
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Cell. Neurosci. , 12 December 2019
Sec. Cellular Neurophysiology
Volume 13 - 2019 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2019.00541
This article is a correction to:
Synaptic Ribbon Active Zones in Cone Photoreceptors Operate Independently from One Another
A Corrigendum on
Synaptic Ribbon Active Zones in Cone Photoreceptors Operate Independently from One Another
by Grassmeyer, J. J., and Thoreson, W. B. (2017). Front. Cell. Neurosci. 11:198. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2017.00198
In the original article, there was a mistake in Figure 6D as published. The ordinate was not corrected for liquid junction potential. The corrected Figure 6 appears below.
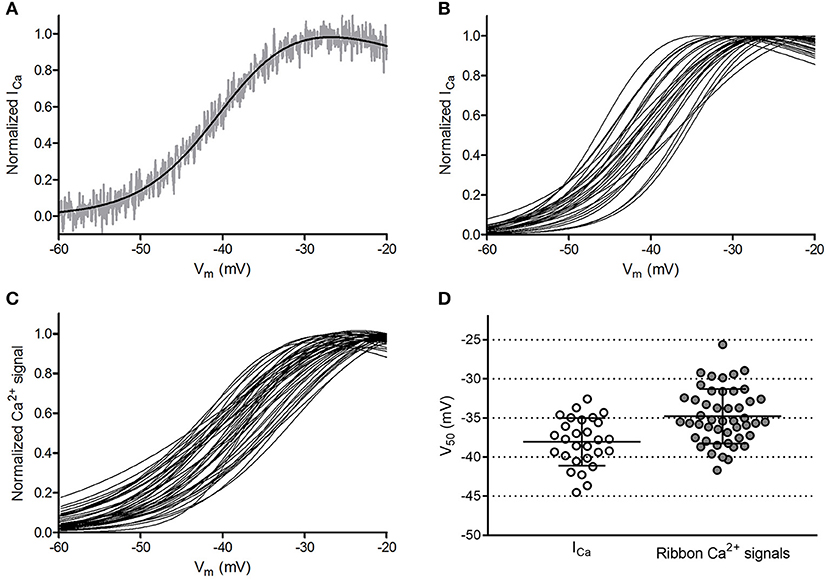
Figure 6. Ribbon-to-ribbon Ca2+ activation is more variable than cone-to-cone ICa activation. (A) ICa in one cone with Rser completely compensated. ICa was normalized to its peak value and plotted against the cone holding potential during the voltage ramp protocol (gray trace). A Boltzmann function adjusted for driving force was fit to these data (black line, V50 = −39.3, slope factor = 4.88). Inward currents are plotted upward to compare more easily with Ca2+ signal measurements. For this illustration, currents were digitally corrected for the passive membrane resistance measured in the range from −85 mV to −70 mV. (B) Overlaid Boltzmann function fits to normalized ICa from the 28 cones in which ribbon Ca2+ signals in Panel (C) were measured. (C) Overlaid Boltzmann function fits to ribbon-associated Ca2+ signals of 47 ribbons in the 28 cones shown in Panel (B). Ribbons were analyzed as illustrated in Figure 1. (D) Distribution of V50 values calculated from Boltzmann function fits to ICa (average = −38.1 ± 3.0 mV) and optical ribbon Ca2+ measurements made with OGB-5N (average = −34.8 ± 3.5 mV). Bars show the mean ± SD.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Keywords: ribbon synapse, retina, exocytosis, calcium imaging, cone photoreceptor, active zone
Citation: Grassmeyer JJ and Thoreson WB (2019) Corrigendum: Synaptic Ribbon Active Zones in Cone Photoreceptors Operate Independently From One Another. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 13:541. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00541
Received: 09 October 2019; Accepted: 22 November 2019;
Published: 12 December 2019.
Edited and reviewed by: Arianna Maffei, Stony Brook University, United States
Copyright © 2019 Grassmeyer and Thoreson. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wallace B. Thoreson, d2J0aG9yZXNAdW5tYy5lZHU=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.