
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
MINI REVIEW article
Front. Immunol. , 24 April 2019
Sec. Cancer Immunity and Immunotherapy
Volume 10 - 2019 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.00875
This article is part of the Research Topic Cell-Cell and Cell-Matrix Adhesion in Immunobiology and Cancer View all 10 articles
Disparity during the resolution of inflammation is closely related with the initiation and progression of the tumorigenesis. The transformed cells, through continuously evolving interactions, participate in various exchanges with the surrounding microenvironment consisting of extracellular matrix (ECM) components, cytokines embedded in the ECM, as well as the stromal cells. Proteoglycans (PGs), complex molecules consisting of a protein core into which one or more glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chains are covalently tethered, are important regulators of the cell/matrix interface and, consecutively, biological functions. The discrete expression of PGs and their interacting partners has been distinguished as specific for disease development in diverse cancer types. In this mini-review, we will critically discuss the roles of PGs in the complex processes of cancer-associated modulation of the immune response and analyze their mechanisms of action. A deeper understanding of mechanisms which are capable of regulating the immune response could be harnessed to treat malignant disease.
Cancer initiation is a multi-faceted process with a contribution of genetic, metabolic and environmental factors. Tumorigenesis is closely associated with chronic inflammation, with approximately 20% of cancer incidences being directly correlated to chronic infections (1). Indeed, all tumors independently of etiology are distinguished by an early inflammatory milieu and characterized by discrete interactions with the immune system at all stages of disease progression (2, 3). During malignant transformation, cells obtain complex biological characteristics correlated with more efficient survival, invasion, metastasis and the ability to evade the immune response. The transformed cells, through continuously evolving interactions, communicate with and alter the surrounding microenvironment consisting of extracellular matrix (ECM) components, cytokines embedded in the ECM, and the stromal cells (e.g., fibroblasts, endothelial cells, adipocytes, and immune cells) (4, 5). The resulting ECM remodeling crucially contributes to the abnormal tumor inflammatory pattern (5, 6).
Proteoglycans (PGs) are complex molecules consisting of a protein core into which one or more glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chains are covalently tethered. The bound GAGs can be the heparan sulfate (HS), the chondroitin sulfate/dermatan sulfate (CS/DS), or the keratan sulfate (KS) type. In mammalian cells PGs are associated to the plasma membranes, released into the ECM or intracellularly localized. Presently, 45 PGs have been identified with each member characterized by immense alterability attributed to the modifications of the protein core and by the type and different stoichiometry of the GAG chain substitutions (7, 8). Thus, PGs have highly specific and multifaceted biological roles, including: (i) contributing to ECM superstructure (9); (ii) defining ECM biochemical and physicochemical properties (9); (iii) acting as receptors of diverse responsiveness as well as a pool of various biologic effectors such as growth factors (10–12).
It is well-established that malignant tumors have discrete PG expression profiles, which are immediately correlated with their behavior and differentiation status. Thus, epithelial tumors exhibit a different PG characterization as compared to mesenchymal tumors (13, 14). Proteolytic cleavage of PGs, due to the action of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), cathepsins, and bone-morphogenetic protein-1, can release bioactive fragments or matrikines with roles in the propagation of tumorigenesis separate from that of parent molecules (15). Importantly, PGs are highly implicated in the processes of cancer-associated inflammation (16, 17). Indeed, PGs are suggested to modulate key events respective to both innate and adaptive immunity (18, 19).
In this review, we provide a critical overview of PGs' roles in the inflammatory cancer milieu and consecutively extrapolate to potential options for the development of targeted cancer therapies.
The input of the immune system, introduced as cancer immunoediting, consists of three phases: elimination (i.e., cancer immunosurveillance), equilibrium, and escape (20). Importantly, the tumor ECM contributes to the development of an immunosuppressive network where stromal cells intertwine with inflammatory immune cells and with cells appending to the vascular system. Within this complex, a newly formed network, secreted cytokines and chemokines can sustain the tumor immune escape (21, 22). The chain of tumorigeneis can be initiated by injury of normal tissue, independently of the causative agent, and concomitant triggering of acute inflammation (23, 24). The maintenance of inflammatory conditions due to various effectors leads to chronic inflammation which may evolve to precancerous lesion (25–29). The evolvement of the pre-cancerous lesion can be attenuated by an active immune defense or driven to primary tumor development (30), as schematically presented in Figure 1. Thus, the immune system has the ability to perceive and destroy many tumors early on in their development, whereas during the stage of equilibrium, a restraint of the tumor is attained. Some tumors will succeed in escaping from the growth restriction maintained by the immune system, and become clinically apparent (20, 31).
