- 1Department of Gastroenterology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
- 2Centre for Inflammatory Bowel Disease, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
- 3Lab of Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Frontiers Science Center for Disease-Related Molecular Network, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
Background: The prospective application of plasma Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DNA load as a noninvasive measure of intestinal EBV infection remains unexplored. This study aims to identify ideal threshold levels for plasma EBV DNA loads in the diagnosis and outcome prediction of intestinal EBV infection, particularly in cases of primary intestinal lymphoproliferative diseases and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Methods: Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were examined to determine suitable thresholds for plasma EBV DNA load in diagnosing intestinal EBV infection and predicting its prognosis.
Results: 108 patients were retrospectively assigned to the test group, while 56 patients were included in the validation group. Plasma EBV DNA loads were significantly higher in the intestinal EBV infection group compared to the non-intestinal EBV infection group (Median: 2.02 × 102 copies/mL, interquartile range [IQR]: 5.49 × 101-6.34×103 copies/mL versus 4.2×101 copies/mL, IQR: 1.07 ×101-6.08×101 copies/mL; P < 0.0001). Plasma EBV DNA levels at 9.21×101 and 6.77×101 copies/mL proved beneficial for the identification and prognostication in intestinal EBV infection, respectively. Values of 0.82 and 0.71 were yielded by the area under the ROC curve (AUC) in the test cohort, corresponding to sensitivities of 84.38% (95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 68.25%-93.14%) and 87.5% (95%CI: 69%-95.66%), specificities of 83.33% (95%CI: 64.15%-93.32%) and 68.09% (95%CI: 53.83%-79.6%), positive predictive values (PPV) of 87.1% (95%CI: 71.15%-94.87%) and 58.33% (95%CI: 42.2%-72.86%), and positive likelihood ratios (LR+) of 5.06 and 2.74 in the validation cohort, respectively. Furthermore, a plasma EBV DNA load of 5.4×102 copies/mL helped differentiate IBD with intestinal EBV infection from primary intestinal EBV-positive lymphoproliferative disorders (PIEBV+LPDs), achieving an AUC of 0.85 within the test cohort, as well as 85% sensitivity (95%CI: 63.96%-94.76%), 91.67% specificity (95%CI: 64.61%-99.57%), 94.44% PPV (95%CI: 74.24%-99.72%), and an LR+ of 10.2 in the validation cohort.
Conclusions: Plasma EBV DNA load demonstrates notable potential in distinguishing between different patient cohorts with intestinal EBV infection, although its sensitivity requires further optimization for clinical application.
1 Introduction
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), a pervasive herpesvirus, is particularly recognized for its oncogenic potential in various malignancies and its association with autoimmune diseases (Young et al., 2016). The pathogenic role of EBV has been well established in multiple diseases, such as infectious mononucleosis (Lennon et al., 2015), Burkitt lymphoma (BL) (López et al., 2022), and nasopharyngeal cancer (NPC) (Wong et al., 2021). However, research into the impact of EBV on intestinal diseases, particularly inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), together with primary intestinal lymphoproliferative diseases (PILPDs), is just beginning (Rizzo et al., 2017; Dang et al., 2023; Chen L. et al., 2024). IBD is a multifaceted disease characterized by persistent inflammation within the gastrointestinal tract, which is often exacerbated by opportunistic infections (Cao et al., 2022; Zeng et al., 2023; Li et al., 2024; Pu et al., 2024). Evidence highlights that the incidence of positive EBV DNA detection from intestinal resection specimens in patients with IBD is 55%-76%, which is markedly higher than the 19% observed in a non-IBD group (Xu et al., 2020). Furthermore, EBV infection is intricately linked to clinical manifestations (Dimitroulia et al., 2013), therapeutic responses (Pezhouh et al., 2018; Chen Y. et al., 2024), surgical interventions (Hosomi et al., 2018), and lymphoma incidence (Nissen et al., 2015; de Francisco et al., 2018) in IBD patients. Moreover, the diagnosis of intestinal diseases is significantly influenced by EBV infection. PILPDs encompass a spectrum of diseases characterized by abnormal lymphocyte proliferation in the intestine, with manifestations ranging from benign to malignant; notably, aggressive PILPDs are linked to an extremely high risk of mortality (Cohen et al., 2009; Montes-Mojarro et al., 2020). Our previous study revealed that 67% of 12 patients with primary intestinal EBV-positive lymphoproliferative disorders (PIEBV+LPDs) were initially diagnosed with IBD, and half of the 12 patients ultimately succumbed to PIEBV+LPDs (Wang Z. et al., 2018). This underscores the fact that overlooking intestinal EBV infection can lead to fatal outcomes. It is equally important to acknowledge that the gold standard for diagnosing EBV infection is histological analysis using EBV-encoded small RNAs in situ hybridization (EBER-ISH) (Weiss and Chen, 2013). However, given the anatomical location of the intestine, the intestinal EBER-ISH test requires invasive procedures, such as endoscopy or surgery. Therefore, the clinical significance of other noninvasive, dependable, and accessible methods for diagnosing intestinal EBV infection needs to be explored.
Measuring peripheral EBV DNA levels shows superiority in simplicity and non-invasiveness for diagnosing and surveilling EBV infection when compared with the histological EBER-ISH test. However, the value of the test is significantly influenced by the choice of peripheral blood components analyzed, such as whole blood, plasma, and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), which may affect sensitivity and specificity. Owing to the latent characteristics of EBV, research proved that measuring EBV DNA levels in plasma has advantages over measuring them in whole blood and PBMCs as indicators of active replication of the virus, thereby improving the diagnostic and prognostic power of diseases associated with EBV (Tsai et al., 2015; Kanakry et al., 2016; Ludvigsen et al., 2023). For instance, the diagnostic sensitivity of a detectable plasma EBV DNA load can reach up to 90% in BL (Hohaus et al., 2011) and as high as 93.2% in NPC (Lou et al., 2023). Furthermore, plasma EBV DNA levels showed considerable predictive power for the outcomes of these diseases (Hui et al., 2020; Qiu et al., 2020). However, in EBV-associated intestinal diseases, although a study reported that IBD patients infected with intestinal EBV exhibited heightened concentrations of EBV DNA within their peripheral whole blood (Xu et al., 2020), no study has employed plasma EBV DNA load, an indicative marker of active infection, to establish definitive thresholds for aiding diagnostic and prognostic assessment of intestinal EBV infection.
Therefore, we conducted a retrospective investigation to define the diagnostic and prognostic cut-off values for intestinal EBV infection based on plasma EBV DNA loads. This approach will facilitate the differential diagnosis of intestinal EBV infections in the clinical setting.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study population and design
This retrospective investigation was performed at the Gastroenterology Department of West China Hospital between January 2013 and January 2024. Initially, patients with positive plasma EBV DNA loads and intestinal diseases were screened through electronic medical record system, followed by verification through the pathology system to confirm whether they had also undergone intestinal EBER-ISH test. Patients with intestinal diseases who tested positive for peripheral blood EBV DNA and completed the intestinal EBER-ISH test were included in the study, while those who did not complete both tests, had incomplete clinical data, or had unclear diagnoses were excluded. Immunomodulator usage was defined as treatment with steroids, immunosuppressants, or biological agents within three months prior to the intestinal EBER-ISH test, and intestinal EBV infection was defined as positive EBER-ISH test in the intestine. The diagnosis of IBD followed recognized criteria, including typical clinical presentations, endoscopic findings, radiological assessments, and histological results (Gomollón et al., 2017; Magro et al., 2017). The diagnostic criteria for PILPDs require the presence of gastrointestinal symptoms and confirmation of abnormal proliferation of lymphocytes within the intestinal tissues through pathology, while excluding primary lymphoproliferative diseases at other sites (Wang Z. et al., 2018). On this basis, a positive result for intestinal EBER-ISH test was defined as PIEBV+LPDs, while a negative result was defined as primary intestinal non-EBV-associated lymphoproliferative diseases (PINEBV+LPDs). Data from the electronic medical record system were also collected to analyze clinical data, such as sex, age, plasma EBV DNA load, and other factors. Furthermore, a follow-up on the prognosis of all patients was conducted, where events such as intestinal resection or death within six months after undergoing intestinal EBER-ISH test were defined as fatal events, while all other outcomes were considered benign events. Ethics approval for the present investigation was obtained from the ethics board of West China Hospital. (Number: 2023-22).
