Featured news
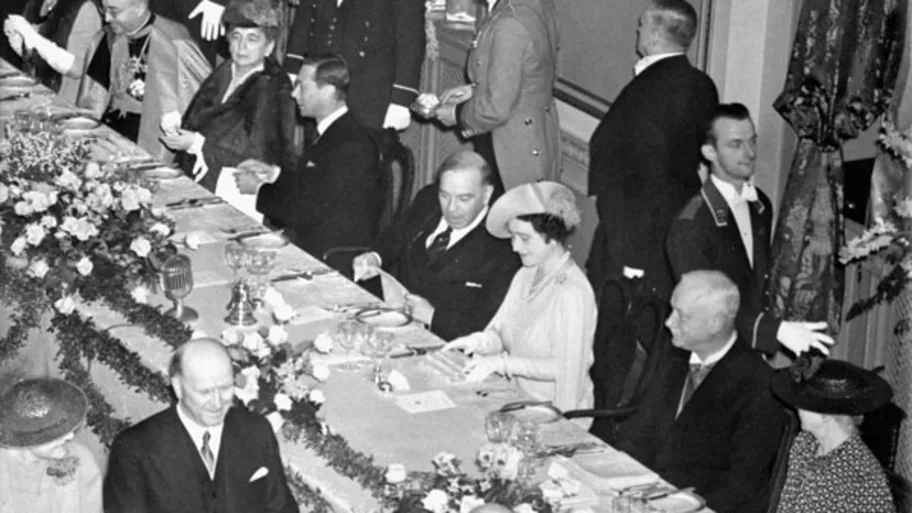
100 years of menus show how food can be used as a diplomatic tool to make and break political alliances
Researchers examined menus from Portuguese diplomatic dinners dating from 1910 to 2023 and showed that meals can play a significant role in a country’s foreign policy.