- 1Centre for Environmental and Climate Science, Lund University, Lund, Sweden
- 2Department of Biology, Microbial Ecology Group, Lund University, Lund, Sweden
Recent studies have shown that dissolved organic matter (DOM) decomposed by ectomycorrhizal (ECM) fungi increases adsorptive properties of organic matter towards soil mineral surfaces. Concomitantly, ECM fungi secrete secondary metabolites with iron reducing capacity that are thought to participate in non-enzymatic Fenton-based decomposition of DOM. The aim of this study was to investigate if the iron reduction induced by the ECM fungus Paxillus involutus during organic matter decomposition was conserved in the decomposed DOM. We explored how the modified DOM reductively dissolved ferrihydrite and goethite nanoparticles and how these processes affected the reactions with H2O2 and the Fenton-based oxidation of mineral-associated organic matter. Culture filtrates were obtained from incubation of the ECM fungus on DOM from forest litter of a spruce forest. This modified DOM was separated by extraction into an ethyl acetate and a water fraction. These fractions were reacted with ferrihydrite and goethite in absence and presence of H2O2. Dissolved Fe2+ and HO• were measured and the reactions at the iron oxide-water interfaces were monitored in real-time with in-situ IR spectroscopy. Experiments showed that decomposition of DOM by P. involutus generated a modified DOM that displayed an increased and persistent reductive capacity. Most of the reductants were isolated in the aromatic- and carboxyl-dominated ethyl acetate fraction but some reduction capacity was also captured in the water fraction mainly containing carbohydrates. Reductive dissolution was more extensive for ferrihydrite than goethite, and this process generated significant oxidation of the DOM-ferrihydrite associations. Oxidation of adsorbed DOM was triggered by H2O2 via heterogenous and homogeneous Fenton reactions. These oxidation processes were favored by ferrihydrite because of a high reduction potential and a high efficiency of heterogeneous Fenton as compared to goethite. An optimal timing between the heterogeneous and homogeneous Fenton processes triggered extensive radical oxidation of the DOM-ferrihydrite associations generating a high concentration of surface-associated oxalate. Overall, the results show that organic matter associated with ferrihydrite may be more susceptible to radical oxidation than on goethite, and that fungal decomposition of DOM in general may have consequences for other important soil processes such as mineral dissolution, adsorption and initiation of radical reactions.
Introduction
Dissolved organic matter (DOM) is central to the biogeochemical cycle of carbon. It is believed to be the most bioavailable fraction of organic carbon compounds (Kaiser and Kalbitz, 2012), and it contributes to the formation of the DOM-mineral associations that lead to the stabilization of soil organic matter, the largest reservoir of carbon in terrestrial ecosystems. DOM is formed from leaching and microbial decomposition of litter material in the upper soil layers, and it is transported either via surface waters to surrounding watersheds or via soil pore waters downwards to deeper soil layers. Irrespective of the hydrological flow paths of DOM, it is progressively modified by microbes as a consequence of decomposition when microbes access nutrients, such as nitrogen (N), from DOM (Rineau, et al., 2013), or via adsorption and desorption processes at mineral surfaces (Kaiser and Kalbitz, 2012; Keiluweit et al., 2015).
Ectomycorrhizal (ECM) fungi are important drivers of nutrient cycling in boreal and temperate forest ecosystems (Hobbie and Högberg, 2012), and these fungi typically occur in the mineral horizon of forest soils and in the organic matter layer of forest soils that may have already been degraded by saprotrophic fungi (Lindahl et al., 2007). Both in the mineral and organic soil horizon, nutrients are complexed and entrapped in organic matter and/or adsorbed to mineral particles. To gain access to nutrients, mycorrhizal symbionts must liberate these nutrients from mineral and organic complexes. Indeed, ECM fungi have been shown to acquire N from complex DOM and this process is accompanied with a substantial secretion of organic molecules increasing the overall affinity of the modified DOM for mineral surfaces (Wang et al., 2017). Moreover, ECM fungi with different evolutionary histories, growth rates or exploration types have been shown to access N from mineral-associated proteins and during this process they reductively dissolve iron oxides (Wang et al., 2020 and 2021).
The observation that decomposition of organic matter by ECM fungi is accompanied with iron reduction raises questions about the properties of the modified DOM and the impacts of the reductive processes on nutrient mobilization and organic matter stabilization. DOM is decomposed by EMC fungi through extracellular enzymatic processes that sometimes operate in concert with non-enzymatic oxidation by reactive oxygen species (ROS). It has been shown that protein decomposition can be initiated by a non-enzymatic oxidative attack from hydroxyl radicals (HO•) followed by enzymatic proteolysis (Op De Beeck et al., 2018). Thus, iron reduction promoted by extracellular secondary metabolites may be a necessary reaction to generate HO• needed for DOM decomposition, e.g., via the Fenton Reaction (1) (Rineau et al., 2012; Tunlid et al., 2016):
While there is empirical evidence for iron reduction and generation of HO• during the decomposition of DOM, it is an open question whether the reductive capacity is conserved in the remaining modified DOM after decomposition. Should this be the case, the increased reductive capacity of DOM can influence other important biogeochemical processes such as the coupled reduction-dissolution processes affecting both Fe speciation and bioavailability (Lindsay, 1991) as well as the liberation of phosphates typically associated with iron (III) minerals (Chacon et al., 2006).
In this study, we have focused on the consequences that fungal transformation of DOM has for DOM-iron oxide interactions, in particular for the coupled adsorption-redox reactions in absence and presence of H2O2. We have determined to what extent the transformation of DOM by an ECM fungus increases the capacity of the DOM to reductively dissolve ferrihydrite and goethite. We have furthermore correlated these results to properties of the modified DOM and the iron oxides to get insight into the reaction mechanisms. Ferrihydrite and goethite were chosen because they are common Fe3+-containing soil minerals that have different reduction potentials and display differences with respect to the reactivity towards H2O2 (Hermanek et al., 2007; Gorski et al., 2016). Moreover, we have investigated how the altered reactivity of the modified DOM affected the generation of HO• and the oxidation of iron oxide-associated organic matter. These research objectives were addressed by collecting culture filtrates from incubation of an ECM fungus, Paxillus involutus, on DOM extracted by water from a forest litter material. In order to facilitate the analysis of the contributions from the major compound classes of DOM, the culture filtrate was extracted into an ethyl acetate and a water fraction, and subsequent experiments were performed on these separate fractions. Ferrihydrite and goethite were exposed to the two fractions of modified DOM and their reductive dissolution was monitored as a function of time and DOM concentration. Also, the effects and consequences of HO• generation were explored by addition of H2O2 to the DOM-iron oxide suspensions. To connect the quantitative Fe2+ and HO• results with the molecular-scale reactions at the water-iron oxide interfaces, we used in-situ infrared spectroscopy to monitor these reactions in real-time during the coupled DOM adsorption and iron oxide dissolution reactions.
Materials and Methods
Collection of Forest Litter, and Preparation and Chemical Characteristics of Dissolved Organic Matter
Forest litter was collected in a Norway spruce forest in Simlångsdalen, Sweden (N: 56°42′-3.17″; E: 13°6′57.51″). The litter layer was collected after removing the moss mat and avoiding the mineral layer of the soil. The collected litter was subsequently sieved through a 2 mm sieve to remove large roots, mineral particles and remaining mosses. 120 g of fresh litter was boiled for 1 h in 1 L of distilled water. The litter slurry was sieved through a cheesecloth and a sequence of filters with decreasing pore size (2.6, 1.6, 0.7, 0.45 and 0.22 µm). This yielded the DOM (denoted DOMini) that was used in subsequent experiments. The composition of a DOM sample extracted from the same soil following the exact same extraction protocol has been characterized in our previous work (Wang et al., 2017) and shown to contain a mixture of carbohydrates, aliphatics and aromatics as well as carbonyl/carboxyl-containing compounds. This overall composition was confirmed by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR, Bruker Avance II 400 MHz NMR spectrometer, Billerica, MA, United States) and Diffuse Reflectance Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (Vertex 80v, Bruker FTIR spectrometer) of DOMini (Supplementary Figures S1, S2). Total Organic Carbon (TOC) was determined using an organic C analyzer (TOC-V(CPH); Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) and a combustion catalytic oxidation method. Total Nitrogen (TN) was measured with the same apparatus equipped with a TNM-1 detector (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). Samples were acidified to pH < 2 with 1 M HCl before TOC and TN measurements.
Because the DOMini was obtained from a forest soil, it contained various elements, in addition to the organic compounds. Most important for this study was the native content of iron and phosphate. Total Fe and P concentrations were analyzed in both fractions using Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy (ICP-OES) (Perkin Elmer Optima 8300, Waltham, MA, United States). The P and Fe concentrations are presented in Supplementary Table S1, re-calculated from the DOM stock solutions to the actual values in the different batch experiments. The iron concentrations were non-negligible and needed to be considered when the reductive dissolution effects of the DOM fractions were analyzed. The phosphate concentrations were low in comparison with the TOC concentrations in the experiments, corresponding to a surface coverage in the range of 0.008–0.012 μmol m−2. As a result, only small competitive adsorption effects from phosphate were expected, and accordingly, very minor IR spectral contributions from phosphate bands to the carbohydrate region 900–1,200 cm−1.
Incubation of Paxillus involutus on DOMini Extract
The ECM fungus P. involutus is commonly found in boreal and northern temperate forests with a soil pH of around 4 (Wallander and Söderström 1999; Hobara et al., 2016). For this reason, all batch and IR experiments were conducted at pH 4.0.
