
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ERRATUM article
Front. Endocrinol., 18 November 2021
Sec. Neuroendocrine Science
Volume 12 - 2021 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2021.804873
This article is part of the Research TopicNeuroendocrine-Immunological Interactions in Health and DiseaseView all 26 articles
This article is an erratum on:
Behavioral Abnormalities in Knockout and Humanized Tau Mice
An Erratum on:
Behavioral Abnormalities in Knockout and Humanized Tau Mice
By Gonçalves RA, Wijesekara N, Fraser PE and De Felice FG (2020). Front. Endocrinol. 11:124. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00124
Due to a production error, there was a mistake in Figure 4A as published. Image 4A has a blank box, containing no data. The corrected Figure 4A appears below.
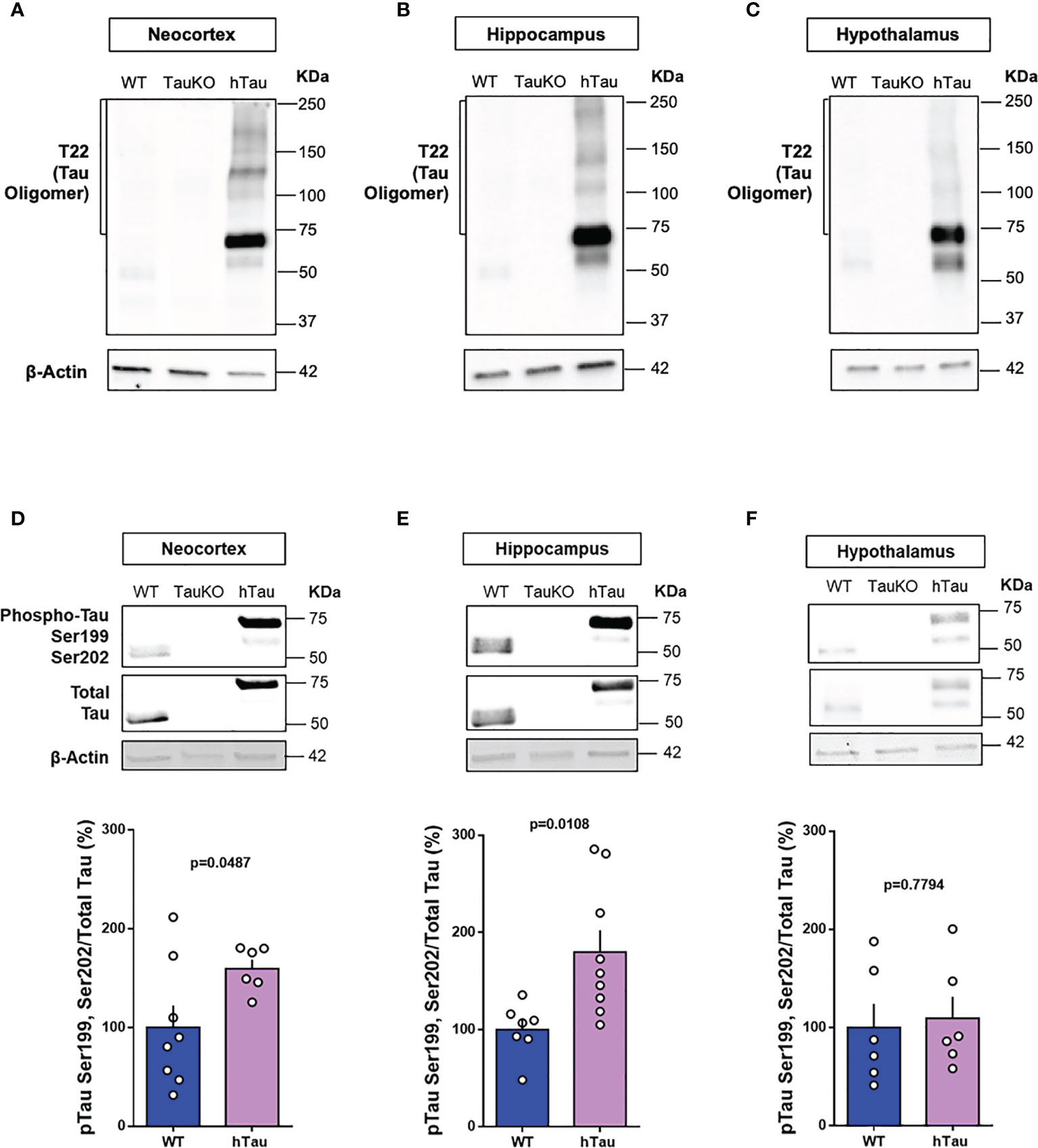
Figure 4 Phospho-tau and tau oligomers are increased in multiple brain regions of hTau mice. Immunoblot analysis of tau oligomers in (A) cortical, (B) hippocampal, and (C) hypothalamic lysates from 20-week-old WT, TauKO, and hTau mice. Immunoblot analysis of pTauSer199Ser202/TotalTau ratio in (D) cortical (n= 8 WT; 6 hTau), (E) hippocampal (n = 7 WT; 9 hTau), and (F) hypothalamic (n = 6 WT; 6 hTau) lysates from 20-week-old WT, TauKO, and hTau mice.
The publisher apologizes for this mistake.
The original version of this article has been updated.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease, MAPT, Tau protein, insulin, anxiety, metabolism, memory
Citation: Frontiers Production Office (2021) Erratum: Behavioral Abnormalities in Knockout and Humanized Tau Mice. Front. Endocrinol. 12:804873. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.804873
Received: 29 October 2021; Accepted: 29 October 2021;
Published: 18 November 2021.
Approved by:
Frontiers Editorial Office, Frontiers Media SA, SwitzerlandCopyright © 2021 Frontiers Production Office. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Frontiers Production Office, cHJvZHVjdGlvbi5vZmZpY2VAZnJvbnRpZXJzaW4ub3Jn
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.