, 33–35). During oocyte maturation, increased cellular sensitivity to IP3, redistribution of organelles such as the ER, and increased [Ca2+]i stores may contribute to variations in Ca2+ response. Increased sensitivity to IP3-dependent Ca2+ release during oocyte maturation is a hallmark of Ca2+ signaling differentiation in many species, including starfish (36), hamsters (37), mice (33), and Xenopus (35). There are three isoforms of IP3R, of which IP3R1 is closely associated with increased IP3 sensitivity. In mice, the protein level of IP3R1 approximately doubled from GV oocytes to MII oocytes (38). Inhibition of the increase in IP3R1 during oocyte maturation decreased the sensitivity of IP3 and shortened the duration of Ca2+ oscillations after fertilization (39). In addition, increased IP3 sensitivity may be associated with the phosphorylation of IP3R1 (9, 40, 41), which enhanced channel conductivity. Cdk1 may be essential for IP3R1 phosphorylation. Research has shown that the Cdk1 consensus sites, ser421 (S421) and threonine799 (T799), undergo phosphorylation in mouse oocytes at the MII stage (9). In somatic cells, phosphorylation of IP3R1 at these sites increased IP3 binding and IP3-gated Ca2+ release (42). In addition, in mouse eggs, expression of heterologous IP3R1 with a phosphorylation mutation corresponding to three M-phase motifs (which should be phosphorylated by M-phase kinase in MII eggs) resulted in greater Ca2+ oscillatory activity and sensitivity to IP3 (41). Besides M-phase kinases, studies in somatic cells have shown that IP3R isoforms can be phosphorylated by more wide-ranging kinases (43). The most commonly implicated kinases include protein kinase A (PKA), protein kinase C (PKC), and CaMKII, all of which have important physiological functions in oocytes and eggs. In mouse oocytes, IP3R1 phosphorylation by PKA, was shown during maturation, with maximal PKA phosphorylation occurring at the GV stage (9).
IP3Rs are also Ca2+ channel proteins that regulate the dynamic balance between the ER and mitochondrial Ca2+. A recent study found that inhibition of IP3R1 expression led to ER dysfunction, contributing to ER calcium release outwards into mitochondria and causing mitochondrial free calcium concentration overload and mitochondrial oxidative stress. Further analysis revealed that IP3R1 functioned by regulating the IP3R1-GRP75-VDAC1 complex between mitochondria and the ER (44). The loss of IR3R1 activity resulted in the failure of porcine oocyte maturation and CC expansion, as well as the obstruction of polar body excretion. These studies suggest that IP3Rs, especially IP3R1, play an important role in egg maturation. To further validate the role of IP3R1 in physiological processes, oocyte-specific knockout (KO) mice are needed.
It is also important to release Ca2+ from ER stores at the appropriate time. Premature Ca2+ release can lead to parthenogenetic activation before fertilization, making it crucial to prevent improper Ca2+ signaling to ensure oocyte MII arrest. Purinergic receptor P2Y2 (P2Y2R) is a G protein-coupled receptor that can induce the opening of IP3R on the ER, causing the release of Ca2+ from Ca2+ stores and leading to an increase in [Ca2+]i. It was found that the inhibition of P2Y2R during cryoprotectant exposure reduced premature [Ca2+]i release and significantly improved the developmental capacity of exposed bovine oocytes (45). Similar to P2Y2R, Regulators of G-protein signaling 2 (RGS2) was also found to inhibit premature Ca2+ release in MII-phase oocytes. Rgs2-/- female mice showed decreased litter size and premature zona pellucida transformation of eggs, suggesting that RGS2 is an important regulatory molecule that inhibits premature Ca2+ release from oocytes before fertilization (46). Thus, preventing the premature release of Ca2+ during oocyte maturation is essential for normal fertilization and early embryonic development. Taken together, these studies imply that ER Ca2+ stores are a very important source of Ca2+ increase and the proper Ca2+ release from ER stores is vital for the oocyte maturation.
Recent studies have found that [Ca2+]e is vital for spontaneous Ca2+ oscillations and the maturation of oocytes. It has been reported that spontaneous Ca2+ oscillations in oocytes are reversibly inhibited in the absence of [Ca2+]e (22). When the medium lacked Ca2+, there was a significant increase in intracytoplasmic Ca2+ in oocytes, leading to oocyte death within two hours after GVBD (47). Consistent with these results, egg Ca2+ oscillations were affected when the channel mediating [Ca2+]e influx was abnormal. TRPM7-like channels expressed in oocytes were capable of mediating Ca2+ influx and spontaneous Ca2+ oscillations disappeared when the channels were blocked by chemical inhibitors (48). The oocyte-specific deletion of Trpm7 in mouse oocytes resulted in a significant reduction in [Ca2+]e influx in GV oocytes (49). These results imply that both spontaneous Ca2+ oscillations and maturation of oocytes require the involvement of [Ca2+]e. In addition, the prolonged culture in a medium without exogenous Ca2+ resulted in chromatin decompression and spindle disintegration in oocytes, which were defined as “interphase-like” (23, 29). All these experimental results demonstrate that extracellular fluid plays a crucial role in oocyte maturation and serves as a significant source of Ca2+ during this process.
Mitochondria are not only the energy powerhouse of the cell but also can serve as a source of Ca2+ in certain cellular processes. Indeed, mitochondria play a pivotal role in cell fate due in large part to their participation in the dynamic regulation of [Ca2+]i (50). [Ca2+]i homeostasis controlled by mitochondria is also crucial for the appropriate maturation of oocytes and the acquisition of competence (51, 52). During oocyte maturation, active mitochondrial Ca2+ ([Ca2+]m) was higher around the nucleus than in the mitochondrial cortical layer, suggesting that higher [Ca2+]m around chromosomes may play a potential role in stimulating mitochondrial energy to promote calmodulin-responsive oocyte spindle formation (53). Recent evidence suggest that mitochondrial calcium uniporters (MCU) are essential for meiotic progression in mouse oocytes (54). MCU knockdown (KD) by injecting a specific MCU siRNA into fully grown oocytes at the GV stage caused a significant reduction in the proportion of GVBD oocytes and significantly decreased the proportion of MII oocytes. This was consistent with the results of using Ru360, a specific inhibitor of MCU. Further research found that MCU KD resulted in low levels of [Ca2+]m, which led to a decline in cytosolic ATP levels, activating and phosphorylating AMP‐activated protein kinase (AMPK). Excessive activation of AMPK resulted in adverse effects on the resumption of meiosis. Together, these findings indicate that the [Ca2+]m homeostasis maintained by MCU is necessary for the orderly meiotic maturation of oocytes (54). Similar to this study, Zhang et al. separately targeted Micu1/Micu2 and the mitochondrial Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (NCLX) for KD with siRNA injected into oocytes to generate the mitochondrial overload model in mouse oocytes. As a consequence, the deficiency of Micu1/Micu2 or NCLX induces increased levels of [Ca2+]m in mouse oocytes. Moreover, overload [Ca2+]m resulted in a delay in meiosis maturation and mitochondrial dysfunction (55). These results highlight the critical role of [Ca2+]m regulation in maintaining mitochondrial function and oocyte maturation. Except for MCU and NCLX, there is another protein named multidrug resistance transporter-1 (MDR-1) expressed in the oocyte mitochondrial membrane. The researchers found that thapsigargin (TG)-induced Ca2+ release from MDR-1 mutant MII oocytes did not change significantly, whereas Ca2+ ionophore-evoked Ca2+ release was significantly increased. These results indicate that MDR-1 mutant oocytes exhibit a greater Ca2+ rise, suggesting the accumulation of internal Ca2+, most likely in the mitochondria. MDR-1 dysfunction in mouse oocyte quality is attributed to several factors, including [Ca2+]m homeostasis. This dysfunction leads to a notable delay in the GV to GVBD transition, chromosome misalignments and a significantly altered meiotic spindle shape (56). Taken together, the Ca2+ homeostasis controlled by mitochondria is essential for oocyte maturation and abnormal mitochondrial function can lead to oocyte development disorders.
In conclusion, ER stores, extracellular fluid and mitochondria are the main sources and regulators of Ca2+ during oocyte maturation. [Ca2+]e or [Ca2+]i affects the formation of the first polar body of oocytes, the first meiotic division, and the maintenance of chromosome and spindle conformation between M I and M II in a unique way.
Unlike FSH, the luteinizing hormone receptor (LHR) is not expressed in oocytes, but in GC of large follicles. LHRs have been detected in GC of human (57), bovine (58), and pig (59), which were weakly expressed in mice (60) and rats (61). In the GC of intact mouse ovarian follicles, LH can cause persistent Ca2+ oscillations that occurred for at least 6 h. This phenomenon is very interesting, but the function of these persistent Ca2+ oscillations in oocyte maturation still needs further investigation (20). In vitro experiments on sheep and cattle have shown that LH can stimulate an increase of Ca2+ in CC, followed by an increase in Ca2+ in oocytes (62, 63). The elevation of Ca2+ in oocytes starts in the cortex and then spreads throughout the oocyte, suggesting that the increase of Ca2+ in the oocyte can be transmitted within the oocyte, but the source of the increase in [Ca2+]i in the oocyte remains unknown. The increased Ca2+ may be due to the release of [Ca2+]i stores (63), or it may be a combination of [Ca2+]i stores release and [Ca2+]e influx (62). Moreover, in cultured cumulus-oocyte complexes, the activation of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor by LH elevated [Ca2+]i in CC, leading to a decrease in natriuretic peptide receptor 2 (NPR2) affinity and cGMP levels. This resulted in the meiotic resumption of mouse oocytes (64). In this study, EGF, another crucial factor for oocyte maturation, was also found to increase [Ca2+]i in CC, consistent with previous research (65). In addition, depolarization may also contribute to the increase of Ca2+ in CC. LH-induced depolarization was also observed in the CC of sheep (66) and pigs (67), which can activate the L-type Ca2+ channel responsible for mediating Ca2+ influx into CC, increasing [Ca2+]i. Unlike in sheep and bovine, mouse cumulus-oocyte complexes or GC did not show an increase in Ca2+ when stimulated by FSH or LH (68). This difference may be due to the different densities of LHR in CC among different species. The long-term effects of LH on Ca2+ in mouse CC require further observation, as LH may influence Ca2+ in mouse CC gradually and persistently.
Similar to the LHR, the highly conserved ER transmembrane protein named transmembrane and coiled coil domains 1 (TMCO1), which acts as a Ca2+ load-activated Ca2+ (CLAC) channel (69), is also important for maintaining Ca2+ homeostasis in the Ca2+ stores of GC (70). TMCO1 gene mutation can induce autosomal recessive TMCO1 defect syndrome, which belongs to the human cerebrofaciothoracic (CFT) dysplasia spectrum (71, 72). In addition to the main clinical CFT dysplasia spectrum, female mice with Tmco1 gene KO exhibited progressive loss of follicles, impaired follicle development, and subfertility, resembling the symptoms of premature ovarian failure in females. Based on the function of TMCO1, the researchers found that Ca2+ signaling was abnormal in response to ionomycin, TG and ATP, which were about 1.3 to 1.5-fold larger in GC of KO female mice compared to wild type (WT). Interestingly, when TMCO1 was deficient, the ER Ca2+ stores in GV and MII oocytes were normal despite the altered pattern of spontaneous Ca2+ oscillations. These results suggest that TMCO1 maintenance of Ca2+ homeostasis in the ER Ca2+ stores of GC is fundamental for follicle development and reproduction, and that disruption of this homeostasis leads to impaired follicle development and reduced fertility (70).
In summary, further research is needed to investigate including, 1) identification and physiological function studies of calcium signaling regulatory molecules, such as calcium channels and calcium pumps in GC and CC; 2) pathological significance of the abnormalities of calcium signaling regulatory molecules in GC and CC; 3) upstream and downstream signaling networks of calcium signaling regulatory molecules involved in cellular function and fate in GC and CC; 4) discovery of new physiological factors regulating calcium homeostasis in GC and CC and reveal pathological and exogenous factors affecting calcium homeostasis in the two types of cells and their corresponding interventions or preventive measures; 5) elucidate the molecular mechanisms by which calcium homeostasis in GC and CC affects oocyte maturation and fertilization; and 6) analyze the similarities and differences, interactions, and their corresponding physiological functions of calcium signaling regulation among the GC, the CC, and the oocyte.
Oocyte activation (OA) is the process by which oocytes arrested in metaphase II are stimulated to resume meiosis (73). Ca2+ signaling is universally recognized as the primary marker of OA in all sexually reproducing species. The sperm-induced pattern of Ca2+ oscillations in mammals is relatively stable, with [Ca2+]i in the egg rising more than 10-fold shortly after sperm-egg fusion and maintaining this level for several minutes before returning to baseline levels. In vitro experiments have shown that Ca2+ oscillations occurred in mature oocytes after 20-35 minutes of sperm addition (74). OA occurred with the onset of Ca2+ oscillations, and it taken approximately 1-2 hours for all oocytes to be activated. After 4-6 hours of Ca2+ oscillations, pronuclei were formed (75). Then, the Ca2+ oscillations disappeared and the fertilization was complete. During egg fertilization, each Ca2+ oscillation may have its own specific role (75). Additionally, the frequency of Ca2+ oscillations is crucial for fertilization (76). These findings suggest that the precise regulation of Ca2+ signaling during fertilization is essential for obtaining well-developed embryos and healthy offspring. Therefore, understanding the mechanisms regulating Ca2+ oscillations in eggs during fertilization is essential for studying female fertility, as abnormal Ca2+ signaling can impact fertility.
The Ca2+ oscillations generated in mammalian eggs after fertilization can be artificially divided into two processes, including the increase and maintenance of [Ca2+]i in the eggs after sperm-egg fusion and the decrease of [Ca2+]i, and restoration of baseline levels. Since Ca2+ signaling is regulated by different Ca2+ channels and transporters, and the same Ca2+ channel or transporter may participate in the regulation of egg activation, fertilization, or embryonic development, we will discuss the role of each Ca2+ channel or transporter separately after sperm-egg fusion to avoid repetition.
