- 1Women's and Children's Health, St. George Hospital, Sydney, NSW, Australia
- 2Faculty of Health, University of Technology, Sydney, NSW, Australia
- 3St George and Sutherland Clinical School UNSW Medicine, University of New South Wales, Sydney, NSW, Australia
- 4Maternal and Child Health Program, Burnet Institute, Melbourne, VIC, Australia
Introduction: Pregnancy and childbirth can be a source of anxiety and worry for women. This is probably more so for women with a complicated pregnancy. Anxiety and worry may contribute to, or exacerbate, mental health disorders including depression and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Mental health is an integral part of health and well-being and poor mental health can be detrimental to the woman's welfare and her infant's behavior and cognitive development. It may be undetected, potentially leading to a burden on the woman, her family, the health system, and society. Women with complicated pregnancies, such as those with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP), may be at greater risk of poor mental health. The aim of this review was to examine whether there is an association between depression, anxiety, and PTSD in postpartum women with a history of HDP.
Methods: A narrative literature review was undertaken. Using the key search terms: preeclampsia, gestational hypertension, hypertensive disorders, pregnancy complications, depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder; electronic databases were searched to determine what is known about depression, anxiety, and PTSD after HDP.
Results: In total, 17 publications were included. The relationship between HDP and depression, anxiety, and PTSD was variable between studies and inconsistent. Although some studies reported no significant association, there is a trend for increased prevalence and symptom severity of depression, anxiety, and PTSD following HDP. This trend was particularly evident following the more severe presentations of HDP. It was uncertain whether this association was due to the hypertensive disorder itself, the sequelae of the HDP, such as giving birth to a preterm baby, or it predated the pregnancy.
Conclusions: Women who experience HDP may be at increased risk of developing postpartum depression, anxiety, and PTSD. Awareness of, and screening for, these mental health disorders in the postpartum period will alert clinicians to the need for additional follow-up and referral for women following HDP. More research on the benefits and risks of such an approach is needed.
Introduction
Pregnancy and childbirth can be a source of stress and worry for many women (1) and mental health disorders following childbirth are common. Worldwide 10% of pregnant women and 13% of women who have just given birth experience a mental health disorder, primarily depression (2). These rates are higher (15.6 and 19.8%, respectively) in low to middle income countries (2). One in 7 women experience depression in the year following birth and one in five experience anxiety, commonly in combination with depression, during the same period (3). Research on the global prevalence of postpartum post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is sparse and has been reported as 1–2% (4) following childbirth, although a literature review by Simpson and Catling (5), including papers from several countries, found that 20–48% of women reported their birth as a traumatic event which could potentially lead to PTSD.
Pregnancy and childbirth are likely to be more stressful for a woman experiencing a pregnancy with complications (6) and as a psychological manifestation, stress may coexist with depression, anxiety, and trauma reactions (7). A pregnancy may be considered complicated when there is an increased risk compared to a healthy pregnancy (1) and implies a threat to the woman's health, well-being, her baby, or both (8). An example of such a pregnancy is one complicated by a hypertensive disorder.
Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP) are common and complicate 10% of pregnancies (9) which equates to ~30,000 pregnancies a year in Australia and 13 million pregnancies a year globally and they are one of the leading causes of maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality (10). The two pregnancy-specific disorders are gestational hypertension (GH) and preeclampsia (PE). GH is the new onset of hypertension after 20 weeks gestation (11) and when it presents at term, is usually a benign condition with little risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes (11, 12). However, the earlier GH presents in the pregnancy or the more severe the hypertension, the greater the risk of it progressing to PE or to an adverse pregnancy outcome (11, 13, 14). PE is a multi-system disorder which is described as the new onset of hypertension after 20 weeks gestation and the involvement of at least one other maternal organ system and/or the unborn baby (11, 12). Two particularly serious manifestations of PE are the syndrome HELLP (11, 12), comprising Hemolysis, Elevated Liver enzymes and a Low Platelet count, and eclampsia, which is seizures in a women with PE (11). There are long term physical health consequences for women after a HDP such as hypertension, stroke, heart attack, kidney disease, and diabetes (11, 15–19), however there is little known about women's mental health following this complication.
Poor mental health can impact both maternal and infant health negatively. In addition to affecting the woman's emotional welfare and everyday functioning, poor mental health may affect her parenting ability and can impair her relationship with her baby (20). Long term and/or untreated poor maternal mental health has been associated with poor infant well-being particularly in terms of behavioral and cognitive development (21). In severe cases, women with postpartum depression may commit suicide (2) and in those women with psychotic illnesses, the risk of infanticide, though rare, must be considered (2). Due to the serious consequences of poor mental health, early diagnosis, and treatment interventions are imperative for the health and well-being of the woman and her infant.
In the postpartum period, poor mental health is often undetected and untreated (22), potentially leading to a burden on the woman, her family, the health system and society. Guidelines highlight the importance of implementing interventions targeting women displaying the early signs and symptoms of poor mental health (23–25). However, it is not always known which women in the postpartum period would benefit from specific interventions. If women who experience HDP are identified as being at increased risk of poor mental health, targeted screening may be useful and lead to more timely referral and treatment initiation.
Aim
The aim of this review was to examine whether there is an increased risk of depression, anxiety, and PTSD in postpartum women with a history of HDP.
Methods
A narrative literature review was undertaken. This approach was used as it enabled a broad search that was able to draw conclusions about the topic and assist in identifying gaps or inconsistencies in the body of knowledge (26). Ethics approval was not required for this review.
Search Strategy
A comprehensive search of the literature was undertaken using the electronic databases of EBM Reviews (Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews), EMBASE, Ovid MEDLINE(R), CINAHL (Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health), Maternity and Infant Care, PsycINFO, and Google Scholar. The key search terms used were: preeclampsia, gestational hypertension, hypertensive disorders, pregnancy complications, depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder. All possible combinations and spellings of these key search terms were used. Additionally, the reference lists of identified papers were manually examined for further studies that may have been missed in the initial search.