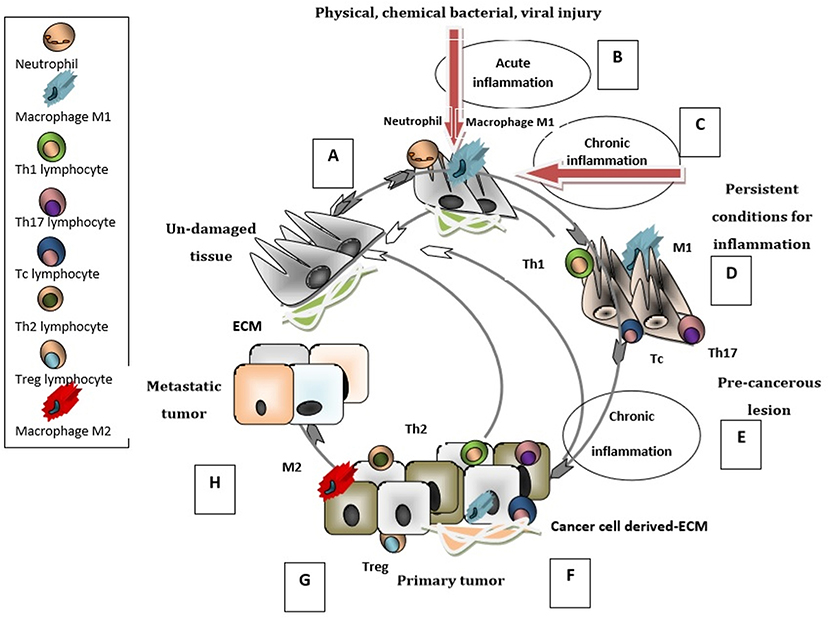
Figure 1. Immunobiology of cancer cycle. When un-damaged tissue (A) is subjected to injury, innate immunity cells (neutrophils and macrophages type M1) infiltrate the tissue and generate an acute inflammation (B) that triggers the repair cascade guiding the tissue to its un-damaged status. ECM is altered and contributes to inflammatory processes. If the inflammation is sustained and has chronic characteristics (C), in addition to M1 macrophages the tissue is infiltrated with adaptive immunity cells (Th1, Tc, Th17); the pre-cancerous lesion (D) can return to its normal un-damaged status. At these stages the elimination of tumor development is possible. If the chronic inflammation persists (E) then the pre-cancerous lesion evolves into a primary tumor. The primary tumor can be infiltrated by M1, Th1, Tc, Th17 cells (F) with intense anti-tumoral activity which can restrain the tumorigenesis process and establish the immune equilibrium stage. In contrast, when the infiltrating cells are M2 type macrophages Th2, Treg lymphocytes (G) a pro-tumorigenesis milieu is enhanced and the primary tumor evolves into an aggressive/metastatic tumor. The ECM is modulated by tumor/stromal -cells and gains new immunosuppressive characteristics that favor metastasis (H). This last stage of the tumor-immune cycle is characterized by the escape of tumor cells from the immune control.
The resolution of disease and response to therapy is likewise affected by the tumor microenvironment as two major subsets of tumors with distinct mechanisms of resistance to immune-mediated destruction have been recognized. Tumors exhibiting the inflamed immunophenotype present with the recruitment of CD8+ cytotoxic T cells, B cells and macrophages. Immune resistance in this case is due to the action of microenvironment-originating negative immune regulators. In non-inflamed tumors an absence of T-cells and innate immunity regulators is evident and leads to immediate immune failure (32, 33). Indeed, the ability of the tumor cells to escape impairment by the immune system has been suggested as a novel “hallmark of cancer” (6).
During tumor progression, an extensive remodeling of the ECM with correlated release of pro-tumorigenic factors and orchestration of surrounding “stroma” cells is initiated. This remodeling of the tumor microenvironment is closely associated to the modulation of the immune response (34, 35). Thus, in cancer pathogenesis the resulting “desmoplastic reaction” among resident fibroblasts, endothelial cells, pericytes, leukocytes and surrounding ECM is directly correlated with invasion and poor patient prognosis (36, 37). The restructuring of the ECM is due to: (i) modulation in the synthesis and release of ECM components; (ii) degradation of the ECM owing to enzyme action or chemical degradation due to radical oxygen species (ROS) (4, 38). Specific ECM remodeling will ultimately result in: (i) the detachment of tumor cells from each other, from adjacent stromal cells or from matrix; (ii) enhanced growth and mobility of tumor cells; (iii) modulation of the immune system and finally in sustaining of the tumorigenic microenvironment (39, 40).
The family of small leucine rich PGs (SLRPGs) was initially correlated with the regulation of innate immunological responses, noteworthy due to the fact that the triggering of these very responses can lead to the initiation of tumorigenesis (41). The role of a pro-inflammatory molecule has been designated to a class I SLRP member, biglycan (17). Importantly, this SLRP is overexpressed and secreted by various cancers including gastric (42), pancreatic (43), ovarian (44), and colon cancer (45). This SLRP can be either freed from the ECM through proteolytic degradation initiated upon tissue injury or de novo produced by activated macrophages and resident cells with various immunological roles (Figure 2) (46). Soluble biglycan can undertake the role of signaling mediator by binding to the Toll-like receptors (TLR)-2 and -4 on the surface of macrophages. The formation of the ligand-receptor complex initiates sterile inflammation and can facilitate pathogen-mediated inflammation through the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, including the tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-1β or chemokine (C–C motif) ligand (CCL)2 (46, 47). It was shown that soluble biglycan utilizes TLR2/4 signaling pathways to activate adaptor molecule myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (MyD88), for the recruitment of neutrophils and macrophages or to initiate Toll/interleukin (IL)-1R domain-containing adaptor inducing interferon (IFN)-β (TRIF) activities for T-lymphocyte recruitment (48). Moreover, the role of a danger signal (DAMP) that triggers the NLRP3 inflammasome through upstream TLR2/4 and P2X receptors signaling has been attributed to biglycan (49), by specifically regulating the crosstalk between TLR2/4- and P2X7-NLRP3-caspase-1 (50, 51). Increasing data proposes that the initiation of TLR2/TLR4 signaling enhances tumor cell growth, downregulates apoptosis, and upregulates the synthesis of growth factors and inflammation-associated cytokines by tumor and stromal cells (50, 52, 53). Recently, biglycan was shown to bind with high affinity to macrophage CD14, an established GPI-anchored TLRs co-receptor. CD14 is mandatory for biglycan-dependent TLRs activation, where biglycan seems to have the role of a re-router as complexing with specific TLR members induces a discrete response. Thus, in macrophages, the biglycan/CD14/TLR2,4 complex induces the TNF-α expression, thebiglycan/CD14/TLR2 co-localization results in HSP70 release, whereas the biglycan/CD14/TLR4 complex initiates CCL5 secretion (54). Moreover, in a mouse model of renal injury, a deficiency of CD14 prevented biglycan-mediated cytokine expression, recruitment of macrophages, and M1 macrophage polarization (54).
