
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
MINI REVIEW article
Front. Cell Dev. Biol., 18 March 2020
Sec. Evolutionary Developmental Biology
Volume 8 - 2020 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.00170
This article is part of the Research TopicEvo Devo Cell by CellView all 8 articles
Developmental gene regulatory networks (GRNs) underpin metazoan embryogenesis and have undergone substantial modification to generate the tremendous variety of animal forms present on Earth today. The nematode Caenorhabditis elegans has been a central model for advancing many important discoveries in fundamental mechanistic biology and, more recently, has provided a strong base from which to explore the evolutionary diversification of GRN architecture and developmental processes in other species. In this short review, we will focus on evolutionary diversification of the GRN for the most ancient of the embryonic germ layers, the endoderm. Early embryogenesis diverges considerably across the phylum Nematoda. Notably, while some species deploy regulative development, more derived species, such as C. elegans, exhibit largely mosaic modes of embryogenesis. Despite the relatively similar morphology of the nematode gut across species, widespread variation has been observed in the signaling inputs that initiate the endoderm GRN, an exemplar of developmental system drift (DSD). We will explore how genetic variation in the endoderm GRN helps to drive DSD at both inter- and intraspecies levels, thereby resulting in a robust developmental system. Comparative studies using divergent nematodes promise to unveil the genetic mechanisms controlling developmental plasticity and provide a paradigm for the principles governing evolutionary modification of an embryonic GRN.
From the moment of fertilization, embryos must follow a highly regulated script that ensures reproducible outcomes, while remaining plastic to accommodate changes that generate morphological diversity. The architectures of the gene regulatory networks (GRNs) are sculpted by, and can greatly influence, evolutionary trajectory, raising central questions in evolutionary developmental biology. How are networks wired in ways that ensure developmental robustness? Which nodes are plastic and which nodes are more rigidly fixed?
The endoderm is the most ancient of the three germ layers in animals and the GATA-driven core regulatory pathway that directs endoderm development is conserved across metazoans, including in the most basal diploblastic animals (Rodaway and Patient, 2001; Martindale et al., 2004; Hashimshony et al., 2015). Thus, understanding the mechanisms that deploy the endoderm GRN is critical to revealing the fundamentals of cell fate acquisition and body plan organization during animal embryogenesis. This brief review will examine evolutionary diversification of the GRN in nematodes. We will discuss developmental system drift (DSD) at both micro- and macroevolutionary scales. Finally, we will visit the developmental hourglass model in relation to endoderm development.
Since Sydney Brenner first introduced a free-living roundworm, Caenorhabditis elegans, to the broad research community, the domesticated laboratory strain, obtained from Bristol, England and named “N2,” has become a key contributor to many important discoveries in developmental, cellular, and molecular biology, owing to its ease of propagation, ready access to genetic analysis, and the plethora of resources available for it, including the complete description of its anatomy (White et al., 1986; Cook et al., 2019) and cell lineage (Sulston and Horvitz, 1977; Sulston et al., 1980, 1983). The potent molecular genetic toolkits available with the system has resulted in identification of a large collection of mutants that have allowed experimentalists to dissect the mechanistic processes that orchestrate development in the animal (Thompson et al., 2013). These discoveries have provided a springboard for understanding the evolutionary steps that result in diversification of developmental mechanisms.
Two major strategies have been taken to investigate evolutionary variation in nematode developmental mechanisms: studies on representative species that span nematode phylogeny (Sommer and Bumbarger, 2012; Haag et al., 2018), and analysis of evolutionarily divergent isolates of one species, C. elegans (Barrière and Félix, 2005). The former strategy has involved both comparative embryology and phylogenomics studies of nematodes arising from distinct clades, revealing deeper changes in both developmental and gene regulatory strategies. These studies have taken advantage of the >50 species spanning the Caenorhabditis genus that have been isolated as well as nematodes from distant clades (1–12), many of which have had their genomes sequenced (Holterman et al., 2006; Kiontke et al., 2011; Sommer and Streit, 2011; Schiffer et al., 2013; Félix et al., 2014; Ferrari et al., 2017; Hiraki et al., 2017; Stevens et al., 2019). In contrast, insights into how endoderm regulatory events occur over shorter evolutionary time-frames have provided a better understanding of how specific steps in the endoderm GRN are tuned during radiation of a species. These latter studies have been facilitated through quantitative genetics approaches, by availing of over 300 wild isolates obtained from different continents over the past decade, whose genomes have been fully sequenced (Andersen et al., 2012; Cook et al., 2016, 2017; Zhao et al., 2018). A recent sampling effort in Hawaii further identified C. elegans strains that show large amount of genetic diversity (Crombie et al., 2019). These rich resources offer a unique and attractive opportunity for both intra- and interspecies comparative studies.
As was first recognized with the nematode Ascaris megalocephala by Theodor Boveri over a century ago (Boveri, 1899), early C. elegans embryogenesis is essentially invariant, resulting in generation of six founder cells (AB, MS, E, C, D, and P4) through a series of asymmetrical cleavages. As is the case with most other nematodes (Malakhov, 1994; Wiegner and Schierenberg, 1998; Houthoofd et al., 2003; Zhao et al., 2008; Schulze and Schierenberg, 2011), the entire C. elegans intestine, is derived clonally from the E blastomere (Sulston et al., 1983), providing a highly tractable system to study cell specification, differentiation and organogenesis. Studies over the past three decades have provided a high-resolution description of the endoderm GRN (reviewed in Maduro and Rothman, 2002; McGhee, 2007; Maduro, 2015, 2017). In brief, maternally provided SKN-1/Nrf activates a zygotically expressed transcriptional cascade comprising a series of GATA-like transcription factors, including the GATA-like factors MED (MesEnDoderm)-1 and MED-2, which bind to a non-canonical RRRAGTATAC site (Broitman-Maduro et al., 2005), and the canonical GATA factors END-3 and END-1. This leads to the activation of ELT-7 and ELT-2, which, together, drive activation of thousands of gut-expressed genes and morphological differentiation of the intestine (Fukushige et al., 1998; McGhee et al., 2009; Sommermann et al., 2010; Dineen et al., 2018). SKN-1 and MED-1/2 also function in the sister of E, MS, to activate mesoderm development (Figure 1).
