
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Chem. , 16 September 2020
Sec. Nanoscience
Volume 8 - 2020 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2020.00822
This article is part of the Research Topic Design and Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles for Targeted Therapy and Diagnostics View all 7 articles
This article is a correction to:
Olax scandens Mediated Biogenic Synthesis of Ag-Cu Nanocomposites: Potential Against Inhibition of Drug-Resistant Microbes
 Anzar Abdul Mujeeb1
Anzar Abdul Mujeeb1 Nuha Abeer Khan1
Nuha Abeer Khan1 Fauzia Jamal1
Fauzia Jamal1 Khan Farheen Badre Alam1
Khan Farheen Badre Alam1 Haris Saeed1
Haris Saeed1 Shadab Kazmi1
Shadab Kazmi1 Ansam Wadia Faid Alshameri1
Ansam Wadia Faid Alshameri1 Mohammad Kashif2
Mohammad Kashif2 Irfan Ghazi3
Irfan Ghazi3 Mohammad Owais1*
Mohammad Owais1*A Corrigendum on
Olax scandens Mediated Biogenic Synthesis of Ag-Cu Nanocomposites: Potential Against Inhibition of Drug-Resistant Microbes
by Mujeeb, A. A., Khan, N. A., Jamal, F., Badre Alam, K. F., Saeed, H., Kazmi, S., et al. (2020). Front. Chem. 8:103. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2020.00103
In the original article, there was a mistake in Figure 5A as published. An incorrect image was used in panel C. The corrected Figure 5A appears below.
There was also a mistake in the legend for Figure 5 as published. The correct legend appears below.
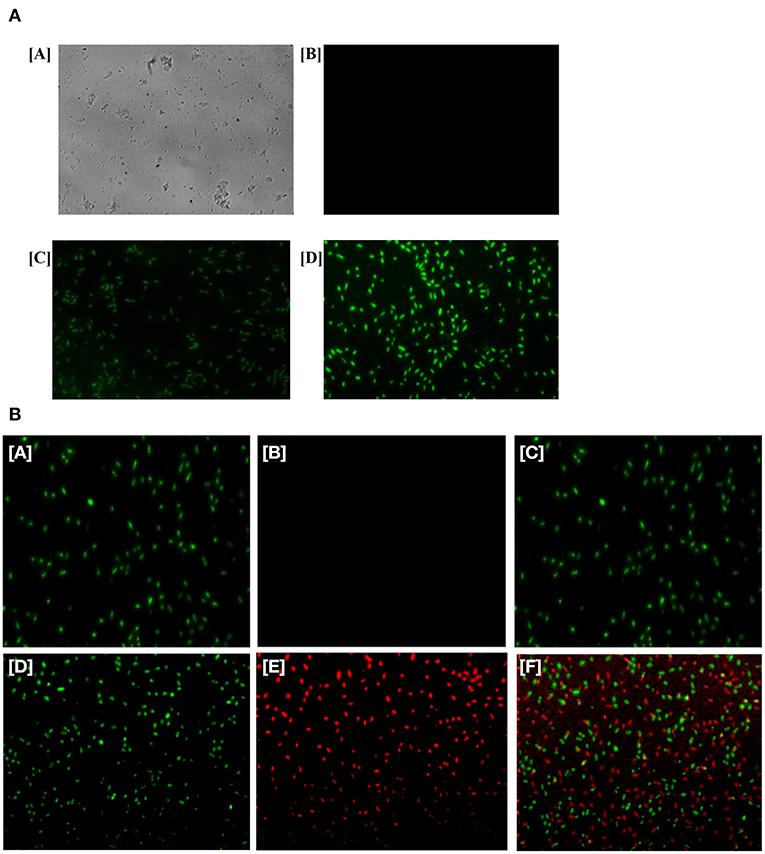
FIGURE 5. (A) Generation of ROS in the bacterial cells upon their treatment with as-formed Ag-Cu NCs. Micrograph showing [A] phase contrast picture of live cells, [B] fluorescence micrograph of untreated live cells, [C] micrograph depicting effect of as-generated ROS in the treated bacteria upon exposure to Ag-Cu NCs (62 μg/ml), and [D] an intensification in fluorescence upon treatment with increasing concentration of Ag-Cu NCs (125 μg/ml). (B) Fluorescence micrograph corresponding to live/dead assay employed to assess the antimicrobial activity of as-formed Ag-Cu NCs. (A, B, and C), untreated bacterial cells are stained with SYTO-9 only, as they fail to acquire PI fluorescence because of their intact membrane; (D, E, and F) micrographs correspond to bacterial cells post exposure to Ag-Cu NCs (125 μg/ml). The bacterial cells are stained with SYTO-9/PI post exposure to Ag-Cu NCs based formulation. The dead bacterial cells acquire PI fluorescence due to their broken membrane. The live cells acquire SYTO-9 stain [D], while dead bacteria are stained with PI [E]. The [F] panel corresponds to merge copy of [D, SYTO-9 fluorescence] and [E, PI fluorescence] images.
The authors apologize for these errors and state that they do not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Keywords: biogenic, Ag-Cu NCs, anti-biofilm potential, reactive oxygen species (ROS), antimicrobial potential
Citation: Mujeeb AA, Khan NA, Jamal F, Badre Alam KF, Saeed H, Kazmi S, Alshameri AWF, Kashif M, Ghazi I and Owais M (2020) Corrigendum: Olax scandens Mediated Biogenic Synthesis of Ag-Cu Nanocomposites: Potential Against Inhibition of Drug-Resistant Microbes. Front. Chem. 8:822. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2020.00822
Received: 20 July 2020; Accepted: 04 August 2020;
Published: 16 September 2020.
Edited and reviewed by: Khalid Umar, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Malaysia
Copyright © 2020 Mujeeb, Khan, Jamal, Badre Alam, Saeed, Kazmi, Alshameri, Kashif, Ghazi and Owais. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mohammad Owais, bWRvd2FpczIwMTJAZ21haWwuY29t
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.