- 1Department of Cardiovascular Disease and Clinical Experimental Center, Jiangmen Central Hospital, Jiangmen, China
- 2Aerospace Center Hospital, Beijing, China
- 3Peking University People's Hospital, Beijing, China
- 4Peking University First Hospital, Beijing, China
- 5Department of Intensive Care Unit and Clinical Experimental Center, Jiangmen Central Hospital, Jiangmen, China
- 6Department of Respiratory Medicine, People's Hospital of Longhua, The Affiliated Hospital of Southern Medical University, Shenzhen, China
Background: Asthma and cardiovascular disease (CVD) share many risk factors. Previous meta-analyses indicated that asthma is associated with an increased risk of CVD and all-cause mortality, but these studies were limited by unstandardized search strategies and the number of articles included.
Objective: We sought to systematically synthesize evidence investigating the impact of asthma on all-cause mortality and CVD morbidity and mortality.
Methods: We searched in PubMed and EMBASE for observational cohort studies (inception dates to November 10, 2021) that had both asthma groups and control groups. We also manually searched the reference lists of correlative articles to include other eligible studies. Data for associations between asthma and all-cause mortality and CVD morbidity and mortality were needed.
Results: We summarized the findings from 30 cohort studies comprising 4,157,823 participants. Asthma patients had increased CVD morbidity [relative risk (RR) = 1.28, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.16–1.40] and increased CVD mortality (RR = 1.25, 95% CI = 1.14–1.38). Asthma patients also had increased risk of all-cause mortality (RR = 1.38, 95% CI = 1.07–1.77). In subgroup analyses, female asthma patients had a higher risk of CVD morbidity and all-cause mortality than male asthma patients, and late-onset asthma patients had a higher risk of CVD morbidity than early-onset asthma patients.
Conclusion: Asthma patients have increased risk of all-cause mortality and CVD morbidity and mortality. This information reminds clinicians to be aware of the risk of CVD and all-cause mortality in asthma patients.
Systematic Review Registration: http://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/, PROSPERO, identifier: CRD 42021290082.
Introduction
Asthma is the most common inflammatory chronic non-infectious pulmonary disease in adults and children, and is estimated to affect 334 million people worldwide (1). Asthma is more common in developed countries and imposes a serious health and economic burden worldwide (2, 3). Chronic airway inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness are the main pathophysiological features of asthma, which manifests as progressive airway remodeling (4, 5). The pathogenesis of asthma involves immune-inflammatory mediators and neuromodulator mechanisms (6). Asthma and cardiovascular disease (CVD) share many risk factors, such as inflammation (7). Patients with asthma suffer from a chronic inflammatory state, and asthma patients have been shown to have persistently elevated levels of inflammatory factors, such as fibrinogen and tumor necrosis factor-1 (8). In addition, poor lung function and eosinophilia, which are characteristic of asthma, have been shown to be predictors of cardiovascular mortality (9–11).
As asthma is very common and the consequences of CVD are critical, understanding their relationship will provide useful information to clinicians treating patients with asthma. Moreover, the long-term prognosis of asthma patients is one of the crucial questions that need to be addressed in this field. Understanding the impact of asthma on long-term mortality and cardiovascular risk and mortality is important for the development of clinical practice guidelines.
Previous meta-analyses have indicated that asthma is associated with an increased risk of CVD and all-cause mortality, but these studies were limited by unstandardized search strategies and a failure to include recent, updated articles (12–14). To overcome these limitations and provide reliable conclusions, we conducted a systematic evaluation and meta-analysis to investigate the impact of asthma on all-cause mortality and CVD morbidity and mortality.
Materials and Methods
We conducted this meta-analysis following Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) guidelines (15) and Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) (Supplementary Table 3). The meta-analysis was registered with the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO identifier: CRD 42021290082).
Literature Search
We searched PubMed and Embase for cohort studies from inception to November 10, 2021, without language restrictions. See the Supplementary File for search details (Supplementary Table 1). We also included other eligible studies by manually searching the reference lists of former similar meta-analyses and relevant studies.
Eligibility Criteria
We included only observational cohort studies without publication time restriction. Both retrospective and prospective cohort studies were included if they had both asthma groups and control groups. Theoretically, in included studies, the difference between asthma groups and control groups should only be whether they had asthma or not. We excluded studies which only included specific asthma patients such as having ICS treatment or overlapping chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. To assess comparability between the asthma groups and the control groups, we included studies that provided baseline characteristics of the population. Outcome measures on the association between asthma and all-cause mortality or CVD morbidity and mortality were necessary. The total number of subjects in the studies must be >1,000 to reduce bias.
Data Extraction
A data collection table was made in advance. The correlative data were extracted by two investigators (Z-FL and Z-YA) independently. When there was disagreement, a third person (BZ) would assist in the discussion and make the final decisions. Any collected data were aggregate, and no individual-level data were included.
Quality Assessment
The risk of bias and quality of studies were evaluated by the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for cohort studies. The NOS ranges from 0 to 9 points. When the NOS is <6 points, the study would be regarded low quality; 6 or 7 points, the study would be regarded medium quality; and more than 7 points, the study would be regarded high quality. Two authors (LZ and J-YW) finished the quality evaluation. When there was disagreement, a third person (BZ) would assist in the discussion and make the final decisions.
Outcomes of Interest
Data for associations between asthma and all-cause mortality and CVD morbidity and mortality were needed, such as relative risk (RR), hazard ratios (HRs), or number of CVD events (morbidity, mortality) or all-cause deaths in the asthma and control groups.
Statistical Analysis
At first, we measured both adjusted and unadjusted RRs/HRs. Then, we pooled the adjusted RRs that were initially provided in the studies or estimated by the HRs. I2 statistic were used to evaluate the heterogeneity of included studies. when I2 >50%, significant heterogeneity was considered existing (16) and the random-effects model was used. Funnel plots were used to evaluate publication bias. RevMan 5.4.1 (Nordic Cochrane Center, Cochrane Collaboration) were used to conduct all calculations and draw forest plots to show the results. Stata version 14.0 (Stata Corp., College Station, TX, USA) were used for sensitivity analysis.
