- Laboratory of Animal infectious Diseases and Molecular Immunology, College of Animal Science and Technology, Guangxi University, Nanning, China
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) has had a devastating impact on the pig industry in China, and monitoring its genetic diversity is important for epidemiological surveillance and understanding its evolution. Here, we determine the complete genome sequences of two PRRSV strains, GXYL1403 and GXNN1839. Comparative, phylogenetic, and recombination detection program analyses show that the two isolates are recombinant strains with large-fragment amino acid deletions in nsp2. GXYL1403 possesses a unique deletion region of 124 amino acids in nsp2, and GXNN1839 contains a deletion of 131 amino acids in nsp2 as compared with VR2332. Further analysis of the full-length sequence suggests that GXYL1403 is a natural recombinant between sublineages 8.1 (CH-1a like) and 8.3 (JXA1-like). The recombination site of GXYL1403 is located in nsp9–nsp12 (8961nt−11181nt). GXNN1839 is a natural recombinant between the lineage 5 (VR-2332-like) and lineage 1 (NADC30-like) strains. The recombination events occurred in nsp9 (7872nt-8162nt) and in ORF2 (12587nt−13282nt) in the genome of GXNN1839. These results provide new evidence that PRRSV strains circulating in the environment have undergone recombination among the different lineages or sublineages of field strains, and these add to our understanding of RNA combination events that occur in PRRSV.
Introduction
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) is an important infectious disease caused by porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV), and it poses a serious threat to the global pig industry (1). PRRSV is a small, enveloped, positive-stranded RNA virus whose genome consists of at least 10 open reading frames (ORFs), namely ORF1a, ORF1b, ORF2a, ORF2b, ORF3, ORF4, ORF5, ORF5a, ORF6, and ORF7 (2). ORF1a and ORF1b are situated at the 5′ end of the genome and encode polyproteins that are self-cleaved to at least 16 non-structural proteins (nsps) by viral proteases (2, 3). ORF2a, ORF2b, ORF3, ORF4, ORF5, ORF5a, ORF6, and ORF7 are situated at the 3′ end of the genome and encode eight structural proteins, namely glycoprotein (GP) 2a, 2b, GP3, GP4, GP5, ORF5a protein, matrix protein (M), and nucleocapsid (N), respectively (3–5). PRRSV is divided into type 1 and 2 PRRSV genotypes, which only have about 60% nucleotide sequence identity (6, 7). Phylogenetic analyses of the ORF5 of type 2 PRRSV strains show that type 2 PRRSV could be divided into nine distinct lineages with each lineage containing several sublineages (8, 9). Type 2 PRRSV strains are prevalent in China and are distributed into four lineages and sublineages: lineages 1, 3, 5, and 8 are representatives of the NADC-30, QYYZ-like, VR-2332, and JXA1 strains, respectively (9). In 2006, a devastating outbreak of PRRS, caused by a highly pathogenic PRRSV (HP-PRRSV) representative with the JXA1 strain (sublineage 8.3) emerged in China, and this caused substantial economic losses for swine farming (10, 11). The lineage 3 PRRSV represented by the QYYZ strain emerged in 2010, and it is mainly circulating in southern China (12, 13). The NADC30-like PRRSV as represented by the WUH6 strain was first isolated in 2011 and is mainly found in northeast and central China (14–17).
The increasing diversity of the type 2 PRRSV is related to point mutations and genetic recombination among the field strains or in between the field and modified live vaccine (MLV) strains, which can lead to some new emerging antigenic variant strains (6, 18–24). In the present study, we identify two novel recombinant PRRSV strains circulating in swine farms in Guangxi, a province of southern China. We perform genome-wide sequence analysis of the two isolates and find new combination patterns in PRRSV evolution.
Materials and Methods
Cell Culture and Virus Isolation
Meat Animal Research Center-145 (MARC-145) cells and porcine alveolar macrophages (PAMs) were maintained in cell cultures as described in our previous study (25). Field samples (sera) were collected from clinically diseased pigs in Guangxi province, China. Samples were detected by RT-PCR using specific primers for the ORF5 gene of genotype 2 PRRSV (26). One positive sample was from 56 dying piglets exhibiting severe respiratory syndrome on a pig farm located in YuLing city, Guangxi Province, which has a total pig population of 823. One positive sample was from 18 pregnant sows suffering reproductive failure in a farm located in Nanning city, Guangxi Province in South China, which has a total sow population of 312. The positive samples were used for virus isolation using MARC-145 cells or PAMs. Cells were observed daily for the appearance of cytopathic effects (CPE). When 75% CPE was observed, the culture media were harvested and used for blinding passage in MARC-145 cells or PAMs. The PRRSV strain (GXYL1403) isolated from MARC-145 cells was then plaque-purified three times on MARC-145 cells for subsequent complete genome sequencing. The third passage of each virus strain was identified by RT-PCR and an indirect immunofluorescence assay (IFA).
RT-PCR Amplification and Complete Genome Determination
The viral genomic RNA was extracted from PRRSV-infected PAMs or MARC-145 cells and reverse transcribed into cDNA using M-MLV reverse transcriptase (Takara) according to the manufacturer's instructions. PCR was performed to amplify the complete genomic sequences of PRRSV isolates GXYL1403 and GXNN1839 by using PRRSV-specific primers as described previously (27, 28). The PCR products were purified using an E.Z.N.A.TM Gel Extraction Kit (OMEGA, USA) and cloned into a pMD18-T vector (TaKaRa, Dalian, China) for nucleotide sequencing. The complete genomic sequences of PRRSV isolates were assembled using the SeqMan program of DNAstar software, version 7.0.
Immunofluorescence Assay (IFA)
IFA was used to detect PRRSV N protein expression in PAMs and MARC-145 cells as described previously (25). At 72 h infection, the isolate-infected PAMs or MARC-145 cells were washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) twice and fixed using cold methanol for 15 min at room temperature and then blocked with 3% BSA (fraction V bovine serum albumin) (Roche, Mannheim, Germany) for 30 min. The cells were treated with a monoclonal antibody (mAb) against PRRSV N protein (SR30-A) (Rural Technologies, Inc., Brookings, SD, USA) as the primary antibody and incubated for 2 h at 37°C. Then, the cells were washed five times with PBS and incubated with goat antirabbit IgG H&L (Alexa Fluor® 488, Abcam) for 1 h at 37°C. Following five further washes with PBS, the cells were observed under a fluorescence microscope.
