- 1'College of Mechanics, Changchun Institute of Technology, Changchun, China
- 2Engineering and Technology Center, The Fourth Medical College of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, China
- 3School of Chemistry, Harbin Normal University, Harbin, China
With the development of computer technology and theoretical chemistry, the speed and accuracy of first-principles calculations have significantly improved. Using first-principles calculations to predict new topological materials is a hot research topic in theoretical and computational chemistry. In this work, we focus on a well-known material, sodium chloride (NaCl), and propose that the triple point (TP), quadratic contact triple point (QCTP), linear and quadratic nodal lines can be found in the phonon dispersion of NaCl with Fm
Introduction
The recent rapid development in topological materials (Kong and Cui, 2011; Cava et al., 2013; Banik et al., 2018; Kumar et al., 2020; Li and Wei, 2021) makes chemists expect these materials to solve the current challenges in quantum chemistry. A series of topological materials, including topological insulators (Müchler et al., 2012; Bradlyn et al., 2017; Kou et al., 2017; Martín Pendás et al., 2019; Isaeva and Ruck, 2020), spin-gapless semiconductors (Gao et al., 2016; Wang et al., 2016; Wang, 2017; Sun et al., 2020; Yue et al., 2020), and topological semimetals/metals (Zhou et al., 2018a; Schoop et al., 2018; Xu et al., 2020a; Klemenz et al., 2020; Zhao et al., 2020), were predicted by researchers, and some of them are confirmed in experiments. Among them, topological semimetals/metals (Zhong et al., 2016; Zhang et al., 2018; Jin et al., 2019a; Jin et al., 2019b; He et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2020a; Wang et al., 2020b; Xu et al., 2020b; Guo et al., 2020; Jin et al., 2021) always have nontrivial band crossings in their electronic band structures. In addition to their potential applications in technology, they also provide a platform for the study of basic quasiparticles in low cost experiments.
