- 1Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Materials Engineering, Wenzhou University, Wenzhou, China
- 2Chemical Biology Research Center, School of Pharmaceutical Science, Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, China
- 3Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, The University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX, United States
Two series of Zn-Ln and Cd-Ln nanoclusters [Ln4Zn8L2(OAc)20(OH)4] [Ln = Nd (1), Yb (2), and Sm (3)] and [Ln2Cd2L2(OAc)2(OH)2(OCH3)2] [Ln = Nd (4), Yb (5), and Sm (6)] were prepared using a long-chain Schiff base ligand with a flexible (CH2)2O(CH2)2O(CH2)2 chain. All these clusters show square-like structures. The Schiff base ligands show “linear” configurations in the structures of 1-6, and the metric dimensions of Zn-Ln and Cd-Ln clusters measure ~8 × 14 × 21 and 8 × 12 × 12 Å, respectively. The study of luminescence properties shows that the Zn/L and Cd/L chromophores can effectively transfer energy to the lanthanide ions, and 1-6 show visible and NIR emissions.
Introduction
The polynuclear d-f nanoclusters may exhibit specific physical and chemical properties due to the interaction between metal ions (Kauffman et al., 2014; Li et al., 2015). Lanthanide ions have abundant electronic energy levels and can show long-lived and line-like emission bands because of their unique 4f electronic configurations. For example, Nd(III), Er(III), and Yb(III) complexes can show near-infrared (NIR) emissions around 900–1,600 nm, where the absorption of the biological systems and fiber media is low. Consequently, these lanthanide complexes have potential applications in bioassays and luminescent probes (Hemmila and Webb, 1997). In addition, polynuclear d-f nanoclusters with well-defined structures and interesting properties have emerged as a new class of nanomaterials for their potential applications in optoelectronics, magnetism, and as porous materials (Peng et al., 2012; Wang et al., 2013).
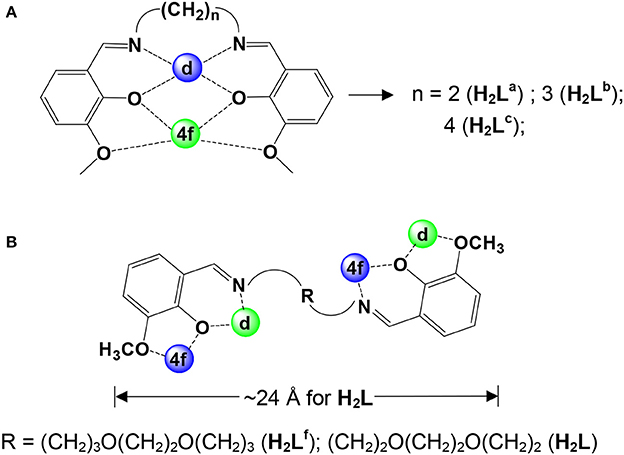
Salen-type Schiff base ligands have been widely used to synthesize d-f heteronuclear clusters (Yamaguchi et al., 2010; Pasatoiu et al., 2011, 2012; Watanabe et al., 2011). For example, some polynuclear 3d-4f complexes (3d = Ni, Zn, and Cu) have been synthesized in our group using Schiff base ligands H2La−c that have flexible carbon-carbon backbones (Scheme 1) (Yang et al., 2014). In these polynuclear clusters, the d-metal ions are bound in the N2O2 cavities and the f-metal ions in the O2O2 cavities, resulting the classical “bending” configurations of the Schiff base ligands (Scheme 1A). Recently, two kinds of luminescent 24- and 32-metal Cd-Ln complexes were constructed in our studies from Schiff base ligands H2Ld and H2Le (Scheme 1), which have 6 and 8 carbon backbones, respectively (Yang et al., 2013). We have found that the backbone structures of these ligands may affect their coordination modes with metal ions. For example, two 12-metal Zn-Ln nanoclusters [Zn8Ln4(Lf)8(OAc)8](OH)4 (Ln = Sm and Nd) were prepared using a long-chain Schiff base ligand with a flexible (CH2)3O(CH2)2O(CH2)3 backbone (Scheme 1B) (Bo et al., 2018). Zinc (II) and Cadmium(II) moieties have been used as efficient energy donors for the luminescence of the Ln(III) ions in Zn- and Cd-Ln complexes (Zheng et al., 2004; Zhu et al., 2006). As part of our continuing studies focused on the studies of luminescent lanthanide-based frameworks, we report here the synthesis and luminescence properties of two series of Zn-Ln and Cd-Ln clusters [Ln4Zn8L2(OAc)20(OH)4] [Ln = Nd (1), Yb (2), and Sm (3)] and [Ln2Cd2L2(OAc)2(OH)2(OCH3)2] [Ln = Nd (4), Yb (5), and Sm (6)] with a long-chain Schiff base ligand N,N'-bis(3-methoxysalicylidene)(1,2-bis(ethoxy)ethane)-1,6-diamine (H2L, Scheme 1B). The Schiff base ligand H2L has a flexible long-chain (CH2)2O(CH2)2O(CH2)2 backbone with two introduced oxygen atoms. Although the long-chain Schiff base ligand H2L only has two fewer -CH2- groups in the backbone than H2Lf (Scheme 1B), 1-3 show different structures from [Zn8Ln4(Lf)8(OAc)8](OH)4 (Ln = Sm and Nd) that have eight Schiff base ligands H2Lf (Bo et al., 2018). Meanwhile, differing from those clusters with H2La−e, all 1-6 show interesting square-like structures. The backbone length of H2L is ~24 Å, which is much longer than H2La−c. It is noticeable that the H2L ligand exhibits a different “linear” configuration in 1-6 (Scheme 1B). Thus, it turns to form large metal clusters. For example, the molecular dimensions of Zn-Ln clusters 1-3 measure ~8 × 14 × 21 Å. The study of luminescence properties shows that all of these clusters display the visible and NIR emissions of lanthanide ions.
