
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Chem. , 20 April 2018
Sec. Green and Sustainable Chemistry
Volume 6 - 2018 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2018.00124
This article is part of the Research Topic Nano-(bio)catalysis in lignocellulosic biomass valorization View all 12 articles
 Sabina Ion1
Sabina Ion1 Cristina Opris1
Cristina Opris1 Bogdan Cojocaru1
Bogdan Cojocaru1 Madalina Tudorache1*
Madalina Tudorache1* Irina Zgura2
Irina Zgura2 Aurelian C. Galca3
Aurelian C. Galca3 Adina M. Bodescu4
Adina M. Bodescu4 Madalin Enache5
Madalin Enache5 Gabriel-Mihai Maria5
Gabriel-Mihai Maria5 Vasile I. Parvulescu1*
Vasile I. Parvulescu1*A novel and efficient one-pot system for green production of artificial lignin bio-composites has been developed. Monolignols such as sinapyl (SA) and coniferyl (CA) alcohols were linked together with caffeic acid (CafAc) affording a polymeric network similar with natural lignin. The interaction of the dissolved SA/CA with CafAc already bound on a solid support (SC2/SC6-CafAc) allowed the attachment of the polymeric product direct on the support surface (SC2/SC6-CafAc-L1 and SC2/SC6-CafAc-L2, from CA and SA, respectively). Accordingly, this procedure offers the advantage of a simultaneous polymer production and deposition. Chemically, oxi-copolymerization of phenolic derivatives (SA/CA and CAfAc) was performed with H2O2 as oxidation reagent using peroxidase enzyme (2-1B mutant of versatile peroxidase from Pleurotus eryngii) as catalyst. The system performance reached a maximum of conversion for SA and CA of 71.1 and 49.8%, respectively. The conversion is affected by the system polarity as resulted from the addition of a co-solvent (e.g., MeOH, EtOH, or THF). The chemical structure, morphology, and properties of the bio-composites surface were investigated using different techniques, e.g., FTIR, TPD-NH3, TGA, contact angle, and SEM. Thus, it was demonstrated that the SA monolignol favored bio-composites with a dense polymeric surface, high acidity, and low hydrophobicity, while CA allowed the production of thinner polymeric layers with high hydrophobicity.
Together with cellulose and hemicellulose, lignin is one of the most abundant natural polymers (Zakzeski et al., 2010). As an effect of the excessive valorization of the natural resources, the pulp-paper and bio-refining industries are important providers of lignins (Lora and Glasser, 2002). However, the papermaking industry produces annually over 50 million tons of lignin wastes that are mainly used as an energy source (by direct combustion). Today, only 2 wt% of it is used for the polymeric industry (e.g., production of phenolic resins, polyurethane foams, bio-dispersants, or epoxy resins) (Gosselink et al., 2004b). Additionally, the wastes of the paper-pulp industry generate serious environmental pollution concerns. So that, an improvement of the market competitiveness of bio-refining industry is necessary. Accordingly, new perspectives for the valorization of the lignin are required.
The general perception on the lignin is that of a “renewable chemical resource” formed from the assembling of functionalized aromatic entities with phenolic hydroxyl, alcoholic hydroxyl, carboxyl, or methoxy groups (Xiong et al., 2015; Aro and Fatehi, 2017). It presents an amorphous polymeric structure assumed to derive from up to three monolignols, e.g., coniferyl alcohol (CA), synapyl alcohol (SA), and coumaryl alcohol. These monolignols are incorporated in phenylpropanoid units expressed in varied modes such as guaiacyl, syringyl, and p-hydroxyphenyl connected by ether and carbon-carbon bonds in a complex three dimensional polymeric network (Nair et al., 2014). Thus, what is named lignin corresponds to a material with a large variety of chemical structures in which the above mentioned entities exist in various proportions. The differences are the direct consequence of its origin (type of the plant species, climate, geographical location) and the extraction process (Gosselink et al., 2004a).
As a bio-polymer, there are many potential value-added applications of lignin with significant impact on industry (Lee and Wendisch, 2017). Derivatization of lignin is often chosen as alternative leading to functionalized bio-polymers with role of the dispersant for cement, pesticide, coal-water slurry, rubber-based material, component of animal feed, surfactants, additive in oil drilling, stabilizers in colloidal suspensions, etc (Xiong et al., 2015; Aro and Fatehi, 2017). The lignin derivatives may also acquire antioxidant, antiviral, antibiotic, and/or anticarcinogenic activities (Yamamoto et al., 1997; Vinardell et al., 2008; Nair et al., 2014). Lignin has been used as alternative to phenol in phenolic resins and also in the composition of thermoplastic polyesters, polyurethanes, active carbons, and carbon fibers (Stewart, 2008; Thanh Binh et al., 2009; Nair et al., 2014). Additionally, lignin-based composites appeared as another low cost eco-friendly reinforcement attractive alternative (Morandim-Giannetti et al., 2012; Pupure et al., 2013; Qian et al., 2014; Thakur et al., 2014). They confirmed as important ingredients for composites with various properties like thermoplastic polymers (Pucciariello et al., 2004; Barzegari et al., 2013), thermosetting polymers (Yin et al., 2012; Stanzione et al., 2013), rubbers (Setua et al., 2000; Kramárová et al., 2007), or foam-based materials (Del Saz-Orozco et al., 2012; Luo et al., 2013). For this purpose, lignin and its derivatives were incorporated in bio-composites using both chemical or/and physical methods leading to homogeneous lignin particles (Nair et al., 2014) or colloidal spheres produced through self-assembly of acetylated lignin (Qian et al., 2014). However, such a valorization of lignin is still restricted due to two main reasons: its relative low reactivity and high heterogeneity of the polymeric mixture (Qu et al., 2015). Therefore, in the last years several chemical methods have been reported to enhance lignin reactivity, e.g., methylation, demethylation, acetylation, etc (Hu et al., 2011). Additionally, the lignin modification has been achieved via catalytic and solvent-free methods (e.g., graft copolymerization of lactides to lignin catalyzed by triazabicyclodecenes) (Chung et al., 2013). However, the heterogeneity of the polymeric mixture of lignin is still a challenge today.