Sequence Comparison and Phylogenetic Analysis
Differences of sequences from the two isolates and reference strains from all over the world were analyzed and aligned using the MegAlign program in DNAstar 7.0 software (DNASTAR Inc., Madison, WI, USA). Phylogenetic trees, including the complete genomes and ORF5 from this study and the representative strains from China and other countries, were constructed by neighbor-joining in MEGA 6.0, using the maximum composite likelihood and bootstrap confidence values from 1,000 replicates. Detailed information on the PRRSV reference sequences is shown in Table 1.
Recombination Analyses
The complete genomic sequences of GXYL1403 and GXNN1839 were compared with PRRSV reference strains JXA1, CH1a, VR-2332, and NADC30 using the Recombination Detection Program (RDP) v4.66 with six different algorithms (RDP, GENECONV, MaxChi, BootScan, SiScan, and 3Seq) (29). The results were presented using the RDP method. Recombinant events were confirmed by Bootscan analysis in Simplot software (v3.5.1, JHK University, Baltimore, MD, USA) with the default parameters. A series of phylogenetic trees based on each of the sequence regions were constructed to further identify these putative recombination events.
Results
Isolation and Identification of PRRSV Strains
Two PRRSV-positive sera were used to inoculate the MARC-145 cells and PAMs for PRRSV isolation. Typical CPE, characterized by cell fusion and shedding, was induced in both MARC-145 cells and PAMs 48 h post-inoculation (hpi) (data not shown). To confirm the isolation of the PRRSV strains, IFA was conducted using a mAb against PRRSV N (SR-30A). PAMs and MARC-145 cells infected with PRRSV isolates reacted with the specific antibody against the PRRSV N protein (data not shown). These results indicate successful isolation of the infectious PRRSV strains. These PRRSV isolates were designated as GXYL1403 and GXNN1839, respectively.
Genomic Characteristics and Phylogenetic Analysis of the Two PRRSV Isolates
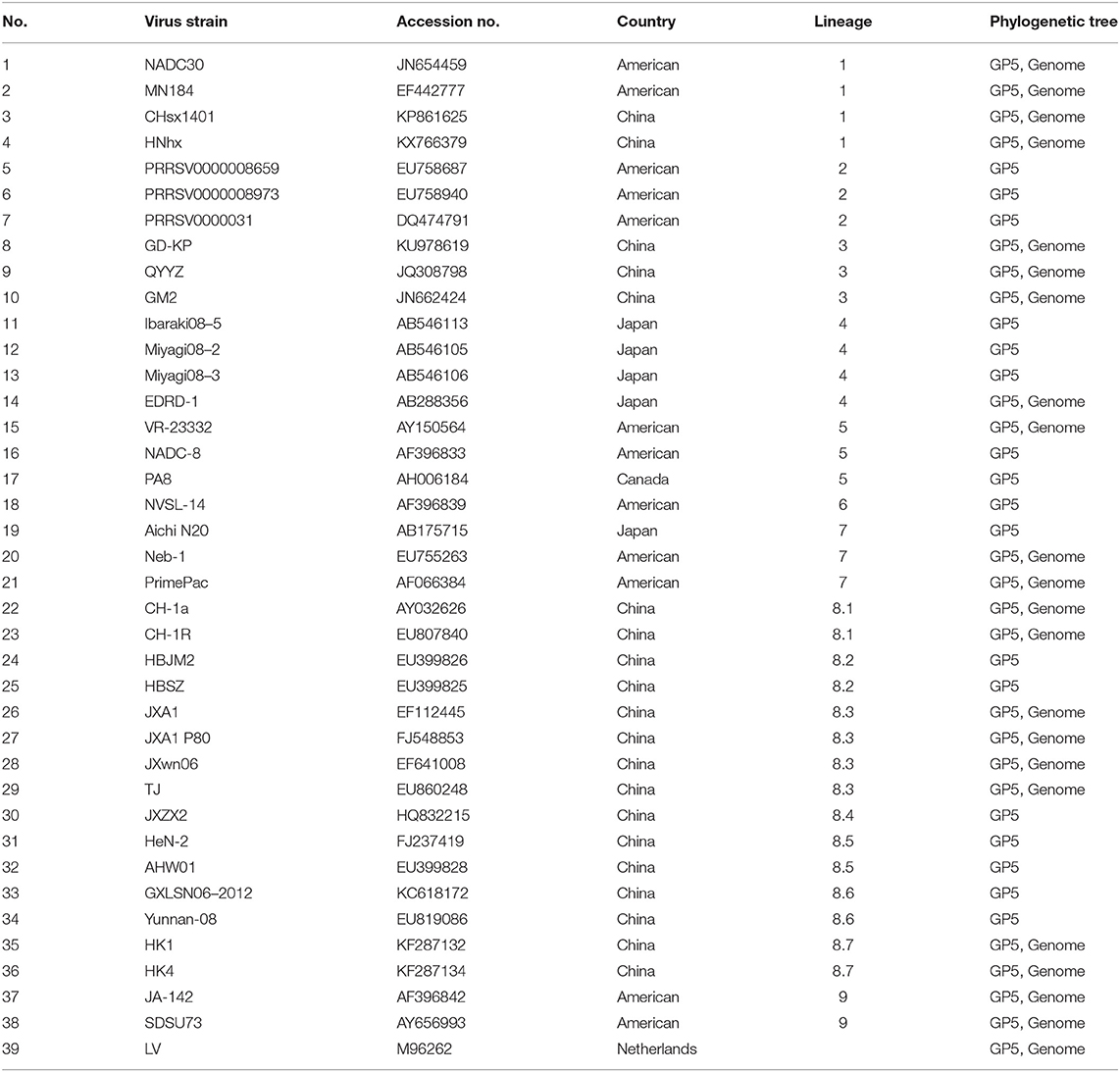