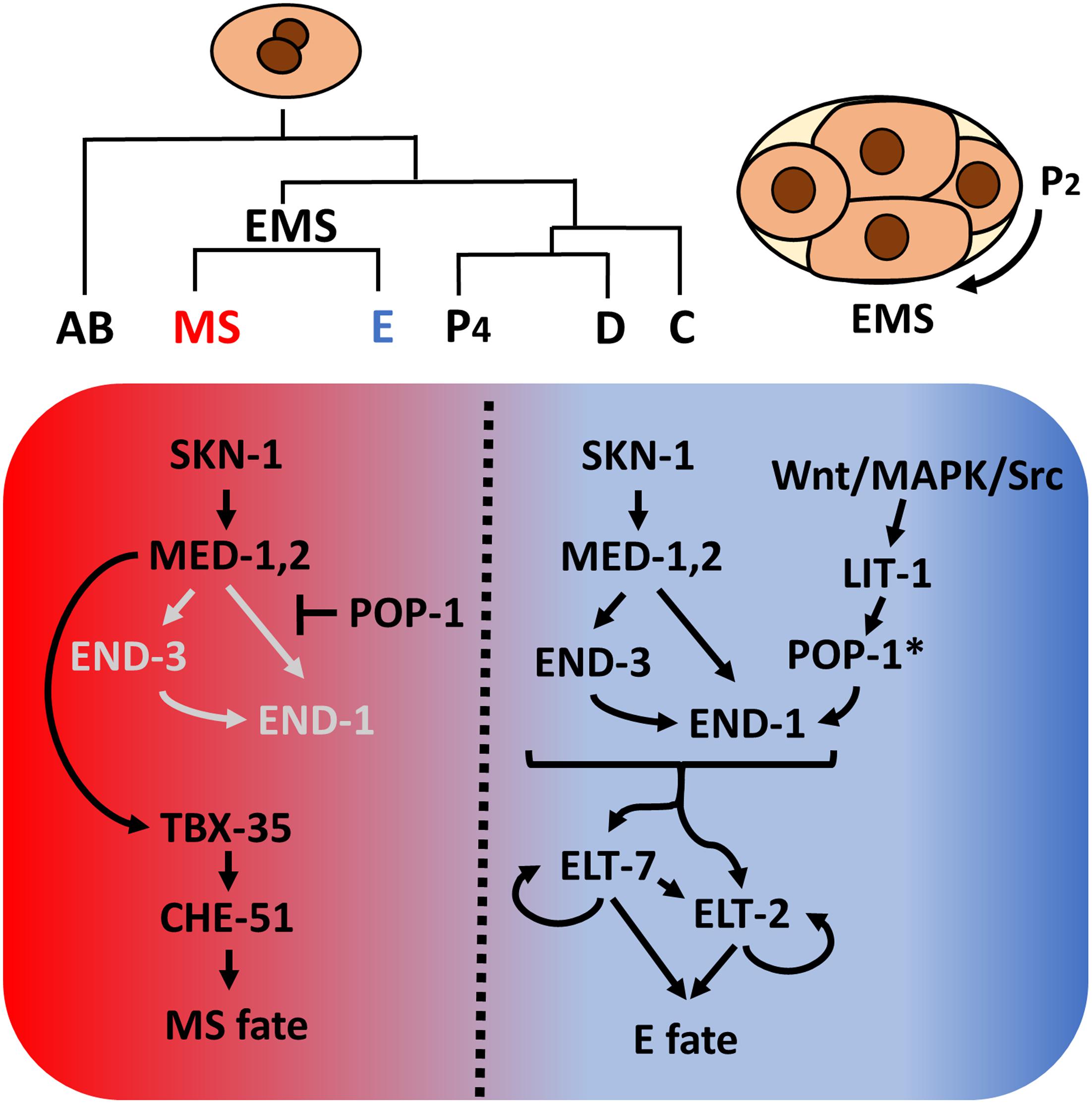
Figure 1. Caenorhabditis elegans founder cells and the endoderm specification network. Asymmetrical cell divisions produce six founder cells, each of which will give rise to specific tissue types. At the four-cell stage, SKN-1 activates the med-1,2 genes, initiating mesendoderm specification. Redundant Wnt/MAPK/Src signaling arising from the neighboring P2 cell polarizes EMS. In the anterior, un-signaled end, POP-1 represses end-1 and end-3 expression while MED-1,2 turn on tbx-35, which in turn specify mesoderm MS fate. In the posterior end, LIT-1 kinase, in response to P2 signals, phosphorylates POP-1 (indicated by *), converting it from a repressor to an activator of endoderm E fate. The two differentiation factors, ELT-7 and ELT-2, once activated, maintain their own expression through autoregulation and regulate thousands of gut genes. In E, Wnt signaling further represses tbx-35 expression (Broitman-Maduro et al., 2006).
Endoderm fate is activated by an inductive cellular interaction: a triply redundant Wnt/MAPK/Src signaling system triggered by signals from the neighboring P2 cell polarizes the mesendodermal EMS cell and subsequently modifies the nucleocytoplasmic distribution and activity of POP-1/Tcf (Maduro et al., 2002; Shetty et al., 2005; Phillips et al., 2007; Owraghi et al., 2010). In the un-signaled MS cell, POP-1 represses end-1 and -3 expression, thereby inhibiting gut fate. In the posterior E cell, the inductive signal results in phosphorylation of POP-1 by LIT-1/Nlk, converting it from a repressor to an activator of E fate. Thus, SKN-1 and POP-1 play a partially redundant role in endoderm specification in C. elegans (Figure 1). In recent years, mutant/RNAi screens, proteomic, and transcriptomic studies revealed many novel regulators implied in endoderm development and embryogenesis (Witze et al., 2009; Du et al., 2014; Sullivan-Brown et al., 2016; Tintori et al., 2016; Dineen et al., 2018; Wiesenfahrt et al., 2018). The elucidation of C. elegans endoderm GRN provides a strong foundation from which to explore the diversification of endoderm GRN in other organisms.
Closely related species in the Elegans supergroup show nearly identical cell lineages to those of C. elegans (Zhao et al., 2008; Levin et al., 2012). Similarly, Pristionchus pacificus, which belongs to clade 9, along with the Caenorhabditis species, shows a similar pattern of early embryonic division, differing mostly in cell cycle timing (Vangestel et al., 2008). Nevertheless, it has been shown that early embryonic development is highly divergent in Nematoda, especially in the basal Enoplae (clades 1 and 2). For example, in Enoplus brevis, only the E lineage is specified in the very early embryo, while the remaining cells become committed later at the 30–60 cell stage (Voronov and Panchin, 1998; Schulze and Schierenberg, 2011). In contrast to Enoplea, perhaps with the exception of Romanomermis culicivorax (clade 2) (Schulze and Schierenberg, 2009), Chromadorea (clades 3–12) contains largely defined cell lineages during early embryogenesis, transitioning from a “regulative” to a more or less “mosaic” pattern of development, although the organization of the founder cells may vary (Dolinski et al., 2001). In the case of Acrobeloides nanus (clade 11), and in sharp contrast to the Elegans group, the founder cells remain multipotent: EMS can become AB, and C can replace EMS at the three-cell stage. Furthermore, unlike in C. elegans, which requires inductive interactions between EMS and P2 cells, endoderm specification in A. nanus appears to occur cell-autonomously, such that isolated EMS, AB, or P2 can give rise to differentiated gut cells and the restriction of cell fate instead depends on the inhibitory interactions between the blastomeres (Wiegner and Schierenberg, 1998, 1999).
While gastrulation in many clades is initiated by the inward movement of two endoderm progenitors on the ventral posterior side of the early embryo following division of the E founder cell, this appears to be a highly derived characteristic that is not typical for protostomes. Interestingly, a basal freshwater nematode, Tobrilus (clade 1), undergoes gastrulation marked by the presence of a large blastocoel and the anterior invagination of endo- and mesodermal precursors (Schierenberg, 2005; Schulze and Schierenberg, 2011; Figure 2). This gastrulation process resembles the classical protostome pattern, in which a collection of cells invaginate at a blastopore that is the future site of the mouth. It should be noted that this is not an inviolable characteristic of protostomes: in some Ecdysozoans, including in Nematomorpha, the sister taxa of Nematoda, gastrulation resembles that of deuterostomes, in which the blastopore forms at the future site of the anus (Montgomery, 1904; Martín-Durán et al., 2012). The invention of the highly derived “phylotypic” pattern of gastrulation seen in C. elegans and in most nematodes, and the transition of a “regulative” to a “mosaic” mechanism of cell fate specification, generally correlate with embryos that undergo rapid development. It is tempting to postulate that increasing reliance on maternal factors during evolution allows for rapid cell cycle and cell specification during early embryogenesis (Wiegner and Schierenberg, 1998; Laugsch and Schierenberg, 2004). This may result in heterochronic (timing) and heterotopic (spatial) shift in the developmental program, leading to the different modes of specification and gastrulation (Figure 2; Joshi and Rothman, 2005).