Results
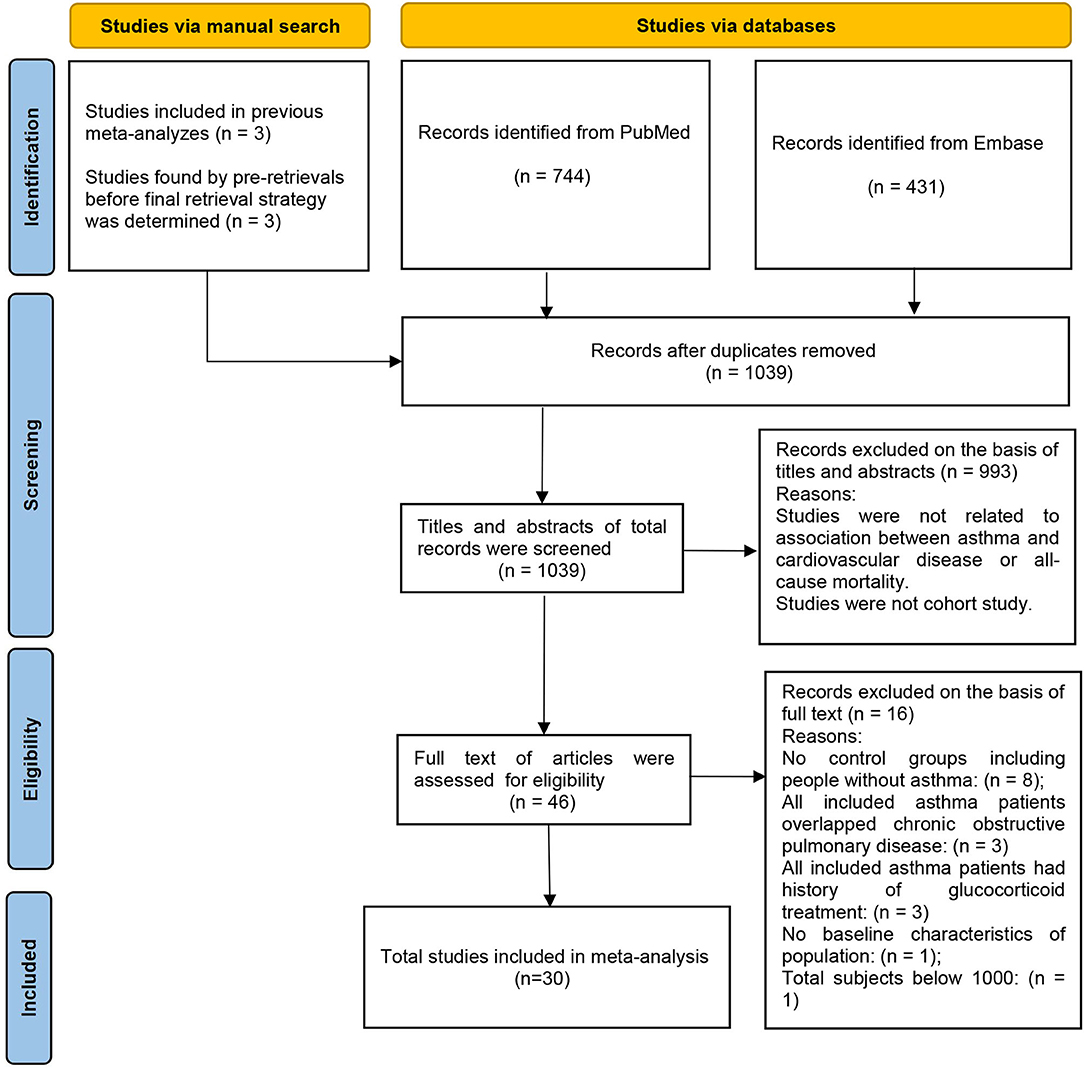
Thousand thirty nine studies were yielded by the electronic search of Pubmed and Embase databases and manual search. After applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria, 30 studies (17–46) were included in the meta-analysis, including 5 studies (42–46) assessed from the manual search and 25 studies (17–41) from the electronic database search (Figure 1).
Description of Studies
All 30 studies were observational cohort studies, including 25 prospective cohort studies and 5 retrospective cohort studies. We collected the baseline characteristics of each study (Table 1). These studies comprised 4,157,823 participants. Thirteen studies were done in Europe, 12 in North America, 3 in Oceania, and 2 in Asia. In our quality assessment used the NOS (Supplementary Table 2), 17 studies were regarded as high quality, 13 as medium quality, and none as low quality. Nine studies included male and female subgroups. Three studies included early and late-onset asthma subgroups.
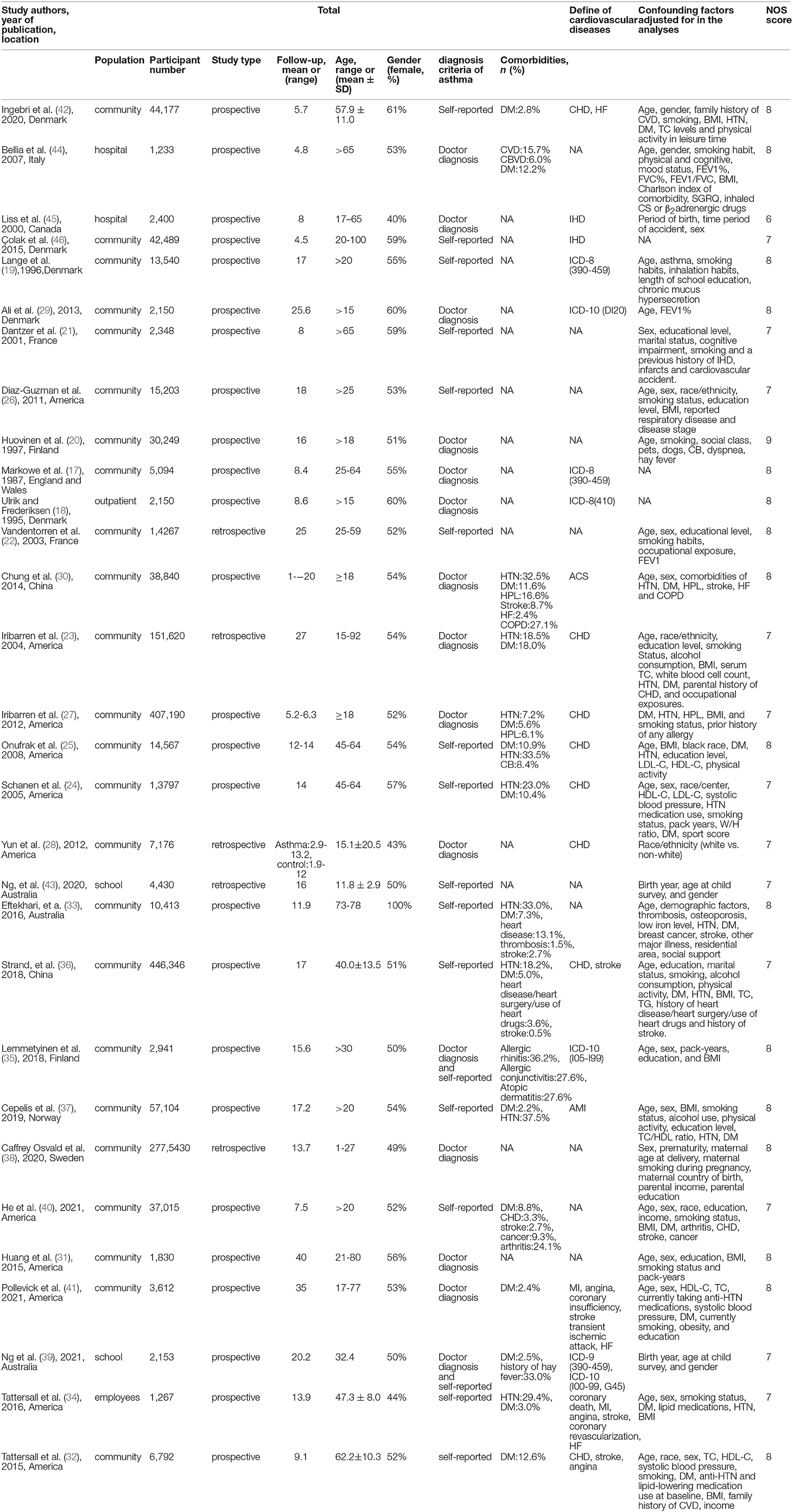
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of participants assessed in the studies included in the meta-analysis.