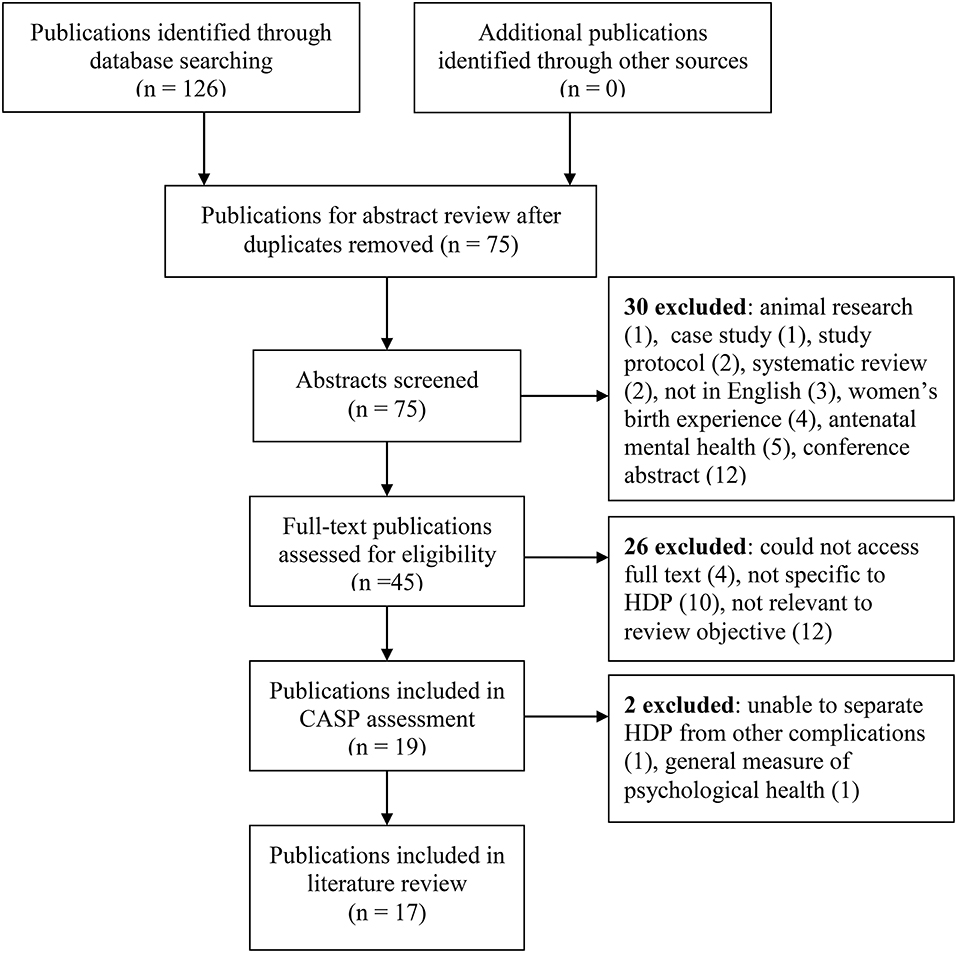
The search was undertaken in May 2019, limited to primary publications published in English from the year 2000 onwards, with full text available. Publications only available in abstract form, conference abstracts, and study protocols were excluded as were systematic reviews (Figure 1). Two systematic reviews were excluded as there was a concern that including these would mean double counting of some studies. All relevant individual studies within these systematic reviews were included in this review. One systematic review (27) focussed on the relationship between PTSD and severe maternal morbidity. Several pregnancy complications were included with PE in four publications (28–31). The other systematic review (32) reported on depression and/or anxiety following a pregnancy complicated with severe PE and included six publications (28, 29, 31, 33–35).
Following title and abstract screening, 45 publications were identified for possible inclusion and the full text was sourced. Subsequent to full text reading, 19 were considered relevant to the search objective and were further assessed using the Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP) (36). The CASP is a tool developed in 1993 which is widely used to systematically examine research articles to help identify the strengths, weaknesses, and usefulness of the study by appraising the validity, results and clinical relevance. Using the CASP checklist 17 publications were included in the review. Two publications were excluded at this stage as they: (1) reported on general quality of life following HDP and not specifically on depression, anxiety, or PTSD. Depression and anxiety are included in the screening instrument (SQL-90), but the overall results were reported as one score, so details specific to depression and anxiety could not be determined; and (2) reported the combined results of mental health for women after HDP and postpartum hemorrhage, making it impossible to separate the results for the HDP cohort.
Results
In the included publications, the definition of HDP was sourced from different national and international guidelines (9, 37–39) (Table 1). Although these different sources were used, the definitions of the hypertensive disorders were consistent. However, the use of different study populations was not all directly comparable. For example, the severity of HDP varied, with some only including women with severe HDP and some only included women at a specific preterm gestation (Table 1).
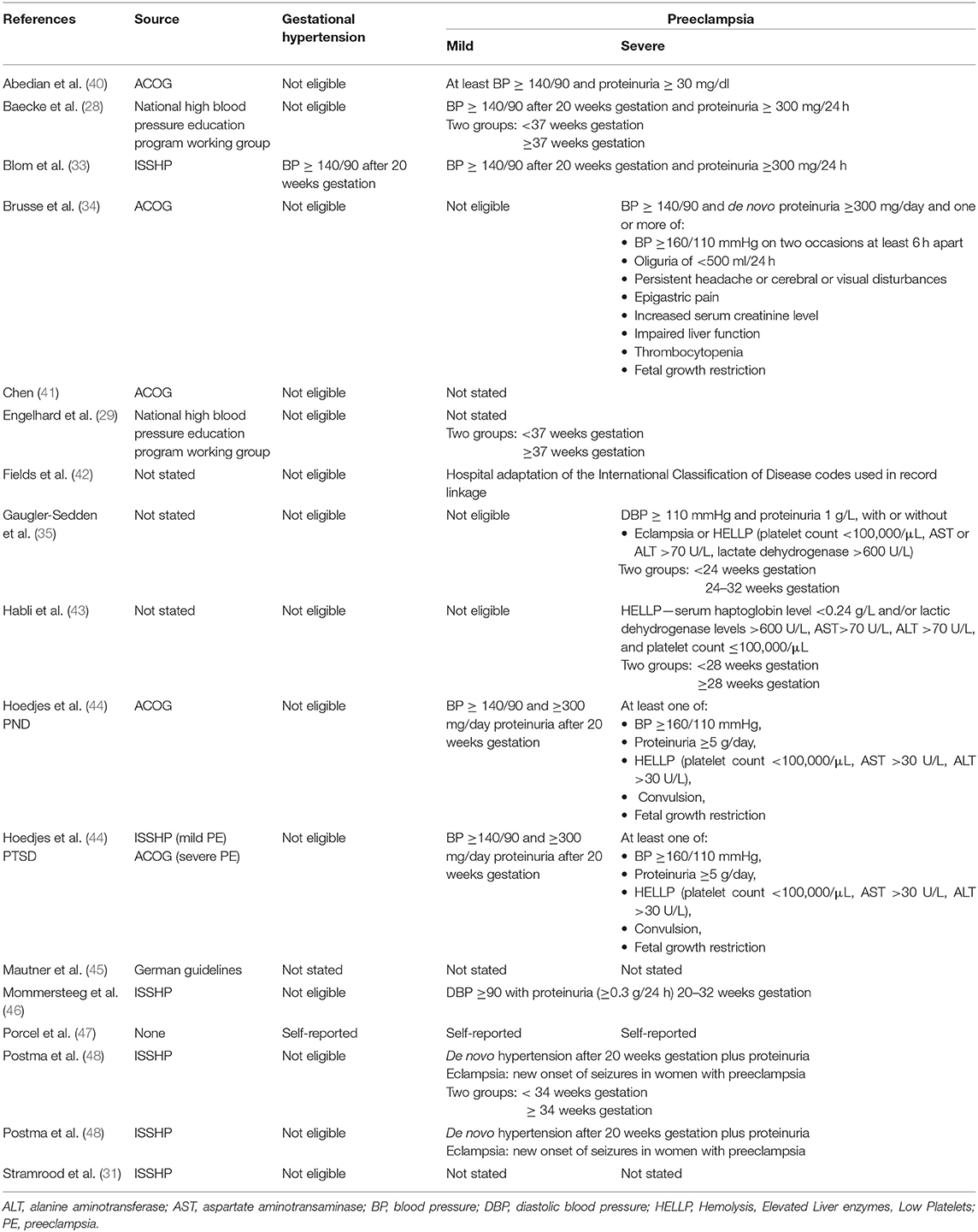
Table 1. The definition of hypertension in pregnancy and inclusion criteria for the included studies.
The identified publications were grouped into three categories of mental health disorder, depression, anxiety, and PTSD. Some studies reported on more than one disorder and were included in more than one group. Furthermore, some studies reported on both prevalence and symptom severity. The results of depression, anxiety and PTSD were reported separately.