In this study, we investigated the production of lignin-composites (bio-composites) using monolignol fractions (e.g., SA or CA) with the aim to find another route for the valorization of lignin. There are evidences that lignin can be efficiently disrupted into a cocktail of monomers and oligomers (Lee et al., 2013; Opris et al., 2016, 2017). The produced fragments can be re-combined leading to an artificial lignin structure with enhanced homogeneity compared to the original lignin (Opris et al., 2018). In this study, particles functionalized with CafAc were used as solid supports allowing the synthesis of bio-composites. Therefore, monolignols can be directly oxi-polymerized on the particles surface involving the CafAc as co-monomer. Accordingly, the coverage process was called oxi-copolymerization. The use of monolignols instead of whole lignin molecule ensures a better control of the composition of the polymeric layer providing to a good structural homogeneity of the polymeric material.
Usually, the functionalization of the particles surface (e.g. silica particles) by either physical or chemical methods requires a prior modification before covering with the polymeric layer. Most of the modifiers are derived from the fossil resources increasing the cost of these materials but also the toxicity (Zou et al., 2008). In this study, the particles surface (methacrylate) was functionalized with a natural modifier, i.e., CafAc (CafAc occurs frequently in fruits, grains, Salvia species) (Hao et al., 2015). Also, the polymeric layer (artificial lignin) covering the surface is bio-derived, mimicking the original lignin. In accordance to its characteristic structure and properties, the lignin-based polymer may afford the required modification of the particles for further bio-applications (e.g., carrier/support for enzymes). Additionally, the lignin bio-composites can provide an important example of a high value utilization of lignin residues.
The oxi-copolymerization of monolignols reported in this study for the synthesis of bio-composites was designed as a biocatalytic process where a peroxidase enzyme assisted the oxidation of both monolignols (SA or CA) and CafAc by means of H2O2. The developed system acts based on an one-pot approach combining the oxi-copolymerization of SA/CA with CafAc, and the attachment of the resulted polymer on the support surface. From our best knowledge, it is the first time when a lignin-composite (bio-composite) with controlled and reproducible composition is prepared based on one-pot approach. Additionally, the influence of a co-solvent (e.g., MeOH, EtOH, THF) on the oxi-copolymerization process has also been investigated. The production of the bio-composites was monitored using spectrophotometric as well as Folin-Ciocalteu analysis. Also, detailed characterization of the lignin-composites was performed using different techniques, e.g., FTIR, TPD-NH3, TGA, contact angle, and SEM.
The oxi-copolymerization process was performed with 2-1B mutant of versatile peroxidase original from Pleurotus eryngii, expressed in Saccharomyces cerevisae (12.95 U mL−1 enzyme activity) (Garcia-Ruiz et al., 2012; Molina-Espeja et al., 2014, 2015). 2-1B mutant was provided by Dr. Miguel Alcalde (Institute of Catalysis, CSIC, Madrid, Spain). The solid support of bio-composites (SC2–amino C2 methacrylate, ECR8309F and SC6–amino C6 methacrylate, ECR8409F) was kindly offered by the Purolite Life Sciences Company. Both supports were constituted from the beads (150–300 μm of diameter) originally functionalized with -NH2 groups using methacrylate cross-linkers.
Ten milli molars of PBS (phosphate buffer saline) solution (pH = 7.4) was used as aqueous buffer solution. Its composition consisted of: 8 g NaCl, 0.2 g KCl, 1.43 g Na2HPO4 × 2H2O and 0.34 g KH2PO4 in 1 L distilled water. 10 mM MES (2-(N-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid) buffer (pH = 4.7) was prepared by dissolving a corresponding MES mass in distilled water followed of NaOH addition for adjusting the pH value of the solution.
CA, SA, CafAc, 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide (ECD), 30 wt% solution of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), methanol (MeOH), ethanol (EtOH), and tetrahydrofuran (THF) were of analytic purity and purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Stock solutions of monolignols (e.g., CA and SA) with concentration of 10 mg mL−1 were prepared in MeOH.
For the attachment of the lignin polymer, the solid supports SC2 and SC6 were functionalized with CafAc in order to ensure the phenolic structures on the particles surface. 0.2 g of SC2/SC6 support were dispersed in 10 mL solution containing 10 mg mL−1 CafAc in MES (10 mM, pH = 4.7). 0.96 g of EDC was added in the suspension under continuous shaking for activating the -COOH groups of CafAc in order to interact with—NH2 groups on the support. Coupling of CafAc on support surface was performed over the night, at room temperature under gentle agitation. Then, the functionalized particles (SC2-CafAc and SC6-CafAc) were separated by centrifugation and washed several times with MES buffer and distilled water.
The bio-composites construction was performed in one-pot system by enzyme oxi-copolymerization of monolignols (e.g., CA or SA) directly on the surface of the previously prepared supports (SC2/SC6 functionalized with CafAc, section SC2/SC6 functionalization). One hundred microliters of monolignol stock solution (10 mg mL−1 SA/CA in MeOH) were diluted with 300 μL PBS (10 mM, pH 7.4). 10 mg of functionalized support (SC2-CafAc or SC6-CafAc) were added in the solution followed by the addition of 10 μL H2O2 (30%) and 50 μL 2-1B peroxidase mutant (H2O2:enzyme molar ratio of 1760:1). The reaction mixture was incubated at 40°C in a thermo-shaker (100 rpm) over night. For comparison, the monolignols polymerization was also performed in the absence of the functionalized support (homogeneous system).