Experimental Section
Preparation of [Nd4Zn8L2(OAc)20(OH)4] (1)
Zn(OAc)2·2H2O (0.40 mmol, 0.0876 g), Nd(OAc)3·4H2O (0.20 mmol, 0.0778 g), and H2L (0.05 mmol, 0.0208 g) were dissolved in 12 mL EtOH at room temperature, and a solution of Et3N in MeOH (0.01 mol/L, 2 mL) was then added. The mixture was stirred and heated for 30 min under reflux and then filtered. The yellow crystals of 1 were obtained by the diffusion of diethyl ether into the filtrate after 3 weeks. Yield (based on Zn(OAc)2·2H2O): 0.0937 g (76%). m. p. > 175°C (dec.). EA: C, 31.98; H, 3.97; N, 1.65% (found). Calc. for C88H128N4Nd4O60Zn8, C, 32.01; H, 3.91; N, 1.70%. IR (cm−1): 1619 (w), 1557 (m), 1445 (m), 1408 (m), 1334 (w), 1303 (m), 1216 (s), 1086 (s), 1011 (s), 968 (m), 943 (s), 856 (s), 738 (m), 670 (m) (Figure S1).
Preparation of [Yb4Zn8L2(OAc)20(OH)4] (2)
The procedure was the same as that for 1 using Yb(OAc)3·4H2O (0.20 mmol, 0.0842 g). Yellow crystals of 2 were formed after 3 weeks. Yield (based on Zn(OAc)2·2H2O): 0.0671 g (53%). m. p. > 176°C (dec.). EA: C, 30.83; H, 3.93; N, 1.63% (found). Calc. for C88H128N4O60Zn8Yb4: C, 30.93; H, 3.78; N, 1.64%. IR (CH3CN, cm−1): 1632 (w), 1557 (w), 1452 (m), 1421 (s), 1291 (m), 1241 (s), 1216 (w), 1080 (s), 1024 (s), 974 (w), 856 (w), 738 (m), 682 (s) (Figure S1).
Preparation of [Sm4Zn8L2(OAc)20(OH)4] (3)
The procedure was the same as that for 1 using Sm(OAc)3·4H2O (0.20 mmol, 0.0803 g). Yellow crystals of 3 were formed after 1 week. Yield (based on Zn(OAc)2·2H2O): 0.0745 g (60%). m. p. > 188°C (dec.). EA: C, 31.87; H, 3.95; N, 1.59% (found). Calc. for C88H128N4O60Zn8Sm4: C, 31.77; H, 3.88; N, 1.68%. IR (CH3CN, cm−1): 1632 (w), 1545 (w), 1452 (m), 1421 (s), 1303 (m), 1241 (s), 1216 (w), 1086 (s), 1030 (s), 974 (w), 937 (w), 862 (m), 744 (s), 676 (s) (Figure S1).
Preparation of [Nd2Cd2L2(OAc)2(OH)2(OCH3)2] (4)
Cd(OAc)2·2H2O (0.20 mmol, 0.0534 g), Nd(NO3)3·6H2O (0.20 mmol, 0.0885 g) and H2L (0.20 mmol, 0.0833 g) were dissolved in 12 mL EtOH and 5 mL DMF at room temperature, and a solution of Et3N in MeOH (0.01 mol/L, 2 mL) was then added. The mixture was stirred and heated for 30 min under reflux and then filtered. The yellow crystals of 4 were obtained by the diffusion of diethyl ether into the filtrate after 1 week. Yield (based on Nd(NO3)3·6H2O): 0.1238 g (52%). m. p. > 167°C (dec.). EA: C, 38.31; H, 4.41; N, 3.42% (found). Calc. for C50H66N4O20Cd2Nd2: C, 38.59; H, 4.27; N, 3.60%. ESI-MS (CH3CN) m/z: 1558 [M+H]+. IR (cm−1): 1619 (w), 1545 (m), 1452 (s), 1408 (m), 1303 (m), 1241 (w), 1216 (m), 1080 (s), 1018 (s), 943 (s), 856 (m), 738 (s), 664 (s) (Figures S1 and S2).
Preparation of [Yb2Cd2L2(OAc)2(OH)2(OCH3)2] (5)
The procedure was the same as that for 1 using Yb(NO3)3·6H2O (0.20 mmol, 0.0907 g). Yellow crystals of 5 were formed after 1 week. Yield (based on Yb(NO3)3·6H2O): 0.1449 g (60%). m. p. > 161°C (dec.). EA: C, 36.99; H, 4.38; N, 3.21% (found). Calc. for C50H66N4O20Cd2Yb2: C, 37.21; H, 4.12; N, 3.47%. ESI-MS (CH3CN) m/z: 1597 [M-OH]+. IR (CH3CN, cm−1): 1632 (w), 1551 (m), 1445 (s), 1402 (m), 1340 (m), 1296 (w), 1241 (m), 1222 (s), 1086 (s), 1018 (s), 968 (m), 850 (s), 782 (s), 738 (s), 695 (s) (Figures S1 and S2).
Preparation of [Sm2Cd2L2(OAc)2(OH)2(OCH3)2] (6)
The procedure was the same as that for 1 using Sm(NO3)3·6H2O (0.20 mmol, 0.0903 g). Yellow crystals of 6 were formed after 1 week. Yield (based on Sm(NO3)3·6H2O): 0.1593 g (68%). m. p. > 190°C (dec.). EA: C, 38.17; H, 4.53; N, 3.26% (found). Calc. for C50H66N4O20Cd2Sm2: C, 38.28; H, 4.24; N, 3.57%. IR (CH3CN, cm−1): 1619 (w), 1545 (m), 1452 (s), 1408 (m), 1303 (m), 1247 (w), 1216 (m), 1080 (s), 1024 (s), 968 (s), 937 (s), 856 (m), 744 (s), 676 (s) (Figure S1).
