Acidic Versus Alkaline Bacterial Degradation of Lignin Through Engineered Strain E. coli BL21(Lacc): Exploring the Differences in Chemical Structure, Morphology, and Degradation Products
- 1Biofuels Institute, School of Environmental Science and Safety Engineering, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang, China
- 2State Key Laboratory of Applied Microbiology Southern China, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Microbial Culture Collection and Application, Guangdong Open Laboratory of Applied Microbiology, Guangdong Institute of Microbiology, Guangdong Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou, China
- 3Botany Department, Faculty of Science, Tanta University, Tanta, Egypt
- 4School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang, China
- 5School of Public Affairs, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China
by Murillo Morales, G., Ali, S. S., Si, H., Zhang, W., Zhang, R., Hosseini, K., et al. (2020). Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 8:671. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00671
In the published article, there were errors in affiliations of the authors Sameh S. Ali, Weimin Zhang and Daochen Zhu. For author Sameh S. Ali, the second affiliation should be “Botany Department, Faculty of Science, Tanta University, Tanta, Egypt” instead of “State Key Laboratory of Applied Microbiology Southern China, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Microbial Culture Collection and Application, Guangdong Open Laboratory of Applied Microbiology, Guangdong Institute of Microbiology, Guangdong Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou, China.” Regarding to the numbering of the affiliations, the affiliation of Botany Department, Faculty of Science, Tanta University, Tanta, Egypt, instead of having affiliation #2, it should have the affiliation #3. For author Weimin Zhang, the affiliation should be “State Key Laboratory of Applied Microbiology Southern China, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Microbial Culture Collection and Application, Guangdong Open Laboratory of Applied Microbiology, Guangdong Institute of Microbiology, Guangdong Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou, China” instead of “Botany Department, Faculty of Science, Tanta University, Tanta, Egypt.” For author Daochen Zhu, the second affiliation should be “State Key Laboratory of Applied Microbiology Southern China, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Microbial Culture Collection and Application, Guangdong Open Laboratory of Applied Microbiology, Guangdong Institute of Microbiology, Guangdong Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou, China” instead of Botany Department, Faculty of Science, Tanta University, Tanta, Egypt. Regarding to the numbering of the affiliations, the affiliation of the State Key Laboratory of Applied Microbiology Southern China, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Microbial Culture Collection and Application, Guangdong Open Laboratory of Applied Microbiology, Guangdong Institute of Microbiology, Guangdong Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou, China, instead of having affiliation #3, it should have the affiliation #2.
Also, in the article's citation, an author name was incorrectly presented as Morales GM. The correct spelling is Murillo Morales G.
Additionally, Figures 1–5 were presented in a wrong order. Figure 1 should be Figure 5, Figure 2 should be Figure 1, Figure 3 should be Figure 2, Figure 4 should be Figure 3, and Figure 5 should be Figure 4.
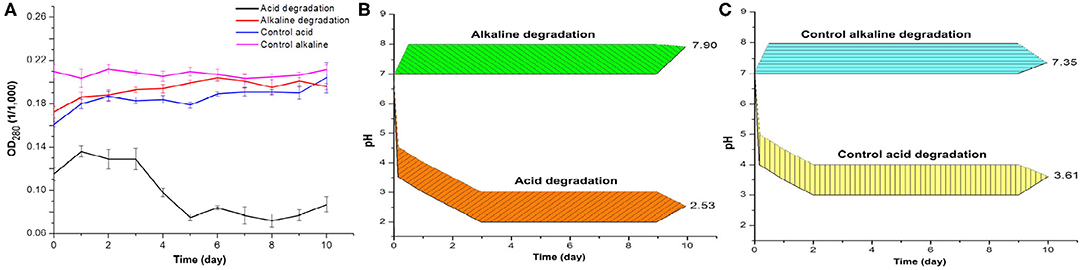
Figure 1. (A) Optical density of acid and alkaline-biodegraded lignin and controls at 280 nm. (B) pH measures of acid and alkaline-biodegraded lignin and (C) pH measures of controls. The range of the pH measures is ±0.50.