2.2 EBV test
As directed by the manufacturer, quantitative measurement of EBV DNA in the plasma was performed using an EBV detection kit with polymerase chain reaction (PCR) fluorescence (Shen Xiang Gene Co.). The EBER gene was amplified using a Bio-Rad CFX96 PCR instrument. A Ct value ≤39 was interpreted as positive, and a standard curve was used to calculate the quantity of EBV DNA copies. EBER-ISH was used to investigate intestinal EBV infection, and the EBV-encoded small RNAs (EBER) peptide nucleic acid probe was sourced from ZSGB-BIO (China). Specifically, tissues from intestinal biopsies of patients were deparaffinized, rehydrated, and permeabilized with proteinase K, followed by overnight hybridization at 37°C with digoxigenin-labeled EBER probes. After incubation with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated anti-digoxigenin antibody, EBER-positive cells were identified by diaminobenzidine staining and exhibited brown-stained nuclei. These cells were quantitatively scored by two experienced pathologists in high-power field (HPF).
2.3 Statistical analysis
Statistical evaluation was performed using SPSS and GraphPad Prism (version 26.0 and 9.5, respectively). This investigation of the demographic and basic features of the patients utilized both frequency distributions and descriptive statistical methods. To compare patient characteristics among different cohorts, either the chi-squared hypothesis evaluation or the exact significance test using Fisher’s exact test was employed, contingent on the distributional features inherent in these data. To evaluate the role of plasma EBV DNA load in the diagnostic and prognostic assessment of intestinal EBV infection, a stepwise analysis was conducted using both the train and validation cohorts. In the first stage, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were utilized to analyze plasma EBV DNA concentrations for diagnosing intestinal EBV infection and predicting its prognosis. These optimal cutoff values were determined based on the maximum Youden’s index, which maximizes the sum of sensitivity and specificity (Youden’s index = sensitivity + specificity-1). This approach ensures the identification of the threshold that achieves the best trade-off between true-positive and true-negative rates for each cohort. In the next stage, the performance of these cutoff values was assessed in the validation cohort by calculating sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), positive likelihood ratio (LR+), and negative likelihood ratio (LR-). These metrics were used to confirm the robustness of the cutoff values derived from the train cohort. Statistical significance was represented by a p-value of < 0.05.
3 Results
3.1 Clinical characteristics among train cohort
Our investigation began with the identification of 213 patients diagnosed with intestinal diseases and tested positive for plasma EBV DNA. After excluding patients with unclear diagnoses and incomplete clinical data, the remaining patients were randomly assigned in a 2:1 ratio, resulting in a cohort of 108 patients in the train group and 56 patients in the validation group (Supplementary Figure 1; Supplementary Table 1). The train cohort consisted of 60 patients (55.56%) who tested negative for intestinal EBER-ISH and 48 patients (44.44%) who tested positive for intestinal EBER-ISH. The median age of the EBER-negative group was 42 years, which was comparable to that of the EBER-positive group (median age, 44 years). Moreover, neither sex distribution nor disease course demonstrated notable differences between the two groups. Additionally, the EBER-positive group did not exhibit a significantly higher frequency of immunomodulator use within three months preceding the intestinal EBER-ISH test than the EBER-negative group. However, a disparity in disease type was observed between the two groups. The EBER-positive group predominantly consisted of patients with PILPDs (50%), followed by IBD (47.9%) and other diseases (2.1%), whereas IBD was the most prevalent disease in the EBER-negative group (76.7%). The symptoms in both groups also differed significantly in clinical terms, with the EBER-positive group showing a higher incidence of fever and hematochezia than the EBER-negative group (Table 1).
3.2 Distribution of plasma EBV DNA loads in intestinal EBV infection
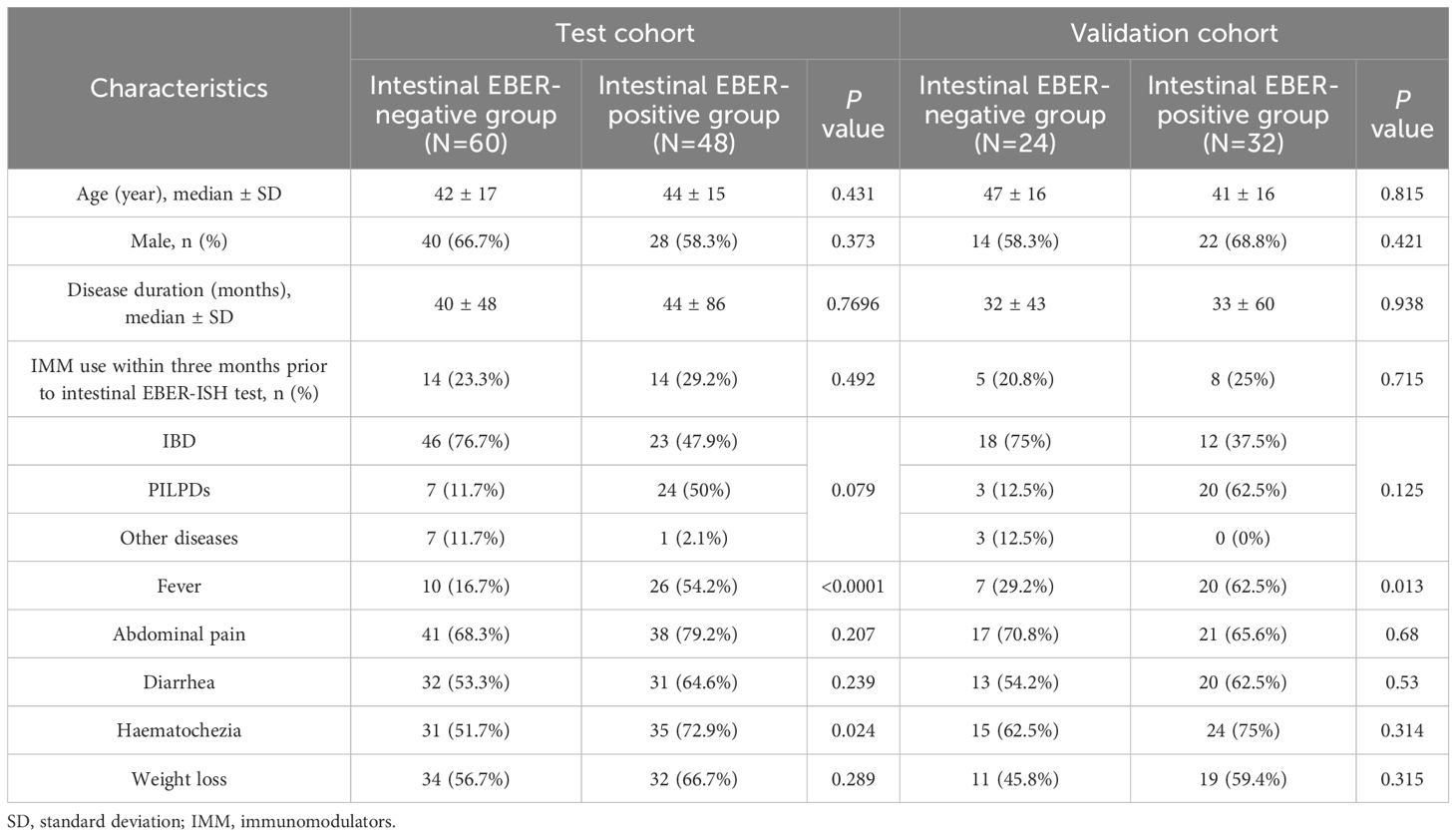
In this study, we conducted comparative analyses of the distribution of plasma EBV DNA load across various intestinal diseases. The findings revealed that the majority of patients (88.3%) in the EBER-negative group had EBV DNA loads <101 copies/ml, with only 11.7% having loads of 102-103 copies/ml, whereas the EBER-positive group exhibited a wider distribution of higher plasma EBV DNA loads, with 33.3% having loads >103 copies/ml and 25% having loads between 102 and 103 copies/ml (P < 0.001; Figure 1A). Additionally, when focusing on patients with IBD, we observed that EBER-positive IBD patients exhibited a notably elevated proportion of plasma EBV DNA loads (102-103 copies/ml) compared to their EBER-negative counterparts (30.4% vs. 6.5%, P = 0.013; Figure 1B). Among patients with PILPDs, 66.6% of PIEBV+LPD patients had EBV DNA loads >103 copies/ml, whereas no patients in the PINEBV+LPD group exhibited similarly high viral loads (P = 0.001; Figure 1C). Despite the overall high occurrence of elevated plasma EBV DNA loads in the EBER-positive IBD and PIEBV+LPD groups, a notable difference was observed in the distribution of viral loads between these two groups. In the PIEBV+LPD group, 66.6% of the patients had EBV DNA loads >103 copies/ml, whereas none of the EBER-positive IBD patients were present within this viral load range (P < 0.001; Figure 1D).