P. involutus (Batsch) Fr. (ATCC 200175) was grown for 9 days in the dark at 20°C on a monolayer of sterile 4 mm diameter glass beads and 10 ml of Fries medium (Supplementary Figure S3) (Fries, 1978). The medium used contained 3.74 mM NH4Cl, 0.41 mM MgSO4·7H2O, 0.22 mM KH2PO4, 0.18 mM CaCl2·2H2O, 0.34 mM NaCl, 1.34 mM KCl, 0.24 mM H3BO3, 20 µM ZnSO4·7H2O, 5.01 µM CuSO4·5H2O, 50.29 µM MnSO4·H2O, 0.16 µM (NH4)6Mo7O24·7H2O, 74 µM FeCl3·6H2O, 33.3 mM D-glucose, 55.51 µM myo-inositol, 0.3 µM thiamine·HCl, 0.1 µM biotin, 0.59 µM pyridoxine, 0.27 µM riboflavin, 0.82 µM nicotinamide, 0.73 µM p-aminobenzoic acid, and 0.46 µM Ca-pantothenate. The pH was corrected to 4.8. After 9 days, the Fries medium was removed and replaced with 10 ml Fries medium minus NH4Cl to starve the cultures for N, which significantly stimulates the DOM-decomposition activity in P. involutus (Nicolas et al., 2018). After 24 h, the N-free medium was removed and replaced with a DOMini solution supplemented with 2.5 g L−1 of glucose, and this DOMini-glucose solution was filter sterilized through a pore size of 0.22 µm prior to the incubation experiments. Glucose was added since previous experiments have shown that the supply of an easily available C-source is required by P. involutus to oxidize DOM (Rineau et al., 2013). Cultures were grown on this extract for another 7 days and culture media were subsequently sampled. After these 7 days, almost all glucose was consumed. The decomposed DOM, now also containing secondary metabolites secreted by P. involutus (Wang et al., 2017), was filtered through a 0.22 µm filter to remove any remaining hyphae and finally freeze-dried for further use. The decomposed DOM is further referred to as modified DOM (DOMmod).
Ethyl Acetate Extraction of Dissolved Organic Matter
It has been shown that the main iron-reducing activity of DOM decomposed by P. involutus can be extracted by ethyl acetate (Shah et al., 2015). Herein, we adopted this extraction procedure to split the DOM samples into an ethyl acetate (DOMini-EtOAc or DOMmod-EtOAc) and a water soluble (DOMini-H2O or DOMmod-H2O) fraction. 60 mg of freeze-dried DOMini or DOMmod collected from the P. involutus cultures were dissolved in 600 ml MilliQ water. Aliquots of 5 ml were acidified with 1 ml 1 M HCl. These mixtures were extracted with 5 ml ethyl acetate during 10 min of vigorous shaking, and phase separation was accomplished using a separatory funnel. This procedure was repeated three times. The resulting ethyl acetate and water fractions were pooled and freeze-dried. These freeze-dried materials were used in subsequent batch and IR experiments. TOC, TON, total Fe and P were determined, and the DOMmod-EtOAc and DOMmod-H2O fractions were also characterized by means of diffuse reflectance IR Spectroscopy and 1H NMR as described in Section Collection of Forest Litter, and Preparation and Chemical Characteristics of Dissolved Organic Matter.
Synthesis and Characterization of the Iron Oxides
6-line ferrihydrite and goethite were synthesized and characterized according to Krumina et al. (2016). The obtained mineral particles were identified by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The specific surface area (SSA) of the goethite was determined to 71.5 m2 g−1 using the BET N2 adsorption method (Micromeritics Gemini VII 2390a, Norcross, GA, United States) (Brunauer et al., 1938). The SSA of the 6-line ferrihydrite was estimated to be 300 m2 g−1, according to a procedure previously described (Krumina et al., 2017). The concentrations of the stock suspensions of goethite and ferrihydrite were 12.8 and 2.3 g L−1, respectively. These suspensions were purged with N2 gas to remove carbonates and dissolved CO2 and stored at 4°C. The ferrihydrite experiments were carried out with particles aged for 1–3 months. This material showed only an XRD pattern characteristic of 6-line ferrihydrite (Supplementary Figure S4). All experiments were performed in 0.1 M NaCl solutions, where pH was adjusted to the desired values with 40 mM NaOH or HCl solutions in 0.1 M NaCl.
Batch Experiments
Batch experiments were conducted at total organic carbon (TOC) concentrations of 4 μmol m−2 (800 µM TOC), 8 μmol m−2 (1,600 µM TOC) and 12 μmol m−2 (2,400 µM TOC) of ferrihydrite and goethite surface area, respectively. All stock solutions and reactions were adjusted to and performed at pH 4.0 in 0.1 M NaCl medium, where pH was adjusted with 40 mM NaOH or HCl solutions in 0.1 M NaCl solution. Stock mineral suspensions were diluted to yield the same surface area per volume liquid of 200 m2 L−1 for all batch experiments. During the experiments, the reaction tubes (15 or 50 ml non-pyrogenic polypropylene, Sarstedt) were covered by aluminum foil to avoid any exposure to light and mixed using a Grant-bio PTR-35 360° vertical multi-functional rotator (Grant Instruments, Royston, United Kingdom). Batch experiments were performed in triplicates.
Fe2+ Measurements
Fe2+ concentrations were measured by means of the ferrozine assay (Goodell et al., 2006). 100 µl of 1% ferrozine (w/v) solution was added to each sample and mixed for 5 min. The measurements were performed at 562 nm using an Ultraspec 3000 UV/Visible spectrophotometer (Pharmacia Biotech, Uppsala, Sweden) with a limit of detection (LoD) of 2.0 µM). Blanks contained 100 µl 1% ferrozine solution in 0.1 M NaCl solution with a total volume of 1 ml Fe2+ concentrations were calculated from a standard curve covering a range of 0–100 µM Fe2+. In the reductive dissolution experiments, the total Fe concentrations measured by ICP-OES were close to the Fe2+ concentrations determined in the ferrozine assay (≤5%) and are therefore not reported here.
Hydroxyl Radical Measurements
300 µM terephthalic acid (TPA) was used as a probe for measuring HO• production. TPA is oxidized by HO• to hydroxy terephtalic acid (hTPA) which can be readily detected by fluorescence spectroscopy (Jing and Chaplin, 2017). After sampling mineral suspensions, an excess of phosphate (3 μmol m−2) was added to the samples and mixed for 1 h in order to remove adsorbed hTPA from the iron oxide surfaces (Lyngsie et al., 2018). The fluorescence intensity was measured at an excitation wavelength of 315 nm and an emission wavelength of 425 nm with an LS50B luminescence spectrometer (Perkin Elmer, Waltham, MA, United States). The LoD of this analytical method was 0.5 nM hTPA. The hTPA concentrations in the batch samples were calculated from a linear standard curve of hTPA (0–500 nM) in 0.1 M NaCl. Two types of experiments were performed: 1) simultaneous addition of DOM, TPA and 100 µM (0.4 μmol m−2) H2O2 to the iron oxide suspensions and 2) pre-adsorption of DOM to the iron oxides for 24 h prior to addition of TPA and 100 µM H2O2. The H2O2 concentration was chosen to be substantially below the total number of surface sites on the iron oxides, and 100 μM H2O2 is only slightly above concentrations detected in natural waters e.g., in rainwater (Yu and Kuzyakov, 2021).
In-Situ IR Spectroscopy of the Iron Oxide-Water Interface
IR spectroscopic measurements were performed according to a method originally presented by Loring et al. (2009) and then slightly modified by Krumina et al. (2016). Iron oxide overlayers were prepared on an attenuated total reflectance (ATR) ZnSe crystal by evaporating 0.7 ml of goethite (2.0 g L−1) or ferrihydrite (2.3 g L−1) suspension. The ATR crystal, which forms the bottom of a titration vessel, was connected to an ATR accessory (FastIR, Harrick Scientific Products, Pleasantville, NY, United States) and placed inside an evacuated (1.42 mbar) Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (Vertex 80v, Bruker, Billerica, MA, United States) in a climate-controlled laboratory with a set temperature of 21°C. Either ferrihydrite or goethite suspensions in 0.1 M NaCl medium were added to the titration vessel and slowly stirred using a propeller stirrer. pH was adjusted to the desired value and kept constant with an automated and computer-controlled burette system (907 Titrando and Tiamo 2.4 software, Metrohm AG, Herisau, Switzerland) during all experiments. A background spectrum of 4096 co-added scans was collected of the overlayer and the iron oxide suspension. In accordance with the batch experiments, two different types of IR experiments were conducted, i.e., one where all reactants were added simultaneously to the iron oxide suspension, and one where DOM was pre-adsorbed for 24 h prior to addition of H2O2. During the first hour of either DOM or DOM + H2O2 addition, data were collected at a rate of 1 min per spectrum. After this initial period, data collection was increased to ∼7.5 min per spectrum. All IR spectra were recorded over the range 700–4,000 cm−1 at a resolution of 4 cm−1.
The IR spectral data sets were analyzed using the multivariate curve resolution-alternating least squares (MCR-ALS) formalism implemented in the MATLAB program PLS Toolbox v. 8.6 (Eigenvector Research Inc., Manson, WA, United States). Non-negative constraints were applied to both the concentrations and the spectra, and the spectral components were modeled with the same maximum intensity. A critical parameter in this analysis is the initial assumption of the number of components needed to explain the variation in the data sets, and this was assessed from singular-value decomposition (Tauler and De Juan, 2006).
Due to difficulties in separating adsorbed DOM from minerals using conventional filtration and centrifugation techniques, we instead estimated roughly the surface saturation of the DOM from IR spectroscopy data. DOM fractions were added to the iron oxide suspension and adsorption was monitored as a function of IR intensity. When no, or a very slow change in IR absorbance was observed, another aliquot of the DOM fractions was added. This procedure was repeated until addition of DOM fractions resulted in no or very little change in IR absorbance, i.e., the final addition of a given DOM fraction increased the IR absorbance by < 5% within several hours of adsorption.
Results
Chemical Characteristics of the DOMmod-EtOAc, and DOMmod-H2O Fractions
In agreement with results from our previous studies, N-starved P. involutus cultures consumed a substantial part of the total N present in DOMini (Supplementary Table S1) (Rineau et al., 2012; Wang et al., 2017). This should be compared to the much smaller decrease in P and Fe after incubation (Supplementary Table S1), which may be due to a limited fungal uptake and/or losses during extraction. The extraction recovered ca. 70% of the starting material (DOMmod) and of this recovered material ca. 30% of the TOC was contained in DOMmod-EtOAc and ca. 70% in DOMmod-H2O. The combined IR and 1H NMR analyses showed that aromatic compounds were extracted into the ethyl acetate phase while carbohydrates remained mainly in the water phase (Supplementary Figures S1, S2). Carboxylic acids were distributed over both solvents but seemed to be relatively more prevalent in the ethyl acetate phase as indicated by the IR data. In Wang et al. (2017) we showed that decomposition of DOMini by P. involutus caused a decrease in reduced sugars and an increase in aromatic and phenolic functional groups as well as an increase in functional groups containing oxidized carbon atoms, presumably carboxylic acids. Moreover, data from 13C-labelling experiments in Wang et al. (2017) showed that parts of these compounds was secreted by the fungus. Thus, both aromatics originally present in DOMini and secreted by the fungus were likely contained in DOMmod-EtOAc whereas modified and unmodified carbohydrates were present mainly in DOMmod-H2O.