In most of the species studied, spermatozoa release sperm factor phospholipase C (PLC) after sperm-egg fusion and subsequently hydrolyze phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) by PLC to generate IP3, which is required for Ca2+ release during fertilization. The specific PLC varies among species, and there are six families of PLC enzymes in animals, including PLCβ, PLCγ, PLCδ, PLCϵ, PLCζ, and PLCη (77). PLCγ was the first specific PLC enzyme identified to activate and produce IP3 upon fertilization (78) and has been studied in several species (78–81). It was found that tyrosine kinase is the most common mechanism for activating PLCγ (82). However, studies in mice have shown that eggs require multiple sperm factors for activation, but not PLCγ (83). Further analysis showed that PLCζ cloned from a cDNA library of mouse sperm was convincingly identified as the protein in sperm extracts with the capable of activating oocytes (Figure 1) (84). Consistent with this result, KD of PLCζ protein in mouse spermatozoa by RNA interference resulted in an abnormal pattern of egg Ca2+ oscillations and premature termination during in vitro fertilization (IVF). Further analysis of the genotypes of the transgenic mice offspring revealed that no new transgenic mice were born, suggesting that the absence of Ca2+ oscillations during fertilization may lead to the failure of proper development of fertilized eggs (85). This finding aligns with previous research indicating that normal Ca2+ oscillations support long-term embryo development (86). PLCζ full-length KO mice exhibited normal spermatogenesis and sperm motility. However, KO mouse sperm failed to induce egg Ca2+ oscillations either by intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) or IVF, and an increased rate of polyspermy was observed after IVF or in vivo fertilization, with males exhibiting severely reduced fertility (87, 88). Human sperm lacking PLCζ have also been identified in infertile men, with patients exhibiting failure to activate eggs by ICSI, and the same failure to induce Ca2+ release by injecting human sperm into mouse eggs (89). In recent years, an increasing number of novel PLCZ1 mutations or abnormalities associated with the failure of human egg activation have been identified (90–92). According to the latest research, a maltose binding protein (MBP)-tagged recombinant human PLCζ protein is capable of inducing Ca2+ oscillations in mouse oocytes similar to those observed at fertilization. MBP-PLCζ did not alter embryonic viability compared to the control, providing a first indication of its safety. These results suggest that recombinant MBP-PLCζ protein holds promise for the treatment of OA failure, which can be more precisely controlled compared to the previously discovered strategy of activating oocytes by direct injection of PLCζ RNA, since the stabilization of the RNA upon entry into the cell and the efficiency of protein translation are difficult to control (93). These studies demonstrate the importance of PLCζ in the initiation of Ca2+ oscillations and in normal mammalian embryonic development (Figure 1).
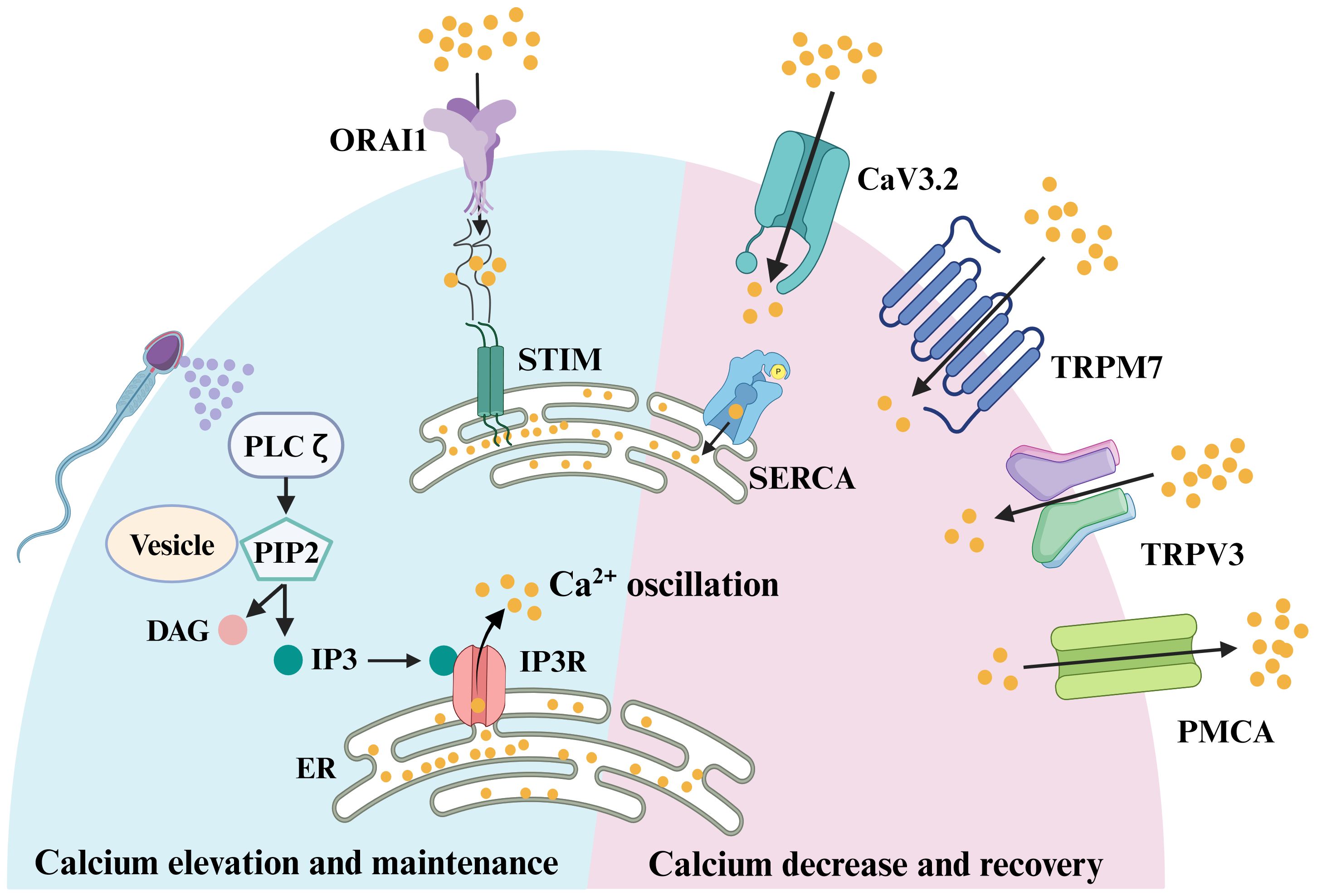
Figure 1. Signaling pathways involved in oocyte fertilization of mammals. Sperm factor PLCζ acts on PIP2 in intracellular vesicles to generate IP3, which stimulates IP3R-mediated Ca2+ release from ER Ca2+ store. Once the ER store is emptied, the egg replenishes the depleted ER store by influx of extracellular Ca2+, which was known as store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE). The main molecular mediators of SOCE are STIM proteins and ORAI proteins. In response to a reduction in ER Ca2+, the STIM proteins interact directly with ORAI channels, inducing Ca2+ influx. This Ca2+ is subsequently pumped back into the ER by the action of sarco-ER Ca2+ ATPases (SERCA). Meanwhile, to avoid cytotoxicity from excessive intracellular Ca2+ in oocytes, plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase (PMCA) pumps transport some of the Ca2+ out of the cytoplasm. When the excess Ca2+ in the cytoplasm are excreted, the egg needs to take in some Ca2+ to balance the intracellular ion level, and this process is mainly achieved through voltage-gated Ca2+ channels, CaV3.2, and transient receptor potential channels, TRPV3 and TRPM7.
It was found that there are two sources of PIP2 in eggs, one from the plasma membrane (PM) and the other from intracellular vesicles. There was evidence indicating that PIP2 levels at the PM did not decrease upon fertilization (94, 95). Moreover, fertilization-induced Ca2+ oscillations were disrupted in the absence of intracellular vesicle-associated PIP2 (94, 95), suggesting that the PIP2 within intracellular vesicles served as the substrate for PLCζ action (Figure 1). However, the question of how PLCζ alters intracellular IP3 ([IP3]i) concentrations during Ca2+ oscillations remains unanswered. Whether the underlying [IP3]i level rises with [Ca2+]i or if the persistently elevated IP3 level drives the Ca2+ oscillations. A recent study addressed this question by detecting a sustained increase in [IP3]i after fertilization of mouse eggs using the FRET method, and it remained high throughout the oscillation. Notably, there was a slight increase in [IP3]i with each increase in [Ca2+]i, reflecting the high Ca2+ sensitivity of PLCζ (96). However, the peak of [IP3]i occurred after the onset of [Ca2+]i elevation. Thus, it was hypothesized that the periodic rise of [Ca2+]i in fertilization-induced oscillations was mainly determined by changes in IP3R1 sensitivity (97), which exerted an important role in triggering the [Ca2+]i rising phase (96) and influx of Ca2+ from the extracellular matrix and thus filling the Ca2+ stores (98). In conclusion, PLCζ released from sperm initiates OA and elevates the Ca2+ oscillations after sperm-egg fusion.
Under normal physiological conditions, PLC-triggered egg Ca2+ oscillations begin after sperm fuse with eggs (Figure 1). During this process, IP3R is the first to respond to PLC (Figure 1). Mammalian oocytes, eggs and cells surrounding the eggs express all three isoforms of IP3R (38), but oocytes and eggs predominantly express the IP3R1 isoform (99, 100). The opening of IP3R requires all three subunits to bind to IP3, along with Ca2+ (101, 102). Ca2+ regulates IP3-induced Ca2+ release in a pendulum-like pattern, with IP3-induced Ca2+ release being stimulated at low [Ca2+]i but inhibited at high [Ca2+]i (97). The dual regulation of IP3R (Ca2+ and IP3) makes it particularly well-suited to support long-term Ca2+ oscillations. In sea urchin eggs, researchers first found increased IP3 levels after fertilization (103), and when IP3 was artificially injected into eggs it could induce Ca2+ release from [Ca2+]i stores (104), as observed in hamster oocytes (105). When an antibody that functionally blocks the IP3 receptor was injected into hamster oocytes using the microinjection technique, it was found that the antibody completely suppressed sperm-induced Ca2+ waves and Ca2+ oscillations (106), and that fertilized eggs exhibited polyspermy and late pronucleus formation was inhibited, indicating that IP3-mediated Ca2+ release is necessary for both early and late events of mouse egg activation (107). As research progressed, the role of IP3R1 in fertilization in other species was also discovered (108). When mouse fertilized eggs transition from MII to interphase, fertilization-induced Ca2+ oscillations become less frequent and cease at the time of pronucleus formation (109). In this process, IP3R1 decreases by about half through ligand-induced hydrolysis (100). Recent study (110) has reported that basal levels of labile Zn2+ are essential for sperm-induced Ca2+ oscillations in mouse eggs, because Zn2+ depleted states evoked by cell-permeable chelators abolished Ca2+ responses induced by fertilization and other physiological and pharmacological agonists. It was also found that eggs with lower labile Zn2+ content, despite stable store and IP3R1 mass, had decreased IP3R1 sensitivity and decreased ER Ca2+ leakage. Zn2+ replenishment resumed Ca2+ oscillations, but excess Zn2+ prevented and aborted these oscillations, thereby compromising IP3R1 responsiveness. These results suggest that oocyte Ca2+ responsiveness and IP3R1 function need a window of Zn2+ concentration to ensure an optimal response to fertilization and OA (110). Since IP3R1 is embryonic lethal in constitutive KO mice, current studies on this channel have mainly relied on chemically synthesized agonists and inhibitors. As an important ion channel that maintains post-fertilization Ca2+ oscillations in eggs, the mechanisms by which IP3R1 regulates oocyte development and post-fertilization Ca2+ oscillations remain to be investigated in oocyte conditional knockout (cKO) mice. Comprehensive study of cKO mice is conducive to exploring the significance of IP3R1 abnormalities in female infertility. It is expected to elucidate the role and mechanism of IP3R1, especially downstream molecules/events that receive IP3R regulation in oocyte activation, which will provide new perspectives for understanding the physiology of human oocytes, exploring the causative factors of embryo development failure after normal fertilization, and developing diagnostic and therapeutic tools by detecting or manipulating the activity of IP3R for female infertility.
During egg Ca2+ oscillations mediated by sperm factor PLC, the IP3R receptor releases Ca2+ from the Ca2+ stores. Subsequently, the egg replenishes the depleted ER store through an influx of [Ca2+]e, a process known as store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE) (111, 112). The mechanism of SOCE to replenish ER Ca2+ stores as soon as they are empty has been confirmed in somatic cell studies (112, 113). The main molecular mediators of SOCE are STIM proteins and ORAI proteins, with STIM sensing Ca2+ levels within the ER Ca2+ stores and ORAI proteins acting as Ca2+ channels on the PM. There are two STIM proteins, STIM1 and STIM2, and three ORAI proteins, ORAI1, ORAI2, and ORAI3, in mammals. In response to a reduction in ER Ca2+, STIM proteins oligomerize and undergo redistribution within the ER to regions closely opposed to the PM, known as ER-PM junctions (Figure 1). There, the STIM proteins interact directly with ORAI channels, inducing Ca2+ influx (Figure 1). This Ca2+ is subsequently pumped back into the ER by the action of sarco-ER Ca2+ ATPases (SERCA) (Figure 1). Whether SOCE is an important physiological mediator in Ca2+ influx after fertilization remains contradictory. Earlier studies explored the function of SOCE mainly by employing inhibitors of SOCE and found that SOCE was not required for fertilization in mice (114, 115). To further clarify the physiological function of SOCE, researchers generated STIM1 and STIM2 oocyte cKO mice and obtained STIM1 and STIM2 double KO females by mating. Both fertility and ER Ca2+ stores were normal in single or double KO females, with no significant effects on Ca2+ influx or Ca2+ oscillations during fertilization. These results suggest that in mouse oocytes, neither STIM1 nor STIM2 is an essential ion channel for Ca2+ influx when the ER Ca2+ store is exhausted (116). Global KO female mice of ORAI1 are also fertile (116, 117), and likewise, there is no significant difference in either ER Ca2+ store or Ca2+ influx after Ca2+ stores are exhausted in MII eggs of Orai1 KO mice. Thus, Orai1 is also not necessary for normal Ca2+ signaling in mouse oocytes and eggs. Perhaps due to species differences, the results in pig oocytes are in contrast to studies in mice, where STIM1 and ORAI1 are required for activation of pig oocytes (118). Based on the present findings, it appears that in mice, SOCE is not the mechanism responsible for replenishing ER stores after fertilization and that SOCE may be applicable in other animals. However, we are not sure whether the lack of significant changes in calcium signaling after ORAI1 and STIM KO is due to the compensation by other channels.
