- 1Department of Medical Biology, Amsterdam University Medical Centers, Amsterdam, Netherlands
- 2Department of Experimental Cardiology, Amsterdam University Medical Centers, Amsterdam, Netherlands
Congenital long-QT syndrome (LQTS) is an inherited cardiac disorder characterized by the prolongation of ventricular repolarization, susceptibility to Torsades de Pointes (TdP), and a risk for sudden death. Various types of congenital LQTS exist, all due to specific defects in ion channel-related genes. Interestingly, almost all of the ion channels affected by the various types of LQTS gene mutations are also expressed in the human sinoatrial node (SAN). It is therefore not surprising that LQTS is frequently associated with a change in basal heart rate (HR). However, current data on how the LQTS-associated ion channel defects result in impaired human SAN pacemaker activity are limited. In this mini-review, we provide an overview of known LQTS mutations with effects on HR and the underlying changes in expression and kinetics of ion channels. Sinus bradycardia has been reported in relation to a large number of LQTS mutations. However, the occurrence of both QT prolongation and sinus bradycardia on a family basis is almost completely limited to LQTS types 3 and 4 (LQT3 and Ankyrin-B syndrome, respectively). Furthermore, a clear causative role of this sinus bradycardia in cardiac events seems reserved to mutations underlying LQT3.
Introduction
Congenital long-QT syndrome (LQTS) is an inherited cardiac disorder characterized by the prolongation of ventricular repolarization, susceptibility to Torsades de Pointes (TdP), and a risk for sudden death (1). Various types of congenital LQTS exist, but the most common forms of LQTS, accounting for ≈90% of genotype-positive LQTS cases (2), are LQT1, LQT2, and LQT3, caused by mutations in the genes encoding the pore-forming α-subunits of the ion channels carrying the slow delayed rectifier K+ current (IKs), rapid delayed rectifier K+ current (IKr), and fast Na+ current (INa), respectively [for reviews, see (3, 4) and, more recent, (5, 6)]. The incidence and occurrence of phenotype is modulated by a large number of conditional factors (4), including heart rate (HR) (7). For example, LQT1 patients are found to be at greatest risk for cardiac events during conditions of elevated HR, while slower HR provokes cardiac events in LQT2 and LQT3 patients (7). Modulation of HR by exercise may also be a diagnostic criterion in LQTS (8), and treatment/prevention of cardiac events in LQTS is frequently accomplished by HR control (7, 9).
Interestingly, almost all of the ion channels affected by the various types of LQTS gene mutations are also expressed in the human sinoatrial node (SAN) (10). It is therefore not surprising that LQTS is frequently associated with a change in basal HR due to impaired SAN pacemaker activity (11). For example, bradycardia is frequently observed in LQT1 mutation carriers, especially in the fetal-neonatal period (12, 13). It has even been concluded that sinus bradycardia in the cardiotocogram may indicate LQTS in the fetus (14) and that fetal bradycardia is an important predictor of LQTS (15). Also, basal HR was found to be significantly slower in patients with LQT1 compared with non-carriers (16). Maximum HR during exercise may also be reduced in LQTS [see (8, 11), and primary references cited therein]. Thus, LQTS may have a direct impact on HR (17), but this is not a consistent finding (18, 19). One may argue that this is because effects on HR differ between types of LQTS and between specific mutations. However, even within a single mutation different effects on HR are described. For example, the A341V mutation in KCNQ1 may result in sinus bradycardia (13), but may also occur in absence of baseline HR changes compared to non-carriers (19).
Because LQTS-related rhythm disorders can be triggered by slow or high HR and sinus pauses (4, 11), detailed knowledge of the relation between LQTS and SAN function is required. In this mini-review, we provide an overview of known LQTS mutations with effects on HR and the underlying changes in expression and kinetics of mutant channels.
LQTS Gene Mutations and Changes in Basal Heart Rate
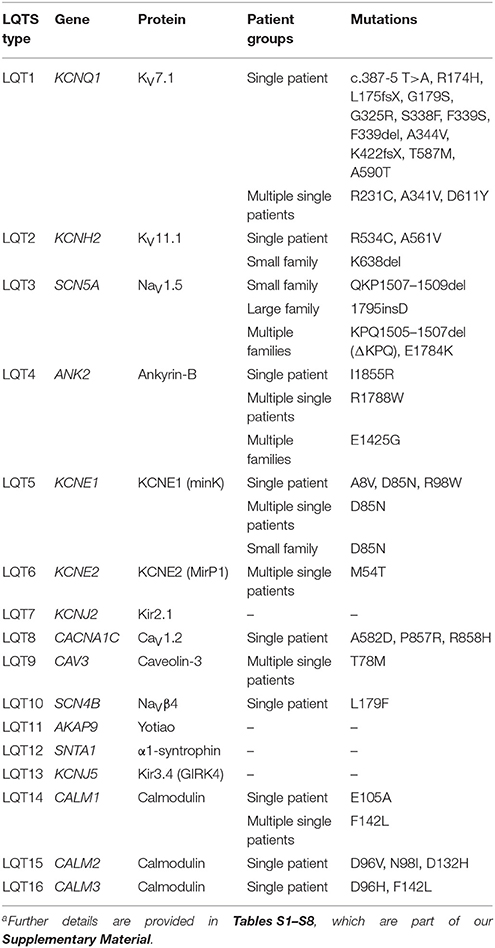
In Tables S1–S8, which are part of our Supplementary Material, we provide a detailed overview of the various autosomal dominant LQTS mutations known to date that are associated with sinus bradycardia, together with data on the mutation-induced changes in expression and kinetics of the respective ion channels. Below, we provide a brief overview of the various types of congenital LQTS and the extent to which each type is associated with sinus bradycardia. This overview is accompanied by Table 1, which summarizes the data of Tables S1–S8.
