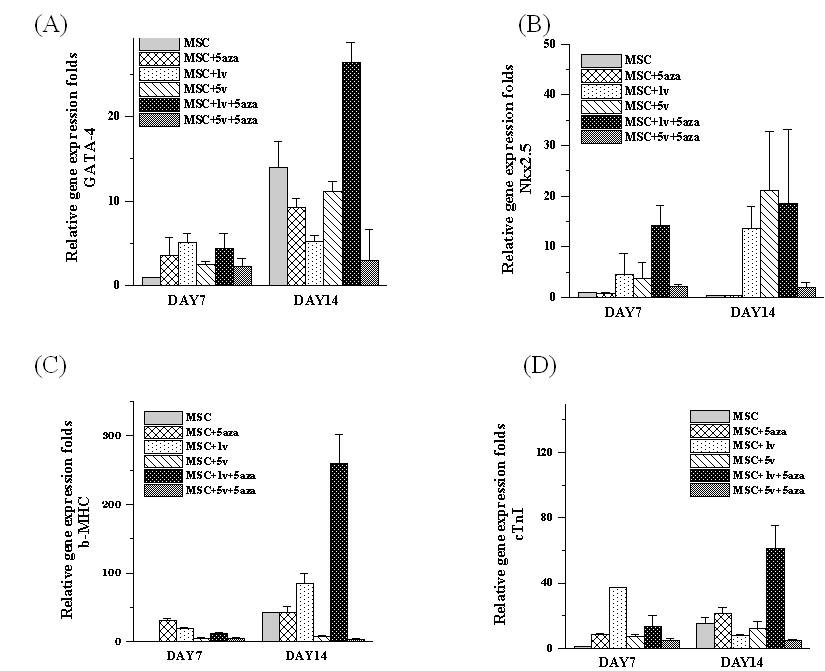
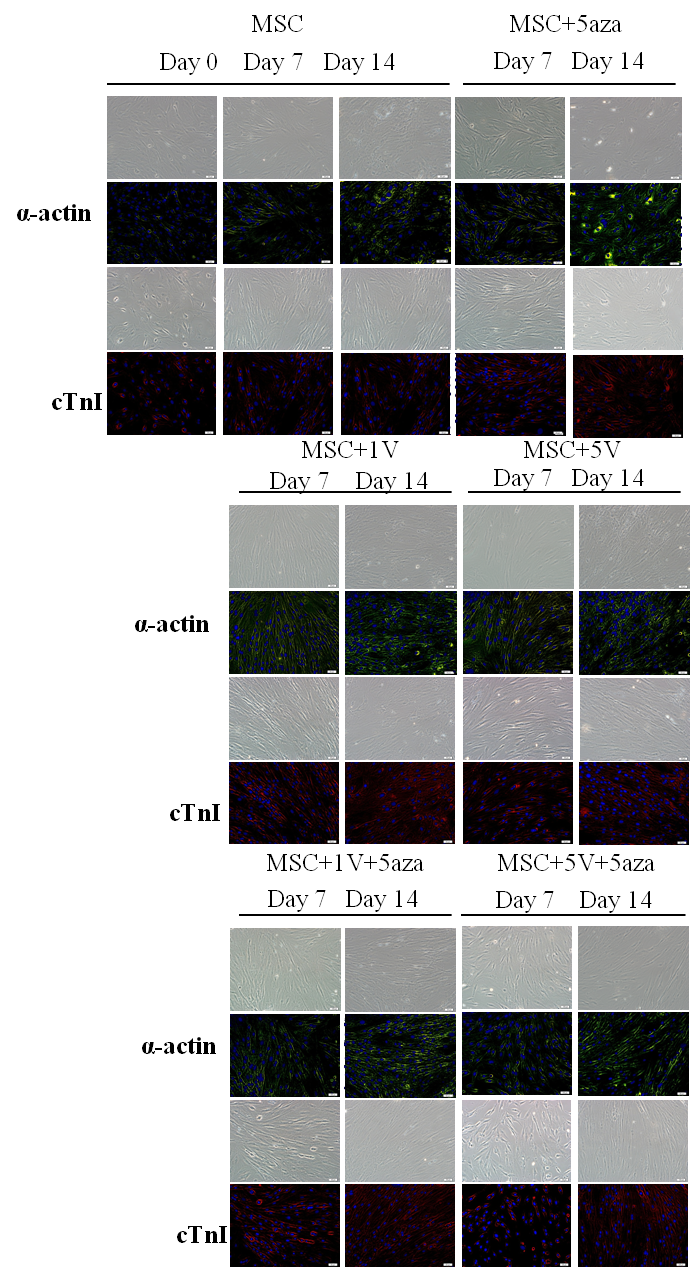
Myocardial tissue has limited self-repair ability due to its loss of differentiation characteristic for most mature cardiomyocytes. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have potential of differentiation into different tissues, thus can be a source for cardiac tissue engineering. Mesenchymal Stem Cell (MSCs) has potential of differentiating into cardiomyocyte via 5-Aza-2′-deoxycytidine(5-aza) induction. However, the differentiation rate is unexpected. And, lacking of cell alignment and functional properties remains the main problem by this method. Many literatures have proven that electrical stimulation gives a physiological clue for in vitro cardiomyocyte differentiation. The main purpose of this project was to utilize an electrical stimulation system which will be able to allow transmission of electrical stimulation to the cultured stem cells, and hope to promote and increase the differentiation of stem cells into myocardial cells. In this study, we used electroporation cuvette as an electrical stimulation system. The second passage MSCs were divided for 4 groups (MSC, MSC+5-aza, MSC+ electrical stimulation, MSC+5-aza + electrical stimulation). MSCs were placed into 4mm gap cuvette that was connected to a function generator with following stimulating parameters: frequency 0-2Hz, voltage1V~10V, plus duration 2ms. After electrical stimulation was completed, MSCs was cultured with 5-aza for 24 hours, and continuously cultured until 7th and 14th days. The cell morphology and cardiac-specific genes expression were measured to evaluate the effect of electrical stimulation with 5-aza on MSCs differentiation. After 14 days culturing, MSCs in control group and in 5-aza alone group lack of regular alignment, which was different from the native heart tissue. After electrical stimulation applied, MSCs elongated and aligned apparently in consistent orientation The result indicated that electrical stimulation can promote MSCs differentiate into cardiomyocte-like tissue. The cardiomyocyte specific protein TnI (Figure1) was analyzed by immunofluorescent stain, which showed higher