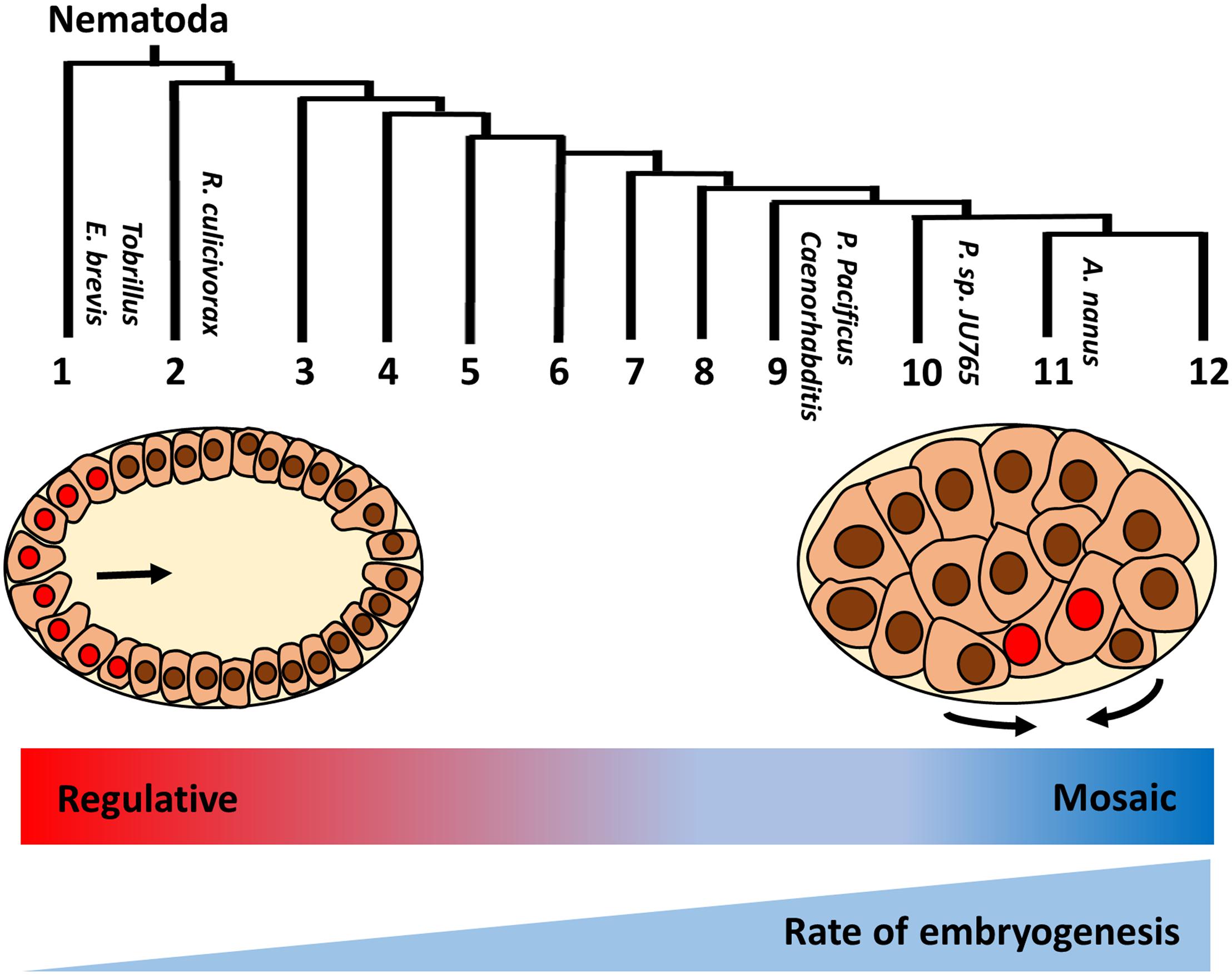
Figure 2. Variation in early embryogenesis in Nematoda. Nematodes are classified into 12 clades based on rDNA sequence (Holterman et al., 2006). Basal Tobrillus undergoes a “canonical” protostome-like gastrulation characterized by invagination of eight endoderm precursors (red nuclei) at the anterior blastopore during 64 cell-stage. Gastrulation in more highly derived nematodes is driven by apical constriction of endoderm precursors at the postero-ventral surface of 28 cell-stage embryo (adapted from Joshi and Rothman, 2005). Unlike species in the early branching clades, in which cell fates are plastic and rely on external signals (“regulative” development), cell lineages are largely fixed during early division (“mosaic development”) in more derived species. In addition, developmental rate is faster in the more derived clades. Thus, it is proposed that heterochronic and heterotopic shift in the developmental program drive the evolution of early embryogenesis in nematodes.
While orthologs of SKN-1, which is essential for initiating mesendoderm specification in C. elegans, are found across divergent nematode species, its action in endoderm development varies dramatically between them. Maternally provided skn-1 RNA is initially present throughout the C. elegans early embryo but becomes differentially lost in somatic blastomeres and is maintained in the germline lineage (Seydoux and Fire, 1994). In contrast, a very different pattern is observed in Propanagrolaimus sp. JU765 (clade 10) and A. nanus, in which skn-1 mRNAs, which are presumably zygotic products, accumulate in all somatic blastomeres through much of embryogenesis (Wiegner and Schierenberg, 1998; Schiffer et al., 2014, 2018). These observations suggest differential regulation of skn-1 expression and that, in addition to activating mesendoderm specification, SKN-1 may perform distinct functions in species from neighboring clades. Remarkably, the requirement for SKN-1 in endoderm specification varies even in closely related Caenorhabditis species. In C. elegans, eliminating SKN-1 results in a partial penetrant loss-of-endoderm phenotype, as SKN-1 and POP-1 function through an “OR” Boolean logic gate (Figure 1). However, in Caenorhabditis briggsae, which diverged from C. elegans ∼20–40 million years ago, both SKN-1 and POP-1 show an absolute requirement in endoderm specification, indicative of an “AND” logic gate (Cutter, 2008; Lin et al., 2009). These observations suggest that the early inputs into the endoderm GRN are rapidly evolving in nematodes.
The gut terminal differentiation factors, including ELT-2/GATA and the FoxO factor PHA-4 are conserved across Nematoda (Schiffer et al., 2014; Maduro, 2020). In contrast, the upstream med and end orthologs are present only in closely related Caenorhabditis species, apparently having arisen as a result of extensive gene duplication events at the base of the Elegans supergroup, as revealed in a recent study that examined the evolutionary variation in the GATA regulatory cascade across 24 species spanning the Caenorhabditis genus (Maduro, 2020). In two strikingly extreme cases, Caenorhabditis doughertyi and Caenorhabditis brenneri each contain ∼30 copies of the med genes (Maduro, 2020). This massive proliferation of protein-coding genes is highly unusual and may reflect adoption of new functions by at least some of the paralogs, as exemplified by the expansion of another class of transcription factors in Caenorhabditis species, the nuclear hormone receptors (NHRs) (Taubert et al., 2011). Most Caenorhabditis NHRs appear to have arisen from an ancestral Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4 (HNF4)-type NHR and appear to have evolved to perform diverse roles ranging from neural development (Zhou and Walthall, 1998; Much et al., 2000) to metabolic control (Gilst et al., 2005; Wang et al., 2015) to sex determination (Ilil et al., 1998). It is conceivable that changes in the cis-regulatory regions lead to differential expression and subsequent functional divergence of the MED paralogs, leading to retention of gene duplicates (True and Haag, 2001; Gissendanner et al., 2004; Taubert et al., 2011), though the function of MEDs beyond mesendoderm development have not been described. Importantly, functional diversification of duplicate genes can also drive rapid changes in developmental programs and DSD (True and Haag, 2001; Haag et al., 2018). For example, the C. briggsae translational regulator PUF (PUmilio and FBF)-2 plays a non-redundant role in pharynx and vulva development, in addition to promoting gametogenesis, the sole known role of its paralog PUF-1.2 and its homologs in C. elegans (Liu et al., 2012; Liu and Haag, 2014). Although morphologically invariant, the molecular mechanisms underlying vulva development vary across nematodes (Sommer and Sternberg, 1994; Félix et al., 2000; Dichtel-Danjoy and Félix, 2004; Zheng et al., 2005; Félix, 2007), which may, at least partly, have been caused by DSD resulting from gene duplication.
What might account for the expansion of GATA factors in the Caenorhabditis endoderm GRN? The cascade of redundant factors may function to ensure developmental robustness during the rapid embryogenesis characteristic of this clade. In C. elegans, and likely in the other Caenorhabditis species (Wiesenfahrt et al., 2016; Maduro, 2020), the endoderm GATA factors form recursive feedforward loops, which may provide a rapid, forward-driven activation switch. In addition, the small size of the MEDs (174 residues) and ENDs (221–242 residues), compared to ELT-2 (433 residues) and SKN-1 (∼600 residues), may allow for more rapid deployment of the cascade and lockdown of gut fate, perhaps owing to more rapid synthesis and access to chromatin (Maeshima et al., 2015). Another potential explanation is that the GATA cascade may allow more robust expression of ELT-2. The provision of maternal factors can vary among individuals (Nuzhdin et al., 2008; Surkova et al., 2008; Perez et al., 2017) especially under conditions of environmental stress, which is mitigated by SKN-1 (An and Blackwell, 2003; Crofton et al., 2018; Jordan et al., 2019). Intercession of the MEDs and ENDs in the cascade may therefore free elt-2 from direct control of SKN-1, thereby buffering against changes in environmental conditions. Finally, redundancy in the system allows for evolutionary experimentation and accumulation of cryptic genetic variants, promoting the evolution of the system (Félix and Wagner, 2008) (see below).