Results and Discussion
Synthesis and Crystal Structures of the Clusters
The Schiff-base ligand H2L was prepared according to literature method (Lam et al., 1996). In the presence of Et3N, reactions of H2L with Zn(OAc)2·2H2O and Ln(OAc)3·4H2O (Ln = Nd, Yb, and Sm) in refluxing methanol/ethanol produced yellow solutions and the yellow crystalline products of 1-3 were obtained by the diffusion of diethyl ether into the solutions. A Smart APEX CCD diffractometer is used to collect the crystal data of all clusters (Supporting information, X-Ray Crystallography) (Tables S1–S4 and Data sheet 2). 1-3 have similar square-like structures, and two views of the crystal structure of 1 are shown in Figure 1. The top view is looking right in front of the square while the lower one is essentially a side-on view. The molecular sizes of 1 are about 8 × 14 × 21 Å. The structure of 1 is centrally symmetric with two equivalent Nd2Zn4L(OAc)10(OH)2 moieties linked by two L ligands. In each Nd2Zn4L(OAc)10(OH)2 moiety, the Nd3+ ion is coordinated with nine oxygen atoms from five OAc−, two OH− ions and one L ligand. Meanwhile, two Nd3+ ions are linked by two OH− ions, and the Nd···Nd distance is 4.190 Å. All Zn2+ ions show similar tetrahedral geometries. For the OAc − anions, each one binds to one Nd3+ and one Zn2+ ion. Each OH− anion bonds to one Zn2+ and two Nd3+ ions. In 1, it is found that the L ligand is coordinated with two Nd3+ and two Zn2+ ions by its N and phenoxide and methoxy O atoms, while two backbone O atoms do not involve in the coordination. Each Nd3+ ion and its closest three Zn2+ ions are bridged together through the L ligand, OAc− anions and/or OH− anions. The Nd···Zn distances range from 3.650 to 3.812 Å.
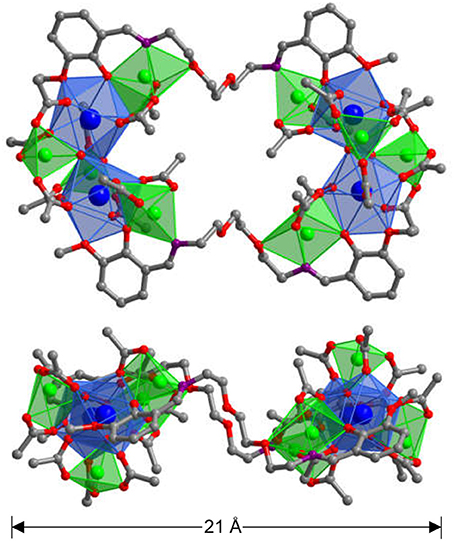
Figure 1. The square-like crystal structure of 1 (Top: viewed along the a-axis; Lower: viewed along the b-axis. The color of Nd3+ and Zn2+ are blue and green, respectively).
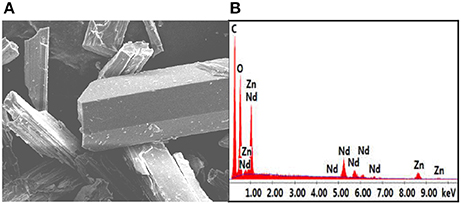
In 1, the bond lengths of Zn-O and Nd-O are 1.942–2.013 Å and 2.392–2.716 Å, respectively. The crystalline morphology of 1 was detected by a panoramic scanning electron microscopy (SEM) (Figure 2A). The Zn:Nd ratio in 1 is determined to be about 2:1 by energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) analysis, consistent with its crystal structure (Figure 2B).
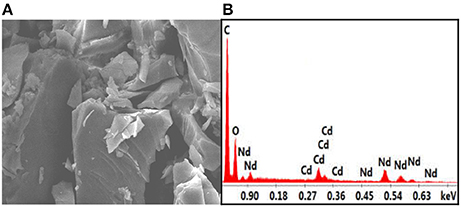
Reactions of H2L with Cd(OAc)2·2H2O and Ln(OAc)3·4H2O (Ln = Nd, Yb, and Sm) in similar reaction conditions as above produced yellow crystalline products of 4-6 (Tables S5–S7 and Data sheet 2). The crystal structure of 4 is shown in Figure 3. The metric dimensions of 4 measure ~8 × 12 × 12 Å, which are smaller than those of 1. As shown in Figure 3, the structure of 4 is also centrally symmetric with two equivalent NdCdL(OAc)(OH)(OCH3) moieties linked by two (OCH3)− anions. In each NdCdL(OAc)(OH)(OCH3) moiety, the Nd3+ ion is coordinated with eight oxygen atoms from two L ligands, one OAc−, one OH−, and one (OCH3)− anions. The Cd2+ ion has an octahedral geometry. The Nd3+ and Cd2+ ions are linked by one L ligand and one (OCH3)− anion with a separation of 3.656 Å. Each (OCH3)− anion bonds to one Cd2+ and two Nd3+ ions. As found in 1, two backbone O atoms of the L ligand are also not coordinated with the metals in 4. Two Cd2+ ions are linked by two (OCH3)− anions, and the Cd···Cd distance is 3.573 Å. In 4, the bond lengths of Cd-O and Nd-O are 2.249–2.419 Å and 2.255–2.480 Å, respectively. The Cd:Nd ratio in 4 is found to be about 1:1 by energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy analysis, consistent with its crystal structure (Figures 4A,B).
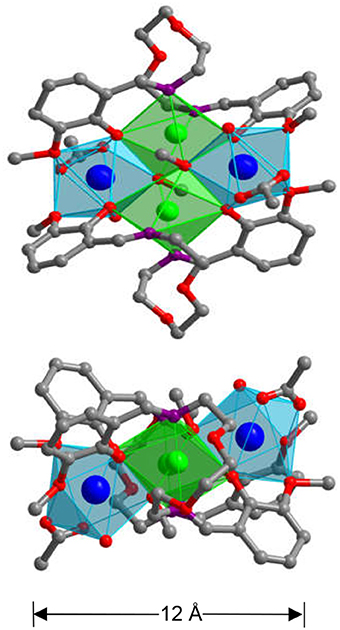
Figure 3. The square-like crystal structure of 4 (Top: viewed along the a-axis; Lower: viewed along the c-axis. The color of Nd3+ and Cd2+ are blue and green, respectively).