The separation of the bio-composite was performed using a set up protocol detailed in Scheme 1. The reacted mixture was treated with 300 μL MeOH for biocatalyst precipitation and solubilization of unattached oligomers. The centrifugation of the new mixture allowed the separation of the two phases: the liquid phase (supernatant) with unreacted monolignols and/or oligolignols, and the solid phase containing the bio-composites and precipitated biocatalyst. The supernatant was analyzed using UV-Vis and Folin-Ciocalteu methods. While the UV-Vis analysis allowed the determination of the aromatic content, the Folin-Ciocalteu method permeated the detection of the phenolic -OH groups. The solid phase was washed consecutively with PBS and distilled water in order to remove the precipitated enzyme (biocatalyst) from the bio-composites surface. The centrifugation step allowed the separation of the bio-composites and the recovery of the enzyme as a PBS solution. Bio-composite surface was investigated based on Folin-Ciocalteu approach.
UV-Vis method was used for the determination of mono-/oligo- lignols (phenolic derivatives) in the liquid phase (Scheme 1). The sample absorbance was read at 280 nm with a Specord 250 (Analytik Jena). The conversion of monolignols based on the oxi-copolymerization process was calculated using the absorbance of the solutions before and after the reaction. Folin-Ciocalteu analysis was performed for the determination of free -OH groups on the aromatic ring (Singleton et al., 1999). The protocol was adapted for the investigation of the bio-composites and the liquid phase (Scheme 1). Twenty microliters of sample solution (supernatant or 10 mg/mL bio-composites in MeOH) were dispersed in 1.5 mL of distilled water and the resulted mixture was enreached with 100 μL Folin-Ciocalteu reagent and 300 μL saturated solution of sodium carbonate as supporting medium (adjusting the pH of solution to a basic value). After 2 h incubation time, the mixture was centrifuged and the supernatant absorbance was read at 765 nm.
GPC analysis was performed for the determination of the average molecular weight of the polymers produced in the absence of the functionalized support. The analysis approach was detailed in our previous report (Opris et al., 2018). Thus, the GPC analysis was carried out using an Agilent Technologies instrument (Model 1260) equipped with two columns (Zorbax PSM 60-S, 6.5 × 250 mm, 5 μm, and Polargel-M, 300 × 7.5 mm) and a multidetection unit (Refractive Index, Light Scattering, and Viscosity detectors). Experimental conditions were set up at 1 mL min−1 THF as mobile phase, 100 μL injection volume of sample, and temperature of the detectors and columns of 35°C. The calibration of the GPC system was performed using polystyrene standards in the range of 162–10,000 g mol−1. The Agilent GPC/SEC Software (Version 1.1, Agilent Technologies) was utilized for the determination of the average molecular weight (MW).
FTIR spectra of bio-composites and simple/functionalized supports were recorded using Vertex 70 (Bruker, Ettlingen, Germany) spectrophotometer equipped with the Total Attenuated Reflectance cell in the range of 600–2000 cm−1. Sixteen scans were collected with a resolution of 4 cm−1 in the range of 600–4000 cm−1.
The total acidity was evaluated by temperature-programmed desorption of ammonia (TPD-NH3) using a Micromeritics Chemisorb 2750 instrument. Before NH3 desorption, the samples were heated to 80°C (20°C min−1) in 30 mL high pure Helium flow. Subsequently, the samples were cooled down to room temperature in helium flow. NH3 adsorption was performed under ambient conditions and saturation for about 60 min in a flow of 10% ammonia in Helium (30 mL min−1). Then, the samples were purged in a Helium flow until a constant baseline level was attained. The desorption of NH3 was carried out with the linear heating rate (10°C min−1) in a flow of Helium until 300°C.
The termo-gravimetric analysis (TGA) was performed with a Shimadzu instrument (SDT Q600) in order to determine the thermo stability of the bio-composite according to the original/functionalized support. Maximum 10 mg of sample were used. The analysis was carried out at increasing temperature with a rate of 10°C min−1 in the range of 30–600°C under N2 atmosphere.
Static contact angle of bio-composites was measured with a Drop Shape Analysis System, model DSA100 (Kruss GmbH). The sample was placed on a horizontal stage, under the tip of a water-dispensing disposable blunt-end stainless steel needle with an outer diameter of 0.5 mm. The water droplet (1 μL) was delivered on the sample surface by the needle attached to a syringe pump controlled with a PC (through DSA3® software supplied with the instrument). The viewing camera for taking the picture was positioned to observe the droplet under an angle of about 2–3° with respect to the plane of the sample surface supporting the droplet. The tests were carried out at room temperature. The contact angle was measured by fitting a polynomial equation of second degree or a circle equation to the shape of the sessile drop. Then, the slope of the tangent to the drop at the liquid-solid vapor interface line was calculated. (Zgura et al., 2010, 2013; Popescu et al., 2011; Duta et al., 2012; Preda et al., 2013).
For scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis, freeze, and dried particles (e.g., bio-composites and original/functionalized supports) were examined using a Jeol instrument (JSM-6610LV). The pretreatment of the samples followed the dispersion of the particles in EtOH solution (30%) and deposition of 10 μL suspension on the microscopic blade covered with gold layer. After EtOH evaporation at room temperature, prepared blades were dried in vacuum followed by metal coating using a sputter coater (Jeol auto fine coater, JFC-1300). SEM investigations were performed under high vacuum conditions.
The concept of the one-pot synthesis of bio-composites has been described above. The oxi-copolymerization of monolignols (e.g., CA or SA) was directly performed on the supports (SC2 and SC6) surface functionalized with CafAc (SC2-CafAc and SC6-CafAc) in the presence of the 2-1B mutant of versatile peroxidase as catalyst using an adapted procedure (Opris et al., 2018). In this study CafAc used as a co-monomer afforded the oxi-copolymerization of monolignols. CA allowed the production of SC2/SC6-CafAc-L1 bio-composite, while the oxi-copolymerization of SA led to SC2/SC6-CafAc-L2.