Most of our understanding of C. elegans biology is based on studies on a single genetic background, that of the laboratory reference strain N2. The identification of wild C. elegans isolates bearing distinct haplotypes has uncovered considerable phenotypic variation and developmental plasticity in this species (Hodgkin and Doniach, 1997; Harvey et al., 2008; Milloz et al., 2008; Andersen et al., 2012; Alcorn et al., 2016; Cook et al., 2016; Greene et al., 2016; Frézal et al., 2018; Gimond et al., 2019; Lee et al., 2019). Knocking down essential genes in the wild strains yielded distinct phenotypes and has uncovered substantial cryptic variation between the spectrum of isotypes (Paaby et al., 2015; Torres Cleuren et al., 2019). In addition, while the overall morphology remains constant, the network architecture underlying vulva induction is variable in wild genetic backgrounds (Milloz et al., 2008; Duveau and Félix, 2012). Environmental cues can modulate activities in the vulva signaling network and the sensitivity of the system varies among divergent C. elegans isotypes (Braendle and Félix, 2008; Grimbert and Braendle, 2014). Thus, potential incipient changes in developmental regulatory networks, and their robustness to environmental variation, can be revealed by examining the requirement for components in the networks in genetically distinct wild isolates.
A recent study uncovered striking variation in the endoderm GRN among the wild isolates, as reflected by the differential requirement of maternal SKN-1 and the endoderm-inducing MOM-2/Wnt (Torres Cleuren et al., 2019). This study revealed in part that the two activating pathways exhibit a partially compensatory relationship, in which a weaker requirement for the SKN-1 input is accompanied by a stronger requirement for the MOM-2 input and vice-versa, which may tune the levels of the activating signals to ensure a constant developmental outcome (Maduro et al., 2015; Choi et al., 2017; Torres Cleuren et al., 2019). Thus, the accumulation of cryptic genetic variants drives rewiring of the inputs into the endoderm GRN. This rapid DSD may be the result of the extensive redundancy in the system, which permits cryptic genetic variants to arise without diminishing fitness, and allows compensatory evolution to occur.
What are the genetic mechanisms governing plasticity in the endoderm GRN? How do the endoderm regulatory inputs respond to environmental perturbation? How do the cis-regulatory elements of endoderm genes differ between wild isolates? Using quantitative genetic methods coupled with molecular tools, the even-expanding collection C. elegans isotypes provides a powerful platform for dissecting the evolution of complex traits and the assembly of GRNs (Cook et al., 2017).
As discussed above, the early inputs into the endoderm GRN are highly variable across nematodes and show dramatic plasticity even within a single species. This is in accordance with the hourglass model of embryonic development, in which divergent developmental mechanisms converge on a phylotypic stage, which may coincide with expression of conserved differentiation factors (Duboule, 1994; Raff, 1996). Comparisons of early embryonic transcripts across many Drosophila species and the mosquito Aedes aegypti has revealed that maternal transcript pools that, like those of C. elegans skn-1, are present only transiently during early embryogenesis, and that their expression levels are highly variable across these species, spanning ∼60 million years of evolution (Atallah and Lott, 2018). Similarly, considerable variation in the expression of maternal factor genes is found between different nematode species (Levin et al., 2012; Macchietto et al., 2017; Schiffer et al., 2018). This hourglass pattern of variation is attributable to the lack of negative selection of maternal-effect genes (Barker et al., 2005; Cruickshank and Wade, 2008; Cutter et al., 2019), as well as to increased developmental constraints during mid-embryogenesis (Raff, 1996; Zalts and Yanai, 2017). It will be of interest to ask whether the variation in SKN-1 dependence between C. briggsae and C. elegans isotypes results from quantitative changes in skn-1 expression and/or alteration of the cis-regulatory sites of its targets (Peter and Davidson, 2011; Verster et al., 2014; Vu et al., 2015). Indeed, the number of putative SKN-1 binding sites in end-3 and end-1 promoters has been found to vary widely, and in some cases the sites are absent or unrecognizable, in many Caenorhabditis species (Maduro, 2020).
It has been shown that, relative to early and late embryonic development, gene expression during morphogenesis is highly conserved, not only across Caenorhabditis, but also across Bilateria (Levin et al., 2012). Cellular patterning during mid-embryogenesis is similar in nematodes from distant clades, despite extensive variation in early division (Schulze and Schierenberg, 2011). In many nematode species, the endodermal daughters migrate from the ventral side into the interior of the embryo during gastrulation, as in C. elegans (Figure 2; Vangestel et al., 2008; Schulze and Schierenberg, 2011; Schulze et al., 2012; Calderón-Urrea et al., 2016). This is followed by proliferation and polarization of the intestine primordia, and subsequent formation of lumen through cell rearrangements and remodeling, similar to gut morphogenesis observed in zebrafish (reviewed in Nowotschin et al., 2019). The action of ELT-2 (and ELT-7) at the end of the endoderm cascade, where they act on thousands of targets that underlie morphological differentiation and function of the gut, presumably restricts evolutionary divergence at this node, whereas the earlier nodes of the GRN involve the action of transcription factors with far fewer target genes, hence allowing for much greater evolutionary plasticity (see also Maduro and Rothman, 2002).
With the molecular details of the C. elegans endoderm GRN in hand, the mechanisms that govern the diversification of the network in other nematode species have begun to emerge. For example, while the endoderm fate is confined to a single cell in C. elegans, all blastomeres are potentiated to become gut and cell fate is regulated through lateral inhibition in A. nanus. Comparing the mechanisms of cell fate restriction between these species will not only enhance our understanding of evolutionary plasticity and reprogramming of GRNs, but also provide important insights into how such a system transitions from one configuration into another during evolution. One curious element of the endoderm GRN is that there appears to be substantial cross-talk between some endoderm components and stress response pathways (An and Blackwell, 2003; Wheeler and Thomas, 2006; Arsenovic et al., 2012; Block et al., 2015; Dresen et al., 2015; Ewe et al., 2019). Pleiotropic genes modulating stress pathways may act cryptically in endoderm development. Changes in environmental conditions may then lead to selection and fixation of cryptic variants, resulting in rapid DSD (Johnson and Porter, 2007; Duveau and Félix, 2012). By availing of nematodes isolated from diverse geographical locations, including those from extreme habitats (Shih et al., 2019), it will be of interest to ask how environment cues shape the endoderm GRN structure.
The mechanisms of early specification of gut fate appear to undergo rapid and widespread changes at both inter- and intraspecies levels. This unexpectedly high degree of evolutionary plasticity in the system that establishes the most ancient germ layer can serve as an excellent paradigm for DSD. The development of molecular genetic tools that can be applied to nematodes outside of C. elegans (Lok and Unnasch, 2007; Wood et al., 2011; Lo et al., 2013; Kanzaki et al., 2018; Cohen and Sternberg, 2019), together with new sequencing technologies that integrate multi-omic analyses (Witze et al., 2009; Daugherty et al., 2017; Guo et al., 2017; Packer et al., 2019), will greatly facilitate the study of complex developmental regulatory systems and their evolutionary trajectory across divergent species.
CE and YT wrote the first draft of the manuscript. JR directed the project and contributed to the manuscript revisions. All authors approved the submitted version.
This work was supported by grants from the NIH (#1R01HD082347 and #1R01HD081266) awarded to JR. YT is supported by the Norwegian Research Council (#250049).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
We apologize to colleagues whose work could not be cited due to limited space. We thank members of the Rothman Lab, especially Pradeep M. Joshi, for helpful feedback and advice.
