- 1Department of Radiology, Center for Magnetic Resonance Research (CMRR), University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, United States
- 2Department of Pediatrics, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, United States
- 3Central European Institute of Technology (CEITEC), Masaryk University, Brno, Czechia
- 4MARBILab, Centro Fermi - Museo Storico Della Fisica e Centro di Studi e Ricerche Enrico Fermi, Rome, Italy
- 5Department of Applied Physics, University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio, Finland
- 6Fondazione Santa Lucia IRCCS, Rome, Italy
- 7Division of Biostatistics, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, United States
- 8Department of Neurology, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, United States
A corrigendum on
Multi-modal Brain MRI in Subjects with PD and iRBD
by Mangia, S., Svatkova, A., Mascali, D., Nissi, M. J., Burton, P. C., Bednarik, P., et al. (2017). Front. Neurosci. 11:709. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00709
In the original paper there were errors in Figure 4 and in the text at page 7. Figure 4 erroneously reported four asterisks, namely on top of T1ρ of putamen, T2ρ of midbrain, RAFF4 of midbrain, and ReHo of amygdala. The figure also did not report one asterisk on top of T1ρ of SNc. The correct version of Figure 4 appears below.
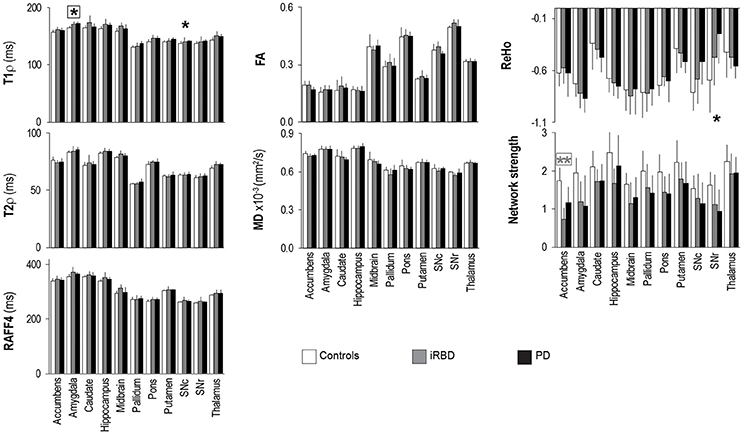
Figure 4. Group summaries of T1ρ, T2ρ, RAFF4, FA, MD, ReHo and network strength. N = 10, 8, 9 in the control, iRBD and PD groups, respectively, for T1ρ, T2ρ, and RAFF4, whereas N = 9, 8, 9 for FA and MD, and N = 10, 8, 8 for network strength and ReHo. Data shown as mean ± SD. * and ** indicate, respectively, p < 0.05 and p < 0.005 with age-adjustments after Holm's correction (gray: iRBD vs. controls; black: PD vs. controls). Asterisks within a box indicate p < 0.05 after correcting FDR for multiple testing (7 modalities).
In addition, the text at page 7 “Group differences between PD and controls were also observed for T2ρ in the amygdala (p = 0.033) and thalamus (p = 0.08)” should read as “Group differences between PD and controls were also observed for T2ρ in the amygdala (p = 0.033) and thalamus (p = 0.008)”.
The authors sincerely apologize for these errors that may cause confusion for the reader. These errors however do not change the interpretation of the results and the main message of the study in any way, because the interpretation was based on the correct results reported in the Supplementary Table.
The original article has been updated.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Keywords: rotating frame MRI, Parkinson's disease, iRBD, functional connectivity, DTI
Citation: Mangia S, Svatkova A, Mascali D, Nissi MJ, Burton PC, Bednarik P, Auerbach EJ, Giove F, Eberly LE, Howell MJ, Nestrasil I, Tuite PJ and Michaeli S (2018) Corrigendum: Multi-modal Brain MRI in Subjects with PD and iRBD. Front. Neurosci. 12:446. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00446
Received: 30 April 2018; Accepted: 12 June 2018;
Published: 26 June 2018.
Edited and reviewed by: Kevin J. Black, Washington University in St. Louis, United States
Copyright © 2018 Mangia, Svatkova, Mascali, Nissi, Burton, Bednarik, Auerbach, Giove, Eberly, Howell, Nestrasil, Tuite and Michaeli. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Silvia Mangia, bWFuZ2lhQHVtbi5lZHU=
 Silvia Mangia
Silvia Mangia Alena Svatkova2,3
Alena Svatkova2,3 Daniele Mascali
Daniele Mascali Mikko J. Nissi
Mikko J. Nissi Philip C. Burton
Philip C. Burton Federico Giove
Federico Giove Lynn E. Eberly
Lynn E. Eberly Igor Nestrasil
Igor Nestrasil Paul J. Tuite
Paul J. Tuite Shalom Michaeli
Shalom Michaeli