Under the investigated homogeneous conditions, the oxi-copolymerization of monolignols (SA/CA) and CafAc led to the results presented in Table 1. A higher conversion was achieved for SA compared to CA (65.3 vs. 21.1%) leading to polymers with different molecular weights (3500 and 856 Da for SA and CA, respectively). The affinity of the biocatalyst for the monolignols can be a reasonable explanation of the system behavior. These results are in accordance with the previous report (Opris et al., 2018).
Under heterogeneous conditions, i.e., with SA/CA dissolved in liquid phase, and CafAc attached on the particles (SC2/SC6-CafAc), the monolignols and immobilized CafAc were linked together in a polymeric structure miming the natural lignin directly attached on the particles surface (Table 1). This heterogeneous design allowed to improve the conversion of monolignols compared to homogeneous system keeping the same advantage of SA vs. CA. Different conversions were also determined as a function of the functionalized support (SC2-CafAc and SC6-CafAc) demonstrating that the solid support influenced the co-polymerization process (Table 1).
Important parameters of this process are the loading of the polymeric products on the solid surface and the percent of the oligomers in the residual phase (supernatant, see Scheme 1). To determine these, both the supernatants and bio-composites were analyzed using spectrophotometric (UV-Vis) and Folin-Ciocalteu approaches (F-C) (Scheme 1). Moreover, the results were converted in the concentration of recovered monolignols (i.e., the ratio between the concentration of monolignol in/on residues/bio-composite and initial concentration of monolignol) (Table 2). The relative low difference between the F-C and UV-Vis results can be an indicative for the insignificant content of the oligolignols in the supernatant. Moreover, the UV-Vis results should be interpreted with caution because of the production of quinone derivatives as secondary products of co-oxipolymerization process. For bio-composites, the same measurements evidenced the presence of small concentration of free OH groups (around 10 times lower than in the supernatant). The participation of the OH groups into the formation of the etheric bonds of the synthetic lignin is a plausible explanation.
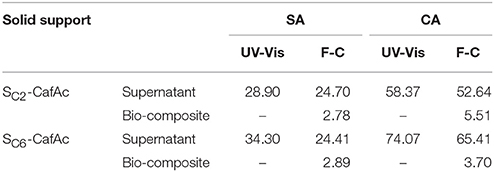
Table 2. Evaluation of supernatant content in monolignols and oligolignols using spectrophotometric (UV-Vis) and Folin-Ciocalteu (F-C) methods (recovered concentration, %).
The effect of the co-solvent (e.g., MeOH, EtOH, THF) has also been evaluated showing a different influence depending on the monolignol type (Figure 1). For SA, the use of MeOH as co-solvent led to better results affording a higher conversion for SC6-CafAc support compared to SC2-CafAc. For CA, the presence of the co-solvent doubled the conversion of monolignols. However, the reproducibility was low, and high standard deviation has been determined for co-solvent (e.g., MeOH, EtOH, THF). In conclusion, poor reproducibility for the bio-composite production using a co-solvent enforces the use of H2O despite of smaller conversions.
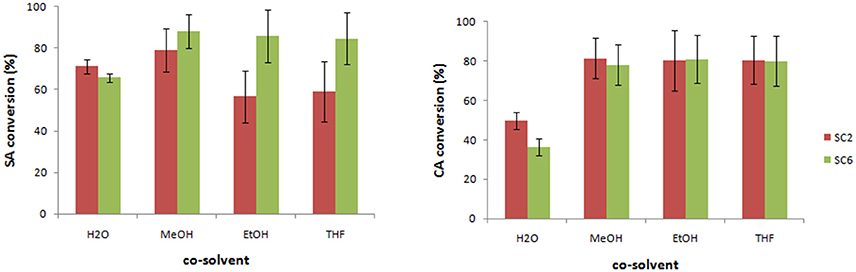
Figure 1. Preparation of the bio-composite in the presence of organic solvent. Experimental conditions: 2 mg/mL monolignol (SA/CA), 1.295 U mL−1 2-1B peroxidase mutant, 0.6% H2O2 20 mg/mL functionalized support for heterogeneous co-polymerization, and 6% added solvent (H2O, MeOH, EtOH, THF) in PBS (10 mM, pH = 7.4); 40°C, 24 h and 100 rpm. (Triplicates analysis were performed).
FTIR analysis confirmed the attachment of the artificial lignin on the support surface during the oxi-copolymerization (Figures S1–S3). Table 3 presents the differences between the spectra collected for SC2-CafAc-L1/L2 and SC6-CafAc-L1/L2, and those of the original/functionalized supports (SC2, SC6, SC2-CafAc and SC6-CafAc). The attachment of the CafAc on the solid support led to a consistent modification of the spectrum (Figure S1). The intensity of the OH band stretching at 3370 cm−1 on the particles surface (SC2/SC6) (Poletto and Zattera, 2013) decreased for SC2/SC6-CafAc. Additionally, new bands occurred at 1041 cm−1 and 1563–1564 cm−1 due to the presence of C-O bonds on the aromatic ring and the formation of amide bonds (CO-NH) by the attachment of CafAc on the support surface. Both functionalized supports (SC2-CafAc and SC6-CafAc) have similar FTIR spectra (Figure S1).
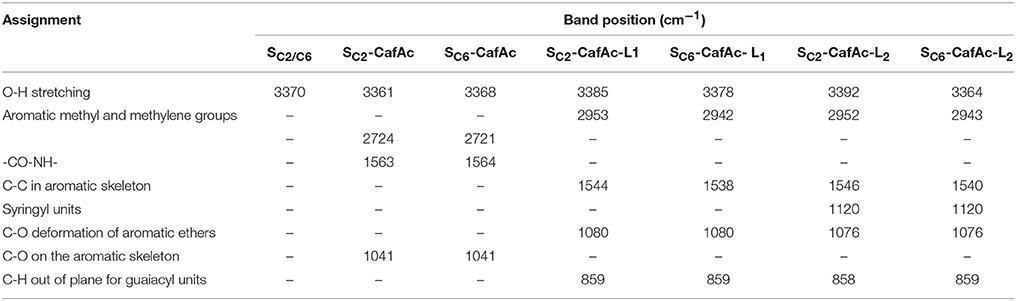
Table 3. Summary of the specific bands observed for bio-composites, original, and functionalized supports.