LQT1
LQT1 is due to loss-of-function mutations in KCNQ1, the gene encoding the pore-forming α-subunit of the IKs channel (KV7.1). A decrease in IKs will result in a prolongation of the ventricular action potential (AP) and a prolongation of the QT interval on the ECG (20). Of note, four KV7.1 α-subunits assemble in a tetramer to create the pore of an IKs channel. Therefore, a mutation in KCNQ1 may affect a large majority of the IKs channels as wild-type and mutant subunits co-assemble in heterotetramers.
Many KCNQ1 mutations exist and some are associated with sinus bradycardia (Table 1). These bradycardia-associated mutations result in “loss-of-function” by a reduced level of channel expression, expression of non-functional channels, activation at more positive membrane potentials, faster deactivation kinetics, and/or inhibited cAMP-dependent stimulation. For example, the A341V mutation strongly suppresses the increase in IKs in response to cAMP (21), which may also explain the more pronounced phenotype during exercise. Sinus bradycardia in LQT1 patients seems limited to isolated, often neonate cases (Table S1).
It is somewhat difficult to envision how a loss of repolarizing IKs per se would lead to a profound increase in the cycle length of SAN cells, thus generating sinus bradycardia. Such loss would lengthen AP duration (APD), but at the same time shorten the considerably longer (22) diastolic phase by increasing the rate of diastolic depolarization. An increase in repolarizing IKs, on the other hand, as observed in short QT syndrome type 2 (SQT2), will inhibit diastolic depolarization and substantially increase cycle length, despite an accompanying decrease in APD, as observed in simulations by Fabbri et al. (23) using their recently developed comprehensive computer model of a single human SAN pacemaker cell. Clinically, sinus bradycardia is indeed relatively common in SQT2 patients [see, e.g., (24)].
LQT2
LQT2 is due to loss-of-function mutations in KCNH2, the gene encoding the pore-forming α-subunit of the IKr channel (KV11.1). Observation of sinus bradycardia in LQT2 patients seems rare (25, 26) and limited to a few isolated cases and a small family (Table 1). Bradycardia does occur in the fetal-neonatal period, but is due to 2:1 atrioventricular block rather than sinus bradycardia (12). Such cases are not included in Table 1. In contrast, Horigome et al. (13) reported that the incidence of sinus bradycardia was comparable between groups of young (<1 year, mostly fetal-neonatal) LQT1, LQT2, and LQT3 patients. However, whether the LQTS observation is due to the bradycardia or the bradycardia results from the mutations (4, 11) is less clear. Bradycardia-associated mutations in KCNH2, so far characterized, result in a decrease in current density, non-functional channels, a shift in voltage of half-activation, and faster deactivation and inactivation rates (Table S2).
The above consideration regarding the potential association between sinus bradycardia and the increase in repolarizing IKs in case of SQT2 similarly holds for the increase in repolarizing IKr in case of short QT syndrome type 1 (SQT1). Sinus bradycardia is indeed observed in SQT1 patients, although being less common than in SQT2 patients (27).
LQT3
LQT3 is due to gain-of-function mutations in SCN5A, the gene encoding the pore-forming α-subunit of the INa channel (NaV1.5). Unlike LQT1 and LQT2, the occurrence of sinus bradycardia is not limited to isolated cases. Several families, including the large Dutch family with the 1795insD founder mutation (28), show both QT prolongation and sinus bradycardia (Table 1). A common feature is the increased late current, also named persistent or sustained current, underlying the QT prolongation. Another common feature is the decrease in “window current” due to a positive shift in the steady-state activation curve and/or a negative shift in the steady-state inactivation curve (Table S3).
Figures 1A–D illustrate the effects of the 1795insD mutation, based on data from recent computer simulations (29), as set out in the Supplementary Material. The observed increase in cycle length (Figure 1A) is largely due to a decrease in net inward current (Inet) during diastole (Figure 1B), which in turn is due to a striking change in the time course of INa (Figure 1C). Where IKs and IKr channels are tetramers, the pore of the INa channel is formed by a single NaV1.5 protein. As a consequence, “mutant INa” (Figure 1D, dotted red trace) is partly flowing through pure wild-type channels (solid green trace) and partly through pure mutant channels (solid orange trace). There is hardly any current flowing through these mutant channels during diastole due to the decrease in window current. There is, on the other hand, some late current flowing during the AP, albeit with a negligible effect on APD, in contrast to ventricular myocytes, in which the current density of INa is much larger. These effects are more pronounced during vagal activity (Figures 1E–H). The slight decrease in diastolic depolarization rate and increase in cycle length as a result of the inhibition of INa (Figures 1A,E) are in line with experimental observations on isolated rabbit SAN cells (30).