There are many other channels involved in the regulation of calcium elevation and maintenance, such as the calcium sensing receptor, ryanodine receptors, and sodium/Ca2+ exchangers (13). However, it is yet to be determined whether they are expressed or play significant roles in oocytes.
For Ca2+ oscillations to be sustained and to avoid cytotoxicity from excessive [Ca2+]i in oocytes, redundant [Ca2+]i needs to be removed rapidly to terminate signaling and return Ca2+ to baseline levels, and refill the Ca2+ stores in anticipation of the next Ca2+ transient (Figure 1). The main channels responsible for transporting excessive Ca2+ out of the cytoplasm in the oocyte membrane is plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase (PMCA) pumps. In addition, the Sarco-ER Ca2+ ATPase (SERCA) pumps act as Ca2+ pumps on the ER, recycling cytoplasmic Ca2+ back into the Ca2+ stores against the concentration gradient to prepare for the next Ca2+ oscillation. When the excess Ca2+ in the cytoplasm is excreted, the egg needs to take in some Ca2+ to balance the intracellular ion level, and this process is mainly achieved through voltage-gated Ca2+ channels and TRP channels such as TRPV3 and TRPM7. So in the next section, we will discuss how these ion channels reduce excess [Ca2+]i and restore basal Ca2+ levels in the oocyte.
As one of the P-type Ca2+ pumps, PMCA maintains [Ca2+]i homeostasis by transporting excessive [Ca2+]i to the extracellular (Figure 1). The mammalian PMCA is encoded by four genes (Atp2b1-4) that generate approximately 30 isoforms through variable splicing. PMCA1 and PMCA4 are commonly expressed and are considered to be housekeeping PMCAs (119). PMCA2 is expressed in the nervous system and mammary gland, whereas PMCA3 is expressed in the nervous system (119). In Xenopus oocytes and eggs, the predominant presence of PMCA on the cell membrane of oocytes was demonstrated using antibodies that recognize the four isoforms of mammalian PMCA (120). Atp2b1-3 can all be detected in mouse GV stage oocytes (121), which is consistent with microarray data (122–124). In mouse oocytes, the expression profiles of Atp2b1 and Atp2b3 were almost identical, but as fertilized eggs developed into blastocysts, Atp2b3 expression became almost undetectable, while Atp2b1 increased instead (121). To gain more insight into the role of the Atb2b1 gene in female mouse oocytes, the researchers crossed the Atb2b1loxP/loxP transgenic mice with Zp3-Cre mice to obtain female mice with oocyte-specific Atb2b1 gene disruption before the first meiotic division. Consequently, deletion of the Atp2b1 isoform did not result in compensatory up-regulation of the alternative isoform and the female fertility was not affected. However, PMCA did have an effect on the Ca2+ oscillations in the oocyte during fertilization. The frequency of Ca2+ oscillations was not significantly altered in KO mouse oocytes within 1 h of fertilization, but the first Ca2+ transients were significantly longer than in wild type (WT) oocytes. Furthermore, oocytes deficient in PMCA1 resulted in larger Ca2+ stores (121). This is similar to the results of post-fertilization oocyte Ca2+ oscillations studied using the PMCA inhibitor gadolinium (Gd3+) (115, 125). Although PMCA1 KO in mouse oocytes did not affect female fertility, abnormal Ca2+ at fertilization have long-term effects on offspring growth and the body composition of male mice (121). Follow-up studies are expected on PMCA3 in oocytes and the impact of PMCA1 and PMCA3 on Ca2+ oscillations during fertilization.
SERCA is also a P-type Ca2+ pump located on the ER membrane that transports Ca2+ from the cytoplasm to the ER lumen against a concentration gradient (Figure 1). In mammals, it is encoded by three genes (Atp2a1-3) that generate three major isoforms (SERCA1-3) (126). SERCA2 is the dominant isoform present during fertilization. In mouse oocytes, SERCA2B is the predominantly expressed isoform (125). SERCA can be inhibited by general P-type ATPase inhibitors, such as La3+ and orthovanadate, as well as the specific inhibitor TG (126). Oocytes treated with TG showed a significant reduction in the magnitude and duration of the first post-fertilization Ca2+ transient and a decrease in the duration of Ca2+ oscillations, suggesting an important role for SERCA in post-fertilization Ca2+ oscillations (127). Although SERCA2B protein levels remained relatively constant during oocyte maturation, there was a spatial redistribution of the protein, similar to the distribution of ER, from the more diffuse pattern in GV oocytes to the cortical clusters of oocytes (125). Localization of the SERCA pump near the IP3 receptor may facilitate rapid replenishment of ER Ca2+ stores after depletion following fertilization. Considering that the current researches are conducted by using SERCA inhibitors, the role of SERCA in oocytes and post-fertilization Ca2+ oscillations in mice needed to be further investigated using the cKO models.
Among the PM channels, the mammalian transient receptor potential (TRP) family of channels includes six subfamilies and nearly 30 human members that are expressed in multiple cell types and tissues (128). Two family members of TRP channels have been identified on oocytes and eggs, including TRP vanilloid member 3 (TRPV3) and transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 7 (TRPM7) (Figure 1) (129). TRPV3 channels are primarily expressed in the oocyte membrane and their expression increases progressively as the oocyte matures. Activation of TRPV3 by the agonists, carvacrol and 2-APB, induced Ca2+ entry, which can parthenogenetically activate eggs (129, 130). TRPV3 channels also mediated Sr2+ influx and subsequent egg activation in mice eggs (129), but these results can’t be replicated in human oocytes (131). Although TRPV3 mediates Ca2+ entry into eggs, but the Ca2+ influx it mediates is not necessary for eggs to maintain Ca2+ oscillations, and fertility is not affected in TRPV3 KO females. Then what is the function of TRPV3 in oocytes and eggs? One possibility is that TRPV3 channels constitutively conduct low levels of Ca2+ to maintain Ca2+ homeostasis. Nevertheless, given the importance of these functions, eggs may have a redundant system that could explain the unchanged oscillation pattern and fertility in TRPV3 KO eggs (129).
TRPM7, expressed in mouse oocytes and eggs (48), is a constitutively active ion channel that is permeable to divalent cations, including Mg2+ and Ca2+ (132, 133). Nevertheless, the roles of TRPM7-mediated calcium signal have not been investigated and confirmed in human oocytes and eggs. To evaluate the capacity of TRPM7 to mediate Ca2+ influx in eggs, the researchers tested the [Ca2+]i responses induced by the TRPM7-specific activator Naltriben. MII eggs responded to a higher concentration of Naltriben and the response appears to be sustained. To confirm that [Ca2+]i increases induced by Naltriben were caused by Ca2+ influx and not due to intracellular off-target effects of the drug, they exposed the cells to Naltriben in media without Ca2+. As a consequence, eggs failed to show [Ca2+]i increase. These results suggest that Naltriben-induced [Ca2+]i increases in eggs were caused by Ca2+ influx mediated by TRPM7 channels (48), which was confirmed through the use of TRPM7 cKO female mice. To determine whether TRPM7 mediates Ca2+ influx following fertilization, control and Trpm7 cKO eggs were fertilized while monitoring [Ca2+]i. There was no difference in the duration of the first Ca2+ transient. However, the oscillation frequency was significantly reduced, which caused abnormal growth in the offspring of Trpm7 cKO eggs (49). Recent study has also reported that TRPM7-mediated Mg2+ influx is indispensable for reaching the blastocyst stage and that TRPM7 underpins Mg2+ homeostasis. Additionally, excess Mg2+ (but not Zn2+ or Ca2+) was found to overcome the arrest of Trpm7-null embryos (134). However, this study doesn’t evaluate the sperm-induced Ca2+ oscillation in eggs. Therefore, we cannot rule out the contributions of TRPM7 in Ca2+ influx during Ca2+ oscillations. These findings indicate that TRPM7 is a key regulator of Ca2+ influx in response to alterations in [Ca2+]e and Mg2+ ion concentrations and plays an important role in offspring growth.
Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels (CaV) intricately regulate the influx of Ca2+. CaV can be divided into three major classes based on their structure and function. Among them, the T-type voltage-gated Ca2+ channel, CaV3.2, is the ion channel responsible for mediating the typical T-type current in mouse oocytes (Figure 1) (135, 136). The Cacna1h−/− females have a reduced litter size. The frequency and amplitude of Ca2+ oscillation in Cacna1h−/− eggs were not significantly different compared to those in Cacna1h+/− eggs during IVF. However, the duration of the first Ca2+ transient in Cacna1h−/− eggs was significantly shorter than that in Cacna1h+/− eggs. Reduced persistence of Ca2+ oscillation in Cacna1h−/− eggs suggests that CaV3.2 channels contribute to Ca2+ influx required for sustained Ca2+ oscillations at fertilization (137). While in some eggs lacking CaV3.2, Ca2+ oscillations can persist long after fertilization. This is likely due to the complementation of other ion channels that mediate Ca2+ influx in the oocyte, such as TRPV3 and TRPM7. To further investigate the role of these channels in oocyte development and maturation, the double knockout (dKO) mouse model was generated.
Double-null mice lacking Trpv3 and Cacna1h genes are subfertile (138). Compared to the WT eggs, the time to initiation of oscillations was longer, and the mean number of Ca2+ transients was lower in the dKO eggs after fertilization. These data suggest that TRPV3 and CaV3.2 channels are not necessary for the initiation of fertilization, but they remarkably affect the periodicity of such oscillations. Therefore, they are physiological contributors to the [Ca2+]i responses during mouse fertilization. They also found that the functional TRPM7 channel is present and upregulated in eggs of dKO mice. TRPM7-like currents are higher in dKO eggs, and Ni2+ influx is also enhanced in dKO eggs. Therefore, it is possible that the alteration in the expression and/or function of TRPM7 in dKO eggs is adequate for the initiation and persistence of the low-frequency oscillations triggered by fertilization (138).
Combined loss of TRPM7 and CaV3.2 dramatically alters Ca2+ signals and impairs female mice fertility (49). Monitoring of [Ca2+]i during IVF revealed that, consistent with the decrease in Ca2+ stores, the duration of the first Ca2+ transient and the frequency of Ca2+ oscillations following IVF were significantly shorter or lower in the dKO eggs compared to eggs lacking only CaV3.2. Interestingly, most of the dKO eggs began oscillating again almost 1 hour after the first Ca2+ transient. These findings indicate that CaV3.2 and TRPM7 support the majority of Ca2+ influx into eggs during the first hour following fertilization. However, other Ca2+ channels should be subsequently activated to allow for the Ca2+ oscillation “restart” (49). Whether the other Ca2+ channel is TRPV3 is not investigated in this article. These researches indicate that TRPV3, TRPM7 and CaV3.2 play a synergistic role in the process of egg Ca2+ oscillation after fertilization. However, the present study showed that deletion of either one (TRPV3/TRPM7/CaV3.2) or both (TRPV3 and CaV3.2 or TRPM7 and CaV3.2) channels did not completely eliminate the egg Ca2+ oscillations after fertilization and the corresponding KO females were not completely infertile. These may be due to redundant effects between ion channels. Therefore, further studies are needed to confirm the role of the three channels through double or triple KO mice. With any luck, new ion channels may be discovered during this process.
In addition to these channels or Ca2+ pumps that directly regulate Ca2+ signaling, other regulatory molecules that indirectly affect the Ca2+ pump or downstream pathways regulated by Ca2+ signaling are also critical for OA and fertilization (Figure 2). The best-characterized event of mammalian OA is the resumption and completion of meiosis. However, high levels of M-phase promoting factor (MPF) activity, mainly consisting of cyclin B and a cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK1), maintain meiotic arrest (Figure 2) (139). Therefore, a protein or a signal is needed to reduce MPF activity. It has been reported that a moderate increase in [Ca2+]i within physiological range induces the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), leading to a decrease of cAMP levels (Figure 2) (18). Abnormalities in ROS, cAMP, and Ca2+ may induce meiotic instability. Instability in the meiotic cell cycle can lead to spontaneous exit from M-II arrest, chromosomal scattering, and incomplete extrusion of the second polar body without forming pronuclei. This phenomenon is known as abortive spontaneous ovum activation (140). Moreover, calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CAMKII (CAMK2A)) is also a key protein that decreases the MPF activity in the downstream of Ca2+ oscillations (141). Microinjection of constitutively active CAMKII into mouse eggs was shown to induce meiotic resumption (142). Furthermore, although eggs from CAMKIIγ KO or KD mice exhibited a normal pattern of Ca2+ oscillations after insemination and undergo cortical granule exocytosis, they failed to resume meiosis (143). CAMKII and meiotic resumption are connected by at least two mechanistic pathways. On the one hand, Ca2+ oscillations activate CAMKII, leading to EMI2 phosphorylation (144). Phosphorylated EMI2 cannot inhibit the anaphase promoting complex or cyclosome (APC/C). As a result, APC/C disrupts EMI2 and cyclin B, leading to a loss of MPF activity (Figure 2) (145). On the other hand, CaMKII activates WEE1B, which phosphorylates CDK1 and inhibits MPF activity (Figure 2) (146). Conversely, when Wee1B is downregulated, oocytes fail to form pronuclei in response to Ca2+ signaling. This suggests that Wee1B activation in the oocytes is essential for MPF inactivation and cyclin B disruption (146). These data suggest a two-pronged action of Ca2+ signaling on reducing MPF activity (Figure 2).