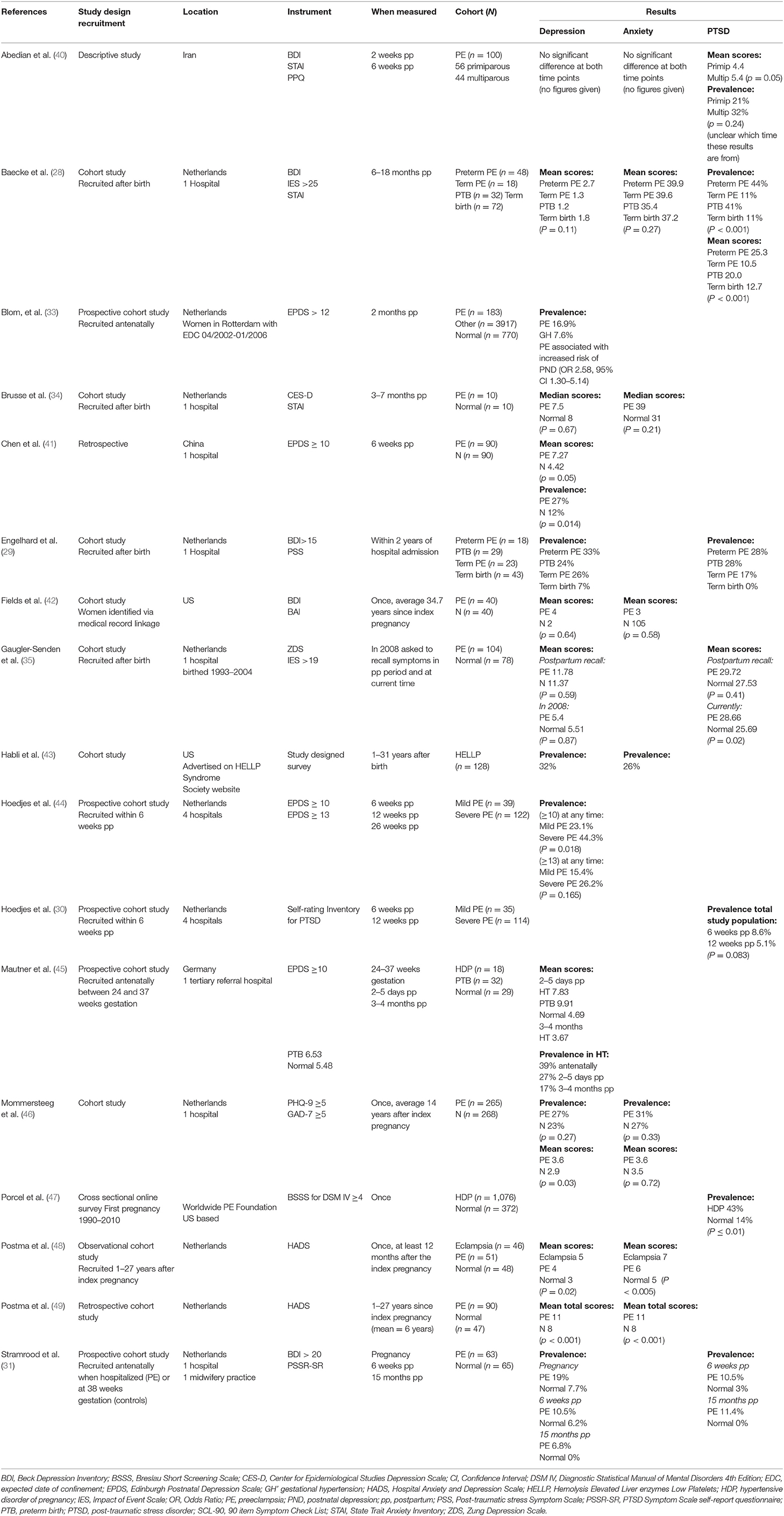
See Box 1 for a summary of each publication included in this review and Table 2 for a summary of the results.
Box 1. Summary of papers selected for review
Abedian et al. (40) was a descriptive study undertaken in Iran. Women diagnosed with PE (n = 100) were studied at 2 weeks and again at 6 weeks postpartum for depression, anxiety, and PTSD. The main focus of the paper was PTSD and the aim was to compare PTSD in primiparous (n = 56) and multiparous (n = 44) women.
Baecke et al. (28) was a cohort study undertaken in The Netherlands that included 170 women six-18 months postpartum, and measured depression, anxiety, and PTSD. Women with PE were included at term and preterm in addition to a normal comparison group who gave birth at term and preterm. The main focus of this study was cognitive function after PE.
Blom et al. (33) was a cohort study undertaken in The Netherlands that recruited 4,941 women over a 4 year period with various pregnancy complications; HDP contributing 254 to the cohort and 770 in the normal comparison group. Women were recruited in the antenatal period and depression was measured at 2 months postpartum.
Brusse et al. (34) was a small pilot study undertaken in The Netherlands that assessed 20 women three-7 months postpartum. Depression and anxiety were measured in 10 women with a history of severe PE and 10 women who had a history of an uncomplicated pregnancy formed the normal comparison group. The main focus of this study was cognitive function after PE.
Chen et al. (41) was a cohort study undertaken in China that examined depression at 6 week postpartum. The study cohort consisted of 90 women with a history of PE and 90 women, matched for the same time period of giving birth, who had normal blood pressure in pregnancy. The cohort was divided into two groups according to whether they screened positive for depression, and the analysis was performed comparing these two groups.
Englehard et al. (29) was a cohort study undertaken in The Netherlands that recruited 113 women within 2 years of hospital admission. Women with preterm and term PE were included and matched for gestational age with a normal comparison group. Depression and PTSD were measured. The women and their partners completed the screening instruments by post.
Fields et al. (42) used a medical data linkage to identify women for a long-term follow-up of cognitive impairment. Forty women who had a history of PE and 40 women with no such history were assessed 35–40 years following their pregnancy. Depression and anxiety formed part of the overall assessment but is reported separately.
Gaugler-Senden et al. (35) was a cohort study undertaken in The Netherlands that recruited 182 women who gave birth over an 11 year period. The cohort consisted of 104 women who had a history of preterm PE (<32 weeks gestation) and 78 women who had normal blood pressure in pregnancy, matched for gestational age at birth. Depression and PTSD was measured at two time points; women were asked to recall how they felt shortly after giving birth and the current time which was 7 years postpartum on average.
Habli et al. (43) was a retrospective cohort study undertaken in the US, using the US based HELLP Syndrome Support website to recruit 128 women. These women had experienced severe PE one to 31 years ago, with the mean follow-up being 5 years. Study designed surveys were completed via post, telephone or interview. Depression and anxiety prevalence was determined according to whether women reported being diagnosed by a physician with either of these mental health disorders.
Hoedjes et al. (44) was a cohort study undertaken in The Netherlands that recruited 174 women within 6 weeks after the birth. Depression was measured in women who experienced mild or severe PE at three time points: 6, 12, and 26 weeks postpartum. Comparisons were made between the two groups at each of the time points.
Hoedjes et al. (30) was a cohort study undertaken in The Netherlands, recruiting 149 women within 6 weeks after the birth. PTSD symptoms were measured in women who experienced mild or severe PE, at 6 and again at 12 weeks postpartum. Comparisons were made between the two groups at each of the time points.
Mautner et al. (45) was a cohort study undertaken in Germany that recruited 90 women with a complicated pregnancy, between 24 and 37 weeks gestation. Depression was measured during the pregnancy, 2-5 days and 3-4 months postpartum. The cohort consisted of women with HDP (n = 18), gestational diabetes (n = 11), preterm birth (32), and an uncomplicated pregnancy (n = 29). Comparisons were made between pregnancy groups at each of the time points.
