- 1Department of Research, Guangxi Medical University Cancer Hospital, Nanning, China
- 2College of Material Sciences and Chemical Engineering, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin, China
- 3National Academy of Sciences of Tajikistan, Dushanbe, Tajikistan
A Corrigendum on
Tailoring mSiO2-SmCox nanoplatforms for magnetic/photothermal effect-induced hyperthermia therapy
by Liang X, Xu W, Li S, Kurboniyon MS, Huang K, Xu G, Wei W, Ning S, Zhang L and Wang C (2023). Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 11:1249775. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1249775
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 5D, 6F as published. The corrected Figure 5D, 6F and its caption appear below.
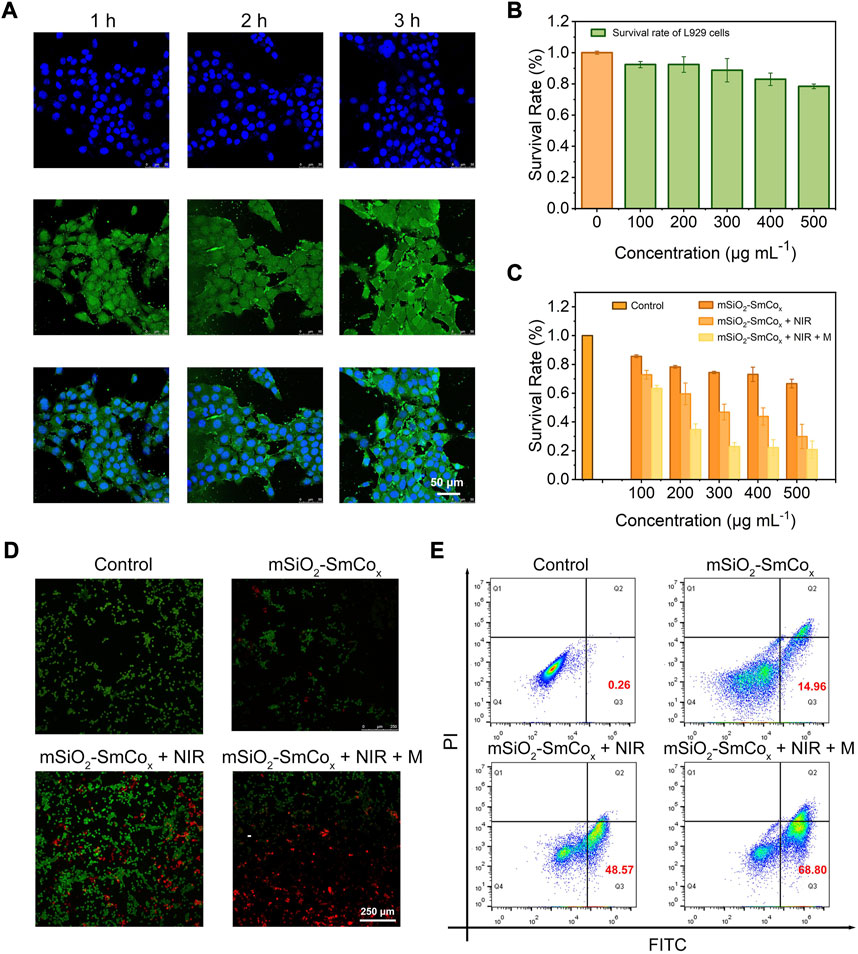
FIGURE 5. (A) CLSM images of 4T1 cells after coincubation with mSiO2-SmCox (Sm/Co = 1:2) NPs for 1, 2, and 3 h (B) The survival rate of L919 cells after coincubation with mSiO2-SmCox (Sm/Co = 1:2) NPs under different concentrations (100, 200, 300, 400, and 500 μg mL−1). (C) The survival rate of 4T1 cells after coincubation with mSiO2-SmCox (Sm/Co = 1:2) NPs, mSiO2-SmCox (Sm/Co = 1:2) NPs + NIR, mSiO2-SmCox (Sm/Co = 1:2) NPs + NIR + M groups under different concentrations (100, 200, 300, 400, and 500 μg mL−1). (D) AM/PI staining of 4T1 cells after different treatments. (E) Flow cytometry results of 4T1 cells after different treatments.