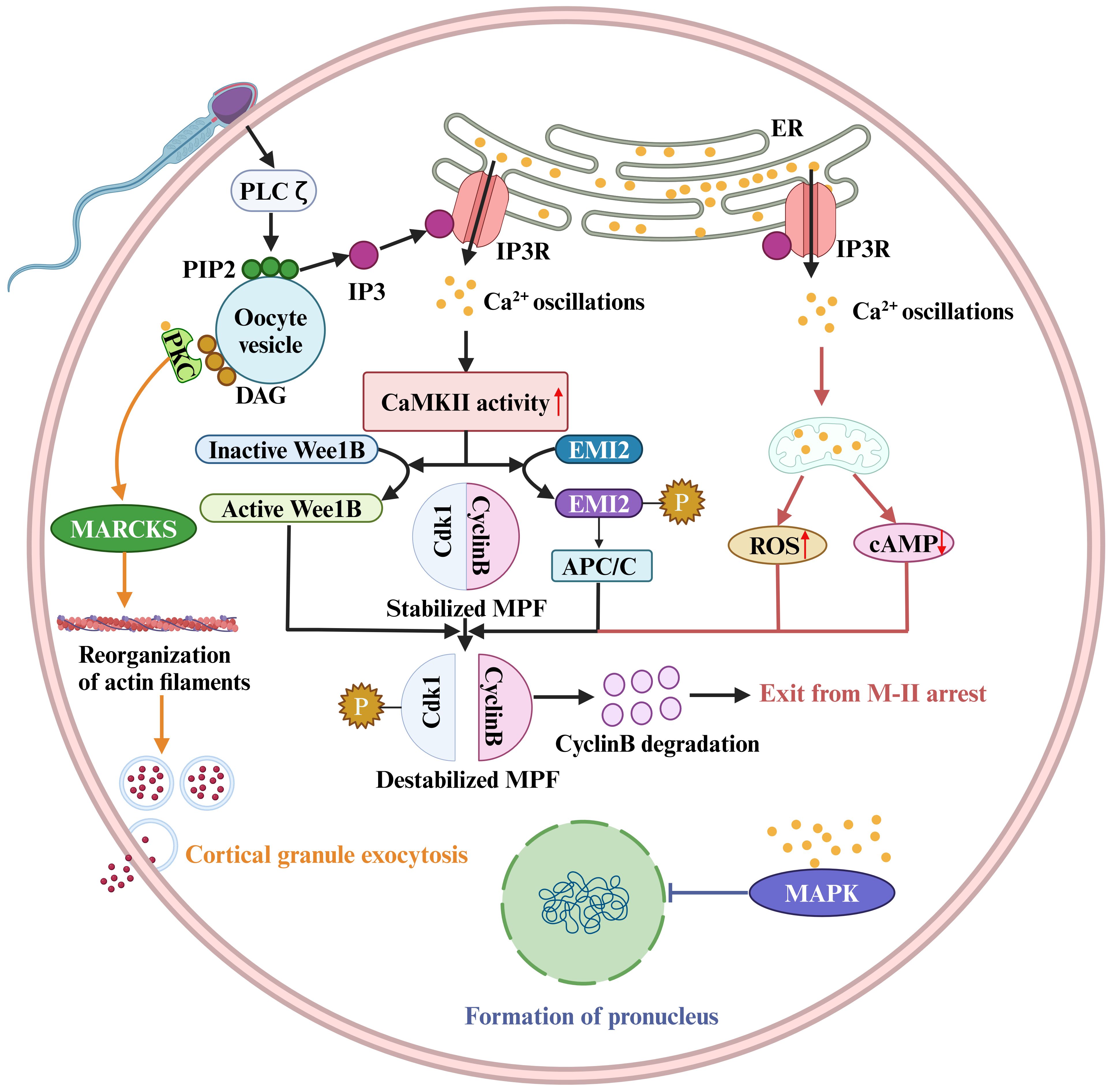
Figure 2. Sperm factor PLCζ acts on PIP2 in intracellular vesicles to generate IP3, which stimulates IP3R-mediated Ca2+ release from ER Ca2+ store. Ca2+ oscillations activate the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII), leading to WEE1B activation. The activate WEE1B phosphorylates CDK1 and inhibits MPF activity. In addition, CaMKII activation results in EMI2 phosphorylation, and phosphorylated EMI2 loses its ability to inhibit the anaphase promoting complex or cyclosome (APC/C). As a result, APC/C disrupts EMI2 and cyclin B, leading to a loss of MPF activity. The destabilized MPF triggers an exit from M-II arrest. Protein kinase C (PKC) binds to synthetic DAGs, which acts on myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate (MARCKS), resulting in reorganization of cortical actin filaments and cortical granule exocytosis. The pronucleus formation of the oocyte also depends on a decrease in MAPK activity. In mouse fertilized eggs, MAPK activity begins to decline when Ca2+ oscillations last for 2 hours and gradually declines for several hours after pronuclear formation.
The ability of the oocyte to complete meiosis and enter interphase also depends on a decrease in MAPK activity, mainly ERK1 and ERK2 activity (147). Physiologically, the phosphorylated kinase MEK maintains high ERK1/2 kinase activity. It has been shown that the phosphatase inhibitors or the injection of constitutively activated MEK can prevent the decrease in MAPK (ERK1/2) activity, thereby inhibiting pronuclear formation (147). In contrast, the MEK inhibitor U0126 induces pronuclear formation (148). In mouse fertilized eggs, MAPK activity begins to decline when calcium oscillations last for 2 hours and gradually decreases for several hours after pronuclear formation (149). However, the decline in MAPK kinase activity is not synchronized with MPF inactivation, and experimental results indicate that a decrease in MAPK kinase activity is detected approximately 2 hours after MPF inactivation (150). The delayed decline in MAPK activity may be due to an increase in protein kinase activity (149), but the underlying molecular mechanism is unclear.
Cortical granule exocytosis is a pivotal event in oocyte fertilization. The cortical response can alter the properties of the oocyte PM and zona pellucida to prevent polyspermy. It was found that the increase in [Ca2+]i in oocytes induced by electrical pulses triggers the release of most cortical granules (151). However, the signaling of cortical granule exocytosis is distinct from that of meiotic resumption, because injection of constitutively active CAMKII triggers meiotic resumption and pronuclear formation, but not exocytosis (142, 143, 152). In addition, oocytes from CAMKII-/- mice or WEE1B KD oocytes do not undergo meiotic resumption after fertilization, but in both cases cortical granule exocytosis occurs (143, 146, 153). Thus, meiotic resumption and cortical granule exocytosis appear to be independent downstream events in the early differentiation of the Ca2+ signaling pathway.
Numerous studies have shown that mammalian oocyte exocytosis is closely linked to protein kinase C (PKC). Increasing PKC activity, for example, by using synthetic DAGs, can stimulate exocytosis in mammalian eggs (154). The detectable PKC stimulation in the oocyte PM may be primarily due to an increase in Ca2+ (155, 156). One idea is that the PKC and calmodulin pathways converge through the translocation of myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate (MARCKS). Exocytosis requires the reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton and the translocation of vesicles to the PM (157). MARCKS is involved in cortical actin reorganization, cytokinesis in other cell types, and cortical granule exocytosis in the egg (158, 159). Vesicle translocation may involve the Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent enzyme myosin light chain kinase (MLCK), which targets myosin II in neuroendocrine cells and is responsible for vesicle translocation to the synaptic membrane (157). MLCK inhibitors such as ML7 inhibit cortical granule exocytosis during mouse egg fertilization (160).
In conclusion, CAMKII appears to act as a Ca2+-dependent event that triggers meiotic resumption and it will also be interesting to determine the signaling pathway for exocytosis. What’s more, it is essential to demonstrate the relationship between the reduction in MPF and the decrease in MAPK activity, as it is the last in a series of triggers of OA in mammals.
Ca2+ oscillations induced by sperm protein PLCζ govern the OA (13) and activate oocyte complex behaviors including meiosis resumption, second polar body extrusion, pronuclear formation, and cortical granule exocytosis. It is clear that the elimination or disruption of Ca2+ release patterns during OA underlies many cases of male infertility and abnormal embryogenesis (161). To this extent, the artificial oocyte activation (AOA) technology aims to induce meiotic resumption in the oocyte by artificially elevating [Ca2+]i during the process of assisted reproductive technology. AOA contains different means (Table 1), including mechanical, electrical, chemical, or some alternative AOA methods, and each means is associated with unique risks and benefits (174).
The application of Ca2+ in AOA has been well described (11, 12), so this section will offer a brief overview and update of the relevant contents.
The electrical method involves applying a voltage electric field to the oocyte, causing the charged lipid-protein oocyte membrane bilayer to move and form pores. This process eventually allows [Ca2+]e to flow into the cytoplasm. The electrical OA has been successfully employed in bovine and human oocytes (162) and the success of the method depends on the size of the pore and the [Ca2+]e concentration. However, electrical stimulation not only causes physical damage to oocytes, but also generates excess ROS (186). Therefore, this method of OA needs to be used with caution. However, it is interesting to note that the measurement of electrical resistance in the cell may also be used as a tool to detect oocyte viability and penetration (12). Thus, although electrical OA may not be the ideal clinical treatment, perhaps some modifications could provide a potential diagnosis of OA.
Mechanical activation refers to two main methods, both of which are based on the destruction of the oocyte. One method, which is more invasive, involves physically disrupting the ER membrane and redistributing mitochondria or manually disrupting the oocyte membrane. This is followed by continuous aspiration of the oocyte cytoplasm, which promotes Ca2+ influx. This mechanism certainly causes a great deal of physical disruption, but it may increase the intimate contact of sperm with the intracellular membrane, further increasing the chances of successful OA (12, 163, 187). Another approach is to increase Ca2+ influx by puncturing the oocyte or injecting trace amounts of Ca2+ directly into the oocyte (164). However, both approaches are difficult to standardize, and this method only induces a single Ca2+ increase (161).
Chemical methods are the most commonly used methods for OA. Chemical activators trigger a single Ca2+ transient or a series of Ca2+ oscillations that mimic physiological Ca2+ release in the oocyte. Single Ca2+ transient activators include Ca2+ ionophores (ionomycin and A23187), ethanol, puromycin (a protein synthesis agent) and 6-dimethyaminopurine (6-DMAP, a protein kinase inhibitor). Ionomycin and A23187 are the most commonly used for AOA in IVF cycles (12, 165). The use of ionophores has been shown to increase fertilization and pregnancy rates (188–191). Eggs can also be artificially activated with ethanol. Recent studies have shown that the calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) is involved in ethanol-induced activation (EIA) (166). EIA has been achieved in mouse (192), bovine (193), and porcine (194) oocytes, however, it does not work in human oocytes (195). In addition, puromycin and 6-DMAP are usually used in combination with other chemical reagents to activate oocytes (196–198).
There are other agents that promote multiple Ca2+ transients, including thimerosal (167), phorbol ester (168), or strontium chloride (SrCl2) (169). Thimerosal increases the sensitivity of the IP3 receptor to Ca2+ primarily by oxidizing sulfhydryl groups, thereby inducing calcium oscillations similar to those induced by sperm (199). Previous studies have shown that thimerosal can activate human oocytes (200–202), resulting in Ca2+ oscillations. However, thimerosal is not commonly used because it induces the oxidation of tubulin, which disrupts polymerization and spindle formation (203). Phorbol ester can activate mouse oocytes by inducing sustained oscillations in cell Ca2+ (168). However, there have been no relevant applications and no new research progress on phorbol esters in recent years. SrCl2 is the preferred compound for OA in rodents (204). Sr2+ also induces OA in bovine, porcine, and equine species, but the activation rate and embryo development are low compared to other activation methods (205–208). Despite its more frequent use in animal models, the role of SrCl2 in human OA remains controversial (131, 209).
There are several drugs that target molecules in the Ca2+ downstream pathway, known as alternative AOA promoters. Some of these drugs include cycloheximide (CHX) (170), N,N,N’,N’-tetrakis(2-pyridylmethyl) ethane-1,2-diamine (TPEN) (171), roscovitine (172), and WEE2 complementary RNA (WEE2 cRNA) (173). These drugs induce maturation-promoting factor inactivation and meiosis resumption and have been tested for their potential in treating fertilization failure. CHX, a non-specific inhibitor of cell cycle protein B synthesis, has been used to induce parthenogenetic activation in bovine and equine mammalian oocytes (208). In addition, the application of CHX in combination with ionomycin to human oocytes significantly improved the fertilization rate from less than 10% to approximately 50% (170). TPEN is a zinc-specific chelator (210) that induces human oocytes from the MII phase of meiosis to enter the mitotic cycle (171). Roscovitine, a specific inhibitor of cyclin-dependent protein kinases, can cause protoplast formation in oocytes arrested in the MII phase due to Wee1B KD by inducing maturation-promoting factor inactivation (146). However, roscovitine must be combined with ionomycin to successfully activate oocytes (172). WEE2 cRNA can be applied to human oocytes with pure WEE2 mutations, which result in fertilization failure, to obtain in vitro blastocysts (173), but the effect on late embryonic development has not been reported. However, the above drugs are still in the early stages of clinical trials and their safety requires further discussion.
Studies have provided evidence that stressors, such as maternal nutrition, environmental contaminants, food-origin toxins and inflammatory disease, have a deleterious effect on the oocyte and ovarian GC. For example, food-origin toxins such as mycotoxins induce ROS production, leading to oxidative damage in oocytes (211). The oocyte achieves its developmental competence through the lengthy process of folliculogenesis. Therefore, exposing animals to these stressors can reduce the ability of oocytes to mature, be fertilized, and develop into viable embryos. Although the intracellular and molecular mechanisms of disruption appear to be multifactorial in nature, oocyte mitochondria are key targets for a variety of stressors.
Simazine, glyphosate and rotenone are widely used pesticides. Exposure to these substances has been shown to increase [Ca2+]i in oocytes, resulting in mitochondrial dysfunction, ROS accumulation and impairment of oocyte maturation (175–177). Consequently, simazine and rotenone induced early apoptosis (175, 177), while glyphosate impaired ER function and disrupted lysosomal function for autophagy (176) (Table 2). Phenanthrene (PHE) is one of the most abundant polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) found in the environment. In vitro experiments showed that PHE significantly reduced the percentage of GVBD and the first polar body extrusion, suggesting that PHE impaired meiotic maturation in mouse oocytes. Furthermore, PHE treatment resulted in mitochondrial dysfunction and increased [Ca2+]i in oocytes (178) (Table 2). Perfluoroalkyl substances (PFHxS), as man-made chemicals with a wide range of consumer and industrial applications, are versatile and resistant to environmental and metabolic degradation. In the in vitro experiment, PFHxS decreased the ovulation rate in female mice, but didn’t alter the oocytes morphology. In terms of mechanism, the [Ca2+]i decreased in mature oocytes exposed to PFHxS in vivo. The researchers hypothesize that this effect is probably due to the deregulation of the ER modulator, Stim1 (179) (Table 2). Perfluorodecanoic acid (PFDA) is one of the PFHxS, but it appears to function differently. PFDA impaired porcine oocyte viability and maturation rates in a concentration-dependent manner, which might be associated with the high levels of [Ca2+]i. Moreover, gap junction intercellular communication between the CC and the oocyte was disrupted. The effects of PFDA on oocyte Ca2+ homeostasis and intercellular communication seem to be responsible for the inhibition of oocyte maturation and oocyte death (180) (Table 2). Bisphenol A (BPA), a representative endocrine disrupter mimicking estrogen-action, can affect spontaneous Ca2+ oscillations during oocyte maturation (22) and disturb oocyte meiosis (181) (Table 2). Some drugs used for treatment can also cause damage to oocytes. Dihydroartemisinin (DHA), an artemisinin derivative, is a highly potent anti-cancer medication. The study found that DHA inhibited porcine oocyte polar body extrusion, blocked cell cycle progression, and impaired early embryo development which were attributed to elevated levels of intracellular and mitochondrial Ca2+ (182) (Table 2).