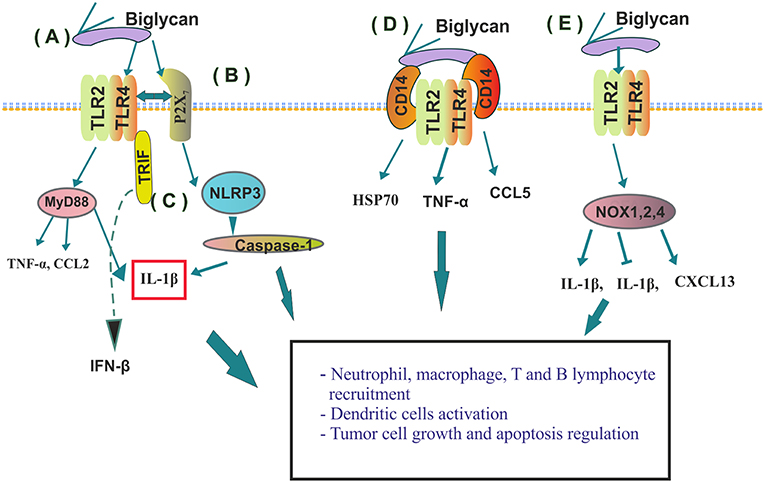
Figure 2. Immunomodulatory roles of biglycan. (A) By binding to TLR2 or 4 on macrophages' biglycan induces cytokine (TNF-α, CCL2 or IL-1β) release; (B) Crosstalk between TLR2/4- and P2X induces NLRP3 inflamozone and IL-1β activation and consequent neutrophil recruitment; (C) Soluble biglycan initiates Toll/interleukin (IL)-1R domain-containing adaptor activation inducing interferon (IFN)-β (TRIF) activities for T-lymphocyte recruitment; (D) Biglycans' binding determines CD14/TLR2/TLR4 complex formation and discrete downstream signaling; (E) Biglycan binding to specific TLR receptors discriminately activates NADPH oxidase (NOX) 1, 2, and 4 enzymes and regulates their downstream ROS production resulting in both positive or negative modulation of IL-1β synthesis; or in the stimulation of macrophages and dendritic cells to express chemokine (C-X-C) ligand 13 (CXCL13), the major chemoattractant for B and B1 lymphocytes.
Moreover, biglycan has been implicated in the regulation of important to tumorigenesis (4), ROS generation (55). Indeed, biglycan through activating discrete TLR receptors discriminately stabilizes NADPH oxidase (NOX) 1, 2, and 4 enzymes and regulates their downstream ROS production, resulting in either a positive or negative modulation of IL-1β synthesis (18). Furthermore, TLR2/4 induced ROS generation by biglycan (56) stimulates macrophages and dendritic cells to express chemokine (C-X-C) ligand 13 (CXCL13), the major chemoattractant for B and B1 lymphocytes (56). In addition to chemoattracting B cells, biglycan through TLR2/4 stimulates RANTES, MCP-1, and MIP-1α secretion, inducing macrophages and T cells recruitment into the kidney. Thus, these developments indicate that biglycan signaling can bridge innate and adaptive immunity (56), with the ability to act at different check points of the tumor immune cycle.
On the other hand, by enhancing NOX-generated ROS, biglycan induces genomic volatility coupled with chromosomal DNA modifications, which results in increased tumor cell growth, viability, and a metastatic ability of inflammation-associated tumors (57). Even though the majority of reports suggest that the activities of biglycan are pro-oncogenic, recent studies provide evidence that biglycan can promote an anti-inflammatory response that is key for the resolution of acute inflammation and hence the switch to acquired immunity response (18). Indeed, it is now proposed that biglycan, even though exhibiting affinity to both TLR2 and 4, will discriminately bind to only one TLR, which will, in combination with specific TLR adaptor molecules, lead to a discrete biological response (17, 18). The summarized regulation of immunity responses by biglycan can conceivably affect the development and resolution of early pre-cancerous lesions as well as the progression of inflamed tumor subtypes. Decorin, likewise an SLRP class I member, has established anti-tumorigenic properties (58). This SLRP member has the ability to initiate the TLR2/4 downstream signaling and cytokine release with an outcome different to that of biglycan. Specifically, utilizing a transforming growth factor –β (TGF-β)/oncogenic microRNA (miR)-21/tumor suppressor programmed cell death protein 4 (PDCD4) axis decorin downregulates the release of IL-10, which is an anti-inflammatory mediator and thus inhibits tumor growth (59). Moreover, decorin mobilizes mononuclear cells to the region of damaged tissue by enhancing CCL2 release and thereby, effectively upholding the inflammatory state (60). In a breast cancer xenographic model it was demonstrated that the decorin protein core inhibits genes obligatory for the regulation of the immunological response. Therefore, Buraschi et al. conclude that the “systemic administration of decorin protein core reveals a fundamental basis of action for decorin to modulate the tumor stroma as a biological mechanism for the ascribed anti-tumorigenic properties.” Indeed, the authors' gene ontology data indicated an inhibitory role in the regulation of proteins implicated in immunomodulatory responses when assigned to decorin protein core (61). The SLRP lumican has been postulated to modulate tumor-associated inflammation by affecting peripheral monocyte extravasation, and Fas–FasL signaling (14). Interestingly, lumican enhances LPS-dependent activation of TLR4 (62).
Versican, a member of the hyalectan family of large chondroitin sulfate PGs (CSPGs) has also been implicated in inflammatory processes (19, 63). These pericellular PGs are localized, among other, to the sub-endothelial compartment where they encounter the infiltrating leukocytes and modulate their biological activities by binding to specific receptors including TLR2, and P- or L-selectins (19). Once bound to the versican-containing ECM, leukocytes degrade the ECM to generate pro-inflammatory fragments that further drive the inflammatory response (64). Versican has been established to be overexpressed in a number of cancers, including prostate, breast, malignant myeloma, glioblastoma, laryngeal, pancreatic ovarian, gastric, testicular germ-cell, and cervical cancer, as recently discussed (65).
Importantly, in cancer-associated inflammation, versican can affect the production of cytokines by both lymphoid and myeloid cells. Thus, Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC) cells overexpress versican in that, by binding to TLR2 and its co-receptors on macrophage cell membranes, it activates the latter and facilitates their TNF-α secretion (66). The initiation of this cascade by versican and the induction of TNF-α by myeloid cells enhances LLC cell metastatic growth (66). Furthermore, an increased expression of versican V1 and V3 isoforms was positively correlated to lung metastasis in a bladder cancer murine model due to the increased release of CCL chemokine by macrophages (67). Specifically, versican was shown to facilitate bladder tumor cell migration, resulting in lung metastasis due to a mechanism involving CCL2/CCR2 secretion by macrophages. Said & Theodorescu propose that the aforementioned cytokine release generates a permissive lung inflammatory environment (68). Likewise, in mesotheliomas, versican downregulates macrophage M1 phenotype and decreases their ability to phagocytose tumor cells (69) contributing to the process of immune “escape.”
