
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. , 30 March 2023
Sec. Biomaterials
Volume 11 - 2023 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2023.1179873
This article is a correction to:
Osteogenic and anti-inflammatory effect of the multifunctional bionic hydrogel scaffold loaded with aspirin and nano-hydroxyapatite
A Corrigendum on
Osteogenic and anti-inflammatory effect of the multifunctional bionic hydrogel scaffold loaded with aspirin and nano-hydroxyapatite
by Li S, Xiaowen Y, Yang Y, Liu L, Sun Y, Liu Y, Yin L and Chen Z (2023). Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 11:1105248. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1105248
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 2 as published. The image selection and order were incorrect. The corrected Figure 2 and its caption appear below.
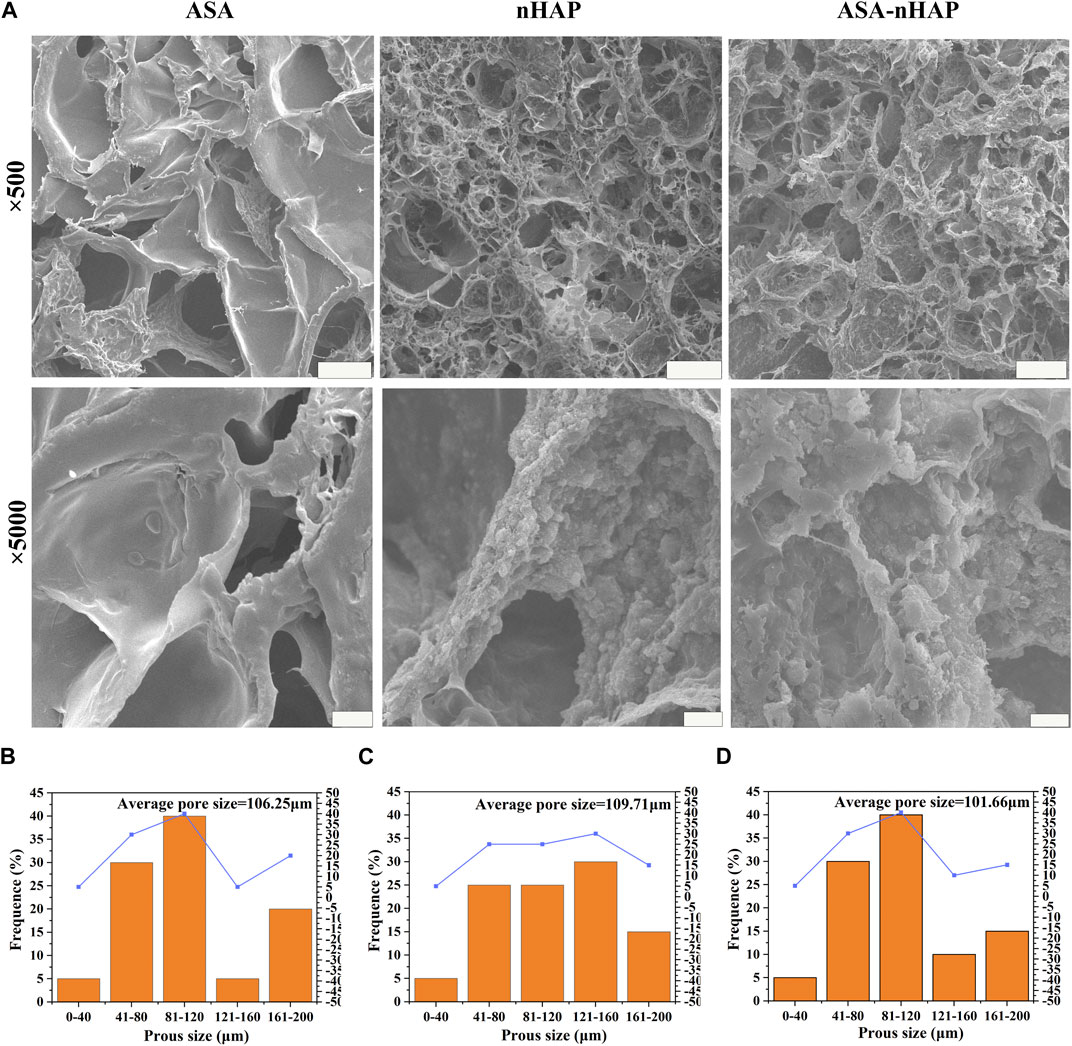
FIGURE 2. Microstructure of hydrogel scaffolds. (A) SEM images of the ASA group, nHAP group, and ASA-nHAP group. The scale bar for low-magnification images is 100 μm; the scale bar for high-magnification images is 10 μm. (B–D) Pore size distribution pattern of the ASA group, nHAP group, and ASA-nHAP group.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: aspirin, multifunctional hydrogel scaffold, sustained release, tissue engineering, nano-hydroxyapatite
Citation: Li S, Xiaowen Y, Yang Y, Liu L, Sun Y, Liu Y, Yin L and Chen Z (2023) Corrigendum: Osteogenic and anti-inflammatory effect of the multifunctional bionic hydrogel scaffold loaded with aspirin and nano-hydroxyapatite. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 11:1179873. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1179873
Received: 05 March 2023; Accepted: 23 March 2023;
Published: 30 March 2023.
Edited and reviewed by:
Jianyun Zhang, Peking University Hospital of Stomatology, ChinaCopyright © 2023 Li, Xiaowen, Yang, Liu, Sun, Liu, Yin and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhiyu Chen, a3F4ZmNoZW5AMTYzLmNvbQ==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.