Introduction: TGF-beta plays an critical role in chondrogenesis. However, it is challenging to optimize dosages, as both high or low dosage could lead to disasters. Several delivery strategies have been developed to optimize controled release of growth factors, such as encapsulation; physically absorbtion; colvalent immobilization as well as immobilization via ionic complexes[1]. Among them, the first two methods are limited by burst release of GFs, while colvalent immobilisation is difficult to assign selectively and spoil bioactivity of GFs during immobilization owing to screening of the active pocket of the protein or damage to bioactive functional groups, so the immobilization via ionic complexes could perform better by overcoming aforementioned shortcomings. Here, we chemically crosslinked crosslinked peptides with TGF-β1 affinity to biodegradable chitosan sponges with hypothesis that optimized TGF-β delivery could potentially promote chondrogenesis of MSCs.
Materials and Methods:
The chitosan sponge was fabricated using a previously described method[2]. Next, peptide HSNGLGP was cross-linked to the chitosan sponge using EDC/NHS method. Chitosan sponges with different molar ratios of peptides (10%, 20%, 30%, chitosan-peptide) were prepared as the experimental groups, chitosan (without peptide) served as the control group. MSCs were isolated from the bone marrow of pigs. For each experimental group, the samples were pre-treated with TGF-β1. During the culturing period, the negative control group was cultured with medium without TGF-β1, whereas the positive one was cultured with TGF-β1 (10 ng/mL). We used real-time-PCR to choose the optimized group for the following experiments. For the F-actin staining, the samples were stained with rhodamine phalloidin and DAPI. For histology analysis, the nude mice were sacrificed 14 d and 28 d after grafting, and the grafted tissues were harvested together with the surrounding tissue for immunohistochemistry staining of Col II.
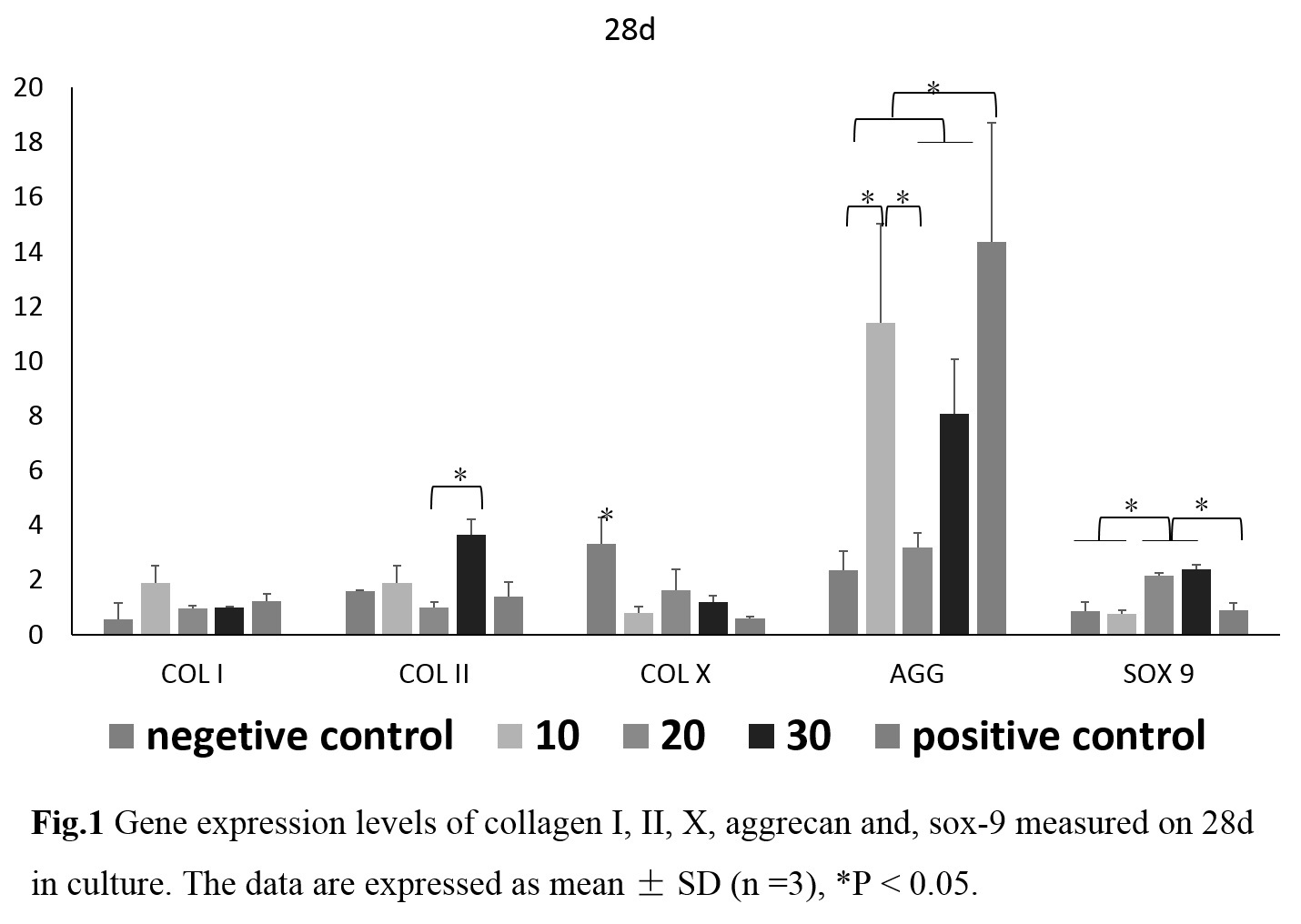
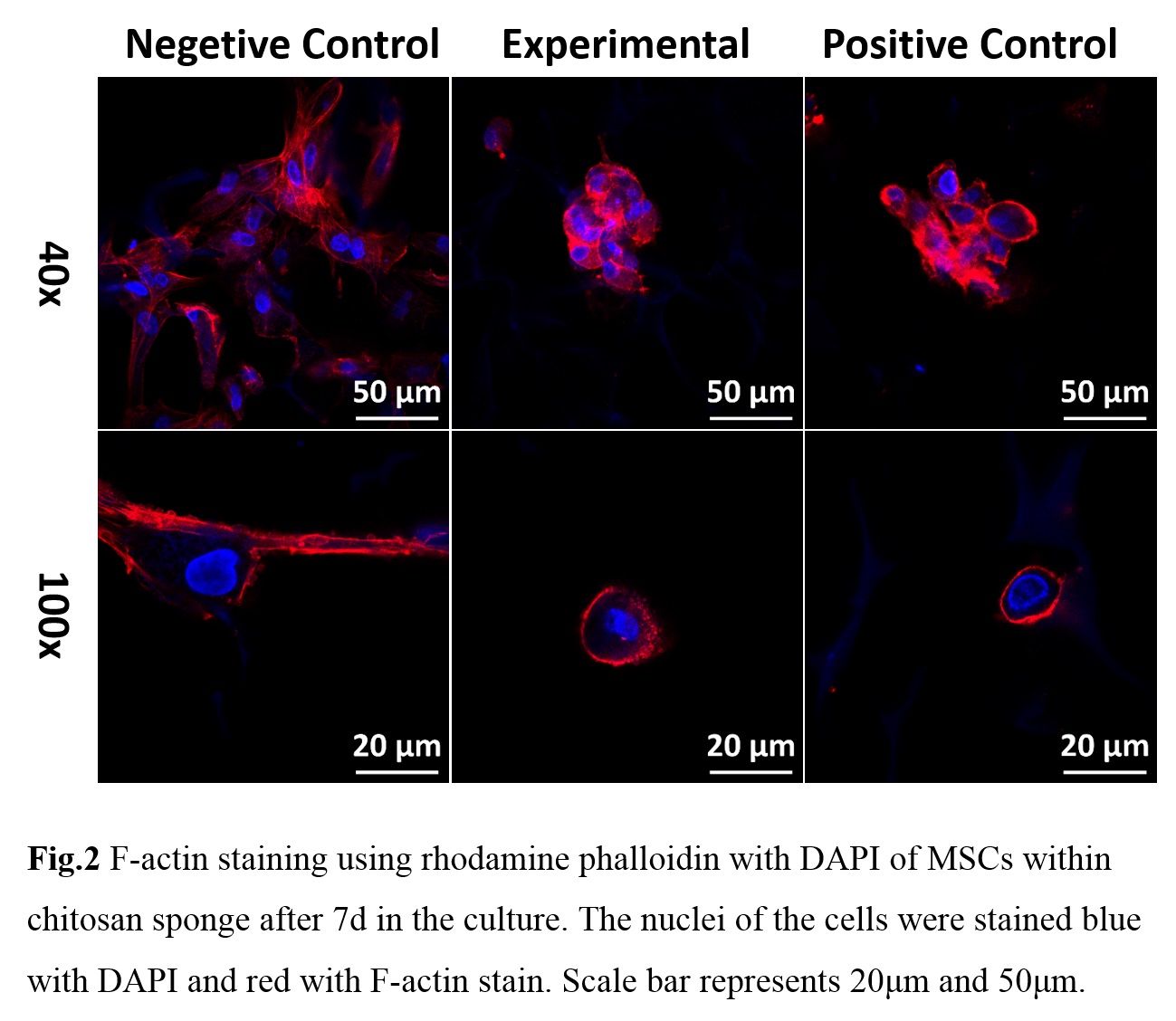
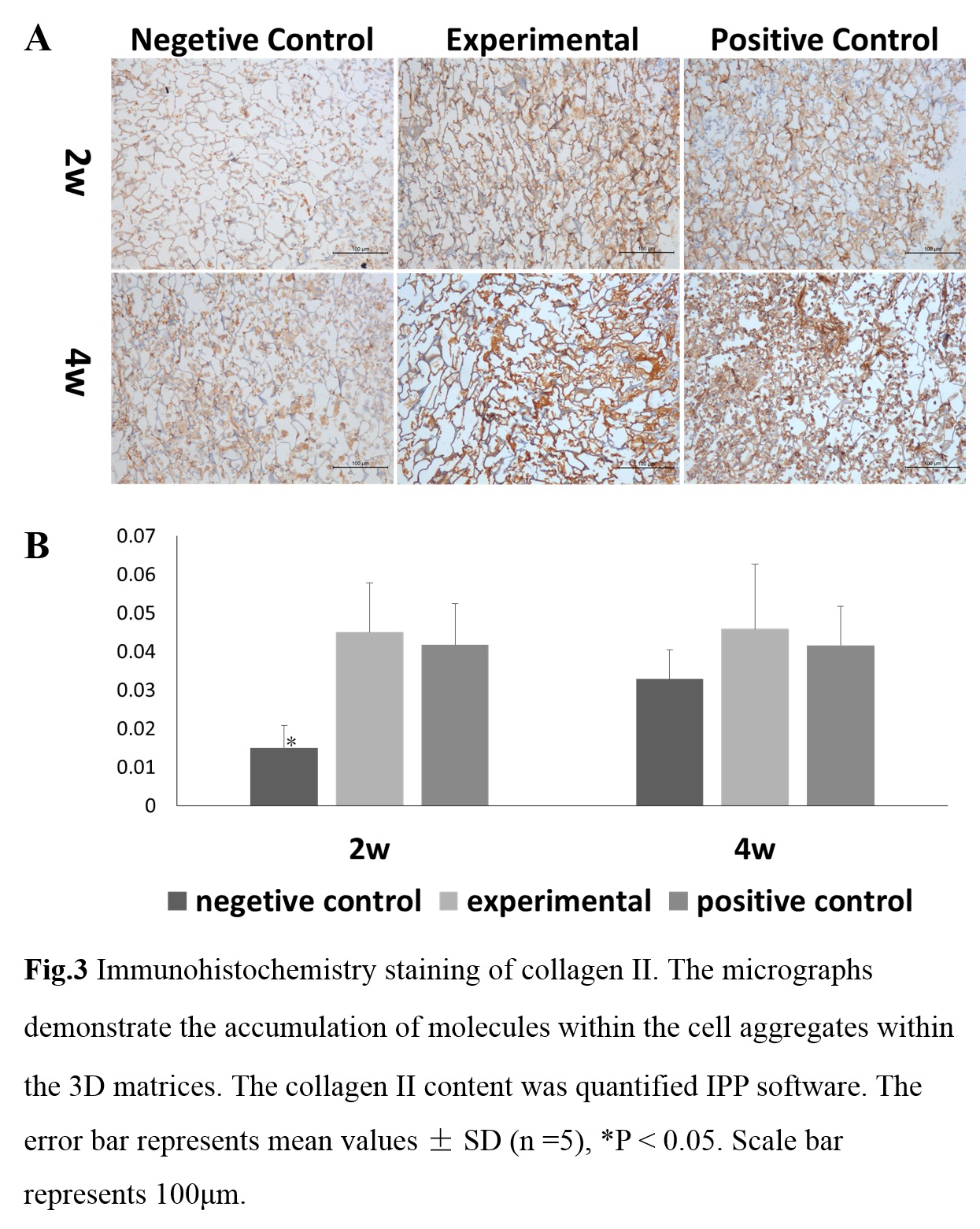
Results and Discussion: On day 28, the gene expression of collagen II, aggrecan and Sox 9 was higher in the 30% peptide crosslinked chitosan scaffolds in comparison to negetive control and some other experimental group (P<0.05) (figure 1), so we choose 30% group as the experimental group for the following experiments. The MSCs morphology and the shape of the cell aggregates was assessed on day 7. The confocal micrographs revealed well-defined F-actin fibers (in red) around the cell aggregates (figure 2). Notably, for the positive control and experimental groups, F-actin fiber arranged firmly surrounding cell clusters to form spherical morphologies, but for the negetive control group, F-actin fiber change to a multilateral shape. The specific immunostaining performed at 2 and 4 weeks confirmed that the construct composed of TGF-beta 1 affinity peptides evidently enhanced the accumulation of collagen II compared to the negative control group (figure 3).
Conclusions: TGF-β1 affinity peptides crosslinked scaffolds maitained the spherical morphologies of the cells and promote the synthesis and expression of the cartilage matrix. Future work will focus on combining this scaffold with microstructure without extra cells and growth factors to confirm if it is a promising therapeutic candidate in clinical cartilage repair.
References:
[1] Chen, F.M., et al., New insights into and novel applications of release technology for periodontal reconstructive therapies. Journal of Controlled Release, 2011. 149(2): p. 92-11
[2] Zhang, J.J., et al., Cells Behave Distinctly Within Sponges and Hydrogels Due to Differences of Internal Structure. Tissue Engineering Part A, 2013. 19(19-20): p. 2166-2175.