Interestingly, monocytes cultured in versican-containing supernatants of colon cancer cells secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-12, TNFα and ROS, whereas monocytes cultured in versican-free supernatants gathered from breast cancer tumors' culture exhibited a different profile of secreted cytokines. Thus, versican seems to have the ability to specifically direct the inflammatory monocyte response (19), conceivably correlated to the differential recruitment of lymphocytes, and differentiation into tumor-associated macrophages and dendritic cells (DC) (70).
DCs are proposed to engage tumor antigens and relocate to draining lymph nodes, where they trigger tumor-specific T cells (71). Importantly, versican derived from tumor ECM activates DCs' TLR2, resulting in the production of immunosuppressive IL-10 and DC dysfunction. This was associated with a TLR2-induced increase of IL-6 and IL-10 cell-surface receptors and a strongly decreased cytokine concentration threshold is needed to trigger STAT3 (72, 73). Intact versican, thus, dampens DC activation (72, 73) and conceivably downstream Th and cytotoxic lymphocyte (CTL) differentiation. Likewise, intact versican secreted by macrophages was shown to have anti-inflammatory properties in a mouse model of acute pulmonary inflammation (74). On the other hand, in myelomas, versican is proteolyticaly processed to the DAMP versikine, which induces the secretion of IL-1β and IL-6 by human myeloma marrow-derived macrophages (MAMs). Importantly, MAMs chiefly synthesized V1, the precursor to versikine, whereas stromal cells secreted the versican-degrading protease. This interplay is suggested to enhance the “T-cell inflammation,” response and downregulate the “tolerogenic consequences of intact versican accumulation” contributing to tumor restraint (75).
Syndecans (SDCs), cell membrane HS containing PGs (76), have also been implicated in tumor immunomodulation. SDC1-defficient mouse model of colitis-related colon carcinoma exhibited higher susceptibleness to malignant transformation due to the enhanced topical release of IL-6, downstream activation of STAT3 and target genes with important roles in colonic tumorigenesis (77). Likewise, in inflammatory breast cancer, SDC1 was shown to upregulate the inflammatory IL-6/STAT3 pathway (78), a crucial part of tumor-stimulating signaling in epithelial-origin tumors (79). The well-described role of the enzyme heparanase, responsible for the cleavage of the HS chains may partly elucidate the role of the HS-bearing SDCs (80). Thus, due to the fact that HS regulates inflammatory processes at various checkpoints, e.g., including the segregation of inflammatory cytokines to the ECM, the configuration of leukocyte binding to the endothelial cells and ECM components, as well as the generation of responses respective to innate immunity by interacting with the TLRs, the reconfiguration of HS due to enzymatic heparanase affects the propagation of inflammatory events (80, 81).
Endocan is an endothelial-derived soluble PG, initially identified in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (82). Interestingly, endothelium activated by inflammatory processes and/or tumor pathogenesis exhibits a strong augmentation in endocan expression correlated to poor patient prognosis (81, 83–85). Glycanated human endocan has been shown to strongly promote tumor growth (86) through its ability to bind to the integrin CD11a/CD18 (LFA-1) and thus to block leukocyte binding to endothelium and subsequent infiltration to tumor tissues (87); or through its promotion of growth factor actions (83, 88). On the other hand, the non-glycanated mouse or human endocan polypeptide was shown, in a murine model, to delay tumor expansion through the induction of pan-leukocytic infiltration of CD122+ expressing cells within tumor and stroma tissues (89).
Serglycin, the only known intracellular PG is shown to be overexpressed in various tumor tissues and cell lines (90, 91). Importantly, serglycin is a key compound of secretory particles produced by CTL/NK cells, suggested to facilitate the safe storage of particle toxins, granzymes and perforin and affect CTL/NK cells' cytotoxic ability (92). Even though no evidence is available as such, these data implicate a plausible contribution of serglycin to processes of cancer-associated inflammation.
The modulation of PGs' activities, as endogenous mediators of cancer-associated inflammation, is a novel approach in the field of cancer immunotherapy. Research efforts up to date have demonstrated the plausibility of this strategy as discussed below. Thus, the administration of the versican fragment characterized as DAMP, versikine, is suggested to “facilitate immune sensing of myeloma tumors and modulate the tolerogenic consequences of intact versican accumulation” which may facilitate tumor restraint and enhance T-cell-activating immunotherapies (75). Blocking the versican/CCL2/CCR2 signaling axis is indicated to purvey novel adjuvant strategies for detaining the emergence of clinical metastasis in bladder cancer patients (68). The non-glycanated mouse or human endocan polypeptide restrains tumor growth by increasing leukocyte infiltration in vivo, enhancing de facto innate immunity response (89). Suppressing the shedding of SDC1 from intestinal epithelial cells decreases intestinal inflammation and putative malignant transformation by augmenting NF-κB, respective downstream signaling, and neutrophil transmigration in ulcerative colitis (93). Indeed, the modulation of SDC1 expression could facilitate immunesurveillance and the positive resolution of precancerous lesions. Biglycan is suggested to bridge innate and adaptive immunity through TLR2/4 downstream signaling due to its' ability to regulate neutrophil, macrophage, T and B lymphocyte, and dendritic cells activities (17, 18, 46–56). Thus, selective inhibition of biglycan-TLR2/TLR4 axis could be a novel therapeutic approach targeting at various checkpoints of the cancer immunobiology cycle. Modulations of PGs post-transcriptional modifications, including their respective sulfation pattern, seems to be a therapy option as inhibition of sulfatase-2 activity had cytotoxic and partial hepatoprotective activity in both in vivo and in vitro hepatocellular carcinoma models (94, 95). Indeed, a clinically relevant pattern of PG and GAG expression and structural modifications was recently determined for PGs and GAG synthesizing enzymes in glioma and breast cancer, which might help in the development of personalized therapy (96).