Alcorn, M. R., Callander, D. C., López-Santos, A., Cleuren, Y. N. T., Birsoy, B., Joshi, P. M., et al. (2016). Heterotaxy in Caenorhabditis: widespread natural variation in left – right arrangement of the major organs. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 371:20150404. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2015.0404
An, J. H., and Blackwell, T. K. (2003). SKN-1 links C. elegans mesendodermal specification to a conserved oxidative stress response. Genes Dev. 17, 1882–1893. doi: 10.1101/gad.1107803
Andersen, E. C., Gerke, J. P., Shapiro, J. A., Crissman, J. R., Ghosh, R., Bloom, J. S., et al. (2012). Chromosome-scale selective sweeps shape Caenorhabditis elegans genomic diversity. Nat. Genet. 44, 285–290. doi: 10.1038/ng.1050
Arsenovic, P. T., Maldonado, A. T., Colleluori, V. D., and Bloss, T. A. (2012). Depletion of the C. elegans NAC engages the unfolded protein response, resulting in increased chaperone expression and apoptosis. PLoS ONE 7:e44038. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044038
Atallah, J., and Lott, S. E. (2018). Evolution of maternal and zygotic mRNA complements in the early Drosophila embryo. PLoS Genet. 14:e1007838. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007838
Barker, M. S., Demuth, J. P., and Wade, M. J. (2005). Maternal expression relaxes constraint on innovation of the anterior determinant, bicoid. PLoS Genet. 1:e57. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0010057
Barrière, A., and Félix, M. A. (2005). Natural variation and population genetics of Caenorhabditis elegans. WormBook 1–19. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.43.1
Block, D. H. S., Twumasi-Boateng, K., Kang, H. S., Carlisle, J. A., Hanganu, A., Lai, T. Y.-J., et al. (2015). The developmental intestinal regulator ELT-2 controls p38-dependent immune responses in adult C. elegans. PLoS Genet. 11:e1005265. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005265
Boveri, T. (1899). Die Entwickelung von Ascaris Megalocephala mit Besonderer Rücksicht auf die Kernverhältnisse. Jena: Gustav Fischer (Opitz Library).
Braendle, C., and Félix, M. A. (2008). Plasticity and errors of a robust developmental system in different environments. Dev. Cell 15, 714–724. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2008.09.011
Broitman-Maduro, G., Lin, K. T.-H., Hung, W. W. K., and Maduro, M. F. (2006). Specification of the C. elegans MS blastomere by the T-box factor TBX-35. Development 133, 3097–3106. doi: 10.1242/dev.02475
Broitman-Maduro, G., Maduro, M. F., and Rothman, J. H. (2005). The noncanonical binding site of the MED-1 GATA Factor defines differentially regulated target genes in the C. elegans mesendoderm. Dev. Cell 8, 427–433. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2005.01.014
Calderón-Urrea, A., Vanholme, B., Vangestel, S., Kane, S. M., Bahaji, A., Pha, K., et al. (2016). Early development of the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita. BMC Dev. Biol. 16:10. doi: 10.1186/s12861-016-0109-x
Choi, H., Broitman-Maduro, G., and Maduro, M. F. (2017). Partially compromised specification causes stochastic effects on gut development in C. elegans. Dev. Biol. 427, 49–60. doi: 10.1016/J.YDBIO.2017.05.007
Cohen, S. M., and Sternberg, P. W. (2019). Genome editing of Caenorhabditis briggsae using CRISPR/Cas9 co-conversion marker dpy-10. microPublication Biol. doi: 10.17912/micropub.biology.000171
Cook, D. E., Zdraljevic, S., Roberts, J. P., and Andersen, E. C. (2017). CeNDR, the Caenorhabditis elegans natural diversity resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 45, D650–D657. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw893
Cook, D. E., Zdraljevic, S., Tanny, R. E., Seo, B., Riccardi, D. D., Noble, L. M., et al. (2016). The genetic basis of natural variation in Caenorhabditis elegans telomere length. Genetics 204, 371–383. doi: 10.1534/genetics.116.191148
Cook, S. J., Jarrell, T. A., Brittin, C. A., Wang, Y., Bloniarz, A. E., Yakovlev, M. A., et al. (2019). Whole-animal connectomes of both Caenorhabditis elegans sexes. Nature 571, 63–71. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1352-7
Crofton, A. E., Cartwright, E. L., Feitzinger, A. A., and Lott, S. E. (2018). Effect of larval nutrition on maternal mRNA contribution to the Drosophila Egg. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 8, 1933–1941. doi: 10.1534/g3.118.200283
Crombie, T. A., Zdraljevic, S., Cook, D. E., Tanny, R. E., Brady, S. C., Wang, Y., et al. (2019). Deep sampling of Hawaiian Caenorhabditis elegans reveals high genetic diversity and admixture with global populations. Elife 8:e50465. doi: 10.7554/eLife.50465
Cruickshank, T., and Wade, M. J. (2008). Microevolutionary support for a developmental hourglass: gene expression patterns shape sequence variation and divergence in Drosophila. Evol. Dev. 10, 583–590. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-142X.2008.00273.x
Cutter, A. D. (2008). Divergence times in Caenorhabditis and Drosophila inferred from direct estimates of the neutral mutation rate. Mol. Biol. Evol. 25, 778–786. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msn024
Cutter, A. D., Garrett, R. H., Mark, S., Wang, W., and Sun, L. (2019). Molecular evolution across developmental time reveals rapid divergence in early embryogenesis. Evol. Lett. 3, 359–373. doi: 10.1002/evl3.122
Daugherty, A. C., Yeo, R. W., Buenrostro, J. D., Greenleaf, W. J., Kundaje, A., and Brunet, A. (2017). Chromatin accessibility dynamics reveal novel functional enhancers in C. elegans. Genome Res. 27, 2096–2107. doi: 10.1101/gr.226233.117
Dichtel-Danjoy, M. L., and Félix, M. A. (2004). The two steps of vulval induction in Oscheius tipulae CEW1 recruit common regulators including a MEK kinase. Dev. Biol. 265, 113–126. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2003.09.010
Dineen, A., Osborne Nishimura, E., Goszczynski, B., Rothman, J. H., and McGhee, J. D. (2018). Quantitating transcription factor redundancy: the relative roles of the ELT-2 and ELT-7 GATA factors in the C. elegans endoderm. Dev. Biol. 435, 150–161. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.12.023
Dolinski, C., Baldwin, J. G., and Thomas, W. K. (2001). Comparative survey of early embryogenesis of Secernentea (Nematoda), with phylogenetic implications. Can. J. Zool. 79, 82–94. doi: 10.1139/z00-179
Dresen, A., Finkbeiner, S., Dottermusch, M., Beume, J. S., Li, Y., Walz, G., et al. (2015). Caenorhabditis elegans OSM-11 signaling regulates SKN-1/Nrf during embryonic development and adult longevity and stress response. Dev. Biol. 400, 118–131. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2015.01.021
Du, Z., Santella, A., He, F., Tiongson, M., and Bao, Z. (2014). De novo inference of systems-level mechanistic models of development from live-imaging-based phenotype analysis. Cell 156, 359–372. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.11.046
Duboule, D. (1994). Temporal colinearity and the phylotypic progression: a basis for the stability of a vertebrate Bauplan and the evolution of morphologies through heterochrony. Development 135–142.