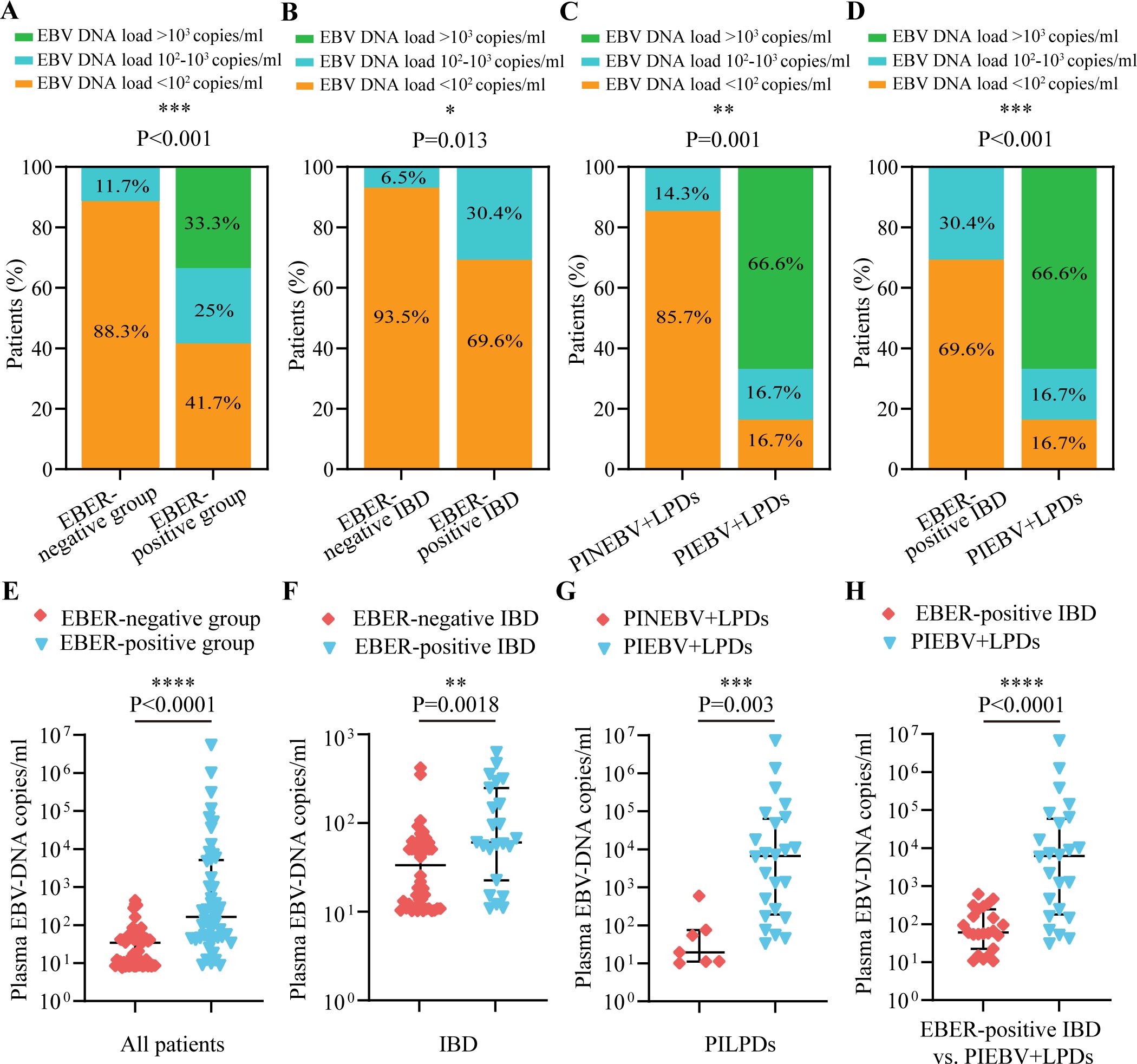
Figure 1. Comparisons of the distribution and quantification of plasma EBV DNA load between EBER-negative and EBER-positive groups. The comparisons include intestinal EBER-positive group vs. intestinal EBER-negative group (A, E), EBER-negative IBD vs. EBER-positive IBD (B, F), PINEBV+LPDs vs. PIEBV+LPDs (C, G), and EBER-positive IBD vs. PIEBV+LPDs (D, H). *p≤0.05, **p≤0.01, ***p≤0.001, and ****p≤0.0001.
Further analysis was conducted to compare plasma EBV DNA levels across EBER-negative and EBER-positive populations. Among the 48 patients in the intestinal EBER-positive group, the plasma EBV DNA level had a median value of 2.02 × 102 copies/mL (Interquartile Range [IQR]: 5.49×101-6.34×103 copies/mL), which represented a significantly elevated level compared to the median of 4.2×10¹ copies/mL (IQR: 1.07×101-6.08×101 copies/mL) observed in 60 patients in the intestinal EBER-negative group (Figure 1E). These median plasma EBV DNA loads were notably elevated in comparison to the respective EBER-negative control groups, including the IBD and PILPD groups, as detailed in Figures 1F, G. Notably, within the intestinal EBER-positive cohort, patients diagnosed with PIEBV+LPDs demonstrated the highest median plasma EBV DNA level at 6.18×103 copies/mL (IQR 1.8×102-5.91×104 copies/mL), significantly surpassing the levels in EBER-positive IBD patients (5.96×101 copies/mL [IQR 2.23×101-2.45×102 copies/mL]), with a P-value of < 0.0001 (Figure 1H).
3.3 Correlation analysis of EBER-positive cell counts with plasma EBV DNA levels in intestinal EBV infection
According to the consensus established on tissue identification and diagnostic pathology of intestinal EBV infection from the Chinese Medical Association (Ye et al., 2019), we divided these patients into three categories based on the number of cells positive for EBER-ISH per HPF: <10 cells per HPF, 10-50 cells per HPF, and >50 cells per HPF. We analyzed the interrelationship between plasma EBV DNA load and the frequency of intestinal EBER-positive cells per HPF in the intestinal EBER-positive cohort and found that the largest segment comprised patients with <10 cells positive for EBER-ISH per HPF (50%), followed by those with 10-50 cells positive for EBER-ISH per HPF (31.3%), and then patients with >50 cells positive for EBER-ISH per HPF (18.7%; Figure 2A). Notably, there was a notable disparity between PIEBV+LPDs and EBER-positive IBD, with 79.2% of PIEBV+LPD patients exhibiting more than 10 cells positive for EBER-ISH per HPF, compared to only 17.4% in the EBER-positive IBD group (P < 0.001; Figure 2A).