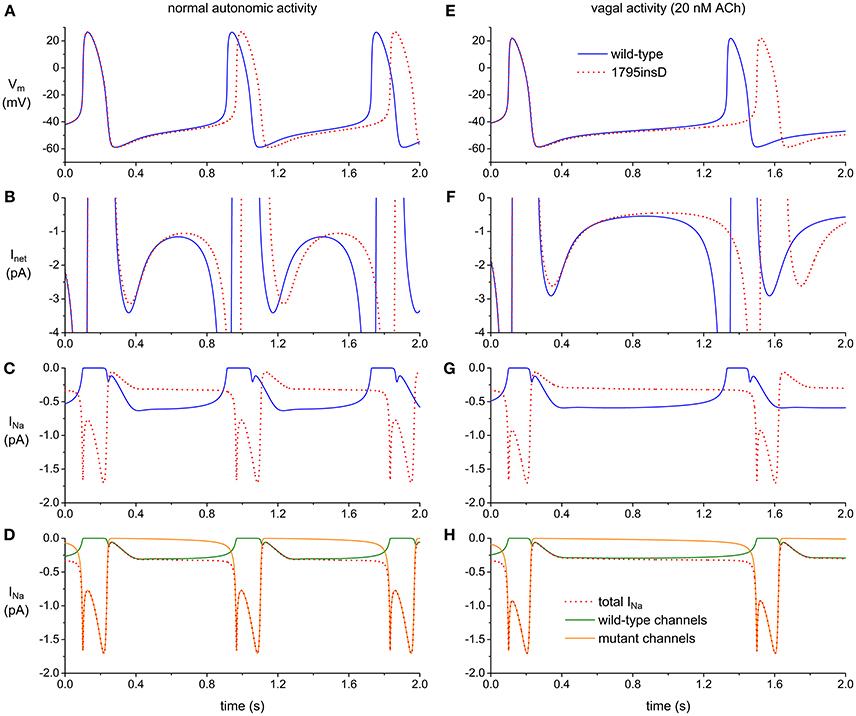
Figure 1. Effect of the 1795insD mutation in SCN5A on the electrical activity of the Fabbri–Severi model cell of a human SAN pacemaker cell (A–D) under control conditions (normal autonomic activity) and (E–H) during vagal activity [based on data from recent computer simulations (29)]. (A,E) Membrane potential (Vm) of wild-type and mutant cell (solid blue and dotted red trace, respectively). (B,F) Associated net membrane current (Inet). (C,G) Associated fast Na+ current (INa). (D,H) Contribution of wild-type and mutant channels (solid green and orange trace, respectively) to INa of the mutant cell (dotted red trace).
The increase in late current (“gain-of-function”) is a prerequisite for QT prolongation, but not for sinus bradycardia. A sole decrease in window current (“loss-of-function”), as for example observed in case of the R376C and D1275N mutations in SCN5A (31, 32), is sufficient to cause sinus bradycardia.
LQT4
Ankyrin-B syndrome, originally named LQT4, is due to heterozygous loss-of-function mutations in ANK2, encoding the widely distributed ankyrin-B adaptor protein. Loss of ankyrin-B results in Ca2+ homeostasis dysfunction by reduced Na+-Ca2+ exchange current (INCX), L-type Ca2+ current (ICa,L), Na+-K+-ATPase, and IP3 receptor expression (Table S4). Mutations in ANK2 associated with both QTc prolongation and sinus bradycardia are observed in both large families and single patients (Table 1).
LQT5
LQT5 is due to loss-of-function mutations in KCNE1. The encoded protein, named KCNE1 or minK, is a β-subunit that may affect both IKs and IKr function. Reports of bradycardia in LQT5 patients are scarce (Table 1). The observations made to date show reduced IKs or IKr density or a shift of IKs activation to more positive potentials (Table S5). Interestingly, the A8V mutation affects IKs but not IKr, whereas the R98W mutation affects IKr but not IKs.
LQT6
LQT6 is due to loss-of-function mutations in KCNE2. The encoded protein, named KCNE2 or MirP1, is a β-subunit that may affect various ion currents. Mutations in KCNE2 may result in an accelerated inactivation time course of IKr (33, 34), but also in an increase of ICa,L (35), and a reduction of the hyperpolarization-activated current (If) (36), the latter important for pacemaker activity in human SAN cells (22). Despite its multiple ion current modulations, KCNE2 mutations associated with sinus bradycardia are limited to M54T and V65M. In case of the M54T mutation, both IKr and If are inhibited (Table S6). It is conceivable that the V65M mutation also acts through If, given the well-established effect of KCNE2 on If (37).