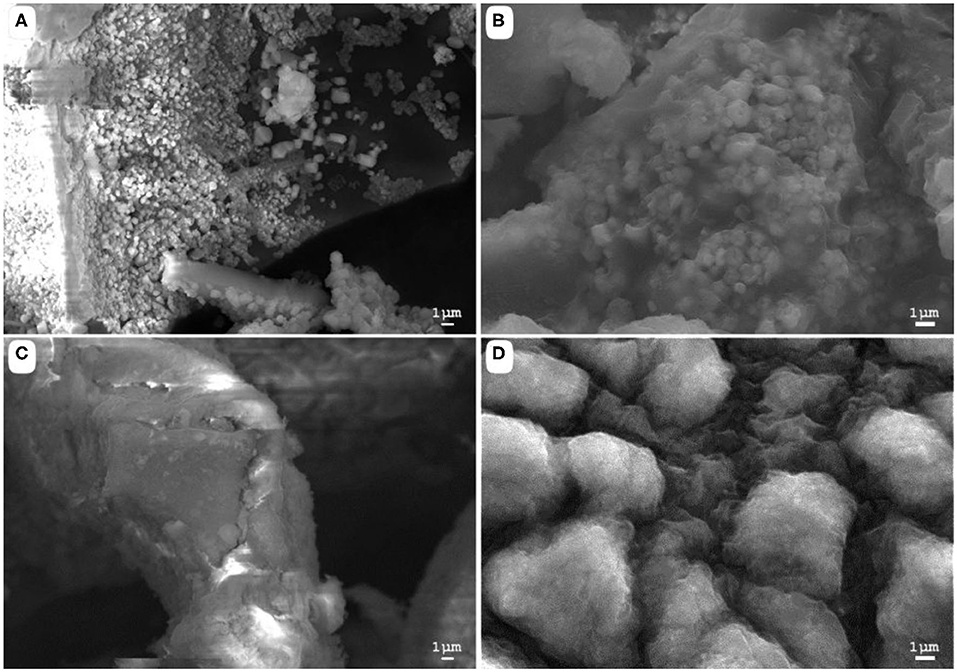

Figure 2. Scanning electron microscopy images of (A) acid-biodegraded lignin, (B) alkaline-biodegraded lignin, (C) control of acid biodegradation, and (D) control of alkaline biodegradation. Scale of reference of 1 μm.
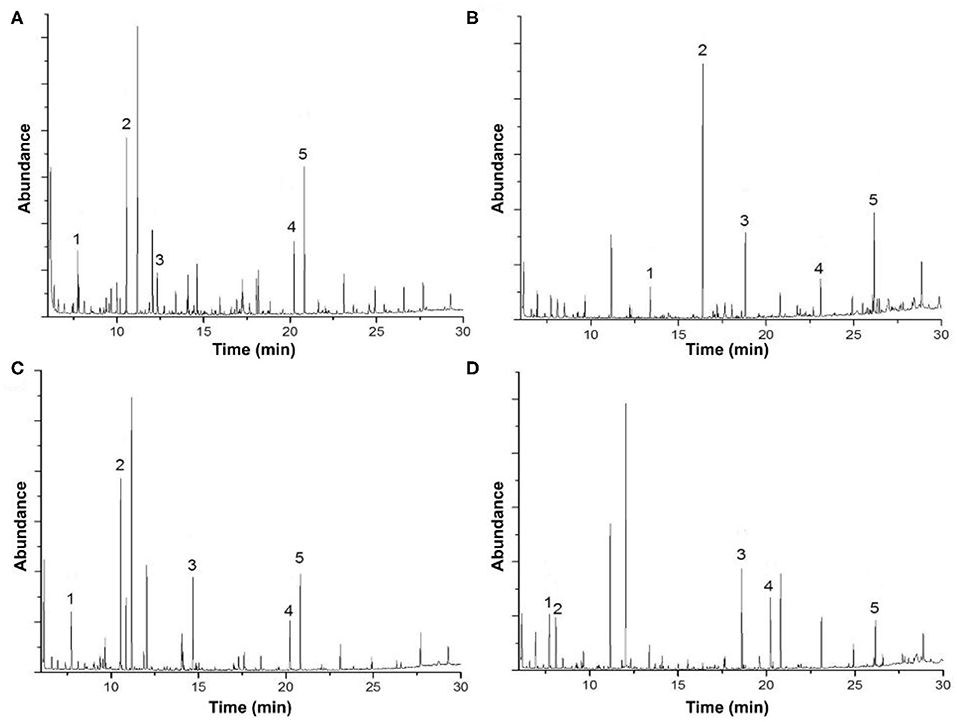
Figure 3. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis of (A) acid biodegradation of lignin, (B) alkaline biodegradation of lignin, (C) control for acid biodegradation, and (D) control for alkaline biodegradation.