Association Between Asthma and All-Cause Mortality
Using the random-effects model, we analyzed 18 studies that included 20 subgroups (Figure 2). Asthma patients had a 38% increased risk of death compared to people without asthma (RR = 1.38, 95% CI = 1.07–1.77, p = 0.01, I2 = 98%, p < 0.00001). Though considerable heterogeneity existed, most studies or subgroups (16 in 20) indicated an increased risk of mortality in asthma patients. We also found high heterogeneity, mainly because a large-scale study (27) conducted by Iribarren et al. in 2012 reported an outlier HR (3.28, 95% CI = 3.15–3.41).
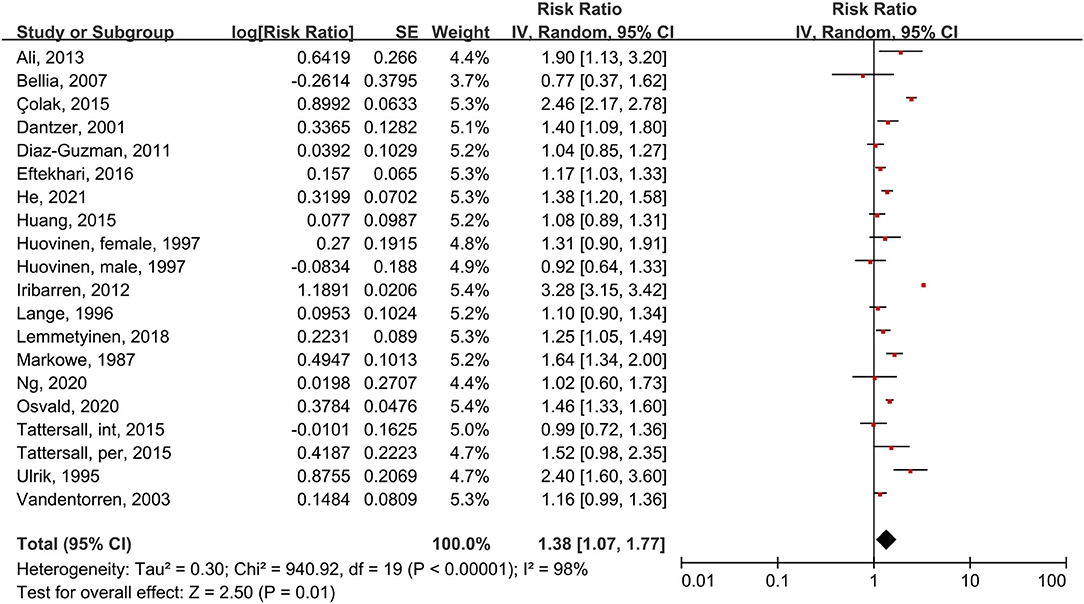
Figure 2. Forest plot shows association between asthma and all-cause mortality. SE, standard error; IV, Inverse Variance method; df, degrees of freedom; int, intermittent; per, persistent.
Five studies were included in the subgroup analysis of male and female patients using the random-effects model (Figure 3). In male asthma patients, risk of all-cause mortality increased 52% compared to people without asthma, though this difference was not significant (RR = 1.52, 95% CI = 0.88–2.62, p = 0.13; I2 = 98%, p < 0.00001). In female patients, risk of all-cause mortality increased 90% compared to people without asthma (RR = 1.90, 95% CI = 1.20–3.00, p = 0.006; I2 = 96%, p < 0.00001).
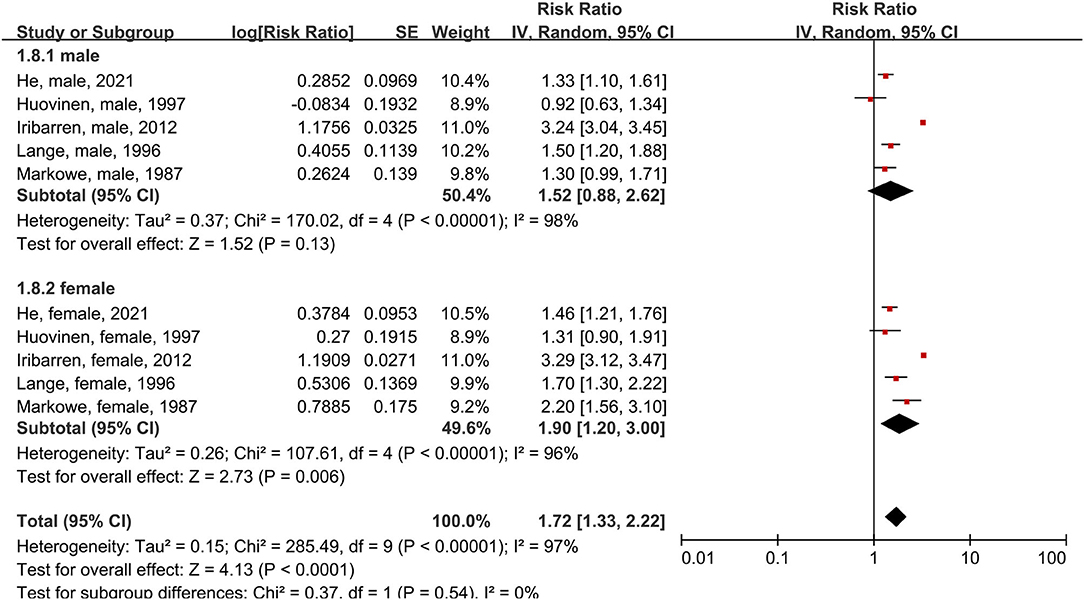
Figure 3. Forest plot shows association between asthma and all-cause mortality in male and female patients. SE, standard error; IV, Inverse Variance method; df, degrees of freedom.