Powder XRD studies of 1-6 show that their experimental patterns are similar to their simulated ones generated from single crystal X-ray data (Figure S3). On heating 1 and 6 before 100 oC results in weight losses of 3–18% (thermogravimetric analysis, Figure S4), which is due to the escaption of the uncoordinated solvent molecules such as H2O, MeOH, and EtOH. The thermodynamically stabilities of the clusters were texted through melting point measurements. It is found that 1-6 start to discompose from 161 to 190oC (Figure S4). Molar conductivity studies show that 1-6 are neutral in solution, in agreement with their solid state structures.
Photophysical Properties
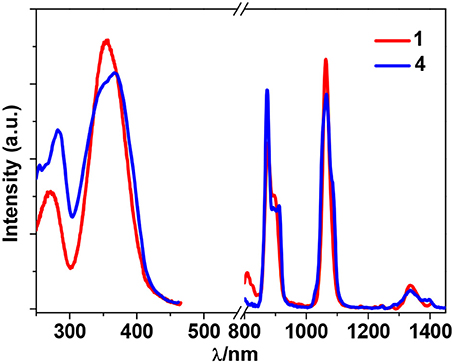
Zn2+ and Cd2+ ions have saturated d10 electronic configuration, which prevents the quenching of lanthanide luminescence through d-d transitions (i.e., f → d energy transfer) (Wen et al., 2007; Jankolovits et al., 2011). Thus, the light-absorbing Zn(II) and Cd(II) chromophores can be used as sensitizers for lanthanide emission. In order to obtain strongly luminescent lanthanide complexes, the chromophoric ligands which coordinate with the lanthanide metals should be able to absorb energy and transfer it efficiently to the central metals (“Antenna Effect”). For the efficiency of energy transfer from the ligand to the lanthanide ion (LMET), the energy gap between the excitation states of the former (donor) and latter (accepter) may play a key role (María et al., 2017). The photophysical properties of 1-6 were studied in CH3CN solution and the solid state. A FLS 980 fluorimeter was used to record luminescence spectra in the visible and NIR regions (Supporting information, Photophysical Studies). The UV-visible absorption spectrum of the free ligand H2L shows three bands at 222, 260, and 330 nm. These bands are found to be red-shifted in 1-6 (Figure 5). The free ligand exhibits emission bands at 416, 429, and 493 nm when excited with 280 or 378 nm light (Figure S5 in the ESI). Excited by ligand-centered absorption bands, 1 and 4 show typical NIR luminescence of Nd3+ (4Ij/2 transitions, j = 9, 11, and 13), 2 and 5 show that of Yb3+ (2F7/2 transition), while 3 and 6 show visible and NIR emission spectra for Sm3+ (4Hj/2 transitions, j = 5, 7, 9, and 11; 4Fj/2 transitions, j = 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9) (Figures 6–9). Each d-f cluster shows similar luminescence spectra in the solution and the solid state. For 1-6, the excitation wavelengths (λex) and molar absorption coefficients (ε), emission lifetimes (τ), quantum yields (Φem) and the energy transfer efficiencies (ηsens) are shown in Table 1.
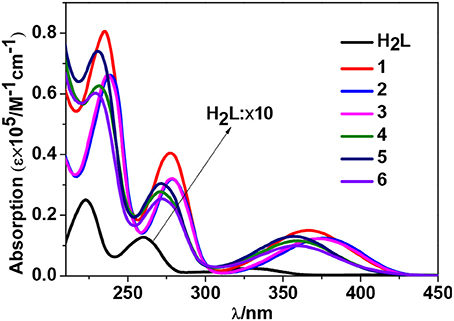
Figure 5. UV-Vis absorption spectra of the free Schiff base ligand H2L and 1-6 in CH3CN. (C = 10−6-10−5 M).
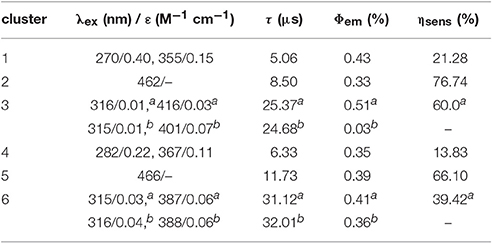
Table 1. The excitation wavelengths (λex) and molar absorption coefficients (ε), emission lifetimes (τ), quantum yields (Φem), and the energy transfer efficiencies (ηsens) of 1-6 in CH3CN (a Visible emission, b NIR emission).
As shown in Figure 6, both 1 and 4 display NIR emission bands of Nd3+ at about 872, 1,065, and 1,334 nm. These two clusters have similar excitation spectra with two bands (λex = 270–367 nm), in agreement with their absorption spectra, confirming that the energy transfers from the Zn/L or Cd/L centers to Nd3+ ions occur (Scheme 2). For either 1 or 4, the intensity of excitation band at the long wavelength (i.e., 355 nm for 1 or 367 nm for 4) is higher than that at the short wavelength (i.e., 270 nm for 1 or 282 nm for 4). For Nd(III) complexes, the Nd3+ ion has many excitation energy levels lying above the emissive 4F3/2 state at 11,300 cm−1, which is helpful for the lanthanide ion to accept energy from the d/L center (Scheme 2) (Bünzli and Piguet, 2005; Shavaleev et al., 2005). The emission lifetimes (τ) of 1 and 4 are found to be 5.06 and 6.33 μs, respectively (Figure S6). The intrinsic quantum yields (ΦLn) of Nd3+ emission in 1 and 4 are calculated as 2.02 and 2.53%, respectively, using ΦLn = τ/τ0 (τ0 = 250 μs (Meshkova et al., 1999), the natural lifetime of Nd3+). The emission quantum yields (Φem) of 1 and 4 are measured as 0.43 and 0.35%, respectively. So the efficiencies (ηsens) of the energy transfer from Zn/L- and Cd/L-center to Nd3+ in 1 and 4 are estimated to be 21.28 and 13.83%, respectively, using ηsens = Φem/ΦLn (Bünzli and Piguet, 2005). This indicates that the Zn/L center in 1 has higher energy transfer efficiency than Cd/L center in 4. The emission quantum yield of 1 is also bigger than 4 (0.43 vs. 0.35%). It is found that the absorption at the excitation wavelength in 1 (ε = 0.15 × 105 M−1 cm−1 at 355 nm) is bigger than that in 4 (ε = 0.11 × 105 M−1 cm−1 at 367 nm), which may be the cause of their differences in luminescence properties.