Duveau, F., and Félix, M.-A. (2012). Role of pleiotropy in the evolution of a cryptic developmental variation in Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS Biol. 10:e1001230. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001230
Ewe, C. K., Cleuren, Y. N. T., Alok, G., and Rothman, J. H. (2019). ICD-1/BTF3 antagonizes SKN-1-mediated endoderm specification in Caenorhabditis elegans. microPublication Biol. doi: 10.17912/micropub.biology.000167
Félix, M.-A. (2007). Cryptic quantitative evolution of the vulva intercellular signaling network in Caenorhabditis. Curr. Biol. 17, 103–114. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2006.12.024
Félix, M. A., Braendle, C., and Cutter, A. D. (2014). A streamlined system for species diagnosis in Caenorhabditis (Nematoda: Rhabditidae) with name designations for 15 distinct biological species. PLoS ONE 9:e0118327. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0094723
Félix, M. A., De Ley, P., Sommer, R. J., Frisse, L., Nadler, S. A., Thomas, W. K., et al. (2000). Evolution of vulva development in the Cephalobina (Nematoda). Dev. Biol. 221, 68–86. doi: 10.1006/dbio.2000.9665
Félix, M.-A., and Wagner, A. (2008). Robustness and evolution: concepts, insights and challenges from a developmental model system. Heredity (Edinb). 100, 132–140. doi: 10.1038/sj.hdy.6800915
Ferrari, C., Salle, R., Callemeyn-Torre, N., Jovelin, R., Cutter, A. D., and Braendle, C. (2017). Ephemeral-habitat colonization and neotropical species richness of Caenorhabditis nematodes. BMC Ecol. 17:43. doi: 10.1186/s12898-017-0150-z
Frézal, L., Demoinet, E., Braendle, C., Miska, E., and Félix, M. A. (2018). Natural genetic variation in a multigenerational phenotype in C. elegans. Curr. Biol. 28, 2588–2596.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2018.05.091
Fukushige, T., Hawkins, M. G., and McGhee, J. D. (1998). The GATA-factor elt-2 is essential for formation of the Caenorhabditis elegans intestine. Dev. Biol. 198, 286–302. doi: 10.1016/S0012-1606(98)80006-7
Gilst, M. R., Van, Hadjivassiliou, H., Jolly, A., and Yamamoto, K. R. (2005). Nuclear hormone receptor NHR-49 controls fat consumption and fatty acid composition in C. elegans. PLoS Biol. 3:e53. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0030053
Gimond, C., Vielle, A., Silva-Soares, N., Zdraljevic, S., McGrath, P. T., Andersen, E. C., et al. (2019). Natural variation and genetic determinants of Caenorhabditis elegans sperm size. Genetics 213, 615–632. doi: 10.1534/genetics.119.302462
Gissendanner, C. R., Crossgrove, K., Kraus, K. A., Maina, C. V., and Sluder, A. E. (2004). Expression and function of conserved nuclear receptor genes in Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev. Biol. 266, 399–416. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2003.10.014
Greene, J. S., Brown, M., Dobosiewicz, M., Ishida, I. G., Macosko, E. Z., Zhang, X., et al. (2016). Balancing selection shapes density-dependent foraging behaviour. Nature 539, 254–258. doi: 10.1038/nature19848
Grimbert, S., and Braendle, C. (2014). Cryptic genetic variation uncovers evolution of environmentally sensitive parameters in Caenorhabditis vulval development. Evol. Dev. 16, 278–291. doi: 10.1111/ede.12091
Guo, F., Li, L., Li, J., Wu, X., Hu, B., Zhu, P., et al. (2017). Single-cell multi-omics sequencing of mouse early embryos and embryonic stem cells. Cell Res. 27, 967–988. doi: 10.1038/cr.2017.82
Haag, E. S., Fitch, D. H. A., and Delattre, M. (2018). From “the worm” to “the worms” and back again: the evolutionary developmental biology of nematodes. Genetics 210, 397–433. doi: 10.1534/genetics.118.300243
Harvey, S. C., Shorto, A., and Viney, M. E. (2008). Quantitative genetic analysis of life-history traits of Caenorhabditis elegans in stressful environments. BMC Evol. Biol. 8:15. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-8-15
Hashimshony, T., Feder, M., Levin, M., Hall, B. K., and Yanai, I. (2015). Spatiotemporal transcriptomics reveals the evolutionary history of the endoderm germ layer. Nature 519, 219–222. doi: 10.1038/nature13996
Hiraki, H., Kagoshima, H., Kraus, C., Schiffer, P. H., Ueta, Y., Kroiher, M., et al. (2017). Genome analysis of Diploscapter coronatus: insights into molecular peculiarities of a nematode with parthenogenetic reproduction. BMC Genomics 18:478. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-3860-x
Hodgkin, J., and Doniach, T. (1997). Natural variation and copulatory plug formation in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 146, 149–164.
Holterman, M., Van Der Wurff, A., Van Den Elsen, S., Van Megen, H., Bongers, T., Holovachov, O., et al. (2006). Phylum-wide analysis of SSU rDNA reveals deep phylogenetic relationships among nematodes and accelerated evolution toward crown clades. Mol. Biol. Evol. 23, 1792–1800. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msl044
Houthoofd, W., Jacobsen, K., Mertens, C., Vangestel, S., Coomans, A., and Borgonie, G. (2003). Embryonic cell lineage of the marine nematode Pellioditis marina. Dev. Biol. 258, 57–69. doi: 10.1016/S0012-1606(03)00101-5
Ilil, C., Kopczynski, J. B., and Meyer, B. J. (1998). The nuclear hormone receptor SEX-1 is an X-chromosome signal that determines nematode sex. Nature 396, 168–173. doi: 10.1038/24164
Johnson, N. A., and Porter, A. H. (2007). Evolution of branched regulatory genetic pathways: directional selection on pleiotropic loci accelerates developmental system drift. Genetica 129, 57–70. doi: 10.1007/s10709-006-0033-2
Jordan, J. M., Hibshman, J. D., Webster, A. K., Kaplan, R. E. W., Leinroth, A., Guzman, R., et al. (2019). Insulin/IGF signaling and vitellogenin provisioning mediate intergenerational adaptation to nutrient stress. Curr. Biol. 29, 2380–2388.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2019.05.062
Joshi, P. M., and Rothman, J. H. (2005). Nematode gastrulation: HAVING a BLASTocoel! Curr. Biol. 15, R495–R498. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.06.030
Kanzaki, N., Tsai, I. J., Tanaka, R., Hunt, V. L., Liu, D., Tsuyama, K., et al. (2018). Biology and genome of a newly discovered sibling species of Caenorhabditis elegans. Nat. Commun. 9:3216.
Kiontke, K. C., Félix, M.-A., Ailion, M., Rockman, M. V., Braendle, C., Pénigault, J.-B., et al. (2011). A phylogeny and molecular barcodes for Caenorhabditis, with numerous new species from rotting fruits. BMC Evol. Biol. 11:339. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-11-339
Laugsch, M., and Schierenberg, E. (2004). Differences in maternal supply and early development of closely related nematode species. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 48, 655–662. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.031758ml
Lee, D., Zdraljevic, S., Cook, D. E., Frézal, L., Hsu, J. C., Sterken, M. G., et al. (2019). Selection and gene flow shape niche-associated variation in pheromone response. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 3, 1455–1463. doi: 10.1038/s41559-019-0982-3
Levin, M., Hashimshony, T., Wagner, F., and Yanai, I. (2012). Developmental milestones punctuate gene expression in the Caenorhabditis embryo. Dev. Cell 22, 1101–1108. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2012.04.004
Lin, K. T.-H., Broitman-Maduro, G., Hung, W. W. K., Cervantes, S., and Maduro, M. F. (2009). Knockdown of SKN-1 and the Wnt effector TCF/POP-1 reveals differences in endomesoderm specification in C. briggsae as compared with C. elegans. Dev. Biol. 325, 296–306. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.10.001
Liu, Q., and Haag, E. S. (2014). Evolutionarily dynamic roles of a PUF RNA-binding protein in the somatic development of Caenorhabditis briggsae. J. Exp. Zool. B Mol. Dev. Evol. 322, 129–141. doi: 10.1002/jez.b.22550
Liu, Q., Stumpf, C., Thomas, C., Wickens, M., and Haag, E. S. (2012). Context-dependent function of a conserved translationalregulatory module. Development 139, 1509–1521. doi: 10.1242/dev.070128
Lo, T. W., Pickle, C. S., Lin, S., Ralston, E. J., Gurling, M., Schartner, C. M., et al. (2013). Precise and heritable genome editing in evolutionarily diverse nematodes using TALENs and CRISPR/Cas9 to engineer insertions and deletions. Genetics 195, 331–348. doi: 10.1534/genetics.113.155382
Lok, J. B., and Unnasch, T. R. (2007). Strongyloides stercoralis: a model for translational research on parasitic nematode biology. WormBook 1–18. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.134.1
Macchietto, M., Angdembey, D., Heidarpour, N., Serra, L., Rodriguez, B., El-Ali, N., et al. (2017). Comparative transcriptomics of steinernema and Caenorhabditis single embryos reveals orthologous gene expression convergence during late embryogenesis. Genome Biol. Evol. 9, 2681–2696. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evx195
Maduro, M. F. (2015). Developmental robustness in the Caenorhabditis elegans embryo. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 82, 918–931. doi: 10.1002/mrd.22582
Maduro, M. F. (2017). Gut development in C. elegans. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 66, 3–11. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.01.001
Maduro, M. F. (2020). Evolutionary dynamics of the Skn-1/Med/end-1,3 regulatory gene cascade in Caenorhabditis endoderm specification. G3 Genes Genomes, Genet. 10, 333–356. doi: 10.1534/g3.119.400724
Maduro, M. F., Broitman-Maduro, G., Choi, H., Carranza, F., Wu, A. C.-Y., and Rifkin, S. A. (2015). MED GATA factors promote robust development of the C. elegans endoderm. Dev. Biol. 404, 66–79. doi: 10.1016/J.YDBIO.2015.04.025
Maduro, M. F., Lin, R., and Rothman, J. H. (2002). Dynamics of a developmental switch: recursive intracellular and intranuclear redistribution of Caenorhabditis elegans POP-1 parallels Wnt-inhibited transcriptional repression. Dev. Biol. 248, 128–142. doi: 10.1006/DBIO.2002.0721
Maduro, M. F., and Rothman, J. H. (2002). Making worm guts: the gene regulatory network of the Caenorhabditis elegans endoderm. Dev. Biol. 246, 68–85. doi: 10.1006/DBIO.2002.0655
Maeshima, K., Kaizu, K., Tamura, S., Nozaki, T., Kokubo, T., and Takahashi, K. (2015). The physical size of transcription factors is key to transcriptional regulation in chromatin domains. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 27:064116. doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/27/6/064116
Malakhov, V. V. (1994). Nematodes: Structure, Development, Classification, and Phylogeny. Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution Press. ed. W. D. Hope.
