Introduction: Despite poor performance, topical drops are by far the most widely used therapy for many ocular diseases. Static barriers including tight junctions of the conjunctiva, the hydrophobic corneal epithelium and hydrophilic corneal stroma, and dynamic barriers including the rapid tear turnover, lacrimal drainage, and the vasculature and lymphatics of the conjunctiva all conspire to prevent the majority of topically applied therapeutics from reaching their site of action. Only 5% of topically administered drug reaches the anterior structures of the eye, while less than 1% reach the posterior[1]. Consequently, drugs delivered via eye drop are massively overdosed, resulting in undesirable systemic exposure and extreme waste (>99% for many glaucoma medications). We propose the use of mucoadhesive self-assembling micelles as a solution to the obvious problems facing topical ocular drug delivery.
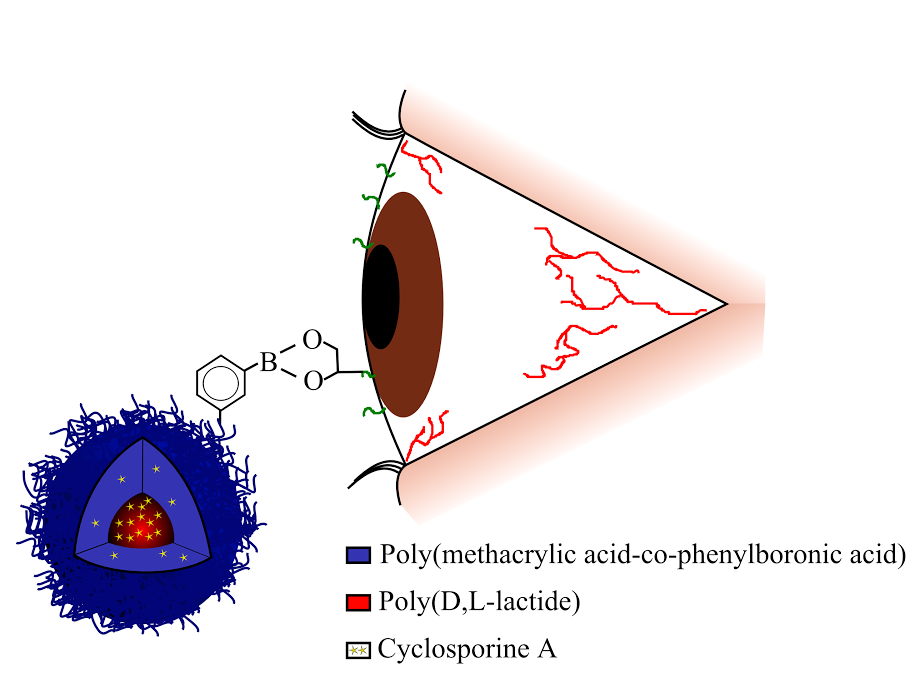
Phenylboronic acid (PBA) is a synthetic molecule with a strong affinity for mucin due to its ability to complex with 1,2-cis-diols. PBA has an extensive pedigree in biomedical engineering, including as part of an ocular delivery scheme for cyclosporine A (CycA)[2]. Thus, a series of block copolymer micelles incorporating mucoadhesive PBA into their outer shells was developed capable of targeted drug delivery to ocular tissues.
Method and Materials: pLA-b-p(MAA-PBA) copolymers were synthesized by RAFT polymerization and contained a spectrum of PBA mole percentages. The resultant copolymer was isolated by precipitation into 10 times excess of cold anhydrous diethyl ether and further purified by repeated precipitation into diethyl ether from tetrahydrofuran two additional times. Copolymer composition and molecular weight were determined using proton nuclear magnetic resonance. Micelles were formed by precipitation into purified water from acetone. Micelle size was determined using dynamic light scattering. Mucoadhesion was determined using Surface Plasmon Resonance with bovine mucin and simulated tear fluid. CycA release from micelles was determined using high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).