LQT7
Andersen-Tawil syndrome (“LQT7”) is a multisystem disorder due to loss-of-function mutations in KCNJ2, the gene encoding the Kir2.1 protein, which assembles in tetramers to build the channels that carry the inward rectifier K+ current (IK1) (38). Given the low expression of Kir2.1 in human SAN (10), it is not surprising that HR seems not affected in Andersen-Tawil syndrome patients (39).
LQT8
Timothy syndrome (TS) is a severe multisystem disorder due to gain-of-function mutations in CACNA1C, encoding the pore-forming α-subunit of the ICa,L channel (CaV1.2), and results in bradycardia in almost all patients known, but caused by 2:1 atrioventricular block rather than sinus bradycardia (see footnote to Table S7). Although TS is also known as LQT8, because of the extreme QT prolongation in TS patients (40, 41), we restricted the LQT8 data in Table S7 to non-TS patients. In isolated cases, these show sinus bradycardia (Table 1). Mutant ICa,L shows an increase in density or slowing of inactivation (Table S7).
LQT9
LQT9 is due to mutations in CAV3, encoding caveolin-3, an important structural component of caveolae membrane in muscle cells (42). CAV3 mutations in heart have been shown to increase the late INa, thus causing QT prolongation as in LQT3 (43, 44). More recently, it has been shown that mutations in CAV3 may affect several other membrane currents (see footnote to Table S8). Sinus bradycardia has been observed in two patients carrying the T78M mutation (Table 1).
LQT10
LQT10 is due to gain-of-function mutations in SCN4B, encoding the NaVβ4 β-subunit of the INa channel. A case report exists for an SCN4B-L179F mutation with impact on SAN function (Table 1). In a 21-month-old girl, profound QT prolongation and bradycardia (<60 bpm) were observed (45). The SCN4B-L179F mutation increases late INa (Table S8) and may thus have effects comparable to LQT3 mutations.
LQT11–LQT16 and Beyond
To the best of our knowledge, no sinus bradycardia has been reported in relation to the rare LQTS types LQT11–LQT13 (see footnote to Table S8). Genetic variation in KCNJ3 and KCNJ5, encoding the pore-forming Kir3.1 and Kir3.4 ion channel subunits of the acetylcholine-sensitive K+ current (IK,ACh), and which the latter may underlie LQT13, seems not involved in pathogenesis of SAN dysfunction (46). However, it is suggested that identification of susceptibility genes for SAN dysfunction requires the construction of a large database of patients and controls whose phenotype should be identified with standard criteria to ensure adequate power for cause-effect studies (47). Thus, the incidence of some LQTS types may be too low to determine clear associations with bradycardia.
Several reports exist of mutations in the CALM1–CALM3 genes, each encoding the ubiquitous Ca2+ sensing protein calmodulin, in relation to LQTS and sinus bradycardia (Table 1 and Table S8). Calmodulin regulates multiple Ca2+-related processes in the cardiomyocyte (48), including, e.g., gating of the IKs channel (49). Mutations in CALM1 and CALM2 may impair Ca2+-dependent inactivation of ICa,L (50, 51), functionally comparable to the slowed inactivation of ICa,L in case of LQT8 (Table S7).
In Table 1 and Table S8, we, like others (52, 53), used LQT14–LQT16 in relation to mutations in CALM1–CALM3. We are, however, well aware that the naming LQT16 has been used in other review articles (54, 55) in relation to mutations in SCN1B (56) and in TRDN (57). Altmann et al. identified autosomal recessive homozygous or compound heterozygous mutations in TRDN, encoding triadin, associated with LQTS, and themselves proposed that “triadin knockout syndrome” or “TRDN-mediated autosomal-recessive LQTS” should be used rather than “LQT17,” because of the atypical phenotype that was observed (57).
Discussion and Conclusion
SAN action potentials are generated from a delicate balance of several inwardly and outwardly directed ionic currents, and “Ca2+ clock” mechanisms [for reviews, see (58–60)]. While LQTS gene mutations may affect HR by changes in SAN action potential repolarization, it is highly likely that they also affect the intrinsic SAN cycle length by changes in the diastolic, phase 4, depolarization rate, as illustrated by the computer simulations of Figure 1.
It is important to realize that a mutation in a single LQTS-related gene may affect several ion currents. This does not only hold for mutations in a Ca2+ sensing protein like calmodulin, but also for mutations in the α-subunit of a specific ion channel. The LQT1-related T587M mutation in KCNQ1 for example does not only reduce IKs, but also fails to increase membrane localization of the KCNH2-encoded KV11.1 protein, as opposed to wild-type KCNQ1, thus also reducing IKr (61). Furthermore, we have to keep in mind that the LQTS-induced changes in rhythm may in turn induce changes in expression of specific ion channels, as demonstrated in studies by Tsuji et al. (62), Yeh et al. (63), and D'Souza et al. (64).