Despite these advances, however, many issues need yet to be addressed for implementation to clinical practice (97). Furthermore, an understanding of tumor microenvironment biology and its PG component is necessary for therapy development.
DN designed the concept and completed the final editing of the manuscript. All authors contributed to writing of the manuscript. DN and MN prepared the figures. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
DN was supported by ELKE KA10038. MN was supported by PN 19.29.01.01, PN-III-P1-1.2-PCCDI-2017-0341/2018 and 7PFE/16.10.2018.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
1. Aggarwal BB, Vijayalekshmi RV, Sung B. Targeting inflammatory pathways for prevention and therapy of cancer: short-term friend, long term foe. Clin Cancer Res. (2009) 15:425–30. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0149
2. Grivennikov SI, Greten FR, Karin M. Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell. (2010) 140:883–99. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.01.025
3. Konsoulova A. Chapter 5. Principles of cancer immunobiology and immunotherapy of solid tumors. In: Metodiev E, editor. Immunopathology and Immunomodulation, INTECH (2015).
4. Nikitovic D, Corsini E, Kouretas D, Tsatsakis A, Tzanakaki G. ROS-major mediators of extracellular matrix remodeling during tumor progression. Food and Chemical Toxicology. (2013) 61:178–86. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2013.06.013
5. Nikitovic D, Berdiaki A, Spyridaki I, Krasanakis T, Tsatsakis A, Tzanakakis GN. Proteoglycans-biomarkers and targets in cancer therapy. Front Endocrinol. (2018) 9:69. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00069
6. Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. (2011) 144:646–7410. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013
7. Iozzo RV, Schaefer L. Proteoglycan form and function: a comprehensive nomenclature of proteoglycans. Matrix Biol. (2015) 42:11–55. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2015.02.003
8. Lindahl U, Couchman J, Kimata K, Esko JD. Chapter 17. Proteoglycans and sulfated glycosaminoglycans. In: Varki A, Cummings RD, Esko JD, Stanley P, Hart GW, Aebi M, et al. editors. Essentials of Glycobiology [Internet]. 3rd ed. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press (2015–2017).
9. Marchand M, Monnot C, Muller L, Germain S. Extracellular matrix scaffolding in angiogenesis and capillary homeostasis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. (2018) S1084–9521:30578–5. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2018.08.007
10. Aggelidakis J, Berdiaki A, Nikitovic D, Papoutsidakis A, Papachristou DJ, Tsatsakis AM, et al. Biglycan regulates MG63 osteosarcoma cell growth through a LPR6/β-catenin/IGFR-IR signaling Axis. Front Oncol. (2018) 8:470. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00470
11. Mytilinaiou M, Nikitovic D, Berdiaki A, Papoutsidakis A, Papachristou DJ, Tsatsakis A, et al. IGF-I regulates HT1080 fibrosarcoma cell migration through a syndecan-2/Erk/ezrin signaling axis. Exp Cell Res. (2017) 1:9–18. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.09.035
12. Nikitovic D, Aggelidakis J, Young MF, Iozzo RV, Karamanos NK, Tzanakakis GN. The biology of small leucine-rich proteoglycans in bone pathophysiology. J Biol Chem. (2012) 287:33926–33. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R112.379602
13. Mytilinaiou M, Nikitovic D, Berdiaki A, Kostouras A, Papoutsidakis A, Tsatsakis AM, et al. Emerging roles of syndecan 2 in epithelial and mesenchymal cancer progression. IUBMB Life. (2017) 69:824–833. doi: 10.1002/iub.1678
14. Nikitovic D, Papoutsidakis A, Karamanos NK, Tzanakakis GN. Lumican affects tumor cell functions, tumor-ECM interactions, angiogenesis and inflammatory response. Matrix Biol. (2014) 35:206–14. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2013.09.003
15. Ricard-Blum S, Vallet SD. Matricryptins network with matricellular receptors at the surface of endothelial and tumor cells. Front Pharmacol. (2016) 7:11. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00011
16. Theocharis AD, Karamanos NK. Proteoglycans remodeling in cancer: Underlying molecular mechanisms. Matrix Biol. (2017) 75–6:220–59. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2017.10.008
17. Schaefer L, Tredup C, Gubbiotti MA, Iozzo RV. Proteoglycan neofunctions: regulation of inflammation and autophagy in cancer biology. FEBS J. (2016) 284:10–26. doi: 10.1111/febs.13963
18. Hsieh LT, Frey H, Nastase MV, Tredup C, Hoffmann A, Poluzzi C, et al. Bimodal role of NADPH oxidases in the regulation of biglycan-triggered IL-1β synthesis. Matrix Biol. (2016) 49:61–81. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2015.12.005
19. Wight TN, Kang I, Merrilees MJ. Versican and the control of inflammation. Matrix Biol. (2016) 35:152–61. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2014.01.015
20. Dunn GP, Old LJ, Schreiber RD. The immunobiology of cancer immunosurveillance and immunoediting. Immunity. (2004) 21:137–48. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2004.07.017
21. Karlou M, Tzelepi V, Efstathiou E. Therapeutic targeting of the prostate cancer microenvironment. Nat Rev Urol. (2010) 7:494–509. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2010.134
22. Vinay DS, Ryan EP, Pawelec G, Talib WH, Stagg J, Elkord E, et al. Immune evasion in cancer: mechanistic basis and therapeutic strategies. Semin Cancer Biol. (2015) 35(Suppl.) S185–98. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.03.004
23. Neagu M, Constantin C, Caruntu C, Dumitru C, Surcel M, Zurac S. Inflammation: A key process in skin tumorigenesis (review). Oncol Lett. (2019) 17:4068–84. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.9735
24. Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A, Balkwill F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. (2008) 454:436–44. doi: 10.1038/nature07205
25. Castle PE, Hillier SL, Rabe LK, Hildesheim A, Herrero R, Bratti MC, et al. An association of cervical inflammation with high-grade cervical neoplasia in women infected with oncogenic human papillomavirus (HPV). Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. (2001) 10:1021–7.
