- Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Gulhane Faculty of Medicine, University of Health Sciences, Ankara, Turkey
“If you define the problem correctly, you almost have the solution”
Steve Jobs
Background
Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is one of the common complications of diabetes mellitus, which substantially decreases the quality of life and increases the risk of premature mortality (1). Although it is the most common cause of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) (2), the mortality is mostly due to cardiovascular diseases and therefore DKD is regarded as a major cardiovascular risk factor (3, 4). Due to its chronic and slowly progressing nature, DKD is generally diagnosed by screening tests showing albuminuria or low eGFR, or both in subjects with diabetes. Up to one-third of patients with type 1 diabetes (T1DM) (5–7)and nearly half of patients with type 2 diabetes (T2DM) have DKD (6, 8–10). Yet, fewer of them receive optimal care to prevent DKD progression and avoid the cardiovascular and renal endpoints (11).
Although the term “Diabetic Nephropathy” is used interchangeably with DKD, the former more specifically describes the histological alterations such as glomerular basement membrane thickening, or mesangial proliferation observed in subjects with T1DM, which predominantly occurs due to chronic hyperglycemia (12). However, DKD observed in subjects with T2DM involves Diabetic Nephropathy but also the alterations seen due to other causes such as aging, hypertension, or obesity. This is probably the reason for observing DKD more frequently in subjects with T2DM. As multiple risk factors play role in the pathogenesis of DKD and its cardiovascular consequences, intensive glucose control is not enough to prevent renal and cardiovascular endpoints in DKD (13). Therefore, chronic risk management is essential along with good glycemic regulation, to prevent the occurrence and progression of DKD and to reduce the premature cardiovascular events in patients with diabetes (14–17).
Unfortunately, the global data shows that people with diabetes are not under good glycemic control, nor they attain the metabolic targets (18–20). We have recently performed a nationwide survey in Turkey (6). Our findings replicate the global data and show that less than half of patients with T2DM reach the target HBA1c levels and only 10% of them simultaneously attain the targets for blood glucose, blood pressure, LDL Cholesterol. The situation is even worse in patients with T1DM, with less than 5% attainment rates of the three targets. When we also consider smoking cessation and regular exercise, only 1.5% of patients with both types of diabetes reach all these targets simultaneously (6). There is also significant inertia in establishing appropriate targets and optimizing treatment to achieve treatment goals (11, 21, 22). To solve this problem, we should better understand the reasons behind it.
Diabetic Kidney Disease (DKD): Scope of the Problem
There are significant problems in the current practice of diabetes management involving the screening of DKD, optimization of therapy, making timely referrals, and managing risk factors and complications (23). The failure to establish appropriate targets and modify treatment to attain the goals, namely “clinical inertia” is responsible for the increased complications and health care burden (11, 24). Some of the main barriers to optimal patient care are touched upon below:
Patient-Related Factors
The capacity of patients to obtain, process, and understand basic health information, so-called “health literacy”, is one of the key factors in the appropriate management of patients with diabetes (25, 26). With diabetes in general have unhealthy lifestyles, which are not easy to modify (27). Older adults and patients with lower socio-economic status are more likely to have diabetes (28, 29) and less likely to follow the recommendations of their physicians (30). Many people with diabetes are not intended to use insulin due to the fear of hypoglycemia or weight gain or becoming dependent on insulin treatment (31, 32). Negative media coverage is also a significant reason for the incompliance especially of statins (22, 33, 34). Polypharmacy is also a major obstacle in reducing patient compliance and the attainment of targets (35).
Physician-Related Factors
Diabetes is so common that most of the patients are inevitably followed up in primary or secondary care facilities. Physicians working in these services may not have enough knowledge or experience in setting appropriate targets or implementing medications or modifying treatment while managing patients with diabetes (11). Low GFR is often not considered for adjusting the dose of antidiabetic drugs that are contraindicated in DKD (36). Also, physicians may not care enough to modify the doses of antidiabetic and antihypertensive medications during the follow-up of patients with diabetes (21). Lack of enough time to communicate with the patients and lack of supporting health staff are always the leading barriers in the crowded outpatient units (23). There are a multitude of diabetes guidelines to fill the knowledge gap in the field (14–17). However, physicians working in crowded outpatient units are bewildered by these long, complicated, and hard-to-read documents. They need concise, and problem-oriented algorithms to help them find their way.