LQT2 and LQT3, but not LQT1, patients have a more pronounced risk for arrhythmias at slower HR (7). LQT2 and LQT3 gene mutations may therefore increase the risk for cardiac events via a direct effect on HR, as indeed clinically was found in a large family with LQT3 (65, 66). In LQT1 patients, on the other hand, cardiac events tend to occur during exercise (7). These differences between LQTS types 1–3 underscore the differences in underlying mechanisms and the potential role of sinus bradycardia in cardiac events.
As shown in Tables S1–S8 and summarized in Table 1, sinus bradycardia has been reported in relation to a large number of LQTS mutations. However, observations are limited to one or a few single patients for most of these mutations (Table 1). The occurrence of both QT prolongation and sinus bradycardia on a family basis is almost completely limited to LQT3 and Ankyrin-B syndrome (“LQT4”). However, the mechanisms of the associated ventricular arrhythmias and sudden death are largely different. Cardiac events, including nocturnal sudden death, are provoked by the bradycardia and associated excessive QT prolongation in case of LQT3 (65, 66), whereas disturbed calcium homeostasis leads to dysfunction of the SAN cells in case of the Ankyrin-B syndrome, with sudden death occurring after physical exertion and emotional stress (67–70).
We conclude that, although sinus bradycardia has been reported in relation to a large number of LQTS mutations, a causative role of this sinus bradycardia in cardiac events is limited to mutations underlying LQTS type 3.
Author Contributions
RW and AV: experimental design, data acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data, drafting manuscript, editing manuscript, and approval.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcvm.2018.00106/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Moss AJ, Schwartz PJ, Crampton RS, Tzivoni D, Locati EH, MacCluer J, et al. The long QT syndrome: prospective longitudinal study of 328 families. Circulation (1991) 84:1136–44. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.84.3.1136
2. Obeyesekere MN, Antzelevitch C, Krahn AD. Management of ventricular arrhythmias in suspected channelopathies. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. (2015) 8:221–31. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.114.002321
3. January CT, Gong Q, Zhou Z. Long QT syndrome: cellular basis and arrhythmia mechanism in LQT2. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. (2000) 11:1413–8. doi: 10.1046/j.1540-8167.2000.01413.x
4. Wehrens XHT, Vos MA, Doevendans PA, Wellens HJJ. Novel insights in the congenital long QT syndrome. Ann Intern Med. (2002) 137:981–92. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-137-12-200212170-00012
5. Bohnen MS, Peng G, Robey SH, Terrenoire C, Iyer V, Sampson KJ, et al. Molecular pathophysiology of congenital long QT syndrome. Physiol Rev. (2017) 97:89–134. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00008.2016
6. Giudicessi JR, Wilde AAM, Ackerman MJ. The genetic architecture of long QT syndrome: a critical reappraisal. Trends Cardiovasc Med. (2018) doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2018.03.003. [Epub ahead of print].
7. Schwartz PJ, Priori SG, Spazzolini C, Moss AJ, Vincent GM, Napolitano C, et al. Genotype-phenotype correlation in the long-QT syndrome: gene-specific triggers for life-threatening arrhythmias. Circulation (2001) 103:89–95. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.103.1.89
8. Swan H, Viitasalo M, Piippo K, Laitinen P, Kontula K, Toivonen L. Sinus node function and ventricular repolarization during exercise stress test in long QT syndrome patients with KvLQT1 and HERG potassium channel defects. J Am Coll Cardiol. (1999) 34:823–9. doi: 10.1016/S0735-1097(99)00255-7
9. Kass RS, Moss AJ. Long QT syndrome: novel insights into the mechanisms of cardiac arrhythmias. J Clin Invest. (2003) 112:810–5. doi: 10.1172/JCI19844
10. Chandler NJ, Greener ID, Tellez JO, Inada S, Musa H, Molenaar P, et al. Molecular architecture of the human sinus node: insights into the function of the cardiac pacemaker. Circulation (2009) 119:1562–75. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.804369
11. Schwartz PJ. Idiopathic long QT syndrome: progress and questions. Am Heart J. (1985) 109:399–411. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(85)90626-X
12. Lupoglazoff J-M, Denjoy I, Villain E, Fressart V, Simon F, Bozio A, et al. Long QT syndrome in neonates: conduction disorders associated with HERG mutations and sinus bradycardia with KCNQ1 mutations. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2004) 43:826–30. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2003.09.049
13. Horigome H, Nagashima M, Sumitomo N, Yoshinaga M, Ushinohama H, Iwamoto M, et al. Clinical characteristics and genetic background of congenital long-QT syndrome diagnosed in fetal, neonatal, and infantile life: a nationwide questionnaire survey in Japan. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. (2010) 3:10–7. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.109.882159
14. Beinder E, Grancay T, Menéndez T, Singer H, Hofbeck M. Fetal sinus bradycardia and the long QT syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol. (2001) 185:743–7. doi: 10.1067/mob.2001.117973
15. Mitchell JL, Cuneo BF, Etheridge SP, Horigome H, Weng H-Y, Benson DW. Fetal heart rate predictors of long QT syndrome. Circulation (2012) 126:2688–95. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.114132
16. Henrion U, Zumhagen S, Steinke K, Strutz-Seebohm N, Stallmeyer B, Lang F, et al. Overlapping cardiac phenotype associated with a familial mutation in the voltage sensor of the KCNQ1 channel. Cell Physiol Biochem. (2012) 29:809–18. doi: 10.1159/000178470
17. Lane CM, Bos JM, Rohatgi RK, Ackerman MJ. Beyond the length and look of repolarization: defining the non-QTc electrocardiographic profiles of patients with congenital long QT syndrome. Heart Rhythm (2018) doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2018.04.033. [Epub ahead of print].