Reductive Dissolution of Ferrihydrite and Goethite by DOMmod-EtOAc and DOMmod-H2O
Initial experiments showed that DOMini caused a small but detectable reductive dissolution of ferrihydrite and goethite (Supplementary Figure S5). In the first time points, though, the concentration of Fe2+ was undetectable or significantly lower than the total Fe contained in DOMini added. Thus, if Fe2+ was present in DOMini it was rapidly removed in the presence of both ferrihydrite and goethite, either via adsorption or re-oxidation (Krumina et al., 2017). The slow increase of Fe2+ that followed the addition of DOMini to the iron oxide suspensions was accordingly a result of reductive dissolution. The reduction of ferrihydrite was more extensive than that of goethite, which is consistent with the higher reduction potential of ferrihydrite (Gorski et al., 2016).
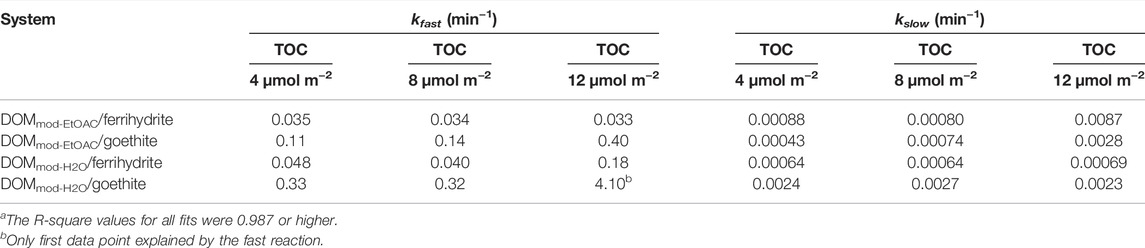
DOMini was extracted into DOMini-EtOAc and DOMini-H2O, and the reductive dissolution of ferrihydrite was compared with the effects caused by the corresponding fractions of DOMmod. In the case of DOMini-EtOAc and DOMini-H2O the Fe2+ reducing activity was completely captured in the ethyl acetate fraction (Figure 1); note that the Fe2+ concentrations in the DOMini-H2O experiments were at or below the LoD of the ferrozine assay. The reductive capacity markedly increased in the DOMmod-EtOAc and DOMmod-H2O, and at the endpoint of the experiment the increase was ca. 2.6 times for both fractions as compared to the corresponding DOMini fractions. Although the extent of reduction promoted by DOMmod-EtOAc was far greater than DOMmod-H2O, the increase caused by the latter was significant (Figure 1). These results showed that DOM decomposition by the ECM fungus P. involutus generated a modified end-product that had a larger Fe-reducing capacity, and that this property was conserved in the lyophilized and re-dissolved culture filtrate.
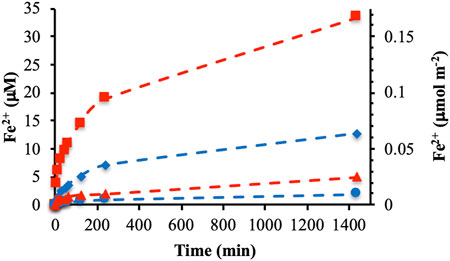
FIGURE 1. Fe2+ concentrations in solution from reductive dissolution of ferrihydrite by DOMini-EtOAc (◆, blue), DOMmod-EtOAc (■, red), DOMini-H2O (•, blue) and DOMmod-H2O (▲, red). All experiments were carried out at 12 µmol TOC m−2 and pH 4.0 in 0.1 M NaCl. The data points represent the average of triplicate experiments, and the standard deviations in Fe2+ concentrations are smaller than the size of the symbols.
Further experiments were focused on the DOMmod-EtOAc and DOMmod-H2O fractions and the effects of TOC concentrations. In general, the extent of reductive dissolution of ferrihydrite and goethite was directly related to the TOC concentrations (Figure 2). The exception was the reaction between DOMmod-EtOAc and goethite where the experiments performed at 8 and 12 μmol m−2 yielded similar results. In agreement with the DOMini experiments, we observed a greater extent of dissolution for ferrihydrite than goethite, as suggested by the difference in reduction potentials of the minerals. However, comparison of the experimental endpoints showed that the relative effects of DOMmod-EtOAc and DOMmod-H2O with respect to ferrihydrite and goethite reduction were quite different. The reductive dissolution promoted by DOMmod-EtOAc in the presence of ferrihydrite increased by a factor of ca. 7 compared to goethite while in the case of DOMmod-H2O the increase was only a factor of ca. 1.5 (Figure 2). Hence, DOMmod-EtOAc seemed to contain a relatively high concentration of compounds with a reduction potential sufficiently low to reduce ferrihydrite but not goethite to any greater extent. In contrast, DOMmod-H2O contained a relatively low total concentration of reducing compounds but with a low reduction potential that allowed a more similar reduction of ferrihydrite and goethite. Thus, decomposition of DOM by P. Involutus and the concomitant secretion of extracellular metabolites seem to generate a modified DOM containing molecules with a range of reduction potentials. Previous experiments where P. Involutus was grown on either DOM or proteins in absence of iron oxides have also shown that this fungus produces an array of iron (III) reducing metabolites (Shah et al., 2015; Shah et al., 2021).
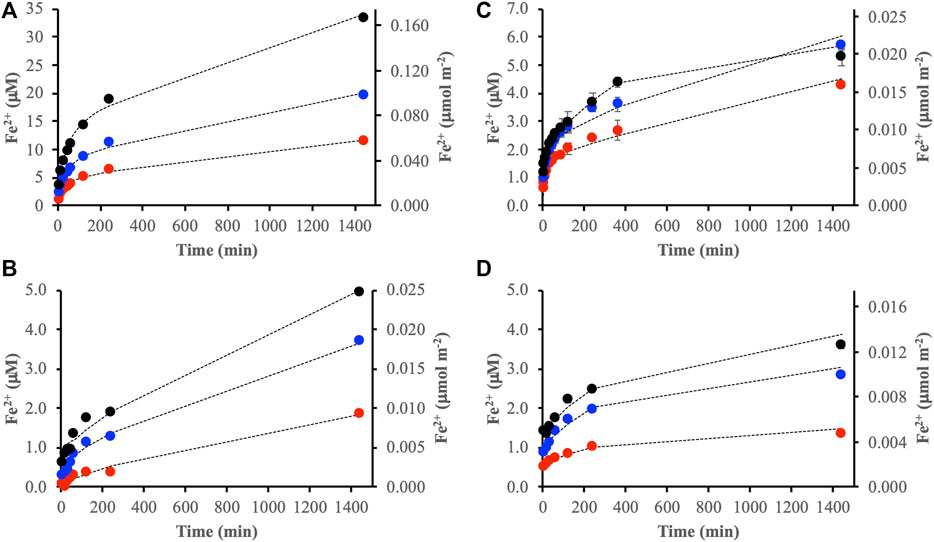
FIGURE 2. Fe2+ concentrations in solution from reductive dissolution by DOMmod-EtOAc of ferrihydrite (A) and goethite (C) and by DOMmod-H2O of ferrihydrite (B) and goethite (D). The experiments were performed at TOC concentrations of 4.0 (red circles), 8.0 (blue circles) and 12.0 μmol m−2 (black circles). The dotted lines represent the best fit of Eq. 2 to the data; the corresponding rate constants are reported in Table 1. The data points represent the average of triplicate experiments, and the standard deviations in Fe2+ concentrations are in most cases smaller than the size of the symbols. For a version of this figures showing the first 250 min only see Supplementay Figure S6.
The extracts from the modified DOM unquestionably promoted significant reductive dissolution of ferrihydrite and goethite. However, compared to typical values of surface site concentrations on the minerals the extent of dissolution was small as can be seen from the Fe2+ concentrations recalculated to units of μmol m−2 (Figures 1, 2). For instance, the concentration of singly coordinated surface groups (≡Fe-OH) on ferrihydrite has been estimated to ca 10 μmol m−2 (Hiemstra and Van Riemsdijk, 2009), which should be compared to the ca. 0.17 μmol m−2 Fe2+ dissolved from ferrihydrite by DOMmod-EtOAc after 24 h (Figure 2A). Accordingly, the net-generation of Fe2+ in solution indicated that only small fractions of the ferrihydrite and goethite surfaces were affected by the reductive dissolution processes.
The Fe2+ concentration data in Figure 2 can be fitted with the equation:
The rate constant describing the fast process, kfast, was poorly constrained because of the limited time resolution at the early stages of our experiments whereas kslow was better defined by the shape of the [Fe2+] increase after the initial 2–10 min of the reactions. As shown in Table 1, kslow is practically independent of TOC concentration except for the DOMmod-EtOAc-goethite system. In this case the rate constant increased with increasing TOC concentration, and as already mentioned the same system showed similar extent of reductive dissolution at 8 and 12 μmol m−2 indicating surface saturation of the reductant (Figure 2C). Thus, the increase in rate constant may be related to the excess of reductant with respect to surfaces sites active in the dissolution process. In contrast, the almost constant kslow obtained for the other systems indicated a high ratio of surface-active sites relative to reducing molecules.
