Multivalent DNA aptamers as potent inhibitors of L-selectin mediated lymphocyte rolling
-
1
Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Institute for Laboratory Medicine, Germany
-
2
University of Muenster, Institute for Physiology, Germany
Introduction: The adhesion receptor L-selectin mediates the extravasation of leukocytes from the blood into the surrounding tissue during inflammation and homeostasis. The single binding event to its ligands is very weak but strongly enhanced by multivalent interactions. We have previously described L-selectin targeting by the pleiotropic synthetic polyanion dPGS [1],[2]. Aptamers are short oligonucleotides with favorable use in clinical settings due to their high specificity and low immunogenicity. In this study, we characterized the structural requirements of an L-selectin aptamer for effective receptor binding and evaluated the impact of multivalency.
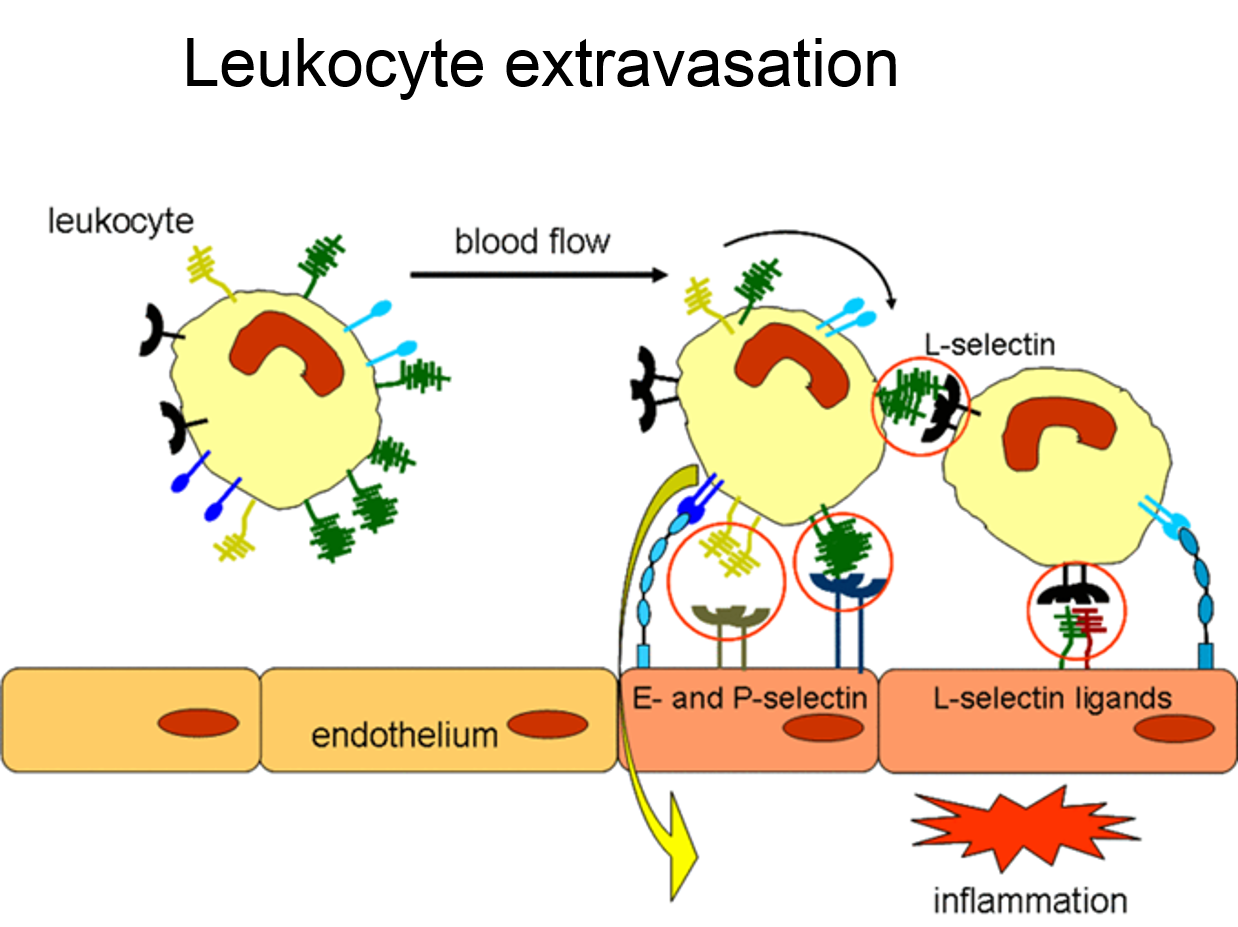
Material and Methods: Deletion and point mutations of the DNA aptamer sequence defined structural essential parts of aptamer sequence. Target binding was initially screened by surface plasmon resonance (SPR). Di- and trimeric aptamers were prepared by linkage to polyadenosine spacers of different length. Again the optimal spacer length was evaluated by SPR. Further evaluation of aptamer functionality was performed in a flow chamber where binding of leukocytes to immobilized ligands was analyzed with respect to aptamer concentrations which block the adhesion receptor L-selectin. Finally, aptamer function was evaluated in vivo, in a model of leukocyte extravasation by intravital microscopy.
Results and Discussion: Structural optimization of the L-selectin targeting aptamer led to a size reduction of 22% while maintaining binding efficiency. Surface plasmon resonance experiments showed superior blocking effects of multivalent aptamers, even compared to the monoclonal inhibitory antibody DREG-200. This finding was confirmed both in flow chamber experiments and in vivo using intravital imaging of the peripheral lymph node. Together, these data demonstrate that optimization of DNA structure and a multivalent display significantly increase the functionality and versatility of aptamer-based drugs.
References:
[1] Dernedde et al., 2010, PNAS, 107, 19679
[2] Oishi et al., 2014, Arthritis Rheumatol, 66, 1864
Keywords:
in vivo,
blood vessel,
Imaging method,
Bioactive molecule
Conference:
10th World Biomaterials Congress, Montréal, Canada, 17 May - 22 May, 2016.
Presentation Type:
Poster
Topic:
Nano-structured materials for unique functions
Citation:
Dernedde
J,
Riese
SS,
Buscher
KK,
Enders
SS,
Kuehne
CC and
Tauber
RR
(2016). Multivalent DNA aptamers as potent inhibitors of L-selectin mediated lymphocyte rolling.
Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol.
Conference Abstract:
10th World Biomaterials Congress.
doi: 10.3389/conf.FBIOE.2016.01.03029
Copyright:
The abstracts in this collection have not been subject to any Frontiers peer review or checks, and are not endorsed by Frontiers.
They are made available through the Frontiers publishing platform as a service to conference organizers and presenters.
The copyright in the individual abstracts is owned by the author of each abstract or his/her employer unless otherwise stated.
Each abstract, as well as the collection of abstracts, are published under a Creative Commons CC-BY 4.0 (attribution) licence (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/) and may thus be reproduced, translated, adapted and be the subject of derivative works provided the authors and Frontiers are attributed.
For Frontiers’ terms and conditions please see https://www.frontiersin.org/legal/terms-and-conditions.
Received:
28 Mar 2016;
Published Online:
30 Mar 2016.