Association Between Asthma and CVD Morbidity
We analyzed 14 studies with a total of 24 subgroups (Figure 4). The random-effects model showed that asthma patients had a 32% increased risk of CVD compared to people without asthma (RR = 1.28, 95% CI = 1.16–1.40, p < 0.00001; I2 = 85%, p < 0.00001). Thus, asthmatic status increases the risk of CVD morbidity.
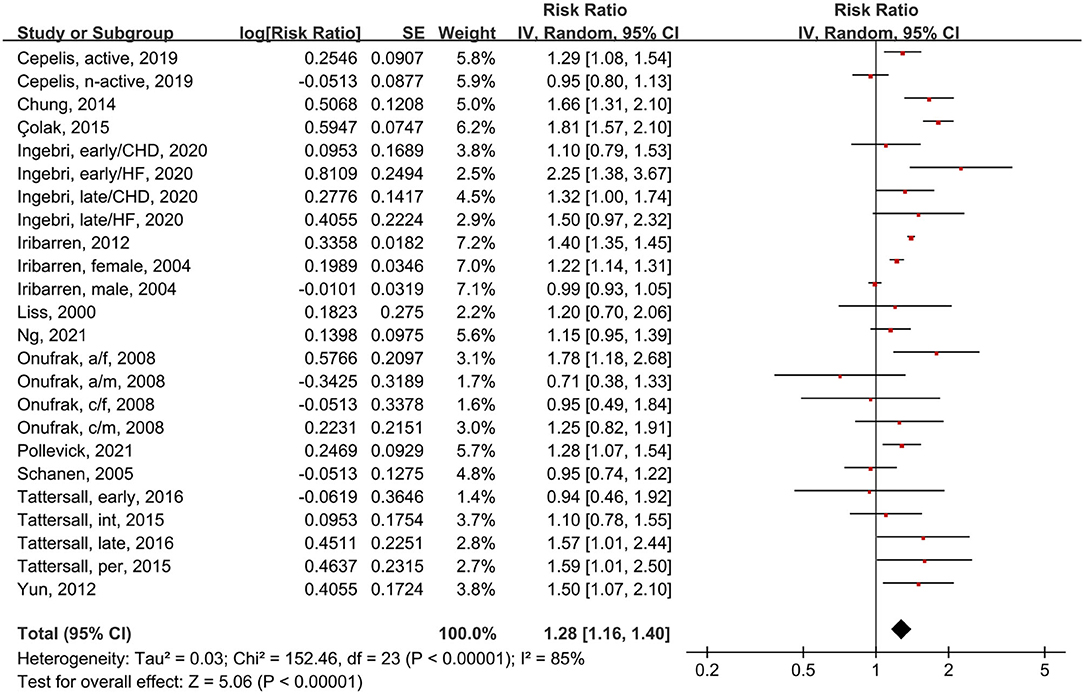
Figure 4. Forest plot shows association between asthma and CVD morbidity. SE, standard error; IV, Inverse Variance method; df, degrees of freedom; HF, heart failure; CHD, coronary heart disease; a/f, adult female; a/m, adult male; c/f, child female; c/m, child male; int, intermittent; per, persistent.
In the subgroup analysis of early and late-onset asthma using the fixed-effects model, three studies had a total of five subgroups (Figure 5). One study (34) defined early-onset as asthma onset prior to 18 years and late-onset as asthma onset at 18 years or older. The other two studies (25, 42) applied the cutoffs of 40 years and 21 years. Early-onset asthma patients has a 26% increased risk of CVD compared to people without asthma (RR = 1.26, 95% CI = 1.02–1.55, p = 0.03; I2 = 46%, p = 0.12). Late-onset asthma patients had a 39% increased risk of CVD compared to people without asthma (RR = 1.39, 95% CI = 1.17–1.66, p = 0.0002; I2 = 37%, p = 0.17). This subgroup analysis reduced the heterogeneity of studies.

Figure 5. Forest plot shows association between asthma and CVD morbidity in early and late-onset asthma patients. SE, standard error; IV, Inverse Variance method; df, degrees of freedom; HF, heart failure; CHD, coronary heart disease; a/f, adult female; a/m, adult male; c/f, child female; c/m, child male.
In the subgroup analysis of male and female patients using the random-effects model, five studies had a total of six subgroups (Figure 6). Male asthma patients had an 18% higher risk of CVD morbidity compared to people without asthma (RR = 1.19, 95% CI = 1.00–1.41, p = 0.05; I2 = 88%, p < 0.00001). Female asthma patients had a 37% higher risk of CVD compared to people without asthma (RR = 1.39, 95% CI = 1.20–1.61, p < 0.00001; I2 = 83%, p < 0.0001).
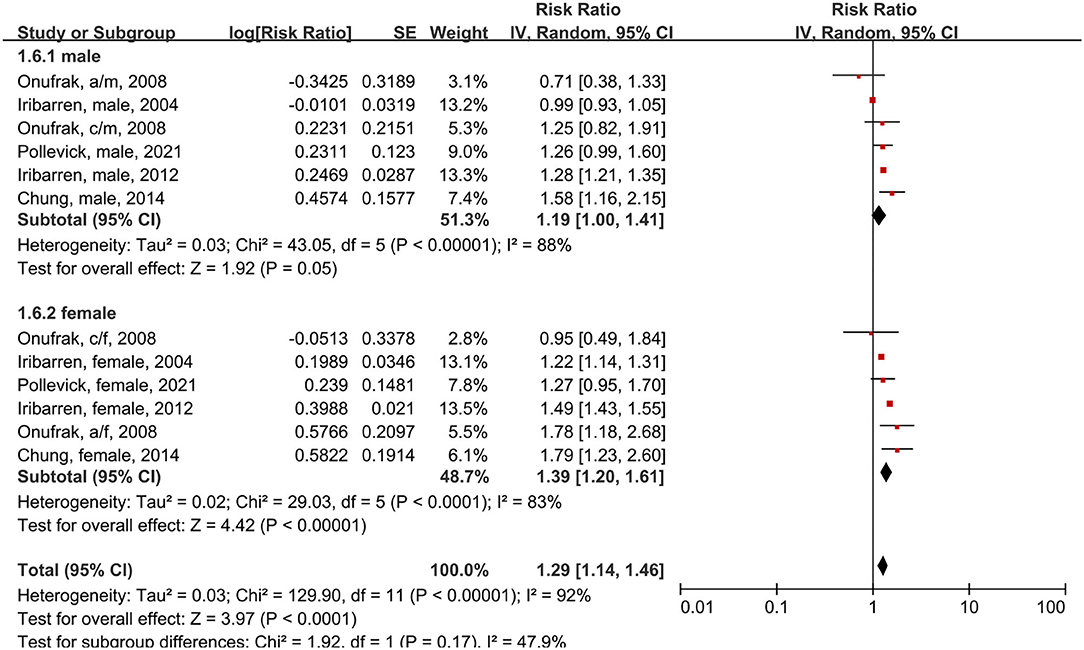
Figure 6. Forest plot shows association between asthma and CVD morbidity in male and female asthma patients. SE, standard error; IV, Inverse Variance method; df, degrees of freedom; a/f, adult female; a/m, adult male; c/f, child female; c/m, child male.