Healthcare System
High quality and sustainable health care depend on well-adjusted infrastructures of the healthcare system, software for the electronic data recording and follow-up, wide-ranging health insurance coverage, and a reasonable reimbursement strategy (37). There are huge differences between the costs of new and old antihyperglycemic medications, which is not easy to be afforded by the patients (38). All these factors significantly differ between different countries. Doctors lack enough time to spend with their patients. The centers may not have enough capacity for necessary laboratory tests and many physicians do not have a consultation link for further management of the complications of their patients.
Grand Challenge in the Prevention and Management of DKD and Its Consequences
We need to cross all these barriers to optimize the management of patients with DKD and prevent its severe outcomes. Strategies should be implemented at every level for judicious patient care. Below I’d like to mention these strategies in brief.
Patient-Level Strategies
The higher the education of the patients, the better the attainment of the treatment targets (6). Therefore, every effort should be spent to increase public health literacy. Moreover, patients with diabetes and their families should be informed about the possible consequences of diabetes, the side effects of medications, and the ways of handling acute and chronic complications. More attention should be paid to the vulnerable patients for the risk of DKD and its consequences, such as the older adults and the patients with lower socioeconomic status. As the establishment of a healthy lifestyle is the key element of better patient care, all patients should be encouraged for healthy eating, performing exercise, and smoke cessation. Also, patients should be assisted by judicious websites and social media pages, which are designed to give evidence-based, comprehensible, and non-biased information about diabetes and its complications. The media should be more sensitive to cover the news about medical and pharmacological innovations and improvements.
Physician-Level Strategies
The prevalence of diabetes is substantially increased in recent decades. Therefore, the graduates of the medical schools should be well educated about the diagnosis and management of diabetes mellitus. Also, postgraduate courses or certification programs should be implemented regularly to improve the information and experience of the physicians working in the field. Lengthy guidelines should be summarized to the rule of thumb brochures for the busy physicians to guide them for the screening, diagnosis, and management of patients with diabetes.
Strategies to Improve Healthcare
To increase the time spent for each patient and to better educate them, interconnected healthcare teams equipped with skilled physicians, nurses, dietitians, podiatrists, and social workers should be established. Intelligent electronic health registries should be implemented not only to store data but also to alert the physicians when to screen for DKD, how to apply appropriate medications, and when to refer patients to nephrologists. The health insurance coverage should be disseminated and the drugs with cardioprotective functions should be reimbursed in general. To improve public healthcare strategies, real-world evidence about health economics should be processed and published. Also, clinical studies should be undertaken to develop biomarkers for the early detection of patients with a high risk of developing DKD.
Objectives of the Diabetic Nephropathy Special Issue
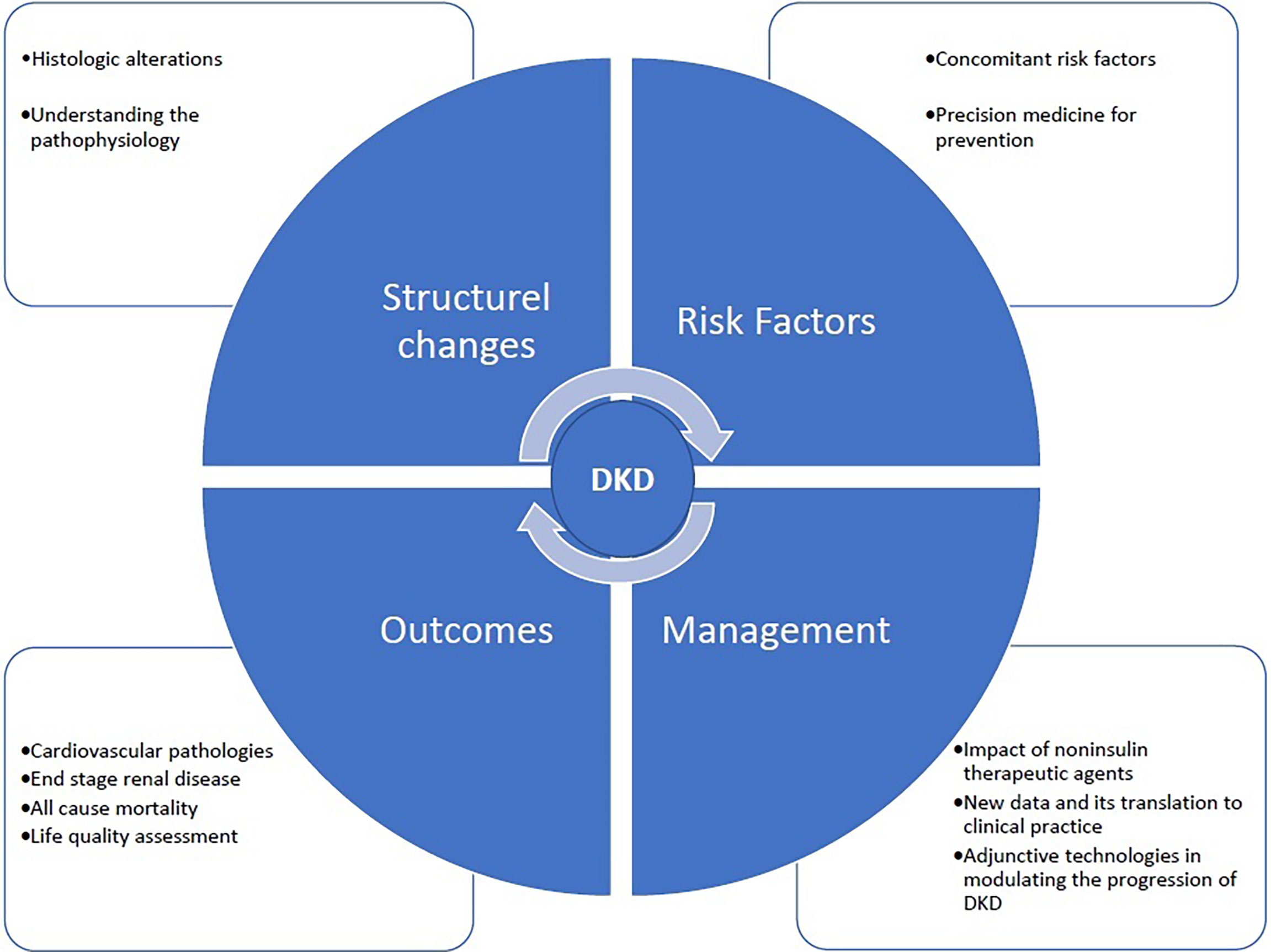
