Introduction: Bacterial and viral DNA containing unmethylated cytosine-guanine (CpG) dinucleotides stimulate the mammalian innate immune system[1]. This process is mediated by the activation of Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9), a member of Toll-like receptor family. Synthetic short, single-stranded oligodeoxynucleotides (ODNs) that contain CpG motifs are similar to those found in bacterial DNA and stimulate a similar immune response. As such, CpG ODNs have potential for clinical applications in the treatment of infectious diseases, allergies, and cancers[2]. However, the immunostimulatory effects are limited by the poor stability and cellular uptake of CpG ODNs. Delivery of unmodified CpG ODNs using carrier nanoparticles is a strategy to improve stability and enhance cellular uptake.
With its novel properties and structural similarity to carbon, boron nitride (BN) has received considerable scientific interest. BN has the advantage of high biocompatibility, with easier cellular uptake and lower toxicity than carbon. Previous results showed that BN nanosphere (BNNS) had little cytotoxicity, and protected unmodified CpG ODNs from degradation by serum nucleases. In addition, BNNS taken up by cells localized to endolysosomes, and this localization was maintained even after cell division. This was particularly advantageous, since TLR9 also localizes to endolysosomes. However, the loading capacity of CpG ODNs on the surface of BNNS was not sufficient to induce a robust cytokine response. Therefore, their immunostimulatory effect was also limited.
In this study, we developed novel delivery systems for CpG ODNs through functionalization of BNNS. First, we identified a peptide with high affinity for BNNS, then we used this peptide as linker molecule to enhance the loading of CpG ODNs on BNNS. Next, we used the cationic polymer to functionalize BNNS and obtain the postitive surface charge which make it easier to bind the nagetive-charged CpG ODNs. Enhanced cytokine stimulation and immunostimulatory effect of CpG ODNs using these delivery systems were also investigated.
Materials and Methods: BNNS with high purity were synthesized by a chemical vapor deposition method. BNNS-binding peptide was identified using phage display technique. Cationic polymer such as chitosan or PEI are functionalized on the surface of BNNS via electrostatic interactions. CpG ODNs loading and releasing behavior on BNNS carriers were studied. Intracellular uptake of CpG ODNs was investigated by confocal laser scanning microscope. Cytokines stimulation from PBMCs were analyzed using ELISA.
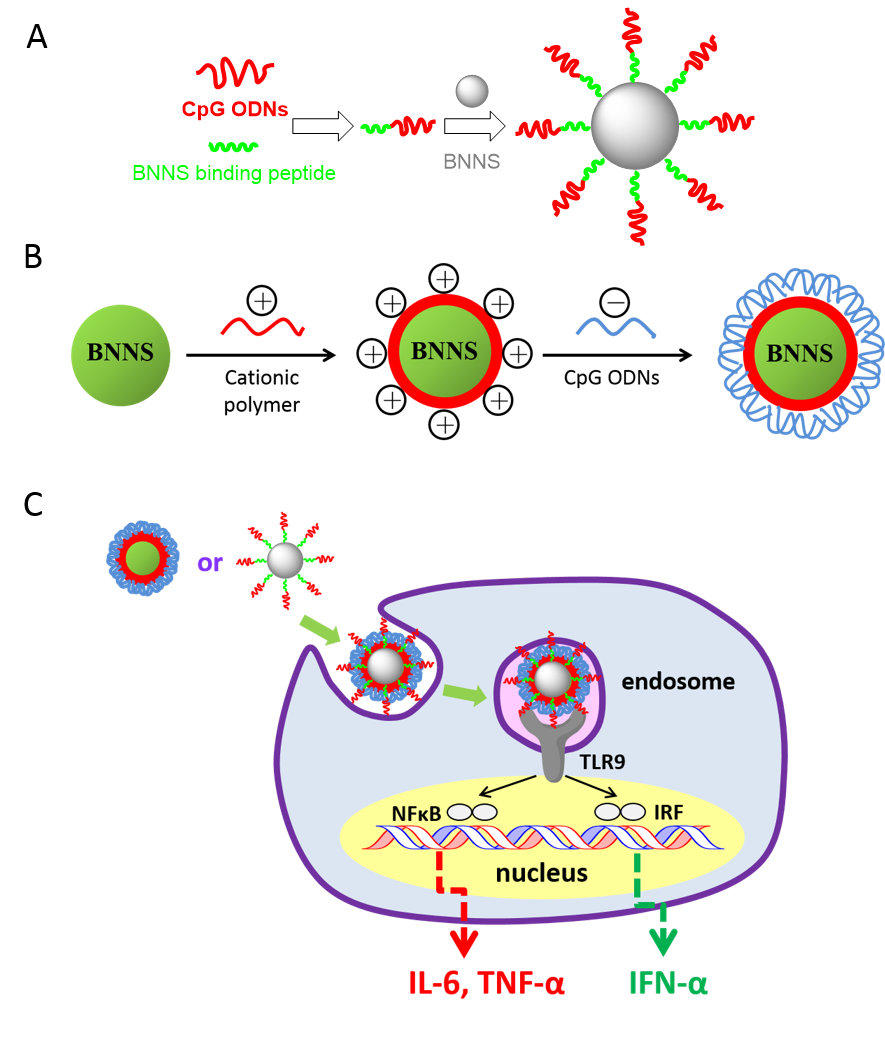
Fig. 1. Schematic illustration of construction of BNNS-based CpG ODNs delivery systems (A,B) and their enhanced immunostimulatory effect (C).
Results and Discussion: These delivery systems greatly improved the loading capacity and cellular uptake of CpG ODNs and increased the interaction between CpG ODNs and TLR9. They are proved to be effective in enhancing the immunostimulatory effect of CpG ODNs.
Conclusions: BNNS-based delivery systems provide a promising strategy to enhance the delivery efficiency and immunostimulatory effect of CpG ODNs.
This work was supported by Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. JUSRP11427) and Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars, State Education Ministry.
References:
[1] Krieg AM, Yi AK, Matson S, et al. CpG motifs in bacterial DNA trigger direct B-cell activation[J]. Nature. 1995,374(6522):546–549.
[2] Klinman DM. Immunotherapeutic uses of CpG oligodeoxynucleotides[J]. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004,4(4):248–257.