18. Takenaka K, Ai T, Shimizu W, Kobori A, Ninomiya T, Otani H, et al. Exercise stress test amplifies genotype-phenotype correlation in the LQT1 and LQT2 forms of the long-QT syndrome. Circulation (2003) 107:838–44. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000048142.85076.A2
19. Brink PA, Crotti L, Corfield V, Goosen A, Durrheim G, Hedley P, et al. Phenotypic variability and unusual clinical severity of congenital long-QT syndrome in a founder population. Circulation (2005) 112:2602–10. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.572453
20. Tristani-Firouzi M, Chen J, Mitcheson JS, Sanguinetti MC. Molecular biology of K+ channels and their role in cardiac arrhythmias. Am J Med. (2001) 110:50–9. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9343(00)00623-9
21. Heijman J, Spätjens RLHMG, Seyen SRM, Lentink V, Kuijpers HJH, Boulet IR, et al. Dominant-negative control of cAMP-dependent IKs upregulation in human long-QT syndrome type 1. Circ Res. (2012) 110:211–9. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.249482
22. Verkerk AO, Wilders R, Van Borren MMGJ, Peters RJG, Broekhuis E, Lam K, et al. Pacemaker current (If) in the human sinoatrial node. Eur Heart J. (2007) 28:2472–8. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehm339
23. Fabbri A, Fantini M, Wilders R, Severi S. Computational analysis of the human sinus node action potential: model development and effects of mutations. J Physiol. (2017) 595:2365–96. doi: 10.1113/JP273259
24. Villafañe J, Fischbach P, Gebauer R. Short QT syndrome manifesting with neonatal atrial fibrillation and bradycardia. Cardiology (2014) 128:236–40. doi: 10.1159/000360758
25. Couderc J-P, McNitt S, Xia J, Zareba W, Moss AJ. Repolarization morphology in adult LQT2 carriers with borderline prolonged QTc interval. Heart Rhythm (2006) 3:1460–6. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2006.08.009
26. Beery TA, Shooner KA, Benson DW. Neonatal long QT syndrome due to a de novo dominant negative hERG mutation. Am J Crit Care (2007) 16:412–5.
27. Harrell DT, Ashihara T, Ishikawa T, Tominaga I, Mazzanti A, Takahashi K, et al. Genotype-dependent differences in age of manifestation and arrhythmia complications in short QT syndrome. Int J Cardiol. (2015) 190:393–402. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.04.090
28. Postema PG, Van den Berg MP, Van Tintelen JP, Van den Heuvel F, Grundeken M, Hofman N, et al. Founder mutations in the Netherlands: SCN5a 1795insD, the first described arrhythmia overlap syndrome and one of the largest and best characterised families worldwide. Neth Heart J. (2009) 17:422–8. doi: 10.1007/BF03086296
29. Wilders R. Sinus bradycardia in carriers of the SCN5A-1795insD mutation: unraveling the mechanism through computer simulations. Int J Mol Sci. (2018) 19:634. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020634
30. Baruscotti M, DiFrancesco D, Robinson RB. A TTX-sensitive inward sodium current contributes to spontaneous activity in newborn rabbit sino-atrial node cells. J Physiol. (1996) 492:21–30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021285
31. Detta N, Frisso G, Limongelli G, Marzullo M, Calabrò R, Salvatore F. Genetic analysis in a family affected by sick sinus syndrome may reduce the sudden death risk in a young aspiring competitive athlete. Int J Cardiol. (2014) 170:e63–5. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2013.11.013
32. Moreau A, Janin A, Millat G, Chevalier P. Cardiac voltage-gated sodium channel mutations associated with left atrial dysfunction and stroke in children. Europace (2018) doi: 10.1093/europace/euy041. [Epub ahead of print].
