
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Biomater. Sci. , 17 July 2024
Sec. Bioinspired and Complex Materials
Volume 3 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fbiom.2024.1458672
This article is part of the Research Topic Women in Biomaterials Science 2023 View all 12 articles
This article is a correction to:
Macrophage variance: investigating how macrophage origin influences responses to soluble and physical cues with immortalized vs. primary cells in 2D and 3D culture
 Jodi Graf1
Jodi Graf1 Kartik Bomb1
Kartik Bomb1 Michael Trautmann-Rodriguez1
Michael Trautmann-Rodriguez1 Bader M. Jarai1
Bader M. Jarai1 Nicole Gill1
Nicole Gill1 April M. Kloxin1,2*†
April M. Kloxin1,2*† Catherine A. Fromen1*†
Catherine A. Fromen1*†by Graf J, Bomb K, Trautmann-Rodriguez M, Jarai BM, Gill N, Kloxin AM and Fromen CA (2024). Front. Biomater. Sci. 3:1399448. doi: 10.3389/fbiom.2024.1399448
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 9G as published. The labels on the images “BMM” and “Raw264.7” were inadvertently switched. The corrected figure and its caption appear below.
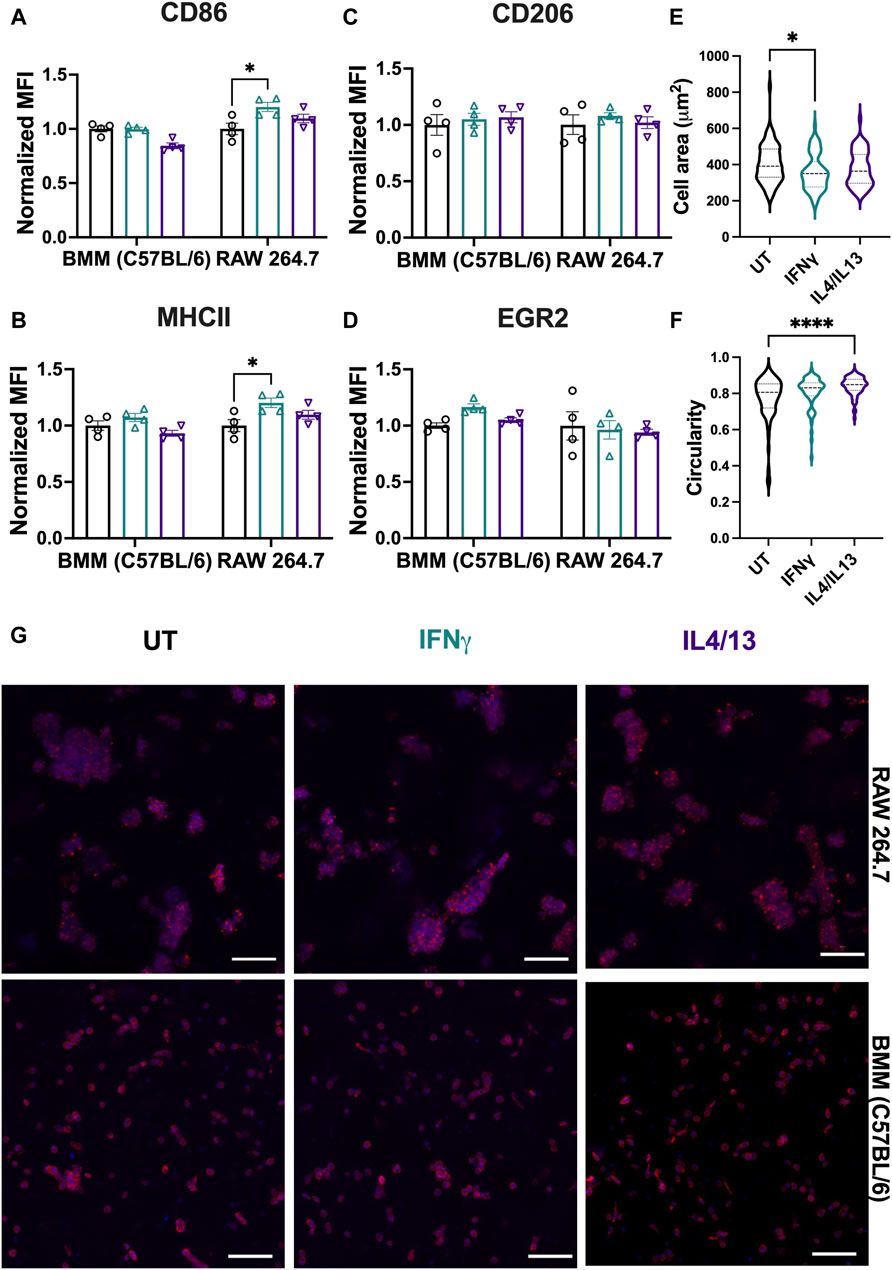
Figure 9. Effect of soluble stimuli on macrophage polarization in well-defined, bioprinted 3D cultures. Effect of polarization stimuli on macrophage polarization was determined for RAW 264.7 cells and primary BMMs (C57BL/6) in 3D culture (1.1 kPa PEG-peptide hydrogels with RGD, GFOGER, YIGSR, and HA). (A) CD86 and (B) MHCII were used as M1 markers. (C) CD206 and (D) EGR2 were used as M2 markers. All data are normalized to the UT control for the respective cell type. (E) Cell area and (F) circularity were quantified for all the cell types across different conditions. (G) Representative images of BMMs with nuclei (blue) and F-actin (red) qualitatively show morphology of BMMs across all the treatment groups. Statistics were performed using Tukey’s post hoc test with one-way ANOVA. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.” Scale bar: 100 µm.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: macrophage, hydrogel, biomaterials, innate immune cell, polarization, 3D culture
Citation: Graf J, Bomb K, Trautmann-Rodriguez M, Jarai BM, Gill N, Kloxin AM and Fromen CA (2024) Corrigendum: Macrophage variance: investigating how macrophage origin influences responses to soluble and physical cues with immortalized vs. primary cells in 2D and 3D culture. Front. Biomater. Sci. 3:1458672. doi: 10.3389/fbiom.2024.1458672
Received: 02 July 2024; Accepted: 03 July 2024;
Published: 17 July 2024.
Approved by:
Frontiers Editorial Office, Frontiers Media SA, SwitzerlandCopyright © 2024 Graf, Bomb, Trautmann-Rodriguez, Jarai, Gill, Kloxin and Fromen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: April M. Kloxin, YWtsb3hpbkB1ZGVsLmVkdQ==; Catherine A. Fromen, Y2Zyb21lbkB1ZGVsLmVkdQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share last authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.