In-situ IR spectra were collected during the simultaneous adsorption-reductive dissolution reactions between the DOM fractions and the iron oxides. Spectra representing the endpoints (i.e., reaction time 1,440 min) as well as experiments performed at a higher TOC concentration (60 μmol m−2) are shown in Figure 3. In accordance with the chemical characterization of the DOM fractions (Supplementary Figures S1, S2) and the results in Wang et al. (2017), IR spectra of adsorbed DOMmod-EtOAc were characterized by features from carboxyl groups (bands (2) and (4), (Figure 3A) and aromatics (band (3), (Figure 3A). While those of DOMmod-H2O displayed typical strong carbohydrate bands between ca. 900–1,200 cm−1 and features indicating other oxidized functional groups such as carbonyls and carboxyls in the region between 1,400–1800 cm−1 (Figure 3B). The IR spectral dependence on TOC concentration was different for ferrihydrite and goethite. In the case of ferrihydrite, an increase of the DOMmod-EtOAc concentration resulted in a significant shift of the asymmetric carboxyl band (band (2)), marked changes in the carbonyl region around band (1) (Figure 3A (I) and (II)), and an increase in band (3) originating from aromatics (Figure 3A (I) and (II)). The goethite spectra, however, were practically unaffected by an increase of DOMmod-EtOAc concentration, except for a stronger relative contribution from the aromatic band (band (3), Figure 3A (III) and (IV)). It is also notable that band 1) at 1,660 cm−1 was not observed in the goethite spectra. The comparison of TOC concentration dependence was more difficult to make for DOMmod-H2O due to a generally low signal-to-noise ratio with resulting baseline problems, in particular for the experiments with goethite performed at low TOC. Still, comparison of the intensities of bands (5) and (6), representing oxidized functional groups, to the carbohydrate signals around 1,030 cm−1 suggested that the former bands displayed a relative increase for ferrihydrite but not for goethite (Figure 3B).
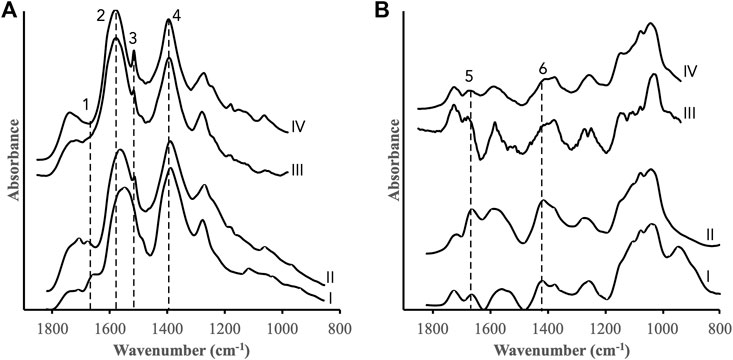
FIGURE 3. IR spectra collected after 1,440 min reaction time between the iron oxides and (A) DOMmod-EtOAc and (B) DOMmod-H2O. Ferrihydrite experiments performed at TOC concentration of (I) 12 μmol m−2, and (II) 60 μmol m−2, and goethite experiments at (III) 12 μmol m−2 and (IV) 60 μmol m−2. The vertical dotted lines highlight bands discussed in the text. These bands likely have predominant contributions from: 1) carbonyl-like modes (1,660 cm−1); 2) asymmetric carboxyl stretch (1,565 cm−1); 3) aromatic skeleton mode (1,515 cm−1); 4) symmetric carboxyl stretch (1,380 cm-1); 5) carbonyl-like mode (1,660 cm−1); 6) symmetric carboxyl stretch (1,415 cm−1) (see Supplementary Table S2 for an overview of the band assignments). The spectra have been shifted in the y-direction for the sake of clarity.
The time evolution of the IR spectra during the coupled adsorption-reductive dissolution reactions was analyzed by means of the MCR-ALS formalism that resolves component IR spectra and the corresponding contribution profiles. The resolution of the different components relies on differences in their rate of spectral change as a function of time, i.e., if two species display very similar rate behavior they will not be resolved, and their spectral characteristics will be included in the same component. Two components were sufficient to explain the IR data sets collected during the reactions between DOMmod-EtAOc and ferrihydrite or goethite yielding fits of 99.99% of the variance or better (Supplementary Figures S7, S8). The ferrihydrite spectra were deconvoluted into a dominant species containing the spectral signatures of both carboxylates and aromatics and a minor species displaying slower kinetics and characteristics of carboxylates together with the band at ca 1,660 cm−1 identified in Figure 3, but no aromatics. The two goethite components were similar and both contained carboxylate and aromatic bands. The main difference between these spectra seemed to be caused by variations in the signal from adsorbed water contributing to the spectra around 1,620 cm−1 (Supplementary Figure S7).
The IR spectra of DOMmod-H2O on ferrihydrite and goethite were analyzed at TOC = 60 μmol m−2 because of the poor signal-to-noise at lower TOC concentrations. On ferrihydrite MCR-ALS resolved two unique spectra, one representing carbohydrates and a second minor carboxylate species (Supplementary Figure S8). This second species also displayed a slow time evolution while the signal from the former species was saturated after ca. 400 min. The two goethite components were characterized by close to identical IR bands of carbohydrates and differed mainly in their baselines close to one of the main goethite bands at 890 cm−1 (Supplementary Figure S8).
The integrated absorbance over the range 1,850–900 cm−1 of the IR spectra provided an estimate of the total adsorption of the DOM fractions. Comparison between these integral values and the Fe2+ concentrations obtained from reductive dissolution revealed a correlation between total adsorption and dissolution (Figure 4). The correlation indicated that the rate of reductive dissolution was controlled by the total adsorption of DOM even though the organic molecules responsible for the actual reduction likely constituted only a minor part of each DOM fraction. Figure 4 also shows that adsorption of the DOM fractions seemed to be faster on goethite than ferrihydrite. Moreover, the goethite data indicated a steady state after ca. 1,000 min while the integrated absorbances for ferrihydrite displayed a continued slow increase.
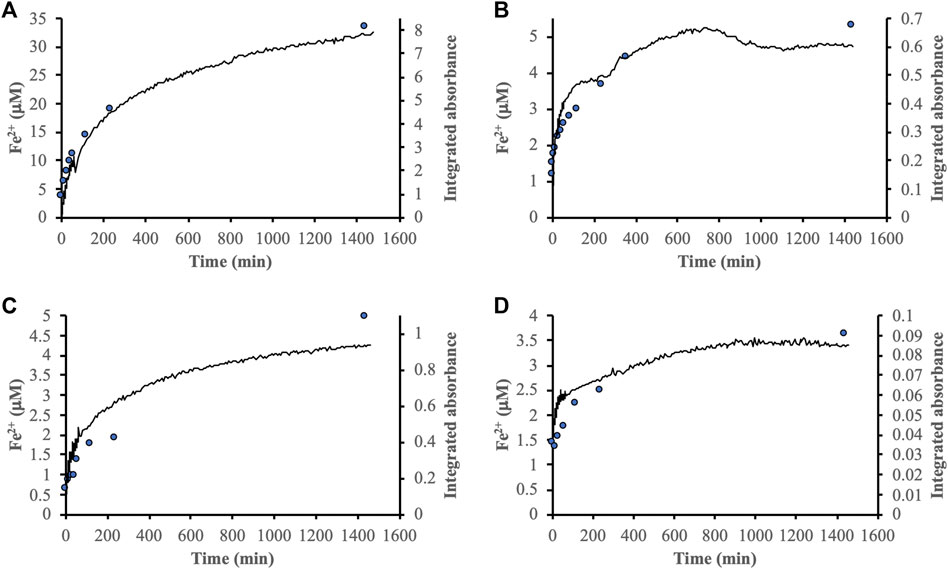
FIGURE 4. Comparison between [Fe2+] generated by reductive dissolution (blue circles) and adsorption of the modified DOM fraction determined from the integrated absorbance of IR spectra between ca. 1,850–900 cm−1 (solid black lines). The panels show the reactions between DOMmod-EtOAc and ferrihydrite (A) and goethite (B), and DOMmod-H2O and ferrihydrite (C) and goethite (D). All experiments were performed at TOC = 12 μmol m−2.
The integrated IR absorbances were also used to analyze the adsorption capacity of ferrihydrite and goethite with respect to DOMmod-EtOAc and DOMmod-H2O (Supplementary Figure S9). Incremental additions of the DOM fractions showed that TOC surface saturation was approached around 50–60 μmol m−2 for DOMmod-EtOAc and the adsorption isotherms were similar for both minerals. The DOMmod-H2O adsorption leveled off at much higher TOC concentrations of 150 μmol m−2 and above, and the difference between the isotherms of ferrihydrite and goethite was quite large. The detailed interpretations of these isotherms are outside the scope of this work, but it is important to note that all dissolution experiments were performed at TOC concentration far below surface saturation.
Generation of Hydroxyl Radicals
The detection of hydroxyl radicals (HO•) was accomplished with TPA, which has been shown to be a suitable probe molecule because it forms one product, is resistant to other oxidative processes that would yield false positives and is not easily reduced (Jing and Chaplin, 2017). All experiments were conducted at a fixed TPA concentration of 1.5 μmol m−2 of ferrihydrite or goethite. A previous study has indicated surface saturation of TPA on ferrihydrite at pH 4.5 around 0.4–0.5 μmol m−2 (Lyngsie et al., 2018), thus in our experiments TPA should be distributed over both the solid surfaces and the bulk water phase. In the presence of the DOM fraction, it is likely that competitive effects shift this distribution and drive more TPA into solution.
Initial experiments performed in absence of DOM showed large differences in reactions between H2O2 and ferrihydrite or goethite (Figure 5). The reaction with ferrihydrite generated significant amounts of HO• that increased almost linearly with time, while radicals generated in the goethite system were barely detectable (Figure 5, green lines).