Recently, parallel to electrons, topological concepts have been extended to boson systems such as phonons in crystal materials, classical elastic waves in macroscopic artificial phonon crystals, and magnetic oscillators in magnets. Especially important is that the topological phonon in crystal materials (Jin et al., 2018; Liu et al., 2019; Zheng et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2020; Xie et al., 2021) can provide a potential prospect for regulating heat transfer and electron-phonon interaction. It should be emphasized that the phonon is not limited by the principle of Pauli incompatibility, which means that the experimental detection can be carried out in the whole frequency region of the phonon spectrum.
This work will focus on a famous realistic material, sodium chloride (NaCl). NaCl is with the Fm
Methods
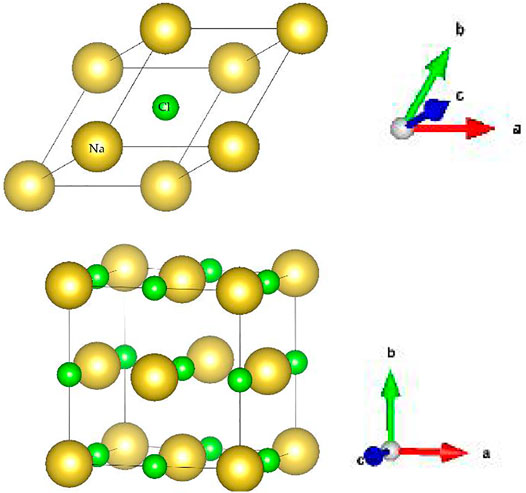
The crystal structure of Fm
Calculated Phonon Dispersion and the Related Topological Signatures
In Figure 2, we plotted the three-dimensional BZ and some high symmetry points, X, K, W, Y, L, and
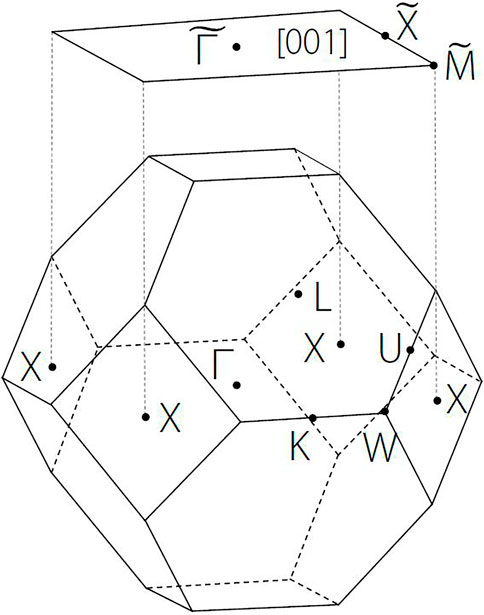
FIGURE 2. Three-dimensional Brillouin zone (BZ) and the two-dimensional (001) surface BZ. The X, K, W, Y, L, Γ are the symmetry points of 3D BZ. Γ, X, and X points are projected to
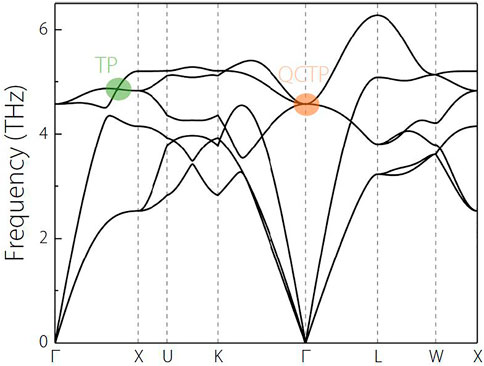
Moreover, from Figure 3, one obtains the following information: 1) Along the
One may wonder whether the doubly degenerate band along the
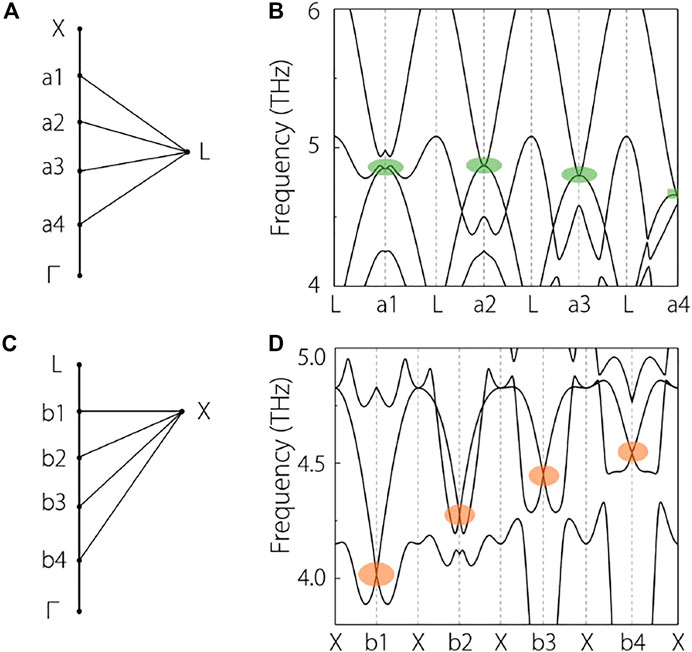
FIGURE 4. (A), (C) some selected symmetry points along the X-
A summary of this section is shown as follow: NaCl phonon hosts a QCTP at the
Calculated Surface States on (001) Surface BZ
In this section, we come to study the project surface states of the [001] NaCl phonons. As shown in Figure 2, we selected some symmetry points,
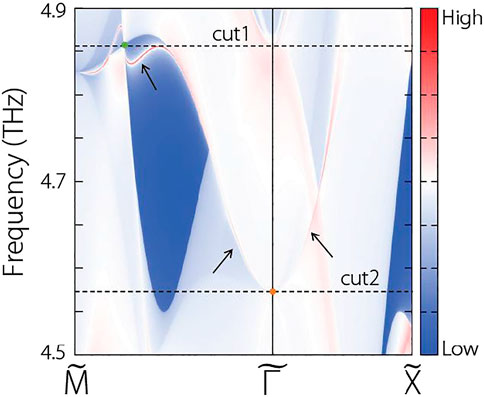
For clarity, we also exhibit the iso-frequency surface contours at 4.86 THz and 4.57 THz in Figure 6A,B, respectively. In Figure 6A, the positions of the projected TP and the connected surface states are marked by a green dot and black arrows, respectively. In Figure 6B, the positions of the projected QCTP and the connected surface states are marked by a black dot and black arrows, respectively. The projected TP/QCTP connected surface states are visible.