Mommersteeg et al. (46) was a long term follow-up study conducted in The Netherlands examining depression and anxiety in women with a history of early onset PE (20–32 weeks gestation at onset), compared with a maternal aged matched non-PE comparison group. Questionnaires regarding depression and anxiety were completed, on average 14 years after the index pregnancy.
Porcel et al. (47) was a cross sectional online survey conducted via the worldwide Preeclampsia Foundation website. Women self-reported a diagnosis of HDP and were asked to invite friends and family who did not have a history of HDP to complete the survey, forming a normal comparison group. It was a large study with 1,076 women in the HDP group and 372 in the normal comparison group. The time between the index pregnancy and completion of the questionnaire is not stated.
Postma et al. (48) was an observational cohort study conducted in The Netherlands. It was a long-term follow-up of women already participating in a research project. There were 46 women with a history of eclampsia, 51 with a history of PE, and 48 women who had a normotensive pregnancy, matched for age. The average elapsed time since the index pregnancy was 7 years. The main focus of this study was neurocognitive function after PE and eclampsia, however depression and anxiety were assessed.
Postma et al. (49) was a retrospective cohort study undertaken in The Netherlands. Women with a history of eclampsia or PE were combined to form one group and the results were compared to women who were normotensive in their pregnancy. Although difficult to confirm, this study seems to have been an extension of the follow-up period in the above study. The cohort consisted of 41 women with prior eclampsia, 49 with a history of PE, and 47 women with no such history. The main focus of the study was cerebral white matter lesions and cognitive functioning following HDP, with depression and anxiety included in the assessment.
Stramrood et al. (31) was a prospective longitudinal cohort study undertaken in The Netherlands. The objective was to compare the prevalence and risk factors for PTSD in women with PE or preterm premature rupture of membranes (PPROM) compared to women with uncomplicated pregnancies. Women with PE were recruited in the antenatal period and depression and PTSD were measured at three time points: in pregnancy, 6 weeks and 15 months after the birth. The cohort consisted of women with PE or PPROM, and controls.
Depression
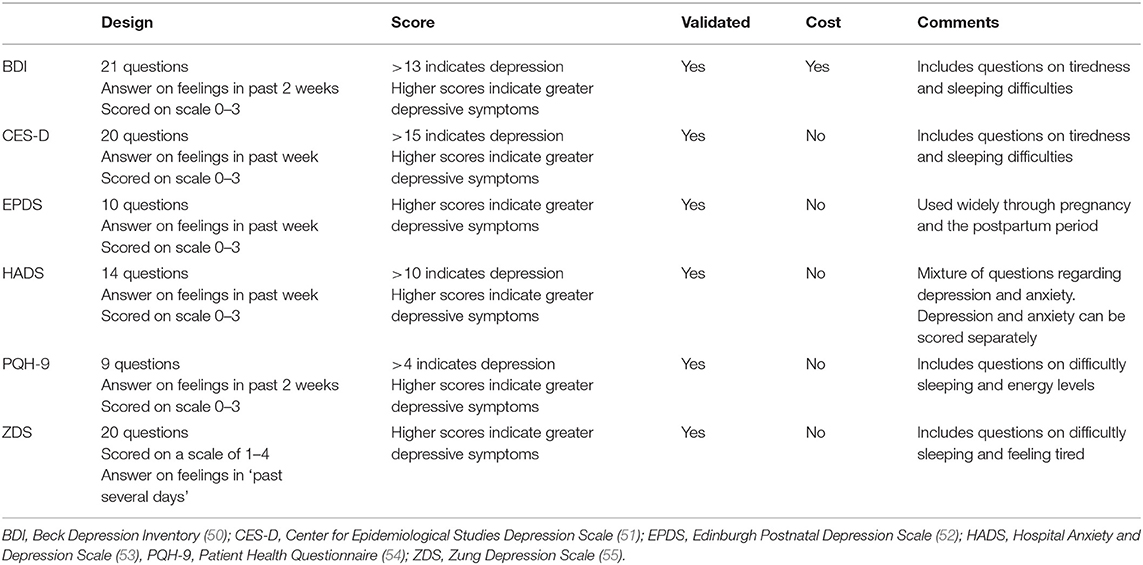
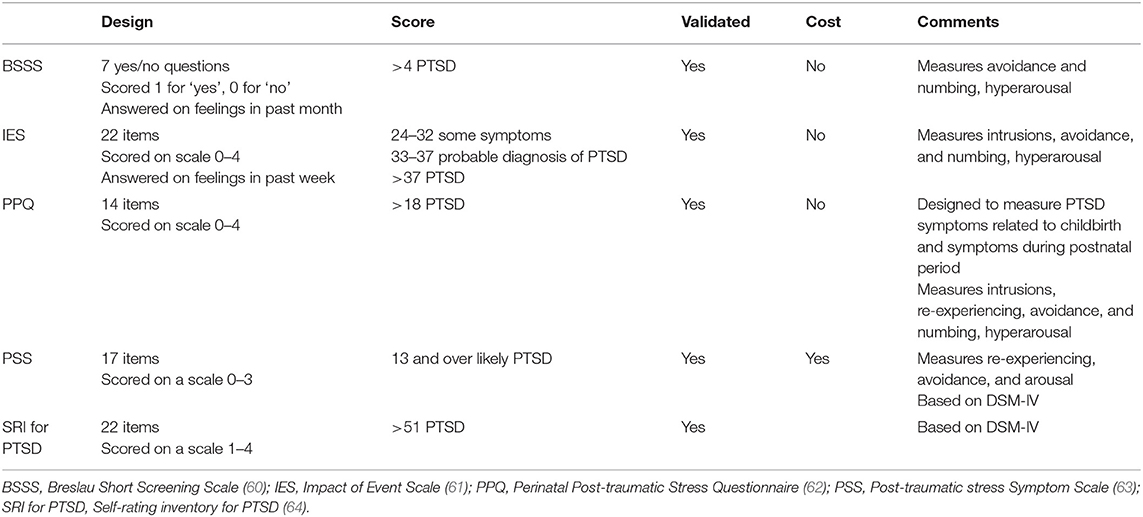
Fifteen publications examined the association between HDP and depression (28, 29, 31, 33–35, 40–46, 48, 49). Eight reported on the prevalence of depression and 10 reported on symptom severity, using mean or median scores of the screening instrument used. Fourteen of these studies were observational cohort studies, and the other a descriptive design. The studies were conducted in The Netherlands (n = 10), United States (US) (n = 2), and one each in Iran, China, and Germany. There were seven different screening instruments used, and all bar one have been validated for accuracy and validity (see Table 3 for the screening instruments used).
Prevalence of Depression
Reports of the prevalence of postpartum depression following HDP varied between 7 and 44% (29, 31, 33, 41, 43, 44, 46), which is up to four times higher than in the general postpartum population. This wide disparity in may be partly attributed to the inconsistencies in study design, particularly with regard to participant selection, severity of the hypertensive disorder, the screening instrument and the cut-off score used, and the timing of the evaluation.
When compared to women who did not have a history of HDP, a higher prevalence of depression was reported in women who experienced HDP (29, 31, 33, 45). It has been suggested that the psychological impact was influenced by the severity of the HDP, as characterized by gestational age at the onset, diagnosis of GH vs. PE, maternal complications, or adverse infant outcomes (29, 44). To investigate this more closely, Blom et al. (33) collected data from women following GH or PE separately and reported the prevalence of postpartum depression to be higher in the PE group compared with the GH group. Similarly, when data from women after mild or severe PE were analyzed separately, the prevalence of depression was higher in women with severe PE (33, 44). These results suggest that the prevalence of postpartum depression increases as the severity of the hypertensive disorder increases, however the results were not always statistically significant (44, 46).