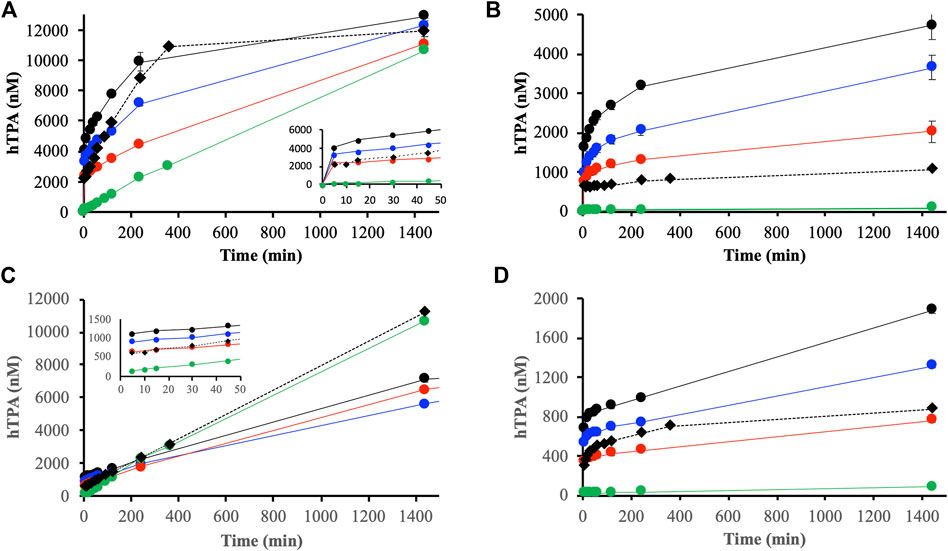
FIGURE 5. Generation of hydroxyls radicals detected by the oxidation of TPA to hTPA from reactions between H2O2 and suspensions containing DOMmod-EtOAc and ferrihydrite (A) and goethite (B), and DOMmod-H2O and ferrihydrite (C) and goethite (D). The experiments were performed at TOC concentrations of 4.0 (red symbols), 8.0 (blue symbols) and 12.0 μmol m−2 (black symbols), and the green symbols represent the reaction between H2O2 and ferrihydrite or goethite in the absence of DOM fraction. Filled circles and solid lines represent experiments where H2O2 was added to suspension containing DOM fractions and iron oxides pre-equilibrated for 24 h. The filled diamonds and dotted lines represent experiments where H2O2 and DOM fractions were added simultaneously to the suspensions. All experiments were performed at pH 4.0, [TPA] = 300 μM and [H2O2] = 100 μM. The data points represent the average of triplicate experiments, and the standard deviations in hTPA concentrations are in most cases smaller than the size of the symbols. The insets in (A,C) show the initial time points 0–50 min.
Addition of H2O2 to the DOM-iron oxide suspensions effectively oxidized Fe2+, and the resulting Fe2+ concentration after addition of H2O2 was below the ferrozine assay LoD in all cases. Equilibration of DOMmod-EtOAc with ferrihydrite or goethite 24 h prior to addition of H2O2 increased the generation of detectable hydroxide radicals (Figures 5A,B). Ferrihydrite was more efficient in generating HO• compared to goethite, which is consistent with the more extensive reductive dissolution of ferrihydrite. Initially, the amounts of HO• detected was correlated to the Fe2+ produced during pre-equilibration (Figure 5; Table 2), but in the case of ferrihydrite the HO• concentrations converged almost to the same value after 1,440 min irrespective of TOC concentration showing that the total concentration of H2O2 was the limiting factor at extended reaction times. For goethite, however, the concentrations of HO• depended on the TOC concentrations and the slow increase in HO• after ca. 200 min was in agreement with the slow release of Fe2+ during extended reaction times between DOMmod-EtOAc and goethite (cf. Figures 2, 5).

TABLE 2. Total Fe2+ concentrations (μM) after pre-equilibrating the DOM fractions with ferrihydrite and goethite for 24 h at pH 4.0. The experiments were performed in triplicates and reported as mean values and accompanying standard deviations.
In line with the low reductive capacity of DOMmod-H2O the amounts of HO• generated from the pre-equilibrated suspensions were initially lower than for DOMmod-EtOAc (Figure 5). For ferrihydrite, though, the HO• concentrations approached those detected in the presence of DOMmod-EtOAc, and showed similar increase with time as observed in the absence of DOM. In fact, simultaneous addition of DOMmod-EtAOc and H2O2 produced identical results to the addition of H2O2 only, whereas pre-equilibration with DOMmod-H2O resulted in lower linear rates that were independent of TOC concentrations. The lower rates in the presence of pre-adsorbed DOM are presumably due to surface competition between H2O2 and DOM. In the goethite system the slow increase of HO• with time was dependent on TOC concentrations and again followed the trends of reductive dissolution (cf. Figures 2D, 5D).
The batch experiments above showed that HO• was formed in ferrihydrite and goethite suspensions containing H2O2 in the absence and presence of DOM fractions, and that the extent and rates strongly depended on the properties of the DOM fractions and the iron oxides. In these experiments, the precise distribution of the TPA probe molecules were unknown but, as discussed above, these molecules were likely present both on the iron oxide surfaces and in bulk solution. Thus, from the TPA measurements we cannot ascertain if the radical oxidation took place at the surface or in solution. Further information was obtained from complementary in-situ IR spectroscopic measurements of the DOM fractions adsorbed to the iron oxides during the reactions with H2O2. In contrast to the TPA batch experiments, these measurements are sensitive to any changes of the adsorbed organic matter caused by the addition of H2O2. The IR spectra recorded of ferrihydrite and goethite surfaces pre-equilibrated with the DOM fractions for 24 h and subsequently reacted with H2O2 showed distinct trends for ferrihydrite but not for goethite (Figure 6). Overall, these results suggest that DOM fractions associated with ferrihydrite were more susceptible to radical oxidation than fractions associated with goethite. The DOMmod-EtOAC-ferrihydrite system displayed the strongest response to H2O2 addition, and bands characterizing oxidized functional groups such as carboxyls and carbonyls increased in relative intensity while the intensities of aromatic/phenolic bands decreased (Figure 6A). The changes in the DOMmod-H2O-ferrihydrite system also indicated a relative increase in oxidized carbon but in this case, it was accompanied with a decrease in carbohydrate bands (Figure 6C). The IR spectra of DOMmod-EtOAc-goethite were practically unaffected by H2O2 addition. The low signal-to-noise of the DOMmod-H2O-goethite spectra and the strong baseline variations close to a major goethite band at 890 cm−1 prevented a closer analysis but there were no indications of systematic changes after H2O2 addition.
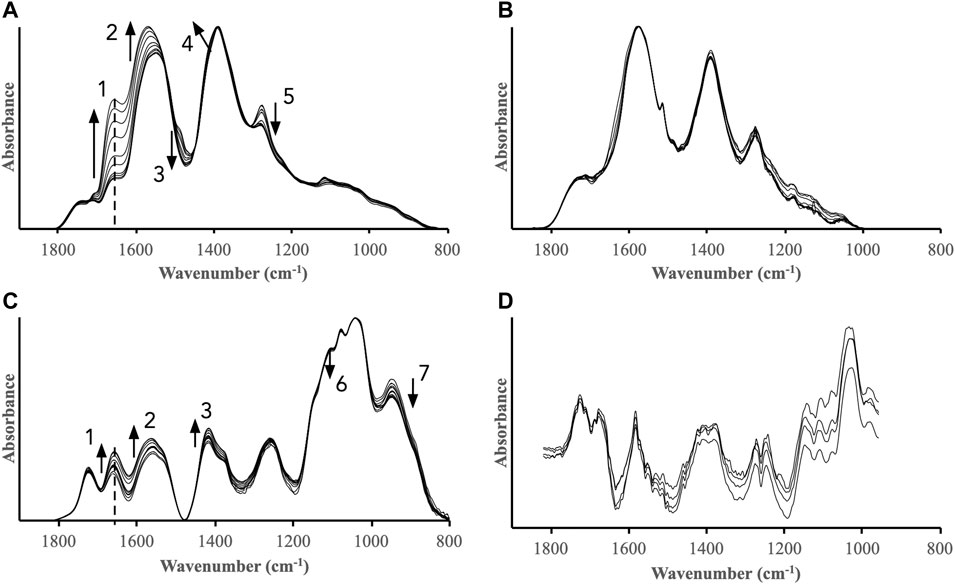
FIGURE 6. IR spectra of (A) DOMmod-EtOAc-ferrihydrite, (B) DOMmod-EtOAc-goethite, (C) DOMmod-H2O-ferrihydrite, and (D) DOMmod-H2O-goethite after addition of H2O2. Spectra collected after t = 1 min and t = 1,440 min are included in all sub-plots together with selected spectra in between these times. The H2O2 concentration was 100 μM and pH was maintained at pH 4.0 with a pH-stat. Note that these experiments were performed in absence of TPA. The dotted lines indicate the 1,660 cm−1 band, and the arrows indicate the direction of intensity change as a function of time. The bands marked with arrows likely have predominant contributions from: 1) carbonyl-like modes;2) asymmetric carboxyl stretch; 3) aromatic skeleton mode; 4) symmetric carboxyl stretch; 5) phenolic C-O-H bend; 6) and 7) carbohydrate skeleton modes (see Supplementary Table S2 for an overview of the band assignments).
The band at 1,660 cm−1 indicated H2O2-promoted oxidation of both DOMmod-EtOAc and DOMmod-H2O adsorbed on ferrihydrite. Notably, in the absence of H2O2 this band also increased during the adsorption of these DOM fractions on ferrihydrite but not on goethite (Figure 3; Supplementary Figures S7, S8). Using the intensity of the 1,660 cm−1 band as a measure of oxidation and plotting this as a function of time showed that the oxidation rates of adsorbed DOM were linearly correlated to the rate of TPA oxidation by H2O2 in presence of ferrihydrite but in absence of DOM fractions (Figure 7) indicating the same mechanism of oxidation in both cases. This implies that the initial fast generation of HO• that was detected with TPA was caused by the Fe2+ already released into solution during pre-equilibration between the DOM fractions and the iron oxides (Figure 3), and that the Fenton reaction occurring in bulk solution had no detectable effect on the adsorbed DOM.
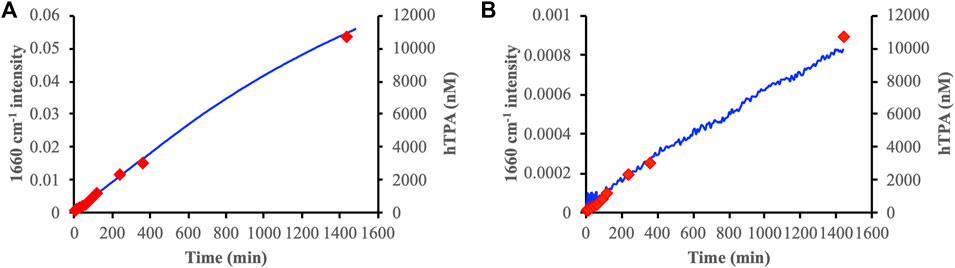
FIGURE 7. The 1,660 cm−1 band intensity as a function of time (blue lines) during the reaction between 100 μM H2O2 and pre-equilibrated (24 h) DOMmod-EtOAc-ferrihydrite (A) and DOMmod-H2O-ferrihydrite (B) suspensions. These experiments were performed at TOC 12 of μmol m−2 and pH 4.0. The hTPA generated by the reaction between H2O2 and ferrihydrite in absence of DOM are shown on the right-hand y-axis as red diamonds.
