- 1National Local Joint Engineering Research Center for Precision Surgery and Regenerative Medicine, Shaanxi Provincial Center for Regenerative Medicine and Surgical Engineering, First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an, China
- 2Department of General Surgery, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an, China
- 3Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an, China
- 4Department of Oncology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an, China
- 5Department of Pediatrics, First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an, China
A Corrigendum on
MFG-E8 maintains cellular homeostasis by suppressing endoplasmic reticulum stress in pancreatic exocrine acinar cells
by Ren Y, Liu W, Zhang J, Bi J, Fan M, Lv Y, Wu Z, Zhang Y and Wu R (2022). Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9:803876. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.803876
In the original article, there was a mistake in Figures 2, 3 as published. The TEM results in the Sham group in Figure 2A inadvertently used the Sham group of mfge8-KO mice. In Figure 3A, the image of MPO with Vehicle treatment was misused from pancreas in CD11b group. The corrected Figures 2, 3 and its caption appear below:
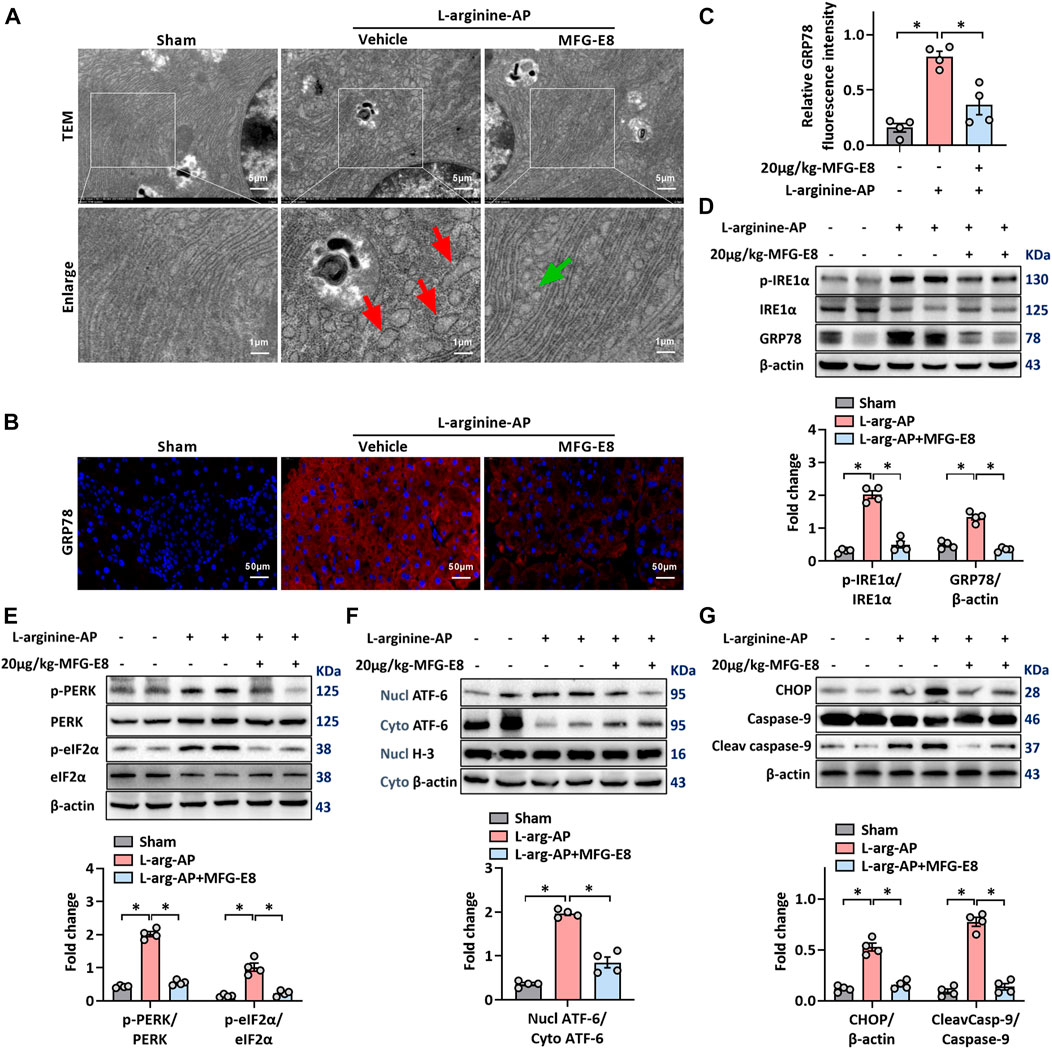
FIGURE 2. Exogenous MFG-E8 alleviates pancreatic ER stress in vivo. In mice, arginine-AP stress was induced by 2 h intraperitoneal injections of 4.0 g/kg L-arginine. At 2 h after the last injection of L-arginine, normal saline (vehicle) or 20 μg/kg MFG-E8 were administered through intraperitoneal injection. The animals were sacrificed at 69 h after