
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Endocrinol. , 09 October 2023
Sec. Clinical Diabetes
Volume 14 - 2023 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2023.1278604
This article is a correction to:
A comparison of physical activity, muscle strength, and sleep between people with type 2 diabetes in Kuwait and the UK: A cross-sectional study
 Ebaa Al Ozairi1,2
Ebaa Al Ozairi1,2 Dalal Alsaeed1
Dalal Alsaeed1 Dherar Al Roudhan1
Dherar Al Roudhan1 Nia Voase1
Nia Voase1 Jill P. Pell3
Jill P. Pell3 Frederick K. Ho3
Frederick K. Ho3 Mohammed Abdulla1
Mohammed Abdulla1 Stuart R. Gray4*
Stuart R. Gray4*A corrigendum on
A comparison of physical activity, muscle strength, and sleep between people with type 2 diabetes in Kuwait and the UK: a cross sectional study
by Al Ozairi E, Alsaeed D, Al Roudhan D, Voase N, Pell JP, Ho FK, Abdulla M and Gray SR (2022) Front. Endocrinol. 13:1067227. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1067227
In the published article, as a result of an error in some of the calculations of physical activity variables, there were mistakes in Figure 1 and Table 2 as published. The corrected Figure 1, Table 2, and their captions appear below.
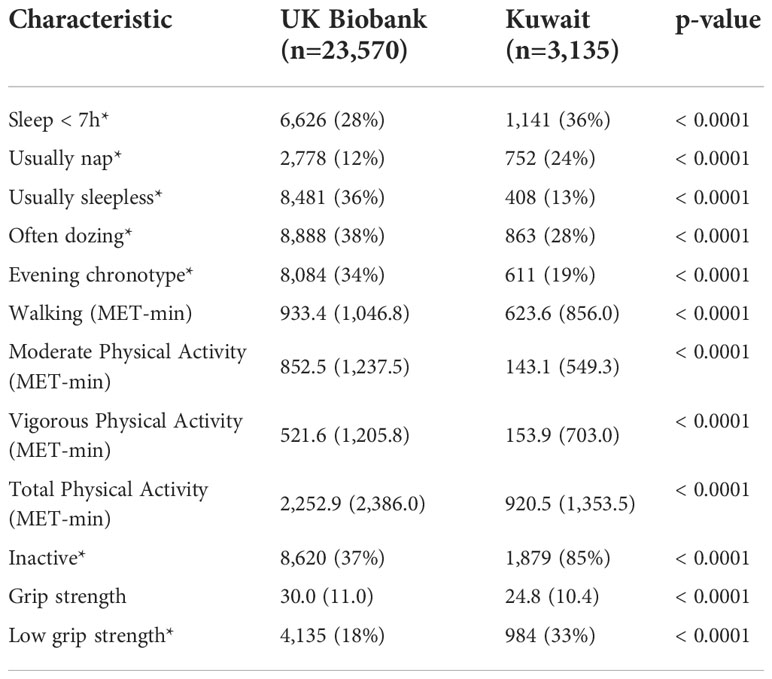
Table 2 Physical activity, sleep and physical function data in UK Biobank and Kuwaiti cohorts of people with type 2 diabetes.
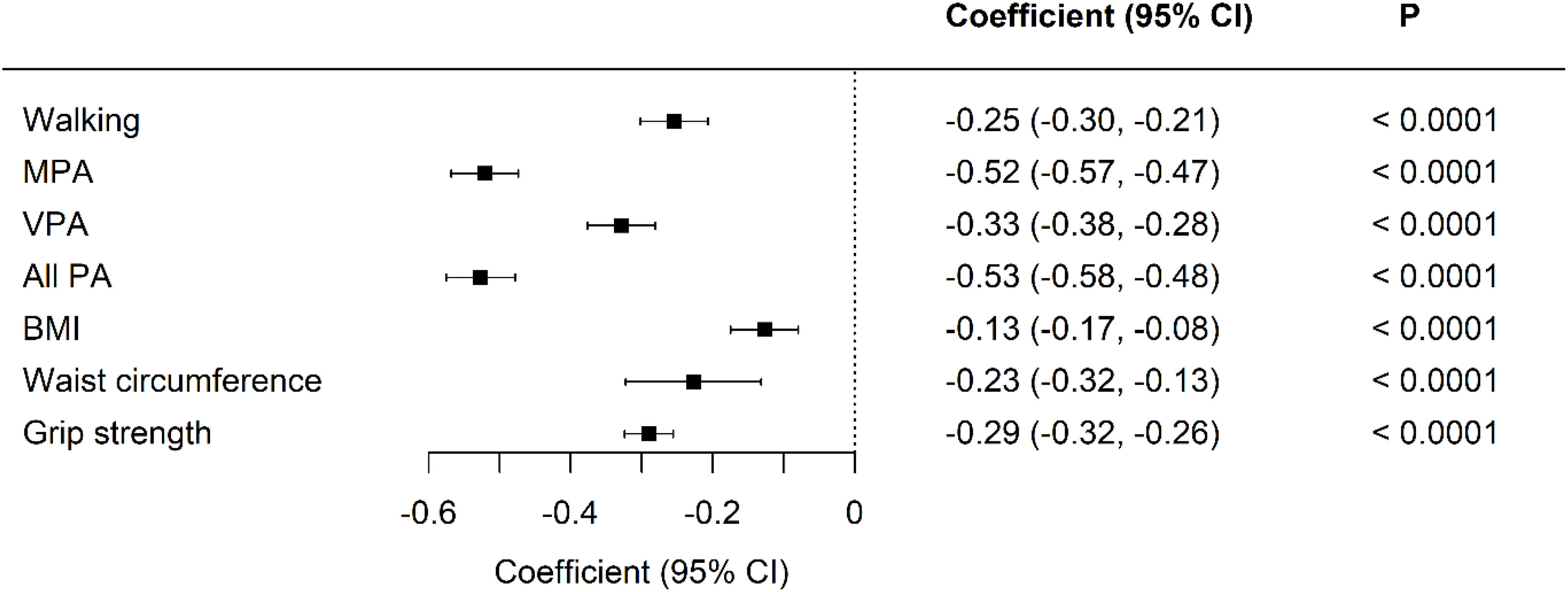
Figure 1 Standardized differences in physical activity, body composition, and grip strength between UK Biobank and Kuwaiti cohorts of people with type 2 diabetes A negative coefficient means a lower value in the Kuwaiti cohort. MET-minutes in MPA, moderate physical activity; VPA, vigorous physical activity; PA, physical activity; BMI, body mass index. Adjusted for age, sex, and duration of diabetes.
Furthermore, because of an error in some of the calculations of physical activity variables, there were some mistakes in the body text in article as published. A correction has been made to [Abstract], [Results], [Paragraph 1]. This sentence previously stated:
“Physical activity levels (−937 (−1,097, −851) Met-min/week: standardized B-coefficient −0.42 (−0.47, −0.37)) and grip strength (3.2 (−3.58, −2.82) kg: standardized B-coefficient (−0.29 (−0.32, −0.26)) were lower in the Kuwaiti cohort, and the odds of having short sleep (OR 1.32 (1.19,1.46), being classed as inactive (OR 8.70 (7.59, 9.98), and having muscle weakness (OR 1.88 (1.69, 2.09) were higher.”