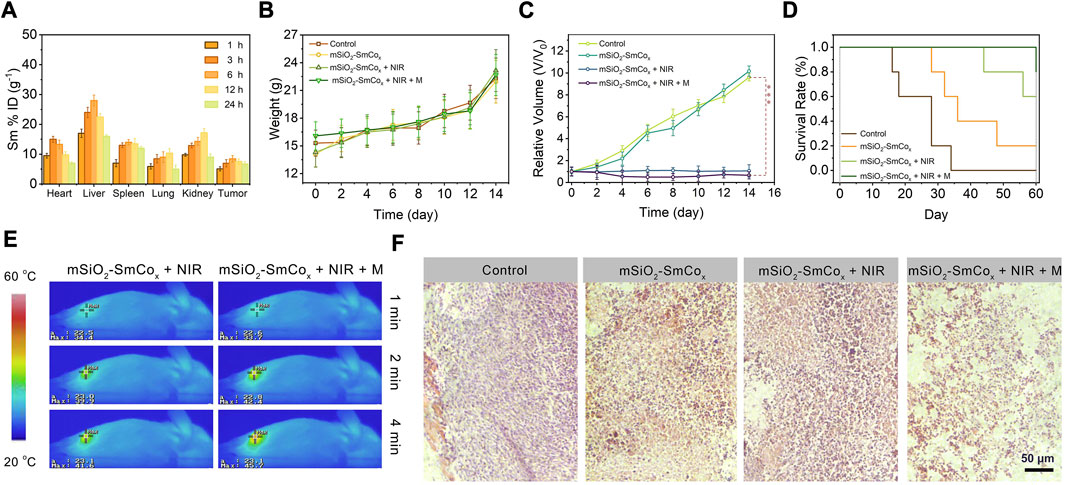
FIGURE 6. (A) Biodistribution of Sm ions (% injected dose (ID) of Sm per Gram of tissues) in main tissues and tumor in 1, 3, 6, 12, and 24 h of intravenous administrations of mSiO2-SmCox (Sm/Co = 1:2) NPs (n = 3). (B) Changes in the average body weight, (C) relative tumor volume, and (D) survival rates of mice with various treatments. (E) Temperature elevation at the tumor sites of 4T1 tumor-bearing mice under 808 nm laser (1.0 W cm−2) irradiation and 808 nm laser irradiation in magnetic conditions with mSiO2-SmCox (Sm/Co = 1:2) NPs for 4 min (F) H&E-stained photographs of tumor slices obtained from tumor-bearing mice after treatments. Error bars are based on the standard errors of the mean. Statistical analysis is assessed by unpaired Student’s two-sided t-test. ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, or *p < 0.05.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: magnetic effect, photothermal effect, permanent magnet, mSiO2, tumor therapy
Citation: Liang X, Xu W, Li S, Kurboniyon MS, Huang K, Xu G, Wei W, Ning S, Zhang L and Wang C (2023) Corrigendum: Tailoring mSiO2-SmCox nanoplatforms for magnetic/photothermal effect-induced hyperthermia therapy. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 11:1281270. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1281270
Received: 22 August 2023; Accepted: 08 September 2023;
Published: 19 September 2023.
Edited and reviewed by:
Arif Gulzar, University of Queensland, AustraliaCopyright © 2023 Liang, Xu, Li, Kurboniyon, Huang, Xu, Wei, Ning, Zhang and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chen Wang, d2FuZ2NoZW44OEBneG11LmVkdS5jbg==; Litu Zhang, emhhbmdsaXR1QGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
 Xinqiang Liang
Xinqiang Liang Wenting Xu1
Wenting Xu1 Siyi Li
Siyi Li Wene Wei
Wene Wei Litu Zhang
Litu Zhang Chen Wang
Chen Wang