Summary
In this study, we proposed the topological signatures of the NaCl’s phonon dispersion. A systematic theoretical investigation found that this material hosts quadratic and linear nodal lines, TP and QCTP in its phonon dispersion. The QCTP is located at the Γ position, the TP is along the X-
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author Contributions
LZ, and FF: conceptualization, methodology, software, formal analysis, data curation, and writing. KW, LC, HL, and LZ: investigation, funding, and project administration. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
This work is supported by Topic Foundation of Changchun Institute of Technology (Grant No. 320200040), Young People Foundation of Changchun Institute of Technology (Grant No. 320200033), Doctor Foundation of Changchun Institute of Technology 2021, Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (Grant No. LH 2020H067), Heilongjiang Postdoctoral Program (LBH-Q16173), Science and Technology Program of Academy of Medical Sciences of Heilongjiang Province (Grant No. 201805), Research Foundation of Education Bureau of Jilin Province (Grant No. JJKH20210666KJ).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
1https://materialsproject.org/materials/mp-22862/
References
Abrahams, S. C., and Bernstein, J. L. (1965). Accuracy of an Automatic Diffractometer. Measurement of the Sodium Chloride Structure Factors. Acta Crystallogr. 18 (5), 926–932. doi:10.1107/s0365110x65002244
Banik, A., Roychowdhury, S., and Biswas, K. (2018). The Journey of Tin Chalcogenides towards High-Performance Thermoelectrics and Topological Materials. Chem. Commun. 54 (50), 6573–6590. doi:10.1039/c8cc02230e
Bradlyn, B., Elcoro, L., Cano, J., Vergniory, M. G., Wang, Z., Felser, C., et al. (2017). Topological Quantum Chemistry. Nature 547 (7663), 298–305. doi:10.1038/nature23268
Cava, R. J., Ji, H., Fuccillo, M. K., Gibson, Q. D., and Hor, Y. S. (2013). Crystal Structure and Chemistry of Topological Insulators. J. Mater. Chem. C 1 (19), 3176–3189. doi:10.1039/c3tc30186a
Chang, T. R., Pletikosic, I., Kong, T., Bian, G., Huang, A., Denlinger, J., et al. (2019). Realization of a Type‐II Nodal‐Line Semimetal in Mg3Bi2. Adv. Sci. 6 (4), 1800897. doi:10.1002/advs.201800897
Chen, H., Zhang, S., Jiang, W., Zhang, C., Guo, H., Liu, Z., et al. (2018). Prediction of Two-Dimensional Nodal-Line Semimetals in a Carbon Nitride Covalent Network. J. Mater. Chem. A 6 (24), 11252–11259. doi:10.1039/c8ta02555j
Gao, G., Ding, G., Li, J., Yao, K., Wu, M., and Qian, M. (2016). Monolayer MXenes: Promising Half-Metals and Spin Gapless Semiconductors. Nanoscale 8 (16), 8986–8994. doi:10.1039/c6nr01333c
Guo, C., Zhao, B., Huang, D., and Fan, S. (2020). Radiative thermal Router Based on Tunable Magnetic Weyl Semimetals. ACS Photon. 7 (11), 3257–3263. doi:10.1021/acsphotonics.0c01376
He, T., Zhang, X., Meng, W., Jin, L., Dai, X., and Liu, G. (2019). Topological Nodal Lines and Nodal Points in the Antiferromagnetic Material β-Fe2PO5. J. Mater. Chem. C 7 (40), 12657–12663. doi:10.1039/c9tc04046c
Hu, J., Wu, W., Zhong, C., Liu, N., Ouyang, C., Yang, H. Y., et al. (2019). Three-dimensional Honeycomb Carbon: Junction Line Distortion and Novel Emergent Fermions. Carbon 141, 417–426. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2018.09.027
Isaeva, A., and Ruck, M. (2020). Crystal Chemistry and Bonding Patterns of Bismuth-Based Topological Insulators. Inorg. Chem. 59 (6), 3437–3451. doi:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.9b03461
Jin, L., Wang, L., Zhang, X., Liu, Y., Dai, X., Gao, H., et al. (2021). Fully Spin-Polarized Weyl Fermions and In/out-Of-Plane Quantum Anomalous Hall Effects in a Two-Dimensional D0 Ferromagnet. Nanoscale 13 (11), 5901–5909. doi:10.1039/d0nr07556f