Association Between Asthma and CVD Mortality
Nine studies provided the outcomes of CVD mortality in asthma patients. These studies were summarized for the first time (Figure 7). Data calculated by the fixed-effects model showed that asthma patients have a 25% increased risk of CVD mortality compared to people without asthma (RR = 1.25, 95% CI = 1.14–1.38, p < 0.00001). There was no considerable heterogeneity between these studies (I2 = 13%, p = 0.32). Eight of nine studies yielded an increased risk of CVD mortality in asthma patients. Six of nine studies were regarded as high quality.
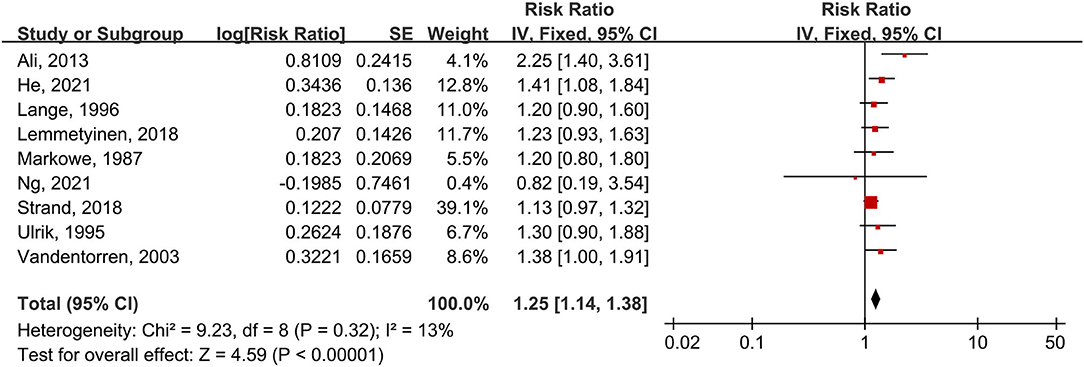
Figure 7. Forest plot shows association between asthma and CVD mortality. SE, standard error; IV, Inverse Variance method; df: degrees of freedom.
Sensitivity Analysis
We conducted sensitivity analysis to examine the robustness of the meta-analyses by omitting each study in turn and recalculating the pooled effect estimates (Supplementary Figures 4–12). In male asthma patients, one study (27) altered the significantly increased risk of all-cause mortality to no significant difference. However, this study did not change the estimate significantly. Two subgroups of two studies (25, 42) decreased the estimate of CVD morbidity in early-onset asthma patients significantly (Supplementary Figure 9). However, this may due to that two studies did not provide the overall estimate, and we input the grouping estimate (male, female and CHD, HF) provided by the studies. Overall mortality analysis has a I square of 98% (highly heterogenous), and we conducted sensitivity analysis by omitting two outliers [Colak et al. (46) and Iribarren et al. (27)] and result still robust (Supplementary Figure 13).
Publication Bias
Publication bias was evaluated using funnel plots, and no clear asymmetry was found by visual inspection (Supplementary Figures 1–3). We noted that one study (27) had relatively high loss to follow-up (24% of asthma subjects, 10% of control subjects) and had a significant outlier outcome (Supplementary Figure 3). Overall, no significant publication bias was found among the included observational cohort studies.
Discussion
In this systematic review, we found that asthma patients have a significantly increased risk of CVD morbidity and mortality and all-cause mortality. Male asthma patients had no significant increased risk of all-cause mortality, and lower risk of CVD morbidity and all-cause mortality than female asthma patients. In addition, early-onset asthma patients had a lower risk of CVD morbidity than late-onset asthma patients.
Association Between Asthma and All-Cause Mortality
Finding that asthma patients have an increased risk of all-cause mortality confirms the results of a previous meta-analysis (14). However, a large-scale study (27) reporting a considerably high risk of all-cause mortality is the main reason for heterogeneity between studies and the most conspicuous outlier in the funnel diagram. We considered two main reasons for this outlier outcome. First, high loss to follow-up can bias the results. Second, the inclusion criteria for asthma patients were one hospitalization, two outpatient visits, or two emergency department visits for asthma within 12 months, whereas most of the other studies based the inclusion criteria on questionnaires about self-reported asthma history. Thus, all of the asthma patients in that study had active and more severe asthma and, therefore, higher CVD morbidity and mortality risk than non-active asthma patients (37, 40).
Though asthma patients have an increased risk of all-cause mortality, only a small number of asthma patients die directly from asthma itself (35). Thus, an increased risk of death in asthma patients is mainly due to comorbidities. Asthma patients always have chronic inflammation and airway limitations, which can elevate the risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and type 2 diabetes (47). In addition, asthma medication can cause comorbidities. Inhaled corticosteroids may be related to osteoporosis, increased fracture risk, and pneumonia (48). Inhaled β2-agonist can increase the risk of CVD (49). Furthermore, suboptimal asthma control can limit physical activity and cause poor sleep quality, which could contribute to obesity, depression, and osteoporosis. All of these comorbidities can increase mortality in patients with asthma (48).
Subgroup analyses showed that male asthma patients have no significantly increased risk of all-cause mortality. We found the negative outcome in male asthma patients mainly because the large-scale study (27) provided a high outlier HR value with small CI. It broadened the CI for the all-cause mortality estimate in male asthma patients so that there was no significant increase. As mentioned above, patients in this large-scale study (27) had active and more severe asthma, which resulted in the high outlier RR value. The other four studies in this subgroup analysis relied on exposure history of asthma, which also includes non-active or mild asthma patients. However, sensitivity analysis showed that this study did not significantly increase the estimate. Therefore, we still concluded that male asthma patients have a 52% increase in all-cause mortality, though this difference was not significant.
