The After-Effect of Accelerated Intermittent Theta Burst Stimulation at Different Session Intervals
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Huashan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
- 2School of Kinesiology, Shanghai University of Sport, Shanghai, China
- 3Shanghai Key Laboratory of Psychotic Disorders, Shanghai Mental Health Center, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
- 4Co-innovation Center of Neuroregeneration, Nantong University, Nantong, China
A Corrigendum on
The After-Effect of Accelerated Intermittent Theta Burst Stimulation at Different Session Intervals
by Yu, F., Tang, X., Hu, R., Liang, S., Wang, W., Tian, S., et al. (2020). Front. Neurosci. 14:576. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00576
In the original article, there was a mistake in the legend for Figure 5(C) and Figure 6(D) as published. It should be “iTBS600×3*30,” but it was written incorrectly to “iTBS×3*10.” The correct legend appears below.
Figure 5. Individual response to iTBS after 1800 pulses stimulation in three different intervals. (A) iTBS1800 (B) iTBS600 × 3*10 (C) iTBS600 × 3*30.
Figure 6. The percentage of subjects that responded to different iTBS conditions. (A) one blocks of iTBS (B) iTBS1800 (C) iTBS600 × 3*10 (D) iTBS600 × 3*30.
In the original article, there was a mistake in Table 2 as published. The corrected Table 2 appears below. The SI1mv data for iTBS600×3*10 was incorrectly filled in as 198.2.
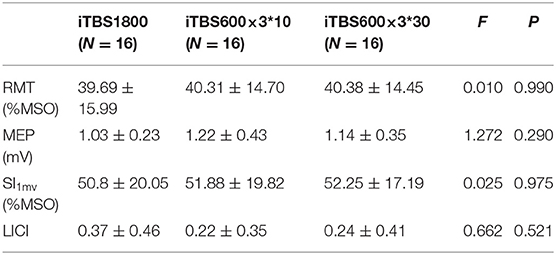
Table 2. Subjects' baseline RMT, MEP amplitude, SI1mv, and LICI when started three different iTBS conditions.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Keywords: theta burst stimulation, accelerated, motor cortex, cortical plasticity, stimulation interval
Citation: Yu F, Tang X, Hu R, Liang S, Wang W, Tian S, Wu Y, Yuan T-F and Zhu Y (2021) Corrigendum: The After-Effect of Accelerated Intermittent Theta Burst Stimulation at Different Session Intervals. Front. Neurosci. 15:687972. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.687972
Received: 30 March 2021; Accepted: 06 April 2021;
Published: 05 May 2021.
Edited and reviewed by: Jinhui Wang, South China Normal University, China
Copyright © 2021 Yu, Tang, Hu, Liang, Wang, Tian, Wu, Yuan and Zhu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ti-Fei Yuan, ytf0707@126.com; Yulian Zhu, zyljully@163.com
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Fengyun Yu
Fengyun Yu Xinwei Tang1†
Xinwei Tang1† Ruiping Hu
Ruiping Hu Ti-Fei Yuan
Ti-Fei Yuan Yulian Zhu
Yulian Zhu