To further explore the mechanisms of H2O2-mediated oxidation of ferrihydrite-associated DOM we conducted additional IR experiments where DOMmod-EtOAc and H2O2 were added simultaneously and where DOMmod-EtOAc was added 60 min prior to H2O2 i.e., H2O2 was added at a point when the dissolution rate of Fe2+ was high and the surface coverage of DOM was also considerable (cf. Figures 2A, 4A). In comparison with the DOMmod-EtOAc experiment conducted in absence of H2O2 we observed a significant increase of the 1,660 cm−1 band irrespective of the timing of H2O2 addition (Figure 8A). However, the extent and rate of the increase was strongly affected by the time and sequence that DOMmod-EtOAc and H2O2 were added to the suspension (Figure 8B). The most pronounced increase in the 1,660 cm−1 intensity was registered when H2O2 was added 1 h after DOMmod-EtOAc, thus during conditions when reductive dissolution occurred in the presence of a high surface concentration of DOMmod-EtOAc. Simultaneous addition of DOMmod-EtOAc and H2O2 yielded an initial rapid increase that quickly leveled off whereas addition of H2O2 to a DOMmod-EtOAc-ferrihydrite suspension that was pre-equilibrated for 24 h resulted in a slow, almost linear increase, as already described in the previous paragraph.
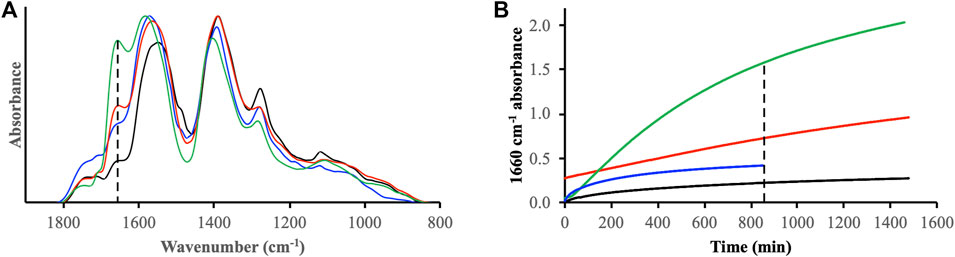
FIGURE 8. (A) IR spectra of ferrihydrite reacted with DOMmod-EtOAc in the absence (black line) and presence (blue, red and green lines) of H2O2. The H2O2 was added together with DOMmod-EtOAc (blue line), and to DOMmod-EtOAc-ferrihydrite suspension pre-equilibrated for 1 h (green line) or 24 h (red line). The IR spectra were collected after the same exposure time to H2O2 of 850 min. (B) The peak intensity at 1,660 cm−1 is plotted as a function of exposure time to H2O2; the color-coding of the lines is the same as in (A). To account for variations in the ferrihydrite film thickness on the ATR crystal the spectra were normalized to the same maximum intensity at t = 850 min. The H2O2 concentration was 100 μM and pH was maintained at pH 4.0 with a pH-stat. In (A) the vertical dotted line marks the 1,660 cm−1 band and in (B) the time point where the spectra in (A) were recorded.
In addition to using a specific IR band intensity as indicator for radical oxidation, the complete IR spectral changes over the region 1,800–800 cm−1 of DOMmod-EtOAc adsorbed to ferrihydrite during reaction with H2O2 were analyzed using the MCR-ALS formalism. These analyses showed that spectral variations in the data sets were explained by two components (Figure 9). Experiments where H2O2 was added 1 or 24 h after pre-equilibration between DOMmod-EtOAc and ferrihydrite were both characterized by one spectral component containing a strong band at 1,660 cm−1 (Figures 9A,C, blue lines). Moreover, the same components increased in importance relative to the second MCR component, and the shape of these increases matched those describing the 1,660 cm−1 intensity (cf. Figures 8B, 9B,D). Note that the MCR contributions in Figure 8 should not viewed as concentrations due to the constraints used in the modeling and the strong correlations between MCR spectral intensities and contribution profiles. Nevertheless, the ratios between the contributions highlight the strong increase of the component characterized by the 1,660 cm−1 band relative to a component containing carboxylic and aromatic groups as previously discussed. The pronounced H2O2-mediated oxidation induced after 1 h pre-equilibration yielded an MCR spectrum that showed a very close resemblance to oxalate adsorbed to ferrihydrite under similar conditions (Figure 9C). Thus, extensive radical oxidation of the adsorbed DOMmod-EtOAc generated substantial amounts of adsorbed oxalate, and the 1,660 cm−1 band was a strong indicator of this process. At the same time, the difference between the MCR spectra of the oxidized component (Figures 9A,C, blue spectra) suggested that oxidation produced not only oxalate but likely a range of oxidized adsorbed DOM fragments.
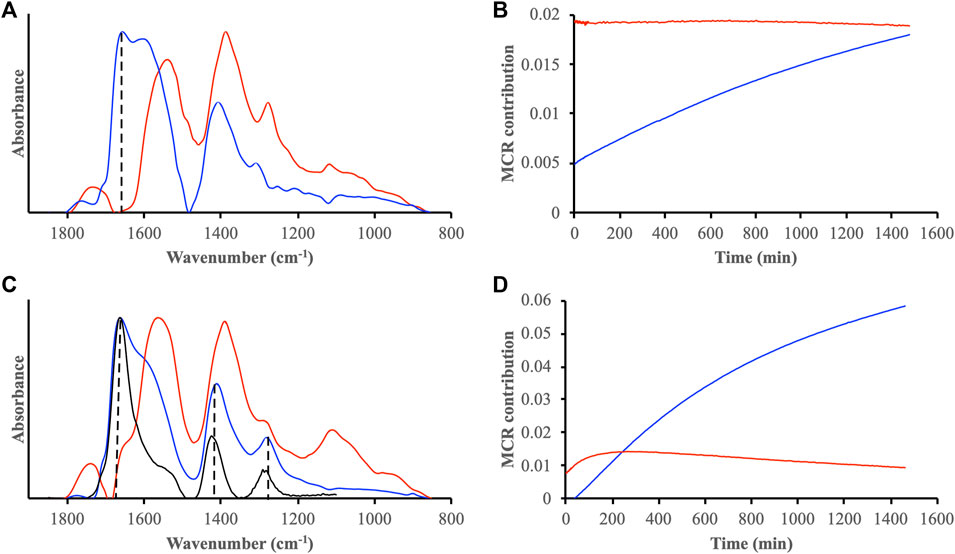
FIGURE 9. Results from MCR-ALS analysis of IR spectral data sets collected during reactions between H2O2 and DOMmod-EtOAc-ferrihydrite associations. The DOMmod-EtOAc-ferrihydrite associations were pre-equilibrated for 24 h (A,B) and 1 h (C,D) prior to addition of H2O2. The resolved MCR spectra are shown in A and C, and the corresponding MCR contributions in B and (D). Included in C is also the spectrum of oxalate adsorbed to ferrihydrite at pH 4.0 and 1.2 μmol m−2 (black line).
Discussion
It has been shown that P. involutus decomposes DOM during N acquisition into smaller and more polar molecules with the concomitant production of secondary metabolites (Wang et al., 2017). Moreover, this modified DOM, including the secondary metabolites, has an overall higher affinity towards iron oxide surfaces, supporting the hypothesis that decomposition contributes to formation of organic matter-mineral associations and thereby to organic matter stabilization (Lehmann and Kleber, 2015; Wang et al., 2017). The results presented in the current study complement and expand this view by showing that decomposition generates a modified DOM that has a higher capacity for reductive dissolution of iron oxides. After extraction, the DOMmod-EtOAc and DOMmod-H2O fractions were dissolved in water, freeze-dried and re-dissolved prior to the dissolution experiments without protection from air. Still, the Fe2+-reducing capacity of these fractions was substantially higher than corresponding fractions of the original DOM, indicating that the metabolites and decomposition products responsible for iron reduction are persistent. Thus, the enhancement of iron oxide reduction by decomposed DOM may contribute to Fe2+ mobilization not only in close vicinity to the hyphae but also at greater distances along the DOM flow paths. In general these results support the previous suggestion that podsolization in boreal forests is linked to reduction of iron minerals by secondary metabolites secreted by ECM fungi and the subsequent mobilization of reduced iron (Van Breemen et al., 2000).
As expected, the DOM fractions reduced ferrihydrite more than goethite due to the higher reduction potential of the former (Gorski et al., 2016). In all cases the extent of reduction was, however, quite low corresponding only to a maximum of a few percent of the proton active sites on the iron oxide surfaces. The concentrations of Fe2+ were also <1% of the added TOC concentrations, indicating that the reductants in the DOM fractions were only minor components. At the same time, we observed that dissolution rates were correlated to the total adsorption of DOM. Moreover, significant differences were observed in the IR spectra of the DOM fractions that were accumulated on the ferrihydrite and goethite surfaces during the dissolution process. While goethite spectra reached a steady state within approximately 12 h, irrespective of DOM fraction, the ferrihydrite spectra displayed a continued increase in overall intensities during the 24 h period of the experiments. This increase of the ferrihydrite spectra was accompanied with changes in the composition of adsorbed DOMmod-EtOAc and DOMmod-H2O, indicated by a steady increase of the 1,660 cm−1 band, i.e., the same band that was favored by H2O2-promoted oxidation. To reconcile the results from the reductive dissolution experiments not only should DOM adsorption and the subsequent reduction be considered but also Fe2+ re-adsorption and re-oxidation processes according to the following set of reactions:
DOM adsorption
DOM-promoted reductive dissolution
Fe2+ adsorption
Surface-catalyzed Fe2+ oxidation and ROS generation
Oxidation of adsorbed DOM by ROS
where ≡ Fe represents the Fe on the surface of the iron oxides. The interplay between these surface reactions is summarized in a conceptual (Figure 10). Oxidized (DOMox) and reduced (DOMred) DOM are adsorbed to ferrihydrite and goethite. The reductive dissolution (Eq. 3) is more extensive on ferrihydrite than on goethite and the concomitant adsorption of negatively charged DOM promotes the re-adsorption of Fe2+ (Eq. 4). This is in accordance with previous studies showing that co-adsorption of Fe2+ and anions enhances Fe2+ adsorption at acidic pH values (Hinkle et al., 2015). Moreover, as shown by Jones et al. (2014) the adsorption of Fe2+ to iron oxides in the pH range 4–4.5 drives heterogeneous oxidation to Fe3+ and that ferrihydrite catalyze this reaction more efficiently than goethite. Accordingly, we propose that Reactions 5, 6 are significant in our ferrihydrite experiments and it is the contribution from Fe2+ re-oxidation and the subsequent oxidative attack on adsorbed DOM by ROS that cause a main part of the difference between the ferrihydrite and goethite results. This implies that ferrihydrite reduction was more extensive than indicated by the Fe2+ concentrations measured in solution, which only represent a net effect taking Reactions 3–7 in account. This would explain why we detected significant signs of oxidation of the adsorbed DOM even though Fe2+ concentrations in solution were low compared to the TOC added. It is also in agreement with the observed correlation between net release of Fe2+ and the total adsorption of DOM because total DOM adsorption will control Fe2+ re-adsorption and re-oxidation.