SC2-CafAc-L1/L2 and SC6-CafAc-L1/L2 presented modified spectra in the regions of 3700–3000 cm−1 and 1200–700 cm−1 compared with SC2-CafAc and SC6-CafAc, respectively (Figure S2). The differences are summarized in Table 3. The shoulder at around 3600 cm−1 is attributed to an aliphatic OH group of the monolignol structure (Poletto and Zattera, 2013), while the new bands at 2952/2953 and 2942/2943 cm−1 were to the C-H stretching vibration of the methyl and methylene groups introduced by the SA and CA monolignols (Xiong et al., 2015). The presence of the aromatic ring has been confirmed by the bands in the range 1538–1546 cm−1. The new band at 1120 cm−1 observed for SC2/SC6-CafAc-L2 represents an evidence of the presence of the syringyl units detected in the polymeric layer of the bio-composites. Guaiacyl units were also detected at low intensity at 858 and 859 cm−1 (Poletto and Zattera, 2013). However, the band at 1264 cm−1 typical for guaiacyl (Poletto and Zattera, 2013; Fitigău et al., 2015) is not visible for SC2/SC6-CafAc-L1 due to a superposition with an already existing band at 1257 cm−1. Poor covering of the support with polymers from CA (Table 1) can represent another reason for the absence of this band. All bio-composites showed also absorbance bands at 1076 and 1080 cm−1 attributed to etheric groups (C-O-C) connecting the aromatic rings (Qu et al., 2015; Xiong et al., 2015). This is also an evidence for the production of the artificial lignin onto the bio-composite surface.
FTIR spectra of bio-composites prepared in the presence of co-solvent showed differences between MeOH and EtOH, on one side, and THF, on the other side (Figure S3). Thus, the presence of MeOH or EtOH led to structures for which the bands at 1076 and 1078 cm−1 were not present anymore while those at 973/949 and 858 cm−1 presented a dramatic decrease in the intensity. These results confirm that MeOH and EtOH inhibit the formation of the artificial lignin structures, and especially of the guaiacyl units. So, the increased conversion for the oxi-copolymerization in the presence of an organic solvent does not correspond to the formation of lignolic structures (i.e., guaiacyl units).
The acidity of the bio-composites has been evaluated from TPD-NH3 measurements (Table 4). The bio-composites incorporating CA have similar acidic properties with the functionalized support confirming the conservation of the phenolic OH group (NH3 desorption peaks at 197°C). However, the number of acidic centers has been doubled for the bio-composite showing an enrichment of phenolic OH owing of the synthetic lignin structure. CA and SA led to bio-composites with two different acidity centers (NH3 desorption peaks at 197 and 210°C) that were assigned to phenolic and aliphatic OH groups. Also, the total number of the acid centers was higher for SA polymer than for the corresponding CA-based bio-composite. These results fit the values of the conversion calculated for the oxi-copolymerization of the monolignols (Table 1).
The thermo-stability of produced lignin bio-composites (SC2-CafAc-L1/L2 and SC6-CafAc-L1/L2) compared to the original/functionalized supports (SC2, SC6, SC2-CafAc, SC6-CafAc) has been evaluated in the temperature range of 30–600°C (Figure 2). TGA profiles of bio-composites were quit similar. The mass loss up to 230°C is mainly due to the removal of water (<8 wt%). The differences in the shape of the profiles for the functionalized support and corresponding bio-composite may account the degradation of propanoid chain of the polymer (Strzemiecka et al., 2016). Further heating (230–430°C) corresponded to a larger mass loss (about 45%). This is related to the decomposition of polymeric material linked to the support surface (L1/L2). The heterogeneity of the bio-composite surface (artificial lignin) is confirmed by the different losses in this temperature range. However, an important information provided by these results is the increased thermo-stability as effect of the covering the support with synthetic lignin. This is confirmed by the shift of the thermal effects to higher temperatures in accordance to literature data (Brebu et al., 2013; Brostow et al., 2016; Strzemiecka et al., 2016).
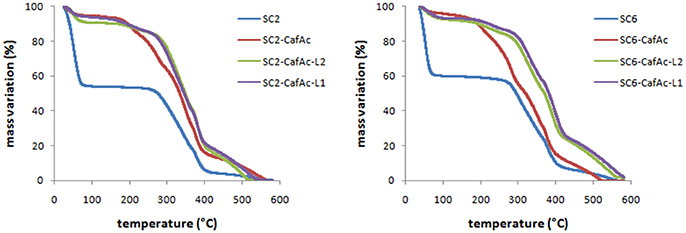
Figure 2. TGA diagrams of the bio-composites (SC2-CafAc-L1/L2 and SC6-CafAc-L1/L2) related to original/functionalized support (SC2, SC6, SC2-CafAc, SC6-CafAc).
The investigation of surface hydrophobicity was performed using contact angle measurements of distilled water onto CafAc-functionalized silica chips (S-CafAc) and corresponding bio-composites (S-CafAc-L1/L2) (Figure 3). The contact angle of the chip (S) was of 29°, while for the bio-composites increased to 63° for CA-based polymer or decreased to 18° for the SA-based polymer. These results indicate an enhancement of the hydrophobicity for the chip surface covered by CA monolignol reported also in the previous literature for natural lignin (Xiong et al., 2015; Salanti et al., 2016). Moreover, the artificial lignin prepared by oxi-copolymerization is more hydrophobic than some natural lignins (e.g., soda lignin from Triticum sp and Saccharumofficiarum with a 35° contact angle) (Buono et al., 2016). SA led to a hydrophilic polymer than the support as an effect of the ratio between phenolic and alkyl OH groups. For L1, the hydrophobicity of the aromatic ring was enforced due to the relative low density of OH confirmed by the TPD-NH3 measurements (Table 4). The hydrophilicity of the L2 surface is also according to TPD-NH3 results (Table 4). The hydrophobicity/hydrophilicity property of bio-composites represents an important characteristics for their further application as support/carrier of biomolecules (e.g., immobilization of lipase enzyme on hydrophobic surface turn on the enzyme in active form; Thomas et al., 2005).
