
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol., 27 September 2023
Sec. Nanobiotechnology
Volume 11 - 2023 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2023.1148674
This article is part of the Research TopicPreparation and Application of Intelligent Bioactive NanocolloidsView all 17 articles
This article is a correction to:
PPy@Fe3O4 nanoparticles inhibit the proliferation and metastasis of CRC via suppressing the NF-κB signaling pathway and promoting ferroptosis
A Corrigendum on
PPy@Fe3O4 nanoparticles inhibit the proliferation and metastasis of CRC via suppressing the NF-κB signaling pathway and promoting ferroptosis
by Yu Z, Tong S, Wang C, Wu Z, Ye Y, Wang S and Jiang K (2022). Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 10:1001994. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.1001994
In the published article, there was an error in Figures 2E, 5 as published. Modifications to UV absorption spectra in Figure 2E and NF-κB related protein typographical errors in the WB experiment in Figure 5 were made after a recheck of the figures, but not included in the final article. The corrected Figures 2, 5 and their captions appear below.
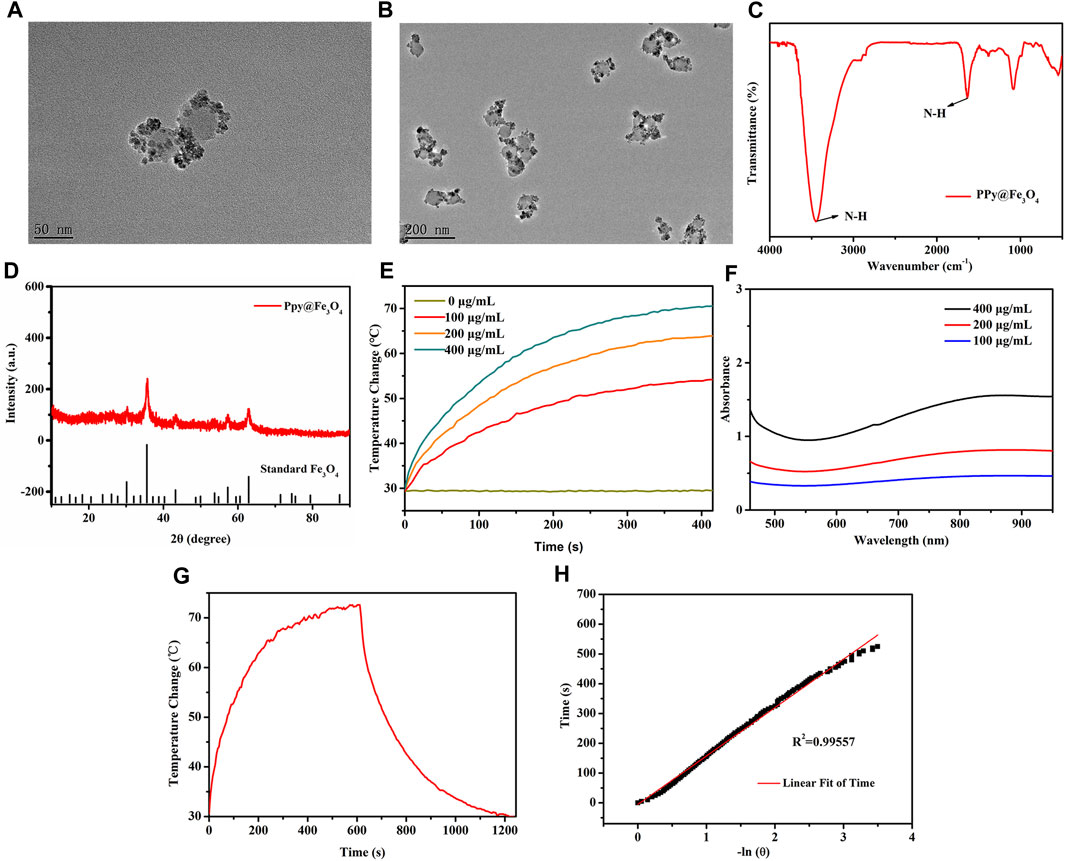
FIGURE 2. The characterization and photothermal properties of the PPy@Fe3O4 NPs. (A,B) High and Low TEM images of PPy@Fe3O4 NPs; (C) FTIR spectra of PPy@Fe3O4 NPs; (D) XRD spectra of PPy@Fe3O4 NPs; (E) UV-Vis-NIR absorption spectra of PPy@Fe3O4 NPs at different concentrations; (F) Temperature change curve with various concentrations of NPs; (G) Temperature curve of rising with irradiation and naturally cooling; (H) Linear regression curve of cooling process (red).