The full-length genomes of GXYL1403 and GXNN1839 were determined and submitted to the GenBank database with accession numbers MN660069 and MN660070. The entire genomes of GXYL1403 and GXNN1839 are 15,018 and 15,019 nucleotides in length, respectively, excluding the poly (A) tails as shown in Tables 2, 3. The nucleotide similarities of GXYL1403 with PRRSV representative strains NADC30, VR-2332, QYYZ, CH-1a, and JXA1 were 82.5, 88.8, 87.2, 94.2, and 98.0%, respectively, with only 60.6% nucleotide similarity with the type 1 PRRSV LV strain (Table 2). The nucleotide similarities of GXNN1839 with NADC30, VR-2332, QYYZ, CH-1a, and JXA1 were 92.2, 84.5, 81.9, 83.6, and 82.9%, respectively, with only 59.8% nucleotide similarity with the LV strain (Table 3). This indicates that the GXYL1403 and GXNN1839 strains belong to type 2 PRRSV. Each region of the GXYL1403 and GXNN1839 genomes were further compared with those of the reference strains as shown in Tables 2, 3. The results show that GXYL1403 exhibits the highest nucleotide similarity (92.8–100%) and amino acid similarity (93.4–100%) with JXA1. The 5′UTR and nsp8-nsp12 of GXYL1403 share the highest nucleotide similarity with that of CH-1a. The other regions of GXYL1403 exhibit the highest nucleotide and amino acid similarities with those of JXA1. GXNN1839 shares the highest nucleotide (86.4–97.9%) and amino acid (83.9–98.9%) similarities with the NADC30 strain (Table 3). ORF2–ORF4 of GXNN1839 share higher (92.6–96.5%) nucleotide and amino acid similarities (93–96.9%) with VR-2332 but exhibit lower nucleotide identity with the other reference strains. The other regions of the GXNN1839 genome exhibit the highest nucleotide and amino acid similarities with NADC30. These results indicate that GXYL1403 and GXNN1839 may be made up of mosaic isolates.
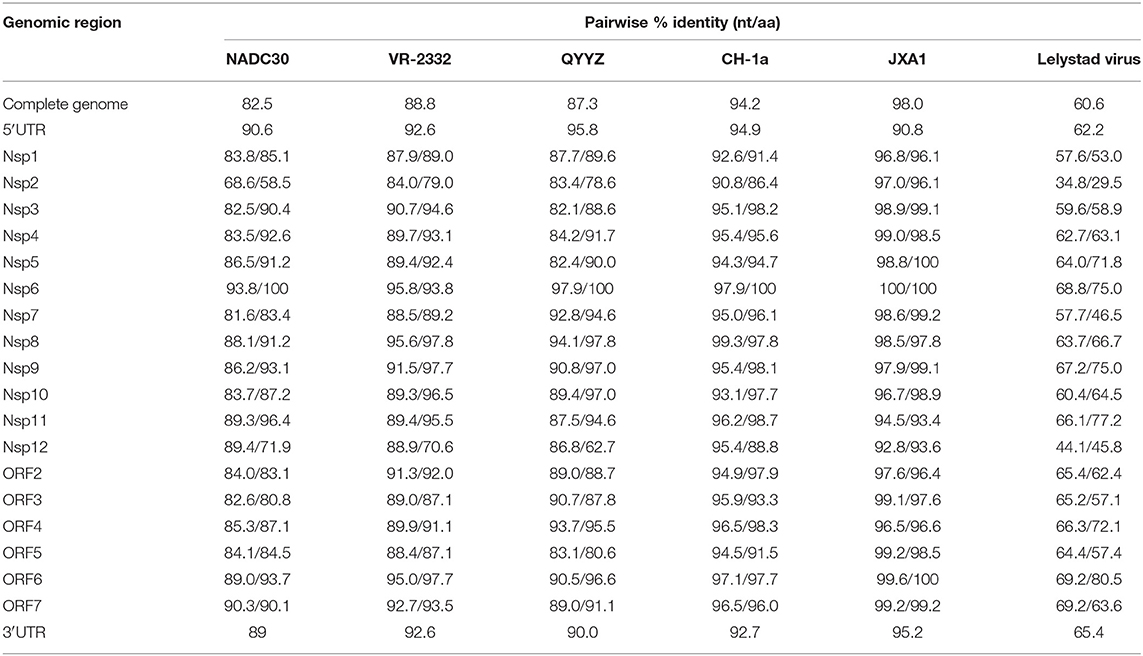
Table 2. Nucleotide and amino acid identities of different regions of GXYL1403 compared with other PRRSV reference strains.
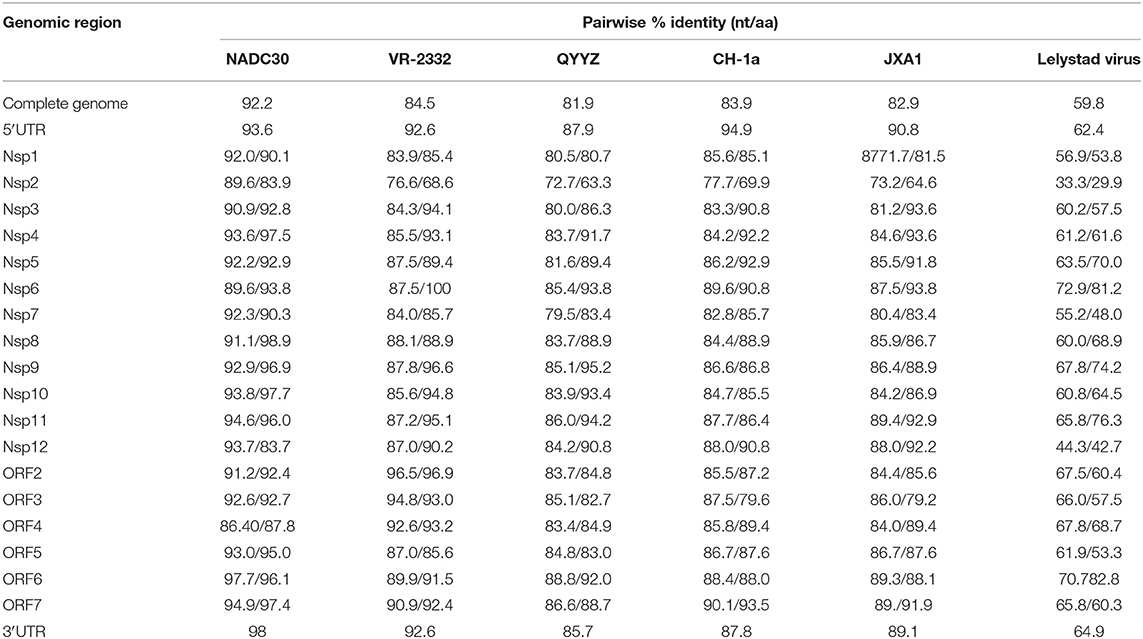
Table 3. Nucleotide and amino acid identities of different regions of GXNN1839 compared with other type 2 PRRSV reference strains.