Association Between Asthma and CVD Morbidity and Mortality
We found that asthma patients have a increased risk of CVD morbidity and mortality than people without asthma. Finding an increased risk of CVD morbidity in asthma patients is consistent with a previous meta-analysis (13, 14, 50). The biological mechanism by which asthma causes and aggravates CVD is still unclear. However, some mechanisms have been suggested. First, asthma and CVD share some risk factors, such as smoking and chronic inflammation (7, 51). Asthma can cause inflammation not only in the airway, but also in the whole body (systemic). Prior studies found that colchicine can reduce the incidence rate of CVD to 69%, strongly suggesting that inflammation takes part in the start and progression of CVD (52). Second, asthma patients have an increased risk of chronic airflow obstruction, which can cause lung function decline (53). Impaired lung function is associated with increased levels of inflammatory biomarkers in the circulation (54) and inflammation. Third, asthma medication can cause CVD. Inhaled β2-agonists are associated with an increased risk of adverse cardiovascular outcomes (49).
Subgroup analyses indicate that both male and female asthma patients have a significantly increased risk of CVD morbidity. This outcome is in contrast to a previous meta-analysis (13, 14) that found no significantly increased risk of CVD morbidity in male asthma patients. Our finding confirmed that asthma patients have a significantly increased risk of CVD morbidity, regardless of gender. However, we noted that female asthma patients suffer from a higher increased risk of CVD morbidity than male asthma patients (39 vs. 19%). This gender difference may be associated with sex hormone. Some studies found that estrogen can cause low levels of systemic inflammation by modulating the release of proinflammatory cytokines and regulating the production of leukotrienes. In contrast, androgen may have anti-inflammation effects and protect against airway inflammation (25). As mentioned above, chronic inflammation is one of the risk factors for CVD. Therefore, for women, asthmatic state and estrogen effects can cause increased CVD risk through chronic inflammation.
Subgroup analyses showed that both early and late-onset asthma patients have a significantly increased risk of CVD morbidity. However, late-onset asthma patients have a higher increased risk than early-onset asthma patients (39 vs. 26%). Early and late-onset asthma patients may have different epidemiological characteristics. Most early-onset asthma cases are caused by allergy, whereas late-onset asthma has a complex etiology, such as smoking, occupational, and non-allergic sensitizers, which are related to CVD risk. Moreover, CVD generally occurs among the elderly. Studies of early-onset asthma had difficulties in following participants until their elderly years, which means that their follow-up was relatively insufficient to meet the outcomes of CVD.
Limitations
The conclusions gained from this study are weakened by the inherent limitations of meta-analyses and observational cohort studies. Although most studies included reported adjusted estimates, the confounding factors of each study were not exactly the same. In addition, some of studies did not adjust for confounding factors. This led to an increased risk of bias in our meta-analysis. Furthermore, most estimates had high heterogeneity, probably because the population characteristics, diagnostic criteria for asthma, and definition of CVD in each study were not completely identical. Finally, all the included data were aggregate, and no individual-level data were available.
Conclusion
Our study provides evidence that asthma patients have increased risk of all-cause mortality and CVD morbidity and mortality. In addition, subgroup analyses showed that female asthma patients have a higher risk of all-cause mortality and CVD morbidity, and that late-onset asthma patients have higher risk of CVD morbidity. This information reminds clinicians to be aware of the risk of CVD and all-cause mortality in asthma patients.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author Contributions
Z-FL: analysis of data, interpretation results, and drafting and editing the article. BZ, Z-YA, DL, A-JS, QR, and W-BC: design of study, solution of problem, and reviewing the article. LZ, J-YW, M-DH, and Y-JJ: extraction of data and assessment of articles quality. All authors contributed to the article and approved this version of article.
Funding
The study was financially supported by the Youth Project of Guangdong Provincial Medical Research Fund (Grant No. B2021353), Outstanding Youth Fund Projects of Jiangmen Central Hospital (Grant Nos. J202101 and J202003), the project of Fundamental Research Funds of Jiangmen Central Hospital (Grant No. D201901), and the projects of Jiangmen City Science and Technology Plans (Grant Nos. 2021YLA01033, 2020YLA100, and 2020YLA133).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcvm.2022.861798/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure 1. Funnel plot depicting publication bias for the association between asthma and CVD morbidity. SE, standard error; RR, relative risk.
Supplementary Figure 2. Funnel plot depicting publication bias for the association between asthma and CVD mortality. SE, standard error; RR, relative risk.
Supplementary Figure 3. Funnel plot depicting publication bias for the association between asthma and all-cause mortality. SE, standard error; RR, relative risk.
Supplementary Figure 4. Sensitivity analysis of association between asthma and CVD morbidity. CI, confidential interval; HF, heart failure; CHD, coronary heart disease; a/f, adult female; a/m, adult male; c/f, child female; c/m, child male; int, intermittent; per, persistent.
Supplementary Figure 5. Sensitivity analysis of association between asthma and CVD mortality. CI, confidential interval.
Supplementary Figure 6. Sensitivity analysis of association between asthma and all-cause mortality. CI, confidential interval; int, intermittent; per, persistent.
Supplementary Figure 7. Sensitivity analysis of association between asthma and all-cause mortality in male patients. CI, confidential interval.
Supplementary Figure 8. Sensitivity analysis of association between asthma and all-cause mortality in female patients. CI, confidential interval.
Supplementary Figure 9. Sensitivity analysis of association between asthma and CVD morbidity in early-onset patients. CI, confidential interval; HF, heart failure; CHD, coronary heart disease; a/f, adult female; a/m, adult male; c/f, child female; c/m, child male.
Supplementary Figure 10. Sensitivity analysis of association between asthma and CVD morbidity in late-onset patients. CI, confidential interval; HF, heart failure; CHD, coronary heart disease; a/f, adult female; a/m, adult male; c/f, child female; c/m, child male.
Supplementary Figure 11. Sensitivity analysis of association between asthma and CVD morbidity in male patients. CI, confidential interval; a/f, adult female; a/m, adult male; c/f, child female; c/m, child mal.
Supplementary Figure 12. Sensitivity analysis of association between asthma and CVD morbidity in female patients. CI, confidential interval; a/f, adult female; a/m, adult male; c/f, child female; c/m, child male.
Supplementary Figure 13. Sensitivity analysis of association between asthma and all-cause mortality by omitting two outliers. CI, confidential interval; int, intermittent; per, persistent.
Supplementary Table 1. Search strategies.
Supplementary Table 2. Newcastle-ottawa scale for assessing the quality of included studies.
Supplementary Table 3. PRISMA 2009 checklist.
Abbreviations
CVD, cardiovascular disease; CI, confidential interval; RR, relative risk; HR, hazard ratio; NOS, Newcastle-Ottawa Scale; PRISMA, Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses; MOOSE, Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology; PROSPERO, Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews.