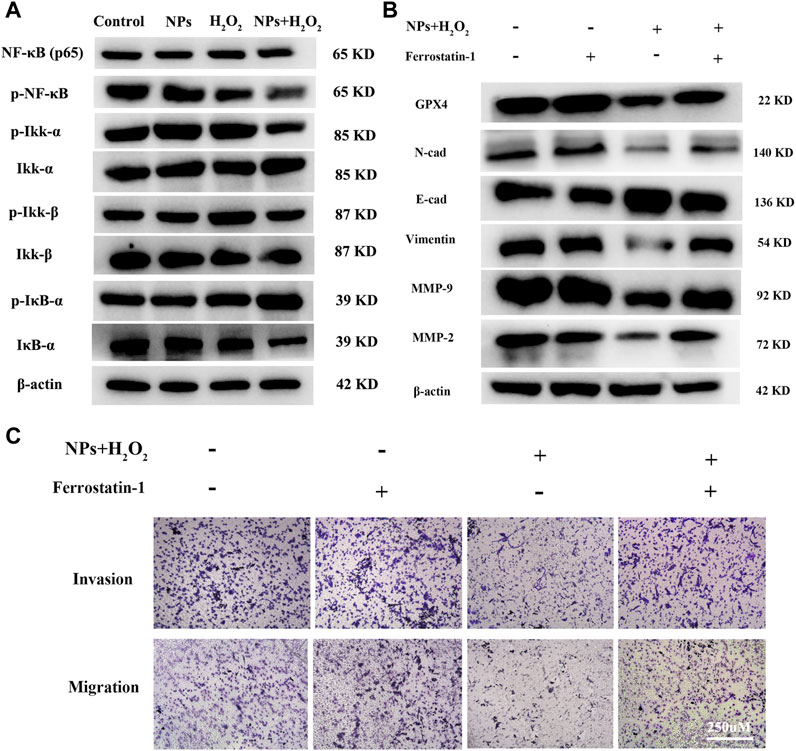
FIGURE 5. PPy@Fe3O4 NPs suppress CRC cells metastasis by promoting cell ferroptosis and inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway. (A) Western blot. Colorectal cancer cell line DLD1 was treated with various groups (Control, H2O2, NPs and NPs + H2O2), and then subjected to Western blot analysis of the key proteins of the NF-KB signaling pathway (Ikk-β, p-Ikk-β, ikk-α, p-Ikk-α, NF-κβ, p-NF-κβ, IκB-α and p-IκB-α). (B) Effects of the ferroptosis inhibitor Ferrostatin-1 on PPy@Fe3O4 NPs-induced metastasis-related proteins expression. (C) Transwell showed that PPy@Fe3O4 NPs-induced cell migration and invasion were abolished after addition of the ferroptosis inhibitor Ferrostatin-1 in CRC cell.
Additionally, the statistical method in the “Statistics” section and “PPy@Fe3O4 NPs inhibited EMT via the NF-κB signaling pathway” section were incorrect due to translation error and clerical error.
A correction has been made to Materials and methods section, subsection Statistics. A correction has also been made to the Results section, subsection PPy@Fe3O4 NPs inhibited EMT via the NF-κB signaling pathway, Paragraph 1. These sentences previously stated, respectively:
“Based on experiments performed in triplicate for cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, all data are presented as mean ± SEM. In the animal study of nude mice, the data are presented as mean ± SEM of 5 mice. Statistical analyses were performed with the χ2 test or the Student’s t-test (two-tailed unpaired). All the data were analyzed using SPSS 22.0 software and p < 0.05 was considered significant.”
“There was an increase in the levels of IKKα and IKKβ in DLD1, as well as a decrease in the amounts of IκBα after treatment with H2O2. P65 levels did not change significantly, but phospho-p65 expression increased. We discovered that the expression of phosphorylated (p)p65, IKKα, IKKβ, and IκBα, which are essential for activating the NF-κB signaling pathway, were downregulated by NPs with H2O in DLD1 cells.”
The corrected sentences appear below:
“All data are presented as mean ± SD. Statistical analyses were performed with the χ2 test or the Student’s t-test (two-tailed unpaired). All the data were analyzed using Origin and Graphpad. Moreover, p < 0.05 is considered statistically significant.”
“There was a decrease in the levels of p-IKKα and p-IKKβ in DLD1, as well as an increase in the amounts of p-IκBα after treatment with NPs and H2O2. P65 levels did not change significantly, but phospho-p65 expression decreased. We discovered that the expression of phosphorylated (p)p65, p-IKKα, p-IKKβ, and IκBα, which are essential for activating the NF-κB signaling pathway, were downregulated by NPs with H2O2 in DLD1 cells.”
There was also an error in the Funding statement. National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 81871962) has expired and ceased. The correct Funding statement appears below.
“This study was supported by the National Scientific Center Project (No. 62088101) and the Industry-University-Research Innovation Fund in Ministry of Education of the People’s Republic of China (No. 2018A01013).”
The authors apologize for these errors and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: colorectal cancer, nanoparticles, metastasis, NF-κB, ferroptosis
Citation: Yu Z, Tong S, Wang C, Wu Z, Ye Y, Wang S and Jiang K (2023) Corrigendum: PPy@Fe3O4 nanoparticles inhibit the proliferation and metastasis of CRC via suppressing the NF-κB signaling pathway and promoting ferroptosis. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 11:1148674. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1148674
Received: 20 January 2023; Accepted: 18 September 2023;
Published: 27 September 2023.
Edited and reviewed by:
Yu Luo, Shanghai University of Engineering Sciences, ChinaCopyright © 2023 Yu, Tong, Wang, Wu, Ye, Wang and Jiang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kewei Jiang, ZHJfamlhbmdrZXdlaUAxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.