Silica nanoparticles (SNPs), a major component of ambient particulate matters, can induce follicular atresia via the promotion of ovarian granulosa cells (OGC) apoptosis. A recent study found that ER stress contributed to SNP-induced ovarian toxicity by activating IP3R1-mediated Ca2+ mobilization, leading to apoptosis, in which the PERK-ATF4-CHOP-ERO1α pathway played an important role in the dysfunction of OGC (183) (Table 2). The interactions between the oocyte and GC are critical for normal follicular development. It is reported that exposure to DHA increased intracellular and mitochondrial Ca2+ levels in OGC, leading to decreased cell viability and increased apoptosis in porcine OGC (184) (Table 2). BPA and its analogues, such as bisphenol S (BPS), bisphenol F (BPF), and bisphenol AF (BPAF), are widely used to produce a variety of everyday household items. Huang et al. reported that exposure to these bisphenols reduced the viability and increased ROS production in KGN cells (a granulosa-like tumor cell line). These damages may result from changes in [Ca2+]i levels in KGN cells induced by bisphenols (185) (Table 2).
In conclusion, when changes in external environmental factors lead to an increase in [Ca2+]i, oocytes or GC will exhibit a state of stress, impacting oocyte maturation or early embryo development.
This article focuses on recent advances in the study of Ca2+ signaling in female reproduction, especially in oocyte maturation and functions. Emerging evidence has shown that abnormal Ca2+ signaling directly obstructs oocyte maturation, disturbs meiosis and fertilization, and impairs the function of GC and CC, which further leads to fertility impairment. Although knockout of single or multiple Ca2+ channel genes in the oocyte does not result in a complete loss of oocyte Ca2+ oscillations or complete sterility in female mice due to mutual compensations between the individual channels or calcium-regulated proteins, there is no doubt that Ca2+ signaling is critical for female reproduction. When we explore the role of Ca2+ in these fields, many questions need to be addressed. First, we are still unaware of the full repertoire of the existence and functions of Ca2+ channels or transporters in mammalian oocytes/eggs. Some important calcium channels and proteins are not well characterized in oocytes/eggs. For example, IP3R is particularly important during Ca2+ oscillations after fertilization, but substantial evidence is lacking. Functionally blocking the IP3 receptor in vitro can completely suppress sperm-induced Ca2+ waves and oscillations (106). However, whether IP3Rs are indispensable in physiological situations remains to be investigated in conditional knockout models or mutated human oocytes. Second, the molecular mechanisms of downstream signaling mediated by Ca2+ are largely unclear. CAMKII governs Ca2+-dependent meiotic resumption, but other key events during fertilization such as cortical granule exocytosis, maternal mRNA recruitment, and maternal-to-zygotic transition are regulated by Ca2+ signaling that remains to be further investigated. Third, NLRP14, a maternal effect factor, is essential for maintaining Ca2+ oscillations and early embryonic development (212). This reminds us that other unknown maternal factors might manipulate Ca2+ oscillations in oocytes. The search for new maternal factors related to Ca2+ oscillations will help us to better understand the failure of fertilization due to abnormal Ca2+ oscillations caused by females in the clinic. Fourth, it is important to investigate the functional couplings between multiple Ca2+-signaling regulatory molecules. Additionally, understanding the specific role of calcium signaling at different stages of oocyte maturation, fertilization, and the transition process (GV-GVBD-MI-MII) is crucial. Fifth, the roles of calcium signaling in gene expression and silencing during oocyte maturation, gene re-activation after fertilization, and other genetic and epigenetic regulations such as DNA methylation, lncRNAs, phase separation and protein post-translational modifications in female reproduction should be uncovered. Last, the safety and efficacy of AOA remain a concern due to a lack of randomized control trials and follow-up risk monitoring studies. Whether there are significant differences between embryos generated by AOA and those generated by natural fertilization, and the risks of AOA-rescued oocytes on the development and growth of the offspring need to be further evaluated. In conclusion, identifying all the Ca2+ ion channels in the oocyte and elucidating their regulatory mechanisms will improve our understanding of oocyte maturation and fertilization. This information might be used to more accurately diagnose female infertility and provide alternative strategies to improve the development of embryos generated from assisted reproductive technology procedures.
CC: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SD: Visualization, Writing – original draft. ZH: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. MD: Validation, Writing – review & editing. JL: Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing. MW: Software, Writing – review & editing. XHZ: Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. XNZ: Conceptualization, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XS: Conceptualization, Project administration, Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by the Nantong Social and People’s Livelihood Science and Technology Plan (MS22022119), the Basic Science Research Program of Nantong (JC22022086) and Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (KYCX22_3355).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
2. Berridge MJ, Lipp P, Bootman MD. The versatility and universality of calcium signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2000) 1:11–21. doi: 10.1038/35036035
3. Zhai X, Sterea AM, Hiani YE. Lessons from the endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ Transporters-A cancer connection. Cells. (2020) 9(6):1536. doi: 10.3390/cells9061536
4. Wakai T, Mehregan A, Fissore RA. Ca(2+) signaling and homeostasis in mammalian oocytes and eggs. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. (2019) 11(12):a035162. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a035162
5. Nader N, Kulkarni RP, Dib M, Machaca K. How to make a good egg!: The need for remodeling of oocyte Ca(2+) signaling to mediate the egg-to-embryo transition. Cell Calcium. (2013) 53:41–54. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2012.11.015
6. Carvacho I, Piesche M, Maier TJ, Machaca K. Ion channel function during oocyte maturation and fertilization. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2018) 6. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2018.00063
7. Hassold T, Hunt P. To err (meiotically) is human: the genesis of human aneuploidy. Nat Rev Genet. (2001) 2:280–91. doi: 10.1038/35066065
8. Horner VL, Wolfner MF. Transitioning from egg to embryo: triggers and mechanisms of egg activation. Dev Dyn. (2008) 237:527–44. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.21454
9. Wakai T, Vanderheyden V, Yoon SY, Cheon B, Zhang N, Parys JB, et al. Regulation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor function during mouse oocyte maturation. J Cell Physiol. (2012) 227:705–17. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22778
10. Deguchi RU, Kondoh E, Itoh J. Spatiotemporal characteristics and mechanisms of intracellular Ca2+ increases at fertilization in eggs of jellyfish (Phylum Cnidaria, Class Hydrozoa). Dev Biol. (2005) 279:291–307. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.11.036
11. Campos G, Sciorio R, Esteves SC. Total fertilization failure after ICSI: insights into pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management through artificial oocyte activation. Hum Reprod Update. (2023) 29:369–94. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmad007
12. Kashir J, Ganesh D, Jones C, Coward K. Oocyte activation deficiency and assisted oocyte activation: mechanisms, obstacles and prospects for clinical application. Hum Reprod Open. (2022) 2022:hoac003. doi: 10.1093/hropen/hoac003
13. Stein P, Savy V, Williams AM, Williams CJ. Modulators of calcium signalling at fertilization. Open Biol. (2020) 10:200118. doi: 10.1098/rsob.200118
14. Homa ST, Carroll J, Swann K. The role of calcium in mammalian oocyte maturation and egg activation. Hum Reprod. (1993) 8:1274–81. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.humrep.a138240
15. Miyara F, Pesty A, Migne C, Djediat C, Huang XB, Dumont-Hassan M, et al. Spontaneous calcium oscillations and nuclear PLC-beta1 in human GV oocytes. Mol Reprod Dev. (2008) 75:392–402. doi: 10.1002/mrd.20749
16. Su YQ, Xia GL, Byskov AG, Fu GD, Yang CR. Protein kinase C and intracellular calcium are involved in follicle-stimulating hormone-mediated meiotic resumption of cumulus cell-enclosed porcine oocytes in hypoxanthine-supplemented medium. Mol Reprod Dev. (1999) 53:51–8. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2795(199905)53:1<51::AID-MRD6>3.0.CO;2-4
17. Fazeli E, Hosseini A, Heidari MH, Farifteh-Nobijari F, Salehi M, Abbaszadeh HA, et al. Meiosis resumption of immature human oocytes following treatment with calcium ionophore in vitro. Cell J. (2021) 23:109–18. doi: 10.22074/cellj.2021.7130
18. Tiwari M, Prasad S, Shrivastav TG, Chaube SK. Calcium signaling during meiotic cell cycle regulation and apoptosis in mammalian oocytes. J Cell Physiol. (2017) 232:976–81. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25670
19. Meduri G, Charnaux N, Driancourt MA, Combettes L, Granet P, Vannier B, et al. Follicle-stimulating hormone receptors in oocytes? J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2002) 87:2266–76. doi: 10.1210/jcem.87.5.8502
20. Egbert JR, Fahey PG, Reimer J, Owen CM, Evsikov AV, Nikolaev VO, et al. Follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone increase Ca2+ in the granulosa cells of mouse ovarian follicles. Biol Reprod. (2019) 101:433–44. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioz085
21. Rodway MR, Steele GL, Baimbridge KG, Leung PC. Prostaglandin F2 alpha and gonadotropin-releasing hormone increase intracellular free calcium in rat granulosa cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. (1992) 84:137–43. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(92)90080-p
22. Mohri T, Yoshida S. Estrogen and bisphenol A disrupt spontaneous [Ca(2+)](i) oscillations in mouse oocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2005) 326:166–73. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.11.024
23. Tombes RM, Simerly C, Borisy GG, Schatten G. Meiosis, egg activation, and nuclear envelope breakdown are differentially reliant on Ca2+, whereas germinal vesicle breakdown is Ca2+ independent in the mouse oocyte. J Cell Biol. (1992) 117:799–811. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.4.799
24. Kaufman ML, Homa ST. Defining a role for calcium in the resumption and progression of meiosis in the pig oocyte. J Exp Zool. (1993) 265:69–76. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402650110
25. Fan HY, Huo LJ, Meng XQ, Zhong ZS, Hou Y, Chen DY, et al. Involvement of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) in meiotic maturation and activation of pig oocytes. Biol Reprod. (2003) 69:1552–64. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.103.015685
26. Edwards RG. Maturation in vitro of mouse, sheep, cow, pig, rhesus monkey and human ovarian oocytes. Nature. (1965) 208:349–51. doi: 10.1038/208349a0
27. Powers RD, Paleos GA. Combined effects of calcium and dibutyryl cyclic AMP on germinal vesicle breakdown in the mouse oocyte. J Reprod Fertil. (1982) 66:1–8. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0660001
28. Jagiello G, Ducayen MB, Downey R, Jonassen A. Alterations of mammalian oocyte meiosis I with divalent cations and calmodulin. Cell Calcium. (1982) 3:153–62. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(82)90011-2
29. Bae IH, Channing CP. Effect of calcium ion on the maturation of cumulus-enclosed pig follicular oocytes isolated from medium-sized graafian follicles. Biol Reprod. (1985) 33:79–87. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod33.1.79
30. De Felici M, Dolci S, Siracusa G. An increase of intracellular free Ca2+ is essential for spontaneous meiotic resumption by mouse oocytes. J Exp Zool. (1991) 260:401–5. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402600314
31. Meng L, Hu H, Liu Z, Zhang L, Zhuan Q, Li X, et al. The role of Ca2+ in maturation and reprogramming of bovine oocytes: A system study of low-calcium model. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 9:746237. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.746237
32. Deng MQ, Huang XY, Tang TS, Sun FZ. Spontaneous and fertilization-induced Ca2+ oscillations in mouse immature germinal vesicle-stage oocytes. Biol Reprod. (1998) 58:807–13. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod58.3.807
33. Mehlmann LM, Kline D. Regulation of intracellular calcium in the mouse egg: calcium release in response to sperm or inositol trisphosphate is enhanced after meiotic maturation. Biol Reprod. (1994) 51:1088–98. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod51.6.1088
34. Mehlmann LM, Mikoshiba K, Kline D. Redistribution and increase in cortical inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors after meiotic maturation of the mouse oocyte. Dev Biol. (1996) 180:489–98. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1996.0322
35. Machaca K. Increased sensitivity and clustering of elementary Ca2+ release events during oocyte maturation. Dev Biol. (2004) 275:170–82. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.08.004
36. Chiba K, Kado RT, Jaffe LA. Development of calcium release mechanisms during starfish oocyte maturation. Dev Biol. (1990) 140:300–6. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90080-3
37. Fujiwara T, Nakada K, Shirakawa H, Miyazaki S. Development of inositol trisphosphate-induced calcium release mechanism during maturation of hamster oocytes. Dev Biol. (1993) 156:69–79. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1059
38. Fissore RA, Longo FJ, Anderson E, Parys JB, Ducibella T. Differential distribution of inositol trisphosphate receptor isoforms in mouse oocytes. Biol Reprod. (1999) 60:49–57. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod60.1.49
39. Xu Z, Williams CJ, Kopf GS, Schultz RM. Maturation-associated increase in IP3 receptor type 1: role in conferring increased IP3 sensitivity and Ca2+ oscillatory behavior in mouse eggs. Dev Biol. (2003) 254:163–71. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(02)00049-0
40. Lee B, Vermassen E, Yoon SY, Vanderheyden V, Ito J, Alfandari D, et al. Phosphorylation of IP3R1 and the regulation of [Ca2+]i responses at fertilization: a role for the MAP kinase pathway. Development. (2006) 133:4355–65. doi: 10.1242/dev.02624
41. Zhang N, Yoon SY, Parys JB, Fissore RA. Effect of M-phase kinase phosphorylations on type 1 inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor-mediated Ca2+ responses in mouse eggs. Cell Calcium. (2015) 58:476–88. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2015.07.004