The corrected sentence appears below:
“Physical activity levels (-1216(-1328,1104 Met-min/wee k: standardized B-coefficient -0.52 (-0.57, -0.47) and grip strength (-3.2(-3.58, -2.82) kg: standardized B-coefficient (-0.29 (-0.32, -0.26) were lower in the Kuwaiti cohort and the odds of having short sleep (OR 1.32 (1.19,1.46), being classed as inactive (OR 8.70 (7.59, 9.98) and having muscle weakness were higher (OR 1.88 (1.69, 2.09).”
In addition, a further correction has been made to [Abstract], [Conclusions], [Paragraph 1]. This sentence previously stated:
“The aim of the current study was to determine the prevalence of low muscle strength and to evaluate physical activity and sleep characteristics in people with type 2 diabetes in Kuwait. Additionally, equivalent data from the UK Biobank cohort were compared”
The corrected sentence appears below:
“This study demonstrates that insufficient sleep, physical inactivity, and muscle weakness are prevalent in people with type 2 diabetes, especially in Kuwait. Importantly, these observations warrant urgent and effective interventions to improve sleep, muscle strength, and physical activity, especially in Kuwait.”
The authors apologize for these errors and state that they do not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: cross-sectional study, diabetes mellitus, type 2, muscle strength, Kuwait, United Kingdom
Citation: Al Ozairi E, Alsaeed D, Al Roudhan D, Voase N, Pell JP, Ho FK, Abdulla M and Gray SR (2023) Corrigendum: A comparison of physical activity, muscle strength, and sleep between people with type 2 diabetes in Kuwait and he UK: a cross sectional study. Front. Endocrinol. 14:1278604. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1278604
Received: 16 August 2023; Accepted: 19 September 2023;
Published: 09 October 2023.
Approved by:
Frontiers Editorial Office, Frontiers Media SA, SwitzerlandCopyright © 2023 Al Ozairi, Alsaeed, Al Roudhan, Voase, Pell, Ho, Abdulla and Gray. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Stuart R. Gray, c3R1YXJ0LmdyYXlAZ2xhc2dvdy5hYy51aw==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.