MFG-E8 treatment (i.e., 72 h after the first injection of L-arginine). Blood and tissue samples were collected. (A) Ultrastructural alterations in the pancreas (Transmission electron microscopy); (B,C) Representative photos of GRP78 staining and quantitative of GRP78 staining; (D) Western blot analysis of the expression of GRP78, phospho-IRE1α and IRE1α in the pancreas; (E) Western blot analysis of the expression of phospho-PERK, PERK, phospho-eIF2α and eIF2α in the pancreas; (F) Western blot analysis of the expression of nucl-ATF-6, cyto-ATF-6, nucl-H3 and cyto-β-actin in the pancreas; (G) Western blot analysis of the expression of CHOP, caspase-9 and cleaved caspase-9 in the pancreas. n = 4–6/group, error bars indicate the SEM; ∗ p < .05 versus Sham group; #p < .05 versus Vehicle group. MFG-E8, milk fat globule EGF factor 8; AP, acute pancreatitis; GRP78, glucose-regulated protein 78; eIF2α, eukaryotic initiation factor 2α; ATF-6, Activating Transcription Factor 6; CHOP, C/EBP homologous protein; Nucl, nucleus; Cyto, cytoplasm; H-3, histone-3; PERK, PKR-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase.
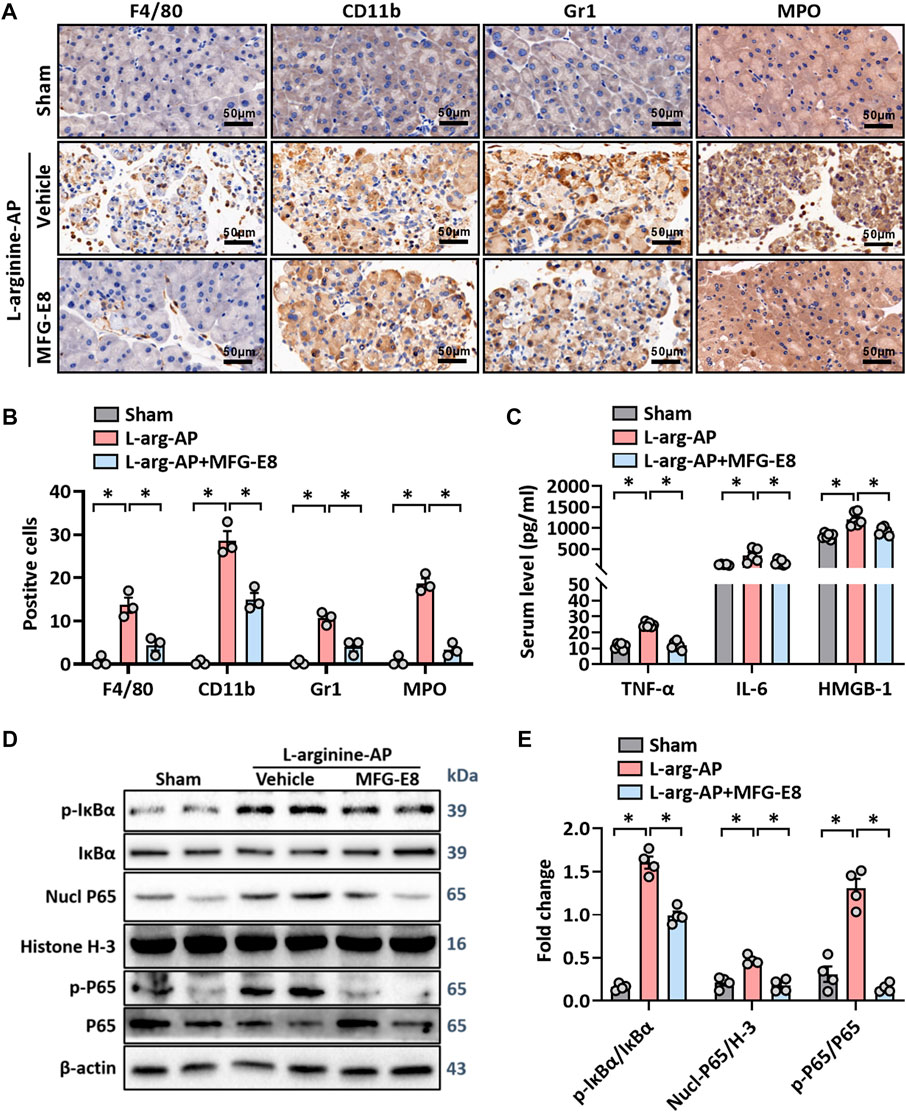
FIGURE 3. MFG-E8 alleviates the inflammatory response in experimental-AP through NF-κB signaling pathway. In mice, arginine-AP stress was induced by 2 h intraperitoneal injections of 4.0 g/kg L-arginine. At 2 h after the last injection of L-arginine, normal saline (vehicle) or 20 μg/kg MFG-E8 were administered through intraperitoneal injection. The animals were sacrificed at 69 h after MFG-E8 treatment (i.e., 72 h after the first injection of L-arginine). Blood and tissue samples