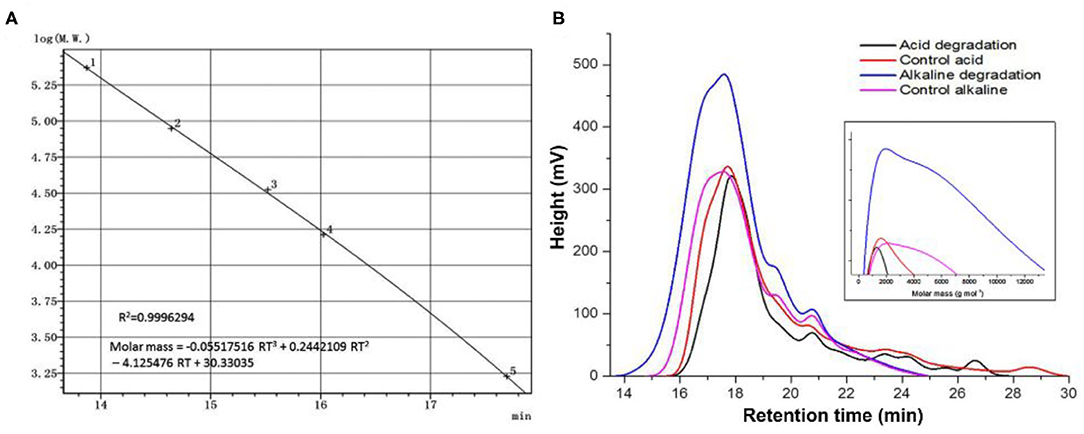
Figure 4. Size exclusion chromatography analysis. (A) Universal calibration, (B) curves of acid, alkaline biodegradation of lignin, and controls. From the equation of the universal calibration, “RT” means “retention time.”
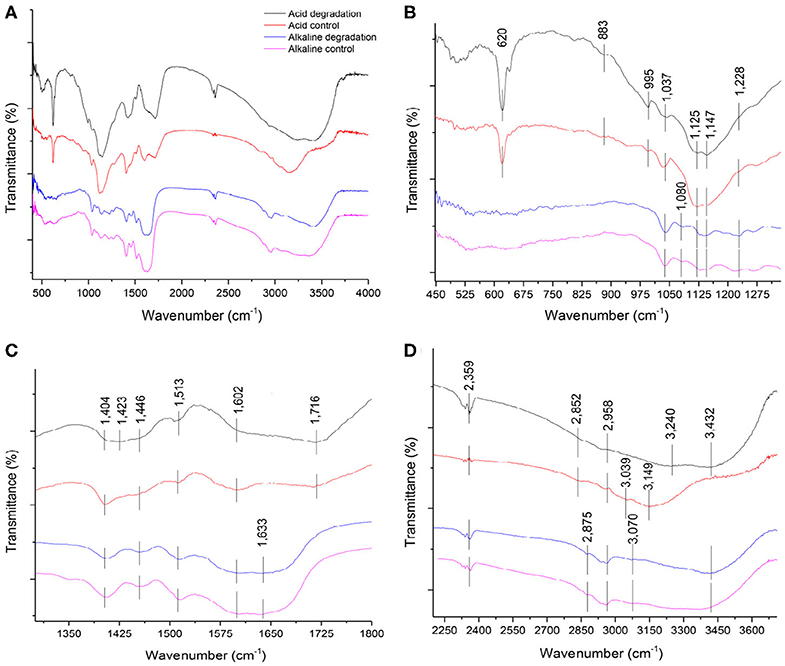
Figure 5. (A) Overall FTIR spectra of acid and alkaline biodegradation of lignin and controls; (B) spectra from wave numbers 450–1,300 cm−1; (C) 1,300–1,800 cm−1; (D) 2,250–3,700 cm−1.
There was also an error in the abstract text. The name of the mutant bacterial strain was incorrectly written as E.coli BL21 (Laccase). Instead, it should be written as E.coli BL21 (Lacc). A correction has been made to abstract, last sentence:
“Lignin biodegradation products from E.coli BL21 (Lacc), under different initial pH conditions, demonstrated a promising potential to enlarge the spectrum of renewable products for biorefinery activities.”
The authors apologize for these errors and state that they do not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Keywords: lignin, E. coli BL21(Lacc), biodegradation compounds, acid/alkaline incubation, depolymerization/repolymerization
Citation: Murillo Morales G, Ali SS, Si H, Zhang W, Zhang R, Hosseini K, Sun J and Zhu D (2020) Corrigendum: Acidic Versus Alkaline Bacterial Degradation of Lignin Through Engineered Strain E. coli BL21(Lacc): Exploring the Differences in Chemical Structure, Morphology, and Degradation Products. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 8:868. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00868
Received: 03 July 2020; Accepted: 06 July 2020;
Published: 11 August 2020.
Approved by:
Frontiers Editorial Office, Frontiers Media SA, SwitzerlandCopyright © 2020 Murillo Morales, Ali, Si, Zhang, Zhang, Hosseini, Sun and Zhu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jianzhong Sun, anpzdW4xMDAyQGhvdG1haWwuY29t; Daochen Zhu, ZGN6aHVjbkBob3RtYWlsLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Gabriel Murillo Morales
Gabriel Murillo Morales Sameh S. Ali
Sameh S. Ali Haibing Si1
Haibing Si1 Weimin Zhang
Weimin Zhang Keyvan Hosseini
Keyvan Hosseini