Martindale, M. Q., Pang, K., and Finnerty, J. R. (2004). Investigating the origins of triploblasty: “mesodermal” gene expression in a diploblastic animal, the sea anemone Nematostella vectensis (phylum, Cnidaria; class, Anthozoa). Development 131, 2463–2474. doi: 10.1242/dev.01119
Martín-Durán, J. M., Janssen, R., Wennberg, S., Budd, G. E., and Hejnol, A. (2012). Deuterostomic development in the protostome Priapulus caudatus. Curr. Biol. 22, 2161–2166. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2012.09.037
McGhee, J. D., Fukushige, T., Krause, M. W., Minnema, S. E., Goszczynski, B., Gaudet, J., et al. (2009). ELT-2 is the predominant transcription factor controlling differentiation and function of the C. elegans intestine, from embryo to adult. Dev. Biol. 327, 551–565. doi: 10.1016/J.YDBIO.2008.11.034
Milloz, J., Duveau, F., Nuez, I., and Felix, M.-A. (2008). Intraspecific evolution of the intercellular signaling network underlying a robust developmental system. Genes Dev. 22, 3064–3075. doi: 10.1101/gad.495308
Montgomery, T. H. (1904). The development and structure of the larva of paragordius. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 56, 738–755.
Much, J. W., Slade, D. J., Klampert, K., Garriga, G., and Wightman, B. (2000). The fax-1 nuclear hormone receptor regulates axon pathfinding and neurotransmitter expression. Development 127, 703–712.
Nowotschin, S., Hadjantonakis, A. K., and Campbell, K. (2019). The endoderm: a divergent cell lineage with many commonalities. Development 146:dev150920. doi: 10.1242/dev.150920
Nuzhdin, S. V., Tufts, D. M., and Hahn, M. W. (2008). Abundant genetic variation in transcript level during early Drosophila development. Evol. Dev. 10, 683–689. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-142X.2008.00281.x
Owraghi, M., Broitman-Maduro, G., Luu, T., Roberson, H., and Maduro, M. F. (2010). Roles of the Wnt effector POP-1/TCF in the C. elegans endomesoderm specification gene network. Dev. Biol. 340, 209–221. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.09.042
Paaby, A. B., White, A. G., Riccardi, D. D., Gunsalus, K. C., Piano, F., and Rockman, M. V. (2015). Wild worm embryogenesis harbors ubiquitous polygenic modifier variation. Elife 4:e09178. doi: 10.7554/eLife.09178
Packer, J. S., Zhu, Q., Huynh, C., Sivaramakrishnan, P., Preston, E., Dueck, H., et al. (2019). A lineage-resolved molecular atlas of C. elegans embryogenesis at single-cell resolution. Science (80-) 365, eaax1971. doi: 10.1126/science.aax1971
Perez, M. F., Francesconi, M., Hidalgo-Carcedo, C., and Lehner, B. (2017). Maternal age generates phenotypic variation in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 552:106. doi: 10.1038/nature25012
Peter, I. S., and Davidson, E. H. (2011). Evolution of gene regulatory networks controlling body plan development. Cell 144, 970–985. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.017
Phillips, B. T., Kidd, A. R., King, R., Hardin, J., and Kimble, J. (2007). Reciprocal asymmetry of SYS-1/beta-catenin and POP-1/TCF controls asymmetric divisions in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104, 3231–3236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0611507104
Raff, R. A. (1996). The Shape of Life?: Genes, Development, and the Evolution of Animal Form. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
Rodaway, A., and Patient, R. (2001). Mesendoderm: an ancient germ layer? Cell 105, 169–172. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00307-5
Schierenberg, E. (2005). Unusual cleavage and gastrulation in a freshwater nematode: developmental and phylogenetic implications. Dev. Genes Evol. 215, 103–108. doi: 10.1007/s00427-004-0454-9
Schiffer, P. H., Kroiher, M., Kraus, C., Koutsovoulos, G. D., Kumar, S., Camps, J. I., et al. (2013). The genome of Romanomermis culicivorax: revealing fundamental changes in the core developmental genetic toolkit in Nematoda. BMC Genomics 14:923. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-923
Schiffer, P. H., Nsah, N. A., Grotehusmann, H., Kroiher, M., Loer, C., and Schierenberg, E. (2014). Developmental variations among Panagrolaimid nematodes indicate developmental system drift within a small taxonomic unit. Dev. Genes Evol. 224, 183–188. doi: 10.1007/s00427-014-0471-2
Schiffer, P. H., Polsky, A. L., Cole, A. G., Camps, J. I. R., Kroiher, M., Silver, D. H., et al. (2018). The gene regulatory program of Acrobeloides nanus reveals conservation of phylum-specific expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 115, 4459–4464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1720817115
Schulze, J., Houthoofd, W., Uenk, J., Vangestel, S., and Schierenberg, E. (2012). Plectus – a stepping stone in embryonic cell lineage evolution of nematodes. Evodevo 3:3. doi: 10.1186/2041-9139-3-13
Schulze, J., and Schierenberg, E. (2009). Embryogenesis of Romanomermis culicivorax: an alternative way to construct a nematode. Dev. Biol. 334, 10–21. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.06.009
Schulze, J., and Schierenberg, E. (2011). Evolution of embryonic development in nematodes. Evodevo 2:18. doi: 10.1186/2041-9139-2-18
Seydoux, G., and Fire, A. (1994). Soma-germline asymmetry in the distributions of embryonic RNAs in Caenorhabditis elegans. Development 120, 2823–2834.