26. Rothenberg SM, Ellisen LW. The molecular pathogenesis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Clin Investig. (2012) 122:1951–7. doi: 10.1172/JCI59889
27. Arzumanyan A, Reis HM, Feitelson MA. Pathogenic mechanisms in HBV- and HCV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Cancer. (2013) 13:123–35. doi: 10.1038/nrc3449
28. Salama NR, Hartung ML, Muller A. Life in the human stomach: persistence strategies of the bacterial pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nat Rev Microbiol. (2013) 11:385–99. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3016
29. Houghton AM. Mechanistic links between COPD and lung cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. (2013) 13:233–45. doi: 10.1038/nrc3477
30. Meiliana A, Dewi NM, Wijaya A. The immunobiology of cancer: an update review. Indones Biomed J. (2017) 9:53–72. doi: 10.18585/inabj.v9i2.342
31. Raval RR, Sharabi AB, Walker AJ, Drake CG, Sharma P. Tumor immunology and cancer immunotherapy: summary of the 2013 SITC primer. J Immunother Cancer. (2014) 2:14. doi: 10.1186/2051-1426-2-14
32. Gajewski TF, Corrales L, Williams J, Horton B, Sivan A, Spranger S. Cancer immunotherapy targets based on understanding the T cell-inflamed versus non-T cell-inflamed tumor microenvironment. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2017) 1036:19–31. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-67577-0_2
33. Spranger S. Mechanisms of tumor escape in the context of the T-cell-inflamed and the non-T-cell-inflamed tumor microenvironment. Int Immunol. (2011) 28:383–91. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxw014
34. Pietras K, Ostman A. Hallmarks of cancer: interactions with the tumor stroma. Experim Cell Res. (2010) 316:1324–31. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2010.02.045
35. Schäfer M, Werner S. Cancer as an overhealing wound: an old hypothesis revisited. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2008) 9:628–38. doi: 10.1038/nrm2455
36. Cardone A, Tolino A, Zarcone R, Borruto Caracciolo G, Tartaglia E. Prognostic value of desmoplastic reaction and lymphocytic infiltration in the management of breast cancer. Panminerva Med. (1997) 39:174–7.
37. Avgustinova A, Iravani M, Robertson D, Fearns A, Gao Q, Klingbeil P, et al. Tumour cell-derived Wnt7a recruits and activates fibroblasts to promote tumour aggressiveness. Nat Commun. (2016) 7:10305. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10305
38. Sung SY, Hsieh CL, Law A, Zhau HE, Pathak S, Multani AS, et al. Coevolution of prostate cancer and bone stroma in three-dimensional coculture: implications for cancer growth and metastasis. Cancer Res. (2008) 68:9996–10003. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2492
39. Lu P, Weaver VM, Werb Z. The extracellular matrix: a dynamic niche in cancer progression. J Cell Biol. (2012) 196:395–406. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201102147
40. Nikitovic D, Tzardi M, Berdiaki A, Tsatsakis A, Tzanakakis GN. Cancer Microenvironment and inflammation: role of hyaluronan. Front Immun. (2015) 6:169. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00169
41. Neill T, Schaefer L, Iozzo RV. Decoding the matrix: Instructive roles of proteoglycan receptors. Biochemistry. (2015) 54:4583–98. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00653
42. Hu L, Duan YT, Li JF, Su LP, Yan M, Zhu ZG, et al. Biglycan enhances gastric cancer invasion by activating FAK signaling pathway. Oncotarget. (2014) 5:1885–96. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1871
43. Avellini C, Reni M, Mazzer M, Foltran L, Rossi D, Cereda S, et al. Biglycan expression and clinical outcome in patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Tumour Biol. (2013) 34:131–7. doi: 10.1007/s13277-012-0520-2
44. Pan S, Cheng L, White JT, Lu W, Utleg AG, Yan X, et al. Quantitative proteomics analysis integrated with microarray data reveals that extracellular matrix proteins, catenins, and p53 binding protein 1 are important for chemotherapy response in ovarian cancers. OMICS J Integr Biol. (2009) 13:345–54. doi: 10.1089/omi.2009.0008
45. Mikula M, Rubel T, Karczmarski J, Goryca K, Dadlez M, Ostrowski J. Integrating proteomic and transcriptomic high-throughput surveys for search of new biomarkers of colon tumors. Funct Integr Genomics. (2011) 11:215–24. doi: 10.1007/s10142-010-0200-5
46. Schaefer L, Babelova A, Kiss E, Hausser HJ, Baliova M, Krzyzankova M, et al. The matrix component biglycan is proinflammatory which signals through the innate immunity Toll-like receptors 4 and 2 (TLR4, 2). J Clin Invest. (2005) 115:2223–33. doi: 10.1172/JCI23755
47. Moreth K, Frey H, Hubo M, Zeng-Brouwers J, Nastase MV, Hsieh LT, et al. Biglycan-triggered TLR-2- and TLR-4-signaling exacerbates the pathophysiology of ischemic acute kidney injury. Matrix Biol. (2014) 35:143–51. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2014.01.010
48. Zeng-Brouwers J, Beckmann J, Nastase MV, Iozzo RV, Schaefer L. De novo expression of circulating biglycan evokes an innate inflammatory tissue response via MyD88/TRIF pathways. Matrix Biol. (2014) 35:132–42. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2013.12.003