The critical mission of Frontiers in Clinical Diabetes and Healthcare section on Diabetes Nephropathy is to provide a global network between the basic and clinical scientists and the clinicians. The fast and easy publication platform of the journal helps the authors to quickly submit their work, which will immediately be evaluated by the distinguished editors and referred to the expert referees without wasting time. Our dedication is to unite the basic and clinical information and radiate them to the physicians working in the field to help improving the management of diabetes and preventing its ominous complication, DKD. The potential fields of publication that will be covered by Diabetes Nephropathy are given in Figure 1.
Author Contributions
The author confirms being the sole contributor to this work and has approved it for publication.
Conflict of Interest
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Stephens JW, Brown KE, Min T. Chronic Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes: Implications for Managing Glycaemic Control, Cardiovascular and Renal Risk. Diabetes Obes Metab (2020) 22:32–45. doi: 10.1111/dom.13942
2. Boer IH de, Rue TC, Hall YN, Heagerty PJ, Weiss NS, Himmelfarb J. Temporal Trends in the Prevalence of Diabetic Kidney Disease in the United States. JAMA (2011) 305:2532–9. doi: 10.1001/jama.2011.861
3. Norris KC, Smoyer KE, Rolland C, Vaart JVd, Grubb EB. Albuminuria, Serum Creatinine, and Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate as Predictors of Cardio-Renal Outcomes in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Kidney Disease: A Systematic Literature Review. BMC Nephrol (2018) 19:36. doi: 10.1186/s12882-018-0821-9
4. Ninomiya T, Perkovic V, de GBE, Zoungas S, Pillai A, Jardine M, et al. Albuminuria and Kidney Function Independently Predict Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes in Diabetes. J Am Soc Nephrol (2009) 20:1813–21. doi: 10.1681/asn.2008121270
5. Abdel-Motal UM GA, Abdelalim EM, Ponnuraja C, Iken K, Jahromi M, Doss GP, et al. Prevalence of Nephropathy in Type 1 Diabetes in the Arab World: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diabetes Metab Res Rev (2018) 34:e3026. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3026
6. Sonmez A, Haymana C, Bayram F, Salman S, Dizdar OS, Gurkan E, et al. Turkish Nationwide SurvEy of Glycemic and Other Metabolic Parameters of Patients With Diabetes Mellitus (TEMD Study). Diabetes Res Clin Pr (2018) 146:138–47. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2018.09.010
7. Gomes MB, Pizarro MH, Muniz LH, Barros BSV, Melo LGN, Santos DC, et al. Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease in an Admixed Population of Patients With Type 1 Diabetes. A Multicenter Study in Brazil. Diabetes Res Clin Pr (2020) 170:108490. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108490
8. Bryson CL, Ross HJ, Boyko EJ, Young BA. Racial and Ethnic Variations in Albuminuria in the US Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III) Population: Associations With Diabetes and Level of CKD. Am J Kidney Dis (2006) 48:720–6. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2006.07.023
9. Pugliese G, Solini A, Bonora E, Fondelli C, Orsi E, Nicolucci A, et al. Chronic Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes: Lessons From the Renal Insufficiency And Cardiovascular Events (RIACE) Italian Multicentre Study. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis (2014) 24:815–22. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2014.02.013
10. Dwyer JP, Parving H-H, Hunsicker LG, Ravid M, Remuzzi G, Lewis JB. Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Management: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care (2021) 44(Suppl 1):S125–50. doi: 10.2337/dc21-S010