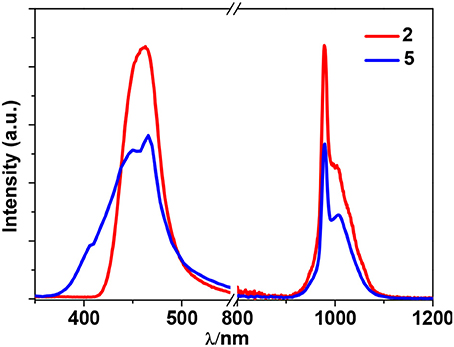
2 and 5 exhibit NIR emission bands of Yb3+ at about 978 nm (Figure 7). They show one excitation band at 462 and 466 nm, respectively, where the clusters have no or very weak absorption (Figure 5). Differing from Nd3+ ion, Yb3+ ion has only a single excited state 2F5/2 at 10,200 cm−1 that is lower than those of Zn/L and Cd/L centers (Scheme 2) (Horrocks et al., 1997; Reinhard and Gudel, 2002). The emission lifetimes (τ) of 2 and 5 are found to be 8.50 and 11.73 μs, respectively (Figure S6). The intrinsic quantum yields (ΦLn) of Yb3+ emission in 2 and 5 are calculated as 0.43 and 0.59%, respectively (Bünzli and Piguet, 2005) (the natural lifetime of Yb3+ is 2,000 μs). The emission quantum yields (Φem) of 2 and 5 in CH3CN are measured as 0.33 and 0.39%, respectively. Thus, the efficiencies (ηsens) of the energy transfer in 2 and 5 are estimated to be 76.74 and 66.10%, respectively (Bünzli and Piguet, 2005).
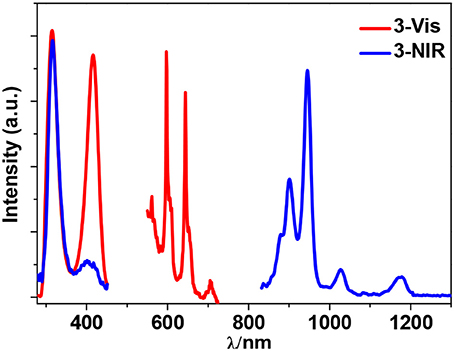
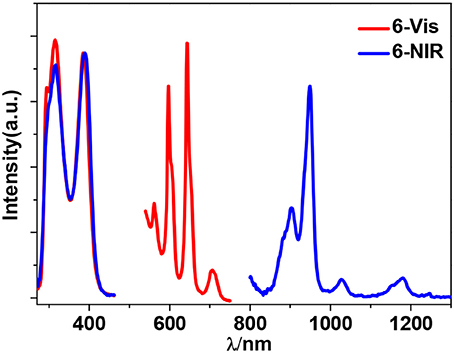
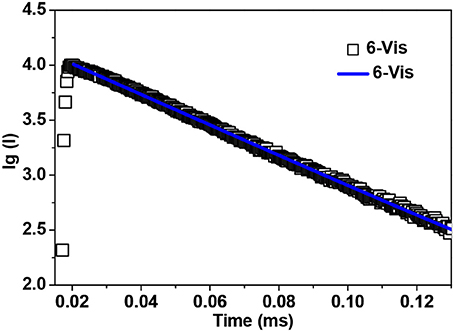
Sm3+ ion may show emission bands both in the visible (4HJ) and in the NIR (4FJ) ranges (Scheme 2) (Chow et al., 2016). However, due to non-radiative loss attributed to multiphonon emission, Sm(III) complexes often display weak luminescence (Sabbatini et al., 2011). For 3 and 6 (Figures 8, 9), the hypersensitive transitions 4H7/2 and 4H9/2 are found at about 595 and 650 nm, respectively, which are responsible for the most intense lines in the visible region. A peak located at 561 nm (4H5/2 transition) has predominant magnetic dipolar character. The intensity ratio of I(4H9/2)/I(4H5/2) can be used as a measure for the polarizability of the chemical environment of the Sm3+ ion. For 3 and 6 they are calculated to be 6.28 and 5.20, respectively, which are comparable to those found in the literature (Lunstroot et al., 2009; Sun et al., 2013). The visible emission lifetimes (τ) of 3 and 6 are 25.37 and 31.12 μs in CH3CN, respectively (Figure 10, Figure S6), which are a little shorter than the value of [ZnSmLb(NO3)3(H2O)] complex reported by Andruh et al. (Pasatoiu et al., 2011), but longer than those reported for some other Sm(III)-based complexes (Chen et al., 2005; Fomina et al., 2014; Foucault-Collet et al., 2014). The intrinsic quantum yields (ΦLn) of Sm3+ emissions in 3 and 6 are calculated as 0.85 and 1.04%, respectively (the natural lifetime of Sm3+ is 3.0 ms; Malba et al., 2015). The visible emission quantum yields (Φem) of 3 and 6 are found to be 0.51 and 0.41%, respectively. So the efficiencies (ηsens) of the energy transfer from Zn/L- and Cd/L-center to Sm3+ are estimated to be 60.0 and 39.42%, respectively (Bünzli and Piguet, 2005). This indicates that the Zn/L center in 4 exhibits higher energy transfer efficiency than the Cd/L center in 6. For either 4 or 6, the most intense line in the NIR area is found at about 960 nm (4F5/2 transition), with a long NIR emission lifetime (τ) up to 24.68 μs for 4 or 32.01 μs for 6 recorded in CH3CN.