Jin, L., Zhang, X., Dai, X., Liu, H., Chen, G., and Liu, G. (2019). Centrosymmetric Li2NaN: a superior Topological Electronic Material with Critical-type Triply Degenerate Nodal Points. J. Mater. Chem. C 7 (5), 1316–1320. doi:10.1039/c8tc05930f
Jin, L., Zhang, X., He, T., Meng, W., Dai, X., and Liu, G. (2019). Topological Nodal Line State in Superconducting NaAlSi Compound. J. Mater. Chem. C 7 (34), 10694–10699. doi:10.1039/c9tc03464a
Jin, Y., Wang, R., and Xu, H. (2018). Recipe for Dirac Phonon States with a Quantized valley berry Phase in Two-Dimensional Hexagonal Lattices. Nano Lett. 18 (12), 7755–7760. doi:10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b03492
Kirby, R. J., Ferrenti, A., Weinberg, C., Klemenz, S., Oudah, M., Lei, S., et al. (2020). Transient Drude Response Dominates Near-Infrared Pump-Probe Reflectivity in Nodal-Line Semimetals ZrSiS and ZrSiSe. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 11 (15), 6105–6111. doi:10.1021/acs.jpclett.0c01377
Klemenz, S., Hay, A. K., Teicher, S. M. L., Topp, A., Cano, J., and Schoop, L. M. (2020). The Role of Delocalized Chemical Bonding in Square-Net-Based Topological Semimetals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142 (13), 6350–6359. doi:10.1021/jacs.0c01227
Kong, D., and Cui, Y. (2011). Opportunities in Chemistry and Materials Science for Topological Insulators and Their Nanostructures. Nat. Chem. 3 (11), 845–849. doi:10.1038/nchem.1171
Kou, L., Ma, Y., Sun, Z., Heine, T., and Chen, C. (2017). Two-dimensional Topological Insulators: Progress and Prospects. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 8 (8), 1905–1919. doi:10.1021/acs.jpclett.7b00222
Kumar, N., Guin, S. N., Manna, K., Shekhar, C., and Felser, C. (2020). Topological Quantum Materials from the Viewpoint of Chemistry. Chem. Rev. 121 (5), 2780–2815. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c00732
Li, C. Z., Wang, A. Q., Li, C., Zheng, W. Z., Brinkman, A., Yu, D. P., et al. (2020). Fermi-arc Supercurrent Oscillations in Dirac Semimetal Josephson Junctions. Nat. Commun. 11 (1), 1150–1157. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-15010-8
Li, Y., Xia, J., and Srivastava, V. (2020). The Tetragonal Monoxide of Platinum: a New Platform for Investigating Nodal-Line and Nodal-point Semimetallic Behavior. Front. Chem. 8, 704. doi:10.3389/fchem.2020.00704
Li, Z., and Wei, B. (2021). Topological Materials and Topologically Engineered Materials: Properties, Synthesis, and Applications for Energy Conversion and Storage. J. Mater. Chem. A 9 (3), 1297–1313. doi:10.1039/d0ta11072h
Liu, Q.-B., Fu, H.-H., Xu, G., Yu, R., and Wu, R. (2019). Categories of Phononic Topological Weyl Open Nodal Lines and a Potential Material Candidate: Rb2Sn2O3. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 10 (14), 4045–4050. doi:10.1021/acs.jpclett.9b01159
Liu, Q. B., Qian, Y., Fu, H. H., and Wang, Z. (2020). Symmetry-enforced Weyl Phonons. npj Comput. Mater. 6 (1), 1–6. doi:10.1038/s41524-020-00358-8
Martín Pendás, A., Contreras-García, J., Pinilla, F., Mella, J. D., Cardenas, C., and Muñoz, F. (2019). A Chemical Theory of Topological Insulators. Chem. Commun. 55 (82), 12281–12287. doi:10.1039/c9cc04054d
Meng, W., Liu, Y., Zhang, X., Dai, X., and Liu, G. (2020). A Nonsymmorphic-Symmetry-Protected Hourglass Weyl Node, Hybrid Weyl Node, Nodal Surface, and Dirac Nodal Line in Pd4X (X = S, Se) Compounds. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 22 (39), 22399–22407. doi:10.1039/d0cp03686b
Morali, N., Batabyal, R., Nag, P. K., Liu, E., Xu, Q., Sun, Y., et al. (2019). Fermi-arc Diversity on Surface Terminations of the Magnetic Weyl Semimetal Co3Sn2S2. Science 365 (6459), 1286–1291. doi:10.1126/science.aav2334