11. Strain WD, Blüher M, Paldánius P. Clinical Inertia in Individualising Care for Diabetes: Is There Time to do More in Type 2 Diabetes? Diabetes Ther (2014) 5:347–54. doi: 10.1007/s13300-014-0077-8
12. Umanath K, Lewis JB. Update on Diabetic Nephropathy: Core Curriculum 2018. Am J Kidney Dis (2018) 71:884–95. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2017.10.026
13. Coca SG, Ismail-Beigi F, Haq N, Krumholz HM, Parikh CR. Role of Intensive Glucose Control in Development of Renal End Points in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arch Intern Med (2012) 172:761–9. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2011.2230
14. Boer IH de, Caramori ML, Chan JCN, Heerspink HJL, Hurst C, Khunti K, et al. KDIGO 2020 Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int (2020) 98:S1–S115. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.06.019
15. American Diabetes Association. Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Management: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care (2021) 44(Suppl 1):S125–50. doi: 10.2337/cd21-pe01
16. Cosentino F, Grant PJ, Aboyans V, Bailey CJ, Ceriello A, Delgado V, et al. ESC Guidelines on Diabetes, Pre-Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Diseases Developed in Collaboration With the EASDThe Task Force for Diabetes, Pre-Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Eur Heart J (2019) 41:255–323. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz486
17. Sattar N, McMurray JJ, Cheng AY. Cardiorenal Risk Reduction Guidance in Diabetes: Can We Reach Consensus? Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol (2020) 8:357–60. doi: 10.1016/s2213-8587(20)30062-0
18. Cotter TG, Dinneen SF, Healy DA, Bell MJ, Cunningham A, O’Shea PM, et al. Glycaemic Control is Harder to Achieve Than Blood Pressure or Lipid Control in Irish Adults With Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pr (2014) 106:e56–9. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2014.09.036
19. Wong ND, Patao C, Wong K, Malik S, Franklin SS, Iloeje U. Trends in Control of Cardiovascular Risk Factors Among US Adults With Type 2 Diabetes From 1999 to 2010: Comparison by Prevalent Cardiovascular Disease Status. Diabetes Vasc Dis Re (2013) 10:505–13. doi: 10.1177/1479164113496828
20. Xu S, Sun F, Xu W, Jiao K, Shi B, Xie X, et al. Simultaneous Control of Blood Glucose, Blood Pressure, and Lipid Among Drug-Treated Type 2 Diabetes Patients From Shaanxi Province, North-Western China: A Multicenter Study. Niger J Clin Pract (2016) 19:784–92. doi: 10.4103/1119-3077.181359
21. Sonmez A, Tasci I, Demirci I, Haymana C, Barcin C, Aydin H, et al. A Cross-Sectional Study of Overtreatment and Deintensification of Antidiabetic and Antihypertensive Medications in Diabetes Mellitus: The TEMD Overtreatment Study. Diabetes Ther (2020) 11:1045–59. doi: 10.1007/s13300-020-00779-0
22. Bayram F, Sonmez A, Haymana C, Sabuncu T, Dizdar OS, Gurkan E, et al. Utilization of Statins and LDL-Cholesterol Target Attainment in Turkish Patients With Type 2 Diabetes - a Nationwide Cross-Sectional Study (TEMD Dyslipidemia Study). Lipids Health Dis (2020) 19:237. doi: 10.1186/s12944-020-01408-2
23. Gembillo G, Ingrasciotta Y, Crisafulli S, Luxi N, Siligato R, Santoro D, et al. Kidney Disease in Diabetic Patients: From Pathophysiology to Pharmacological Aspects With a Focus on Therapeutic Inertia. Int J Mol Sci (2021) 22:4824. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094824
24. Phillips LS, Branch WT, Cook CB, Doyle JP, El-Kebbi IM, Gallina DL, et al. Clinical Inertia. Ann Intern Med (2001) 135:825. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-135-9-200111060-00012