References
1. Vos T, Flaxman AD, Naghavi M, Lozano R, Michaud C, Ezzati M, et al. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. (2012) 380:2163–96. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61729-2
2. Asher MI, Montefort S, Björkstén B, Lai CK, Strachan DP, Weiland SK, et al. Worldwide time trends in the prevalence of symptoms of asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and eczema in childhood: ISAAC phases one and three repeat multicountry cross-sectional surveys. Lancet. (2006) 368:733–43. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69283-0
3. To T, Stanojevic S, Moores G, Gershon AS, Bateman ED, Cruz AA, et al. Global asthma prevalence in adults: findings from the cross-sectional world health survey. BMC Public Health. (2012) 12:204. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-12-204
4. Holgate ST, Wenzel S, Postma DS, Weiss ST, Renz H, Sly PD. Asthma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2015) 1:15025. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2015.25
5. Papi A, Brightling C, Pedersen SE, Reddel HK. Asthma. Lancet. (2018) 391:783–800. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)33311-1
6. Mims JW. Asthma: definitions and pathophysiology. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. (2015) 5(Suppl. 1):S2–6. doi: 10.1002/alr.21609
7. Guite HF, Dundas R, Burney PG. Risk factors for death from asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and cardiovascular disease after a hospital admission for asthma. Thorax. (1999) 54:301–7. doi: 10.1136/thx.54.4.301
8. Halasz A, Cserhati E, Magyar P, Kovacs M, Cseh K. Role of TNF-alpha and its 55 and 75 kDa receptors in bronchial hyperreactivity. Respir Med. (2002) 96:262–7. doi: 10.1053/rmed.2001.1256
9. Barr RG, Cooper DM, Speizer FE, Drazen JM, Camargo CA. beta-Adrenoceptor polymorphism and body mass index are associated with adult-onset asthma in sedentary but not active women. Chest. (2001) 120:1474–9. doi: 10.1378/chest.120.5.1474
10. Guerra S, Sherrill DL, Bobadilla A, Martinez FD, Barbee RA. The relation of body mass index to asthma, chronic bronchitis, and emphysema. Chest. (2002) 122:1256–63. doi: 10.1378/chest.122.4.1256
11. Hospers JJ, Rijcken P, Schouten JP, Postma DS, Weiss ST. Eosinophilia and positive skin tests predict cardiovascular mortality in a general population sample followed for 30 years. Am J Epidemiol. (1999) 150:482–91. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a010037
12. Axson EL, Ragutheeswaran K, Sundaram V, Bloom CI, Bottle A, Cowie MR, et al. Hospitalisation and mortality in patients with comorbid COPD and heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Respir Res. (2020) 21:54. doi: 10.1186/s12931-020-1312-7
13. Wang L, Gao S, Yu M, Sheng Z, Tan W. Association of asthma with coronary heart disease: a meta analysis of 11 trials. PLoS ONE. (2017) 12:e0179335. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179335
14. Xu M, Xu J, Yang X. Asthma and risk of cardiovascular disease or all-cause mortality: a meta-analysis. Ann Saudi Med. (2017) 37:99–105. doi: 10.5144/0256-4947.2017.99
15. Hutton B, Salanti G, Caldwell DM, Chaimani A, Schmid CH, Cameron C, et al. The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses of health care interventions: checklist and explanations. Ann Intern Med. (2015) 162:777–84. doi: 10.7326/M14-2385
16. Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. (2002) 21:1539–58. doi: 10.1002/sim.1186
17. Markowe HL, Bulpitt CJ, Shipley MJ, Rose G, Crombie DL, Fleming DM. Prognosis in adult asthma: a national study. Br Med J. (1987) 295:949–52. doi: 10.1136/bmj.295.6604.949
18. Ulrik CS, Frederiksen J. Mortality and markers of risk of asthma death among 1,075 outpatients with asthma. Chest. (1995) 108:10–5. doi: 10.1378/chest.108.1.10
19. Lange P, Ulrik CS, Vestbo J. Mortality in adults with self-reported asthma. Copenhagen city heart study group. Lancet. (1996) 347:1285–9. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(96)90937-X
20. Huovinen E, Kaprio J, Vesterinen E, Koskenvuo M. Mortality of adults with asthma: a prospective cohort study. Thorax. (1997) 52:49–54. doi: 10.1136/thx.52.1.49
21. Dantzer C, Tessier JF, Nejjari C, Barberger-Gateau P, Dartigues JF. Mortality of elderly subjects with self-reported asthma in a French cohort, 1991-1996. Eur J Epidemiol. (2001) 17:57–63. doi: 10.1023/A:1010996718008
22. Vandentorren S, Baldi I, Annesi Maesano I, Charpin D, Neukirch F, Filleul L, et al. Long-term mortality among adults with or without asthma in the PAARC study. Eur Respir J. (2003) 21:462–7. doi: 10.1183/09031936.03.00030303
23. Iribarren C, Tolstykh IV, Eisner MD. Are patients with asthma at increased risk of coronary heart disease? Int J Epidemiol. (2004) 33:743–8. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyh081
24. Schanen JG, Iribarren C, Shahar E, Punjabi NM, Rich SS, Sorlie PD, et al. Asthma and incident cardiovascular disease: the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Thorax. (2005) 60:633–8. doi: 10.1136/thx.2004.026484
25. Onufrak SJ, Abramson JL, Austin HD, Holguin F, McClellan WM, Vaccarino LV. Relation of adult-onset asthma to coronary heart disease and stroke. Am J Cardiol. (2008) 101:1247–52. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2007.12.024
26. Diaz-Guzman E, Khosravi M, Mannino DM. Asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and mortality in the U.S population. COPD. (2011) 8:400–7. doi: 10.3109/15412555.2011.611200
27. Iribarren C, Tolstykh IV, Miller MK, Sobel E, Eisner MD. Adult asthma and risk of coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, and heart failure: a prospective study of 2 matched cohorts. Am J Epidemiol. (2012) 176:1014–24. doi: 10.1093/aje/kws181
28. Yun HD, Knoebel E, Fenta Y, Gabriel SE, Leibson CL, Loftus EV Jr, et al. Asthma and proinflammatory conditions: a population-based retrospective matched cohort study. Mayo Clin Proc. (2012) 87:953–60. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2012.05.020
29. Ali Z, Dirks CG, Ulrik CS. Long-term mortality among adults with asthma: a 25-year follow-up of 1,075 outpatients with asthma. Chest. (2013) 143:1649–55. doi: 10.1378/chest.12-2289
30. Chung WS, Shen TC, Lin CL, Chu YH, Hsu WH, Kao CH. Adult asthmatics increase the risk of acute coronary syndrome: a nationwide population-based cohort study. Eur J Intern Med. (2014) 25:941–5. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2014.10.023
31. Huang S, Vasquez MM, Halonen M, Martinez FD, Guerra S. Asthma, airflow limitation and mortality risk in the general population. Eur Respir J. (2015) 45:338–46. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00108514