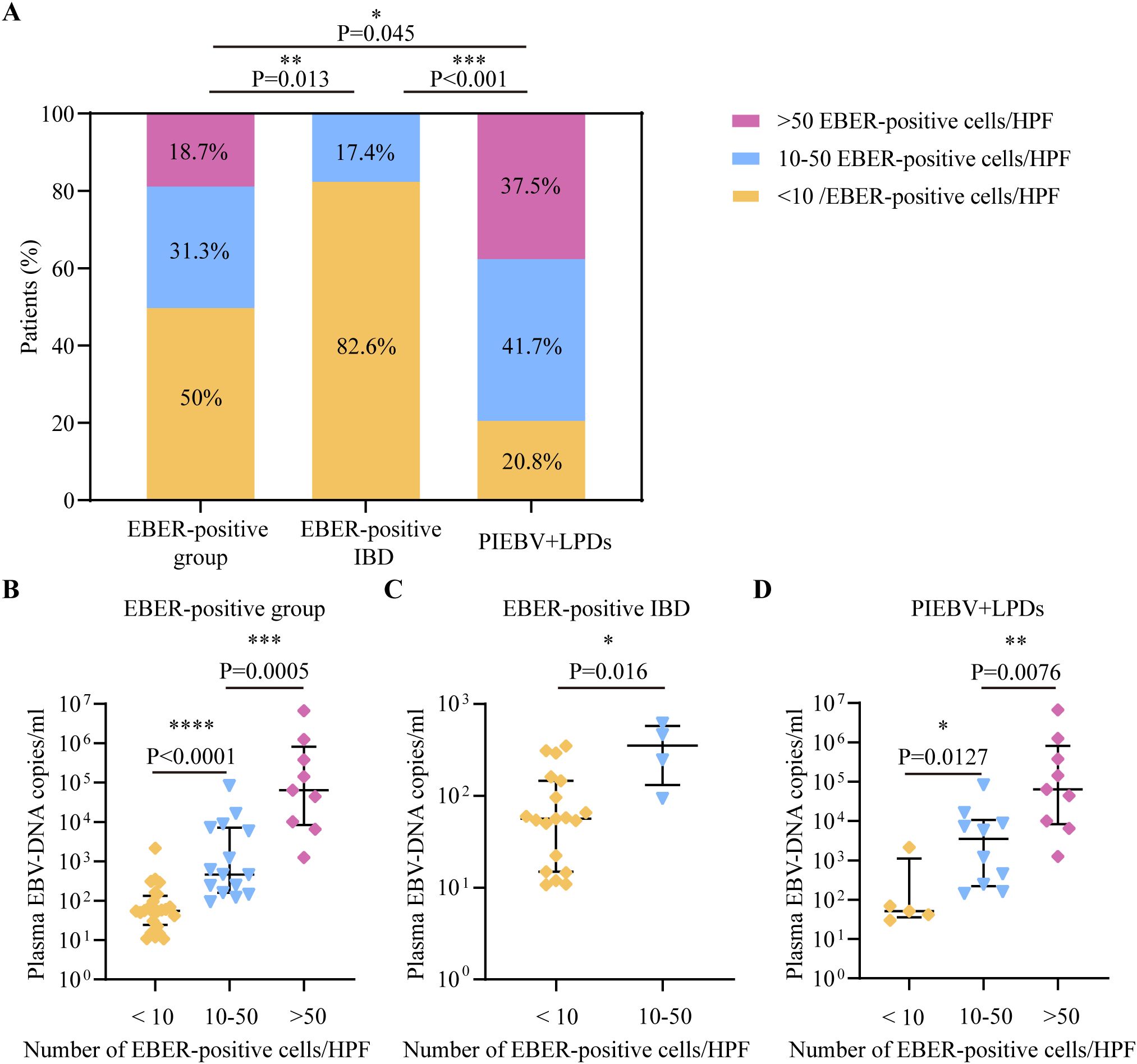
Figure 2. Comparative analysis of EBV DNA concentrations in plasma in accordance with total count of cells positive for EBER per HPF in intestinal tissue. (A) Distribution of total cells positive for EBER-ISH per HPF in intestinal tissue across different intestinal diseases with EBV infection. (B) Plasma EBV DNA quantity within EBER-positive patients. (C) Plasma EBV DNA quantity in EBER-positive IBD. (D) Plasma EBV-DNA quantity in PIEBV+LPDs. *p≤0.05, **p≤0.01, ***p≤0.001, and ****p≤0.0001.
For a profound evaluation of EBV DNA load in plasma within intestinal EBV infection, we assessed the median plasma EBV DNA concentrations across different count ranges of EBER-positive cells per HPF, and we discovered that the median plasma DNA concentrations of EBV in the group with >50 EBER-positive cells per HPF (6.41×104copies/mL) and in the group with 10-50 EBER-positive cells per HPF (4.62×102 copies/mL) were both markedly elevated compared to the level within the group with <10 EBER-positive cells per HPF (5.53×101 copies/mL), as shown in Figure 2B. Similarly, within the EBER-positive IBD subgroup, patients with 10-50 EBER-positive cells per HPF demonstrated significantly elevated plasma EBV DNA levels compared to those with <10 EBER-positive cells per HPF (3.54×102 copies/mL vs. 5.62×101 copies/mL; Figure 2C). Furthermore, in PIEBV+LPD group, patients with >50 EBER-positive cells per HPF exhibited markedly higher plasma EBV DNA levels (median 6.41×104 copies/mL), which were much superior in comparison with those with 10-50 EBER-positive cells per HPF (median 3.52×103 copies/mL, P = 0.0076) and those with <10 EBER-positive cells per HPF (median 5.09×101 copies/mL, P = 0.0127), as delineated in Figure 2D.
3.4 Diagnostic implication of plasma EBV DNA quantification in intestinal EBV infection
Considering that the density of intestinal cells positive for EBER-ISH per HPF exhibited a positive correlation with plasma EBV DNA levels, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve examination was initiated to ascertain the potency of plasma EBV DNA load for screening intestinal EBV infection in the test cohort. The analysis indicated that the area under the ROC curve (AUC) for distinguishing intestinal EBER positivity from EBER negativity was 0.82 at a concentration of 9.21×101 copies/mL of EBV DNA in plasma (Figure 3A), with a sensitivity of 64.58% and a specificity of 88.33%, indicating its potential utility in initial screening for EBV status. Furthermore, subgroup analyses stratified by intestinal EBER-ISH status identified 5.28×101 copies/mL as the cutoff value for differentiating EBV infection from non-EBV infection in IBD, yielding an AUC of 0.73 (Figure 3B), with a sensitivity of 69.57% and a specificity of 71.74%. This result suggests that plasma EBV DNA load has moderate discriminatory power in distinguishing EBV-positive IBD from EBV-negative IBD. Additionally, the analysis was extended to differentiate between EBER-positive IBD and PIEBV+LPDs. The ROC curve analysis for these two diseases produced an AUC of 0.85, with a discriminative threshold established at 5.4×102 copies/mL with high specificity (95.65%) to ensure diagnostic accuracy for this rare but severe condition (Figure 3C).
Figure 3. Analysis in the test cohort to assess the diagnostic utility of plasma EBV DNA quantification. (A) EBER-negative vs. EBER-positive group; (B) EBER-negative vs. EBER-positive IBD. (C) EBER-positive IBD vs. PIEBV+LPDs.
The detection capacity achieved by plasma EBV DNA cutoff values indicating intestinal EBV infection was evaluated in the validation cohort. Analysis of clinical characteristics revealed no significant differences in demographic features and clinical presentations within the test and validation cohorts (Supplementary Table S1). In the validation cohort, a threshold of 9.21×101 copies/mL for EBV DNA load in plasma demonstrated an LR+ calculated at 5.06, attaining values of 83.33%, 84.38%, 80%, and 87.1% in terms of specificity, sensitivity, NPV, and PPV, respectively, for identifying intestinal EBER-positive and EBER-negative diseases (Table 2). For IBD, the sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV, and LR+ of a threshold of 5.28×101 copies/mL to differentiate intestinal EBV infection from non-EBV infection were 66.67%, 55.56%, 50%, 71.43%, and 1.5, respectively (Table 2). Furthermore, at a cutoff value of 5.4×102 copies/mL, the sensitivity for distinguishing PIEBV+LPDs from EBER-positive IBD reached 85%, with an LR+ of 10.2 (Table 2).
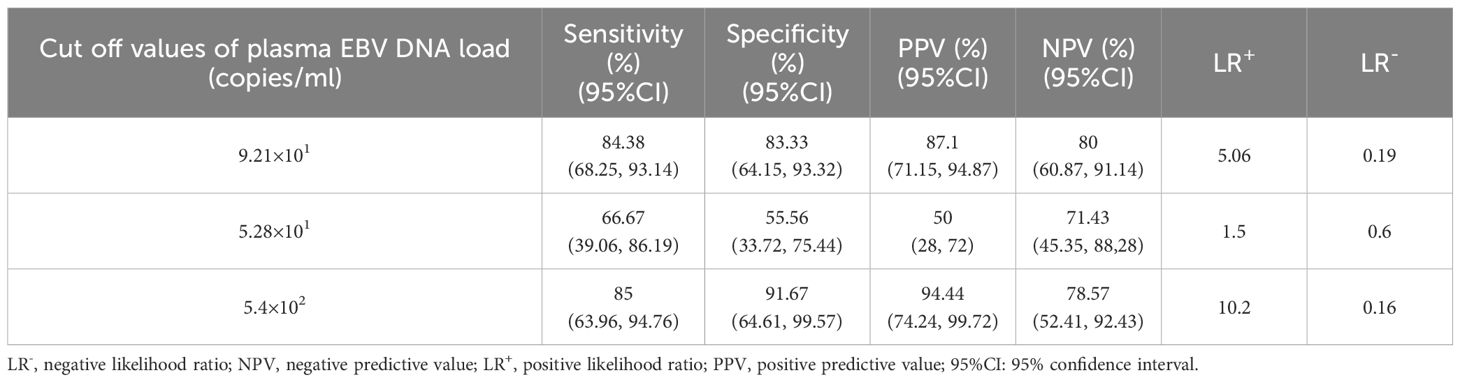
Table 2. Detection capacity of plasma EBV DNA cutoff values for intestinal EBV infection within the validation subset.