A higher prevalence of depression was reported by women who gave birth preterm or term with PE when compared to women matched for gestation at birth with an otherwise uncomplicated pregnancy (29) suggesting that the PE contributed to the depression. In contrast, a Dutch study reported no difference in depression for women who gave birth preterm with or without PE (28), suggesting that maybe it was the consequences of a preterm birth rather than the HDP that was more strongly associated with depression.
When depression has been measured longitudinally at several postpartum time points following HDP, the prevalence was shown to decrease over time. A decrease from 27% at two-5 days postpartum to 17% at three-4 months postpartum was reported in one study (45) while a decrease from 10.5% at 6 weeks postpartum to 6.8% at 15 months postpartum was reported in another (31). However, there is no mention of any treatment that may have been undertaken during the period of the study, so it is unclear what contributed to the lessening depression.
Depression Symptom Severity
With regard to the severity of depressive symptoms, the evidence was mixed and inconclusive. Some studies report significantly higher mean scores on the screening instrument by women following HDP compared with women in the normal comparison group (41, 46, 48, 49). However, others report no significant difference in mean scores between women with or without prior HDP (28, 34, 35, 42), although there was a trend toward higher scores from women in the HDP group. Having a preterm birth, stillbirth, or neonatal death was significantly associated with higher depressive symptoms in one study (46) which reported on depression, on average, 14 years following the index pregnancy.
No significant differences in scores were reported comparing primiparous and multiparous women at 2 and 6 weeks postpartum following a pregnancy complicated with PE (40), although there were no details of the scores given. In another study, no significant difference in mean scores was found in four groups of women; preterm PE, term PE, preterm birth without HDP, and term birth without HDP (p = 0.11) (28). In a study examining depression following eclampsia and PE, statistically significant higher mean scores were reported by women who had experienced eclampsia compared to those women with a history of PE and those who were normotensive in pregnancy (p = 0.02) (48).
Mean scores between women with a history of preterm severe PE and preterm birth without PE at two time points postpartum reported no statistical difference in scores between the two groups (36), but notes that the mean scores improved with time (36). Women in this study were asked to recall and score symptoms from the immediate postpartum period for the first time point, with an average elapsed time of 7 years since the index pregnancy for the second time point.
Anxiety
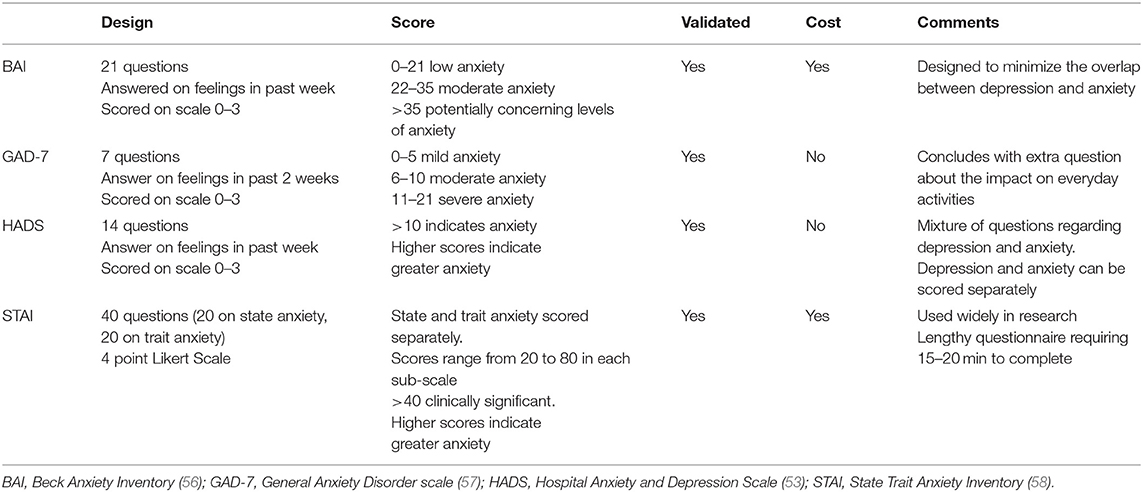
There were eight studies that investigated the association between HDP and anxiety (28, 34, 40, 42, 43, 46, 48, 49). Prevalence of anxiety was reported in six of these studies and symptom severity in seven using mean or median scores. Seven of the studies were observational cohort studies and one was a descriptive study. The studies originated from three different countries; The Netherlands (n = 5), US (n = 2), and Iran (n = 1). There were five different screening instruments used, and all except one have been validated for accuracy and validity (Table 4).
Prevalence of Anxiety
The prevalence of anxiety following HDP was reported between 26 and 32% in two publications (43, 46), which is slightly higher than the general postpartum population. Both of these studies were long term follow-up studies with assessment of anxiety undertaken up to 31 years postpartum.
There was no difference in the prevalence of mild anxiety in women who had experienced early onset PE compared to women without a history of PE (46), with a reported prevalence of 31 vs. 27%, respectively (p = 0.325). The average time elapsed since the index pregnancy in this study was 14 years. On further analysis, adjusting for age, education level, body mass index (BMI), having a partner, being unemployed, and physical activity, the results showed no difference in the prevalence of anxiety between the two groups.
The prevalence of anxiety in women who experienced HELLP syndrome was reported as 26% (43). In this study anxiety was measured by women within 1 month of the birth, self-reporting a diagnosis made by a physician and treated accordingly. The gestation at the time of birth was not important, with 27% of those who gave birth at 28 weeks gestation or less and 26% of those women giving birth after 28 weeks gestation, reporting a diagnosis of postpartum anxiety (p > 0.99).
Anxiety Symptom Severity
Seven studies reported on anxiety symptom severity using mean or median scores derived from a validated instrument (28, 34, 40, 42, 46, 48, 49). Higher scores were reported from women in the HDP group when compared with women in the normal comparison group, however the majority of studies did not reach statistical significance. The two studies that reported statistically significant higher anxiety scores in the PE group compared to the comparison group (48, 49) were small studies where women completed the questionnaire, on average, 6 years after their pregnancy. The main focus of both these studies was cognitive functioning after a pregnancy complicated with PE, and there was no reporting of any other factors or life events that may have affected the woman's anxiety.
No significant difference in anxiety scores was reported by primiparous compared with multiparous women at both the 2 and 6 week postpartum following a pregnancy complicated with PE (40), although there were no details of the scores given in the publication. No significant difference in mean scores was found in the four groups studied by Baecke et al. (28). These groups were women who experienced preterm PE, term PE, preterm birth without HDP, and term birth without HDP (p = 0.27). In a study examining anxiety following eclampsia and PE, statistically significant higher mean scores were reported by women who had experienced eclampsia compared to those women with a history of PE and those who were normotensive in pregnancy (p < 0.005) (48), suggesting that the more severe the HDP, the more severe the anxiety is.
Post-traumatic Stress Disorder
There were seven studies that investigated the association of PTSD with HDP (28–31, 35, 40, 59), with six reporting on prevalence and three reporting on symptom severity by using mean scores for the instruments used. There were five observational cohort studies, one descriptive study and one cross-sectional on-line survey. The studies were conducted in The Netherlands (n = 5), Iran (n = 1), and the remaining one was a world-wide survey led by researchers in the US. All studies used validated instruments to screen for PTSD and there were five different instruments used (Table 5).