SEM images of bio-composites and original/functionalized supports are presented in Figure 4. The parent particles (SC2 and SC6) presented a smooth surface, while the functionalized particles (SC2/SC6-CafAc) showed roughened morphology. Differences in the morphologies of the bio-composites (SC2/SC6-CafAc-L1/L2) were also induced by the monolignol oxi-copolymerization (the polymeric layer looks more dense for L2 than L1).
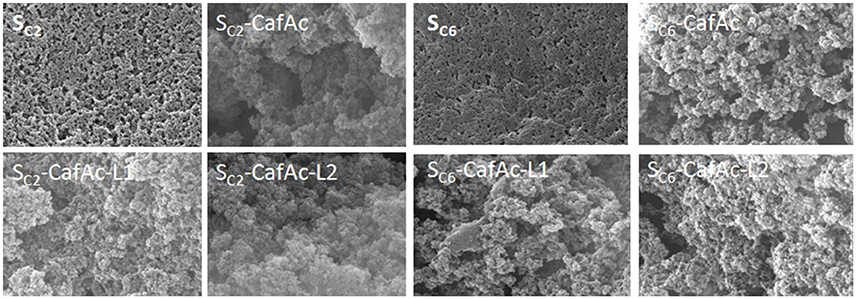
Figure 4. SEM images of the particles with different composition: original particles (SC2 and SC6), CafAc-functionalized particles (SC2/SC6-CafAc), and bio-composites based on CA (SC2/SC6-CafAc-L1), and SA (SC2/SC6-CafAc-L2) oxi-copolymerization.
These results confirm the success of the one-pot approach for the production of lignin bio-composites via an enzyme oxi-copolymerization process. Monolignols such as SA and CA were easily attached on a support surface based on the interaction with immobilized CafAc leading to artificial lignin covering the support surface. SA allowed an advanced polymerization (L2 polymer) and coverage compared to CA (L1 polymer). Accordingly, L1-based bio-composites exhibited higher hydrophobicity than L2, while SA provided a more acidic bio-composite surface. Therefore, the developed protocol allows the synthesis of artificial lignin-based composites with predictable surface properties.
Based on these, the reported work offers a new alternative for the valorization of lignin residues with the production of new bio-composites following a green route. The versatility of the method may offer an easy control of the properties of the prepared bio-composites and an instrument to adjust them to different applications (e.g., support/ carrier for biomolecules).
All authors listed have made a substantial, direct and intellectual contribution to the work, and approved it for publication. SI and CO performed the experiments for the preparation of the bio-composites and also UV-Vis/F-C analysis; BC performed TPD-NH3 analysis; MT coordinated the research study and wrote the manuscript; IZ and AG characterized the bio-composites based on contact angle technique; AB performed FTIR analysis; ME and G-MM performed the SEM analysis and the interpretation of the corresponding results; VP revised and improved the manuscript.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
This work was financially supported by PN III TE program, contract no. 103/2015 and Core project PN-III-16-48-01 from MEN-UEFISCDI. We thank Purolite Life Sciences Company for Lifetech ECR8309F and Lifetech ECR8409F particles. Many thanks to dr. Miguel Alcalde (Institute of Catalysis, CSIC, Madrid, Spain) for 2-1B mutant of versatile peroxidase and dr. ing. Alexandru Branzan (Institute of Biology Bucharest of the Romanian Academy, Romania) for SEM analysis.
The authors are also grateful to the COST Action FP1306 for the financial support and transfer of knowledge.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fchem.2018.00124/full#supplementary-material
Aro, T., and Fatehi, P. (2017). Production and application of lignosulfonates and sulfonated lignin. ChemSusChem 10, 1861–1877. doi: 10.1002/cssc.201700082
Barzegari, M. R., Alemdar, A., Zhang, Y., and Rodrigue, D. (2013). Thermal analysis of highly filled composites of polystyrene with lignin. Polym. Polymer Composites 21, 357–366.