3.5 Prognostic implication of plasma EBV DNA quantification in intestinal EBV infection
The analysis further explored and compared the six-month prognosis following intestinal EBER-ISH test among patients with intestinal diseases who were positive for EBV DNA load in plasma. The results confirmed that individuals in the intestinal EBER-positive group displayed significantly poorer prognoses than those in the EBER-negative group of the test cohort (50% vs. 15%, P < 0.001). Moreover, EBER-positive IBD and PIEBV+LPD patients demonstrated worse outcomes than their EBER-negative counterparts (26.1% vs. 15.2%, P =0.334 and 75% vs. 28.6%, P = 0.067, respectively). Details comparing the prognostic outcomes of various intestinal diseases are presented in Supplementary Table 2.
Comparative analyses of plasma EBV DNA concentrations between the fatal and benign groups with various intestinal diseases were also conducted. As depicted in Figure 4A, patients with a fatal prognosis had greater median plasma EBV DNA loads than those with a benign outcome (2.9×102 copies/mL vs. 5.02×101 copies/mL, P = 0.0003). Furthermore, patients with PIEBV+LPDs and those with PINEBV+LPDs had significantly different median plasma EBV DNA levels (6.86×102 copies/mL vs. 5.09×101 copies/mL, P < 0.0001, Figure 4C). However, patients with fatal prognosis did not show a statistically significant difference in plasma EBV DNA load compared to those with benign prognosis in IBD (P=0.8824) (Figure 4B).
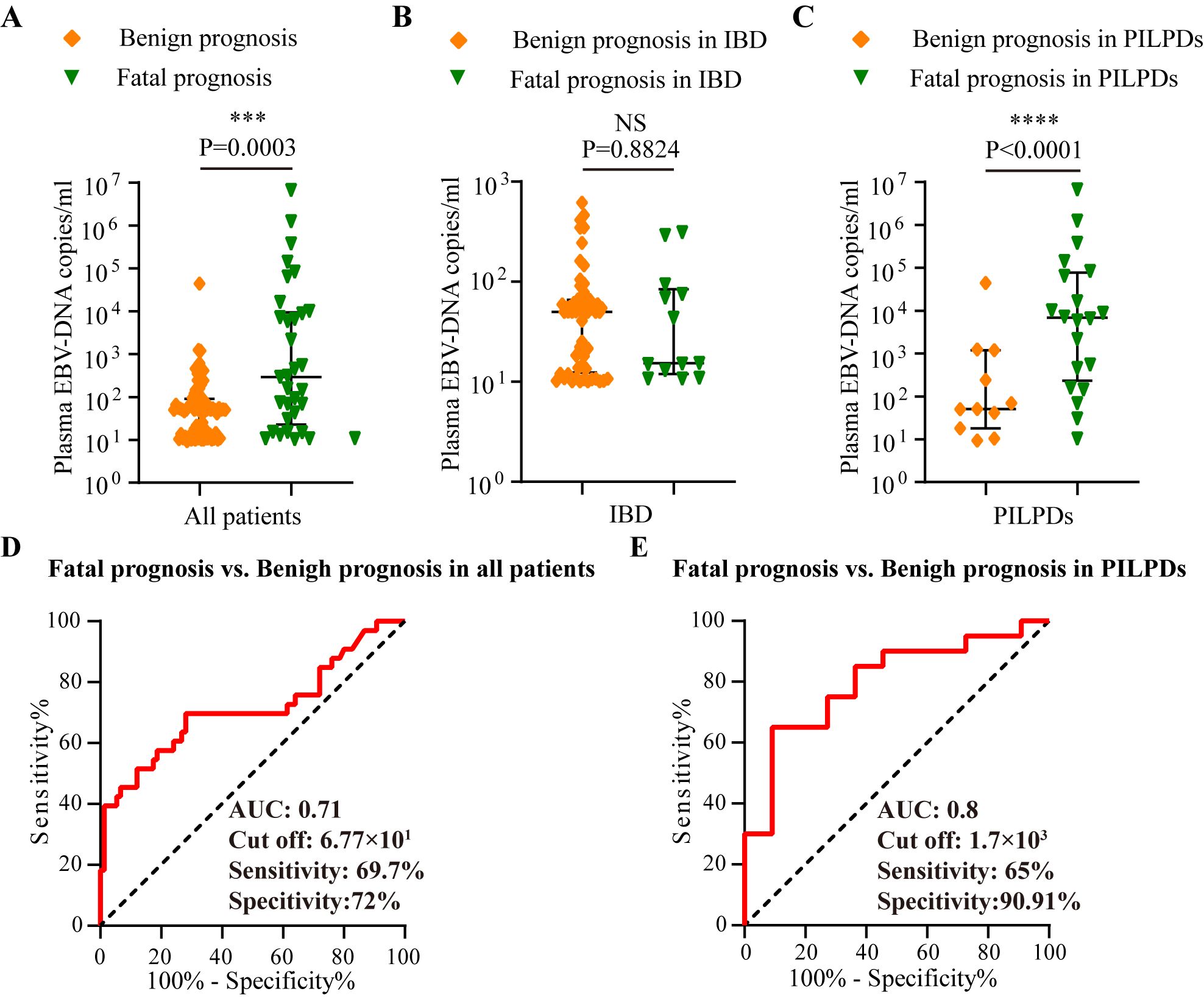
Figure 4. Analysis in the test cohort to assess the prognostic utility of plasma EBV DNA quantification. Comparative analysis of plasma EBV-DNA concentrations among various prognosis within the test cohort, including (A) Overall cohort, (B) IBD cohort, and (C) PILPD cohort. (D) ROC curve comparing fatal versus benign prognoses in all patients. (E) ROC curve comparing the fatal and benign prognoses in patients with PILPDs. ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. NS, not significant.
ROC curve analysis revealed that there was an excellent connection between plasma EBV DNA concentrates and prognosis for intestinal EBV infection, demonstrating an AUC of 0.71 in the test cohort (Figure 4D), with a sensitivity of 69.7% and a specificity of 72%, demonstrating moderate ability to differentiate between fatal and benign prognoses. By establishing a threshold of 6.77×101 copies/mL for plasma EBV DNA load, we established the sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV, LR+, and LR- for differentiating between fatal and benign prognoses in the validation cohort. The resulting values were 87.5%, 68.09%, 58.33%, 91.43%, 2.74, and 0.18, respectively (Table 3). Furthermore, plasma EBV DNA concentration at 1.7×103 copies/mL was shown to be the most effective threshold for predicting PILPD prognosis, with an AUC of 0.8 (Figure 4E), with a high specificity of 90.91% and relatively low sensitivity of 65%, ensuring the accurate identification of patients at risk of severe outcomes of PILPDs. Within the validation subset, the established cutoff offered a sensitivity of 64.71%, specificity of 83.33%, PPV of 91.67%, NPV of 45.45%, LR+ of 3.88, and LR- of 0.42, effectively distinguishing between benign and fatal outcomes in PILPDs (Table 3).