Prevalence of PTSD
The prevalence of PTSD following HDP varied between 5.1 and 43% across the seven studies. When compared to women who did not have a history of HDP, a higher prevalence of PTSD was reported in women who experienced HDP in some of the studies (29, 31, 47). In the world wide survey via the PE Foundation website (47), 43% of women with a history of HDP screened positive for PTSD compared to 14% of women in the normal comparison group (p < 0.01). In this study, after adjusting for psychiatric treatment, parity, and age at the time of the pregnancy, women with a history of PE were more than four times as likely to screen positive for PTSD when compared to women with a normotensive pregnancy (OR = 4.46, 95% CI: 3.20–6.20).
The study by Stramrood et al. (31) measured PTSD at two postpartum time points (6 weeks and 15 months) and compared results between women in the PE and normotensive groups at each of these time points. There was a slight change in prevalence over time in both groups (10.5–11.4% in the PE group and 3–0% in the normotensive group), with the PE group consistently reporting a higher prevalence of PTSD. The other study to report PTSD prevalence at two time points (30), found no statistically significant difference in PTSD in women with a history of PE, at 6 and 12 weeks postpartum, with rates of 8.6 and 5.1%, respectively (p = 0.083).
Irrespective of the cause of the preterm birth, Baecke et al. (28) found that more women with a history of a preterm birth met the threshold score for PTSD than women who gave birth at term (preterm PE 44%, preterm birth 41%, term PE 11%, term uneventful 11%). This study suggests that the sequelae of a preterm birth led to PTSD, not the PE itself. In the Dutch study by Engelhard et al. (29), 28% of women who gave birth preterm, with or without PE, met the diagnostic criteria for PTSD, suggesting that the preterm birth rather than PE is the trigger. However, in this same study, the term PE group reported a PTSD prevalence of 17%, similar to that in preterm PTSD, while the normotensive term group women had no PTSD, suggesting that PE may have an impact at term.
A further study compared PTSD prevalence in multiparous and primiparous women with a history of PE (40). Although the reported PTSD prevalence was higher in the multiparous PE group, the result was not significant (32 vs. 21%, respectively p = 0.24) suggesting that parity is not a contributing factor.
PTSD Symptom Severity
There were three studies that reported on PTSD symptom severity following PE (28, 35, 40), all with different study designs and all using a validated instrument to score PTSD symptoms.
When mean scores were compared between primiparous and multiparous women following PE, the results were not statistically significant although the multiparous women scored slightly higher (mean score 4.4 for primiparous women and 5.4 for multiparous women p = 0.05) (40).
The mean PTSD scores for women with a history of preterm birth, irrespective of the cause, were higher than the term birth group, suggesting a preterm birth contributes to more symptom severity (28).
Another study (35) compared mean PTSD scores between women with a history of preterm severe PE and preterm birth without PE at two time points. There was no difference in mean scores between the groups at the postpartum recall time-point. However, there was a significant difference (p = 0.02) between the groups at the time of the study being undertaken which was, on average, 7 years after the index pregnancy, despite the mean score being slightly lower. There is no information about other life events that may have contributed to this difference.
Discussion
There is limited literature available to address the important issue of depression, anxiety, and PTSD following pregnancies complicated by hypertension with only 17 studies identified that looked specifically at this association. The current evidence suggests that women with a history of HDP have a greater likelihood of depression and PTSD, but the heterogeneity, different study populations and different methods of assessment preclude any definitive interpretation. There was no association found between HDP and the prevalence or severity of postpartum anxiety in the majority of studies included in this review. The current literature also suggests that the severity of the HDP may be positively correlated with the severity of depressive, anxiety and PTSD symptoms. However, it is not clear what the main driver for the psychological morbidity might be—the demands of PE, the associated events such as a preterm birth or if it predated the pregnancy. The focus of this review was on postpartum mental health conditions, hence pre-existing and/or antenatal mental conditions were not investigated.
The literature on the psychological impact of HDP was methodologically varied, including selection and recall bias and most study sample sizes were small. There was a variation in the study populations including gestation, severity of HDP and time since the index pregnancy. Furthermore, multiple instruments were used, along with different threshold cut-off scores to define abnormal results. These methodological limitations made it difficult to determine if there is a true association between HDP and depression, anxiety and PTSD.
A key feature with the studies included is that they originate from just five countries; 11 from The Netherlands, three from the US, and one each from China, Germany, and Iran. It may not be possible to accurately translate the results of these studies to other countries, due to the differences in culture, health care systems, and management of HDP and/or mental health disorders. The performance of the measuring instruments may also be affected by cultural practices, differences in access and availability of, obstetric and psychiatric care and differences in emotional support provided. Some researchers (65, 66) suggest that culture affects the response people make to psychiatric assessments due to the differences in their underlying attitudes, beliefs, and behavior. Beliefs of mental health distress, cultural understanding of mental health, and culturally or context specific terms can also lead to different scores on measuring instruments (67).
Previous reviews of women's mental health following HDP have made similar conclusions to those drawn here. A systematic review (32) reported on postpartum depression, anxiety, and PTSD following a pregnancy complicated with HDP. The authors conclude that the evidence regarding depression is mixed but overall suggests an association between PE/HELLP and depression, with higher depression prevalence and severity in the women with previous PE/HELLP compared to women without such history. In regards to anxiety, there were no significant associations between PE and anxiety scores although higher scores were reported among women with PE. PTSD was reported in this same review and although higher PTSD prevalence and severity was reported by women following PE/HELLP, results were not statistically significant. In another systematic review (27) investigating the possible association between PTSD and several pregnancy complications, including PE, the authors conclude that there may be some evidence to suggest a link between PE and PTSD but the evidence was not robust (27). However, they suggest that PTSD and its symptoms may present following particularly severe cases of maternal morbidity (not specifically HDP), that involve poor neonatal outcomes.
Conclusion
While there is no definitive evidence that having HDP leads to increased postpartum depression, anxiety, or PTSD, women who experience HDP may be at increased risk of developing these mental health disorders. This is particularly true for those women who experience the more severe forms of HDP and/or give birth preterm. Routine screening for all these mental health disorders on all women in the postpartum period may be beneficial, however there is an increased need for screening to be undertaken in women who experience HDP. Screening this group of high risk women will alert clinicians to the need for additional follow-up and referral. More research on the benefits and risks of such an approach is needed.
Author Contributions
LR, GD, and CH contributed to the conception and design of the review. LR led the review of the literature, the analysis, and wrote the first draft including drafting the tables and figure. All authors contributed to manuscripts drafts and revisions, and all approved the final submitted version.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
1. Fairbrother N, Young A, Zhang A, Janssen P, Antony M. The prevalence and incidence of perinatal anxiety disorders among women experiencing a medically complicated pregnancy. Arch Women Ment Health. (2016) 20:311–9. doi: 10.1007/s00737-016-0704-7
2. World Health Organisation. Maternal Mental Health. (2019). Available online at: https://www.who.int/mental_health/maternal-child/maternal_mental_health/en/ (accession August 19, 2019).