FIGURE 10. Conceptual figure describing possible adsorption and redox reactions between DOM and an iron oxide. The numbers refer to the reactions in the text above.
In the presence of H2O2 there are two dominant paths for the generation of HO•: the homogeneous Fenton reaction and heterogeneous Fenton-like processes (Wang et al., 2013). At the pH of our study (pH 4.0) the solubility of ferrihydrite and goethite is low in absence of DOM fractions, and as shown in a recent study the reaction between H2O2 and iron oxides occurs at the mineral-water interface (Chen et al., 2021). Thus, HO• is generated by reduction of surface Fe3+ followed by re-oxidation according to:
These reactions together with the higher reduction potential of ferrihydrite explain why the reactions between H2O2 and ferrihydrite generated HO• while the reactions on goethite did not. This difference is further reinforced by the catalytic decomposition of H2O2 into H2O and O2 which is more efficient on crystalline iron oxides, such as goethite, than on ferrihydrite surfaces (Hermanek et al., 2007). Note that also non-lattice oxygens may play an important role in the catalytic reactions generating ROS as shown in a recent study by Yu et al. (2020). In the present work, however, we lack an in-situ probe to detect the possible involvement of such surface sites.
Ferrihydrite can thus trigger substantial heterogeneous Fenton processes that may act in concert with homogeneous Fenton, which depends on the generation of soluble Fe2+ via reductive dissolution by the DOM fractions. Goethite, however, mainly triggers the latter process. This difference between ferrihydrite and goethite in combination with the IR results of DOMmod-iron oxide suspensions that were pre-equilibrated for 24 h prior to H2O2 addition and indicated only oxidation of ferrihydrite-associated DOMmod show that under these reactions conditions only the heterogeneous Fenton processes oxidize the adsorbed DOM. The Fe2+ dissolved prior to H2O2 addition merely generated HO• in solution with no appreciable effect on the adsorbed DOM. Overall, these results emphasized the importance of the co-location of the processes generating HO• and the potential target compounds for oxidation, which is consistent with the very short lifetime and diffusion length of HO• (Hoffmann et al., 1995; Arslan-Alaton, 2003). When the proximity of the HO• and the substrates is sufficiently close the results from the DOMmod-EtOAc and DOMmod-H2O fractions showed that both adsorbed aromatics and carbohydrates are attacked and oxidized.
At conditions where the heterogeneous Fenton process act in concert with reductive dissolution induced by the DOM, and the timing is favorable, these simultaneous processes can create a cascade of radical reactions that very efficiently oxidize the adsorbed DOM. This was observed in our system when H2O2 was added 1 h after pre-equilibration of DOMmod-EtOAc and ferrihydrite. In this case, the extensive oxidative reactions converted a large part of the adsorbed DOM into adsorbed oxalate ions. The identification of oxalate as a predominant species agreed with recent results showing that oxalate-ferrihydrite complexes are quite resistant towards oxidation by HO• (Chen et al., 2021). Since we observed that other adsorbed organic structures, such as aromatic compounds and carbohydrates, are attacked by radicals adsorption alone is not sufficient to protect organic molecules from oxidation by radicals. Instead, it is likely the actual structures of the oxalate surface complexes that make them less susceptible with respect to these radical processes and mineralization. Oxalic acid is among the most common low molecular weight organic acid present in soils (Lapeyrie et al., 1987; Jones et al., 2003). Many soil microorganisms including ECM fungi have the capacity to secrete oxalic acids, and it is thought that oxalate plays a key role in the acquisition of nutrients from mineral particles (Landeweert et al., 2001; Keiluweit et al., 2015). The results from our experiments are in line with those of Studenroth et al. (2013) and suggest an additional and overlooked extracellular source of oxalic acid in soils that needs to be considered.
Based on our current and previous work (Op De Beeck et al., 2018; Wang et al., 2021), ECM fungi reduce a large proportion of the Fe3+ it encounters in its environment. The question is why these fungi that thrive in oxic environments need a strong capacity to reduce ferric ions. The results presented herein show that iron reduction in oxic conditions is an efficient process for the fungi to probe its surroundings via oxidative reactions, especially if combined with generation of H2O2. Infrared microspectroscopic analysis have shown that hyphal tips of P. involutus being active in oxidative decomposition are surrounded by an extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) matrix. Such EPS layers and the fact that generation of radicals occur at the mineral-water interface, provided that the timing of reactants is correct, may protect the fungi from ROS during the organic matter decomposition (Op De Beeck et al., 2018). It is also possible that iron reduction is a strategy to dissolve iron oxide and thereby liberate associated nutrients such as phosphate. A similar process may also destabilize tertiary structures of soil organic matter by reducing Fe3+-bridges, which can make the organic matter available to further decomposition for example by hydrolytic enzymes.
Conclusion
In this study, we investigated how the iron reduction during organic matter decomposition by the ECM fungus P. involutus is conserved in the modified DOM, and how this modified DOM impacted the reductive dissolution of iron oxides and, in turn, how these processes affected the reactions with H2O2 and the production of HO•. The results showed that decomposition increased the reductive capacity of the modified DOM, and that ferrihydrite was more susceptible to reductive dissolution than goethite, which is in accordance with the reduction potential of the minerals. An implication of our results is that ECM decomposition of DOM might play an important role in translocation of Fe (and potentially other redox-active metals) in soils also under oxic conditions. This may further impact the accessibility of nutrients in soils that are either strongly associated with iron oxide surfaces or protected in other soil structures influenced by Fe3+. The in-situ, real-time IR analysis of the iron oxide-water interface has identified three principal pathways yielding significant oxidation of surface-associated DOM: 1) Oxidation of DOM by Fe3+ reduction coupled with subsequent re-adsorption and re-oxidation of Fe2+ that generate ROS; 2) Heterogenous Fenton processes through reactions between H2O2 and the iron oxide surfaces; 3) Near-surface homogenous Fenton reaction between Fe2+ released via reductive dissolution and H2O2. These pathways are favored by a high reduction potential of the iron oxide and a high catalytic efficiency with respect to the heterogenous Fenton reaction while the catalytic decomposition of H2O2 into H2O and O2 should be low. This implies that all three processes are favored by amorphous iron oxides and disfavored by crystalline ones, as was shown by the extensive oxidation of DOM-ferrihydrite associations whereas DOM-goethite associations remained practically unaffected by these oxidative processes. Accordingly, our findings suggest that the iron oxide mineralogy may exert a considerable control over the stability of iron oxide-associated organic matter.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author Contributions
AT, LK, MB, and PP conceived the study. LK, MB, and VM performed experiments. LK and PP analyzed the data. LK, MB, and PP wrote the manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Funding
The work was supported by grants from the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation (2013.0073) and the Swedish Research Council (621-2012-03890, 2016-04561, 2020-04293).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/feart.2022.763695/full#supplementary-material
References
Arslan‐Alaton, I. (2003). A Review of the Effects of Dye‐assisting Chemicals on Advanced Oxidation of Reactive Dyes in Wastewater. Coloration Technol. 119, 345–353. doi:10.1111/j.1478-4408.2003.tb00196.x
Brunauer, S., Emmett, P. H., and Teller, E. (1938). Adsorption of Gases in Multimolecular Layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 60, 309–319. doi:10.1021/ja01269a023
Chen, Y., Miller, C. J., and Waite, T. D. (2021). Heterogeneous Fenton Chemistry Revisited: Mechanistic Insights from Ferrihydrite-Mediated Oxidation of Formate and Oxalate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 55, 14414–14425. doi:10.1021/acs.est.1c00284
Fries, N. (1978). Basidiospore Germination in Some Mycorrhiza-Forming Hymenomycetes. Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 70, 319–324. doi:10.1016/S0007-1536(78)80128-4
Goodell, B., Daniel, G., Jellison, J., and Qian, Y. (2006). Iron-reducing Capacity of Low-Molecular-Weight Compounds Produced in wood by Fungi. Holzforschung 60, 630–636. doi:10.1515/HF.2006.106
Gorski, C. A., Edwards, R., Sander, M., Hofstetter, T. B., and Stewart, S. M. (2016). Thermodynamic Characterization of Iron Oxide-Aqueous Fe2+ Redox Couples. Environ. Sci. Technol. 50, 8538–8547. doi:10.1021/acs.est.6b02661
Hermanek, M., Zboril, R., Medrik, I., Pechousek, J., and Gregor, C. (2007). Catalytic Efficiency of Iron(III) Oxides in Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide: Competition between the Surface Area and Crystallinity of Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 10929–10936. doi:10.1021/ja072918x