49. Babelova A, Moreth K, Tsalastra-Greul W, Zeng-Brouwers J, Eickelberg O, Young MF, et al. Biglycan, a danger signal that activates the NLRP3 inflammasome via toll-like and P2X receptors. J Biol Chem. (2009) 284:24035–42408. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.014266
50. Schaefer L, Iozzo RV. Small leucine-rich proteoglycans, at the crossroad of cancer growth and inflammation. Curr Opin Genet Dev. (2012) 22:56–7. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2011.12.002
51. Moreth K, Iozzo RV, Schaefer L. Small leucine-rich proteoglycans orchestrate receptor crosstalk during inflammation. Cell Cycle. (2012) 11:2084–91. doi: 10.4161/cc.20316
52. Dajon M, Iribarren K, Cremer I. Toll-like receptor stimulation in cancer: a pro- and anti-tumor double-edged sword. Immunobiology. (2016) 222:89–100. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2016.06.009
53. Farnebo L, Shahangian A, Lee Y, Shin JH, Scheeren FA, Sunwoo JB. Targeting Toll-like receptor 2 inhibits growth of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. (2015) 6:9897–907. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3393
54. Roedig H, Nastase MV, Frey H, Moreth K, Zeng-Brouwers J, Poluzzi C, et al. Biglycan is a new high-affinity ligand for CD14 in macrophages. Matrix Biol. (2018) 17:4–22. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2018.05.006
55. Nastase MV, Janicova A, Wygrecka M, Schaefer L. Signaling at the crossroads: matrix-derived proteoglycan and reactive oxygen species signaling. Antioxid Redox Signal. (2017) 27:855–73. doi: 10.1089/ars.2017.7165
56. Moreth K, Brodbeck R, Babelova A, Gretz N, Spieker T, Zeng-Brouwers J, et al. The proteoglycan biglycan regulates expression of the B cell chemoattractant CXCL13 and aggravates murine lupus nephritis. J Clin Invest. (2010) 120:4251–72. doi: 10.1172/JCI42213
57. Wu Y, Antony S, Meitzler JL, Doroshow JH. Molecular mechanisms underlying chronic inflammation-associated cancers. Cancer Lett. (2014) 34:164–73. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.08.014
58. Gubbiotti MA, Vallet SD, Ricard-Blum S, Iozzo RV. Decorin interacting network: a comprehensive analysis of decorin-binding partners and their versatile functions. Matrix Biol. (2016) 55:7–21. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2016.09.009
59. Merline R, Moreth K, Beckmann J, Nastase MV, Zeng-Brouwers J, Tralhão JG, et al. Signaling by the matrix proteoglycan decorin controls inflammation and cancer through PDCD4 and microRNA-21. Sci Signal. (2011) 4:75. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2001868
60. Koninger J, Giese NA, Bartel M, di Mola FF, Berberat PO, di Sebastiano P, et al. The ECM proteoglycan decorin links desmoplasia and inflammation in chronic pancreatitis. J Clin Pathol. (2006) 59:21–7. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2004.023135
61. Buraschi S, Neill T, Owens RT, Iniguez LA, Purkins G, Vadigepalli R, et al. Decorin protein core affects the global gene expression profile of the tumor microenvironment in a triple-negative orthotopic breast carcinoma xenograft model. PLoS ONE. (2012) 7:e45559. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045559
62. Wu F, Vij N, Roberts L, Lopez-Briones S, Joyce S, Chakravarti S. A novel role of the lumican core protein in bacterial lipopolysaccharide-induced innate immune response. J Biol Chem. (2007) 282:6409–26417. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M702402200
63. Frevert CW, Felgenhauer J, Wygrecka M, Nastase MVIII, Schaefer L. Danger-associated molecular patterns derived from the extracellular matrix provide temporal control of innate immunity. J Histochem Cytochem. (2018) 66:213–27. doi: 10.1369/0022155417740880
64. Adair-Kirk TL, Senior RM. Fragments of extracellular matrix as mediators of inflammation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. (2008) 40:1101–10. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2007.12.005
65. Binder MJ, McCoombe S, Williams ED, McCulloch DR, Ward AC. The extracellular matrix in cancer progression: role of hyalectan proteoglycans and ADAMTS enzymes. Cancer Lett. (2017) 385:55–6. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.11.001
66. Kim S, Takahashi H, Lin WW, Descargues P, Grivennikov S, Kim Y, et al. Carcinoma-produced factors activate myeloid cells through TLR2 to stimulate metastasis. Nature. (2009) 457:102–6. doi: 10.1038/nature07623
67. Said N, Sanchez-Carbayo M, Smith SC, Theodorescu D. RhoGDI2 suppresses lung metastasis in mice by reducing tumor versican expression and macrophage infiltration. J Clin Investig. (2012) 122:1503–18. doi: 10.1172/JCI61392
68. Said N, Theodorescu D. RhoGDI2 suppresses bladder cancer metastasis via reduction of inflammation in the tumor microenvironment. OncoImmunology. (2012) 1:1175–17. doi: 10.4161/onci.20594
69. Pappas AG, Magkouta S, Pateras IS, Skianis I, Moschos C, Vazakidou ME, et al. Versican modulates tumor-associated macrophage properties to stimulate mesothelioma growth. Oncoimmunology. (2018) 8:e1537427. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2018.1537427
70. Olingy CE, Dinh HQ, Hedrick CC. Monocyte heterogeneity and functions in cancer. J Leukoc Biol. (2019) doi: 10.1002/JLB.4RI0818-311R. [Epub ahead of print].