were collected. (A) Representative photos of F4/80, CD11b, Gr1 and MPO staining; (B) Quantitative of F4/80, CD11b, Gr1 and MPO staining; (C) Serum TNF-α, IL-6 and HMGB-1 levels; (D,E) Western blot analysis of the expression of phospho-IκBα, IκBα, nucl-P65, cyto-P65, nucl-H3 and cyto-β-actin in the pancreas. n = 4–6/group, error bars indicate the SEM; ∗ p < .05 versus Sham group; #p < .05 versus Vehicle group. MFG-E8, milk fat globule EGF factor 8; AP, acute pancreatitis; MPO, myeloperoxidase; HMGB-1, High mobility group box 1; Nucl, nucleus; Cyto, cytoplasm; H-3, histone-3; IκBα, inhibitor of NF-κB-α; NF-κB p65, Nuclear Factor Kappa-B p65.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: pancreatic exocrine acinar cells, endoplasmic reticulum stress, acute pancreatitis, MFG-E8, αvβ3/5 integrins, FAK-STAT3 pathway
Citation: Ren Y, Liu W, Zhang J, Bi J, Fan M, Lv Y, Wu Z, Zhang Y and Wu R (2023) Corrigendum: MFG-E8 maintains cellular homeostasis by suppressing endoplasmic reticulum stress in pancreatic exocrine acinar cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 10:1121052. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1121052
Received: 11 December 2022; Accepted: 22 December 2022;
Published: 06 January 2023.
Edited and reviewed by:
Yongye Huang, Northeastern University, ChinaCopyright © 2023 Ren, Liu, Zhang, Bi, Fan, Lv, Wu, Zhang and Wu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yuanyuan Zhang, eXVhbnl1YW56aGFuZ0B4anR1LmVkdS5jbg==; Rongqian Wu, cnd1MDAxQG1haWwueGp0dS5lZHUuY24=
 Yifan Ren
Yifan Ren Wuming Liu
Wuming Liu Jia Zhang
Jia Zhang Jianbin Bi1,4
Jianbin Bi1,4 Rongqian Wu
Rongqian Wu