Hiemstra, T., and Van Riemsdijk, W. H. (2009). A Surface Structural Model for Ferrihydrite I: Sites Related to Primary Charge, Molar Mass, and Mass Density. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 73, 4423–4436. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2009.04.032
Hinkle, M. A. G., Wang, Z., Giammar, D. E., and Catalano, J. G. (2015). Interaction of Fe(II) with Phosphate and Sulfate on Iron Oxide Surfaces. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 158, 130–146. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2015.05.03210.1016/j.gca.2015.02.030
Hobara, S., Kushida, K., Kim, Y., Koba, K., Lee, B.-Y., and Ae, N. (2016). Relationships Among pH, Minerals, and Carbon in Soils from Tundra to Boreal Forest across Alaska. Ecosystems 19 (6), 1092–1103. doi:10.1007/s10021-016-9989-7
Hobbie, E. A., and Högberg, P. (2012). Nitrogen Isotopes Link Mycorrhizal Fungi and Plants to Nitrogen Dynamics. New Phytol. 196, 367–382. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2012.04300.x
Hoffmann, M. R., Martin, S. T., Choi, W., and Bahnemann, D. W. (1995). Environmental Applications of Semiconductor Photocatalysis. Chem. Rev. 95, 69–96. doi:10.1021/cr00033a004
Jing, Y., and Chaplin, B. P. (2017). Mechanistic Study of the Validity of Using Hydroxyl Radical Probes to Characterize Electrochemical Advanced Oxidation Processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 51, 2355–2365. doi:10.1021/acs.est.6b05513
Jones, A. M., Griffin, P. J., Collins, R. N., and Waite, T. D. (2014). Ferrous Iron Oxidation under Acidic Conditions - the Effect of Ferric Oxide Surfaces. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 145, 1–12. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2014.09.020
Jones, D. L., Dennis, P. G., Owen, A. G., and van Hees, P. A. W. (2003). Organic Acid Behavior in Soils - Misconceptions and Knowledge Gaps. Plant and Soil 248, 31–41. doi:10.1023/A:1022304332313
Kaiser, K., and Kalbitz, K. (2012). Cycling Downwards - Dissolved Organic Matter in Soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 52, 29–32. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2012.04.002
Keiluweit, M., Bougoure, J. J., Nico, P. S., Pett-Ridge, J., Weber, P. K., and Kleber, M. (2015). Mineral protection of Soil Carbon Counteracted by Root Exudates. Nat. Clim. Change 5, 588–595. doi:10.1038/NCLIMATE2580
Krumina, L., Kenney, J. P. L., Loring, J. S., and Persson, P. (2016). Desorption Mechanisms of Phosphate from Ferrihydrite and Goethite Surfaces. Chem. Geology. 427, 54–64. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2016.02.016
Krumina, L., Lyngsie, G., Tunlid, A., and Persson, P. (2017). Oxidation of a Dimethoxyhydroquinone by Ferrihydrite and Goethite Nanoparticles: Iron Reduction versus Surface Catalysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 51, 9053–9061. doi:10.1021/acs.est.7b02292
Landeweert, R., Hoffland, E., Finlay, R. D., Kuyper, T. W., and van Breemen, N. (2001). Linking Plants to Rocks: Ectomycorrhizal Fungi Mobilize Nutrients from Minerals. Trends Ecol. Evol. 16, 248–254. doi:10.1016/S0169-5347(01)02122-X
Lapeyrie, F., Chilvers, G. A., and Bhem, C. A. (1987). Oxalic Acid Synthesis by the Mycorrhizal Fungus Paxillus Involutus (Batsch. Ex Fr.) Fr. New Phytol. 106, 139–146. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.1987.tb04797.x
Lehmann, J., and Kleber, M. (2015). The Contentious Nature of Soil Organic Matter. Nature 528, 60–68. doi:10.1038/nature16069
Lindahl, B. D., Ihrmark, K., Boberg, J., Trumbore, S. E., Högberg, P., Stenlid, J., et al. (2007). Spatial Separation of Litter Decomposition and Mycorrhizal Nitrogen Uptake in a Boreal forest. New Phytol. 173, 611–620. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2006.01936.x
Lindsay, W. L. (1991). Iron Oxide Solubilization by Organic Matter and its Effect on Iron Availability. Plant Soil 130, 27–34. doi:10.1007/BF00011852
Loring, J. S., Sandström, M. H., Norén, K., and Persson, P. (2009). Rethinking Arsenate Coordination at the Surface of Goethite. Chem. Eur. J. 15, 5063–5072. doi:10.1002/chem.200900284
Lyngsie, G., Krumina, L., Tunlid, A., and Persson, P. (2018). Generation of Hydroxyl Radicals from Reactions between a Dimethoxyhydroquinone and Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 8, 108341–108349. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-29075-5
Nicolás, C., Martin-Bertelsen, T., Floudas, D., Bentzer, J., Smits, M., Johansson, T., et al. (2018). The Soil Organic Matter Decomposition Mechanisms in Ectomycorrhizal Fungi Are Tuned for Liberating Soil Organic Nitrogen. ISME J. 13, 977–988. doi:10.1038/s41396-018-0331-6
Op De Beeck, M., Troein, C., Peterson, C., Persson, P., and Tunlid, A. (2018). Fenton Reaction Facilitates Organic Nitrogen Acquisition by an Ectomycorrhizal Fungus. New Phytol. 218, 335–343. doi:10.1111/nph.14971
Rineau, F., Roth, D., Shah, F., Smits, M., Johansson, T., Canbäck, B., et al. (2012). The Ectomycorrhizal Fungus Paxillus Involutus Converts Organic Matter in Plant Litter Using a Trimmed Brown‐rot Mechanism Involving Fenton Chemistry. Environ. Microbiol. 14, 1477–1487. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2012.02736.x
Rineau, F., Shah, F., Smits, M. M., Persson, P., Johansson, T., Carleer, R., et al. (2013). Carbon Availability Triggers the Decomposition of Plant Litter and Assimilation of Nitrogen by an Ectomycorrhizal Fungus. ISME J. 7, 2010–2022. doi:10.1038/ismej.2013.91
Shah, F., Gressler, M., Nehzati, S., Op De Beeck, M., Gentile, L., Hoffmeister, D., et al. (2021). Secretion of Iron(III)-Reducing Metabolites during Protein Acquisition by the Ectomycorrhizal Fungus Paxillus Involutus. Microorganisms 935, 35–16. doi:10.3390/microorganisms9010035
Shah, F., Schwenk, D., Nicolás, C., Persson, P., Hoffmeister, D., and Tunlid, A. (2015). Involutin Is an Fe 3+ Reductant Secreted by the Ectomycorrhizal Fungus Paxillus Involutus during Fenton-Based Decomposition of Organic Matter. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 81, 8427–8433. doi:10.1128/AEM.02312-15
Studenroth, S., Huber, S. G., Kotte, K., and Schöler, H. F. (2013). Natural Abiotic Formation of Oxalic Acid in Soils: Results from Aromatic Model Compounds and Soil Samples. Environ. Sci. Technol. 47, 130111153849003–1329. doi:10.1021/es304208a
Tauler, R., and De Juan, A. (2006). “Multivariate Curve Resolution,” in Practical Guide to Chemometrics. Editor P. J. Gemeperline (Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press), 418–467. doi:10.1201/9781420018301.ch11
Tunlid, A., Floudas, D., Koide, R., and Rineau, F. (2016). “Soil Organic Matter Decomposition Mechanisms in Ectomycorrhizal Fungi,” in Soil Organic Matter Decomposition Mechanisms in Ectomycorrhizal fungi in Molecular Mycorrhizal Symbiosis. Editor F. Martin (Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons), 257–275. doi:10.1002/9781118951446.ch15
Van Breemen, N., Lundström, U. S., and Jongmans, A. G. (2000). Do plants Drive Podzolization via Rock-Eating Mycorrhizal Fungi? Geoderma 94, 163–171. doi:10.1016/S0016-7061(99)00050-6
Wallander, H., and Söderström, B. (1999). “Paxillus,” in Ectomycorrhizal Fungi Key Genera in Profile. Editors J. W. G. Cairney,, and S. M. Chambers (Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer), 231–252. doi:10.1007/978-3-662-06827-4_9
Wang, B., Yin, J.-J., Kurash, I., Chai, Z., Zhao, Y., Zhou, X., et al. (2013). Physicochemical Origin for Free Radical Generation of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in Biomicroenvironment: Catalytic Activities Mediated by Surface Chemical States. J. Phys. Chem. C 117, 383–392. doi:10.1021/jp3101392
Wang, T., Persson, P., and Tunlid, A. (2021). A Widespread Mechanism in Ectomycorrhizal Fungi to Access Nitrogen from mineral‐associated Proteins. Environ. Microbiol. 23, 5837–5849. doi:10.1111/1462-2920.15539
Wang, T., Tian, Z., Bengtson, P., Tunlid, A., and Persson, P. (2017). Mineral Surface-Reactive Metabolites Secreted during Fungal Decomposition Contribute to the Formation of Soil Organic Matter. Environ. Microbiol. 19, 5117–5129. doi:10.1111/1462-2920.13990
Wang, T., Tian, Z., Tunlid, A., and Persson, P. (2020). Nitrogen Acquisition from mineral‐associated Proteins by an Ectomycorrhizal Fungus. New Phytol. 228, 697–711. doi:10.1111/nph.16596
Yu, G.-H., Chi, Z.-L., Kappler, A., Sun, F.-S., Liu, C.-Q., Teng, H. H., et al. (2020). Fungal Nanophase Particles Catalyze Iron Transformation for Oxidative Stress Removal and Iron Acquisition. Curr. Biol. 30, 2943–2950. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2020.05.058
Keywords: ferrihydrite, goethite, hydroxyl radicals, reductive dissolution, Fenton reactions, Paxillus involutus, dissolved organic matter (DOM), infrared spectroscopy
Citation: Krumina L, Op De Beeck M, Meklesh V, Tunlid A and Persson P (2022) Ectomycorrhizal Fungal Transformation of Dissolved Organic Matter: Consequences for Reductive Iron Oxide Dissolution and Fenton-Based Oxidation of Mineral-Associated Organic Matter. Front. Earth Sci. 10:763695. doi: 10.3389/feart.2022.763695
Received: 24 August 2021; Accepted: 05 April 2022;
Published: 26 April 2022.
Edited by:
Andrew C. Mitchell, Aberystwyth University, United KingdomReviewed by:
Guanghui Yu, Tianjin University, ChinaHarald Foerstendorf, Helmholtz Association of German Research Centres (HZ), Germany
Copyright © 2022 Krumina, Op De Beeck, Meklesh, Tunlid and Persson. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Per Persson, cGVyLnBlcnNzb25AY2VjLmx1LnNl
 Lelde Krumina1,2
Lelde Krumina1,2 Michiel Op De Beeck
Michiel Op De Beeck Viktoriia Meklesh
Viktoriia Meklesh Anders Tunlid
Anders Tunlid Per Persson
Per Persson