
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Pharmacol. , 22 May 2019
Sec. Experimental Pharmacology and Drug Discovery
Volume 10 - 2019 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.00541
This article is a correction to:
Berberine Improves Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia via Suppression of 5 Alpha Reductase and Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase in Vivo and in Vitro
 Dong-Hyun Youn1,2
Dong-Hyun Youn1,2 Jinbong Park1,2
Jinbong Park1,2 Hye-Lin Kim1
Hye-Lin Kim1 Yunu Jung1,2
Yunu Jung1,2 JongWook Kang1,2
JongWook Kang1,2 Seona Lim1,2
Seona Lim1,2 Gahee Song1,2
Gahee Song1,2 Hyun Jeong Kwak1
Hyun Jeong Kwak1 Jae-Young Um1,2*
Jae-Young Um1,2*A Corrigendum on
Berberine Improves Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia via Suppression of 5 Alpha Reductase and Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase in Vivo and in Vitro
by Youn, D.-H, Park, J., Kim, H.-L., Jung, Y., Kang, J., Lim, S., et al. (2018) Front. Pharmacol. 9:773. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00773
In the original article, there was a mistake in the legend for Figure 1 as published. The magnifications of Figure 1A were stated as ×100 and ×400, when they were actually ×200 and ×400. The correct legend appears below.
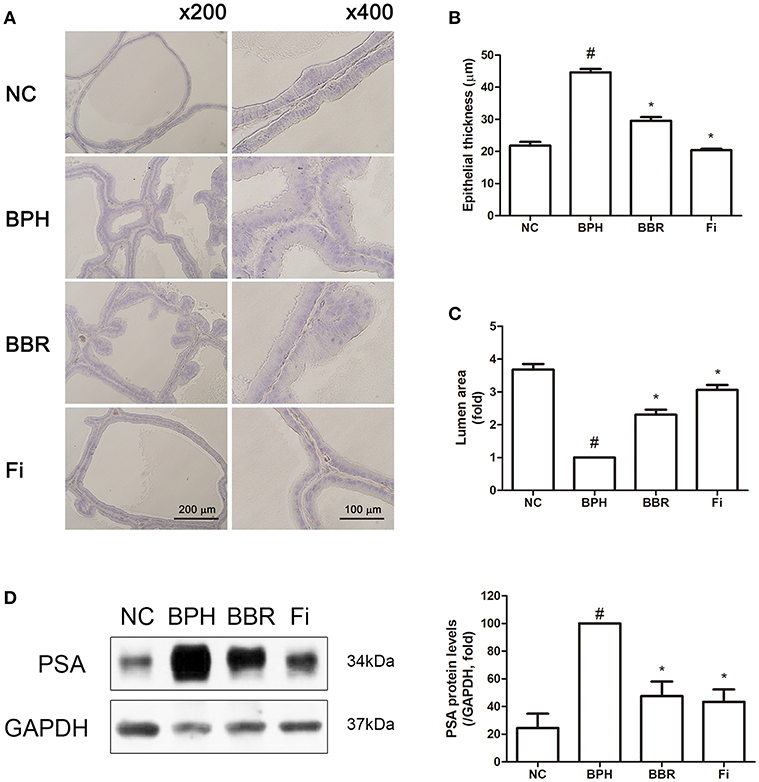
Figure 1. Effect of BBR on histological changes and protein expression of PSA in prostate tissues of TP-induced BPH rats. (A) Representative photomicrographs of H&E stained prostate tissues (left panels, magnification ×200; right panels, magnification ×400) are shown. (B) The epithelial thickness and (C) the relative lumen area of the prostate tissues were measured using Image J software. Values are mean ± S.D. of ten or more separate measurements. (D) The protein expression of PSA was analyzed by a western blot analysis. Values are mean ± S.D. of three or more separate measurements. #P < 0.05 when compared to NC; *P < 0.05 when compared to BPH. The protein expression differences are normalized to GAPDH. NC, normal control group; BPH, TP-induced BPH group; BBR, BBR-treated BPH group; Fi, finasteride-treated BPH group.
In the original article, there was a mistake in Figure 1 as published. The wrong photomicrographs of prostate tissues were presented by mistake. The corrected Figure 1 appears below. The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Keywords: berberine, benign prostatic hyperplasia, 5 alpha reductase, androgen receptor, mitogen-activated protein kinase, extracellular signal-regulated kinase
Citation: Youn D-H, Park J, Kim H-L, Jung Y, Kang J, Lim S, Song G, Kwak HJ and Um J-Y (2019) Corrigendum: Berberine Improves Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia via Suppression of 5 Alpha Reductase and Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase in Vivo and in Vitro. Front. Pharmacol. 10:541. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00541
Received: 28 March 2019; Accepted: 30 April 2019;
Published: 22 May 2019.
Edited and reviewed by: Salvatore Salomone, Università degli Studi di Catania, Italy
Copyright © 2019 Youn, Park, Kim, Jung, Kang, Lim, Song, Kwak and Um. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jae-Young Um, anl1bUBraHUuYWMua3I=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.