42. Malathi K, Li X, Krizanova O, Ondrias K, Sperber K, Ablamunits V, et al. Cdc2/cyclin B1 interacts with and modulates inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor (type 1) functions. J Immunol. (2005) 175:6205–10. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.9.6205
43. Bezprozvanny I. The inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors. Cell Calcium. (2005) 38:261–72. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2005.06.030
44. Zhang C, Gao L, Wu D, Wang G, Lan H, Li L, et al. IP3R1 regulates calcium balance in porcine oocyte maturation and early embryonic development. Theriogenology. (2023) 209:151–61. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2023.06.021
45. Fonseca E, Mesquita P, Marques CC, Baptista MC, Pimenta J, Matos JE, et al. Modulation of P2Y2 receptors in bovine cumulus oocyte complexes: effects on intracellular calcium, zona hardening and developmental competence. Purinergic Signal. (2020) 16:85–96. doi: 10.1007/s11302-020-09690-6
46. Bernhardt ML, Lowther KM, Padilla-Banks E, McDonough CE, Lee KN, Evsikov AV, et al. Regulator of G-protein signaling 2 (RGS2) suppresses premature calcium release in mouse eggs. Development. (2015) 142:2633–40. doi: 10.1242/dev.121707
47. Wang F, Fan LH, Li A, Dong F, Hou Y, Schatten H, et al. Effects of various calcium transporters on mitochondrial Ca2+ changes and oocyte maturation. J Cell Physiol. (2021) 236:6548–58. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30327
48. Carvacho I, Ardestani G, Lee HC, McGarvey K, Fissore RA, Lykke-Hartmann K. TRPM7-like channels are functionally expressed in oocytes and modulate post-fertilization embryo development in mouse. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:34236. doi: 10.1038/srep34236
49. Bernhardt ML, Stein P, Carvacho I, Krapp C, Ardestani G, Mehregan A, et al. TRPM7 and CaV3.2 channels mediate Ca2+ influx required for egg activation at fertilization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2018) 115:E10370–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1810422115
50. Marchi S, Patergnani S, Missiroli S, Morciano G, Rimessi A, Wieckowski MR, et al. Mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticulum calcium homeostasis and cell death. Cell Calcium. (2018) 69:62–72. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2017.05.003
51. Boyman L, Karbowski M, Lederer WJ. Regulation of mitochondrial ATP production: Ca2+ Signaling and quality control. Trends Mol Med. (2020) 26:21–39. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2019.10.007
52. Kirillova A, Smitz JEJ, Sukhikh GT, Mazunin I. The role of mitochondria in oocyte maturation. Cells. (2021) 10:2484. doi: 10.3390/cells10092484
53. Wang F, Meng TG, Li J, Hou Y, Luo SM, Schatten H, et al. Mitochondrial Ca2+ Is related to mitochondrial activity and dynamic events in mouse oocytes. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2020) 8:585932. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.585932
54. Zhang LY, Lin M, Qingrui Z, Zichuan W, Junjin L, Kexiong L, et al. Mitochondrial Calcium uniporters are essential for meiotic progression in mouse oocytes by controlling Ca2+ entry. Cell Prolif. (2021) 54:e13127. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13127
55. Zhang L, Wang Z, Lu T, Meng L, Luo Y, Fu X, et al. Mitochondrial ca2+ Overload leads to mitochondrial oxidative stress and delayed meiotic resumption in mouse oocytes. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2020) 8:580876. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.580876
56. Nabi D, Bosi D, Gupta N, Thaker N, Fissore R, Brayboy LM. Multidrug resistance transporter-1 dysfunction perturbs meiosis and Ca2+ homeostasis in oocytes. Reprod (Cambridge England). (2023) 165:79–91. doi: 10.1530/REP-22-0192
57. Jeppesen JV, Kristensen SG, Nielsen ME, Humaidan P, Dal Canto M, Fadini R, et al. LH-receptor gene expression in human granulosa and cumulus cells from antral and preovulatory follicles. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2012) 97:E1524–31. doi: 10.1210/jc.2012-1427
58. Baltar AE, Oliveira MA, Catanho MT. Bovine cumulus/oocyte complex: quantification of LH/hCG receptors. Mol Reprod Dev. (2000) 55:433–7. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2795(200004)55:4<433::AID-MRD11>3.0.CO;2-5
59. Shimada M, Nishibori M, Isobe N, Kawano N, Terada T. Luteinizing hormone receptor formation in cumulus cells surrounding porcine oocytes and its role during meiotic maturation of porcine oocytes. Bio Reprod. (2003) 68:1142–9. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.102.010082
60. Fu M, Chen X, Yan J, Lei L, Jin S, Yang J, et al. Luteinizing hormone receptors expression in cumulus cells closely related to mouse oocyte meiotic maturation. Front Biosci. (2007) 12:1804–13. doi: 10.2741/2189
61. Bukovsky A, Chen TT, Wimalasena J, Caudle MR. Cellular localization of luteinizing hormone receptor immunoreactivity in the ovaries of immature, gonadotropin-primed and normal cycling rats. Bio Reprod. (1993) 48:1367–82. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod48.6.1367
62. Silvestre F, Fissore RA, Tosti E, Boni R. [Ca2+]i rise at in vitro maturation in bovine cumulus-oocyte complexes. Mol Reprod Dev. (2012) 79:369–79. doi: 10.1002/mrd.22038
63. Mattioli M, Gioia L, Barboni B. Calcium elevation in sheep cumulus-oocyte complexes after luteinising hormone stimulation. Mol Reprod Dev. (1998) 50:361–9. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2795(199807)50:3<361::AID-MRD13>3.0.CO;2-7
64. Hao X, Wang Y, Kong N, Zhang Y, Zhao Y, Xia G, et al. Epidermal growth factor-mobilized intracellular calcium of cumulus cells decreases natriuretic peptide receptor 2 affinity for natriuretic peptide type C and induces oocyte meiotic resumption in the mouse. Biol Reprod. (2016) 95:45. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.116.140137
65. O’Donnell JB, Hill JL, Gross DJ. Epidermal growth factor activates cytosolic [Ca2+] elevations and subsequent membrane permeabilization in mouse cumulus-oocyte complexes. Reproduction. (2004) 127:207–20. doi: 10.1530/rep.1.00027
66. Mattioli M, Barboni B, Gioia L. Activation of protein kinase A and protein kinase C mediates the depolarising effect of LH in ovine cumulus-corona cells. J Endocrinol. (1996) 150:445–56. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1500445
67. Mattioli M, Barboni B, Bacci ML, Seren E. Maturation of pig oocytes: observations on membrane potential. Biol Reprod. (1990) 43:318–22. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod43.2.318
68. Webb RJ, Bains H, Cruttwell C, Carroll J. Gap-junctional communication in mouse cumulus-oocyte complexes: implications for the mechanism of meiotic maturation. Reproduction. (2002) 123:41–52. doi: 10.1530/rep.0.1230041
69. Wang QC, Zheng Q, Tan H, Zhang B, Li X, Yang Y, et al. TMCO1 is an ER ca(2+) load-activated ca(2+) channel. Cell. (2016) 165:1454–66. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.04.051
70. Sun ZS, Zhang H, Wang X, Wang QC, Zhang CC, Wang JQ, et al. TMCO1 is essential for ovarian follicle development by regulating ER Ca2+ store of granulosa cells. Cell Death Differ. (2018) 25:1686–701. doi: 10.1038/s41418-018-0067-x
71. Alanay Y, Erguner B, Utine E, Hacariz O, Kiper PO, Taskiran EZ, et al. TMCO1 deficiency causes autosomal recessive cerebrofaciothoracic dysplasia. Am J Med Genet A. (2014) 164A:291–304. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.36248
72. Xin B, Puffenberger EG, Turben S, Tan H, Zhou A, Wang H. Homozygous frameshift mutation in TMCO1 causes a syndrome with craniofacial dysmorphism, skeletal anomalies, and mental retardation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2010) 107:258–63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0908457107
73. Carroll J. The initiation and regulation of Ca2+ signalling at fertilization in mammals. Semin Cell Dev Biol. (2001) 12:37–43. doi: 10.1006/scdb.2000.0215
74. Sun B, Yeh J. Calcium oscillatory patterns and oocyte activation during fertilization: a possible mechanism for total fertilization failure (TFF) in human in vitro fertilization. Reprod Sci (Thousand Oaks Calif). (2021) 28:639–48. doi: 10.1007/s43032-020-00293-5
75. Ducibella T, Huneau D, Angelichio E, Xu Z, Schultz RM, Kopf GS, et al. Egg-to-embryo transition is driven by differential responses to Ca(2+) oscillation number. Dev Biol. (2002) 250:280–91.
76. Ozil JP, Banrezes B, Toth S, Pan H, Schultz RM. Ca2+ oscillatory pattern in fertilized mouse eggs affects gene expression and development to term. Dev Biol. (2006) 300:534–44. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.08.041
77. Katan M, Cockcroft S. Phospholipase C families: Common themes and versatility in physiology and pathology. Prog Lipid Res. (2020) 80:101065. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2020.101065
78. Carroll DJ, Ramarao CS, Mehlmann LM, Roche S, Terasaki M, Jaffe LA. Calcium release at fertilization in starfish eggs is mediated by phospholipase Cgamma. J Cell Biol. (1997) 138:1303–11. doi: 10.1083/jcb.138.6.1303
79. Runft LL, Jaffe LA. Sperm extract injection into ascidian eggs signals Ca(2+) release by the same pathway as fertilization. Development. (2000) 127:3227–36. doi: 10.1242/dev.127.15.3227
80. Sato K, Tokmakov AA, Iwasaki T, Fukami Y. Tyrosine kinase-dependent activation of phospholipase Cgamma is required for calcium transient in Xenopus egg fertilization. Dev Biol. (2000) 224:453–69. doi: 10.1006/dbio.2000.9782
81. Giusti AF, O’Neill FJ, Yamasu K, Foltz KR, Jaffe LA. Function of a sea urchin egg Src family kinase in initiating Ca2+ release at fertilization. Dev Biol. (2003) 256:367–78. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(03)00043-5
82. Kadamur G, Ross EM. Mammalian Phospholipase C. Annu Rev Physiol. (2013) 75:127–54. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-030212-183750
83. Heyers S, Sousa M, Cangir O, Schmoll F, Schellander K, van der Ven H, et al. Activation of mouse oocytes requires multiple sperm factors but not sperm PLCgamma1. Mol Cell Endocrinol. (2000) 166:51–7. doi: 10.1016/s0303-7207(00)00297-5
84. Saunders CM, Larman MG, Parrington J, Cox LJ, Royse J, Blayney LM, et al. PLC zeta: a sperm-specific trigger of Ca(2+) oscillations in eggs and embryo development. Development. (2002) 129:3533–44. doi: 10.1242/dev.129.15.3533
85. Knott JG, Kurokawa M, Fissore RA, Schultz RM, Williams CJ. Transgenic RNA interference reveals role for mouse sperm phospholipase Czeta in triggering Ca2+ oscillations during fertilization. Biol Reprod. (2005) 72:992–6. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.104.036244
86. Ozil JP, Huneau D. Activation of rabbit oocytes: the impact of the Ca2+ signal regime on development. Development. (2001) 128:917–28. doi: 10.1242/dev.128.6.917
87. Hachem A, Godwin J, Ruas M, Lee HC, Buitrago MF, Ardestani G, et al. PLC zeta is the physiological trigger of the Ca2+ oscillations that induce embryogenesis in mammals but conception can occur in its absence. Development. (2017) 144:2914–24. doi: 10.1242/dev.150227
88. Nozawa K, Satouh Y, Fujimoto T, Oji A, Ikawa M. Sperm-borne phospholipase C zeta-1 ensures monospermic fertilization in mice. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:1315. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-19497-6
89. Yoon SY, Jellerette T, Salicioni AM, Lee HC, Yoo MS, Coward K, et al. Human sperm devoid of PLC, zeta 1 fail to induce Ca(2+) release and are unable to initiate the first step of embryo development. J Clin Invest. (2008) 118:3671–81. doi: 10.1172/JCI36942
90. Xin A, Qu R, Chen G, Zhang L, Chen J, Tao C, et al. Disruption in ACTL7A causes acrosomal ultrastructural defects in human and mouse sperm as a novel male factor inducing early embryonic arrest. Sci Adv. (2020) 6:eaaz4796. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaz4796
91. Dai J, Zhang T, Guo J, Zhou Q, Gu Y, Zhang J, et al. Homozygous pathogenic variants in ACTL9 cause fertilization failure and male infertility in humans and mice. Am J Hum Genet. (2021) 108:469–81. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2021.02.004
92. Parrella A, Medrano L, Aizpurua J, Gómez-Torres MJ. Phospholipase C zeta in human spermatozoa: A systematic review on current development and clinical application. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:1344. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021344
93. Saleh A, Thanassoulas A, Aliyev E, Swann K, Naija A, Yalcin HC, et al. Development of recombinant PLC-zeta protein as a therapeutic intervention for the clinical treatment of oocyte activation failure. Biomedicines. (2024) 12:1183. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12061183
94. Halet G, Tunwell R, Balla T, Swann K, Carroll J. The dynamics of plasma membrane PtdIns(4,5)P(2) at fertilization of mouse eggs. J Cell Sci. (2002) 115:2139–49. doi: 10.1242/jcs.115.10.2139
95. Yu Y, Nomikos M, Theodoridou M, Nounesis G, Lai FA, Swann K. PLCzeta causes Ca(2+) oscillations in mouse eggs by targeting intracellular and not plasma membrane PI(4,5)P(2). Mol Biol Cell. (2012) 23:371–80. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-08-0687
96. Matsu-Ura T, Shirakawa H, Suzuki KGN, Miyamoto A, Sugiura K, Michikawa T, et al. Dual-FRET imaging of IP3 and Ca(2+) revealed Ca(2+)-induced IP3 production maintains long lasting Ca(2+) oscillations in fertilized mouse eggs. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:4829. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-40931-w
97. Iino M. Biphasic Ca2+ dependence of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced Ca2+ release in smooth muscle cells of the Guinea pig taenia caeci. J Gen Physiol. (1990) 95:1103–22. doi: 10.1085/jgp.95.6.1103
98. Wakai T, Fissore RA. Ca(2+) homeostasis and regulation of ER Ca(2+) in mammalian oocytes/eggs. Cell Calcium. (2013) 53:63–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2012.11.010
99. Parrington J, Brind S, De Smedt H, Gangeswaran R, Lai FA, Wojcikiewicz R, et al. Expression of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors in mouse oocytes and early embryos: the type I isoform is upregulated in oocytes and downregulated after fertilization. Dev Biol. (1998) 203:451–61. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1998.9071
100. Jellerette T, He CL, Wu H, Parys JB, Fissore RA. Down-regulation of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor in mouse eggs following fertilization or parthenogenetic activation. Dev Biol. (2000) 223:238–50. doi: 10.1006/dbio.2000.9675
101. Marchant JS, Taylor CW. Cooperative activation of IP3 receptors by sequential binding of IP3 and Ca2+ safeguards against spontaneous activity. Curr Biol. (1997) 7:510–8. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(06)00222-3
102. Alzayady KJ, Wang L, Chandrasekhar R, Wagner LE, Van Petegem F, Yule DI. Defining the stoichiometry of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate binding required to initiate Ca2+ release. Sci Signal. (2016) 9:ra35. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aad6281
103. Turner PR, Sheetz MP, Jaffe LA. Fertilization increases the polyphosphoinositide content of sea urchin eggs. Nature. (1984) 310:414–5. doi: 10.1038/310414a0
104. Clapper DL, Lee HC. Inositol trisphosphate induces calcium release from nonmitochondrial stores i sea urchin egg homogenates. J Biol Chem. (1985) 260:13947–54.