32. Tattersall MC, Guo M, Korcarz CE, Gepner AD, Kaufman JD, Liu KJ, et al. Asthma predicts cardiovascular disease events: the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2015) 35:1520–5. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.305452
33. Eftekhari P, Forder PM, Majeed T, Byles JE. Impact of asthma on mortality in older women: an Australian cohort study of 10,413 women. Respir Med. (2016) 119:102–8. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2016.08.026
34. Tattersall MC, Barnet JH, Korcarz CE, Hagen EW, Peppard PE, Stein JH. Late-onset asthma predicts cardiovascular disease events: the wisconsin sleep cohort. J Am Heart Assoc. (2016) 5:e003448. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.116.003448
35. Lemmetyinen RE, Karjalainen JV, But A, Renkonen RLO, Pekkanen JR, Toppila-Salmi SK, et al. Higher mortality of adults with asthma: a 15-year follow-up of a population-based cohort. Allergy. (2018) 73:1479–88. doi: 10.1111/all.13431
36. Strand LB, Tsai MK, Wen CP, Chang SS, Brumpton BM. Is having asthma associated with an increased risk of dying from cardiovascular disease? a prospective cohort study of 446 346 Taiwanese adults. BMJ Open. (2018) 8:e019992. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-019992
37. Cepelis A, Brumpton BM, Laugsand LE, Dalen H, Langhammer A, Janszky I, et al. Asthma, asthma control and risk of acute myocardial infarction: HUNT study. Eur J Epidemiol. (2019) 34:967–77. doi: 10.1007/s10654-019-00562-x
38. Caffrey Osvald E, Bower H, Lundholm C, Larsson H, Brew BK, Almqvist C. Asthma and all-cause mortality in children and young adults: a population-based study. Thorax. (2020) 75:1040–6. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2020-214655
39. Ng C, Knuiman MW, Murray K, Divitini ML, Musk AWB, James AL. Childhood asthma increases respiratory morbidity, but not all-cause mortality in adulthood: the busselton health study. Respir Med. (2020) 171:106095. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2020.106095
40. He X, Cheng G, He L, Liao B, Du Y, Xie X, et al. Adults with current asthma but not former asthma have higher all-cause and cardiovascular mortality: a population-based prospective cohort study. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:1329. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-79264-4
41. Pollevick ME, Xu KY, Mhango G, Federmann EG, Vedanthan R, Busse P, et al. The relationship between asthma and cardiovascular disease: an examination of the framingham offspring study. Chest. (2021) 159:1338–45. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.11.053
42. Ingebrigtsen TS, Marott JL, Vestbo J, Nordestgaard BG, Lange P. Coronary heart disease and heart failure in asthma, COPD and asthma-COPD overlap. BMJ Open Respir Res. (2020) 7:e000470. doi: 10.1136/bmjresp-2019-000470
43. Ng C, Knuiman MW, Murray K, Divitini ML, Musk AWB, James AL. Childhood asthma and cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in adulthood: the busselton health study. Pediatr Pulmonol. (2021) 56:1915–23. doi: 10.1002/ppul.25386
44. Bellia V, Pedone C, Catalano F, Zito A, Davi E, Palange S, et al. Asthma in the elderly: mortality rate and associated risk factors for mortality. Chest. (2007) 132:1175–82. doi: 10.1378/chest.06-2824
45. Liss GM, Tarlo SM, Macfarlane Y, Yeung KS. Hospitalization among workers compensated for occupational asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2000) 162:112–8. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.162.1.9906108
46. Colak Y, Afzal S, Nordestgaard BG, Lange P. Characteristics and prognosis of never-smokers and smokers with asthma in the copenhagen general population study. A prospective cohort study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2015) 192:172–81. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201502-0302OC
47. Odegaard AO, Jacobs DR Jr, Sanchez OA, Goff DC Jr, Reiner AP, Gross MD. Oxidative stress, inflammation, endothelial dysfunction and incidence of type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2016) 15:51. doi: 10.1186/s12933-016-0369-6
48. Gershon AS, Wang C, Guan J, To T. Burden of comorbidity in individuals with asthma. Thorax. (2010) 65:612–8. doi: 10.1136/thx.2009.131078
49. Au DH, Curtis JR, Every NR, McDonell MB, Fihn SD. Association between inhaled beta-agonists and the risk of unstable angina and myocardial infarction. Chest. (2002) 121:846–51. doi: 10.1378/chest.121.3.846
50. Liu H, Fu Y, Wang K. Asthma and risk of coronary heart disease: a meta-analysis of cohort studies. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. (2017) 118:689–95. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2017.03.012
51. Enright PL, Ward BJ, Tracy RP, Lasser EC. Asthma and its association with cardiovascular disease in the elderly. The cardiovascular health study research group. J Asthma. (1996) 33:45–53. doi: 10.3109/02770909609077762
52. Nidorf SM, Fiolet ATL, Mosterd A, Eikelboom JW, Schut A, Opstal TSJ, et al. Colchicine in patients with chronic coronary disease. N Engl J Med. (2020) 383:1838–47. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2021372
53. James AL, Palmer LJ, Kicic E, Maxwell PS, Lagan SE, Ryan GF, et al. Decline in lung function in the busselton health study: the effects of asthma and cigarette smoking. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2005) 171:109–14. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200402-230OC
Keywords: asthma, cardiovascular disease, cardiovascular disease morbidity, cardiovascular disease mortality, all-cause mortality
Citation: Zhang B, Li Z-F, An Z-Y, Zhang L, Wang J-Y, Hao M-D, Jin Y-J, Li D, Song A-J, Ren Q and Chen W-B (2022) Association Between Asthma and All-Cause Mortality and Cardiovascular Disease Morbidity and Mortality: A Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 9:861798. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.861798
Received: 25 January 2022; Accepted: 16 February 2022;
Published: 17 March 2022.
Edited by:
Rajeev Gupta, Mediclinic, United Arab EmiratesReviewed by:
Jayadevan Sreedharan, Gulf Medical University, United Arab EmiratesTiny Nair, PRS Hospital, India
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Li, An, Zhang, Wang, Hao, Jin, Li, Song, Ren and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wen-Biao Chen, Y2hhbndlbmJpYW9Ac2luYS5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Bin Zhang
Bin Zhang Zhi-Fei Li2†
Zhi-Fei Li2† Zhuo-Yu An
Zhuo-Yu An Yi-Jing Jin
Yi-Jing Jin Wen-Biao Chen
Wen-Biao Chen