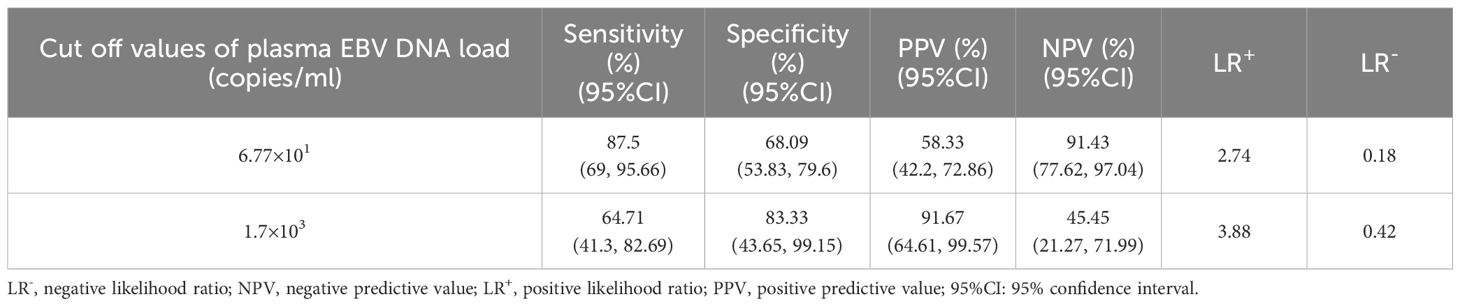
Table 3. The ability to evaluate prognostic outcomes based on plasma EBV DNA cutoff values for intestinal EBV infection within the validation subset.
4 Discussion
This investigation found a positive alignment between plasma EBV DNA quantification and the number of cells positive for EBER-ISH per HPF in intestinal diseases. Further studies were performed to determine the significance of EBV DNA concentrations in plasma with respect to identifying intestinal EBV infection and predicting its outcome, and specific threshold values were established. These results indicate that the EBV DNA quantity in plasma functions as a credible marker for the diagnostic and prognostic assessment of intestinal EBV infection.
Emphasizing clinical characteristics plays a crucial role in identifying EBV infection. Our study found no difference in immunosuppressant use between infected and non-infected patients, whereas previous studies have identified immunosuppressant administration as a pivotal element in triggering intestinal EBV activation (Ford and Peyrin-Biroulet, 2013; Magro et al., 2013; Lapsia et al., 2016). This may be due to the fact that all participants in both cohorts of this study were patients with detectable plasma EBV DNA, indicating that both groups were already in a state of EBV activation, which could mask the potential impact of immunosuppressant use. Research has shown that the main clinical manifestations of primary EBV infection include fever, pharyngitis, lymphadenopathy, and hepatosplenomegaly (Song et al., 2023; Ye et al., 2023). Consistent with this, our research demonstrated that compared to those who did not have EBV infection in their intestines, those with intestinal EBV infection exhibited fever symptoms more frequently. Moreover, our investigation is the first cohort study to affirm that patients with intestinal EBV infection strongly exhibit a higher predisposition to gastrointestinal manifestations with hematochezia than those without infection, which aligns with sporadic reports of primary intestinal EBV infection (Karlitz et al., 2011; Chen et al., 2016; Wang Y. et al., 2018). Therefore, our study suggests that it is essential to raise clinical vigilance in screening for intestinal EBV infection in patients with gastrointestinal complaints and fever symptoms.
In general, EBV maintains latency within a robust immune system. However, immunodeficiencies triggered by many factors can result in the reactivation of EBV (Chan et al., 2021). In such scenarios, a detectable level of EBV DNA signifies that the virus is actively undergoing infection and replication, whereas the histological EBER-ISH test is used to ascertain the presence of EBV in tissue samples (Kanakry et al., 2013; Liang et al., 2015; Zhou et al., 2020a). In this study, a substantial increase in the detection of plasma EBV DNA was observed among patients suffering from intestinal EBV infection, in contrast to those who were unaffected. The median plasma EBV DNA loads were reported as 2.02×102 copies/ml in infected patients versus 4.2×101 copies/ml in non-infected individuals, corroborating the findings of prior studies on EBV-associated diseases (Yu et al., 2021; Shen et al., 2022). This discrepancy indicates that patients with intestinal EBV infection typically experience persistent viral replication, leading to elevated plasma viral loads. Furthermore, consistent with earlier studies (Zhou et al., 2020b; Wang et al., 2022), our study found that IBD patients with intestinal EBV infection showed higher plasma EBV DNA levels than those not infected. Even though the value of EBV DNA load varies across studies owing to the different samples and methods used for EBV DNA testing, the trends observed in these studies are consistent.
The results of our study indicate that plasma EBV DNA load is positively correlated with the number of intestinal EBER-positive cells per HPF. This is consistent with the findings reported by Zhou et al. (Zhou et al., 2020b) in IBD patients with intestinal EBV infection, and aligns with the results from other studies related to EBV-associated diseases (Kanakry et al., 2016; Yu et al., 2021; Shen et al., 2022). Moreover, an indicator of intestinal EBER positivity based on plasma EBV DNA levels was examined using ROC analysis, revealing an AUC of 0.82. The optimal cut-off was established at 9.21×101 copies/ml, which is sensitive to 64.58% and specific to 88.33% in distinguishing intestinal EBV infection from non-infection. This is consistent with a previous study that used detectable EBV DNA to segregate EBV-associated diseases from those unrelated to EBV, exhibiting a sensitivity of 83.9% and specificity of 93.5% (Yu et al., 2021). It is evident that our investigation proposed an EBV DNA cut-off value with greater precision for diagnosing intestinal EBV infection. Moreover, our study revealed that patients with IBD with intestinal EBV infection can be distinguished from those with PIEBV+LPDs when their plasma EBV DNA concentration is below 5.4×102 copies/ml, which contributes to the differential diagnosis of the two diseases. Hence, our study demonstrates that it is possible to use plasma DNA load as a screening and monitoring tool for intestinal EBV infection. Nevertheless, it is vital to recognize that histological EBER-ISH test might yield underestimations of EBV infection because of the minimal thickness of tissue sections, whereas the high sensitivity of PCR technology in detecting EBV DNA might lead to overestimation of EBV infection. Furthermore, in clinical practice, IBD with intestinal EBV infection is generally regarded as an opportunistic infection, whereas PIEBV+LPDs represent conditions in which EBV acts as a direct pathogenic factor (Ye et al., 2019). This fundamental difference explains the distinct cutoff values derived for each cohort in this study, reflecting their unique disease contexts. Therefore, selecting an appropriate test method and cutoff value of plasma EBV DNA load, based on real-world clinical needs, is essential to achieve optimal diagnostic performance and prognostic assessment for intestinal EBV infection, such as improving the detection accuracy of EBV infection in IBD patients or ensuring precise differentiation in PIEBV+LPDs.
The heterogeneity of outcomes associated with EBV infection spans a continuum from benign to malignant manifestations, leading to prognostic variability in EBV-associated diseases. Prior studies have demonstrated plasma EBV DNA load for predicting the outcome and therapeutic response of EBV-associated diseases (Kanakry et al., 2013; Ito et al., 2016). In cases of intestinal EBV infection, EBV infection has been linked to refractory responses and the necessity for surgical treatment in patients with IBD (Hosomi et al., 2018; Pezhouh et al., 2018). Analysis of a cohort of 12 patients with PIEBV+LPDs revealed a 50% mortality rate within a follow-up interval of 1-21 months (Wang Z. et al., 2018). Our investigation contributes to this body of evidence by demonstrating a significant correlation between elevated plasma EBV DNA levels and fatal prognoses in patients with intestinal EBV infection within six months after the intestinal EBER-ISH test, marked by an AUC of 0.71. Additionally, for patients with PILPDs, when the plasma EBV DNA load exceeds 1.7×103 copies/ml, there is a significant increase in the occurrence of severe adverse outcomes, with an AUC of 0.8. These results further confirm the utility of monitoring plasma EBV DNA load as an indicator of poor outcomes in patients with intestinal EBV-infected infection.
