
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Microbiol., 02 April 2019
Sec. Infectious Agents and Disease
Volume 10 - 2019 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.00601
This article is a correction to:
Bacteroides fragilis Prevents Clostridium difficile Infection in a Mouse Model by Restoring Gut Barrier and Microbiome Regulation
 Huimin Deng1
Huimin Deng1 Siqi Yang1
Siqi Yang1 Yucheng Zhang1
Yucheng Zhang1 Kai Qian1
Kai Qian1 Zhaohui Zhang1
Zhaohui Zhang1 Yangyang Liu2
Yangyang Liu2 Ye Wang2
Ye Wang2 Yang Bai1
Yang Bai1 Hongying Fan3*
Hongying Fan3* Xinmei Zhao1*
Xinmei Zhao1* Fachao Zhi1*
Fachao Zhi1*A Corrigendum on
Bacteroides fragilis Prevents Clostridium difficile Infection in a Mouse Model by Restoring Gut Barrier and Microbiome Regulation
by Deng, H., Yang, S., Zhang, Y., Qian, K., Zhang, Z., Liu, Y., et al. (2018). Front. Microbiol. 9:2976. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02976
In the original article, there was a mistake in the Supplementary Figure 3 as published. The same Figure 3 used in the original article was also used for Supplementary Figure 3. The corrected Supplementary Figure 3 appears below.
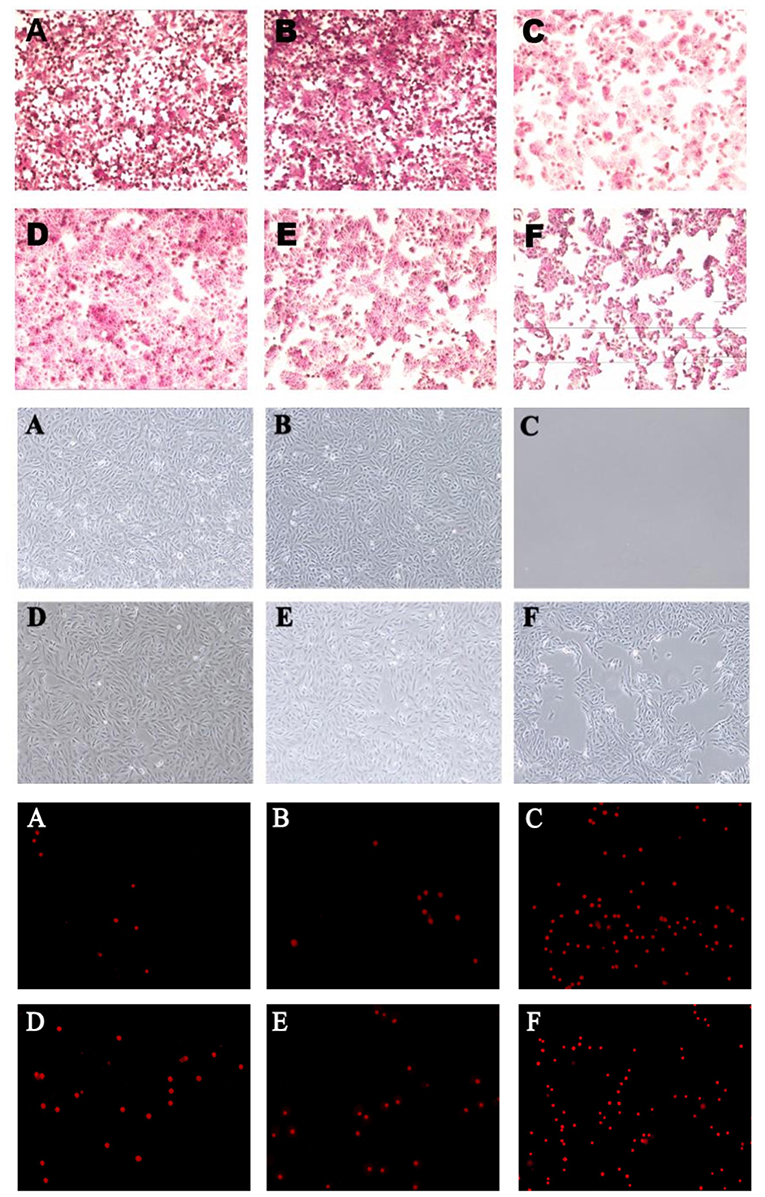
Supplementary Figure 3. B. fragilis ZY-312 inhibits colon cell apoptosis induced by C. difficile. Representative images of PAS staining (top) for Muc-2 protein visualization in HT-29 cell monolayers are shown for all groups. Microscopic observations (middle) of Vero cell morphology and viability and PI staining (bottom) of Vero cells in all groups are shown. (A) Blank control group, 5 × 105 HT-29 or Vero cells were cultured without treatment; (B) B. fragilis group, cells were incubated with 5 × 108 cfu B. fragilis; (C) C. difficile group, cells were incubated with 5 × 107 cfu C. difficile; (D) Exclusion group, cells were infected with 5 × 108 cfu B. fragilis for the first hour and 5 × 107 cfu C. difficile for the second hour; (E) Competition group, cells were co-infected with B. fragilis and C. difficile; (F) Substitution group, cells were infected with C. difficile for the first hour and B. fragilis for the second hour. The cells were incubated at 37°C under anaerobic conditions for 2 h in total.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original Supplementary Material has been updated.
Keywords: next-generation probiotic, gut barrier, gut microbiota, Clostridium difficile, commensal bacteria
Citation: Deng H, Yang S, Zhang Y, Qian K, Zhang Z, Liu Y, Wang Y, Bai Y, Fan H, Zhao X and Zhi F (2019) Corrigendum: Bacteroides fragilis Prevents Clostridium difficile Infection in a Mouse Model by Restoring Gut Barrier and Microbiome Regulation. Front. Microbiol. 10:601. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00601
Received: 03 March 2019; Accepted: 11 March 2019;
Published: 02 April 2019.
Edited by:
George Grant, University of Aberdeen, United KingdomReviewed by:
Nobuhiko Kamada, University of Michigan Health System, United StatesCopyright © 2019 Deng, Yang, Zhang, Qian, Zhang, Liu, Wang, Bai, Fan, Zhao and Zhi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hongying Fan, YmlvZmh5QDEyNi5jb20=
Xinmei Zhao, enhtMDMxNzIwMTE0OThAMTYzLmNvbQ==
Fachao Zhi, emhpZmM0MTUzMkAxNjMuY29t
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.