Nsp2 is one of the most heterogeneous proteins in PRRSV and contains different patterns of amino acid insertions and deletions. Compared with VR-2332, GXYL1403 contains a discontinuous 124-amino acid deletion in the hypervariable region (HVR) of nsp2. GXNN1839 has a discontinuous 131-amino acid deletion in the HVR of nsp2, which has the same amino acid deletion pattern as the NADC30-like strain (Figure 1). This data suggest that novel PRRSV strains with amino acid deletions in nsp2 are emerging.
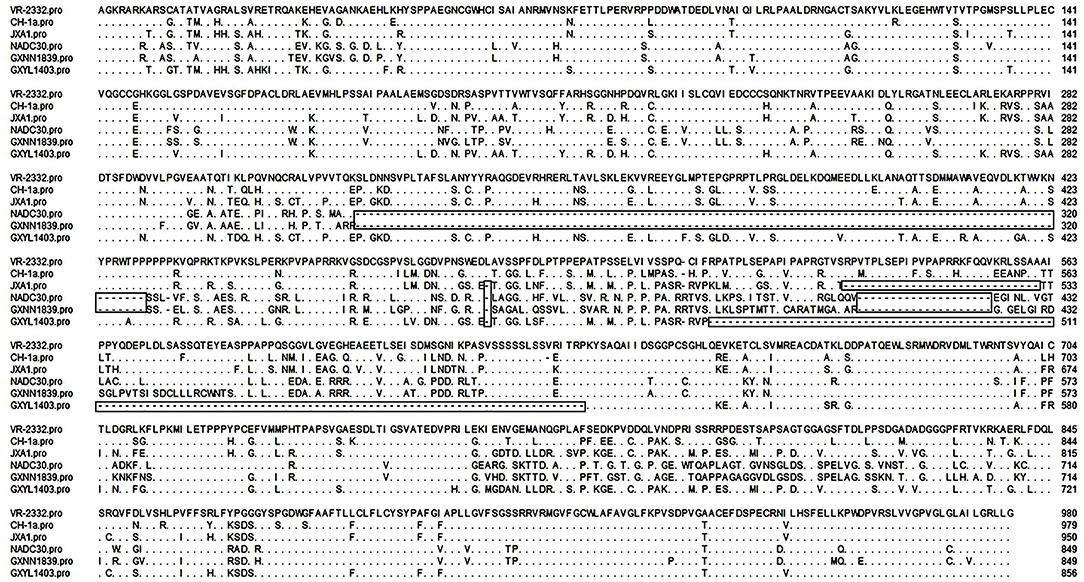
Figure 1. Identification of PRRSV strains with amino acid deletion in nsp2. Multiple alignments of nsp2 were performed by Clustal W. The sequence of VR-2332 is shown on the top; the residues conserved with it are hidden. The deleted amino acids are labeled with boxes.
The phylogenetic tree based on GP5 shows that the type 2 PRRSV strains can be classified into nine different lineages. GXYL1403 belongs to sublineage 8.3, which is represented by the reference strain JXA1. GXNN1839 belongs to lineage 3, which is represented by the reference strain NADC30 (Figure 2A). The phylogenetic tree based on the complete genome also shows that GXYL1403 belongs to sublineage 8.3, and GXNN1839 belongs to lineage 3 (Figure 2B).
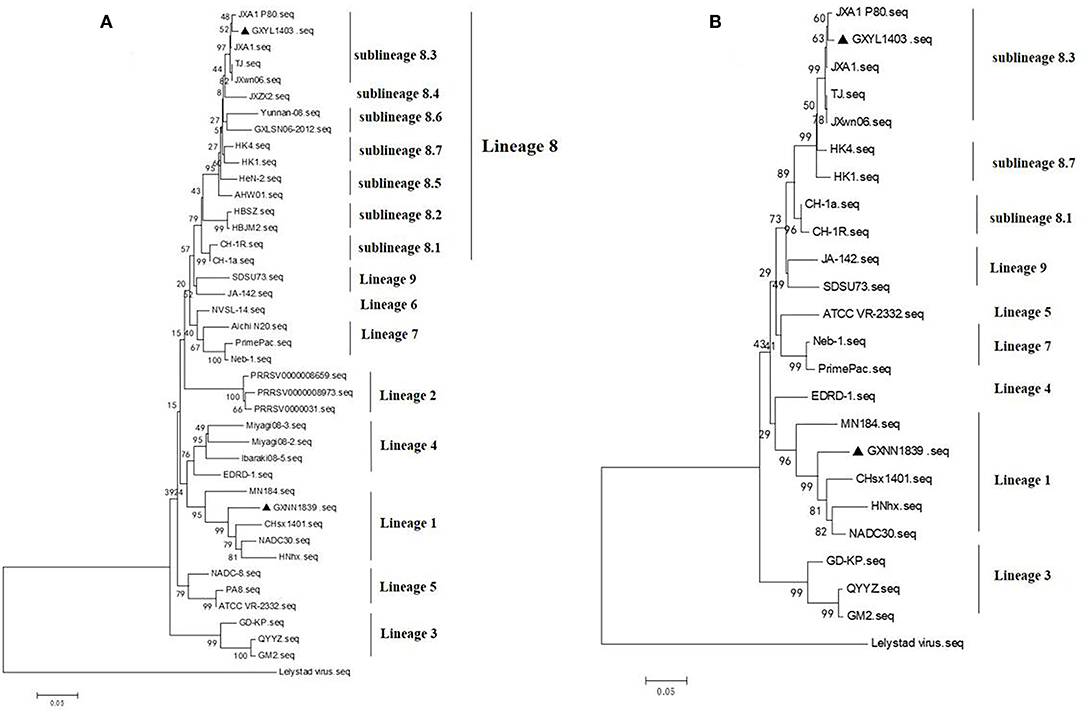
Figure 2. (A) Phylogenetic tree based on ORF5 sequences of isolates from this study and reference ORF5 sequences from PRRSV strains originating from China and other countries. The phylogenetic tree was constructed using the neighbor-joining algorithm based on the p-distance model. The PRRSV ORF5 sequences collected in this study are marked with black triangles. (B) Phylogenetic tree based on full-length genomic sequences of isolates. The GXYL1403 and GXNN1839 in this study and PRRSV reference strains are available in GenBank. The strains isolated in this study are labeled with black triangles.