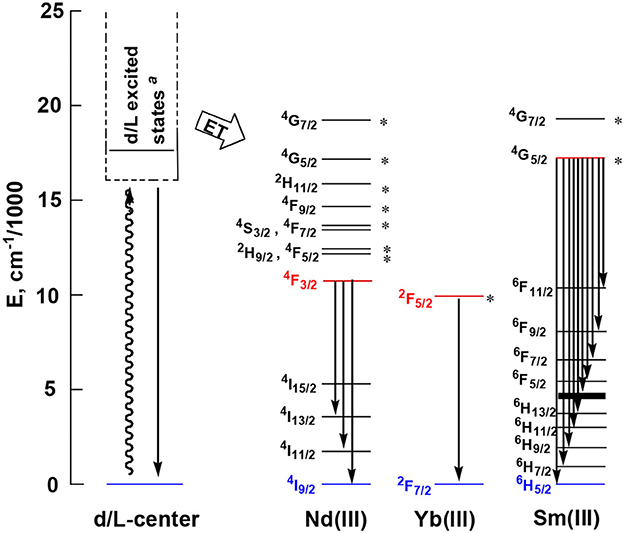
Scheme 2. Energy level diagram of lanthanide ions in 1-6 (The excited states marked with * can accept energy from d/L center by either Förster or Dexter mechanism) (Bünzli and Piguet, 2005).
The emission of the Schiff base ligand is also found in the visible emission spectra of 3 and 6, indicating the energy transfer from Zn/L- and Cd/L-center to Sm3+ is not complete and the emission of Sm3+ is not strong enough to conceal the emission of the ligand. As we know, the coordinated OH− anions in the clusters are closed to the lanthanide ions and can partially quench their emission (Richardson, 1982; Yanagida et al., 1998). As shown in Figures 8, 9, for either visible or NIR emission, 3 and 6 exhibit two excitation bands (λex = 315–416 nm, Table 1), which are from ligand-centered excited states. For 6, these two excitation bands have similar intensities. It is noticeable that, for the NIR emission of 3, the intensity of the excitation band at 315 nm is much higher than that at 401 nm, indicating that the NIR luminescence of 3 is dominated by the former. However, the absorption of 3 at 315 nm is very low (ε = 0.01 × 105 M−1 cm−1), which is not advantageous for the ligand-center to absorb energy for sensitizing the lanthanide luminescence. As shown in Table 1, the NIR emission quantum yield of 3 is found to be only 0.03%, which is more than ten times less than that of 6. Thus, the ability of these clusters to absorb energy at the excitation wavelengths can efficiently affect their luminescence properties. We were naturally interested in the difference in the luminescence properties between the Zn-Ln clusters formed by H2L and H2Lf (Scheme 1B). It is found that, the Zn-Nd cluster 1 has a lower energy transfer efficiency (ηsens) than [Zn8Nd4(Lf)8(OAc)8](OH)4 (21.28 vs. 39.89%), while the ηsens value of the Zn-Sm cluster 3 is similar as [Zn8Sm4(Lf)8(OAc)8](OH)4 (60.0 vs. 58.24%) (Bo et al., 2018).
In additional, the d metal ions may perturb the electronic structure of the ligand and affect its singlet and triplet excited states. These changes, in turn, can also affect how effectively the emissive states of the Ln3+ ion are sensitized by the ligand (Tang et al., 2013), resulting in chelation enhancement of the quenching (CHEQ) or chelation enhancement of the fluorescence emission (CHEF). The influence of Cu2+ ion on the luminescence of 1 was investigated in DMF. The intensities of the NIR emission of 1 were recorded as the Cu2+ ion was added with different concentration. Interestingly, the addition of Cu2+ ion resulted in the decrease of the emission intensities (Figure 11). The Cu2+ ion has an unsaturated d electronic configuration (d9) and may quench the luminescence through d-d transitions (i.e., f → d energy transfer, CHEQ) (Wen et al., 2007; Jankolovits et al., 2011).
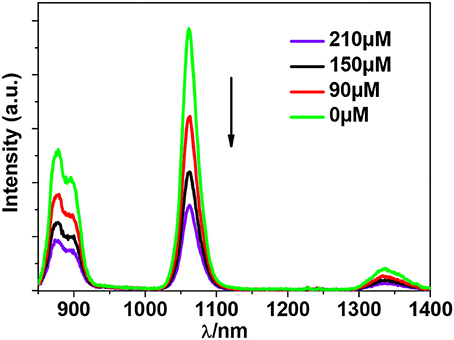
Figure 11. Decrease in the luminescence intensity of 1 in DMF upon the addition of different concentrations of Cu(OAc)2.
Conclusions
In summary, six Zn-Ln and Cd-Ln (Ln = Nd, Yb, and Sm) square-like clusters were constructed successfully from a flexible long-chain Schiff base ligand featuring a long (CH2)2O(CH2)2O(CH2)2 chain backbone. These clusters are of nanoscale proportions (i.e., 8 × 14 × 21 Å for 1), with the Schiff base ligands showing “linear” configurations. The study of luminescence properties shows that the Zn/L and Cd/L chromophores of the clusters can effectively transfer energy to the lanthanide ions, and the formers in 1, 2, and 3 have higher energy transfer efficiencies than the latters in 4, 5, and 6, respectively. The luminescence properties of the clusters may be efficiently affected by some factors such as the presence of coordinated OH− anions in the structures, the absorption at the excitation wavelengths, and the energy transfer efficiencies between the donors and accepters.