72. Tang M, Diao J, Cattral MS. Molecular mechanisms involved in dendritic cell dysfunction in cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2017) 74:761–76. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2317-8
73. Tang M, Diao J, Gu H, Khatri I, Zhao J, Cattral MS. Toll-like receptor 2 activation promotes tumor dendritic cell dysfunction by regulating IL-6 and IL-10 receptor signaling. Cell Rep. (2015) 13:2851–64. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.11.053
74. Chang MY, Kang I, Gale MJr, Manicone AM, Kinsella MG, Braun KR, et al. Versican is produced by Trif- and type I interferon-dependent signaling in macrophages and contributes to fine control of innate immunity in lungs. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. (2017) 313:L1069–86. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00353.2017
75. Hope C, Foulcer S, Jagodinsky J, Chen SX, Jensen JL, Patel S, et al. Immunoregulatory roles of versican proteolysis in the myeloma microenvironment. Blood. (2016) 128:680–5. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-03-705780
76. Afratis NA, Nikitovic D, Multhaupt HA, Theocharis AD, Couchman JR, Karamanos NK. Syndecans – key regulators of cell signaling and biological functions. FEBS J. (2017) 284:27–41. doi: 10.1111/febs.13940
77. Binder Gallimidi A, Nussbaum G, Hermano E, Weizman B, Meirovitz A, Vlodavsky I, et al. Elkin M. Syndecan-1 deficiency promotes tumor growth in a murine model of colitis-induced colon carcinoma. PLoS ONE. (2017) 12:e0174343. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174343
78. Ibrahim SA, Gadalla R, El-Ghonaimy EA, Samir O, Mohamed HT, Hassan H, et al. Syndecan-1 is a novel molecular marker for triple negative inflammatory breast cancer and modulates the cancer stem cell phenotype via the IL-6/STAT3, Notch and EGFR signaling pathways. Mol Cancer. (2017) 16:57. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0621-z
79. Grivennikov S, Karin E, Terzic J, Mucida D, Yu GY, Vallabhapurapu S, et al. IL-6 and Stat3 are required for survival of intestinal epithelial cells and development of colitis-associated cancer. Cancer Cell. (2009) 15:103–13. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2009.01.001
80. Goodall KJ, Poon IK, Phipps S, Hulett MD. Soluble heparan sulfate fragments generated by heparanase trigger the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines through TLR-4. PLoS ONE. (2014) 9:e109596. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109596
81. Vlodavsky I, Singh P, Boyango I, Gutter-Kapon L, Elkin M, Sanderson RD, et al. Heparanase: From basic research to therapeutic applications in cancer and inflammation. Drug Resist Updates. (2016) 29:54–75. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2016.10.001
82. Lassalle P, Molet S, Janin A, Heyden JV, Tavernier J, Fiers W, et al. ESM-1 is a novel human endothelial cell-specific molecule expressed in lung and regulated by cytokines. J Biol Chem. (1996) 271:20458–64. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.34.20458
83. Sarrazin S, Maurage CA, Delmas D, Lassalle P, Delehedde M. Endocan as a biomarker of endothelial dysfunction in cancer. J Cancer Sci Ther. (2010) 2:47–52. doi: 10.4172/1948-5956.1000022
84. Roudnicky F, Poyet C, Wild P, Krampitz S, Negrini F, Huggenberger R, et al. Endocan is upregulated on tumor vessels in invasive bladder cancer where it mediates VEGF-A-induced angiogenesis. Cancer Res. (2013) 73:1097–106. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-1855
85. Grigoriu BD, Depontieu F, Scherpereel A, Gourcerol D, Devos P, Ouatas T, et al. Endocan expression and relationship with survival in human non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. (2006) 12:4575–82. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0185
86. Kali A, Shetty KS. Endocan: a novel circulating proteoglycan. Indian J Pharmacol. (2014) 46:579–83. doi: 10.4103/0253-7613.144891
87. Béchard D, Scherpereel A, Hammad H, Gentina T, Tsicopoulos A, Aumercier M, et al. Human endothelial-cell specific molecule-1 binds directly to the integrin CD11a/CD18 (LFA-1) and blocks binding to intercellular adhesion molecule-1. J Immunol. (2001) 167:3099–106. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.6.3099
88. Scherpereel A, Gentina T, Grigoriu B, Sénéchal S, Janin A, Tsicopoulos A, et al. Overexpression of endocan induces tumor formation. Cancer Res. (2003) 63:6084–9.
89. Yassine H, De Freitasm Cairesm NM, Depontieum F, Scherpereel A, Awad A, Tsicopoulos A, et al. The non glycanated endocan polypeptide slows tumor growth by inducing stromal inflammatory reaction. Oncotarget. (2015) 6:2725–35. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2614
90. Korpetinou A, Papachristou DJ, Lampropoulou A, Bouris P, Labropoulou VT, Noulas A, et al. Increased expression of serglycin in specific carcinomas and aggressive cancer cell lines. Biomed Res Int. (2015) 2015:690721. doi: 10.1155/2015/690721
91. Fadnes B, Husebekk A, Svineng G, Rekdal Ø, Yanagishita M, Kolset SO, et al. The proteoglycan repertoire of lymphoid cells. Glycoconj J. (2012) 29:513–23. doi: 10.1007/s10719-012-9427-9
92. Sutton VR, Brennan AJ, Ellis S, Danne J, Thia K, Jenkins MR, et al. Serglycin determines secretory granule repertoire and regulates natural killer cell and cytotoxic T lymphocyte cytotoxicity. FEBS J. (2016) 283:947–61. doi: 10.1111/febs.13649
93. Zhang Y, Wang Z, Liu J, Zhang S, Fei J, Li J, et al. Cell surface-anchored syndecan-1 ameliorates intestinal inflammation and neutrophil transmigration in ulcerative colitis. J Cell Molec Med. (2017) 21:13–25. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12934
94. Yang JD, Sun Z, Hu C, Lai J, Dove R, Nakamura I. Sulfatase 1 and sulfatase 2 in hepatocellular carcinoma: associated signaling pathways, tumor phenotypes, and survival. Genes Chromo Cancer. (2011) 50:122–35. doi: 10.1002/gcc.20838
95. Alyoussef A, Al-Gayyar MMH. Cytotoxic and partial hepatoprotective activity of sodium ascorbate against hepatocellular carcinoma through inhibition of sulfatase-2 in vivo and in vitro. Biomed Pharmacother. (2018) 103:362–72. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.04.060
96. Subbarayan K, Seliger B. Tumor-dependent effects of proteoglycans and various glycosaminoglycan synthesizing enzymes and sulfotransferases on patients' outcome. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. (2019) 19:210–21. doi: 10.2174/1568009618666180706165845
Keywords: proteoglycans, immunobiology, cancer, extracellular matrix, remodeling
Citation: Tzanakakis G, Neagu M, Tsatsakis A and Nikitovic D (2019) Proteoglycans and Immunobiology of Cancer—Therapeutic Implications. Front. Immunol. 10:875. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00875
Received: 31 January 2019; Accepted: 05 April 2019;
Published: 24 April 2019.
Edited by:
Toshiyuki Murai, Osaka University, JapanReviewed by:
James McCarthy, University of Minnesota Twin Cities, United StatesCopyright © 2019 Tzanakakis, Neagu, Tsatsakis and Nikitovic. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dragana Nikitovic, bmlraXRvdmljQHVvYy5ncg==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.