Recombination Analysis
To determine the recombinant events in the genomes of the GXYL1403 and GXNN1839 isolates, we performed recombinant detection using RDP4 and SimPlot by comparing GXYL1403 and GXNN1839 with the representative PRRSV strains from different lineages in the phylogenetic tree, including strains from lineage 1 (NADC30), lineage 3 (QYYZ), lineage 5 (VR2332), and lineage 8 (CH-1a and JX1A). The results show that putatively recombinant breakpoints located at positions 8961nt−11181nt in the GXYL1403 genome were detected with a high degree of reliability (Table 4). The breakpoints in the GXYL1403 genome separated its genome into three regions (Figure 3A). The phylogenetic trees also paralleled and confirmed the recombinant events as shown in Figure 3B. The region 1nt−8961nt is closely genetically related to the JXA1-like strain. The region 8961nt−11181nt is closely genetically related to the CH-1a-like strain, and the region 11182nt−5018nt is closely related to the JXA1-like strain (Figure 3B). It was suggested that GXYL1403 is a natural recombinant between sublineage 8.1 (CH-1a-like) and sublineage 8.3 (JXA1-like). Two putatively major recombinant breakpoints in the GXNN1839 genome were detected with high reliability, and they are located at the nsp9 coding region (7872nt−8162nt) and the ORF2 coding region (12587nt−13282nt), respectively (Table 4). The breakpoints in the GXNN1839 genome separated its genome into five regions (Figure 4A). The phylogenetic trees also paralleled and confirmed the recombinant events as shown in Figure 4B. This suggests that GXNN1839 is a natural recombinant between linage 5 (VR-2332-like) and lineage 1 (NADC30-like).
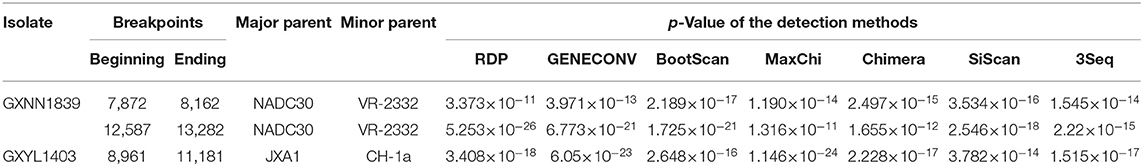
Table 4. Recombination breakpoints identified in GXYL1403, GXNN1839, and associated parental strains of PRRSV.
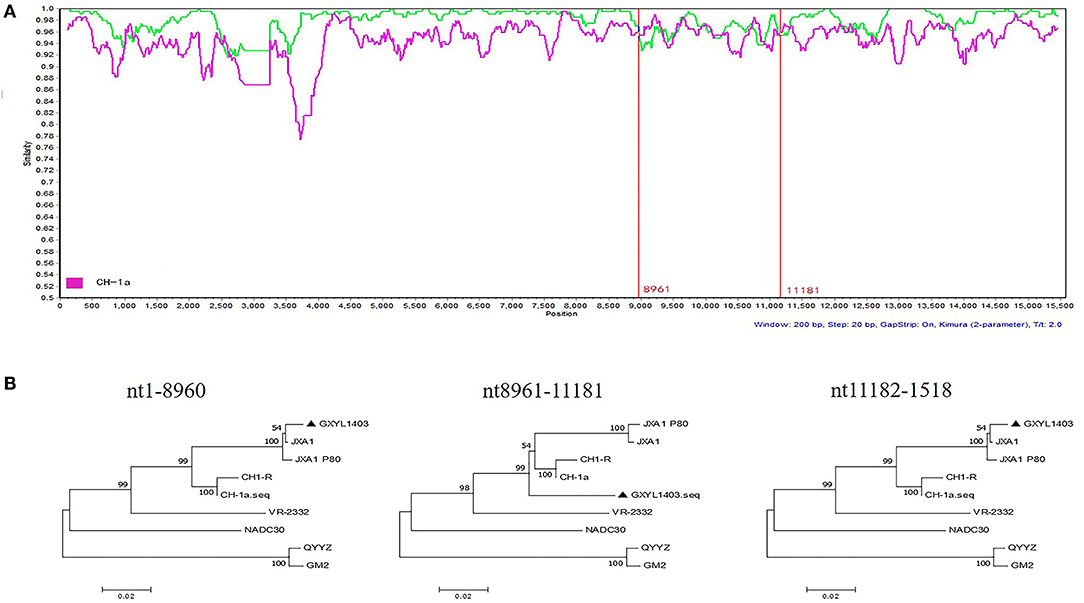
Figure 3. Identification of potential recombination events in the genome of the GXYL1403 strain using RDP3.44. (A) Comparisons of genetic similarities between recombinant and parental strains were made by SimPlot. The complete genome of GXYL1403 was chosen as the query sequence. The y-axis indicates the percentage similarity between the parental sequences and the query sequence. The red real diagram indicates the recombination breakpoints. (B) Phylogenetic trees of different regions in the PRRSV GXYL1403 genome were analyzed by RDP3.44 with UPGMA parsimony. Three trees were generated by the recombinant region (position: nt8961–nt11181) and the non-recombinant regions (position: nt1–8960 and nt11182–1518).