This is an initial investigation to assess the EBV DNA load in plasma as a diagnostic and prognostic tool for intestinal EBV infection. This noninvasive approach promises to diminish the reliance on invasive diagnostic interventions for patients with intestinal EBV infection during the initial diagnosis and subsequent follow-up and holds particular significance for diagnosing and differentiating intestinal diseases associated with EBV. Nonetheless, our study has several limitations. First, our research did not explore the diagnostic and prognostic utility of other types of blood samples, such as whole blood or PBMCs, for intestinal EBV infection. This omission leaves a gap in our understanding of the optimal blood sample type for the accurate diagnosis and prognosis of intestinal EBV infection. Future studies should address this gap by comparing the effectiveness of EBV DNA quantification in different types of blood samples. Second, the retrospective, single-center nature of our study, coupled with a limited sample size, introduces potential biases and limits the generalizability of our findings. To mitigate these limitations and validate the proposed cut-off values for plasma EBV DNA levels, extensive multicenter studies with larger cohorts are essential. Third, the sensitivity of our study was relatively low. To address this limitation, future studies should incorporate additional biomarkers, such as EBV antibody levels and inflammatory markers, as well as other factors, including clinical characteristics and histopathological features, which could collectively enhance the overall diagnostic and prognostic accuracy of plasma EBV DNA load in intestinal EBV infection. Lastly, IBD and PILPD patients constituted the majority of the subjects in this study. Thus, our data do not rule out intestinal EBV infection in patients with other EBV-associated diseases who did not undergo colonoscopy for intestinal EBER-ISH. Studies on a greater variety of study populations with other EBV-associated diseases are needed to evaluate intestinal EBV infection.
The conclusions drawn from this investigation reinforce the importance of plasma EBV DNA quantification in the detection and outcome prediction of intestinal EBV infection. Specifically, the cutoff values of EBV DNA in the plasma at 9.21×101 and 6.77×101 copies/mL facilitate the diagnosis and prognosis of this disease, respectively. This noninvasive method provides robust evidence for the management of intestinal EBV infection. Detection of EBV DNA using various blood samples and larger-scale multicenter studies will be pivotal in advancing the clinical use of EBV DNA quantification in peripheral blood for managing intestinal EBV infection.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the ethics board of West China Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The ethics committee/institutional review board waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin because This study is a retrospective analysis.
Author contributions
CM: Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. MJ: Formal analysis, Investigation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. JL: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. ZZ: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YW: Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing. RC: Investigation, Validation, Writing – review & editing. HL: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. JP: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. FY: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YJ: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. LL: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. HZ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Science and Technology Foundation of Sichuan Province of China (2023YFS0279 and 2024YFFK0347).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2024.1526633/full#supplementary-material
References
Cao, X., Dong, A., Kang, G., Wang, X., Duan, L., Hou, H., et al. (2022). Modeling spatial interaction networks of the gut microbiota. Gut. Microbes 14, 2106103. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2022.2106103
Chan, J. Y., Lim, J. Q., Ong, C. K. (2021). Checkpoint immunotherapy for NK/T cell lymphoma-Time for a showdown? Precis. Clin. Med. 4, 70–72. doi: 10.1093/pcmedi/pbab004
Chen, H., Zhang, Y., Jiang, Z., Zhou, W., Cao, Q. (2016). A case report of NK-cell lymphoproliferative disease with a wide involvement of digestive tract develop into Epstein-Barr virus associated NK/T cell lymphoma in an immunocompetent patient. Med. (Baltimore). 95, e3176. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000003176
Chen, L., Wang, Y., Zhou, H., Liang, Y., Zhu, F., Zhou, G. (2024). The new insights of hyperbaric oxygen therapy: focus on inflammatory bowel disease. Precis. Clin. Med. 7, pbae001. doi: 10.1093/pcmedi/pbae001
Chen, Y., Xiao, L., Zhou, M., Zhang, H. (2024). The microbiota: a crucial mediator in gut homeostasis and colonization resistance. Front. Microbiol. 15. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1417864
Cohen, J. I., Kimura, H., Nakamura, S., Ko, Y. H., Jaffe, E. S. (2009). Epstein-Barr virus-associated lymphoproliferative disease in non-immunocompromised hosts: a status report and summary of an international meeting, 8-9 September 2008. Ann. Oncol. 20, 1472–1482. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdp064
Dang, Y., Ma, C., Chen, K., Chen, Y., Jiang, M., Hu, K., et al. (2023). The effects of a high-fat diet on inflammatory bowel disease. Biomolecules 13, 905. doi: 10.3390/biom13060905
de Francisco, R., Castaño-García, A., Martínez-González, S., Pérez-Martínez, I., González-Huerta, A. J., Morais, L. R., et al. (2018). Impact of Epstein-Barr virus serological status on clinical outcomes in adult patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 48, 723–730. doi: 10.1111/apt.14933
Dimitroulia, E., Pitiriga, V. C., Piperaki, E. T., Spanakis, N. E., Tsakris, A. (2013). Inflammatory bowel disease exacerbation associated with Epstein-Barr virus infection. Dis. Colon. Rectum. 56, 322–327. doi: 10.1097/DCR.0b013e31827cd02c
Ford, A. C., Peyrin-Biroulet, L. (2013). Opportunistic infections with anti-tumor necrosis factor-α therapy in inflammatory bowel disease: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 108, 1268–1276. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2013.138
Gomollón, F., Dignass, A., Annese, V., Tilg, H., Van Assche, G., Lindsay, J. O., et al. (2017). 3rd European evidence-based consensus on the diagnosis and management of Crohn’s disease 2016: part 1: diagnosis and medical management. J. Crohns. Colitis. 11, 3–25. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjw168
Hohaus, S., Santangelo, R., Giachelia, M., Vannata, B., Massini, G., Cuccaro, A., et al. (2011). The viral load of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DNA in peripheral blood predicts for biological and clinical characteristics in Hodgkin lymphoma. Clin. Cancer. Res. 17, 2885–2892. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-10-3327
Hosomi, S., Watanabe, K., Nishida, Y., Yamagami, H., Yukawa, T., Otani, K., et al. (2018). Combined infection of human herpes viruses: A risk factor for subsequent colectomy in ulcerative colitis. Inflamm. Bowel. Dis. 24, 1307–1315. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izy005
Hui, E. P., Li, W. F., Ma, B. B., Lam, W. K. J., Chan, K. C. A., Mo, F., et al. (2020). Integrating postradiotherapy plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA and TNM stage for risk stratification of nasopharyngeal carcinoma to adjuvant therapy. Ann. Oncol. 31, 769–779. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.03.289
Ito, Y., Suzuki, M., Kawada, J., Kimura, H. (2016). Diagnostic values for the viral load in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with chronic active Epstein-Barr virus disease. J. Infect. Chemother. 22, 268–271. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2015.11.002
Kanakry, J. A., Hegde, A. M., Durand, C. M., Massie, A. B., Greer, A. E., Ambinder, R. F., et al. (2016). The clinical significance of EBV DNA in the plasma and peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with or without EBV diseases. Blood 127, 2007–2017. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-09-672030
Kanakry, J. A., Li, H., Gellert, L. L., Lemas, M. V., Hsieh, W. S., Hong, F., et al. (2013). Plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA predicts outcome in advanced Hodgkin lymphoma: correlative analysis from a large North American cooperative group trial. Blood 121, 3547–3553. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-09-454694
Karlitz, J. J., Li, S. T., Holman, R. P., Rice, M. C. (2011). EBV-associated colitis mimicking IBD in an immunocompetent individual. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 8, 50–54. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2010.192
Lapsia, S., Koganti, S., Spadaro, S., Rajapakse, R., Chawla, A., Bhaduri-McIntosh, S. (2016). Anti-TNFα therapy for inflammatory bowel diseases is associated with Epstein-Barr virus lytic activation. J. Med. Virol. 88, 312–318. doi: 10.1002/jmv.24331
Lennon, P., Crotty, M., Fenton, J. E. (2015). Infectious mononucleosis. BMJ 350, h1825. doi: 10.1136/bmj.h1825