Shetty, P., Lo, M.-C., Robertson, S. M., and Lin, R. (2005). C. elegans TCF protein, POP-1, converts from repressor to activator as a result of Wnt-induced lowering of nuclear levels. Dev. Biol. 285, 584–592. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2005.07.008
Shih, P. Y., Lee, J. S., Shinya, R., Kanzaki, N., Pires-daSilva, A., Badroos, J. M., et al. (2019). Newly identified nematodes from mono lake exhibit extreme arsenic resistance. Curr. Biol. 29, 3339.e–3344.e. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2019.08.024
Sommer, R. J., and Bumbarger, D. J. (2012). Nematode model systems in evolution and development. Wiley Interdiscipl. Rev. Dev. Biol. 1, 389–400. doi: 10.1002/wdev.33
Sommer, R. J., and Sternberg, P. W. (1994). Changes of induction and competence during the evolution of vulva development in nematodes. Science (80-) 265, 114–118. doi: 10.1126/science.8016644
Sommer, R. J., and Streit, A. (2011). Comparative genetics and genomics of nematodes: genome structure, development, and lifestyle. Annu. Rev. Genet. 45, 1–20. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-110410-132417
Sommermann, E. M., Strohmaier, K. R., Maduro, M. F., and Rothman, J. H. (2010). Endoderm development in Caenorhabditis elegans: the synergistic action of ELT-2 and -7 mediates the specification→differentiation transition. Dev. Biol. 347, 154–166. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.08.020
Stevens, L., Félix, M.-A., Beltran, T., Braendle, C., Caurcel, C., Fausett, S., et al. (2019). Comparative genomics of 10 new Caenorhabditis species. Evol. Lett. 3, 217–236. doi: 10.1002/evl3.110
Sullivan-Brown, J. L., Tandon, P., Bird, K. E., Dickinson, D. J., Tintori, S. C., Heppert, J. K., et al. (2016). Identifying regulators of morphogenesis common to vertebrate neural tube closure and Caenorhabditis elegans gastrulation. Genetics 202, 123–139. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.183137
Sulston, J. E., Albertson, D. G., and Thomson, J. N. (1980). The Caenorhabditis elegans male: postembryonic development of nongonadal structures. Dev. Biol. 78, 542–576. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90352-8
Sulston, J. E., and Horvitz, H. R. (1977). Post-embryonic cell lineages of the nematode, Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev. Biol. 56, 110–156. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90158-0
Sulston, J. E., Schierenberg, E., White, J. G., and Thomson, J. N. (1983). The embryonic cell lineage of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev. Biol. 100, 64–119. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90201-4
Surkova, S., Kosman, D., Kozlov, K., Manu, Myasnikova, E., Samsonova, A. A., et al. (2008). Characterization of the Drosophila segment determination morphome. Dev. Biol. 313, 844–862. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.10.037
Taubert, S., Ward, J. D., and Yamamoto, K. R. (2011). Nuclear hormone receptors in nematodes: evolution and function. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 334, 49–55. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2010.04.021
Thompson, O., Edgley, M., Strasbourger, P., Flibotte, S., Ewing, B., Adair, R., et al. (2013). The million mutation project: a new approach to genetics in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genome Res. 23, 1749–1762. doi: 10.1101/gr.157651.113
Tintori, S. C., Osborne Nishimura, E., Golden, P., Lieb, J. D., and Goldstein, B. (2016). A transcriptional lineage of the early C. elegans embryo. Dev. Cell 38, 430–444. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2016.07.025
Torres Cleuren, Y. N., Ewe, C. K., Chipman, K. C., Mears, E. R., Wood, C. G., Al-Alami, C. E. A., et al. (2019). Extensive intraspecies cryptic variation in an ancient embryonic gene regulatory network. Elife 8:e48220. doi: 10.7554/eLife.48220
True, J. R., and Haag, E. S. (2001). Developmental system drift and flexibility in evolutionary trajectories. Evol. Dev. 3, 109–119. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-142x.2001.003002109.x
Vangestel, S., Houthoofd, W., Bert, W., and Borgonie, G. (2008). The early embryonic development of the satellite organism Pristionchus pacificus: differences and similarities with Caenorhabditis elegans. Nematology 10, 301–312. doi: 10.1163/156854108783900267
Verster, A. J., Ramani, A. K., McKay, S. J., and Fraser, A. G. (2014). Comparative RNAi Screens in C. elegans and C. briggsae reveal the impact of developmental system drift on gene function. PLoS Genet. 10:e1004077. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004077
Voronov, D. A., and Panchin, Y. V. (1998). Cell lineage in marine nematode Enoplus brevis. Development 125, 143–150.
Vu, V., Verster, A. J., Schertzberg, M., Chuluunbaatar, T., Spensley, M., Pajkic, D., et al. (2015). Natural variation in gene expression modulates the severity of mutant phenotypes. Cell 162, 391–402. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.06.037
Wang, Z., Stoltzfus, J., You, Y., Ranjit, N., Tang, H., Xie, Y., et al. (2015). The nuclear receptor DAF-12 regulates nutrient metabolism and reproductive growth in nematodes. PLoS Genet. 11:e1005027. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005027
Wheeler, J. M., and Thomas, J. H. (2006). Identification of a novel gene family involved in osmotic stress response in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 174, 1327–1336. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.059089
White, J. G., Southgate, E., Thomson, J. N., and Brenner, S. (1986). The structure of the nervous system of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 314, 1–340. doi: 10.1098/RSTB.1986.0056
Wiegner, O., and Schierenberg, E. (1998). Specification of gut cell fate differs significantly between the nematodes Acrobeloides nanus and Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev. Biol. 204, 3–14. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1998.9054
Wiegner, O., and Schierenberg, E. (1999). Regulative development in a nematode embryo: a hierarchy of cell fate transformations. Dev. Biol. 215, 1–12. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1999.9423
Wiesenfahrt, T., Duanmu, J., Snider, F., Moerman, D., Au, V., Li-Leger, E., et al. (2018). A strategy to isolate modifiers of Caenorhabditis elegans lethal mutations: investigating the endoderm specifying ability of the intestinal differentiation GATA factor ELT-2. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 8, 1425–1437. doi: 10.1534/g3.118.200079
Wiesenfahrt, T., Osborne Nishimura, E., Berg, J. Y., and McGhee, J. D. (2016). Probing and rearranging the transcription factor network controlling the C. elegans endoderm. Worm 5:e1198869. doi: 10.1080/21624054.2016.1198869
Witze, E. S., Field, E. D., Hunt, D. F., and Rothman, J. H. (2009). C. elegans pur alpha, an activator of end-1, synergizes with the Wnt pathway to specify endoderm. Dev. Biol. 327, 12–23. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.11.015
Wood, A. J., Lo, T. W., Zeitler, B., Pickle, C. S., Ralston, E. J., Lee, A. H., et al. (2011). Targeted genome editing across species using ZFNs and TALENs. Science (80-) 333:307. doi: 10.1126/science.1207773
Zalts, H., and Yanai, I. (2017). Developmental constraints shape the evolution of the nematode mid-developmental transition. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 1:0113. doi: 10.1038/s41559-017-0113
Zhao, Y., Long, L., Xu, W., Campbell, R. F., Large, E. E., Greene, J. S., et al. (2018). Changes to social feeding behaviors are not sufficient for fitness gains of the Caenorhabditis elegans N2 reference strain. Elife 7:e38675. doi: 10.7554/eLife.38675
Zhao, Z., Boyle, T. J., Bao, Z., Murray, J. I., Mericle, B., and Waterston, R. H. (2008). Comparative analysis of embryonic cell lineage between Caenorhabditis briggsae and Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev. Biol. 314, 93–99. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.11.015
Zheng, M., Messerschmidt, D., Jungblut, B., and Sommer, R. J. (2005). Conservation and diversification of Wnt signaling function during the evolution of nematode vulva development. Nat. Genet. 37, 300–304. doi: 10.1038/ng1512
Keywords: Caenorhabditis, developmental system drift, developmental hourglass, plasticity, robustness
Citation: Ewe CK, Torres Cleuren YN and Rothman JH (2020) Evolution and Developmental System Drift in the Endoderm Gene Regulatory Network of Caenorhabditis and Other Nematodes. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 8:170. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00170
Received: 22 January 2020; Accepted: 02 March 2020;
Published: 18 March 2020.
Edited by:
Maike Kittelmann, Oxford Brookes University, United KingdomReviewed by:
Morris Maduro, University of California, Riverside, United StatesCopyright © 2020 Ewe, Torres Cleuren and Rothman. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yamila N. Torres Cleuren, eWFtaWxhLmNsZXVyZW5AdWliLm5v; Joel H. Rothman, am9lbC5yb3RobWFuQHVjc2IuZWR1
†ORCID: Chee Kiang Ewe, orcid.org/0000-0003-1973-1308; Yamila N. Torres Cleuren, orcid.org/0000-0003-2218-7243; Joel H. Rothman, orcid.org/0000-0002-6844-1377
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.