105. Miyazaki S. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced calcium release and guanine nucleotide-binding protein-mediated periodic calcium rises in golden hamster eggs. J Cell Biol. (1988) 106:345–53. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.2.345
106. Miyazaki S, Yuzaki M, Nakada K, Shirakawa H, Nakanishi S, Nakade S, et al. Block of Ca2+ wave and Ca2+ oscillation by antibody to the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor in fertilized hamster eggs. Science. (1992) 257:251–5. doi: 10.1126/science.1321497
107. Xu Z, Kopf GS, Schultz RM. Involvement of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-mediated Ca2+ release in early and late events of mouse egg activation. Development. (1994) 120:1851–9. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.7.1851
108. Wakai T, Vanderheyden V, Fissore RA. Ca2+ signaling during mammalian fertilization: requirements, players, and adaptations. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. (2011) 3:a006767. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a006767
109. Deguchi R, Shirakawa H, Oda S, Mohri T, Miyazaki S. Spatiotemporal analysis of Ca(2+) waves in relation to the sperm entry site and animal-vegetal axis during Ca(2+) oscillations in fertilized mouse eggs. Dev Biol. (2000) 218:299–313. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1999.9573
110. Akizawa H, Lopes EM, Fissore RA. Zn2+ is essential for Ca2+ oscillations in mouse eggs. ELife. (2023) 12:RP88082. doi: 10.7554/eLife.88082
111. Putney JW Jr.A model for receptor-regulated calcium entry. Cell Calcium. (1986) 7:1–12. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(86)90026-6
112. Prakriya M, Lewis RS. Store-operated calcium channels. Physiol Rev. (2015) 95:1383–436. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00020.2014
113. Feske S, Wulff H, Skolnik EY. Ion channels in innate and adaptive immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. (2015) 33:291–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-032414-112212
114. Takahashi T, Kikuchi T, Kidokoro Y, Shirakawa H. Ca(2)(+) influx-dependent refilling of intracellular Ca(2)(+) stores determines the frequency of Ca(2)(+) oscillations in fertilized mouse eggs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2013) 430:60–5. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.11.024
115. Miao YL, Stein P, Jefferson WN, Padilla-Banks E, Williams CJ. Calcium influx-mediated signaling is required for complete mouse egg activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2012) 109:4169–74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1112333109
116. Bernhardt ML, Padilla-Banks E, Stein P, Zhang Y, Williams CJ. Store-operated Ca(2+) entry is not required for fertilization-induced Ca(2+) signaling in mouse eggs. Cell Calcium. (2017) 65:63–72. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2017.02.004
117. Davis FM, Janoshazi A, Janardhan KS, Steinckwich N, D’Agostin DM, Petranka JG, et al. Essential role of Orai1 store-operated calcium channels in lactation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2015) 112:5827–32. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1502264112
118. Zhang L, Chao CH, Jaeger LA, Papp AB, Machaty Z. Calcium oscillations in fertilized pig oocytes are associated with repetitive interactions between STIM1 and ORAI1. Biol Reprod. (2018) 98:510–9. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioy016
119. Chen J, Sitsel A, Benoy V, Sepulveda MR, Vangheluwe P. Primary active Ca2+ transport systems in health and disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. (2020) 12:a035113. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a035113
120. El-Jouni W, Jang B, Haun S, Machaca K. Calcium signaling differentiation during Xenopus oocyte maturation. Dev Biol. (2005) 288:514–25. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2005.10.034
121. Savy V, Stein P, Shi M, Williams CJ. PMCA1 depletion in mouse eggs amplifies calcium signaling and impacts offspring growth. Biol Reprod. (2022) 107:1439–51. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioac180
122. Pan H, Ma P, Zhu W, Schultz RM. Age-associated increase in aneuploidy and changes in gene expression in mouse eggs. Dev Biol. (2008) 316:397–407. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.01.048
123. Pan H, O’Brien MJ, Wigglesworth K, Eppig JJ, Schultz RM. Transcript profiling during mouse oocyte development and the effect of gonadotropin priming and development. Dev Biol. (2005) 286:493–506. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2005.08.023
124. Zeng F, Baldwin DA, Schultz RM. Transcript profiling during preimplantation mouse development. Dev Biol. (2004) 272:483–96. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.05.018
125. Wakai T, Zhang N, Vangheluwe P, Fissore RA. Regulation of endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) oscillations in mammalian eggs. J Cell Sci. (2013) 126:5714–24. doi: 10.1242/jcs.136549
126. Brini M, Carafoli E. Calcium pumps in health and disease. Physiol Rev. (2009) 89:1341–78. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00032.2008
127. Kline D, Kline JT. Thapsigargin activates a calcium influx pathway in the unfertilized mouse egg and suppresses repetitive calcium transients in the fertilized egg. J Biol Chem. (1992) 267:17624–30.
128. Wu LJ, Sweet TB, Clapham DE, International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. Current progress in the mammalian TRP ion channel family. Pharmacol Rev. (2010) 62:381–404. doi: 10.1124/pr.110.002725
129. Carvacho I, Lee HC, Fissore RA, Clapham DE. TRPV3 channels mediate strontium-induced mouse-egg activation. Cell Rep. (2013) 5:1375–86. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.11.007
130. Lee HC, Yoon S-Y, Lykke-Hartmann K, Fissore RA, Carvacho I. TRPV3 channels mediate Ca²⁺ influx induced by 2-APB in mouse eggs. Cell Calcium. (2016) 59:21–31. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2015.12.001
131. Lu Y, Reddy R, Ferrer Buitrago M, Vander Jeught M, Neupane J, De Vos WH, et al. Strontium fails to induce Ca2+ release and activation in human oocytes despite the presence of functional TRPV3 channels. Hum Reprod Open. (2018) 2018:hoy005. doi: 10.1093/hropen/hoy005
132. Nadler MJ, Hermosura MC, Inabe K, Perraud AL, Zhu Q, Stokes AJ, et al. LTRPC7 is a Mg.ATP-regulated divalent cation channel required for cell viability. Nature. (2001) 411:590–5. doi: 10.1038/35079092
133. Xiao E, Yang HQ, Gan YH, Duan DH, He LH, Guo Y, et al. Brief reports: TRPM7 Senses mechanical stimulation inducing osteogenesis in human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells. (2015) 33:615–21. doi: 10.1002/stem.1858
134. Gupta N, Soriano-Úbeda C, Stein P, Savy V, Papas BN, Ardestani G, et al. Essential role of Mg2+ in mouse preimplantation embryo development revealed by TRPM7 chanzyme-deficient gametes. Cell Rep. (2023) 42:113232. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113232
135. Day ML, Johnson MH, Cook DI. Cell cycle regulation of a T-type calcium current in early mouse embryos. Pflugers Arch. (1998) 436:834–42. doi: 10.1007/s004240050712
136. Peres A. The calcium current of mouse egg measured in physiological calcium and temperature conditions. J Physiol. (1987) 391:573–88. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016757
137. Bernhardt ML, Zhang Y, Erxleben CF, Padilla-Banks E, McDonough CE, Miao YL, et al. CaV3.2 T-type channels mediate Ca(2)(+) entry during oocyte maturation and following fertilization. J Cell Sci. (2015) 128:4442–52. doi: 10.1242/jcs.180026
138. Mehregan A, Ardestani G, Akizawa H, Carvacho I, Fissore R. Deletion of TRPV3 and CaV3.2 T-type channels in mice undermines fertility and Ca2+ homeostasis in oocytes and eggs. J Cell Sci. (2021) 134:jcs257956. doi: 10.1242/jcs.257956
139. He M, Zhang T, Yang Y, Wang C. Mechanisms of oocyte maturation and related epigenetic regulation. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 19:654028. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.654028
140. Premkumar KV, Prasad S, Tiwari M, Pandey AN, Gupta A, Sharma A, et al. Meiotic instability generates a pathological condition in mammalian ovum. Stem Cell Rev Rep. (2021) 17:777–84. doi: 10.1007/s12015-020-10072-z
141. Markoulaki S, Matson S, Ducibella T. Fertilization stimulates long-lasting oscillations of CaMKII activity in mouse eggs. Dev Biol. (2004) 272:15–25. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.04.008
142. Knott JG, Gardner AJ, Madgwick S, Jones KT, Williams CJ, Schultz RM. Calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II triggers mouse egg activation and embryo development in the absence of Ca2+ oscillations. Dev Biol. (2006) 296:388–95. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.06.004
143. Backs J, Stein P, Backs T, Duncan FE, Grueter CE, McAnally J, et al. The gamma isoform of CaM kinase II controls mouse egg activation by regulating cell cycle resumption. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2010) 107:81–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0912658106
144. Madgwick S, Jones KT. How eggs arrest at metaphase II: MPF stabilisation plus APC/C inhibition equals Cytostatic Factor. Cell Div. (2007) 2:4. doi: 10.1186/1747-1028-2-4
145. Hansen DV, Tung JJ, Jackson PK. CaMKII and polo-like kinase 1 sequentially phosphorylate the cytostatic factor Emi2/XErp1 to trigger its destruction and meiotic exit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2006) 103:608–13. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0509549102
146. Oh JS, Susor A, Conti M. Protein tyrosine kinase Wee1B is essential for metaphase II exit in mouse oocytes. Science. (2011) 332:462–5. doi: 10.1126/science.1199211
147. Moos J, Xu Z, Schultz RM, Kopf GS. Regulation of nuclear envelope assembly/disassembly by MAP kinase. Dev Biol. (1996) 175:358–61. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1996.0121
148. Phillips KP, Petrunewich MA, Collins JL, Booth RA, Liu XJ, Baltz JM. Inhibition of MEK or cdc2 kinase parthenogenetically activates mouse eggs and yields the same phenotypes as Mos(-/-) parthenogenotes. Dev Biol. (2002) 247:210–23. doi: 10.1006/dbio.2002.0680
149. Gonzalez-Garcia JR, Bradley J, Nomikos M, Paul L, Machaty Z, Lai FA, et al. The dynamics of MAPK inactivation at fertilization in mouse eggs. J Cell Sci. (2014) 127:2749–60. doi: 10.1242/jcs.145045
150. Tatemoto H, Muto N. Mitogen-activated protein kinase regulates normal transition from metaphase to interphase following parthenogenetic activation in porcine oocytes. Zygote. (2001) 9:15–23. doi: 10.1017/s0967199401001034
151. Abbott AL, Fissore RA, Ducibella T. Incompetence of preovulatory mouse oocytes to undergo cortical granule exocytosis following induced calcium oscillations. Dev Biol. (1999) 207:38–48. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1998.9159
152. Gardner AJ, Knott JG, Jones KT, Evans JP. CaMKII can participate in but is not sufficient for the establishment of the membrane block to polyspermy in mouse eggs. J Cell Physiol. (2007) 212:275–80. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21046
153. Ducibella T, LeFevre L. Study of protein kinase C antagonists on cortical granule exocytosis and cell-cycle resumption in fertilized mouse eggs. Mol Reprod Dev. (1997) 46:216–26. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2795(199702)46:2<216::AID-MRD12>3.0.CO;2-Z
154. Eliyahu E, Shalgi R. A role for protein kinase C during rat egg activation. Biol Reprod. (2002) 67:189–95. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod67.1.189
155. Yu Y, Halet G, Lai FA, Swann K. Regulation of diacylglycerol production and protein kinase C stimulation during sperm- and PLCzeta-mediated mouse egg activation. Biol Cell. (2008) 100:633–43. doi: 10.1042/BC20080033
156. Halet G. PKC signaling at fertilization in mammalian eggs. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2004) 1742:185–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2004.09.012
157. Ducibella T, Matson S. Secretory mechanisms and Ca2+ signaling in gametes: similarities to regulated neuroendocrine secretion in somatic cells and involvement in emerging pathologies. Endocr Pathol. (2007) 18:191–203. doi: 10.1007/s12022-007-0015-7
158. Eliyahu E, Shtraizent N, Tsaadon A, Shalgi R. Association between myristoylated alanin-rich C kinase substrate (MARCKS) translocation and cortical granule exocytosis in rat eggs. Reproduction. (2006) 131:221–31. doi: 10.1530/rep.1.00794
159. Tsaadon L, Kaplan-Kraicer R, Shalgi R. Myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate, but not Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II, is the mediator in cortical granules exocytosis. Reproduction. (2008) 135:613–24. doi: 10.1530/REP-07-0554
160. Matson S, Markoulaki S, Ducibella T. Antagonists of myosin light chain kinase and of myosin II inhibit specific events of egg activation in fertilized mouse eggs. Biol Reprod. (2006) 74:169–76. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.105.046409
161. Kashir J, Heindryckx B, Jones C, De Sutter P, Parrington J, Coward K. Oocyte activation, phospholipase C zeta and human infertility. Hum Reprod Update. (2010) 16:690–703. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmq018
162. Yanagida K, Fujikura Y, Katayose H. The present status of artificial oocyte activation in assisted reproductive technology. Reprod Med Biol. (2008) 7:133–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1447-0578.2008.00210.x
163. Ebner T, Moser M, Sommergruber M, Jesacher K, Tews G. Complete oocyte activation failure after ICSI can be overcome by a modified injection technique. Hum Reprod. (2004) 19:1837–41. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deh325