Müchler, L., Zhang, H., Chadov, S., Yan, B., Casper, F., Kübler, J., et al. (2012). Topological Insulators from a Chemist's Perspective. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51 (29), 7221–7225. doi:10.1002/anie.201202480
Schoop, L. M., Pielnhofer, F., and Lotsch, B. V. (2018). Chemical Principles of Topological Semimetals. Chem. Mater. 30 (10), 3155–3176. doi:10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b05133
Sun, Q., Ma, Y., and Kioussis, N. (2020). Two-dimensional Dirac Spin-Gapless Semiconductors with Tunable Perpendicular Magnetic Anisotropy and a Robust Quantum Anomalous Hall Effect. Mater. Horiz. 7 (8), 2071–2077. doi:10.1039/d0mh00396d
Tian, L., Liu, Y., Yu, W. W., Zhang, X., and Liu, G. (2021). Triple Degenerate point in Three Dimensions: Theory and Realization. Phys. Rev. B 104 (4), 045137. doi:10.1103/physrevb.104.045137
Togo, A., and Tanaka, I. (2015). First Principles Phonon Calculations in Materials Science. Scripta Materialia 108, 1–5. doi:10.1016/j.scriptamat.2015.07.021
Wang, J. R., Li, W., and Zhang, C. J. (2020). Possible Instabilities in Quadratic and Cubic Nodal-Line Fermion Systems with Correlated Interactions. Phys. Rev. B 102 (8), 085132. doi:10.1103/physrevb.102.085132
Wang, S., and Yang, B. (2021). Dirac Nodal Line Semimetal of Three-Dimensional Cross-Linked Graphene Network as Anode Materials for Li-Ion Battery beyond Graphite. ACS Appl. Energ. Mater. 4 (3), 2091–2097. doi:10.1021/acsaem.0c02408
Wang, X.-L. (2017). Dirac Spin-Gapless Semiconductors: Promising Platforms for Massless and Dissipationless Spintronics and New (Quantum) Anomalous Spin Hall Effects. Natl. Sci. Rev. 4 (2), 252–257. doi:10.1093/nsr/nww069
Wang, X., Cheng, Z., Wang, J., Wang, X.-L., and Liu, G. (2016). Recent Advances in the Heusler Based Spin-Gapless Semiconductors. J. Mater. Chem. C 4 (30), 7176–7192. doi:10.1039/c6tc01343k
Wang, X., Ding, G., Cheng, Z., Surucu, G., Wang, X.-L., and Yang, T. (2020). Novel Topological Nodal Lines and Exotic Drum-head-like Surface States in Synthesized CsCl-type Binary alloy TiOs. J. Adv. Res. 22, 137–144. doi:10.1016/j.jare.2019.12.001
Wang, X., Ding, G., Cheng, Z., Surucu, G., Wang, X.-L., and Yang, T. (2020). Rich Topological Nodal Line Bulk States Together with Drum-head-like Surface States in NaAlGe with Anti-PbFCl Type Structure. J. Adv. Res. 23, 95–100. doi:10.1016/j.jare.2020.01.017
Wu, Q., Zhang, S., Song, H.-F., Troyer, M., and Soluyanov, A. A. (2018). WannierTools: An Open-Source Software Package for Novel Topological Materials. Comput. Phys. Commun. 224, 405–416. doi:10.1016/j.cpc.2017.09.033
Xie, C., Liu, Y., Zhang, Z., Zhou, F., Yang, T., Kuang, M., et al. (2021). Sixfold Degenerate Nodal-point Phonons: Symmetry Analysis and Materials Realization. Phys. Rev. B 104 (4), 045148. doi:10.1103/physrevb.104.045148
Xu, L., Zhang, X., Meng, W., He, T., Liu, Y., Dai, X., et al. (2020). Centrosymmetric TiS as a Novel Topological Electronic Material with Coexisting Type-I, Type-II and Hybrid Nodal Line States. J. Mater. Chem. C 8 (40), 14109–14116. doi:10.1039/d0tc03600e
Xu, S.-Y., Liu, C., Kushwaha, S. K., Sankar, R., Krizan, J. W., Belopolski, I., et al. (2015). Observation of Fermi Arc Surface States in a Topological Metal. Science 347 (6219), 294–298. doi:10.1126/science.1256742
Xu, Y., Elcoro, L., Song, Z.-D., Wieder, B. J., Vergniory, M. G., Regnault, N., et al. (2020). High-throughput Calculations of Magnetic Topological Materials. Nature 586 (7831), 702–707. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2837-0
Materials Project (2021). Available at: https://materialsproject.org/materials/mp-22862/ (Accessed October 23, 2021).