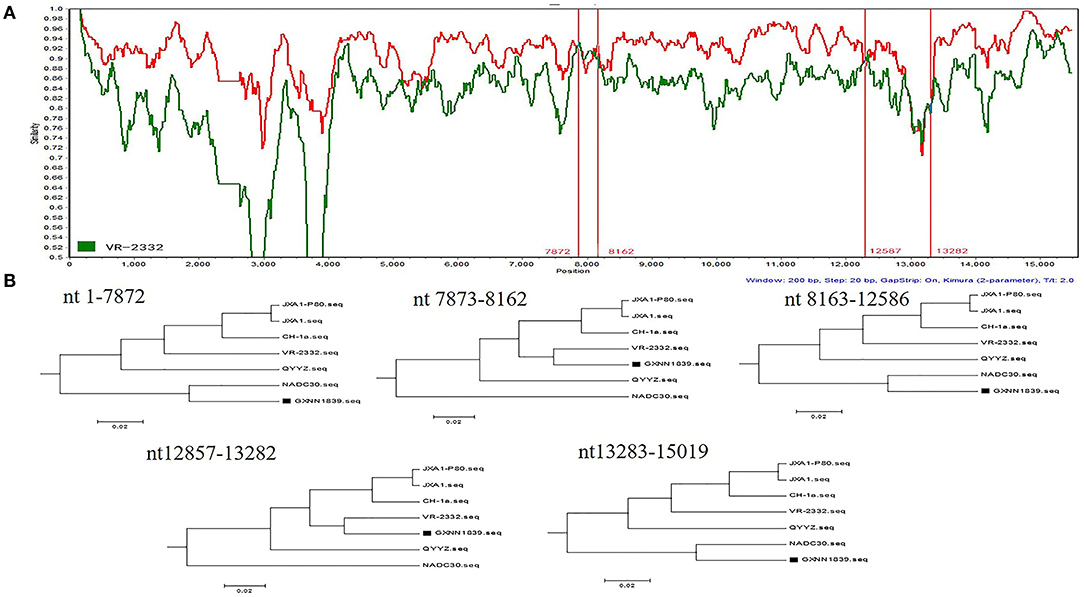
Figure 4. Identification of potential recombination events in the genome of the GXNN1839 strain using RDP3.44. (A) Comparisons of genetic similarities between recombinant and parental strains were made by SimPlot. The complete genome of GXNN1839 was chosen as the query sequence. The y-axis indicates the percentage similarity between the parental sequences and the query sequence. The red real diagram indicates the recombination breakpoints. (B) Phylogenetic trees of different regions in the GXYL1403 genome were analyzed by RDP3.44 with UPGMA parsimony. Five trees were generated by the recombinant regions (position: nt7873–8162 and nt12857–13282) and the non-recombinant regions (position: nt1–7872, nt8163–12586, and nt13283–15019).
Discussion
PRRSV has had a large impact on the Chinese swine industry since its initial outbreak in China in 1996. In 2006, a large outbreak of PRRS caused by HP-PRRSV (10, 11, 26) emerged in most areas of China and caused major economic losses for swine farming. With the emergence of lineages 3 and 1 PRRSV in some areas in China in 2010 and 2015 (12, 14–17), respectively, the genetic diversity of RPRSV has significantly expanded and has further complicated vaccine development. In the present study, we isolated two PRRSV strains (GXYL1403 and GXNN1839) and determined their complete genome sequences. Consistent with previous studies, phylogenetic trees based on GP5 show type 2 PRRSV strains isolated in China are divided into four lineages (1, 3, 5, and 8) (9). The GXYL1403 and GXNN1839 strains reported in this study are grouped into lineages 1 and 3, respectively. The nsp2 is the most heterogeneous protein in PRRSV (26, 30, 31). Compared to strain VR-2332, the nsp2 of the two isolates in this study contain different amino acid deletions, which suggest that novel PRRSV strains with amino acid deletions in nsp2 are emerging.
Recombination plays a critical role in the genetic evolution of PRRSV and presents great challenges for the prevention and control of the disease it causes. Recombination can occur during the virus-replication process. It has been shown that there are different patterns of recombination among the different lineages and sublineages of PRRSV strains (14, 32–39). In the present study, whole genome sequence comparison and recombination analysis reveals that the two isolates (GXYL1403 and GXNN1839) show novel recombination patterns. GXNN1839 is a recombinant virus that originated from recombination events that occurred in nsp9 and GP2 between strains of lineages 1 (NADC30-like) and 5 (VR2332-like). Many recombinant PRRSV strains that originated from recombination events between NADC30-like and VR2332-like strains have also been identified in previous studies (23, 32, 38, 40). Indeed, the NADC30-like strains seem to be prone to recombine with other PRRSV strains. Numerous recombinant PRRSV strains originated from recombination events between NADC30-like strains and other lineages of PRRSV strains that were found in the field (14, 23, 24, 34, 40–42). GXYL1403 was detected as a recombinant virus from strains of sublineages 8.1 (Ch-1a-like) and 8.3 (JX1A-like) that have circulated in China in recent years. Recombinant PRRSV strains that originated from recombination events that occurred in nsp9 between sublineages 8.1 (Ch-1a-like) and 8.3 (JX1A-like) are also reported in a previous study (42). The emergence of new PRRSV recombination variants poses a major obstacle to the effective control of the spread of virus infection and complicates vaccine development for adequate preventative measures (43). The exact mechanism of genetic recombination in PRRSV remains unknown. The breakpoints of recombination sites in the genome among different PRRS strains can be found at each region of the PRRSV genome and seem to appear randomly. A recently published study shows that nsp9 and GP2–GP3 are the hot spots for PRRSV RNA recombination (44). In this study, we find the two strains (GXYL1403 and GXNN1839) both display a breakpoint in nsp9, and GXNN1839 has an additional breakpoint in GP2, indicating that PRRSV gains genetic diversity through the frequency of recombination events at specific regions with PRRSV strains located in China.
In summary, we determined the complete genome sequences of two novel PRRSV isolates (GXYL1403 and GXNN1839). Both of these are natural recombinant strains that contain amino acid deletions in nsp2. Our findings suggest that PRRSV strains circulating in southern China have undergone recombination among the different lineages or sublineages of field strains, and RNA recombination contributes to their genetic diversity.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated for this study can be found in the nucleotide sequences generated in present study were submitted to the NCBI GenBank with accession numbers, MN660069 and MN660070.