164. Heindryckx B, De Gheselle S, Gerris J, Dhont M, De Sutter P. Efficiency of assisted oocyte activation as a solution for failed intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Reprod BioMed Online. (2008) 17:662–8. doi: 10.1016/S1472-6483(10)60313-6
165. Xu Z, Yao G, Niu W, Fan H, Ma X, Shi S, et al. Ionophore (A23187) rescues the activation of unfertilized oocytes after intracytoplasmic sperm injection and chromosome analysis of blastocyst after activation. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2021) 12:692082. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.692082
166. Jin CH, Chen RR, Feng XY, Zhao JG, Xu MT, Zhang M, et al. Effects of calcium-free ageing on ethanol-induced activation and developmental potential of mouse oocytes. Zygote. (2023) 31:393–401. doi: 10.1017/S0967199423000291
167. Fissore RA, Pinto-Correia C, Robl JM. Inositol trisphosphate-induced calcium release in the generation of calcium oscillations in bovine eggs. Biol Reprod. (1995) 53:766–74. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod53.4.766
168. Cuthbertson KS, Cobbold PH. Phorbol ester and sperm activate mouse oocytes by inducing sustained oscillations in cell Ca2+. Nature. (1985) 316:541–2. doi: 10.1038/316541a0
169. Kim JW, Kim SD, Yang SH, Yoon SH, Jung JH, Lim JH. Successful pregnancy after SrCl2 oocyte activation in couples with repeated low fertilization rates following calcium ionophore treatment. Syst Biol Reprod Med. (2014) 60:177–82. doi: 10.3109/19396368.2014.900832
170. Wang M, Zhu L, Liu C, He H, Wang C, Xing C, et al. A novel assisted oocyte activation method improves fertilization in patients with recurrent fertilization failure. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 9:672081. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.672081
171. Duncan FE, Que EL, Zhang N, Feinberg EC, O’Halloran TV, Woodruff TK. The zinc spark is an inorganic signature of human egg activation. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:24737. doi: 10.1038/srep24737
172. Iba T, Yano Y, Umeno M, Hinokio K, Kuwahara A, Irahara M, et al. Roscovitine in combination with calcium ionophore induces oocyte activation through reduction of M-phase promoting factor activity in mice. Zygote. (2012) 20:321–5. doi: 10.1017/s0967199411000591
173. Sang Q, Li B, Kuang Y, Wang X, Zhang Z, Chen B, et al. Homozygous mutations in WEE2 cause fertilization failure and female infertility. Am J Hum Genet. (2018) 102:649–57. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2018.02.015
174. Vanden Meerschaut F, Nikiforaki D, Heindryckx B, De Sutter P. Assisted oocyte activation following ICSI fertilization failure. Reprod BioMed Online. (2014) 28:560–71. doi: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2014.01.008
175. Shang J-Z, Li S-R, Li X-Q, Zhou Y-T, Ma X, Liu L, et al. Simazine perturbs the maturational competency of mouse oocyte through inducing oxidative stress and DNA damage. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. (2022) 230:113105. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.113105
176. Xing C, Chen S, Wang Y, Pan Z, Zou Y, Sun S, et al. Glyphosate exposure deteriorates oocyte meiotic maturation via induction of organelle dysfunctions in pigs. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. (2022) 13:80. doi: 10.1186/s40104-022-00732-0
177. Wang X, Li H, Mu H, Zhang S, Li Y, Han X, et al. Melatonin improves the quality of rotenone-exposed mouse oocytes through association with histone modifications. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. (2023) 262:115186. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.115186
178. Wang Y, Li S-H, Yang S-J, Li X-Q, Liu L, Ma X, et al. Exposure to phenanthrene affects oocyte meiosis by inducing mitochondrial dysfunction and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Prolif. (2023) 56:e13335. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13335
179. Adyeni BS, Carlos U, Tatiana HM, Luisa G, Jessica T, Eduardo C, et al. Perfluorohexane sulfonate (PFHxS) disturbs the estrous cycle, ovulation rate, oocyte cell communication and calcium homeostasis in mice. Reprod Biol. (2023) 23:100768. doi: 10.1016/j.repbio.2023.100768
180. Domínguez A, Salazar Z, Betancourt M, Ducolomb Y, Casas E, Fernández F, et al. Effect of perfluorodecanoic acid on pig oocyte viability, intracellular calcium levels and gap junction intercellular communication during oocyte maturation in vitro. Toxicol In Vitro. (2019) 58:224–9. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2019.03.041
181. Li Y, Liu S, Gao F, Peng Z, Zhang J, Li S, et al. BPA interferes with granulosa cell development and oocyte meiosis in mouse preantral follicles. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). (2023) 248:1145–58. doi: 10.1177/15353702231179940
182. Luo Y, Che M-J, Liu C, Liu H-G, Fu X-W, Hou Y-P. Toxicity and related mechanisms of dihydroartemisinin on porcine oocyte maturation in vitro. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. (2018) 341:8–15. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2018.01.002
183. Chen F, Sun J, Wang Y, Grunberger JW, Zheng Z, Khurana N, et al. Silica nanoparticles induce ovarian granulosa cell apoptosis via activation of the PERK-ATF4-CHOP-ERO1α pathway-mediated IP3R1-dependent calcium mobilization. Cell Biol Toxicol. (2023) 39:1715–34. doi: 10.1007/s10565-022-09776-4
184. Luo Y, Guo Q, Zhang L, Zhuan Q, Meng L, Fu X, et al. Dihydroartemisinin exposure impairs porcine ovarian granulosa cells by activating PERK-eIF2α-ATF4 through endoplasmic reticulum stress. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. (2020) 403:115159. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2020.115159
185. Huang M, Liu S, Fu L, Jiang X, Yang M. Bisphenol A and its analogues bisphenol S, bisphenol F and bisphenol AF induce oxidative stress and biomacromolecular damage in human granulosa KGN cells. Chemosphere. (2020) 253:126707. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126707
186. Koo OJ, Jang G, Kwon DK, Kang JT, Kwon OS, Park HJ, et al. Electrical activation induces reactive oxygen species in porcine embryos. Theriogenology. (2008) 70:1111–8. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2008.06.031
187. Tesarik J, Rienzi L, Ubaldi F, Mendoza C, Greco E. Use of a modified intracytoplasmic sperm injection technique to overcome sperm-borne and oocyte-borne oocyte activation failures. Fertil Steril. (2002) 78:619–24. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(02)03291-0
188. Tejera A, Molla M, Muriel L, Remohi J, Pellicer A, De Pablo JL. Successful pregnancy and childbirth after intracytoplasmic sperm injection with calcium ionophore oocyte activation in a globozoospermic patient. Fertil Steril. (2008) 90:1202.e1–5. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2007.11.056
189. Ebner T, Montag M, Oocyte Activation Study G, Montag M, van der Ven K, van der Ven H, et al. Live birth after artificial oocyte activation using a ready-to-use ionophore: a prospective multicentre study. Reprod BioMed Online. (2015) 30:359–65. doi: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2014.11.012
190. Murugesu S, Saso S, Jones BP, Bracewell-Milnes T, Athanasiou T, Mania A, et al. Does the use of calcium ionophore during artificial oocyte activation demonstrate an effect on pregnancy rate? A meta-analysis. Fertil Steril. (2017) 108:468–482.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2017.06.029
191. Karabulut S, Aksünger Ö, Ata C, Sağıroglu Y, Keskin İ. Artificial oocyte activation with calcium ionophore for frozen sperm cycles. Syst Biol Reprod Med. (2018) 64:381–8. doi: 10.1080/19396368.2018.1452311
192. Rickords LF, White KL. Electroporation of inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate induces repetitive calcium oscillations in murine oocytes. J Exp Zool. (1993) 265:178–84. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402650209
193. Meo SC, Leal CL, Garcia JM. Activation and early parthenogenesis of bovine oocytes treated with ethanol and strontium. Anim Reprod Sci. (2004) 81:35–46. doi: 10.1016/j.anireprosci.2003.09.004
194. Yi YJ, Park CS. Parthenogenetic development of porcine oocytes treated by ethanol, cycloheximide, cytochalasin B and 6-dimethylaminopurine. Anim Reprod Sci. (2005) 86:297–304. doi: 10.1016/j.anireprosci.2004.07.007
195. Balakier H, Casper RF. Experimentally induced parthenogenetic activation of human oocytes. Hum Reprod. (1993) 8:740–3. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.humrep.a138132
196. Lu Q, Zhao Y, Gao X, Li Y, Ma S, Mullen S, et al. Combination of calcium ionophore A23187 with puromycin salvages human unfertilized oocytes after ICSI. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. (2006) 126:72–6. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2005.10.038
197. Nakagawa K, Yamano S, Moride N, Yamashita M, Yoshizawa M, Aono T. Effect of activation with Ca ionophore A23187 and puromycin on the development of human oocytes that failed to fertilize after intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Fertil Steril. (2001) 76:148–52. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(01)01839-8
198. Menéndez-Blanco I, Soto-Heras S, Catalá MG, Piras A-R, Izquierdo D, Paramio M-T. Effect of vitrification of in vitro matured prepubertal goat oocytes on embryo development after parthenogenic activation and intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Cryobiology. (2020) 93:56–61. doi: 10.1016/j.cryobiol.2020.02.011
199. Cheek TR, McGuinness OM, Vincent C, Moreton RB, Berridge MJ, Johnson MH. Fertilisation and thimerosal stimulate similar calcium spiking patterns in mouse oocytes but by separate mechanisms. Development. (1993) 119:179–89. doi: 10.1242/dev.119.1.179
200. Herbert M, Murdoch AP, Gillespie JI. The thiol reagent, thimerosal induces intracellular calcium oscillations in mature human oocytes. Hum Reprod. (1995) 10:2183–6. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.humrep.a136265
201. Herbert M, Gillespie JI, Murdoch AP. Development of calcium signalling mechanisms during maturation of human oocytes. Mol Hum Reprod. (1997) 3:965–73. doi: 10.1093/molehr/3.11.965
202. Sousa M, Barros A, Mendoza C, Tesarik J. Effects of protein kinase C activation and inhibition on sperm-, thimerosal-, and ryanodine-induced calcium responses of human oocytes. Mol Hum Reprod. (1996) 2:699–708. doi: 10.1093/molehr/2.9.699
203. Alexandre H, Delsinne V, Goval JJ. The thiol reagent, thimerosal, irreversibly inhibits meiosis reinitiation in mouse oocyte when applied during a very early and narrow temporal window: a pharmacological analysis. Mol Reprod Dev. (2003) 65:454–61. doi: 10.1002/mrd.10319
204. Fraser LR. Strontium supports capacitation and the acrosome reaction in mouse sperm and rapidly activates mouse eggs. Gamete Res. (1987) 18:363–74. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1120180410
205. Wang ZG, Wang W, Yu SD, Xu ZR. Effects of different activation protocols on preimplantation development, apoptosis and ploidy of bovine parthenogenetic embryos. Anim Reprod Sci. (2008) 105:292–301. doi: 10.1016/j.anireprosci.2007.03.017
206. Che L, Lalonde A, Bordignon V. Chemical activation of parthenogenetic and nuclear transfer porcine oocytes using ionomycin and strontium chloride. Theriogenology. (2007) 67:1297–304. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2007.02.006
207. Yamazaki W, Ferreira CR, Meo SC, Leal CL, Meirelles FV, Garcia JM. Use of strontium in the activation of bovine oocytes reconstructed by somatic cell nuclear transfer. Zygote. (2005) 13:295–302. doi: 10.1017/S0967199405003333
208. Fernandes CB, Devito LG, Martins LR, Blanco ID, de Lima Neto JF, Tsuribe PM, et al. Artificial activation of bovine and equine oocytes with cycloheximide, roscovitine, strontium, or 6-dimethylaminopurine in low or high calcium concentrations. Zygote. (2014) 22:387–94. doi: 10.1017/S0967199412000627
209. Fawzy M, Emad M, Mahran A, Sabry M, Fetih AN, Abdelghafar H, et al. Artificial oocyte activation with SrCl2 or calcimycin after ICSI improves clinical and embryological outcomes compared with ICSI alone: results of a randomized clinical trial. Hum Reprod. (2018) 33:1636–44. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dey258
210. Lee K, Davis A, Zhang L, Ryu J, Spate LD, Park KW, et al. Pig oocyte activation using a Zn²⁺ chelator, TPEN. Theriogenology. (2015) 84:1024–32. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2015.05.036
211. Hajarizadeh A, Eidi A, Arefian E, Tvrda E, Mohammadi-Sangcheshmeh A. Aflatoxin B1 impairs in vitro early developmental competence of ovine oocytes. . Theriogenology. (2022) 183:53–60. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2022.02.013
Keywords: calcium, oocyte maturation, oocyte activation, fertilization, Ca2+ oscillations, female fertility
Citation: Chen C, Huang Z, Dong S, Ding M, Li J, Wang M, Zeng X, Zhang X and Sun X (2024) Calcium signaling in oocyte quality and functionality and its application. Front. Endocrinol. 15:1411000. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1411000
Received: 02 April 2024; Accepted: 29 July 2024;
Published: 16 August 2024.
Edited by:
Ge Lin, Central South University, ChinaReviewed by:
Ellis Fok, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, ChinaCopyright © 2024 Chen, Huang, Dong, Ding, Li, Wang, Zeng, Zhang and Sun. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xuhui Zeng, emVuZ3h1aHVpQG50dS5lZHUuY24=; Xiaoning Zhang, emhhbmd4bkBudHUuZWR1LmNu; Xiaoli Sun, c3hsenlAbnR1LmVkdS5jbg==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.