Li, L., Cheng, R., Wu, Y., Lin, H., Gan, H., Zhang, H. (2024). Diagnosis and management of inflammatory bowel disease. J. Evid. Based. Med. 17, 409–433. doi: 10.1111/jebm.12626
Liang, J. H., Lu, T. X., Tian, T., Wang, L., Fan, L., Xu, J., et al. (2015). Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DNA in whole blood as a superior prognostic and monitoring factor than EBV-encoded small RNA in situ hybridization in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 21, 596–602. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2015.02.017
López, C., Burkhardt, B., Chan, J. K. C., Leoncini, L., Mbulaiteye, S. M., Ogwang, M. D., et al. (2022). Burkitt lymphoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 8, 78. doi: 10.1038/s41572-022-00404-3
Lou, P. J., Jacky Lam, W. K., Hsu, W. L., Pfeiffer, R. M., Yu, K. J., Chan, C. M. L., et al. (2023). Performance and operational feasibility of Epstein-Barr virus-based screening for detection of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: direct comparison of two alternative approaches. J. Clin. Oncol. 41, 4257–4266. doi: 10.1200/jco.22.01979
Ludvigsen, L. U. P., Andersen, A. S., Hamilton-Dutoit, S., Jensen-Fangel, S., Bøttger, P., Handberg, K. J., et al. (2023). A prospective evaluation of the diagnostic potential of EBV-DNA in plasma and whole blood. J. Clin. Virol. 167, 105579. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2023.105579
Magro, F., Gionchetti, P., Eliakim, R., Ardizzone, S., Armuzzi, A., Barreiro-de Acosta, M., et al. (2017). Third European evidence-based consensus on diagnosis and management of ulcerative colitis. Part 1: definitions, diagnosis, extra-intestinal manifestations, pregnancy, cancer surveillance, surgery, and Ileo-anal Pouch disorders. J. Crohns. Colitis. 11, 649–670. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjx008
Magro, F., Santos-Antunes, J., Albuquerque, A., Vilas-Boas, F., Macedo, G. N., Nazareth, N., et al. (2013). Epstein-Barr virus in inflammatory bowel disease-correlation with different therapeutic regimens. Inflamm. Bowel. Dis. 19, 1710–1716. doi: 10.1097/MIB.0b013e318281f31c
Montes-Mojarro, I. A., Kim, W. Y., Fend, F., Quintanilla-Martinez, L. (2020). Epstein - Barr virus positive T and NK-cell lymphoproliferations: Morphological features and differential diagnosis. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 37, 32–46. doi: 10.1053/j.semdp.2019.12.004
Nissen, L. H., Nagtegaal, I. D., de Jong, D. J., Kievit, W., Derikx, L. A., Groenen, P. J., et al. (2015). Epstein-Barr virus in inflammatory bowel disease: the spectrum of intestinal lymphoproliferative disorders. J. Crohns. Colitis. 9, 398–403. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjv040
Pezhouh, M. K., Miller, J. A., Sharma, R., Borzik, D., Eze, O., Waters, K., et al. (2018). Refractory inflammatory bowel disease: is there a role for Epstein-Barr virus? A case-controlled study using highly sensitive Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small RNA1 in situ hybridization. Hum. Pathol. 82, 187–192. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2018.08.001
Pu, D., Yao, Y., Zhou, C., Liu, R., Wang, Z., Liu, Y., et al. (2024). FMT rescues mice from DSS-induced colitis in a STING-dependent manner. Gut. Microbes 16, 2397879. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2024.2397879
Qiu, M. Z., He, C. Y., Lu, S. X., Guan, W. L., Wang, F., Wang, X. J., et al. (2020). Prospective observation: Clinical utility of plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA load in EBV-associated gastric carcinoma patients. Int. J. Cancer. 146, 272–280. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32490
Rizzo, A. G., Orlando, A., Gallo, E., Bisanti, A., Sferrazza, S., Montalbano, L. M., et al. (2017). Is Epstein-Barr virus infection associated with the pathogenesis of microscopic colitis? J. Clin. Virol. 97, 1–3. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2017.10.009
Shen, Z., Hu, L., Yao, M., He, C., Liu, Q., Wang, F., et al. (2022). Disparity analysis and prognostic value of pretreatment whole blood Epstein-Barr virus DNA load and Epstein-Barr encoding region status in lymphomas: A retrospective multicenter study in Huaihai Lymphoma Working Group. Int. J. Cancer. 150, 327–334. doi: 10.1002/ijc.33802
Song, J., Zhu, K., Wang, X., Yang, Q., Yu, S., Zhang, Y., et al. (2023). Utility of clinical metagenomics in diagnosing Malignancies in a cohort of patients with Epstein-Barr virus positivity. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 13. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1211732
Tsai, D. E., Luskin, M. R., Kremer, B. E., Chung, A. K., Arnoldi, S., Paralkar, V. R., et al. (2015). A pilot trial of quantitative Epstein-Barr virus polymerase chain reaction in patients undergoing treatment for their Malignancy: potential use of Epstein-Barr virus polymerase chain reaction in multiple cancer types. Leuk. Lymphoma. 56, 1530–1532. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2014.963577
Wang, W., Chen, X., Pan, J., Zhang, X., Zhang, L. (2022). Epstein-Barr virus and human cytomegalovirus infection in intestinal mucosa of Chinese patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Front. Microbiol. 13. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.915453
Wang, Y., Li, Y., Meng, X., Duan, X., Wang, M., Chen, W., et al. (2018). Epstein-Barr virus-associated T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder presenting as chronic diarrhea and intestinal bleeding: A case report. Front. Immunol. 9. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02583
Wang, Z., Zhang, W., Luo, C., Zhu, M., Zhen, Y., Mu, J., et al. (2018). Primary intestinal Epstein-Barr virus-associated natural killer/T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder: A disease mimicking inflammatory bowel disease. J. Crohns. Colitis. 12, 896–904. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjy043
Weiss, L. M., Chen, Y. Y. (2013). EBER in situ hybridization for Epstein-Barr virus. Methods Mol. Biol. 999, 223–230. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-357-2_16
Wong, K. C. W., Hui, E. P., Lo, K. W., Lam, W. K. J., Johnson, D., Li, L., et al. (2021). Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: an evolving paradigm. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 18, 679–695. doi: 10.1038/s41571-021-00524-x
Xu, S., Chen, H., Zu, X., Hao, X., Feng, R., Zhang, S., et al. (2020). Epstein-Barr virus infection in ulcerative colitis: a clinicopathologic study from a Chinese area. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 13, 1756284820930124. doi: 10.1177/1756284820930124
Ye, Y., Xiao, S., Zhao, J., Shi, X., Zheng, R., Wang, X., et al. (2019). Consensus on tissue detection and pathological diagnosis of intestinal EB virus infection. Chi. J. Dig. 39, 433–437. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-1432.2019.07.001
Ye, Z., Chen, L., Zhong, H., Cao, L., Fu, P., Xu, J. (2023). Epidemiology and clinical characteristics of Epstein-Barr virus infection among children in Shanghai, China 2017-2022. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 13. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1139068
Young, L. S., Yap, L. F., Murray, P. G. (2016). Epstein-Barr virus: more than 50 years old and still providing surprises. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 16, 789–802. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2016.92
Yu, S., Yang, Q., Wu, J., Zhu, M., Ai, J., Zhang, H., et al. (2021). Clinical application of Epstein-Barr virus DNA loads in Epstein-Barr virus-associated diseases: A cohort study. J. Infect. 82, 105–111. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.11.027
Zeng, Z., Jiang, M., Li, X., Yuan, J., Zhang, H. (2023). Precision medicine in inflammatory bowel disease. Precis. Clin. Med. 6, pbad033. doi: 10.1093/pcmedi/pbad033
Zhou, J. Q., Zeng, L., Zhang, Q., Wu, X. Y., Zhang, M. L., Jing, X. T., et al. (2020a). Clinical features of Epstein-Barr virus in the intestinal mucosa and blood of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Saudi. J. Gastroenterol. 26, 312–320. doi: 10.4103/sjg.SJG_30_20
Keywords: Epstein-Barr virus DNA load, diagnosis, prognosis, inflammatory bowel diseases, primary intestinal lymphoproliferative diseases, intestinal Epstein-Barr Virus infection
Citation: Ma C, Jiang M, Li J, Zeng Z, Wu Y, Cheng R, Lin H, Pang J, Yin F, Jia Y, Li L and Zhang H (2025) Plasma Epstein-Barr Virus DNA load for diagnostic and prognostic assessment in intestinal Epstein-Barr Virus infection. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 14:1526633. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1526633
Received: 12 November 2024; Accepted: 16 December 2024;
Published: 07 January 2025.
Edited by:
Ariadna Petronela Fildan, Ovidius University, RomaniaReviewed by:
Tatina Todorova, Medical University of Varna, BulgariaShigao Huang, Air Force Medical University, China
Copyright © 2025 Ma, Jiang, Li, Zeng, Wu, Cheng, Lin, Pang, Yin, Jia, Li and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hu Zhang, emhhbmdodUBzY3UuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Chunxiang Ma
Chunxiang Ma Mingshan Jiang
Mingshan Jiang Jiaxin Li1,2,3†
Jiaxin Li1,2,3† Zhen Zeng
Zhen Zeng Hao Lin
Hao Lin Lili Li
Lili Li Hu Zhang
Hu Zhang