Author Contributions
XY and DS designed the experiments. TZ, HC, DJ and CW performed the experiments. SW, LB and XZ analyzed the data. TZ wrote the paper. XY, DS and XZ revised the paper.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21771141).
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fchem.2018.00321/full#supplementary-material
References
Bo, L., Wang, S., Schipper, D., Yang, X., Zhu, T., and Tao, J. (2018). Self-assembly of luminescent Zn–Ln (Ln = Sm and Nd) nanoclusters with a long-chain schiff base ligand. New J. Chem. 42, 7241–7246. doi: 10.1039/C7NJ04967F
Bünzli, J. C., and Piguet, C. (2005). Taking advantage of luminescent lanthanide ions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 34, 1048–1077. doi: 10.1039/b406082m
Chen, X., Jensen, M. P., and Liu, G. (2005). Analysis of energy level structure and excited-state dynamics in a Sm3+ complex with soft-donor ligands: Sm(Et2Dtc)3(bipy). J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 13991–13999. doi: 10.1021/jp0516700
Chow, C. Y., Eliseeva, S. V., Trivedi, E. R., Nguyen, T. N., Kampf, J. W., Petoud, S., et al. (2016). Ga3+/Ln3+ metallacrowns: a promising family of highly luminescent lanthanide complexes that covers visible and near-infrared domains. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 5100–5109. doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b00984
Fomina, I. G., Dobrokhotova, Z. V., Ilyukhin, A. B., Zhilov, V. I., Bogomyakov, A. S., Antoshkov, A. A., et al. (2014). Heterodinuclear (Sm,Tb) lanthanide pivalates with heterocyclic N-donors: synthesis, structure, thermal behavior, and magnetic and photoluminescence properties. Dalton Trans. 43, 18104–18116. doi: 10.1039/C4DT02590C
Foucault-Collet, A., Shade, C. M., Nazarenko, I., Petoud, S., and Eliseeva, S. V. (2014). Polynuclear SmIII polyamidoamine-based dendrimer: a single probe for combined visible and near-infrared live-cell imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 53, 2927–2930. doi: 10.1002/anie.201311028
Hemmila, I., and Webb, S. (1997). Time-resolved fluorometry: an overview of the labels and core technologies for drug screening applications. Drug Disc. Today 2, 373–381. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6446(97)01080-5
Horrocks, W. D., Bolender, J. P., Smith, W. D., and Supkowski, R. M. (1997). Photosensitized near infrared luminescence of ytterbium(III) in proteins and complexes occurs via an internal redox process. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 119, 5972–5973. doi: 10.1021/ja964421l
Jankolovits, J., Andolina, C. M., Kampf, J. W., Raymond, K. N., and Pecoraro, V. L. (2011). Assembly of near-fnfrared luminescent lanthanide host(host-guest) complexes with a metallacrown sandwich motif. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 50, 9660–9664. doi: 10.1002/anie.201103851
Kauffman, D. R., Alfonso, D., Matranga, C., Ohodnicki, P., Deng, X., Siva, R. C., et al. (2014). Probing active site chemistry with differently charged Au25q nanoclusters (q = −1, 0, +1). Chem. Sci. 5, 3151–3157. doi: 10.1039/c4sc00997e
Lam, F., Xu, J. X., and Chan, K. S. (1996). Binucleating ligands: synthesis of acyclic achiral and chiral Schiff base-pyridine and Schiff base-phosphine ligands. J. Org. Chem. 61, 8414–8418. doi: 10.1021/jo961020f
Li, M., Tian, S., Wu, Z., and Jin, R. (2015). Cu2+ induced formation of Au44(SC2H4Ph)32 and its high catalytic activity for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol at low temperature. Chem. Commun. 51, 4433–4436.
Lunstroot, K., Nockemann, P., Hecke, K. V., Meervelt, L. V., Gorller-Walrand, C., Binnemans, K., et al. (2009). Visible and near-infrared emission by samarium(III)-containing ionic liquid mixtures. Inorg. Chem. 48, 3018–3026. doi: 10.1021/ic8020782
Malba, C. M., Enrichi, F., Facchin, M., Demitri, N., Plaisier, J. R., Natile, M. M., et al. (2015). Phosphonium-based tetrakis dibenzoylmethane Eu(III) and Sm(III) complexes: synthesis, crystal structure and photoluminescence properties in a weakly coordinating phosphonium ionic liquid. RCS Adv. 5, 60898–60907. doi: 10.1039/C5RA03947A
María, J. B. L., Plinio, C. L., César, Z., Ana, B. F., Dayán, P. H., and Ramiro, A. P. (2017). Theoretical method for an accurate elucidation of energy transfer pathways in europium(III) complexes with dipyridophenazine (dppz) ligand: one more step in the study of the molecular antenna effect. Inorg. Chem. 56, 9200–9208. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.7b01221
Meshkova, S. B., Topilova, Z. M., Bolshoy, D. V., Beltyukova, S. V., Tsvirko, M. P., Venchikov, V. Y., et al. (1999). Quantum efficiency of the luminescence of Ytterbium(III) β-diketonates. Acta Phys. Pol. Ser. A 95, 983–990. doi: 10.12693/APhysPolA.95.983
Pasatoiu, T. D., Madalan, A. M., Zamfirescu, M., Tiseanu, C., and Andruh, M. (2012). One- and two-photon induced emission in heterobimetallic ZnII–SmIII and ZnII–TbIII complexes with a side-off compartmental ligand. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 14, 11448–11456. doi: 10.1039/c2cp41026e