troponin I level in electrical stimulation group. After electrical stimulation in 4mm gap cuvette and subsequent culturing with 5-aza, cardiomyocyte specific protein(α-actin、Troponin I) expression were evaluated by immunofluorescence stain. Cardiac specific gene Nkx2.5、GATA、α-actin、β-MHC and Troponin I expression were higher than control group(Figure 2). Either obvious cell alignment and elongation or marked cardiac-specific gene expression was observed in 1v+ 5-aza group. This model provides a great potential of future functional cardiac tissue engineering.
This work was financially supported by Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital under Contract of VGHK104-077.
References:
[1] Hedeer Jawad, Alex R. Lyon, Sian E. Harding, Nadire N. Ali and Aldo R. Boccaccini, Myocardial tissue engineering. British Medical Bulletin. 87(1):31-47, 2008.
[2] Milica Radisic, Hyoungshin Park, Helen Shing, Thomas Consi, Frederick J. Schoen, Robert Langer, Lisa E. Freed, Gordana Vunjak-Novakovic, Functional assembly of engineered myocardiumby electrical stimulation of cardiac myocytes cultured on scaffolds, PNAS, 101(52), 18129–18134, 2004.
[3] Janny Bøkenes, Ivar Sjaastad and Ole M. Sejersted. Artifactual contractions triggered by field stimulation of cardiomyocytes, J Appl Physiol, 98, 1712-1719, 2005.
[4] Masahisa Yamada, Kentaro Tanemura, Seiji Okada, Akio Iwanami, Masaya Nakamura, Hideaki Mizuno, Michiru Ozawa, Ritsuko Ohyama-Goto, Naohito Kitamura, Masako Kawano, Kyoko Tan-Takeuchi, Chiho Ohtsuka, Atsushi Miyawaki, Akihiko Takashima, Masaharu Ogawa, Yoshiaki Toyama, Hideyuki Okano, Takashi Kondo, Electrical Stimulation Modulates Fate Determination of Differentiating Embryonic Stem Cells, Stem Cells, 25(3), 562-570, 2007.
[5] Nina Tandon, Anna Marsano, RobertMaidhof, LeoWan, Hyoungshin Park, Gordana Vunjak-Novakovic. Optimization of electrical stimulation parameters for cardiac tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med ,2011.
[6] N. Tandon, A. Marsano, C. Cannizzaro, J. Voldman, and G. Vunjak-Novakovic, Design of Electrical Stimulation Bioreactors for Cardiac Tissue Engineering . Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc; 3594–3597, 2008.