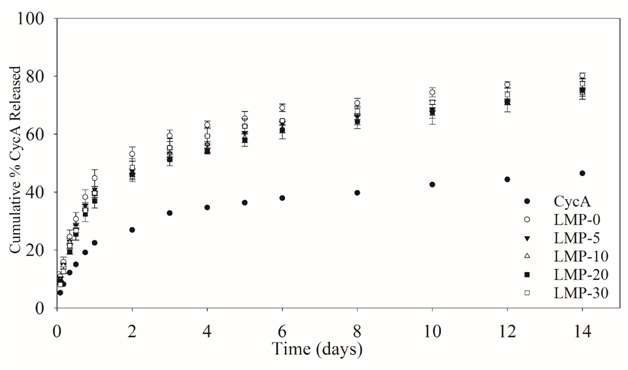
Results: DLS determined the diameter and polydispersity (PDI) of the micelles. Micelle diameter is dependent on the PBA content in the micelle corona and ranges from 35nm to 65nm in diameter as the mole percentage of PBA is increased from 0% to 30%. The PDI in all cases was acceptable, with a maximum value of 0.29. CycA was entrapped within the LMP micelles by dissolving both components in acetone followed by addition into purified water at a ratio of 20 mg copolymer to 3 mg CycA. All micelles showed entrapment efficiencies greater than 99.8% and excellent release characteristics.
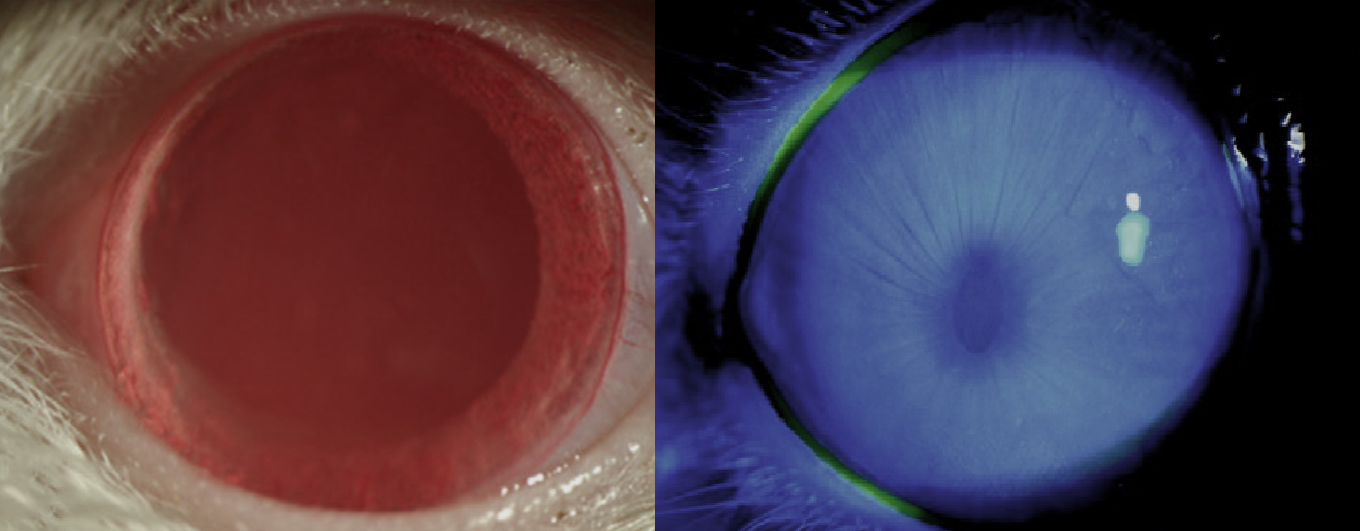
SPR showed an unambiguous relationship between the molde percentage of PBA and mucoadhesion. After a standard battery of cell viability testing which showed no adverse reaction using human corneal epithelial cells, these micelles were tested in vivo using Sprague-Dawley rats by dropping their eyes for a period of 10 days, showing excellent biocompatibility.
Conclusions: Mucoadhesive micelles offer significant potential to increase the efficacy of topically applied ophthalmic drugs by decrease the dosage, frequency of dose, and off-target systemic toxicity. We have synthesized a series of poly(L-lactide)-b-poly(methacrylic acid-co-phenylboronic acid) copolymer micelles with varying amounts of phenylboronic acid which show excellent mucoadhesivity, drug release characteristics, and biocompatibility.
References:
[1] K. Cholkar, S.P. Patel, A.D. Vadlapudi, A.K. Mitra, Novel Strategies for Anterior Segment Ocular Drug Delivery, J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 29 (2013) 106–123
[2] S. Liu, L. Jones, F.X. Gu, Development of mucoadhesive drug delivery system using phenylboronic acid functionalized poly(D,L-lactide)-b-dextran nanoparticles., Macromol. Biosci. 12 (2012) 1622–1626