Pasatoiu, T. D., Tiseanu, C., Madalan, A. M., Jurca, B., Duhayon, C., Sutter, J. P., et al. (2011). Study of the luminescent and magnetic properties of a series of heterodinuclear [ZnIILnIII] complexes. Inorg. Chem. 50, 5879–5889. doi: 10.1021/ic200426w
Peng, J. B., Zhang, Q. C., Kong, X. J., Zheng, Y. Z., Ren, Y. P., Long, L. S., et al. (2012). High-nuclearity 3d-4f clusters as enhanced magnetic coolers and molecular magnets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 3314–3317. doi: 10.1021/ja209752z
Reinhard, C., and Gudel, H. U. (2002). High-resolution optical spectroscopy of Na3[Ln(dpa)3]·13H2O with Ln = Er3+, Tm3+, Yb3+. Inorg. Chem. 41, 1048–1055. doi: 10.1021/ic0108484
Richardson, F. S. (1982). Terbium(III) and europium(III) ions as luminescent probes and stains for biomolecular systems. Chem. Rev. 82, 541–552. doi: 10.1021/cr00051a004
Sabbatini, N., Dellonte, S., and Blasse, G. (2011). The luminescence of the rare earth cryptates [terbium ⊂ 2.2.1]3+ and [samarium ⊂ 2.2.1]3+. Chem. Phys. Lett. 129, 541–545. doi: 10.1016/0009-2614(86)80397-9
Shavaleev, N. M., Accorsi, G., Virgili, D., Bell, D. R., Lazarides, T., Calogero, G., et al. (2005). Syntheses and crystal structures of dinuclear complexes containing d-block and f-block luminophors. sensitization of nir luminescence from Yb(III), Nd(III), and Er(III) centers by energy transfer from Re(I)- and Pt(II)-bipyrimidine metal centers. Inorg. Chem. 44, 61–72. doi: 10.1021/ic048875s
Sun, L., Qiu, Y., Liu, T., Peng, H., Deng, W., Wang, Z., et al. (2013). Visible-light sensitized sol-gel-based lanthanide complexes (Sm, Yb, Nd, Er, Pr, Ho, Tm): microstructure, photoluminescence study, and thermostability. RCS Adv. 3, 26367–26375. doi: 10.1039/c3ra45202f
Tang, Q., Liu, S., Liu, Y., Miao, J., Li, S., Zhang, L., et al. (2013). Cation sensing by a luminescent metal-organic framework with multiple lewis basic sites. Inorg. Chem. 52, 2799–2801. doi: 10.1021/ic400029p
Wang, B., Zang, Z., Wang, H., Dou, W., Tang, X., Liu, W., et al. (2013). Multiple lanthanide helicate clusters and the effects of anions on their configuration. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 52, 3756–3759. doi: 10.1002/anie.201210172
Watanabe, R., Fujiwara, K., Okazawa, A., Tamnaka, G., Yoshii, S., Nojiri, H., et al. (2011). Chemical trend of Ln-M exchange couplings in heterometallic complexes with Ln = Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er and M = Cu, V. Chem. Commun. 47, 2110–2112. doi: 10.1039/C0CC04669H
Wen, V., Zhao, Y., Wang, L., Zhang, M., and Gao, D. (2007). Synthesis and fluorescence properties of Europium, Terbium doped Zn2+, Cd2+ and Cr3+ complexes. J. Rare Earths 25, 679–683. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0721(08)60006-X
Yamaguchi, T., Costes, J. P., Kishima, Y., Kojima, M., Sunatsuki, Y., Bréfuel, N., et al. (2010). Face-sharing heterotrinuclear MII-LnIII-MII (M = Mn, Fe, Co, Zn; Ln = La, Gd, Tb, Dy) complexes: synthesis, structures, and magnetic properties. Inorg. Chem. 49, 9125–9135. doi: 10.1021/ic100460w
Yanagida, S., Hasegawa, Y., Murakoshi, K., Wada, Y., Nakashima, N., and Yamanaka, T. (1998). Strategies for enhancing photoluminescence of Nd3+ in liquid media. Coord. Chem. Rev. 171, 461–480. doi: 10.1016/S0010-8545(98)90069-8
Yang, X. P., Jones, R. A., and Huang, S. M. (2014). Luminescent 4f and d-4f polynuclear complexes and coordination polymers with flexible salen-type ligands. Coord. Chem. Rev. 273, 63–75. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2013.11.012
Yang, X. P., Schipper, D., Jones, R. A., Lytwak, L. A., Holliday, B. J., and Huang, S. M. (2013). Anion dependent self-assmbly of NIR luminescent 24- and 32-metal Cd-Ln complexes with drum-like architectures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 8468–8471. doi: 10.1021/ja4031243
Zheng, S., Yang, J., Yu, X., Chen, X., and Wong, W. (2004). Syntheses, structures, photoluminescence, and theoretical studies of d10 metal complexes of 2,2'-Dihydroxy-[1,1']Binaphthalenyl-3,3'-dicarboxylate. Inorg. Chem. 43, 830–838. doi: 10.1021/ic034847i
Keywords: self-assembly, lanthanide, flexible long-chain schiff base ligand, nanoclusters, visible and NIR luminescent
Citation: Zhu T, Yang X, Zheng X, Wang S, Bo L, Wang C, Chen H, Jiang D and Schipper D (2018) Luminescent Polynuclear Zn- and Cd-Ln Square-Like Nanoclusters With a Flexible Long-Chain Schiff Base Ligand. Front. Chem. 6:321. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2018.00321
Received: 11 March 2018; Accepted: 10 July 2018;
Published: 31 July 2018.
Edited by:
Carlos Lodeiro, Universidade Nova de Lisboa, PortugalReviewed by:
Ramiro Arratia-Perez, Universidad Andrés Bello, ChileFernando Novio, Instituto Catalán de Nanociencia y Nanotecnología (CIN2), Spain
Copyright © 2018 Zhu, Yang, Zheng, Wang, Bo, Wang, Chen, Jiang and Schipper. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaoping Yang, eHB5YW5nQHd6dS5lZHUuY24=
 Ting Zhu
Ting Zhu Xiaoping Yang
Xiaoping Yang Xiaohui Zheng2
Xiaohui Zheng2 Chengri Wang
Chengri Wang Hongfen Chen
Hongfen Chen Dongmei Jiang
Dongmei Jiang Desmond Schipper
Desmond Schipper