Introduction: In these years, we have succeeded in the syntheses of novel diamine and diol monomers containing phosphorylcholine (PC) moiety as monomers to develop new biocompatible polymer materials[1]-[4]. The obtained PC-containing polymers from these monomers exhibited the excellent biocompatibility derived from PC unit in addition to the processability, the thermal stability and the mechanical strength. On the other hand, we focused on the processing for free-standing ultrathin films with a thickness less than 100 nm (so-called nanosheets), which exhibited the unique properties such as high adhesive strength, flexibility and smoothness[5],[6]. If the nanosheets could be fabricated from the PC-containing polymers, the applications as new biomaterials would be significantly advanced. In this paper, we prepared the nanosheets from polyimides and polyurethanes containing PC moiety and investigated the biocompatibility of the nanosheet surface.
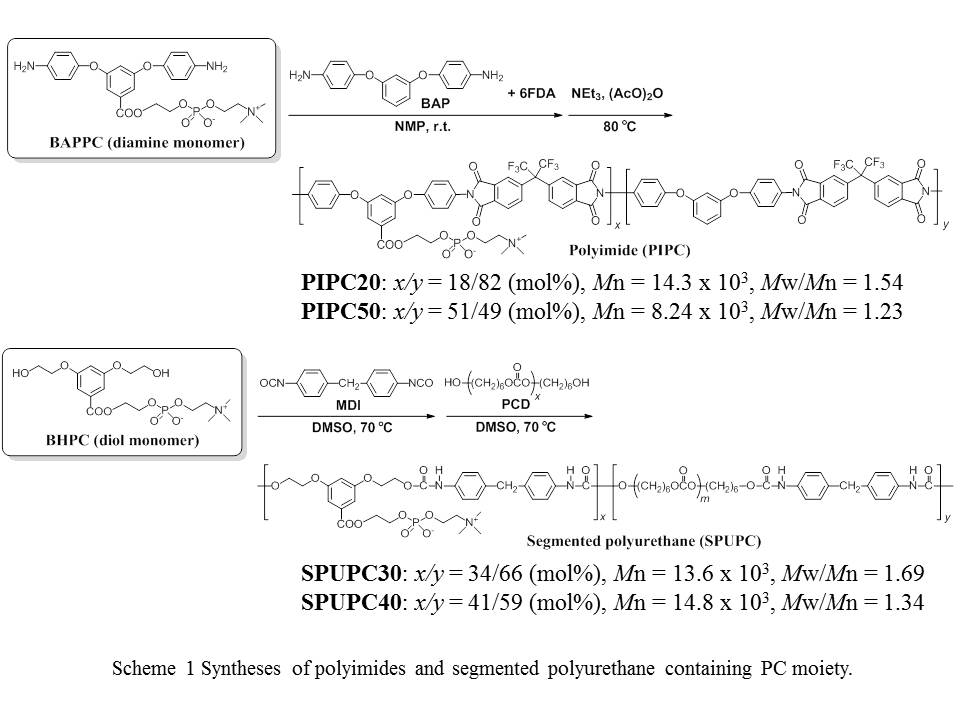
Materials and Methods: A diamine monomer, 2-[3,5-bis(4-aminophenoxy)phenylcarbonyloxy]ethyl phosphorylcholine (BAPPC), and a diol monomer, 2-(3,5-bis(2-hydroxyethoxy)benzoyloxy)ethyl phosphorylcholine (BHPC) were synthesized according to the literatures[1],[3]. Then, polyimides (PIPC) and segmented polyurethanes (SPUPC) containing PC component were prepared by using these monomers, as shown in Scheme 1.
Self-standing nanosheets were fabricated by spin-coating with “sacrificial layer method” as described in the literature[5]. The large area of nanosheets was also fabricated by a roll-to-roll method, and was homogenized in water to obtain the dispersion of fragmented nanosheets. For example, the average surface area of fragmented PIPC50 and SPUPC40 nanosheets were 6.8 x 10-3 mm2 and 3.9 x 10-3 mm2, respectively.
Results and Discussion: Polyimides (PIPC20, 50) and polyurethanes (SPUPC30, 40) were prepared by polycondensation or polyaddition using these PC-containing monomers. These polymers had a thermal stability up to 200°C, and the polyurethane films exhibited the elastomeric properties. In fact, the nanosheets were successfully prepared, the thickness of which was 40 - 100 nm. The adhesive strength of the nanosheets increased as the thickness was less than 100 nm, because the nanosheets could conform to the roughness of the substrate due to its flexibility. Furthermore, the fragmented nanosheets were effectively coated with patchwork-like adhesion behavior by just casting or dipping on the substrate. It was also confirmed that the excellent blood compatibility was observed on the surfaces coated with the fragmented PC-polymer nanosheets, as shown in Figure 1.

Conclusion: We have developed the fragmented nanosheets with submillimeter-size to coat irregular and uneven surfaces with the biocompatible polymers. Hence, these nanosheets composed of PC-containing polymers may be great promise as novel surface modifiers to provide the biocompatibility to the surface of various medical devices such as catheters, artificial organs, microfluidic devices, etc.
References:
[1] K. Horiguchi, N. Shimoyamada, D. Nagawa Y. Nagase, Y. Iwasaki, K. Ishihara, Trans. Mater. Res. Soc. Jpn. 33, 1261-1264 (2008).
[2] Y. Nagase, K. Horiguchi, Biomedical Engineering - Frontiers and Challenges, Chapter 11 217-232 (2011), InTech, Croatia.
[3] Y. Sakagami, K. Horiguchi, Y. Narita, W. Sirithep, K. Morita, Y. Nagase, Polym. J. 45, 1159-1166 (2013).
[4] W. Sirithep, K. Morita, A. Iwano, T. Komachi, Y. Okamura, Y. Nagase, J. Biomater. Sci., Polym. Ed. 25, 1540-1557 (2014) .
[5] Y. Okamura, K. Kabata, M. Kinoshita, D. Saito, S. Takeoka, Adv. Mater. 21, 4388-4392 (2009).
[6] Y. Okamura, K. Kabata, M. Kinoshita, H. Miyazaki, A. Saito, T. Fujie, S. Ohtsubo, D. Saito, S. Takeoka, Adv. Mater. 25, 545–551 (2013).