Brebu, M., Tamminen, T., and Spiridon, I. (2013). Thermal degradation of various lignins by TG-MS/FTIR and Py-GC-MS. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 104, 531–539. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2013.05.016
Brostow, W., Datashvili, T., Jiang, P., and Miller, H. (2016). Recycled HDPE reinforced with sol-gel silica modified wood sawdust. Eur. Polym. J. 76, 28–39. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2016.01.015
Buono, P., Duval, A., Verge, P., Averous, L., and Habibi, Y. (2016). New insights on the chemical modification of Lignin: acetylation versus Silylation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 4, 5212–5222. doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b00903
Chung, Y. L., Olsson, J. V., Li, R. J., Frank, C. W., Waymouth, R. M., Billington, S. L., et al. (2013). A renewable lignin-lactide copolymer and application in biobased composites. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 1, 1231–1238. doi: 10.1021/sc4000835
Del Saz-Orozco, B., Oliet, M., Alonso, M. V., Rojo, E., and Rodríguez, F. (2012). Formulation optimization of unreinforced and lignin nanoparticle-reinforced phenolic foams using an analysis of variance approach. Compos. Sci. Technol. 72, 667–674. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2012.01.013
Duta, L., Popescu, A. C., Dorcioman, G., Mihailescu, I. N., Stan, G. E., Zgura, I., et al. (2012). “ZnO thin films deposited on textile material substrates for biomedical applications: ZnO thin films deposited on textiles,” in NATO Science for Peace and Security Series A: Chemistry and Biology, eds A. Vaseashta, E. Braman, and P. Susmann (Dordrecht: Springer), 207–210. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-2488-4_20
Fitigău, I. F., Boeriu, C. G., and Peter, F. (2015). Enzymatic modification of different lignins through oxidative coupling with hydrophilic compounds. Macromol. Symp. 352, 78–86. doi: 10.1002/masy.201400157
Garcia-Ruiz, E., Gonzalez-Perez, D., Ruiz-Dueñas, F. J., Martínez, A. T., and Alcalde, M. (2012). Directed evolution of a temperature-, peroxide- and alkaline pH-tolerant versatile peroxidase. Biochem. J. 441, 487–498. doi: 10.1042/BJ20111199
Gosselink, R. J. A., Abächerli, A., Semke, H., Malherbe, R., Käuper, P., Nadif, A., et al. (2004a). Analytical protocols for characterisation of sulphur-free lignin. Ind. Crops Prod. 19, 271–281. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2003.10.008
Gosselink, R. J. A., de Jong, E., Guran, B., and Abächerli, A. (2004b). Co-ordination network for lignin—standardisation, production and applications adapted to market requirements (EUROLIGNIN). Ind. Crops Prod. 20, 121–129. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2004.04.015
Hao, D. C., Gu, X.-J., and Xiao, P. G. (eds.). (2015). “14 - Phytochemical and biological research of Salvia medicinal resources,” in Medicinal Plants (Cambridge: Woodhead Publishing), 587–639. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-08-100085-4.00001-3
Hu, L., Pan, H., Zhou, Y., and Zhang, M. (2011). Methods to improve lignin's reactivity as a phenol substitute and as replacement for other phenolic compounds: a brief review. Bioresources 6, 3515–3525.
Kramárová, Z., Alexy, P., Chodák, I., Špirk, E., Hudec, I., Košíková, B., et al. (2007). Biopolymers as fillers for rubber blends. Polym. Adv. Technol. 18, 135–140. doi: 10.1002/pat.803
Lee, J. H., and Wendisch, V. F. (2017). Biotechnological production of aromatic compounds of the extended shikimate pathway from renewable biomass. J. Biotechnol. 257, 211–221. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.11.016
Lee, R. A., Bédard, C., Berberi, V., Beauchet, R., and Lavoie, J. M. (2013). UV–Vis as quantification tool for solubilized lignin following a single-shot steam process. Bioresour. Technol. 144(Suppl. C), 658–663. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2013.06.045
Lora, J. H., and Glasser, W. G. (2002). Recent industrial applications of lignin: a sustainable alternative to nonrenewable materials. J. Polym. Environ. 10, 39–48. doi: 10.1023/A:1021070006895
Luo, X., Mohanty, A., and Misra, M. (2013). Lignin as a reactive reinforcing filler for water-blown rigid biofoam composites from soy oil-based polyurethane. Ind. Crops Prod. 47, 13–19. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.01.040
Molina-Espeja, P., Garcia-Ruiz, E., Gonzalez-Perez, D., Ullrich, R., Hofrichter, M., and Alcalde, M. (2014). Directed evolution of unspecific peroxygenase from Agrocybe aegerita. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 80, 3496–3507. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00490-14
Molina-Espeja, P., Ma, S., Mate, D. M., Ludwig, R., and Alcalde, M. (2015). Tandem-yeast expression system for engineering and producing unspecific peroxygenase. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 73–74, 29–33. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2015.03.004
Morandim-Giannetti, A. A., Agnelli, J. A. M., Lanças, B. Z., Magnabosco, R., Casarin, S. A., and Bettini, S. H. P. (2012). Lignin as additive in polypropylene/coir composites: thermal, mechanical and morphological properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 87, 2563–2568. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.11.041
Nair, S. S., Sharma, S., Pu, Y., Sun, Q., Pan, S., Zhu, J. Y., et al. (2014). High shear homogenization of lignin to nanolignin and thermal stability of nanolignin-polyvinyl alcohol blends. ChemSusChem 7, 3513–3520. doi: 10.1002/cssc.201402314
Opris, C., Amanov, N., Parvulescu, V. I., and Tudorache, M. (2018). Peroxidase-based oxidative polymerization of monolignols. Comp. Rendus Chim. 21, 362–368. doi: 10.1016/j.crci.2017.09.002
Opris, C., Cojocaru, B., Gheorghe, N., Tudorache, M., Coman, S. M., Parvulescu, V. I., et al. (2016). Lignin fragmentation over magnetically recyclable composite Co@Nb2O5@Fe3O4 catalysts. J. Catal. 339, 209–227. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2016.04.002
Opris, C., Cojocaru, B., Gheorghe, N., Tudorache, M., Coman, S. M., Parvulescu, V. I., et al. (2017). Lignin fragmentation onto multifunctional Fe3O4@Nb2O5@Co@Re catalysts: the role of the composition and deposition route of rhenium. ACS Catal. 7, 3257–3267. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.6b02915