33. Isbrandt D, Friederich P, Solth A, Haverkamp W, Ebneth A, Borggrefe M, et al. Identification and functional characterization of a novel KCNE2 (MiRP1) mutation that alters HERG channel kinetics. J Mol Med. (2002) 80:524–32. doi: 10.1007/s00109-002-0364-0
34. Lu Y, Mahaut-Smith MP, Huang CL-H, Vandenberg JI. Mutant MiRP1 subunits modulate HERG K+ channel gating: a mechanism for pro-arrhythmia in long QT syndrome type 6. J Physiol. (2003) 551:253–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2003.00253.x
35. Liu W, Deng J, Wang G, Zhang C, Luo X, Yan D, et al. KCNE2 modulates cardiac L-type Ca2+ channel. J Mol Cell Cardiol. (2014) 72:208–18. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2014.03.013
36. Nawathe PA, Kryukova Y, Oren RV, Milanesi R, Clancy CE, Lu JT, et al. An LQTS6 MiRP1 mutation suppresses pacemaker current and is associated with sinus bradycardia. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. (2013) 24:1021–7. doi: 10.1111/jce.12163
37. Decher N, Bundis F, Vajna R, Steinmeyer K. KCNE2 modulates current amplitudes and activation kinetics of HCN4: influence of KCNE family members on HCN4 currents. Pflügers Arch. (2003) 446:633–40. doi: 10.1007/s00424-003-1127-7
38. Nguyen H-L, Pieper GH, Wilders R. Andersen-Tawil syndrome: clinical and molecular aspects. Int J Cardiol. (2013) 170:1–16. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2013.10.010
39. Zhang L, Benson DW, Tristani-Firouzi M, Ptacek LJ, Tawil R, Schwartz PJ. Electrocardiographic features in Andersen-Tawil syndrome patients with KCNJ2 mutations: characteristic T-U-wave patterns predict the KCNJ2 genotype. Circulation (2005) 111:2720–6. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.472498
40. Splawski I, Timothy KW, Sharpe LM, Decher N, Kumar P, Bloise R, et al. CaV1.2 calcium channel dysfunction causes a multisystem disorder including arrhythmia and autism. Cell (2004) 119, 19–31. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.09.011
41. Splawski I, Timothy KW, Decher N, Kumar P, Sachse FB, Beggs AH, et al. Severe arrhythmia disorder caused by cardiac L-type calcium channel mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2005) 102:8089–96. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0502506102
42. Gazzerro E, Sotgia F, Bruno C, Lisanti MP, Minetti C. Caveolinopathies: from the biology of caveolin-3 to human diseases. Eur J Hum Genet. (2010) 18:137–45. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2009.103
43. Vatta M, Ackerman MJ, Ye B, Makielski JC, Ughanze EE, Taylor EW, et al. Mutant caveolin-3 induces persistent late sodium current and is associated with long-QT syndrome. Circulation (2006) 114:2104–12. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.635268
44. Cronk LB, Ye B, Kaku T, Tester DJ, Vatta M, Makielski JC, et al. Novel mechanism for sudden infant death syndrome: persistent late sodium current secondary to mutations in caveolin-3. Heart Rhythm (2007) 4:161–6. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2006.11.030
45. Medeiros-Domingo A, Kaku T, Tester DJ, Iturralde-Torres P, Itty A, Ye B, et al. SCN4B-encoded sodium channel β4 subunit in congenital long-QT syndrome. Circulation (2007) 116:134–42. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.659086
46. Holmegard HN, Theilade J, Benn M, Duno M, Haunso S, Svendsen JH. Genetic variation in the inwardly rectifying K+ channel subunits KCNJ3 (GIRK1) and KCNJ5 (GIRK4) in patients with sinus node dysfunction. Cardiology (2010) 115:176–81. doi: 10.1159/000279319
47. Lian J, Yan G-X, Kowey PR. Born to be bradycardic? Cardiology (2010) 115:229–31. doi: 10.1159/000297573
48. Sorensen AB, Søndergaard MT, Overgaard MT. Calmodulin in a heartbeat. FEBS J. (2013) 280:5511–32. doi: 10.1111/febs.12337
49. Shamgar L, Ma L, Schmitt N, Haitin Y, Peretz A, Wiener R, et al. Calmodulin is essential for cardiac IKS channel gating and assembly: impaired function in long-QT mutations. Circ Res. (2006) 98:1055–63. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000218979.40770.69
50. Limpitikul WB, Dick IE, Joshi-Mukherjee R, Overgaard MT, George AL Jr, Yue DT. Calmodulin mutations associated with long QT syndrome prevent inactivation of cardiac L-type Ca2+ currents and promote proarrhythmic behavior in ventricular myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. (2014) 74:115–24. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2014.04.022
51. Pipilas DC, Johnson CN, Webster G, Schlaepfer J, Fellmann F, Sekarski N, et al. Novel calmodulin mutations associated with congenital long QT syndrome affect calcium current in human cardiomyocytes. Heart Rhythm (2016) 13:2012–9. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2016.06.038
52. Giudicessi JR, Ackerman MJ. Calcium revisited: new insights into the molecular basis of long-QT syndrome. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. (2016) 9:e002480. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.116.002480
53. Mascia G, Arbelo E, Solimene F, Giaccardi M, Brugada R, Brugada J. The long-QT syndrome and exercise practice: the never-ending debate. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. (2018) 29:489–96. doi: 10.1111/jce.13410