Author Contributions
ZW, TL, and WH conceived and designed the experiments. JW, SL, DQ, WH, and JH performed the experiments. TR, YC, and KO analyzed the data. JW wrote the manuscript. ZW and TL revised the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2018YFD0500100), Natural Sciences Foundation of China (No. 31660716), Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi province (No. 2018GXNSFDA281021), and Guangxi Science and Technology Bureau (No. AA17204057).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Dev Sooranna, Imperial College London, for edited the manuscript.
References
1. Neumann EJ, Kliebenstein JB, Johnson CD, Mabry JW, Bush EJ, Seitzinger AH, et al. Assessment of the economic impact of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome on swine production in the United States. J Am Vet Med Assoc. (2005) 227:385–92. doi: 10.2460/javma.2005.227.385
2. Fang Y, Snijder EJ. The PRRSV replicase: exploring the multifunctionality of an intriguing set of nonstructural proteins. Virus Res. (2010) 154:61–76. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2010.07.030
3. Snijder EJ, Meulenberg JJ. The molecular biology of arteriviruses. J Gen Virol. (1998) 79:961–79. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-79-5-961
4. Johnson CR, Griggs TF, Gnanandarajah J, Murtaugh MP. Novel structural protein in porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus encoded by an alternative ORF5 present in all arteriviruses. J Gen Virol. (2011) 92:1107–16. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.030213-0
5. Wu WH, Fang Y, Farwell R, Steffen-Bien M, Rowland RR, Christopher-Hennings J, et al. A 10-kDa structural protein of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus encoded by ORF2b. Virology. (2001) 287:183–91. doi: 10.1006/viro.2001.1034
6. Murtaugh MP, Stadejek T, Abrahante JE, Lam TT, Leung FC. The ever-expanding diversity of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Virus Res. (2010) 154:18–30. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2010.08.015
7. Nelsen CJ, Murtaugh MP, Faaberg KS. Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus comparison: divergent evolution on two continents. J Virol. (1999) 73:270–80. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.1.270-280.1999
8. Shi M, Lam TT, Hon CC, Murtaugh MP, Davies PR, Hui RK, et al. Phylogeny-based evolutionary, demographical, and geographical dissection of North American type 2 porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome viruses. J Virol. (2010) 84:8700–11. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02551-09
9. Gao JC, Xiong JY, Ye C, Chang XB, Guo JC, Jiang CG, et al. Genotypic and geographical distribution of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome viruses in mainland China in 1996–2016. Vet Microbiol. (2017) 208:164–72. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2017.08.003
10. Tian K, Yu X, Zhao T, Feng Y, Cao Z, Wang C, et al. Emergence of fatal PRRSV variants: unparalleled outbreaks of atypical PRRS in China and molecular dissection of the unique hallmark. PLoS ONE. (2007) 2:e526. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000526
11. Tong GZ, Zhou YJ, Hao XF, Tian ZJ, An TQ, Qiu HJ. Highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome, China. Emerg Infect Dis. (2007) 13:1434–36. doi: 10.3201/eid1309.070399
12. Lu WH, Tun HM, Sun BL, Mo J, Zhou QF, Deng YX, et al. Re-emerging of porcine respiratory and reproductive syndrome virus (lineage 3) and increased pathogenicity after genomic recombination with vaccine variant. Vet Microbiol. (2015) 175:332–40. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2014.11.016
13. Wenhui L, Zhongyan W, Guanqun Z, Zhili L, JingYun M, Qingmei X, et al. Complete genome sequence of a novel variant porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) strain: evidence for recombination between vaccine and wild-type PRRSV strains. J Virol. (2012) 86:9543. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01341-12
14. Zhao K, Ye C, Chang XB, Jiang CG, Wang SJ, Cai XH, et al. Importation and recombination are responsible for the latest emergence of highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in China. J Virol. (2015) 89:10712–6. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01446-15
15. Zhou L, Wang Z, Ding Y, Ge X, Guo X, Yang H. NADC30-like strain of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus, China. Emerg Infect Dis. (2015) 21:2256–7. doi: 10.3201/eid2112.150360
16. Zhang Q, Jiang P, Song Z, Lv L, Li L, Bai J. Pathogenicity and antigenicity of a novel NADC30-like strain of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus emerged in China. Vet Microbiol. (2016) 197:93–101. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2016.11.010
17. Li C, Zhuang J, Wang J, Han L, Sun Z, Xiao Y, et al. Outbreak Investigation of NADC30-Like PRRSV in South-East China. Transbound Emerg Dis. (2016) 63:474–9. doi: 10.1111/tbed.12530
18. Marton S, Szalay D, Kecskemeti S, Forro B, Olasz F, Zadori Z, et al. Coding-complete sequence of a vaccine-derived recombinant porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus strain isolated in Hungary. Arch Virol. (2019) 164:2605–8. doi: 10.1007/s00705-019-04338-2
19. Liu J, Wei C, Lin Z, Fan J, Xia W, Dai A, et al. Recombination in lineage 1, 3, 5 and 8 of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome viruses in China. Infect Genet Evol. (2019) 68:119–26. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2018.12.006
20. Zhang Q, Xu X, You S, Li Y, Wang H, Bai J, et al. Emerging of two new subgenotypes of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome viruses in Southeast China. Microb Pathog. (2016) 97:27–33. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2016.05.011
21. Sun YK, Li Q, Yu ZQ, Han XL, Wei YF, Ji CH, et al. Emergence of novel recombination lineage 3 of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome viruses in Southern China. Transbound Emerg Dis. (2019) 66:578–87. doi: 10.1111/tbed.13067
22. Shi M, Holmes EC, Brar MS, Leung FC. Recombination is associated with an outbreak of novel highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome viruses in China. J Virol. (2013) 87:10904–7. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01270-13
23. Liu Y, Li J, Yang J, Zeng H, Guo L, Ren S, et al. Emergence of different recombinant porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome viruses, China. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:4118. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22494-4