Poletto, M., and Zattera, A. J. (2013). Materials produced from plant biomass: part III: degradation kinetics and hydrogen bonding in lignin. Mater. Res. 16, 1065–1070. doi: 10.1590/S1516-14392013005000112
Popescu, A. C., Duta, L., Dorcioman, G., Mihailescu, I. N., Stan, G. E., Pasuk, I., et al. (2011). Radical modification of the wetting behavior of textiles coated with ZnO thin films and nanoparticles when changing the ambient pressure in the pulsed laser deposition process. J. Appl. Phys. 110:064321. doi: 10.1063/1.3639297
Preda, N., Enculescu, M., Zgura, I., Socol, M., Matei, E., Vasilache, V., et al. (2013). Superhydrophobic properties of cotton fabrics functionalized with ZnO by electroless deposition. Mater. Chem. Phys. 138, 253–261. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2012.11.054
Pucciariello, R., Villani, V., Bonini, C., D'Auria, M., and Vetere, T. (2004). Physical properties of straw lignin-based polymer blends. Polymer 45, 4159–4169. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2004.03.098
Pupure, L., Varna, J., Joffe, R., and Pupurs, A. (2013). An analysis of the nonlinear behavior of lignin-based flax composites. Mech. Composite Mater. 49, 139–154. doi: 10.1007/s11029-013-9330-x
Qian, Y., Deng, Y., Qiu, X., Li, H., and Yang, D. (2014). Formation of uniform colloidal spheres from lignin, a renewable resource recovered from pulping spent liquor. Green Chem. 16, 2156–2163. doi: 10.1039/c3gc42131g
Qu, Y., Luo, H., Li, H., and Xu, J. (2015). Comparison on structural modification of industrial lignin by wet ball milling and ionic liquid pretreatment. Biotechnol. Rep. 6(Suppl. C), 1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.btre.2014.12.011
Salanti, A., Zoia, L., Zanini, S., and Orlandi, M. (2016). Synthesis and characterization of lignin–silicone hybrid polymers as possible consolidants for decayed wood. Wood Sci. Technol. 50, 117–134. doi: 10.1007/s00226-015-0772-2
Setua, D. K., Shukla, M. K., Nigam, V., Singh, H., and Mathur, G. N. (2000). Lignin reinforced rubber composites. Polymer Composites 21, 988–995. doi: 10.1002/pc.10252
Singleton, V. L., Orthofer, R., and Lamuela-Raventos, R. M. (1999). Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of Folin-Ciocalteu Reagent. Methods Enzymol. 299, 152–178. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(99)99017-1
Stanzione, J. F. III., Giangiulio, P. A., Sadler, J. M., La Scala, J. J., and Wool, R. P. (2013). Lignin-based bio-oil mimic as biobased resin for composite applications. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 1, 419–426. doi: 10.1021/sc3001492
Stewart, D. (2008). Lignin as a base material for materials applications: chemistry, application and economics. Ind. Crops Prod. 27, 202–207. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2007.07.008
Strzemiecka, B., Klapiszewski, Ł., Jamrozik, A., Szalaty, T. J., Matykiewicz, D., Sterzynski, T., et al. (2016). Physicochemical characterization of functional lignin-silica hybrid fillers for potential application in abrasive tools. Materials 9:E517. doi: 10.3390/ma9070517
Thakur, V. K., Thakur, M. K., Raghavan, P., and Kessler, M. R. (2014). Progress in green polymer composites from lignin for multifunctional applications: a review. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2, 1072–1092. doi: 10.1021/sc500087z
Thanh Binh, N. T., Luong, N. D., Kim, D. O., Lee, S. H., Kim, B. J., Lee, Y. S., et al. (2009). Synthesis of lignin-based thermoplastic copolyester using kraft lignin as a macromonomer. Composite Interfaces 16, 923–935. doi: 10.1163/092764409X12477479344485
Thomas, A., Allouche, M., Basyn, F., Brasseur, R., and Kerfelec, B. (2005). Role of the lid hydrophobicity pattern in pancreatic lipase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 40074–40083. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M502123200
Vinardell, M. P., Ugartondo, V., and Mitjans, M. (2008). Potential applications of antioxidant lignins from different sources. Ind. Crops Prod. 27, 220–223. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2007.07.011
Xiong, W., Yang, D., Zhong, R., Li, Y., Zhou, H., and Qiu, X. (2015). Preparation of lignin-based silica composite submicron particles from alkali lignin and sodium silicate in aqueous solution using a direct precipitation method. Ind. Crops Prod. 74, 285–292. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.05.021
Yamamoto, Y., Shirono, H., Kono, K., and Ohashi, Y. (1997). Immunopotentiating activity of the water-soluble lignin rich fraction prepared from lem—the extract of the solid culture medium of Lentinus edodes mycelia Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 61, 1909–1912. doi: 10.1271/bbb.61.1909
Yin, Q., Yang, W., Sun, C., and Di, M. (2012). Preparation and properties of lignin-epoxy resin composite. Bioresources 7, 5737–5748. doi: 10.15376/biores.7.4.5737-5748
Zakzeski, J., Bruijnincx, P. C., Jongerius, A. L., and Weckhuysen, B. M. (2010). The Catalytic valorization of lignin for the production of renewable chemicals. Chem. Rev. 110, 3552–3599. doi: 10.1021/cr900354u
Zgura, I., Beica, T., Mitrofan, I. L., Mateias, C. G., Pirvu, D., and Patrascu, I. (2010). Assessment of the impression materials by investigation of the hydrophilicity. Digest. J. Nanomat. Biostruct. 5, 749–755.
Zgura, I., Moldovan, R., Negrila, C. C., Frunza, S., Cotorobai, V. F., and Frunza, L. (2013). Surface free energy of smooth and dehydroxylated fused quartz from contact angle measurements using some particular organics as probe liquids. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 15, 627–634.
Keywords: bio-composites, oxi-copolymerization, monolignols, peroxidase enzyme, lignin
Citation: Ion S, Opris C, Cojocaru B, Tudorache M, Zgura I, Galca AC, Bodescu AM, Enache M, Maria G-M and Parvulescu VI (2018) One-Pot Enzymatic Production of Lignin-Composites. Front. Chem. 6:124. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2018.00124
Received: 14 December 2017; Accepted: 03 April 2018;
Published: 20 April 2018.
Edited by:
Rafael Luque, Universidad de Córdoba, SpainReviewed by:
Regina De Fatima Peralta Muniz Moreira, Universidade Federal de Santa Catarina, BrazilCopyright © 2018 Ion, Opris, Cojocaru, Tudorache, Zgura, Galca, Bodescu, Enache, Maria and Parvulescu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Madalina Tudorache, bWFkYWxpbmEuc2FuZHVsZXNjdUBnLnVuaWJ1Yy5ybw==
Vasile I. Parvulescu, dmFzaWxlLnBhcnZ1bGVzY3VAZy51bmlidWMucm8=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.