54. Campuzano O, Allegue C, Partemi S, Iglesias A, Oliva A, Brugada R. Negative autopsy and sudden cardiac death. Int J Legal Med. (2014) 128:599–606. doi: 10.1007/s00414-014-0966-4
55. Gray B, Behr ER. New insights into the genetic basis of inherited arrhythmia syndromes. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. (2016) 9:569–77. doi: 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.116.001571
56. Riuró H, Campuzano O, Arbelo E, Iglesias A, Batlle M, Pérez-Villa F, et al. A missense mutation in the sodium channel β1b subunit reveals SCN1B as a susceptibility gene underlying long QT syndrome. Heart Rhythm (2014) 11:1202–9. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2014.03.044
57. Altmann HM, Tester DJ, Will ML, Middha S, Evans JM, Eckloff BW, et al. Homozygous/compound heterozygous triadin mutations associated with autosomal-recessive long-QT syndrome and pediatric sudden cardiac arrest: elucidation of the triadin knockout syndrome. Circulation (2015) 131:2051–60. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.015397
58. Verkerk AO, Van Ginneken ACG, Wilders R. Pacemaker activity of the human sinoatrial node: role of the hyperpolarization-activated current, If. Int J Cardiol. (2009) 132:318–36. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2008.12.196
59. Lakatta EG, DiFrancesco D. What keeps us ticking: a funny current, a calcium clock, or both? J Mol Cell Cardiol. (2009) 47:157–70. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2009.03.022
60. Monfredi O, Maltsev VA, Lakatta EG. Modern concepts concerning the origin of the heartbeat. Physiology (2013) 28:74–92. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00054.2012
61. Biliczki P, Girmatsion Z, Brandes RP, Harenkamp S, Pitard B, Charpentier F, et al. Trafficking-deficient long QT syndrome mutation KCNQ1-T587M confers severe clinical phenotype by impairment of KCNH2 membrane localization: evidence for clinically significant IKr-IKs α-subunit interaction. Heart Rhythm (2009) 6:1792–801. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2009.08.009
62. Tsuji Y, Zicha S, Qi X-Y, Kodama I, Nattel S. Potassium channel subunit remodeling in rabbits exposed to long-term bradycardia or tachycardia: discrete arrhythmogenic consequences related to differential delayed-rectifier changes. Circulation (2006) 113:345–55. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.552968
63. Yeh Y-H, Burstein B, Qi XY, Sakabe M, Chartier D, Comtois P, et al. Funny current downregulation and sinus node dysfunction associated with atrial tachyarrhythmia: a molecular basis for tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome. Circulation (2009) 119:1576–85. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.789677
64. D'Souza A, Bucchi A, Johnsen AB, Logantha SJRJ, Monfredi O, Yanni J, et al. Exercise training reduces resting heart rate via downregulation of the funny channel HCN4. Nat Commun. (2014) 5:3775. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4775
65. Van den Berg MP, Wilde AAM, Viersma JW, Brouwer J, Haaksma J, Van der Hout AH, et al. (2001). Possible bradycardic mode of death and successful pacemaker treatment in a large family with features of long QT syndrome type 3 and Brugada syndrome. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 12, 630–6. doi: 10.1046/j.1540-8167.2001.00630.x
66. Beaufort-Krol GCM, Van den Berg MP, Wilde AAM, Van Tintelen JP, Viersma JW, Bezzina CR, et al. Developmental aspects of long QT syndrome type 3 and Brugada syndrome on the basis of a single SCN5A mutation in childhood. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2005) 46:331–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2005.03.066
67. Schott J-J, Charpentier F, Peltier S, Foley P, Drouin E, Bouhour JB, et al. Mapping of a gene for long QT syndrome to chromosome 4q25-27. Am J Hum Genet. (1995) 57:1114–22.
68. Mohler PJ, Schott J-J, Gramolini AO, Dilly KW, Guatimosim S, duBell WH, et al. Ankyrin-B mutation causes type 4 long-QT cardiac arrhythmia and sudden cardiac death. Nature (2003) 421:634–9. doi: 10.1038/nature01335
69. Mohler PJ, Splawski I, Napolitano C, Bottelli G, Sharpe L, Timothy K, et al. A cardiac arrhythmia syndrome caused by loss of ankyrin-B function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2004) 101:9137–42. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0402546101
Keywords: mutations, sinus bradycardia, human, long-QT syndrome, heart rate, sinoatrial node, ion channel, computer simulation
Citation: Wilders R and Verkerk AO (2018) Long QT Syndrome and Sinus Bradycardia–A Mini Review. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 5:106. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2018.00106
Received: 18 June 2018; Accepted: 16 July 2018;
Published: 03 August 2018.
Edited by:
Giannis G. Baltogiannis, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, BelgiumReviewed by:
Daniel M. Johnson, Cardiovascular Research Institute Maastricht, Maastricht University, NetherlandsOsmar Antonio Centurión, Universidad Nacional de Asunción, Paraguay
Copyright © 2018 Wilders and Verkerk. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Arie O. Verkerk, a.o.verkerk@amc.uva.nl
 Ronald Wilders
Ronald Wilders Arie O. Verkerk
Arie O. Verkerk