Yan, L., Liu, P.-F., Bo, T., Zhang, J., Tang, M.-H., Xiao, Y.-G., et al. (2019). Emergence of Superconductivity in a Dirac Nodal-Line Cu2Si Monolayer: Ab Initio Calculations. J. Mater. Chem. C 7 (35), 10926–10932. doi:10.1039/c9tc03740c
Yu, Z.-M., Wu, W., Sheng, X.-L., Zhao, Y. X., and Yang, S. A. (2019). Quadratic and Cubic Nodal Lines Stabilized by Crystalline Symmetry. Phys. Rev. B 99 (12), 121106. doi:10.1103/physrevb.99.121106
Yue, Z., Li, Z., Sang, L., and Wang, X. (2020). Spin‐Gapless Semiconductors. Small 16 (31), 1905155. doi:10.1002/smll.201905155
Zhang, X., Guo, R., Jin, L., Dai, X., and Liu, G. (2018). Intermetallic Ca3Pb: a Topological Zero-Dimensional Electride Material. J. Mater. Chem. C 6 (3), 575–581. doi:10.1039/c7tc04989g
Zhao, Z., Zhang, Z., and Guo, W. (2020). A Family of All Sp2-Bonded Carbon Allotropes of Topological Semimetals with Strain-Robust Nodal-Lines. J. Mater. Chem. C 8 (5), 1548–1555. doi:10.1039/c9tc05470g
Zheng, B., Xia, B., Wang, R., Zhao, J., Chen, Z., Zhao, Y., et al. (2019). Tunable Ferromagnetic Weyl Fermions from a Hybrid Nodal Ring. npj Comput. Mater. 5 (1), 1–7. doi:10.1038/s41524-019-0214-z
Zhong, C., Chen, Y., Xie, Y., Yang, S. A., Cohen, M. L., and Zhang, S. B. (2016). Towards Three-Dimensional Weyl-Surface Semimetals in Graphene Networks. Nanoscale 8 (13), 7232–7239. doi:10.1039/c6nr00882h
Zhou, P., Ma, Z. S., and Sun, L. Z. (2018). Coexistence of Open and Closed Type Nodal Line Topological Semimetals in Two Dimensional B2C. J. Mater. Chem. C 6 (5), 1206–1214. doi:10.1039/c7tc05095j
Zhou, P., Ma, Z. S., and Sun, L. Z. (2018). Coexistence of Open and Closed Type Nodal Line Topological Semimetals in Two Dimensional B2C. J. Mater. Chem. C 6 (5), 1206–1214. doi:10.1039/c7tc05095j
Keywords: DFT, first-principles calculations, phonon dispersion, surface state, NaCl
Citation: Zhang L, Fang F, Cheng L, Lin H and Wang K (2021) Obvious Surface States Connecting to the Projected Triple Points in NaCl’s Phonon Dispersion. Front. Chem. 9:789522. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.789522
Received: 05 October 2021; Accepted: 18 October 2021;
Published: 15 November 2021.
Edited by:
Junjie He, Charles University, CzechiaReviewed by:
Zhimin Wu, Chongqing Normal University, ChinaMinquan Kuang, Southwest University, China
Copyright © 2021 Zhang, Fang, Cheng, Lin and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kai Wang, d2FuZ2thaUBocmJtdS5lZHUuY24=; Li Zhang, bGl6aGFuZ0BjY2l0LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Li Zhang
Li Zhang Fang Fang2†
Fang Fang2† Huiming Lin
Huiming Lin Kai Wang
Kai Wang