25. Health literacy: report of the Council on Scientific Affairs. Ad Hoc Committee on Health Literacy for the Council on Scientific Affairs, American Medical Association. JAMA (1999) 281:552–7. doi: 10.1001/jama.281.6.552
26. Baker DW. The Meaning and the Measure of Health Literacy. J Gen Intern Med (2006) 21:878–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1497.2006.00540.x
27. Cramer JA. A Systematic Review of Adherence With Medications for Diabetes. Diabetes Care (2004) 27:1218–24. doi: 10.2337/diacare.27.5.1218
28. Connolly V, Unwin N, Sherriff P, Bilous R, Kelly W. Diabetes Prevalence and Socioeconomic Status: A Population Based Study Showing Increased Prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Deprived Areas. J Epidemiol Commun Health (2000) 54:173. doi: 10.1136/jech.54.3.173
29. Kalyani RR, Golden SH, Cefalu WT. Diabetes and Aging: Unique Considerations and Goals of Care. Diabetes Care (2017) 40:440–3. doi: 10.2337/dci17-0005
30. García-Pérez L-E, Álvarez M, Dilla T, Gil-Guillén V, Orozco-Beltrán D. Adherence to Therapies in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Ther (2013) 4:175–94. doi: 10.1007/s13300-013-0034-y
31. Nakar S, Yitzhaki G, Rosenberg R, Vinker S. Transition to Insulin in Type 2 Diabetes: Family Physicians’ Misconception of Patients’ Fears Contributes to Existing Barriers. J Diabetes Complicat (2007) 21:220–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2006.02.004
32. Peyrot M, Rubin RR, Lauritzen T, Skovlund SE, Snoek FJ, Matthews DR, et al. Resistance to Insulin Therapy Among Patients and Providers: Results of the Cross-National Diabetes Attitudes, Wishes, and Needs (DAWN) Study. Diabetes Care (2005) 28:2673–9. doi: 10.2337/diacare.28.11.2673
33. Matthews A, Herrett E, Gasparrini A, Staa TV, Goldacre B, Smeeth L, et al. Impact of Statin Related Media Coverage on Use of Statins: Interrupted Time Series Analysis With UK Primary Care Data. BMJ Clin Res Ed (2016) 353:i3283. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i3283
34. Haymana C, Berlik H, Güneş Y, Tunçez OE, Aytekin C, Tapıkara Z, et al. Identifying Undiagnosed or Undertreated Patients With Familial Hypercholesterolemia From the Laboratory Records of a Tertiary Medical Center. Turk Kardiyoloji Dernegi Arsivi Archives Turkish Soc Cardiol (2017) 45:731–8. doi: 10.5543/tkda.2017.63846
35. Jaam M, Ibrahim MIM, Kheir N, Awaisu A. Factors Associated With Medication Adherence Among Patients With Diabetes in the Middle East and North Africa Region: A Systematic Mixed Studies Review. Diabetes Res Clin Pr (2017) 129:1–15. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2017.04.015
36. Trifirò G, Parrino F, Pizzimenti V, Giorgianni F, Sultana J, Muscianisi M, et al. The Management of Diabetes Mellitus in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease: A Population-Based Study in Southern Italy. Clin Drug Invest (2016) 36:203–12. doi: 10.1007/s40261-015-0367-6
37. Müller L, Oakley RE, Saad M, Mokdad AH, Etolhi GA, Flahault A. A Multidimensional Framework for Rating Health System Performance and Sustainability: A Nine Plus One Ranking System. J Glob Health (2021) 11:4025. doi: 10.7189/jogh.11.04025
Keywords: diabetic nephropathy, diabetic kidney disease, diabetes mellitus, clinical inertia, cardiovascular risk
Citation: Sonmez A (2021) Challenges in the Prevention and Management of Diabetic Kidney Diseases. Front. Clin. Diabetes Healthc. 2:728320. doi: 10.3389/fcdhc.2021.728320
Received: 21 June 2021; Accepted: 06 August 2021;
Published: 23 August 2021.
Edited by:
Claudia Torino, Italian National Research Council, ItalyReviewed by:
Ali A. Rizvi, Emory University, United StatesCopyright © 2021 Sonmez. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Alper Sonmez, YWxwZXJzb25tZXpAeWFob28uY29t
 Alper Sonmez
Alper Sonmez