3. Austin M, Hadzi-Pavlovic D, Priest S, Reilly N, Wilhelm K, Saint K, et al. Depressive and anxiety disorders in the postpartum period: how prevalent are they and can we improve their detection? Arch Women Ment Health. (2010) 13:395–401. doi: 10.1007/s00737-010-0153-7
4. Ayers S, Pickering A. Do women get posttraumatic stress disorder as a result of childbirth? A prospective study of incidence. Birth. (2011) 28:111–8. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-536X.2001.00111.x
5. Simpson M, Catling C. Understanding psychological traumatic birth experiences: a literature review. Women Birth. (2016) 29:203–7. doi: 10.1016/j.wombi.2015.10.009
6. Furuta M, Sandall J, Cooper D, Bick D. The relationship between maternal morbidity and psychological health symptoms at 6–8 weeks postpartum: a prospective cohort study in one English maternity unit. BMC Pregnancy Childb. (2014) 14:133. doi: 10.1186/1471-2393-14-133
7. Alcorn K, O'Donovan A, Patrick J, Creedy D, Devilly G. A prospective longitudinal study of the prevalence of post-traumatic stress disorder resulting from childbirth events. Psychol Med. (2010) 40:1849–59. doi: 10.1017/S0033291709992224
9. Tranquilli A, Dekker G, Magee L, Roberts J, Sibai B, Steyn W, et al. The classification, diagnosis and management of the hypertensive disorders of pregnancy: a revised statement from the ISSHP. Pregnancy Hypertens. (2014) 4:97–104. doi: 10.1016/j.preghy.2014.02.001
10. Gillon T, Pels A, von Dadelszen P, MacDonell K, Magee L. Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy: a systematic review of international clinical practice guidelines. PLoS ONE. (2014) 9:e113715. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113715
11. Brown M, Magee L, Kenny L, Ananth Karumanchi S, McCarthy F, Saito S, et al. The hypertensive disorders of pregnancy: ISSHP classification, diagnosis and management recommendations for international practice. Pregnancy Hypertens. (2018) 72:24–43. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.117.10803
12. Lowe S, Bowyer L, Lust K, McMahon L, Morton M, North R, et al. The SOMANZ guidelines for the management of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy 2014. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. (2015) 55:11–6. doi: 10.1111/ajo.12253
13. Buchbinder A, Sibai B, Caritis S, Macpherson C, Hauth J, Lindheimer M, et al. Adverse perinatal outcomes are significantly higher in severe gestational hypertension than in mild preeclampsia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. (2002) 186:66–71. doi: 10.1067/mob.2002.120080
14. Lowe S, Brown M, Dekker G, Gatt S, McLintoc K, MaMahon L, et al. Guidelines for the Management of Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy. Australia and New Zealand J Obstet Gynecol. (2009) 49:242–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1479-828X.2009.01003.x
15. Bushnell C, Chireau M. Preeclampsia and stroke: risks during and after pregnancy. Stroke Res Treatment. (2011) 2011:1–9. doi: 10.4061/2011/858134
16. Carpenter MW. Gestational diabetes, pregnancy hypertension, and late vascular disease. Diabetes Care. (2007) 30:S246–50. doi: 10.2337/dc07-s224
17. Cassidy-Bushrow AE, Bielak LF, Rule AD, Sheedy PF, Turner ST, Garovic VD, et al. Hypertension during pregnancy is associated with coronary artery calcium independent of renal function. J Women Health. (2009) 18:1709–16. doi: 10.1089/jwh.2008.1285
18. Chen C, Jaffe I, Karamunchi S. Pre-eclampsia and cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc Res. (2014) 101:579–86. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvu018
19. Gamble D, Brikinns B, Myint P, Bhattacharya S. Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and subsequent cardiovascular disease: current national and international guidelines and the need for future research. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2019) 6:55. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2019.00055
20. Brockington I, Butterworth R, Glangeaud-Freudenthal N. An international position paper on mother-infant (perinatal) mental health, with guidelines for clinical practice Arch Women Mental health. (2016) 20:113–20. doi: 10.1007/s00737-016-0684-7
21. Beck C. Predictors of postpartum depression: an update. Nurs Res. (2001) 50:275–85. doi: 10.1097/00006199-200109000-00004
22. Austin M-P, Highet N, The Expert Advisory Committee. Mental Health Care in the Perinatal Period: Australian Clinical Practice Guideline. Melbourne: Centre of Perinatal Excellence (2017).
23. Community Mental Health Strategy 2007–2012: From Prevention and Early Intervention to Recovery. Gladesville, NSW: Better Health Centre – Publications Warehouse. Available online at: https://www.health.nsw.gov.au/mentalhealth/resources/Publications/mental-health-strategy.pdf
24. NHS England Public Health Englan Health Education England Monitor Care Quality Commission NHS Trust Development Authority Five Year Forward View. Available online at: http://www.england.nhs.uk/wp-content/uploads/2014/10/5yfv-web.pdf
25. World Health Organisation. Improving Maternal Mental Health. Geneva: World Health Organisation (2008).
26. Dudovskiy J. The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Dissertation in Business Studies: A Step-by-Step Assistance (2018).
27. Furuta M, Sandall J, Bick D. A systematic review of the relationship between severe maternal morbidity and post-traumatic stress disorder. BMC Pregnancy Childb. (2012) 12:125. doi: 10.1186/1471-2393-12-125
28. Baecke M, Spaanderman ME, Van Der Werf SP. Cognitive function after pre-eclampsia: an explorative study. J Psychosom Obstet Gynecol. (2009) 30:58–64. doi: 10.1080/01674820802546212
29. Engelhard I, van Rij M, Boullart I, Ekhart T, Spaanderman M, van den Hout M, et al. Posttraumatic stress disorder after pre-eclampsia: an exploratory study. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. (2002) 24:260–4. doi: 10.1016/S0163-8343(02)00189-5
30. Hoedjes M, Berks D, Vogel I, Franx A, Visser W, Duvekot J, et al. Symptoms of post-traumatic stress after preeclampsia. J Psychosom Obstet Gynecol. (2011) 32:126–34. doi: 10.3109/0167482X.2011.599460
31. Stramrood C, Wessel I, Doornbos B, Aarnoudse J, Van Den Berg P, Schultz W, et al. Posttraumatic stress disorder following preeclampsia and PPROM: a prospective study with 15 months follow-up. Reprod Sci. (2011) 18:645–53. doi: 10.1177/1933719110395402
32. Delahaije D, Dirksen C, Peeters L, Smits L. Anxiety and depression following preeclmpsia or hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets syndrome. A sytematic review. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. (2013) 92:746–61. doi: 10.1111/aogs.12175
33. Blom EA, Jansen PW, Verhulst FC, Hofman A, Raat H, Jaddoe VW, et al. Perinatal complications increase the risk of postpartum depression. The generation R study. Br J Obstet Gynecol. (2010) 117:1390–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2010.02660.x
34. Brusse I, Duvekot J, Jongerling J, Steegers E, De Koning I. Impaired maternal cognitive functioning after pregnancies complicated by severe pre-eclampsia: a pilot case-control study. Acta Obstet Gynecol. (2008) 87:408–12. doi: 10.1080/00016340801915127
35. Gaugler-Senden I, Duivenvoorden H, Filius A, De Groot C, Steegers E, Passchier J. Maternal psychological outcome after early onset preeclampsia and preterm birth. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. (2012) 25:272–6. doi: 10.3109/14767058.2011.573829
36. Public Health Resource Unit (2006). The Critical Skills Appraisal Programme: Making Sense of Evidence. Public Health Resource Unit, England. Retrieved from: http://www.casp-uk.net/
37. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Diagnosis and management of preeclampsia and eclampsia. Int J Gynecol Obstet. (2002) 77:67–75. doi: 10.1016/S0020-7292(02)80002-9
38. Duetsche Gesellschaft fur Gynakologie und Geburtshilfe (DGGG). Diagnostik und Therapie hypertensiver Schwangerschaftserkrankungen Leitinien Empfehlungen, Stellungnahmen. Association of the Scientific Medical Societies in Germany (2007). p. 1–36.