24. Zhou L, Kang R, Zhang Y, Ding M, Xie B, Tian Y, et al. Whole genome analysis of two novel type 2 porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome viruses with complex genome recombination between lineage 8, 3, and 1 strains identified in Southwestern China. Viruses. (2018) 10:328. doi: 10.3390/v10060328
25. Wei Z, Lin T, Sun L, Li Y, Wang X, Gao F, et al. N-linked glycosylation of GP5 of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus is critically important for virus replication in vivo. J Virol. (2012) 86:9941–51. doi: 10.1128/JVI.07067-11
26. Hong S, Wei Y, Lin S, Huang J, He W, Yao J, et al. Genetic analysis of porcine productive and respiratory syndrome virus between 2013 and 2014 in Southern parts of China: identification of several novel strains with amino acid deletions or insertions in nsp2. BMC Vet Res. (2019) 15:171. doi: 10.1186/s12917-019-1906-9
27. Leng X, Li Z, Xia M, Li X, Wang F, Wang W, et al. Mutations in the genome of the highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus potentially related to attenuation. Vet Microbiol. (2012) 157:50–60. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2011.12.012
28. Zhang H, Leng C, Ding Y, Zhai H, Li Z, Xiang L, et al. Characterization of newly emerged NADC30-like strains of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in China. Arch Virol. (2019) 164:401–11. doi: 10.1007/s00705-018-4080-7
29. Martin DP, Lemey P, Lott M, Moulton V, Posada D, Lefeuvre P. RDP3: a flexible and fast computer program for analyzing recombination. Bioinformatics. (2010) 26:2462–3. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq467
30. Kedkovid R, Nuntawan Na Ayudhya S, Amonsin A, Thanawongnuwech R. NSP2 gene variation of the North American genotype of the Thai PRRSV in central Thailand. Virol J. (2010) 7:340. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-7-340
31. Yoshii M, Okinaga T, Miyazaki A, Kato K, Ikeda H, Tsunemitsu H. Genetic polymorphism of the nsp2 gene in North American type–porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Arch Virol. (2008) 153:1323–34. doi: 10.1007/s00705-008-0098-6
32. Li Y, Ji G, Wang J, Tan F, Zhuang J, Li X, et al. Complete genome sequence of an NADC30-like porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus characterized by recombination with other strains. Genome Announc. (2016) 4:e00330–16. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.00330-16
33. Zhang Z, Zhou L, Ge X, Guo X, Han J, Yang H. Evolutionary analysis of six isolates of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus from a single pig farm: MLV-evolved and recombinant viruses. Infect Genet Evol. (2018) 66:111–9. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2018.09.024
34. Zhou L, Kang R, Ji G, Tian Y, Ge M, Xie B, et al. Molecular characterization and recombination analysis of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus emerged in southwestern China during 2012–2016. Virus Genes. (2018) 54:98–110. doi: 10.1007/s11262-017-1519-y
35. Zhao H, Han Q, Zhang L, Zhang Z, Wu Y, Shen H, et al. Emergence of mosaic recombinant strains potentially associated with vaccine JXA1-R and predominant circulating strains of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in different provinces of China. Virol J. (2017) 14:67. doi: 10.1186/s12985-017-0735-3
36. Dong J, Wang Y, Yu L, Zhang P, Liu X, Zhang L, et al. Pathogenicity of a newly emerged recombined porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus strain (subgenotype III) in China. Vet Microbiol. (2017) 210:162–6. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2017.09.018
37. Han G, Xu H, Wang K, He F. Emergence of Two different recombinant PRRSV strains with low neutralizing antibody susceptibility in China. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:2490. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-39059-8
38. Zhou L, Kang R, Xie B, Tian Y, Wu X, Lv X, et al. Identification of a novel recombinant type 2 porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in China. Viruses. (2018) 10:151. doi: 10.3390/v10040151
39. Chen N, Ye M, Li S, Huang Y, Zhou R, Yu X, et al. Emergence of a novel highly pathogenic recombinant virus from three lineages of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus 2 in China 2017. Transbound Emerg Dis. (2018) 65:1775–85. doi: 10.1111/tbed.12952
40. Zhou L, Kang R, Yu J, Xie B, Chen C, Li X, et al. Genetic characterization and pathogenicity of a novel recombined porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus 2 among Nadc30-like, Jxa1-like, and Mlv-like strains. Viruses. (2018) 10:551. doi: 10.3390/v10100551
41. Bian T, Sun Y, Hao M, Zhou L, Ge X, Guo X, et al. A recombinant type 2 porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus between NADC30-like and a MLV-like: genetic characterization and pathogenicity for piglets. Infect Genet Evol. (2017) 54:279–86. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2017.07.016
42. Zhou L, Kang R, Zhang Y, Yu J, Xie B, Chen C, et al. Emergence of two novel recombinant porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome viruses 2 (lineage 3) in Southwestern China. Vet Microbiol. (2019) 232:30–41. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2019.01.026
43. Huang YW, Meng XJ. Novel strategies and approaches to develop the next generation of vaccines against porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV). Virus Res. (2010) 154:141–9. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2010.07.020
Keywords: PRRSV, phylogenetic analysis, nsp2, deletion, recombination
Citation: Wang J, Lin S, Quan D, Wang H, Huang J, Wang Y, Ren T, Ouyang K, Chen Y, Huang W, Luo T and Wei Z (2020) Full Genomic Analysis of New Variants of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Revealed Multiple Recombination Events Between Different Lineages and Sublineages. Front. Vet. Sci. 7:603. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.00603
Received: 12 February 2020; Accepted: 27 July 2020;
Published: 10 September 2020.
Edited by:
Francisco Ruiz-Fons, Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC), SpainReviewed by:
Ping Jiang, Nanjing Agricultural University, ChinaYifeng Jiang, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS), China
Copyright © 2020 Wang, Lin, Quan, Wang, Huang, Wang, Ren, Ouyang, Chen, Huang, Luo and Wei. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zuzhang Wei, enV6aGFuZ3dlaUBneHUuZWR1LmNu; Tingrong Luo, dGluZ3JvbmdsdW9AZ3h1LmVkdS5jbg==
 Jinglong Wang
Jinglong Wang Zuzhang Wei
Zuzhang Wei