Introduction: The combination of several processing technologies can open the possibility for producing scaffolds with superior performance for tissue engineering (TE) applications. Hydrogels are structurally similar to the natural extracellular matrix microenvironment presenting high elasticity and resistance to compression forces. They have been extensively used in biomedical devices fabrication and for TE applications, including for cartilage defects repair[1]. Recently, it was found that proteins like silk fibroin (SF), presenting tyrosine groups can be used to prepare fast formed hydrogels with controlled gelation properties, via an enzyme-mediated cross-linking reaction using horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)[2],[3]. Moreover, the high versatility, processability and tailored mechanical properties of SF, make this natural polymer attractive for the development of innovative scaffolding strategies for cartilage TE applications[4],[5].
Materials and Methods: The present work proposes a novel route for developing SF-based scaffolds derived from high-concentrated SF (16wt%) enzymatically cross-linked by a HRP/H2O2 complex. The combination of salt-leaching and freeze-drying methodologies was used to prepare macro/microporous SF scaffolds with an interconnected structure and specific features regarding biodegradation and mechanical properties (Fig. 1a). The scaffolds morphology and porosity were analyzed by SEM and micro-CT. The mechanical properties (Instron) and protein conformation (FTIR, XRD) were also assessed. In order to evaluate the scaffolds structural integrity, swelling ratio and degradation profile studies were performed for a period of 30 day. This work also aims to evaluate the in vitro chondrogenic differentiation response by culturing human adipose derived stem cells (hASCs) over 21 days in basal and chondrogenic conditions. Cell behaviour in the presence of the macro/microporous structures will be evaluated through different quantitative (Live/Dead, DNA, GAGs, RT PCR) and qualitative (SEM, histology, immunocytochemistry) assays.
Results and Discussion: The macro/microporous SF scaffolds showed high porosity and interconnectivity with the trabecular structures evenly distributed (Fig. 1b,c). A dramatic decrease of compressive modulus was observed for samples in hydrated state. Chemical analysis revealed that SF scaffolds displayed the characteristic peaks for β-sheet conformation. Swelling ratio data demonstrated a large swelling capacity, maintaining their structural integrity for 30 days. As expected, when immersed in protease XIV the degradation rate of SF scaffolds increased. Based on the promising morphology and physicochemical properties of the developed SF scaffolds, in vitro chondrogenic differentiation studies with hASCs are envisioned in order to validate their performance for cartilage regeneration applications.
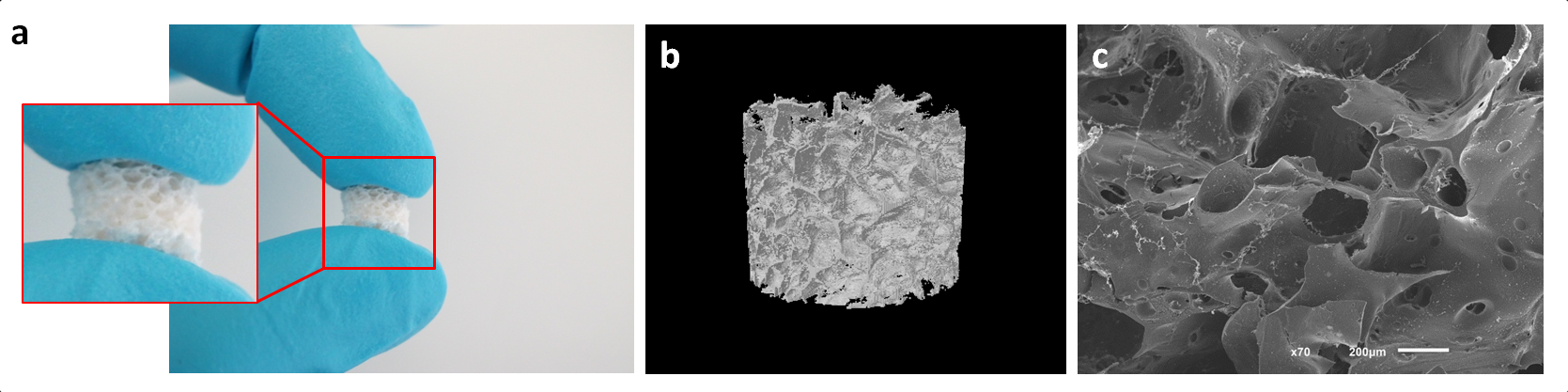
Figure 1- (a) Macroscopic image, (b)Three-dimensional micro-CT image and (c) SEM micrograph (cross-section) of the SF scaffolds.
Conclusion: This study proposes an innovative approach to produce fast-formed porous SF scaffolds using enzymatically cross-linked SF hydrogels structured by the combination of salt-leaching and freeze-drying methodologies. The obtained results can provide a valuable reference of SF as a tunable and versatile biomaterial with great potential for applications in cartilage TE scaffolding.
Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT) project PEst-C/SAU/LA0026/201; ERDP funding through POCTEP Project 0687_NOVOMAR_1_P; Investigator FCT program IF/00423/2012 and IF/00411/2013
References:
[1] Xia, L.-W., R. Xie, X.-J. Ju, W. Wang, Q. Chen, and L.-Y. Chu, Nano-structured smart hydrogels with rapid response and high elasticity. Nature communications, 2013. 4.
[2] Sofia, S.J., A. Singh, and D.L. Kaplan, Peroxidase-catalyzed crosslinking of functionalized polyaspartic acid polymers. Journal of Macromolecular Science, Part A, 2002. 39(10): p. 1151-1181.
[3] Reis, R.L., L.-P. Yan, A.L. Oliveira, J.M. Oliveira, D.R. Pereira, C. Correia, and R.A. Sousa, Hydrogels derived from silk fibroin: Methods and uses thereof. 2014. 107426.
[4] Chen, C.-H., J.M.-J. Liu, C.-K. Chua, S.-M. Chou, V.B.-H. Shyu, and J.-P. Chen, Cartilage tissue engineering with silk fibroin scaffolds fabricated by indirect additive manufacturing technology. Materials, 2014. 7(3): p. 2104-2119.
[5] Yan, L.-P., J.M. Oliveira, A.L. Oliveira, S.G. Caridade, J.F. Mano, and R.L. Reis, Macro/microporous silk fibroin scaffolds with potential for articular cartilage and meniscus tissue engineering applications. Acta biomaterialia, 2012. 8(1): p. 289-301.