39. National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group. Report of the national high blood pressure education program working group on high blood pressure in pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. (2000) 183:S1–22. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9378(00)40820-3
40. Abedian Z, Soltani N, Mokhber N, Esmaily H. Depression and anxiety in pregnancy and postpartum in women with mild and severe preeclampsia. Iran J Nurs Midwif Res. (2015) 20:454–9. doi: 10.4103/1735-9066.161013
41. Chen L, Wang X, Ding Q, Shan N, Qi H. Development of postpartum depression in pregnant women with preelampsia: a retrospective study. Biomed Res Int. (2019) 2019:1–7. doi: 10.1155/2019/9601476
42. Fields J, Garovic V, Mielke M, Kantarci K, Jayachandran M, White W, et al. Preeclampsia and cognitive impairment later in life. Am J Obstet Gynecol. (2017) 217:e1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2017.03.008
43. Habli M, Eftekhari N, Wiebracht E, Bombrys A, Khabbaz M, How H, et al. Long-term maternal and subsequent pregnancy outcomes 5 years after hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets (HELLP) syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol. (2009) 201:385.e1–5. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2009.06.033
44. Hoedjes M, Berks D, Vogel I, Franx A, Bangma M, Darlington A, et al. Postpartum depression after mild and severe preeclampsia. J Women Health. (2011) 20:1535–42. doi: 10.1089/jwh.2010.2584
45. Mautner E, Greimel E, Trutnovsky G, Daghofer F, Egger J, Lang U. Quality of life outcomes in pregnancy and postpartum complicated by hypertensive disorders, gestational diabetes, and preterm birth. J Psychosom Obstet Gynecol. (2009) 30:231–7. doi: 10.3109/01674820903254757
46. Mommersteeg P, Drost J, Ottervanger J, Maas A. Long-term followup of psychosocial distress after early onset preeclampsia: the Preeclampsia Risk EValuation in FEMales cohort study. J Psychosom Obstet Gynecol. (2016) 37:101–9. doi: 10.3109/0167482X.2016.1168396
47. Porcel J, Feigal, Poye L, Postma I, Zeeman G, Olowoyeye A, et al. Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and risk of screening positive for posttraumatic stress disorder: a cross sectional study. Pregnancy Hypertens. (2013) 3:254–60. doi: 10.1016/j.preghy.2013.07.004
48. Postma I, Bouma A, Ankersmit F, Zeeman GG. Neurocognitive functioning following preeclampsia and eclampsia: a long-term follow-up study. Am J Obstet Gynecol. (2014) 211:e1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2014.01.042
49. Postma I, Bouma A, de Groot J, Aukes A, Aarnoudse J, Zeeman G. Cerebral white matter lesions, subjective cognitive failures and objective neurocognitive functioning: a follow-up study in women after hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. (2016) 38:585–98. doi: 10.1080/13803395.2016.1143453
50. Beck A, Steer R, Carbin M. Psychometric properties of the beck depression inventory: twenty-five years of evaluation. Clin Psychol Rev. (1988) 8:77–100. doi: 10.1016/0272-7358(88)90050-5
51. Radloff L. The CES-D scale: a self report depression scale for research in the general population. Appl Psychol Measurem. (1977) 1:385–401. doi: 10.1177/014662167700100306
52. Cox JL, Holden J, Sagovsky R. Detection of postnatal depression. Development of the ten point Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale. Br J Psychiatry. (1987) 150:782–6. doi: 10.1192/bjp.150.6.782
53. Zigmond A, Snaith R. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatr Scand. (1983) 67:361–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1983.tb09716.x
54. Kroenke K, Spitzer R, Williams W. The PHQ-9; validity of a brief depression severity measure. J Gen Intern Med. (2001) 16:606–16. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1497.2001.016009606.x
55. Zung W. A self-rating depression scale. Arch Gen Psychiatry. (1965) 12:63–70. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1965.01720310065008
56. Beck A, Epstein N, Brown G, Steer R. An inventory for measuring clinical anxiety: psychometric properties. J Consult Clin Psychol. (1988) 56:893–7. doi: 10.1037/0022-006X.56.6.893
57. Spitzer R, Kroenke K, Williams J, Lowe B. A brief measure for assessing generalised anxiety disorder: the GAD-7. Arch Intern Med. (2006) 166:1092–7. doi: 10.1001/archinte.166.10.1092
58. Spielberger C, Sydeman S. State-trait anxiety inventory and state-trait anger expression inventory. In: Maruish ME editor. The Use of Psychological Testing for Treatment Planning and Outcome Assessment, Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Inc. (1994). p. 292–321.
59. Porcel J, Tsigas E, Poye L, Wilson M. Pregnancies involving hypertensive disorders of pregnancy are associated with posttraumatic stress disorder. Pregnancy Hypertens. (2012) 2:237–8. doi: 10.1016/j.preghy.2012.04.108
60. Breslau N, Peterson E, Kessler R, Schultz L. Short screening scale for DSM-IV PTSD. Am J Psychiatry. (1999) 156:908–11. doi: 10.1176/ajp.156.6.908
61. Horowitz M, Wilner N, Alvare W. Impact of event scale: a measure of subjective stress. Psychosom Med. (1979) 41:209–18. doi: 10.1097/00006842-197905000-00004
62. Callahan J, Borja S. Psychological outcomes and measurement of maternal posttraumatic stress disorder during the perinatal period. J Perinatal Neonatal Nurs. (2008) 22:49–59. doi: 10.1097/01.JPN.0000311875.38452.26
63. Foa E, Riggs D, Dancu C, Rothbaum B. Reliability and validity of a brief istrument for assessing posttraumatic stress disorder. J Trauma Stress. (1993) 6:459–73. doi: 10.1002/jts.2490060405
64. Hovens J, van der Ploeg H, Bramsen I, Klaarenbeek M, Schreuder N, Rivero V. The development of the self-rating inventory for posttraumatic stress disorder. Acta Psychiatr Scand. (1994) 90:172–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1994.tb01574.x
65. Guamaccia P. The role of culture on psychiatric epidemiology: an examination of research on Latin American mental health. Sante Ment Que. (1991) 16:27–43. doi: 10.7202/032202ar
66. Sabone M. The promotion of mental health through cultural values, institutions, and practices: a reflection on some aspects of Botswana culture. Issues Ment Health Nurs. (2009) 30:777–87. doi: 10.3109/01612840903263579
Keywords: depression, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder, postpartum, hypertensive disorder of pregnancy, gestational hypertension, preeclampsia
Citation: Roberts L, Davis GK and Homer CSE (2019) Depression, Anxiety, and Post-traumatic Stress Disorder Following a Hypertensive Disorder of Pregnancy: A Narrative Literature Review. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 6:147. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2019.00147
Received: 08 August 2019; Accepted: 24 September 2019;
Published: 09 October 2019.
Edited by:
Dexter Canoy, University of Oxford, United KingdomReviewed by:
Piyali Chatterjee, Central Texas Veterans Health Care System, United StatesNikolina Basic-Jukic, University Hospital Centre Zagreb, Croatia
Copyright © 2019 Roberts, Davis and Homer. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lynne Roberts, lynne.roberts2@health.nsw.gov.au
 Lynne Roberts
Lynne Roberts Greg K. Davis1,2,3
Greg K. Davis1,2,3 Caroline S. E. Homer
Caroline S. E. Homer