Dual-Targeting Nanoparticle-Mediated Gene Therapy Strategy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Delivering Small Interfering RNA
- 1Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
- 2Department of Vascular Surgery, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
A Corrigendum on
Dual-Targeting Nanoparticle-Mediated Gene Therapy Strategy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Delivering Small Interfering RNA
by Zheng, Q. C., Jiang, S., Wu, Y. Z., Shang, D., Zhang, Y., Hu, S. B., et al. (2020). Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 8:512. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00512
In the published article, there was an error in affiliations 1 and 2. Affiliation 1 should be “Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China”. Affiliation 2 should be “Department of Vascular Surgery, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology,Wuhan, China”.
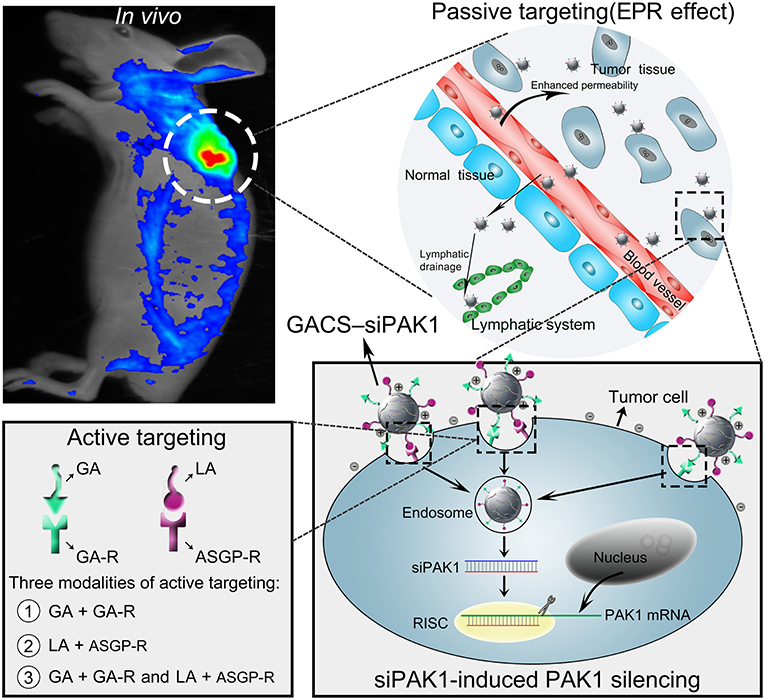
In the original article, there was a mistake in the Graphical Abstract and in Figure 1 as published. “EPR effect” was incorrectly written as “ERP effect”. The corrected Graphical Abstract and Figure 1 appear below.
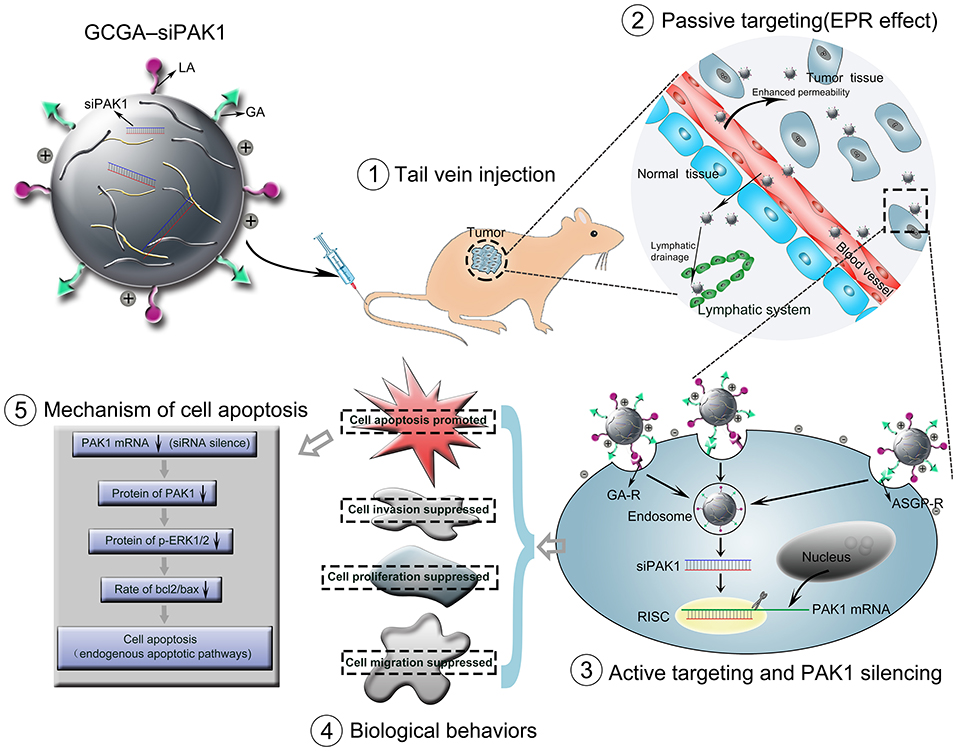
Figure 1. Schematic representation of GCGA–siPAK1 promoting targeted delivery and therapeutic efficacy in HCC xenograft mouse model. The process includes four steps: (1) intravenous administration of GCGA–siPAK1 via tail vein; (2) NPs accumulation in tumor tissue via passive targeting (commonly known as the EPR effect); (3) three modalities of active targeting via dual-ligand-receptor-mediated endocytosis and mechanism of RNAi (siPAK1-induced PAK1 silencing); (4) tumor biological behaviors after PAK1 silencing; and (5) molecular mechanism of promoting cell apoptosis via PAK1/MEK/ERK pathway.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Keywords: small interfering RNA, gene therapy, targeted therapy, chitosan, hepatocellular carcinoma, drug delivery
Citation: Zheng QC, Jiang S, Wu YZ, Shang D, Zhang Y, Hu SB, Cheng X, Zhang C, Sun P, Gao Y, Song ZF and Li M (2021) Corrigendum: Dual-Targeting Nanoparticle-Mediated Gene Therapy Strategy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Delivering Small Interfering RNA. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 9:656268. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.656268
Received: 20 January 2021; Accepted: 21 January 2021;
Published: 11 February 2021.
Approved by:
Frontiers Editorial Office, Frontiers Media SA, SwitzerlandCopyright © 2021 Zheng, Jiang, Wu, Shang, Zhang, Hu, Cheng, Zhang, Sun, Gao, Song and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zi Fang Song, zsong@hust.edu.cn; Min Li, liminmed@hust.edu.cn
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Qi Chang Zheng1†
Qi Chang Zheng1† Shuai Jiang
Shuai Jiang Yu Zhe Wu
Yu Zhe Wu Ping Sun
Ping Sun Zi Fang Song
Zi Fang Song